World record in time-resolved tomography
Researchers from the Helmholtz Zentrum Berlin (HZB) and the TOMCAT beamline have achieved a new world record in time-resolved tomography by measuring over 200 tomographies per second during heating of an evolving aluminium metal foam.
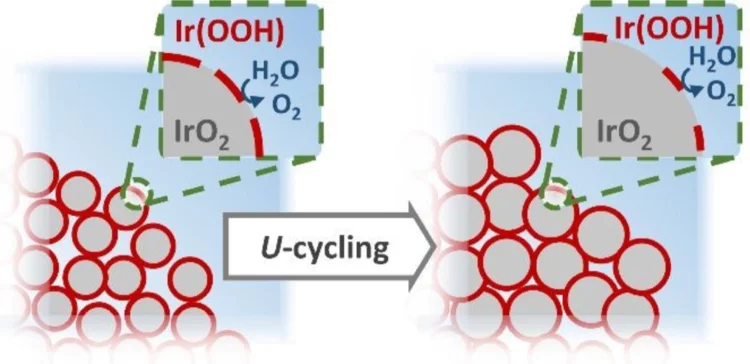
Operando X-ray Characterization of High Surface Area Iridium Oxides to Decouple their Activity Losses for the Oxygen Evolution Reaction
The increasingly popular power-to-gas technology for the utilization of hydrogen as a clean energy vector involves the use of electrolyzers to convert water into H2 and O2. The oxygen evolution reaction (OER) is the least efficient among these processes, and a catalyst is required to speed up its kinetics at the high potentials (customarily ≥ 1.4 V vs. the reversible hydrogen electrode) at which the reaction takes place.
Spin fluctuation induced Weyl semimetal state in the paramagnetic phase of EuCd2As2
Weyl fermions as emergent quasiparticles can arise in Weyl semimetals (WSMs) in which the energy bands are nondegenerate, resulting from inversion or time-reversal symmetry breaking. Nevertheless, experimental evidence for magnetically induced WSMs is scarce. Here, using photoemission spectroscopy, we observe that the degeneracy of Bloch bands is already lifted in the paramagnetic phase of EuCd2As2. We attribute this effect to the itinerant electrons experiencing quasi-static and quasi–long-range ferromagnetic fluctuations.
Molecular energy machine as a movie star
Using the Swiss Light Source SLS, PSI researchers have recorded a molecular energy machine in action and thus revealed how energy production at cell membranes works. For this purpose, they developed a new investigative method that could make the analysis of cellular processes significantly more effective than before.
PSI School for Master Degree Students - Introducing Photons, Neutrons and Muons for Condensed Matter Physics and Materials Science
From 17 – 21 June 2019 the Neutron and Muon Division (NUM) and the Photon Science Division (PSD) of PSI hosted 18 Master Degree students of physics, chemistry, materials and interdisciplinary science, as well as nuclear engineering to provide an introduction to the characterization of materials with large scale facilities like SINQ, SμS, SLS and SwissFEL. The course taught a basic understanding of how photons, neutrons and muons interact with matter, and how this knowledge can be used to solve specific problems in materials research.
Details of the program can be found at http://indico.psi.ch/event/PSImasterschool
New material also reveals new quasiparticles
Researchers at PSI have investigated a novel crystalline material at the Swiss Light Source SLS that exhibits electronic properties never seen before. Among other things, they were able to detect a new type of quasiparticle: so-called Rarita-Schwinger fermions.
