Here you find current and previous news from the PSI Center for Neutron and Muon Sciences.
Magnetic Field Control of Cycloidal Domains and Electric Polarization in Multiferroic BiFeO3
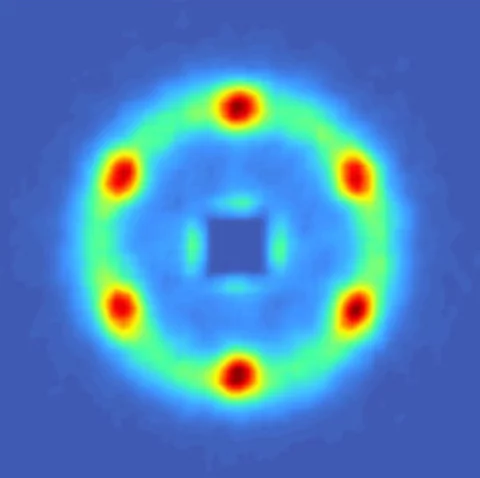
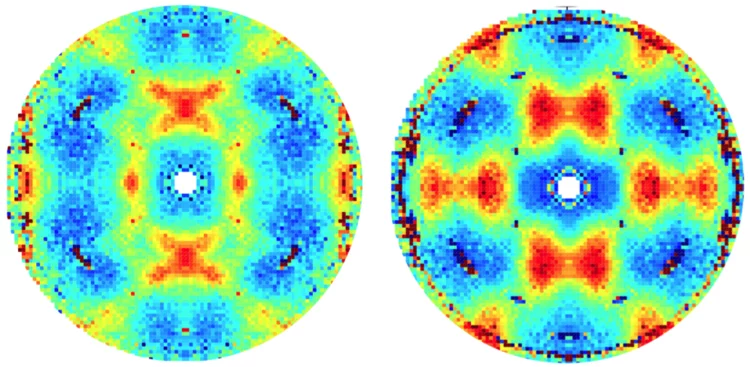
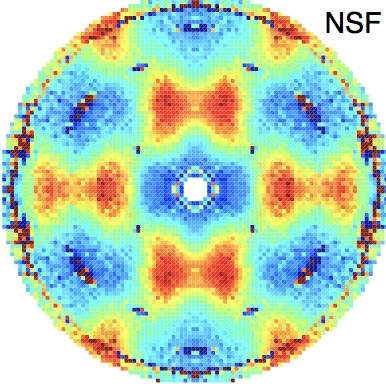
The magnetic field induced rearrangement of the cycloidal spin structure in ferroelectric monodomain single crystals of the room-temperature multiferroic BiFeO3 is studied using small-angle neutron scattering. The cycloid propagation vectors are observed to rotate when magnetic fields applied perpendicular to the rhombohedral (polar) axis exceed a pinning threshold value of ∼5T.
Dipolar Spin Ice States with a Fast Monopole Hopping Rate in CdEr2X4 (X = Se, S)
Excitations in a spin ice behave as magnetic monopoles, and their population and mobility control the dynamics of a spin ice at low temperature. CdEr2Se4 is reported to have the Pauling entropy characteristic of a spin ice, but its dynamics are three orders of magnitude faster than the canonical spin ice Dy2Ti2O7.
Spin-liquid-like state in a spin-1/2 square-lattice antiferromagnet perovskite induced by d10 – d0 cation mixing
A quantum spin liquid state has long been predicted to arise in spin-1/2 Heisenberg square-lattice antiferromagnets at the boundary region between Néel (nearest-neighbor interaction dominates) and columnar (next-nearest-neighbor interaction dominates) antiferromagnetic order. However, there are no known compounds in this region. Here we use d10 – d0 cation mixing to tune the magnetic interactions on the square lattice while simultaneously introducing disorder.
