Anomalous Hall Effect due to Magnetic Fluctuations in a Ferromagnetic Weyl Semimetal
The anomalous Hall effect (AHE) has emerged as a key indicator of time-reversal symmetry breaking (TRSB) and topological features in electronic band structures. Absent of a magnetic field, the AHE requires spontaneous TRSB but has proven hard to probe due to averaging over domains. The anomalous component of the Hall effect is thus frequently derived from extrapolating the magnetic field dependence of the Hall response. We show ....
Two Characteristic Contributions to the Superconducting State of 2H-NbSe2
Multiband superconductivity arises when multiple electronic bands contribute to the formation of the superconducting state, allowing distinct pairing interactions and gap structures. Here, we present field- and temperature-dependent data ...
Observation of the spiral spin liquid in a triangular-lattice material
The spiral spin liquid (SSL) is a highly degenerate state characterized by a continuous contour or surface in reciprocal space spanned by a spiral propagation vector. Although the SSL state has been predicted in a number of various theoretical models, very few materials are so far experimentally identified to host such a state. Via combined single-crystal wide-angle and small-angle neutron scattering, we report observation ...
Doping dependence of the dipolar correlation length scale in metallic SrTiO3
Superconducting domes, ubiquitous across a variety of quantum materials, are often understood as a window in which pairing is favored, opened by the fluctuations of competing orders. Yet, the understanding of how such a window closes is missing. Here, we show that inelastic neutron scattering ...
Pressure-enhanced splitting of density wave transitions in La3Ni2O7–δ
The observation of superconductivity in La3Ni2O7–δ under pressure, following the suppression of a high-temperature density wave state, has attracted considerable attention. The nature of this density wave order was not clearly identified. Here we probe the magnetic response of the zero-pressure phase of La3Ni2O7–δ as hydrostatic pressure is applied, and find that the apparent single density wave transition at zero applied pressure splits into two. The comparison of our muon-spin rotation ...
Outstanding Paper Award
A recent paper by the "Applied Materials Group" of the LNS and their coworkers received the "Outstanding Paper Award" of the journal "Materials and Structures".
Spin-orbit control of antiferromagnetic domains without a Zeeman coupling
Encoding information in antiferromagnetic (AFM) domains is a promising solution for the ever growing demand in magnetic storage capacity. The absence of a macroscopic magnetization avoids crosstalk between different domain states, enabling ultrahigh density spintronics while being detrimental to the domain detection and manipulation. Disentangling these merits and disadvantages seemed so far unattainable. We report evidence ...
Electronic Commensuration of a Spin Moiré Superlattice in a Layered Magnetic Semimetal
Spin moiré superlattices (SMSs) formed by interfacing conventional electronic states with a multi-q magnetic lattice have been proposed as a magnetic analog of crystallographic moiré systems. The electron-minibands created in an SMS are expected to be enriched by the vector-field nature of the magnetic interaction and offer new types of moiré tunability, topological protection, and Berry curvature effects. However, most spin-vortex-hosting systems discovered to date have carrier mean free paths lmfp significantly shorter than their spin-moiré lattice constant aspin, inhibiting mini-band-formation. Furthermore ...
Anisotropic Skyrmion and Multi-q Spin Dynamics in Centrosymmetric Gd2PdSi3
Skyrmions are particlelike vortices of magnetization with nontrivial topology, which are usually stabilized by Dzyaloshinskii-Moriya interactions (DMI) in noncentrosymmetric bulk materials. Exceptions are centrosymmetric Gd- and Eu-based skyrmion-lattice (SL) hosts with zero DMI, where both the SL stabilization mechanisms and magnetic ground states remain controversial. We address these here by investigating both the static and dynamical spin properties ...
Concurrent Operando Neutron Imaging and Diffraction Analysis Revealing Spatial Lithiation Phase Evolution in an Ultra-Thick Graphite Electrode
Energy-efficient, safe, and reliable Li-ion batteries (LIBs) are required for a wide range of applications. The introduction of ultra-thick graphite anodes, desired for high energy densities, meets limitations in internal electrode transport properties, leading to detrimental consequences. Yet, there is a lack of experimental tools capable of providing a complete view of local processes. Here, a multi-modal operando measurement approach is introduced, enabling quantitative spatio-temporal observations of Li concentrations and intercalation phases in ultra-thick graphite electrodes.