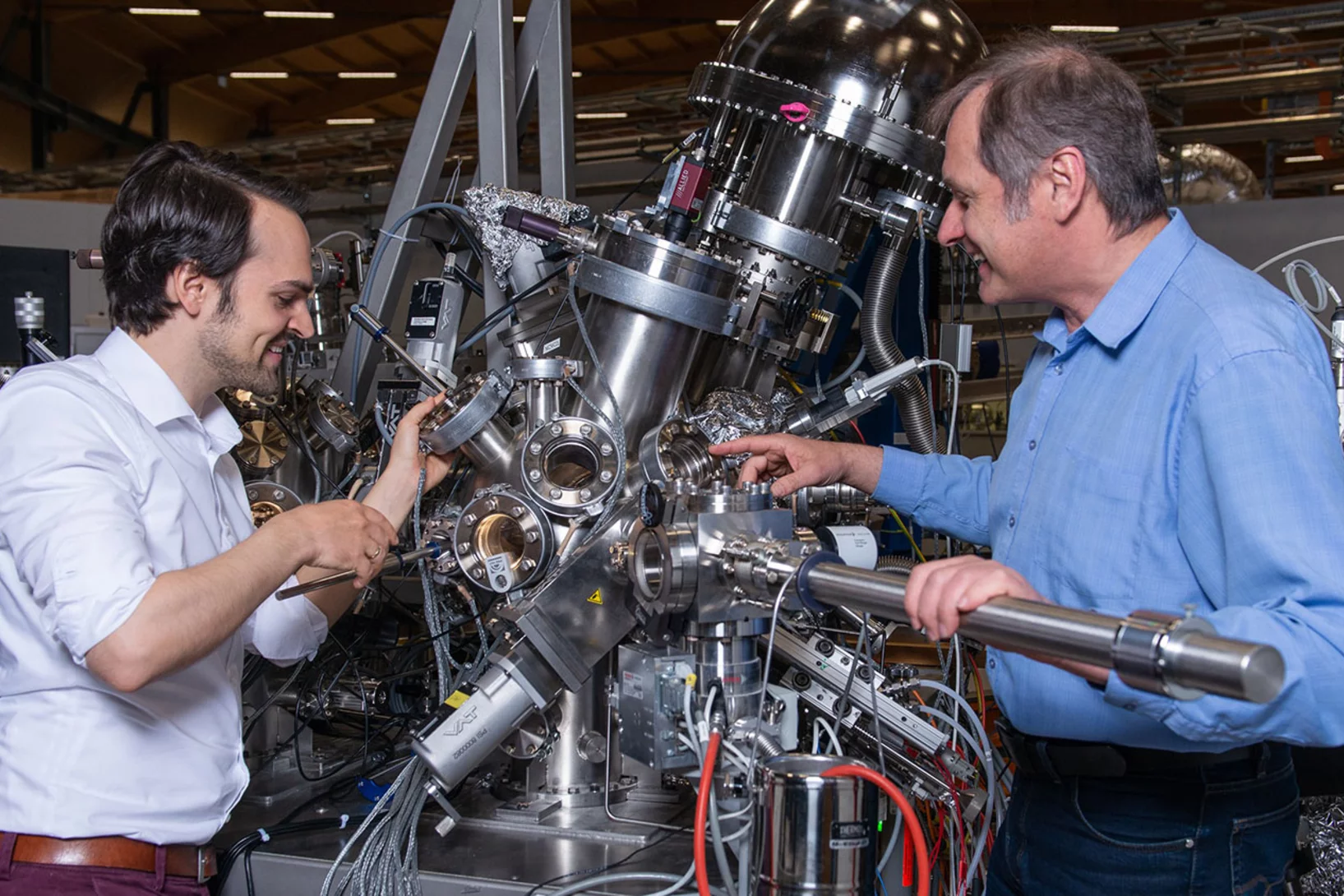
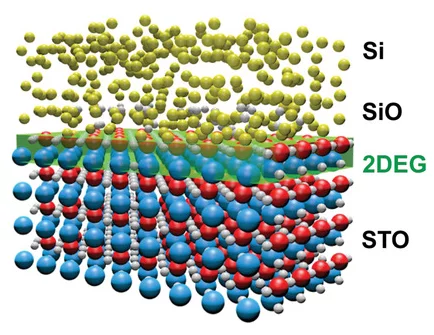
X‐Ray Writing of Metallic Conductivity and Oxygen Vacancies at Silicon/SrTiO3 Interfaces
Lithography‐like writing of conducting regions at the interface between SrTiO3 and amorphous Si using X‐ray irradiation opens ways for spatially controlled functionalities in oxide heterostructures.