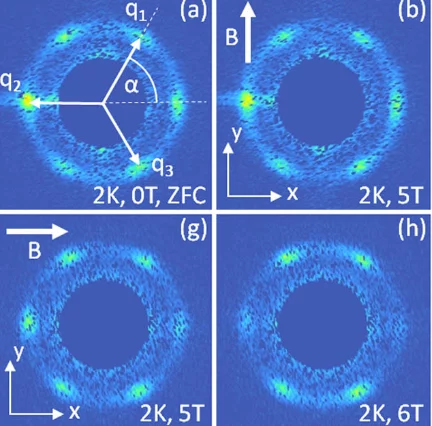
Multi-q Mesoscale Magnetism in CeAuSb2
We report the discovery of a field driven transition from a single-q to multi-q spin density wave (SDW) in the tetragonal heavy fermion compound CeAuSb2. Polarized along c, the sinusoidal SDW amplitude is 1.8(2)μB/Ce for T<N=6.25(10)K with a wave vector q1=(η,η,1/2) [η=0.136(2)]. For H || c, harmonics appearing at 2q1 evidence a striped magnetic texture below μ0H1=2.78(1) T.
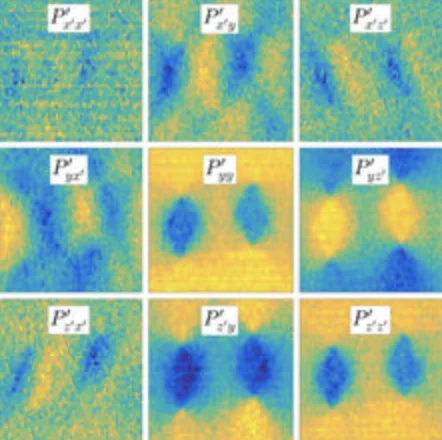
Quasistatic antiferromagnetism in the quantum wells of SmTiO3/SrTiO3 heterostructures
High carrier density quantum wells embedded within a Mott insulating matrix present a rich arena for exploring unconventional electronic phase behavior ranging from non-Fermi-liquid transport and signatures of quantum criticality to pseudogap formation. Probing the proposed connection between unconventional magnetotransport and incipient electronic order within these quantum wells has however remained an enduring challenge due to the ultra-thin layer thicknesses required.
Crystal-to-Crystal Transition of Ultrasoft Colloids under Shear
Ultrasoft colloids typically do not spontaneously crystallize, but rather vitrify, at high concentrations. Combining in situ rheo–small-angle-neutron-scattering experiments and numerical simulations we show that shear facilitates crystallization of colloidal star polymers in the vicinity of their glass transition. With increasing shear rate well beyond rheological yielding, a transition is found from an initial bcc-dominated structure to an fcc-dominated one.
Three Dimensional Polarimetric Neutron Tomography of Magnetic Fields
Through the use of Time-of-Flight Three Dimensional Polarimetric Neutron Tomography (ToF 3DPNT) we have for the first time successfully demonstrated a technique capable of measuring and reconstructing three dimensional magnetic field strengths and directions unobtrusively and non-destructively with the potential to probe the interior of bulk samples which is not amenable otherwise.