Neutron imaging and diffraction concurrently provide ...
Operando Neutron Characterization During 3D Printing
A new laser powder bed fusion device enables real-time neutron diffraction and imaging, providing detailed insights into structural evolution, defect formation, and temperature mapping during metal additive manufacturing.
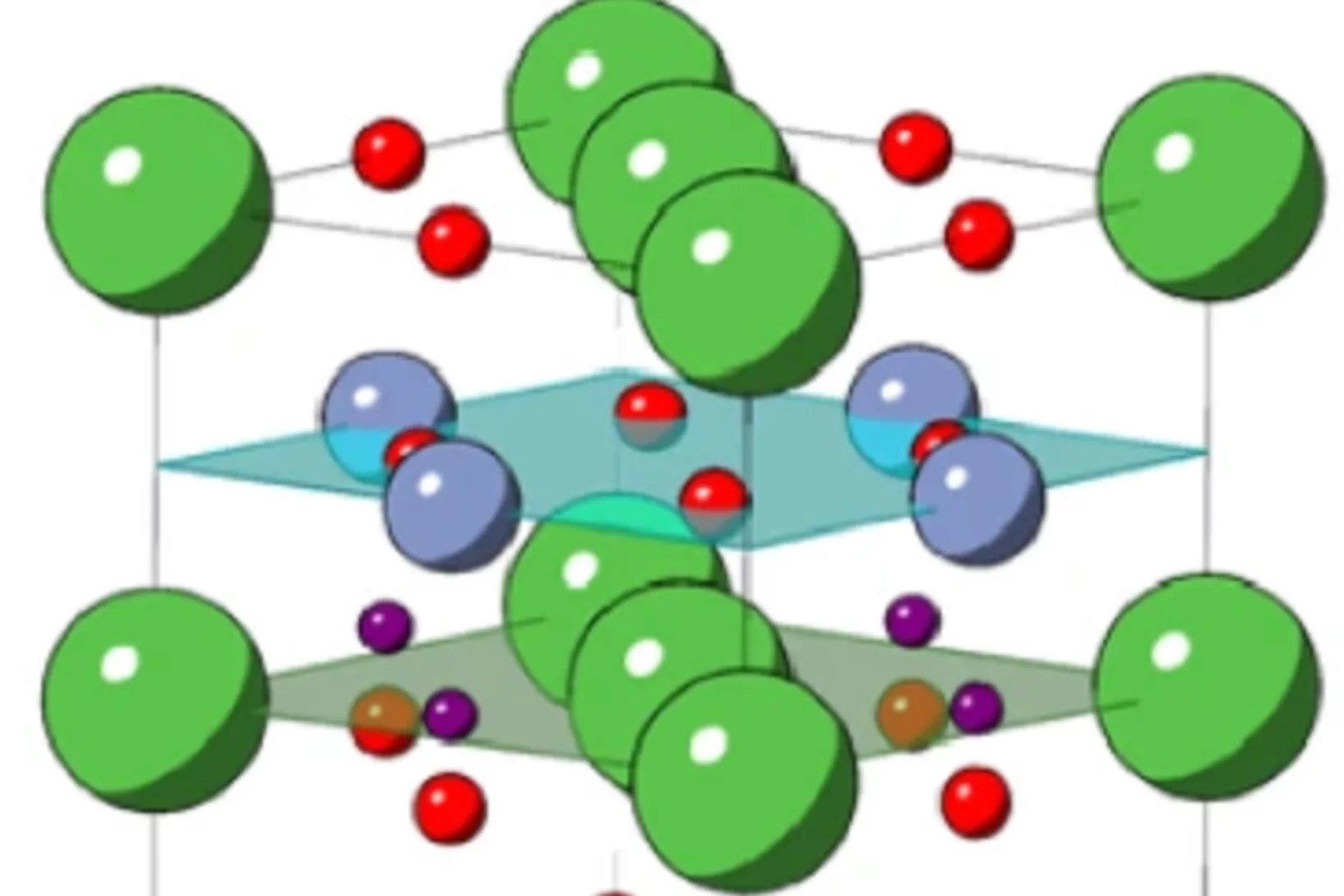
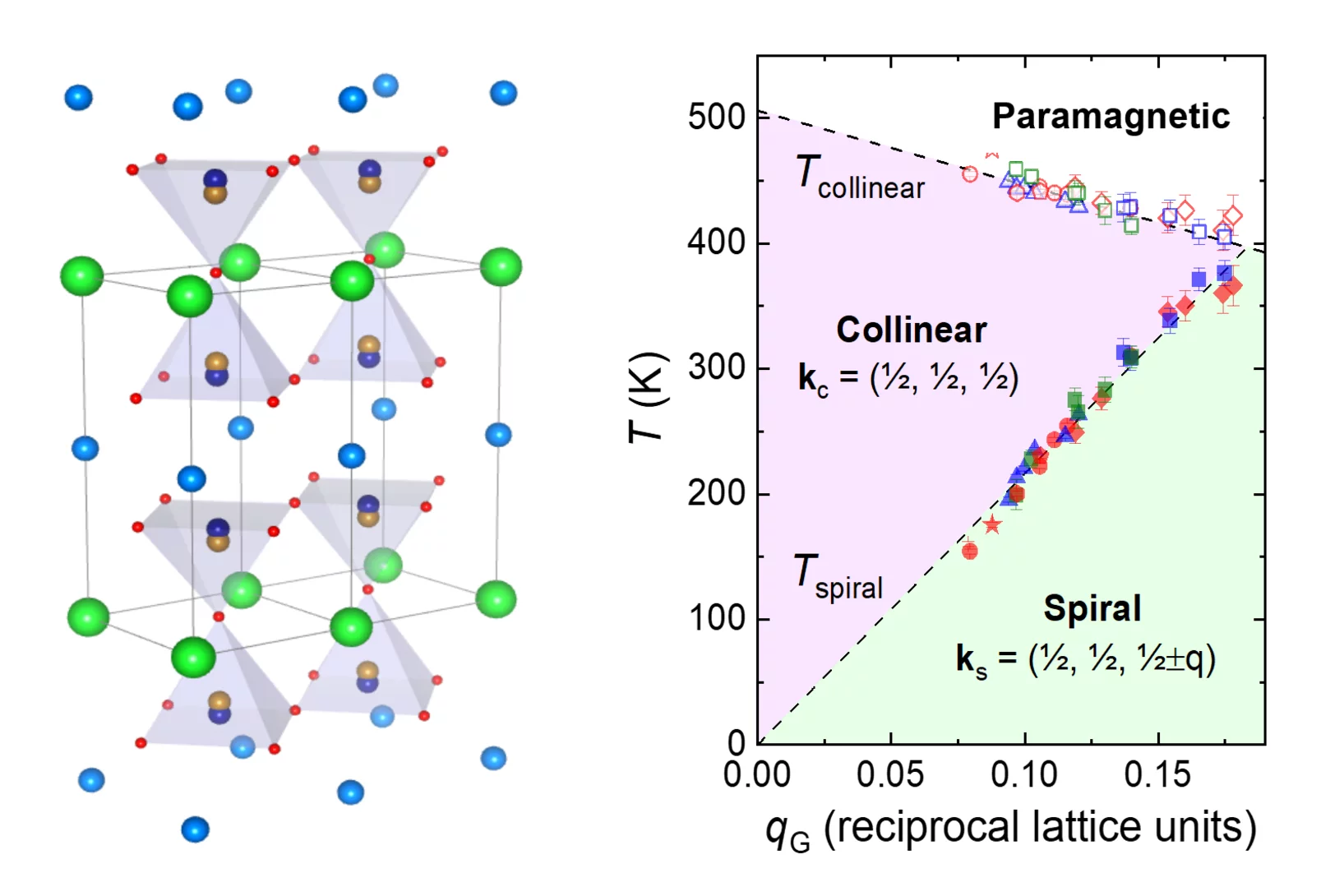
YBa1−𝑥Sr𝑥CuFeO5 layered perovskites: An attempt to explore the magnetic order beyond the paramagnetic-collinear-spiral triple point
Layered perovskites of general formula AA'CuFeO5 are characterized by the presence of spiral magnetic phases whose ordering temperatures 𝑇spiral can be tuned far beyond room temperature by introducing modest amounts of Cu/Fe chemical disorder in the crystal structure. This rare property makes these materials prominent candidates to host multiferroicity and magnetoelectric coupling at temperatures suitable for applications. Moreover, it has been proposed that the highest 𝑇spiral value that can be reached in this structural family ( ∼400 K) corresponds to a paramagnetic-collinear-spiral triple point with potential to show exotic physics. Since generating high amounts of Cu/Fe disorder is experimentally difficult, the phase diagram region beyond the triple point has been barely