HERCULES school 2019 at SLS
In the week of April 1-5 PSI welcomes 20 PhD students and postdocs taking part in the European HERCULES 2019 school on Neutron and Synchrotron Radiation. They will attend lectures and perform two days of practical courses at several beam lines of the Swiss Light Source.
Inside Batteries
Lithium ion batteries (LIB) are essential in modern everyday life, with increasing interest in enhancing their performance and lifetime. Secondary particles of Li-rich cathode material were examined with correlated ptychographic X-ray tomography and diffraction microscopy at different stages of cycling to probe the aging mechanism.
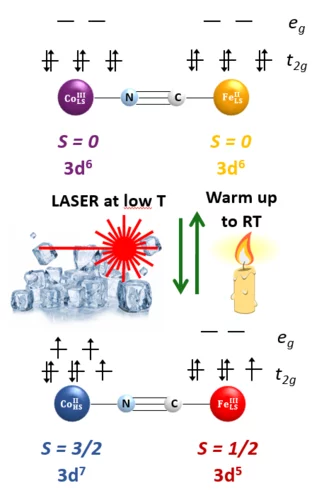
Photoswitching in a Molecular Cube
Niéli’s paper is accepted in the Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters! We use X-ray absorption spectroscopy and X-ray magnetic circular dichroism to watch directly how the Co and Fe ions in a molecular cube change their oxidation states and turn from diamagnetic into paramagnetic units upon light irradiation.
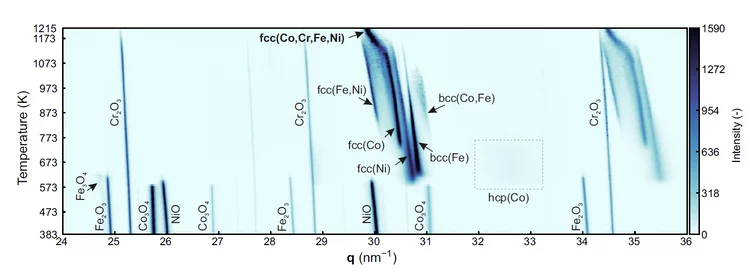
Additive Manufacturing of High Entropy Alloys
Additive manufacturing of high-entropy alloys combines the mechanical properties of this novel family of alloys with the geometrical freedom and complexity required by modern designs. An approach to additive manufacturing of high-entropy alloys has been developed based on 3D extrusion of inks containing a blend of oxide nanopowders (Co3O4 + Cr2O3 + Fe2O3 + NiO), followed by co-reduction to metals, inter-diffusion and sintering to near-full density CoCrFeNi in H2. A complex phase evolution path is observed by in-situ X-ray diffraction in extruded filaments: the oxide phases undergo reduction and the resulting metals inter-diffuse, ultimately forming the desired fcc-CoCrFeNi alloy (see figure). Linked to this phase evolution is a complex micro-structural one, from loosely packed oxide particles to fully-annealed, metallic CoCrFeNi with 99.6 ± 0.1% relative density. CoCrFeNi micro-lattices are created with strut diameters as low as 100 μm and excellent mechanical properties at ambient and cryogenic temperatures.