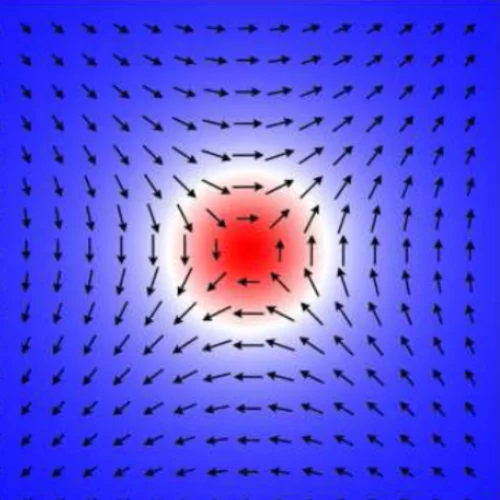
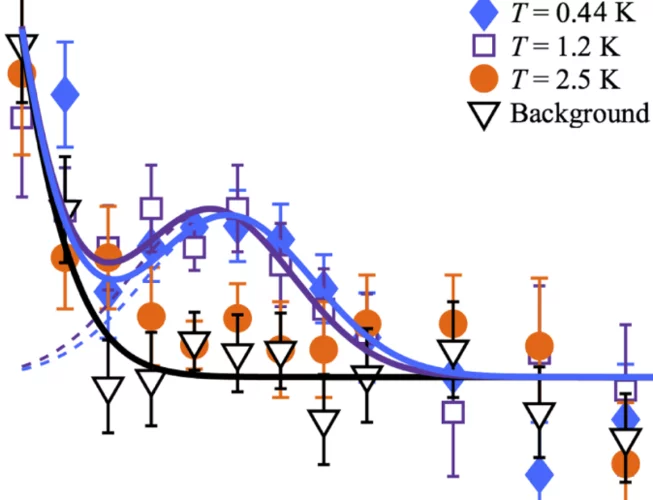
Low-Field Bi-Skyrmion Formation in a Noncentrosymmetric Chimney Ladder Ferromagnet
The real-space spin texture and the relevant magnetic parameters were investigated for an easy-axis non-centrosymmetric ferromagnet Cr11Ge19 with Nowotny chimney ladder structure. Using Lorentz transmission electron microscopy,we report the formation of bi-Skyrmions,i.e., pairs of spin vortices with opposite magnetic helicities.
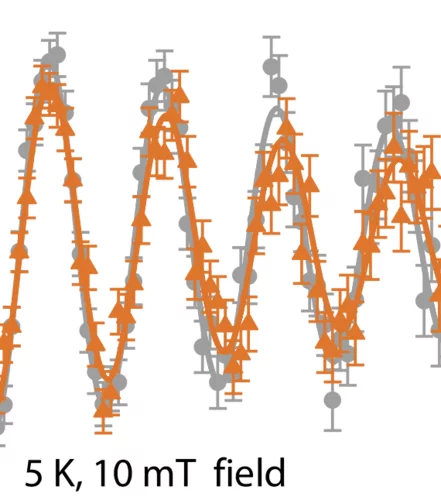
Macroscopic phase separation of superconductivity and ferromagnetism in Sr0.5Ce0.5FBiS2-xSex revealed by μSR
The compound Sr0.5Ce0.5FBiS2 belongs to the intensively studied family of layered BiS2 superconductors. It attracts special attention because superconductivity at Tsc = 2.8 K was found to coexist with local-moment ferromagnetic order with a Curie temperature TC = 7.5 K. Recently it was reported that upon replacing S by Se TC drops and ferromagnetism becomes of an itinerant nature.
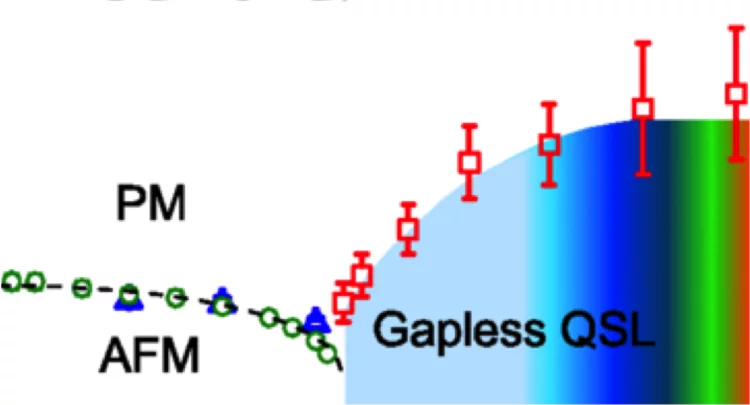
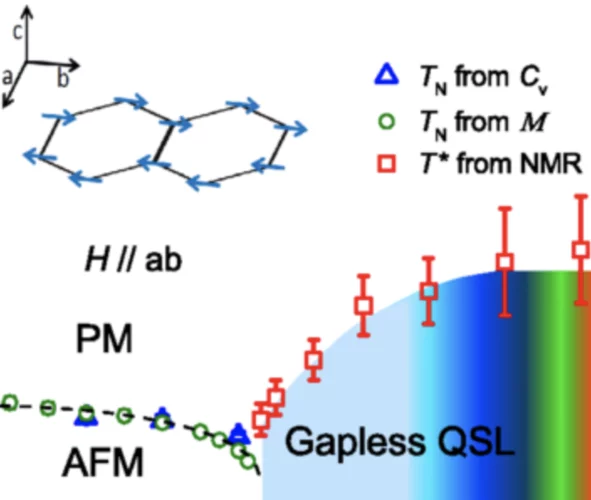
The field-induced quantum spin-liquid phase of α−RuCl3 is gapless
Throughout 2017, the material α−RuCl3 has continued to inspire and fascinate those interested in correlated condensed matter. New experimental data now provide unique insight, and pose fresh challenges.
Jean-Baptiste Mosset winner of PSI Founder Fellowship
Jean-Baptiste Mosset from the Laboratory of Particle Physics is the winner of a PSI Founder Fellowship and plans now to commercialise a neutron detector to spot plutonium and uranium. With his new technology, less expensive and more efficient neutron detectors could be developed. In the next 18 months, Mosset wants to further develop his prototype and find out if demand for this technology exists in industry.
The Charpak-Ritz Prize 2018 is awarded to Roland Paul Horisberger
The Charpak-Ritz Prize 2018, jointly awarded by the French Physical Society and the Swiss Physical Society, has been bestowed to Roland Paul Horisberger for his numerous contributions to the development of precision silicon vertex detectors for particle physics experiments as well as for the application of these technologies in X-ray photon sciences.
Tuning Nanoparticle–Micelle Interactions and Resultant Phase Behavior
The evolution of the interaction between an anionic nanoparticle and a nonionic surfactant and their resultant phase behavior in aqueous solution in the presence of electrolyte and ionic surfactants have been studied. The mixed system of anionic silica nanoparticles (Ludox LS30) with nonionic surfactant decaethylene glycol monododecylether (C12E10) forms a highly stable clear phase over a wide concentration range of surfactant.
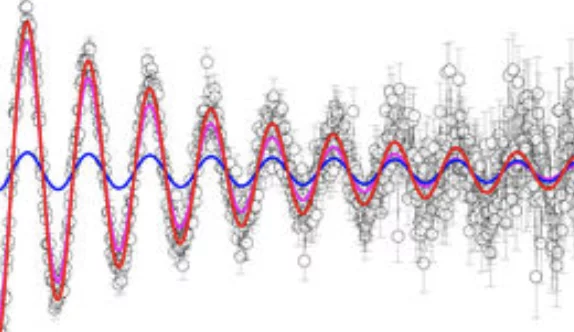
Gapless Spin Excitations in the Field-Induced Quantum Spin Liquid Phase of α-RuCl3
α-RuCl3 is a leading candidate material for the observation of physics related to the Kitaev quantum spin liquid (QSL). By combined susceptibility, specific-heat, and nuclear-magnetic-resonance measurements, we demonstrate that α-RuCl3 undergoes a quantum phase transition to a QSL in a magnetic field of 7.5 T applied in the ab plane. We show further that this high-field QSL phase has gapless spin excitations over a field range up to 16 T.
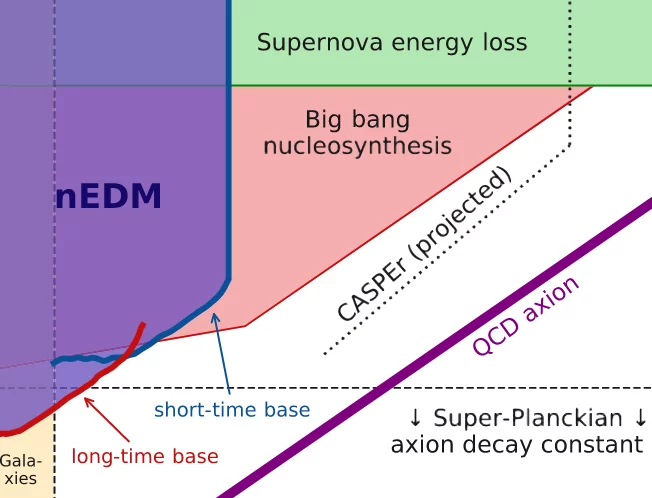
Search for Axionlike Dark Matter through Nuclear Spin Precession in Electric and Magnetic Fields
We report on a search for ultralow-mass axionlike dark matter by analyzing the ratio of the spin-precession frequencies of stored ultracold neutrons and 199Hg atoms for an axion-induced oscillating electric dipole moment of the neutron and an axion-wind spin-precession effect. No signal consistent with dark matter is observed for the axion mass range 10-24 ≤ ma ≤ 10-17eV.
A null result full of insights
A laboratory-based search for axion dark matter ended, not unexpectedly, without a discovery. It provides, however, valuable constraints for the properties that these hypothetical particles can have — and thus a guide to where to look next.
Spin Resonance and Magnetic Order in an Unconventional Superconductor
Unconventional superconductivity in many materials is believed to be mediated by magnetic fluctuations. It is an open question how magnetic order can emerge from a superconducting condensate and how it competes with the magnetic spin resonance in unconventional superconductors. Here we study a model d-wave superconductor that develops spin-density wave order, and find that the spin resonance is unaffected by the onset of static magnetic order.
Emergent dynamic chirality in a thermally driven artificial spin ratchet
Modern nanofabrication techniques have opened the possibility to create novel functional materials, whose properties transcend those of their constituent elements. In particular, tuning the magnetostatic interactions in geometrically frustrated arrangements of nanoelements called artificial spin ice can lead to specific collective behaviour, including emergent magnetic monopoles, charge screening and transport, as well as magnonic response.
Magnetic structures take a new turn
The unexpected finding that in an ‘artificial spin ice’ magnetostatic energy can be transformed into directed rotation of magnetization provides fresh insights into such nano-patterned magnetic structures — and might enable novel applications in nanoscale devices.
The importance of knowing your stripes
A collaboration between three NUM laboratories has found that magnetic ‘stripe order’ in high-temperature superconductors not only co-exists with superconducting order, but might very well be intimately connected with it.
MultiFLEXX - The new multi-analyzer at the cold triple-axis spectrometer FLEXX
The first experimental characterization of a multiple energy analysis wide angle backend for a cold triple-axis spectrometer is reported. The multi-analyzer module MultiFLEXX employs 155 detection channels which simultaneously probe an extensive range in wavevector and energy transfer. Successful mapping of magnetic excitations in MnF2 and Ho demonstrate order of magnitude gains in data collection efficiency using this novel type backend.
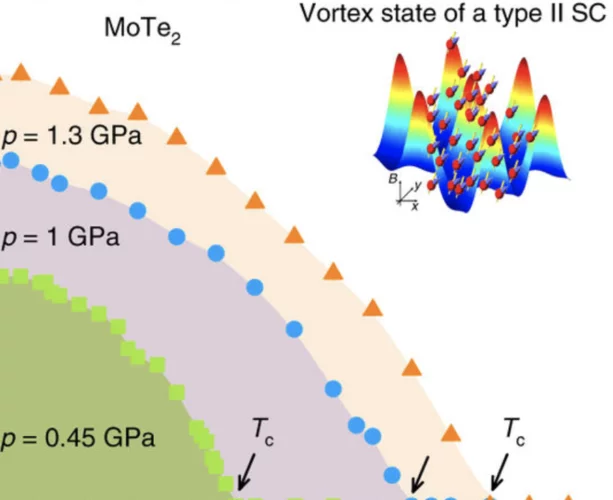
Signatures of the topological s+- superconducting order parameter in the type-II Weyl semimetal Td-MoTe2
In its orthorhombic Td polymorph, MoTe2 is a type-II Weyl semimetal, where the Weyl fermions emerge at the boundary between electron and hole pockets. Non-saturating magnetoresistance and superconductivity were also observed in Td-MoTe2. Understanding the superconductivity in Td-MoTe2, which was proposed to be topologically non-trivial, is of eminent interest.
Frustratingly disordered
A study of how disorder affects a ‘frustrated’ magnet reveals a surprising robustness of the underlying quantum many-body state, and provides evidence for emerging quantum phenomena induced by disorder.
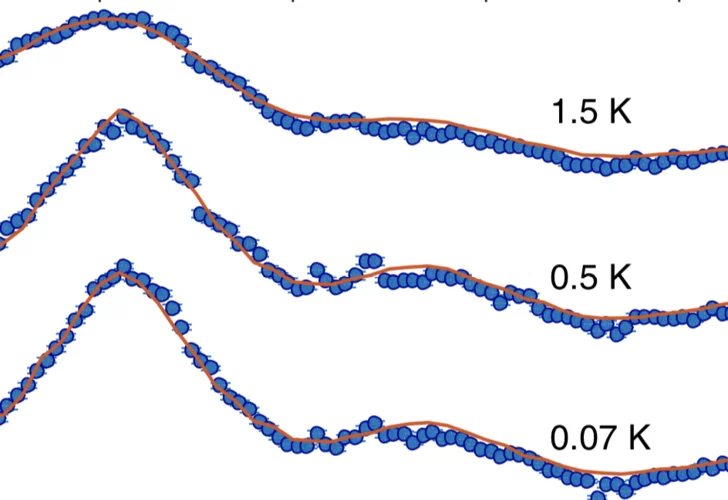
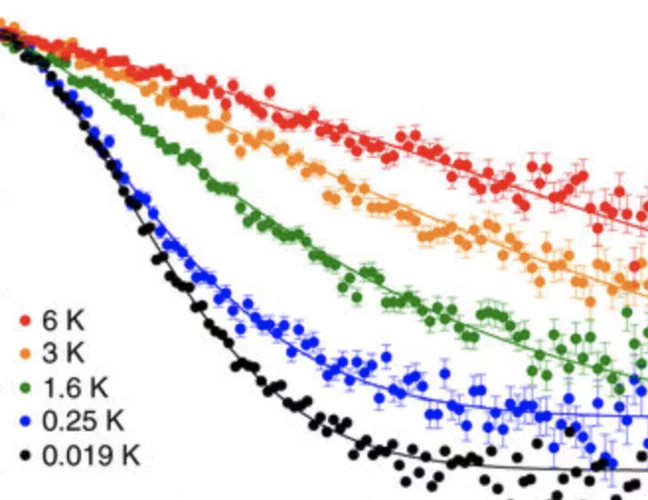
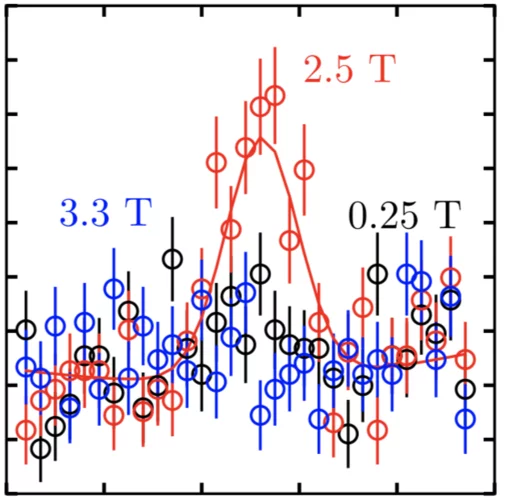
Coulomb spin liquid in anion-disordered pyrochlore Tb2Hf2O7
The charge ordered structure of ions and vacancies characterizing rare-earth pyrochlore oxides serves as a model for the study of geometrically frustrated magnetism. The organization of magnetic ions into networks of corner-sharing tetrahedra gives rise to highly correlated magnetic phases with strong fluctuations, including spin liquids and spin ices. It is an open question how these ground states governed by local rules are affected by disorder.
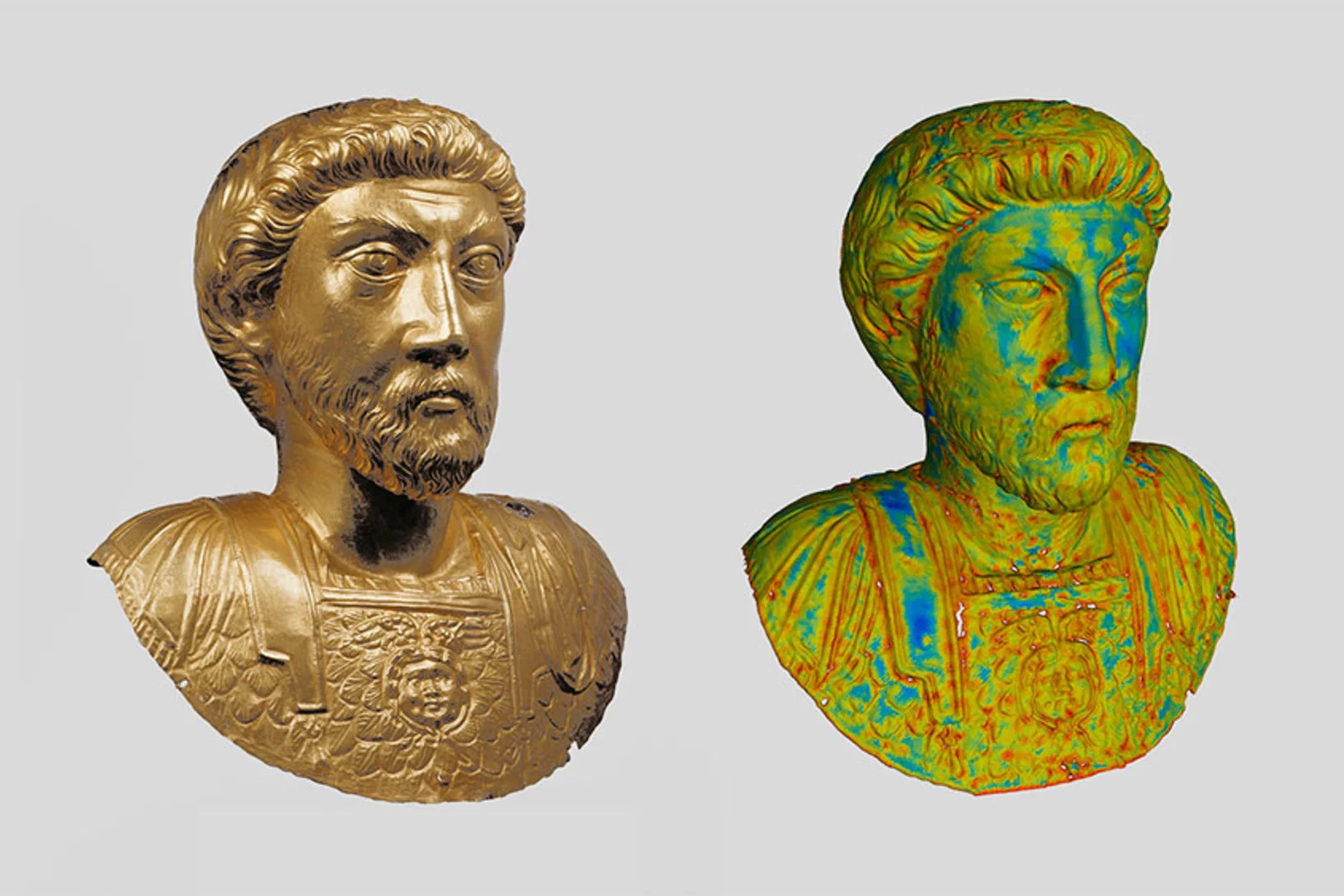
De l'Empereur doré au Bouddha garni
A l'Institut Paul Scherrer PSI, on radiographie des objets métalliques antiques avec des neutrons. Les chercheurs peuvent ainsi identifier ce qu'ils renferment, la manière dont ils ont été fabriqués et comment les conserver.
Commissioning and first performance studies of the new CMS pixel detector
In the previous months the new CMS pixel detector was brought into operation. The detector was moved from PSI to CERN and installed in February, followed by an intensive period of commissioning and calibration. This process mostly involved the adjustment of many operational parameters which influence the detector performance, e.g.
Le travailleur de force du val Mesolcina
Aldo Antognini a la physique et la convivialité dans le sang. Aldo Antognini, chercheur au PSI, a reçu plus de 2 200 000 francs de l’UE pour sa nouvelle expérience. Son objectif: déterminer la répartition du magnétisme dans le proton. Pour y arriver, ce physicien des particules devra mettre ses talents scientifiques et techniques à contribution, mais aussi son entregent.
Complementary Response of Static Spin-Stripe Order and Superconductivity to Nonmagnetic Impurities in Cuprates
We report muon-spin rotation and neutron-scattering experiments on nonmagnetic Zn impurity effects on the static spin-stripe order and superconductivity of the La214 cuprates. Remarkably, it was found that, for samples with hole doping x ≈ 1/8, the spin-stripe ordering temperature Tso decreases linearly with Zn doping y and disappears at y ≈ 4%, demonstrating a high sensitivity of static spin-stripe order to impurities within a CuO2 plane.
Equilibrium Skyrmion Lattice Ground State in a Polar Easy-plane Magnet
The skyrmion lattice state (SkL), a crystal built of mesoscopic spin vortices, gains its stability via thermal fluctuations in all bulk skyrmion host materials known to date. Therefore, its existence is limited to a narrow temperature region below the paramagnetic state. This stability range can drastically increase in systems with restricted geometries, such as thin films, interfaces and nanowires.
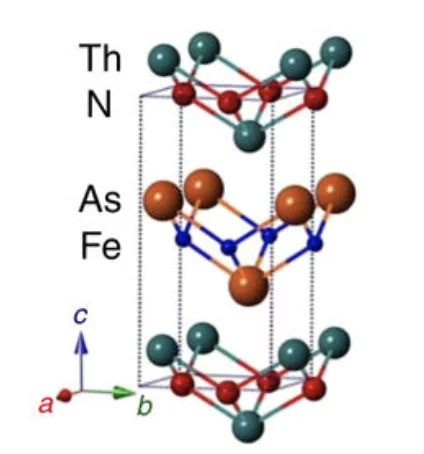
High-Tc superconductivity in undoped ThFeAsN
Unlike the widely studied ReFeAsO series, the newly discovered iron-based superconductor ThFeAsN exhibits a remarkably high critical temperature of 30 K, without chemical doping or external pressure. Here we investigate in detail its magnetic and superconducting properties via muon-spin rotation/relaxation and nuclear magnetic resonance techniques and show that ThFeAsN exhibits strong magnetic fluctuations, suppressed below ≈35 K, but no magnetic order.