explored. To fill this gap we investigate here eleven YBa1−𝑥Sr𝑥CuFeO5 solid solutions (0≤𝑥≤1 ), where we replace Ba with Sr with the aim of enhancing the impact of the experimentally available Cu/Fe disorder. Using a combination of bulk magnetization measurements, synchrotron x-ray and neutron powder diffraction we show that the spiral state with 𝐤𝑠=(1/2,1/2,1/2±𝑞) is destabilized beyond a critical Sr content, being replaced by a fully antiferromagnetic state with ordering temperature 𝑇coll2≥𝑇spiral and propagation vector 𝐤𝑐2=(1/2,1/2,0). Interestingly, both 𝑇spiral and 𝑇coll2 increase with 𝑥 with comparable rates. This suggests a common, disorder-driven origin for both magnetic phases, consistent with theoretical predictions.
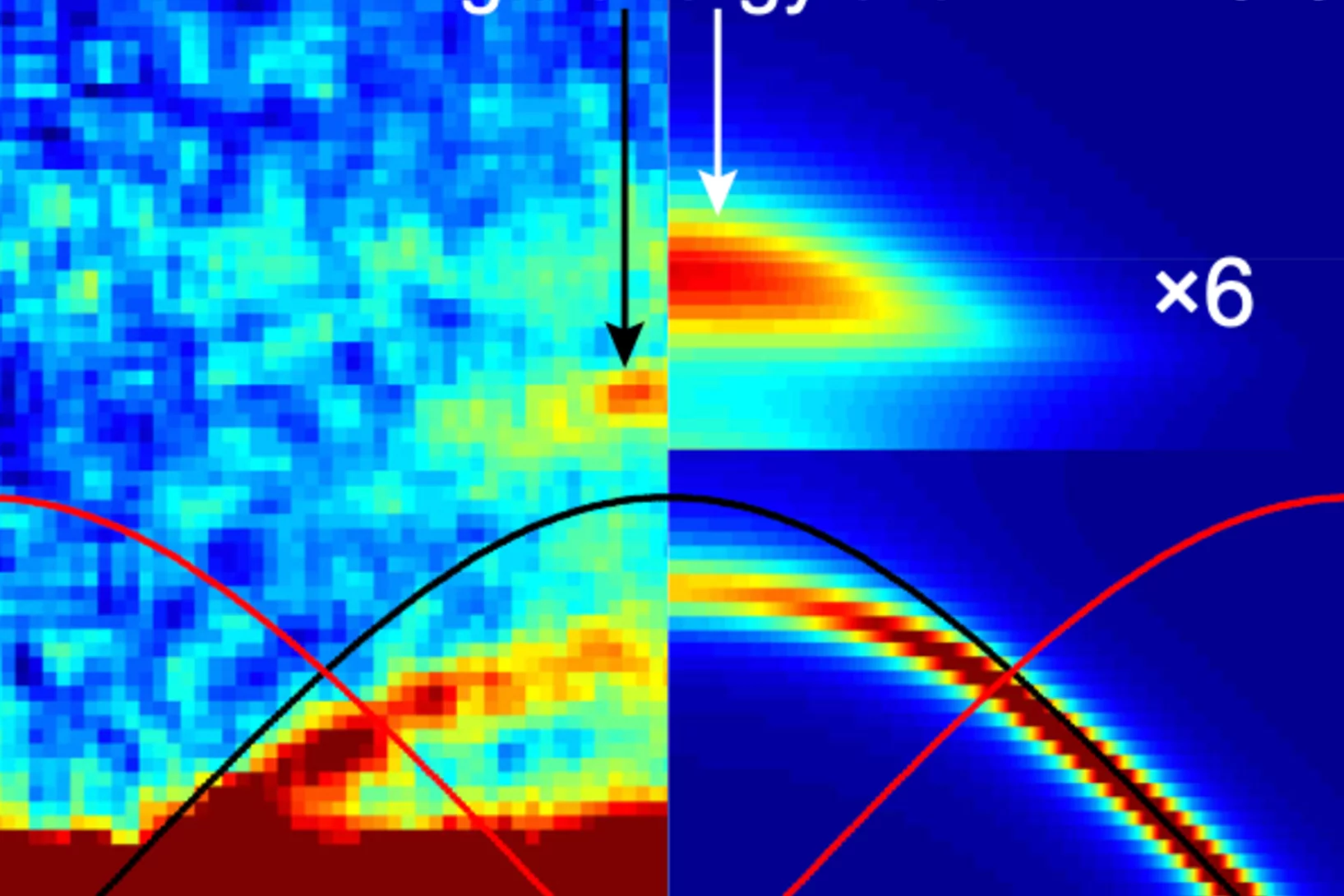
Connection between f-electron correlations and magnetic excitations in UTe2
The detailed anisotropic dispersion of the low-temperature, low-energy magnetic excitations of the candidate spin-triplet superconductor UTe2 is revealed using inelastic neutron scattering. The magnetic excitations emerge from the Brillouin zone boundary at the high symmetry Y and T points and disperse along the crystallographic b-axis. In applied magnetic fields ...
Small-angle scattering interferometry with neutron orbital angular momentum states