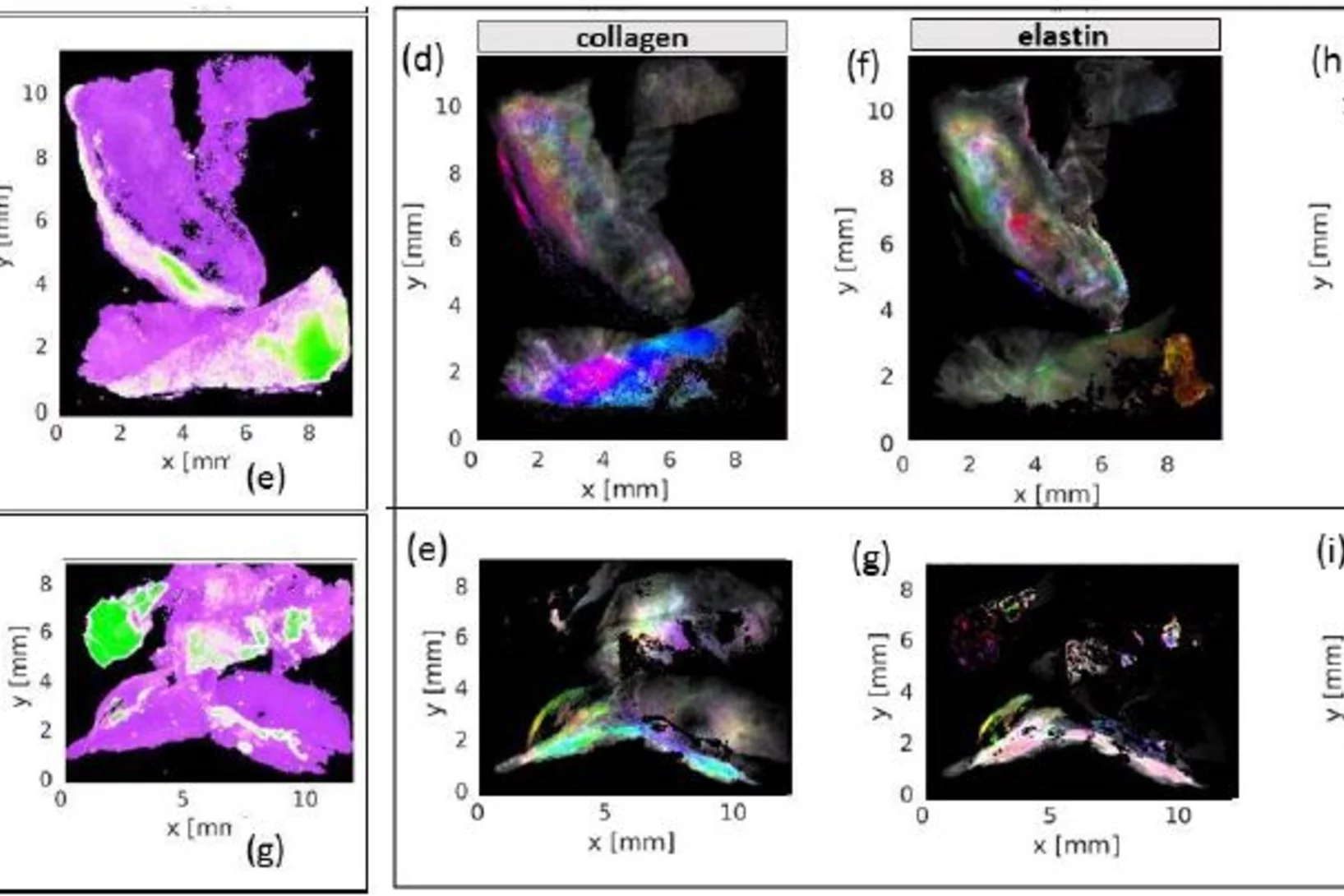
Insights into a well-known disease in ageing populations: Abdominal and popliteal aneurysm
Abdominal aortic aneurysm, an enlargement of the abdominal aorta, may lead to rupture and thus acute health issues and death. Scanning X-ray imaging enabled new insights in the nano-structure of calcifications associated with abdonimal and popliteal aneurysm and allowed mapping the distribution of nano- and micro-calcifications as well as of collagen, elastin and myofilament as building blocks of connective tissue across samples from human donors.
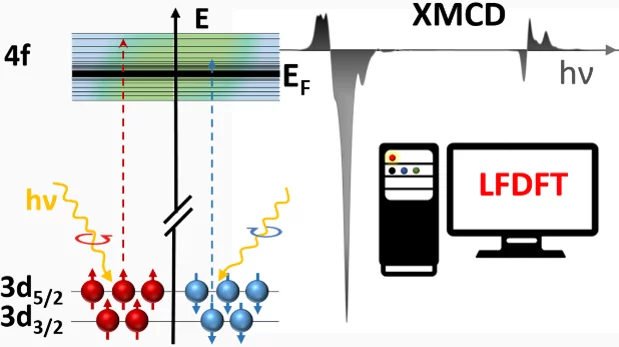
New Method for Calculating Soft X-ray Magnetic Circular Dichroism Spectra
Scientists have demonstrated in a combined theoretical and experimental effort that the new ligand-field density functional theory method (LF-DFT) can be used to calculate the X-ray absorption spectra (XAS) and X-ray magnetic circular dichroism (XMCD) of lanthanide compounds from purely structural input.