Methods to prepare and characterize neutron helical waves carrying orbital angular momentum (OAM) were recently demonstrated at small-angle neutron scattering (SANS) facilities. These methods enable access to the neutron orbital degree of freedom which provides new avenues of exploration in fundamental science experiments as well as in material characterization applications.
However, ....
Fractional quasiparticles in three dimensions
Specific signatures of fractionalization have been observed in a three-dimensional system known as quantum spin ice.
Mapping the Nanoscale Architecture of Functional Materials
A new X-ray technique reveals the 3D orientation of ordered material structures at the nanoscale, allowing new insights into material functionality.
Evidence of antiferromagnetism in ultrathin metallic (111)-oriented LaNiO3 films
Antiferromagnets with exotic spin textures promise low-power spintronic devices with extremely high operating frequencies and resistance to external perturbations. In particular, the combination of highly tunable correlated electron physics, as in complex oxides, with metallicity and antiferromagnetism is desirable but exceedingly rare. LaNiO3, the lone example of a perovskite nickelate which is metallic across all temperatures, has long been a promising candidate, but the antiferromagnetic metallic state has remained elusive. We demonstrate the emergence ...
Together for Science with Neutrons, Muons and X-rays
Strategic partnership between research facilities in UK and Switzerland will create new capabilities to address global challenges using neutrons, muons and X-rays.
Origin of the Suppression of Magnetic Order in MnSi under Hydrostatic Pressure
We experimentally study the evolution of the magnetic moment 𝑚 and exchange interaction 𝐽 as a function of hydrostatic pressure in the zero-field helimagnetic phase of the strongly correlated electron system MnSi. The suppression of magnetic order at ≈1.5 GPa is shown to arise from the 𝐽 collapse and not from a quantum fluctuations induced reduction of 𝑚. Our work provides benchmarks ...
Operando phase mapping in multi-material laser powder bed fusion
Additive manufacturing (AM) or “3D printing” of metals, which builds structure layer by layer, has revolutionized the production of intricate 3D designs. Among its techniques, laser powder bed fusion (PBF-LB) excels in creating metallic parts with intricate designs and high precision. This process can combine different metals into innovative multi-material components with tailored properties, with regards to e.g., strength and thermal conductivity, surpassing the capabilities of single-material designs. However, ....