Virtual lens improves X-ray microscopy
A method developed by PSI researchers makes X-ray images of materials even better. The researchers took a number of individual images while moving an optical lens. From these, with the help of computer algorithms, they generated one overall image.
EU grants 14 million to Swiss Researchers
A team with three researchers from the ETH Domain has been awarded a prestigious EU grant. Today, they received the contract signed by the EU confirming the extraordinary 14 million euros funding. With it, they will investigate quantum effects which could become the backbone of future electronics.
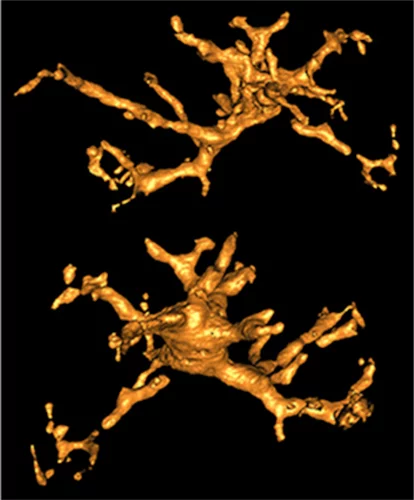
Soft-tissue evidence for homeothermy and crypsis in a Jurassic ichthyosaur
Synchrotron-based X-ray tomographic microscopy of melanophores (skin pigment cells) of an amazingly well preserved 180 million years old ichtyosaur (extinct marine reptile similar to whales) contributed in a multidisciplinary investigation to the new findings published today in Nature.
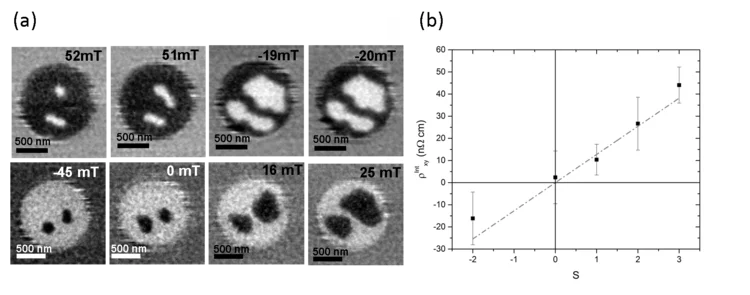
Discrete Hall contribution of magnetic skyrmions
The reliable electrical detection of magnetic skyrmions is of fundamental importance for the application of such topological magnetic quasi-particles for data storage devices. Researchers in a joint collaboration between the University of Leeds and the PolLux endstation have investigated the electrical detection of isolated magnetic skyrmions in applications-relevant nanostructured devices, observing the presence of a strong skyrmion-dependent contribution to the Hall resistivity.
On the path to new high-performance transistors
The electronics industry expects a novel high-performance transistor made of gallium nitride to offer considerable advantages over present-day high-frequency transistors. Yet many fundamental properties of the material remain unknown. Now, for the first time, researchers at the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI have observed electrons while they were flowing in this promising transistor. For that they used one of the world's best sources of soft X-rays at PSI's Swiss Light Source SLS.
MOOCs – a paradigm shift in education
In March 2018, the nine-week MOOC “Introduction to synchrotrons and x-ray free-electron lasers” (abbreviated to “SYNCHROTRONx”) came online via the edX provider of the École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL), created by Phil Willmott of the Swiss Light Source, Paul Scherrer Institute. “MOOC” is an acronym for “massive open online course”, a teaching platform started in the first decade of this century, which has become increasingly popular in the last five to six years. MOOCs have no limits to participation and are free. Some of the most popular MOOCs can attract many tens of thousands of participants. Even the most specialized subjects may have an initial enrollment of over a thousand, more than an order of magnitude larger than that typically found in traditional higher education. There were over 70 million MOOC enrollments covering nearly 10’000 subjects offered by the top five providers in 2017 alone!
HERCULES at the Swiss Light Source
In the week of March 18-23 PSI welcomes 20 PhD students and postdocs taking part in the HERCULES 2018 school on Neutron and Synchrotron Radiation. They will attend lectures and perform two days of practical courses at several beam lines of the Swiss Light Source.
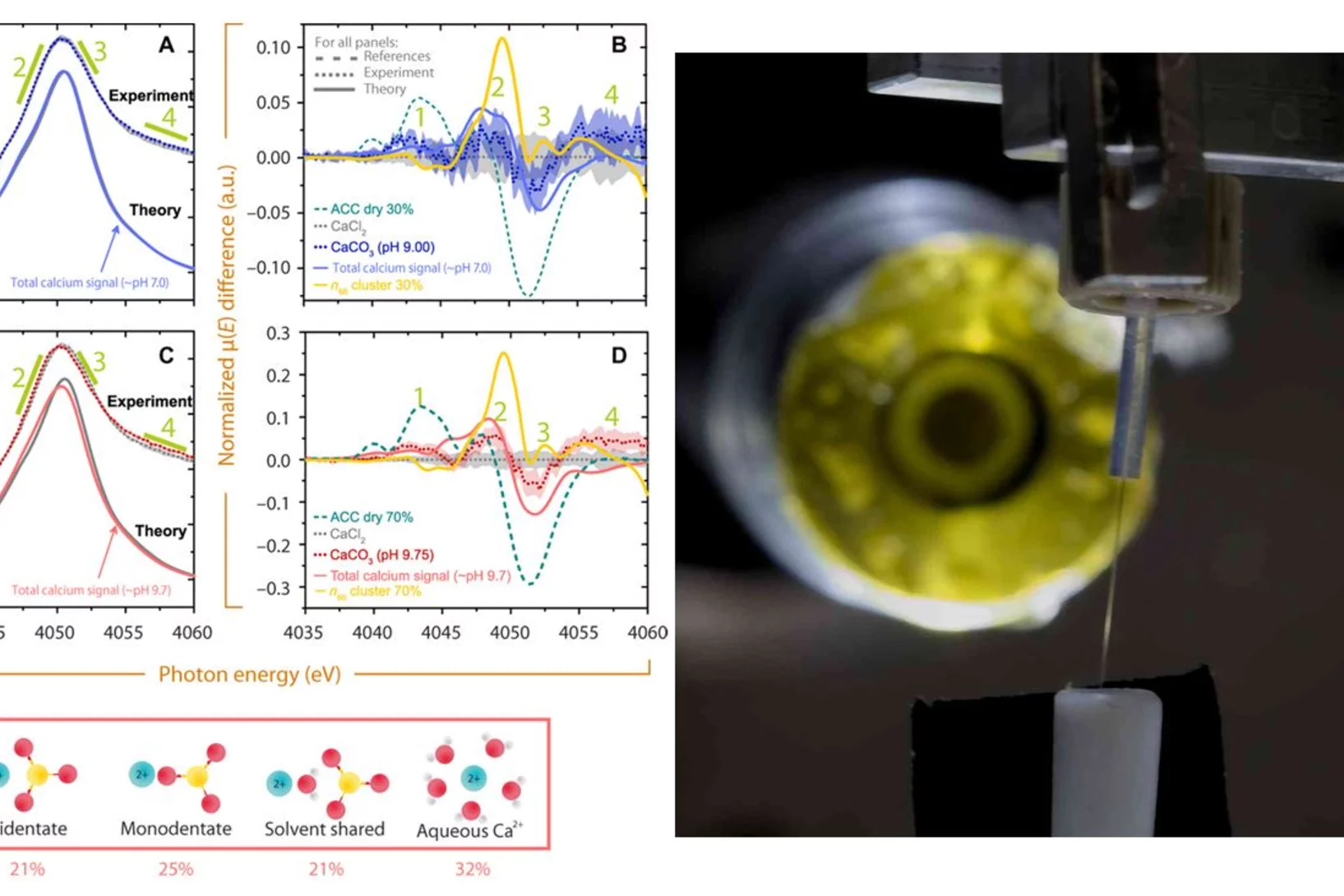
Are supersaturated calcium carbonate solutions classical or non-classical ?