Continuum Excitations in a Spin Supersolid on a Triangular Lattice
Magnetic, thermodynamic, neutron diffraction and inelastic neutron scattering are used to study spin correlations in the easy-axis XXZ triangular lattice magnet K2Co(SeO3)2. Despite the presence of quasi-2D “supersolid” magnetic order, the low-energy excitation spectrum contains no sharp modes and is instead a broad and structured multiparticle continuum. Applying a weak magnetic field ...
Kagome breaks the rules at record breaking temperatures
Discovery of quantum phenomenon at accessible temperatures could be useful for quantum technologies.
Reentrant multiple-q magnetic order and a “spin meta-cholesteric” phase in Sr3Fe2O7
Topologically nontrivial magnetic structures such as skyrmion lattices are well known in materials lacking lattice inversion symmetry, where antisymmetric exchange interactions are allowed. Only recently, topological multi-q magnetic textures that spontaneously break the chiral symmetry, for example, three-dimensional hedgehog lattices, were discovered in centrosymmetric compounds, where they are instead driven by frustrated interactions. Here we show that ...
Ferromagnetic quantum critical point protected by nonsymmorphic symmetry in a Kondo metal
Quantum critical points (QCPs), zero-temperature phase transitions, are win- dows to fundamental quantum-mechanical phenomena associated with universal behaviour. Magnetic QCPs have been extensively investigated in the vicinity of antiferromagnetic order. However, QCPs are rare in metallic ferromagnets due to the coupling of the order parameter to electronic soft modes. Recently, antisymmetric spin-orbit coupling in noncentrosymmetric systems was suggested to protect ferromagnetic QCPs. Nonetheless, multiple centrosymmetric materials ...
Quantum Spin Dynamics Due to Strong Kitaev Interactions in the Triangular-Lattice Antiferromagnet CsCeSe2
The extraordinary properties of the Kitaev model have motivated an intense search for new physics in materials that combine geometrical and bond frustration. In this Letter, we employ inelastic neutron scattering, spin wave theory, and exact diagonalization to study the spin dynamics in the perfect triangular-lattice antiferromagnet (TLAF) CsCeSe2. This material orders into a stripe phase, which is demonstrated to arise as a consequence of the off-diagonal bond-dependent terms in the spin Hamiltonian ...
Evidence for time-reversal symmetry-breaking kagome superconductivity
Superconductivity and magnetism are often antagonistic in quantum matter, although their intertwining has long been considered in frustrated-lattice systems. Here we utilize scanning tunnelling microscopy and muon spin resonance to demonstrate time-reversal symmetry-breaking superconductivity in kagome metal Cs(V, Ta)3Sb5, where the Cooper pairing exhibits magnetism and is modulated by it. In the magnetic channel, we observe spontaneous internal magnetism ...
Chiral kagome superconductivity modulations with residual Fermi arcs
Superconductivity involving finite-momentum pairing can lead to spatial-gap and pair-density modulations, as well as Bogoliubov Fermi states within the superconducting gap. However, the experimental realization of their intertwined relations has been challenging. Here we detect chiral kagome superconductivity modulations with residual Fermi arcs in KV3Sb5 and CsV3Sb5 using normal and Josephson scanning tunnelling microscopy down to 30 millikelvin with a resolved electronic energy difference at the microelectronvolt level. We observe a U-shaped ...
Room temperature magnetoelectric magnetic spirals by design
Frustrated magnets with ordered magnetic spiral phases that spontaneously break inversion symmetry have received significant attention from both fundamental and applied sciences communities due to the experimental demonstration that some of these materials can couple to the lattice and induce electric polarization. In these materials, the common origin of the electric and magnetic orders guarantees substantial coupling between them, which is highly desirable for applications ...
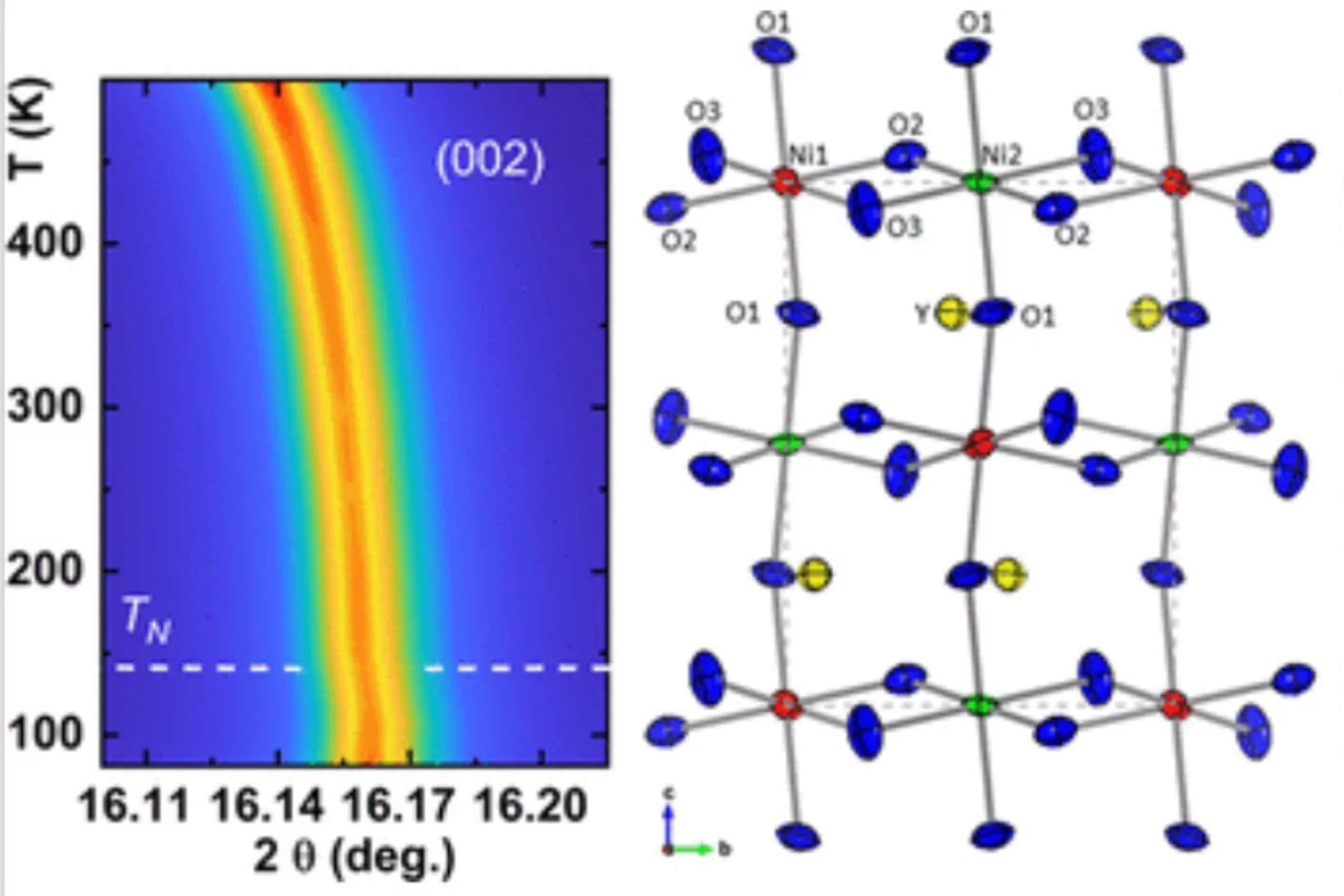
Magnetostructural Coupling at the Néel Point in YNiO3 Single Crystals
The recent discovery of superconductivity in infinite layer thin films and bulk Ruddlesden–Popper nickelates has stimulated the investigation of other predicted properties of these materials. Among them, the existence of magnetism-driven ferroelectricity in the parent compounds RNiO3 (R = 4f lanthanide and Y) at the onset of the Néel order, TN, has remained particularly elusive. Using diffraction techniques, we reveal here the existence of magnetostriction at TN in bulk YNiO3 single crystals. Interestingly, the associated lattice anomalies ...
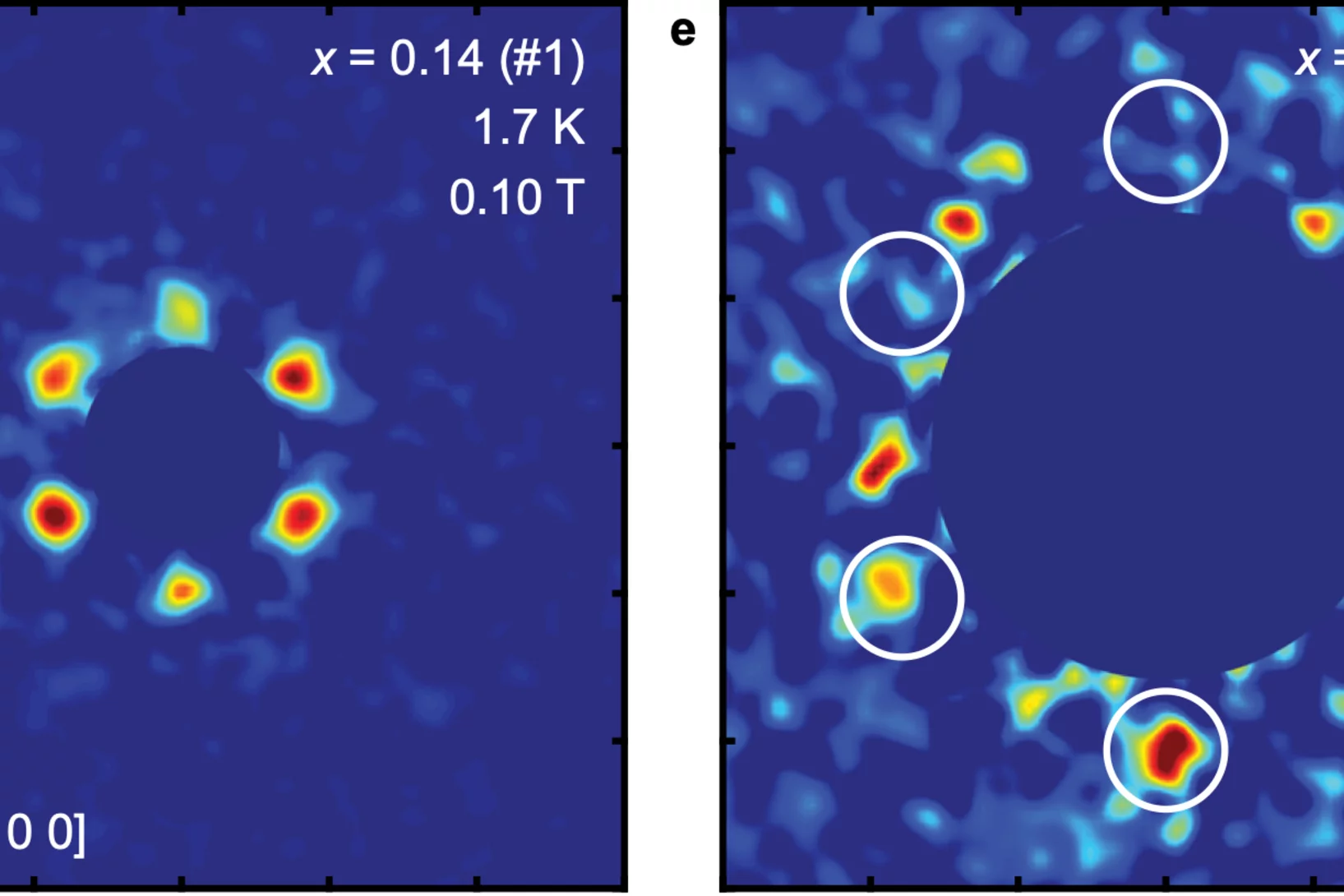
Conventional superconductivity in the doped kagome superconductor Cs(V0.86Ta0.14)3Sb5 from vortex lattice studies
A hallmark of unconventional superconductors is a complex electronic phase diagram where intertwined orders of charge-spin-lattice degrees of freedom compete and coexist. While the kagome metals such as CsV3Sb5 also exhibit complex behavior, involving coexisting charge density wave order and superconductivity, much is unclear about the microscopic origin of the superconducting pairing. We study the vortex lattice in the superconducting state of Cs(V0.86Ta0.14)3Sb5, where the Ta-doping suppresses charge order and enhances superconductivity. Using small-angle neutron scattering ...