Classical theory predicts that supersaturated carbonate solutions consist mostly of ions and ion pairs, with a small number of larger clusters present in the solution. The population of the different sized clusters in a solution is solely defined by the cluster’s size dependent Free Energy. If clusters are large enough they serve as nucleation germs for a new solid phase. The nucleation occurs once the surface free energy barrier posed by the new solid-liquid interface is overcome by the free energy win from bulk phase growth.
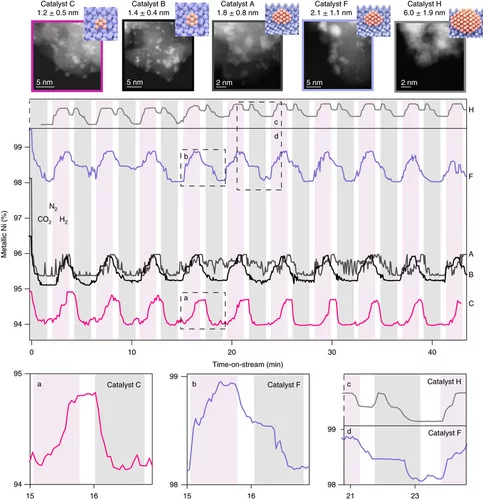
Unravelling structure sensitivity in CO2 hydrogenation over nickel
Using a unique set of well-defined silica-supported Ni nanoclusters (1–7 nm) and advanced characterization methods it was proved how structure sensitivity influences the mechanism of catalytic CO2 reduction, the nature of which has been long debated.
First experiment at SwissFEL carried out successfully
The years of careful planning and construction have paid off: At the newest large-scale research facility of the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI – the X-ray free-electron laser SwissFEL – the first experiment has been carried out successfully. With that, two goals have been achieved: First, a new scientific result is already expected. Second, the interaction of the many individual components of the highly complex facility is being optimised.
PSI spin-off GratXray wins Swiss Technology Award 2017
A spin-off from PSI has received this year's Swiss Technology Award: The young company GratXray is developing a new method for early diagnosis of breast cancer.
Magnetic structures take a new turn
The unexpected finding that in an ‘artificial spin ice’ magnetostatic energy can be transformed into directed rotation of magnetization provides fresh insights into such nano-patterned magnetic structures — and might enable novel applications in nanoscale devices.
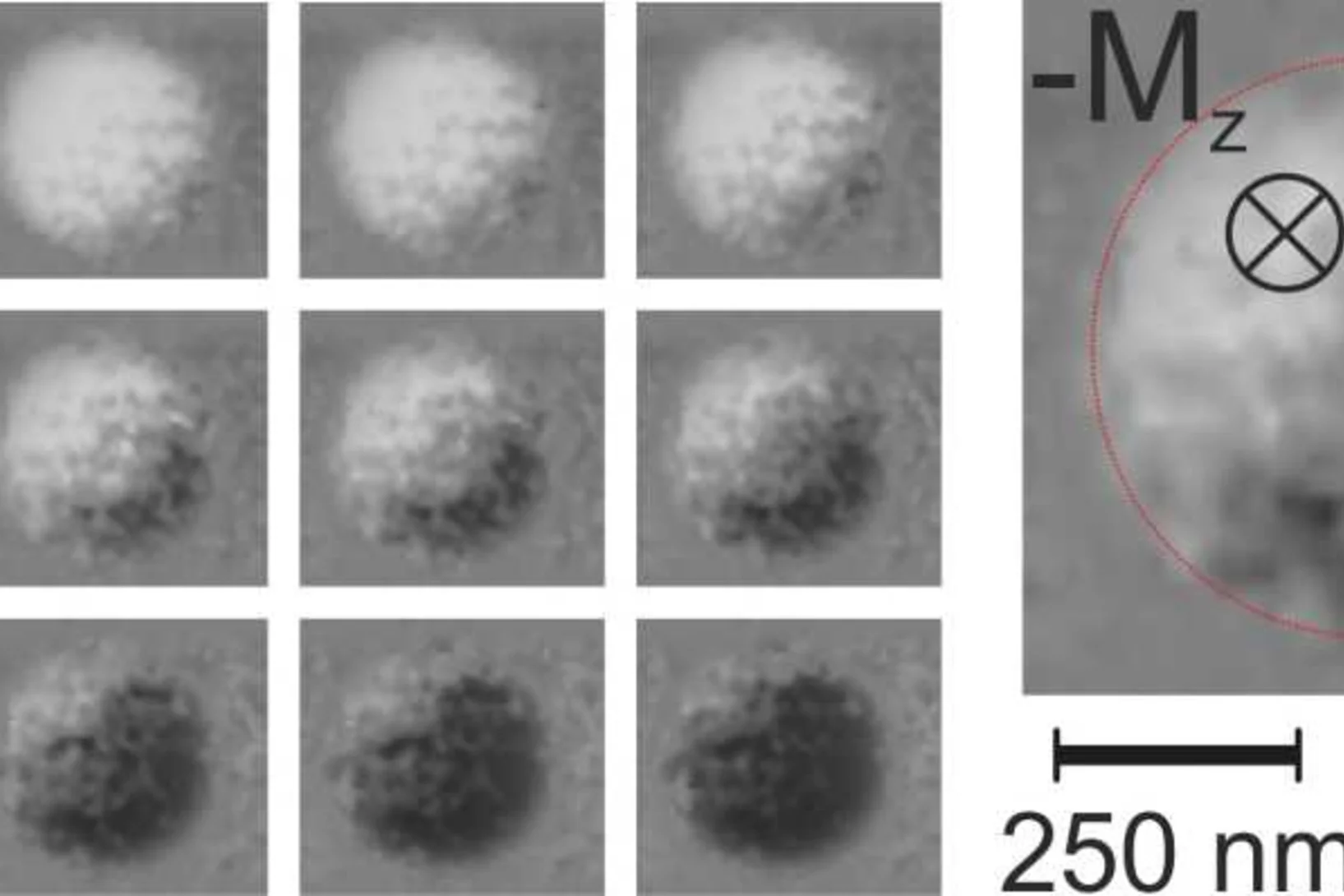
Time- and spatially-resolved magnetization dynamics driven by spin-orbit torques
Current-induced spin-orbit torques hold a great potential for manipulation of magnetization at ultrafast timescales. Researchers at ETH Zürich have demonstrated, using time-resolved STXM imaging at the Swiss Light Source, the influence of spin-orbit torques on the switching behaviour of Pt/Co/AlOx nanostructured elements.
Making the world go round - a look into the structure of a prominent heterogeneous catalyst
Fluid catalytic cracking catalysts, which are composite particles of hierarchical porosity, were examined using ptychographic X-ray tomography. These particles are essential to the conversion of crude oil into gasoline. Examination of catalysts at decreasing levels of catalytic conversion efficacy allowed the detection of possible deactivation causes.
Highly Crystalline C8-BTBT Thin-Film Transistors by Lateral Homo-Epitaxial Growth on Printed Templates
Highly crystalline thin films of organic semiconductors offer great potential for high-performance, low-cost flexible electronics. Researchers at IMEC Belgium have developed a new double-step thin film fabrication process that offers higher performance devices. Soft X-ray spectro-microscopy at the Swiss Light Source was used to prove that the increased performance comes from larger areas of material sharing the same molecular orientation.
Atmosphere in X-ray light
PSI researchers have developed an experimental chamber in which they can recreate atmospheric processes and probe them with unprecedented precision, using X-ray light from the Swiss Light Source SLS. In the initial experiments, they have studied the production of bromine, which plays an essential role in the decomposition of ozone in the lower layers of the atmosphere. In the future, the new experiment chamber will also be available for use by researchers from other scientific fields.
Dr. Nan Xu awarded SPS 2017 Prize in Condensed Matter Physics
The SPS 2017 Prize in Condensed Matter Physics, sponsored by IBM, has been awarded to Dr. Nan Xu for his excellent work on topological quantum states. Dr. Nan Xu is a joint postdoc of Paul Scherrer Institute (PSI) and the École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL).