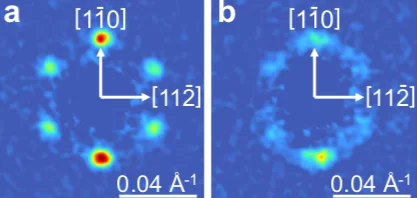
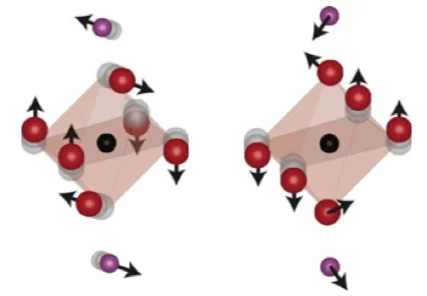
Macroscopic manifestation of domain-wall magnetism and magnetoelectric effect in a Néel-type skyrmion host
We report a magnetic state in GaV4Se8 which emerges exclusively in samples with mesoscale polar domains and not in polar mono- domain crystals. It is manifested by a sharp anomaly in the magnetic susceptibility and the magnetic torque, distinct from other anomalies observed also in polar mono-domain samples upon transitions between the cycloidal, the Néel-type skyrmion lattice and the ferromagnetic states.
Thermal Control of Spin Excitations in the Coupled Ising-Chain Material RbCoCl3
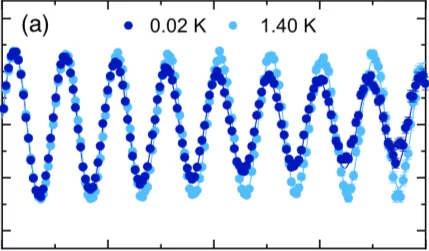
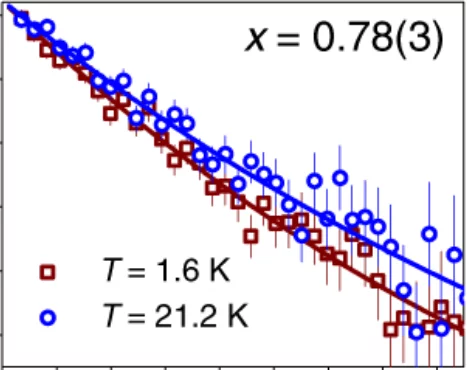
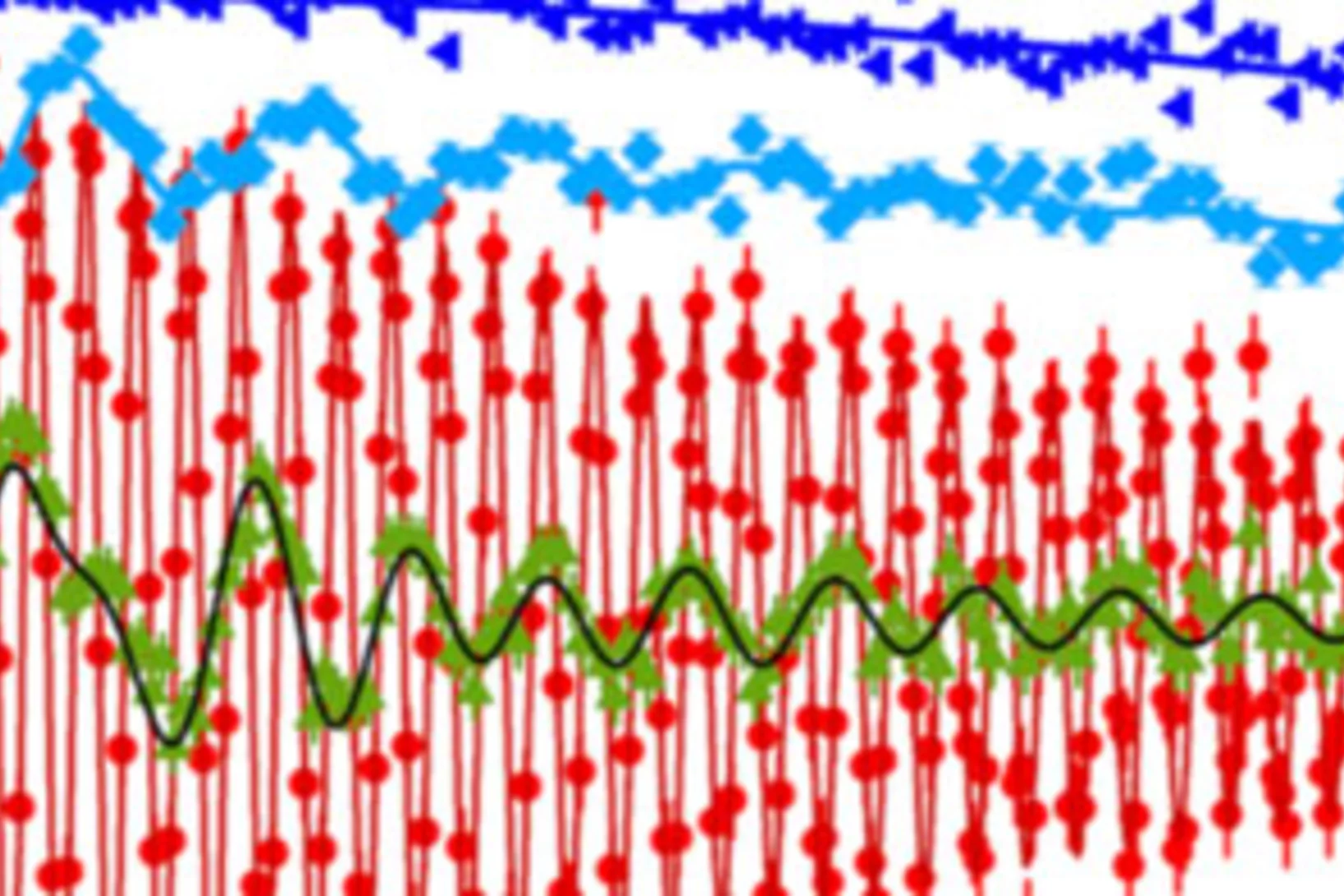
We have used neutron spectroscopy to investigate the spin dynamics of the quantum (S=1/2) antiferromagnetic Ising chains in RbCoCl3. The structure and magnetic interactions in this material conspire to produce two magnetic phase transitions at low temperatures, presenting an ideal opportunity for thermal control of the chain environment. The high-resolution spectra we measure ...
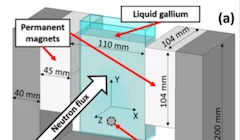
Phase boundary dynamics of bubble flow in a thick liquid metal layer under an applied magnetic field
We investigate argon bubble flow in liquid gallium within a container large enough to avoid wall effects. Flow with and without applied horizontal magnetic field is studied. We demonstrate the successful capture and quantification of the effects of applied magnetic field using dynamic neutron radiography and the previously developed and validated robust image processing pipeline, supported by the in silico reproduction of our experiment.
Z3-vestigial nematic order due to superconducting fluctuations in the doped topological insulators NbxBi2Se3 and CuxBi2Se3
A state of matter with a multi-component order parameter can give rise to vestigial order. In the vestigial phase, the primary order is only partially melted, leaving a remaining symmetry breaking behind, an effect driven by strong classical or quantum fluctuations. Vestigial states due to primary spin and charge-density-wave order have been discussed in iron-based and cuprate materials. Here we present the observation of a partially melted superconductivity in which pairing fluctuations condense at a separate phase transition and form a nematic state with broken Z3, i.e., three-state Potts-model symmetry.
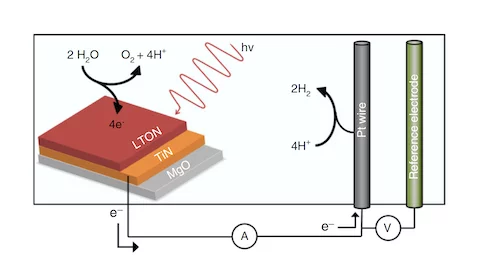
Zooming in on water splitting
Perovskite oxynitride materials can act as effective photocatalysts for water splitting driven by visible light. A combined neutron and x-ray study now provides unique insight into the underlying processes at the solid–liquid interface and highlights how solar-to-hydrogen conversion can be improved.
Simultaneous Nodal Superconductivity and Time-Reversal Symmetry Breaking in the Noncentrosymmetric Superconductor CaPtAs
By employing a series of experimental techniques, we provide clear evidence that CaPtAs represents a rare example of a noncentrosymmetric superconductor which simultaneously exhibits nodes in the superconducting gap and broken time-reversal symmetry (TRS) in its superconducting state (belowTc ≈ 1.5 K). Unlike in fully gapped superconductors, the magnetic penetration depth λ(T) does not saturate at low temperatures, but instead it shows a T2 dependence, characteristic of gap nodes.
Superconductivity with broken time-reversal symmetry inside a superconducting s-wave state
In general, magnetism and superconductivity are antagonistic to each other. However, there are several families of superconductors in which superconductivity coexists with magnetism, and a few examples are known where the superconductivity itself induces spontaneous magnetism. The best known of these compounds are Sr2RuO4 and some non-centrosymmetric superconductors. Here, we report the finding of ...
Laser focus on mesons
The first demonstration of laser spectroscopy of a meson, achieved at PSI's πE5 beamline, opens up new avenues for precision studies of ‘exotic atoms’.
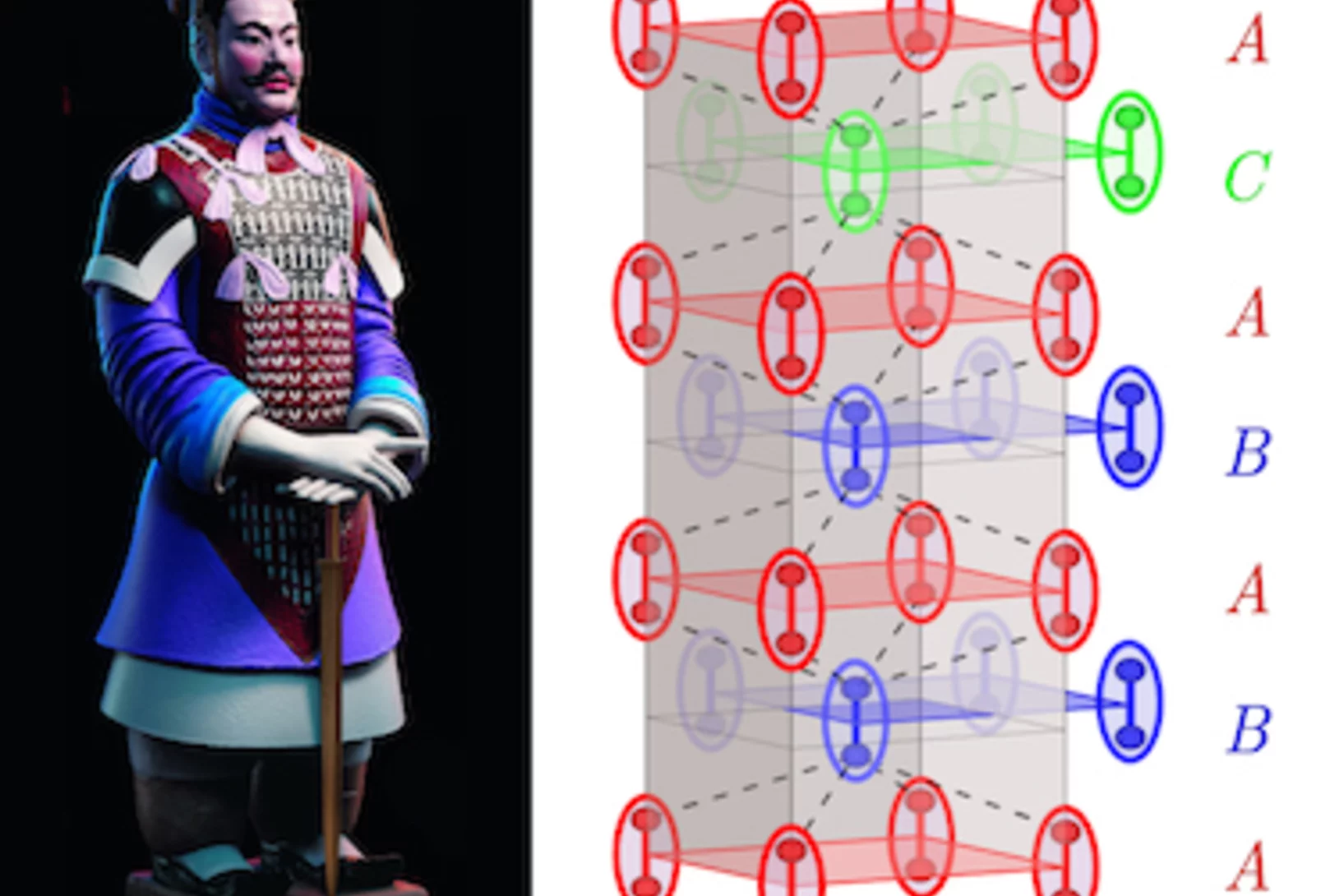
Understanding Quantum Critical Magnetism in Han Purple
The ancient purple pigment used to paint the terracotta warriors, BaCuSi2O6, is also a quantum magnetic material which consists of stacked Cu2+ bilayers hosting spin dimers. Magnetometry and NMR experiments have revealed puzzling critical phenomena at the quantum phase transition (QPT) caused by an applied magnetic field, which suggest that the universal behaviour of the system is not three- but only two-dimensional. By performing high-resolution neutron spectroscopy measurements .....
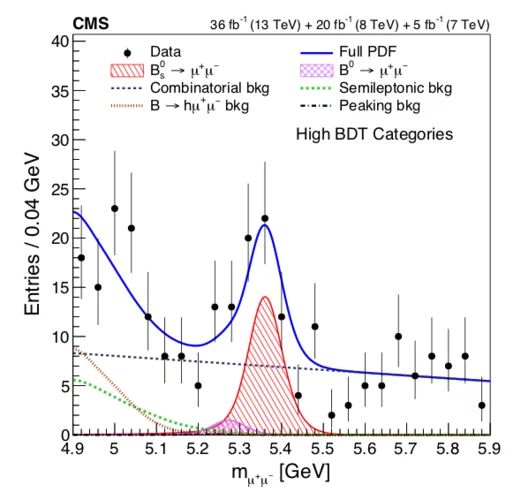
Measurement of properties of Bs0 → μ+μ− decays and search for B0 → μ+μ− with the CMS experiment
Results are reported for the B0s → μ+μ− branching fraction and effective lifetime and from a search for the decay B0 → μ+μ−. The analysis uses a data sample of proton-proton collisions accumulated by the CMS experiment in 2011, 2012, and 2016, with center-of-mass energies (integrated luminosities) of 7TeV (5fb−1), 8TeV (20fb−1),and 13TeV (36fb−1).
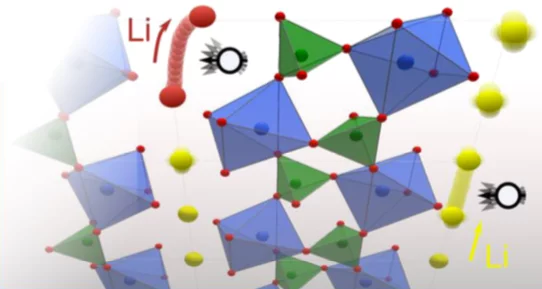
Batteries under the neutron stroboscope
The first application of stroboscopic neutron diffraction to studying lithium-ion batteries during operation establishes a new approach to unravelling the complex processes playing out in energy-storage materials.
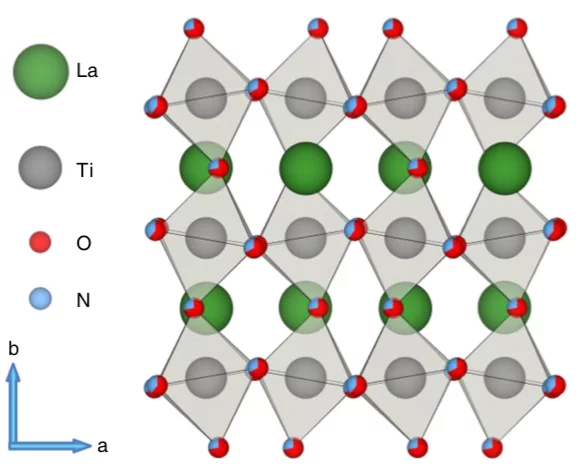
Examining the surface evolution of LaTiOxNy an oxynitride solar water splitting photocatalyst
LaTiOxNy oxynitride thin films are employed to study the surface modifications at the solid- liquid interface that occur during photoelectrocatalytic water splitting. Neutron reflectometry and grazing incidence x-ray absorption spectroscopy were utilised to distinguish between the surface and bulk signals, with a surface sensitivity of 3 nm.
Electron–phonon-driven three-dimensional metallicity in an insulating cuprate
Elucidating the role of different degrees of freedom in a phase transition is crucial in the comprehension of complex materi- als. A phase transformation that attracts significant interest is the insulator-to-metal transition of Mott insulators, in which the electrons are thought to play the dominant role. Here, we use ultrafast laser spectroscopy and theoretical calculations ....
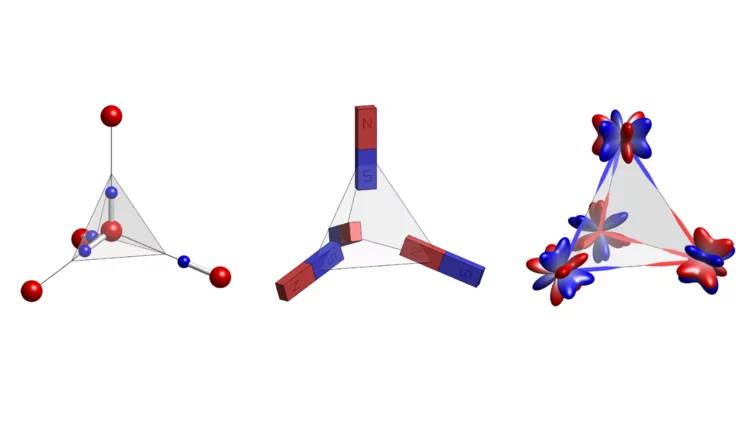
Spin ice expands to higher orders
With experimental work demonstrating that the correlated ground state of the pyrochlore system Ce2Sn2O7 is a quantum liquid of magnetic octupoles, an international team led by PSI researcher Romain Sibille establishes a fundamentally new state of matter: higher-rank multipole ice.
A quantum liquid of magnetic octupoles on the pyrochlore lattice
With experimental work demonstrating that the correlated ground state of the pyrochlore system Ce2Sn2O7 is a quantum liquid of magnetic octupoles, an international team led by PSI researcher Romain Sibille establishes a fundamentally new state of matter: higher-rank multipole ice.
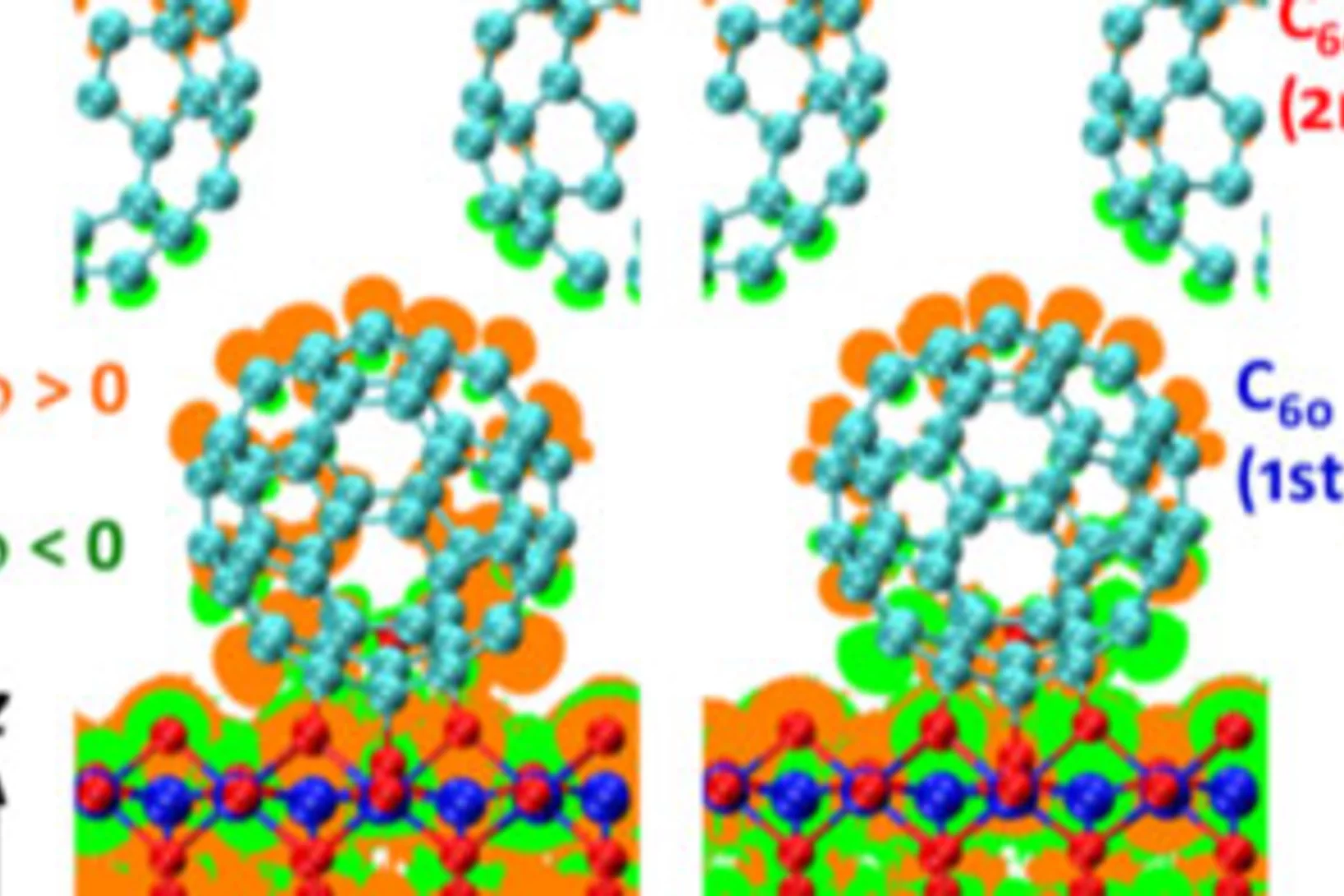
Reversible spin storage in metal oxide - fullerene heterojunctions
We show that hybrid MnOx/C60 heterojunctions can be used to design a storage device for spin-polarized charge: a spin capacitor. Hybridization at the carbon-metal oxide interface leads to spin-polarized charge trapping after an applied voltage or photocurrent. Strong electronic structure changes, including a 1-eV energy shift and spin polarization in the C60 lowest unoccupied molecular orbital, are then revealed by x-ray absorption spectroscopy, in agreement with density functional theory simulations.
Quantifying Diffusion through Interfaces of Lithium-Ion Battery Active Materials
Detailed understanding of charge diffusion processes in a lithium-ion battery is crucial to enable its systematic improvement. Experimental investigation of diffusion at the interface between active particles and the electrolyte is challenging but warrants investigation as it can introduce resistances that, for example, limit the charge and discharge rates. Here, we show an approach to study diffusion at interfaces using muon spin spectroscopy.
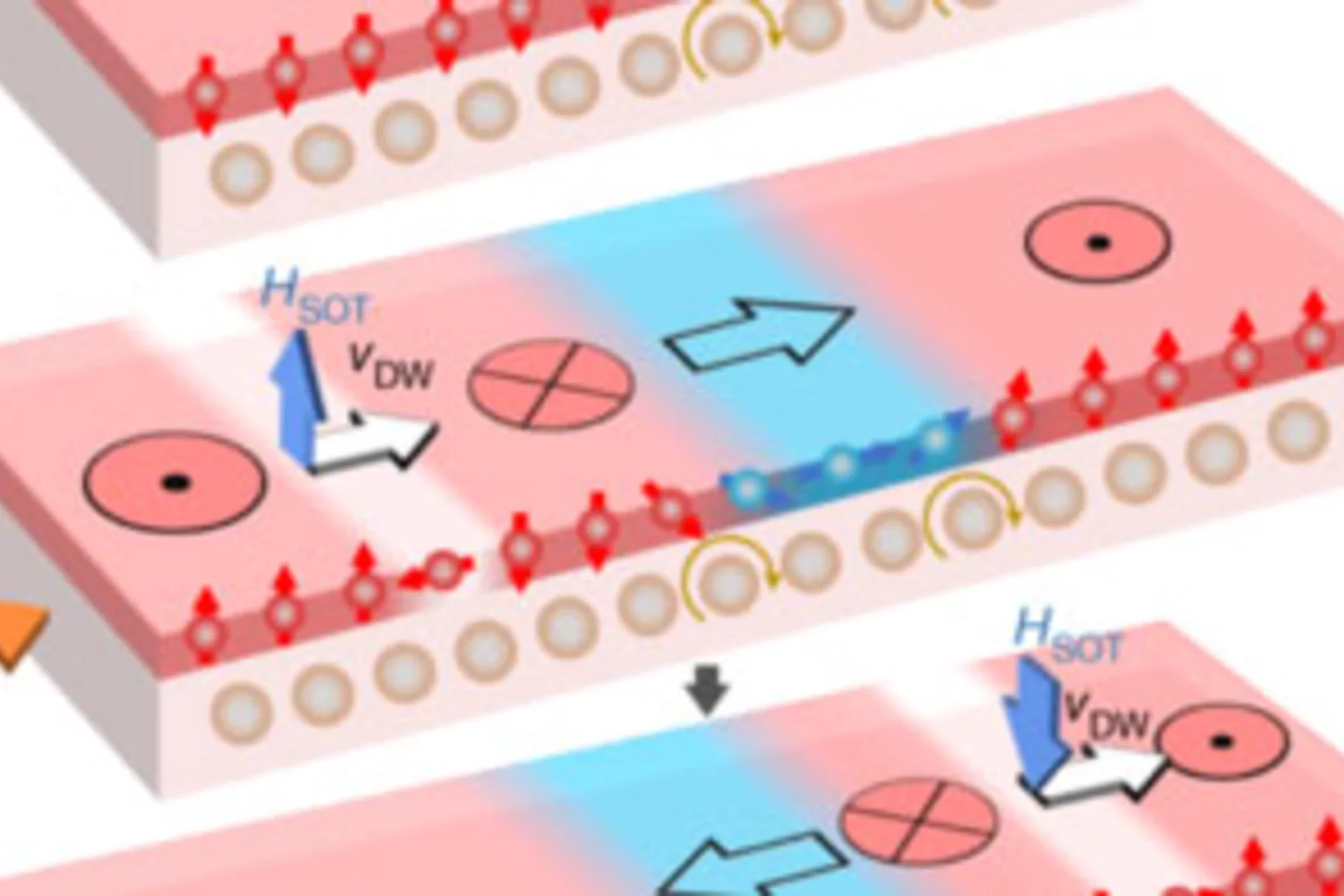
Current-driven magnetic domain-wall logic
Spin-based logic architectures provide nonvolatile data retention, near-zero leakage, and scalability, extending the technology roadmap beyond complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor logic. Architectures based on magnetic domain walls take advantage of the fast motion, high density, non-volatility and flexible design of domain walls to process and store information. Such schemes, however, rely on domain-wall manipulation and clocking using an external magnetic field, which limits their implementation in dense, large-scale chips.
Broken time-reversal symmetry in the topological superconductor UPt3
Topological properties of materials are of fundamental as well as practical importance. Of particular interest are unconven- tional superconductors that break time-reversal symmetry, for which the superconducting state is protected topologically and vortices can host Majorana fermions with potential use in quantum computing. However, in striking contrast to the unconventional A phase of superfluid 3He where chiral symmetry was directly observed, .....
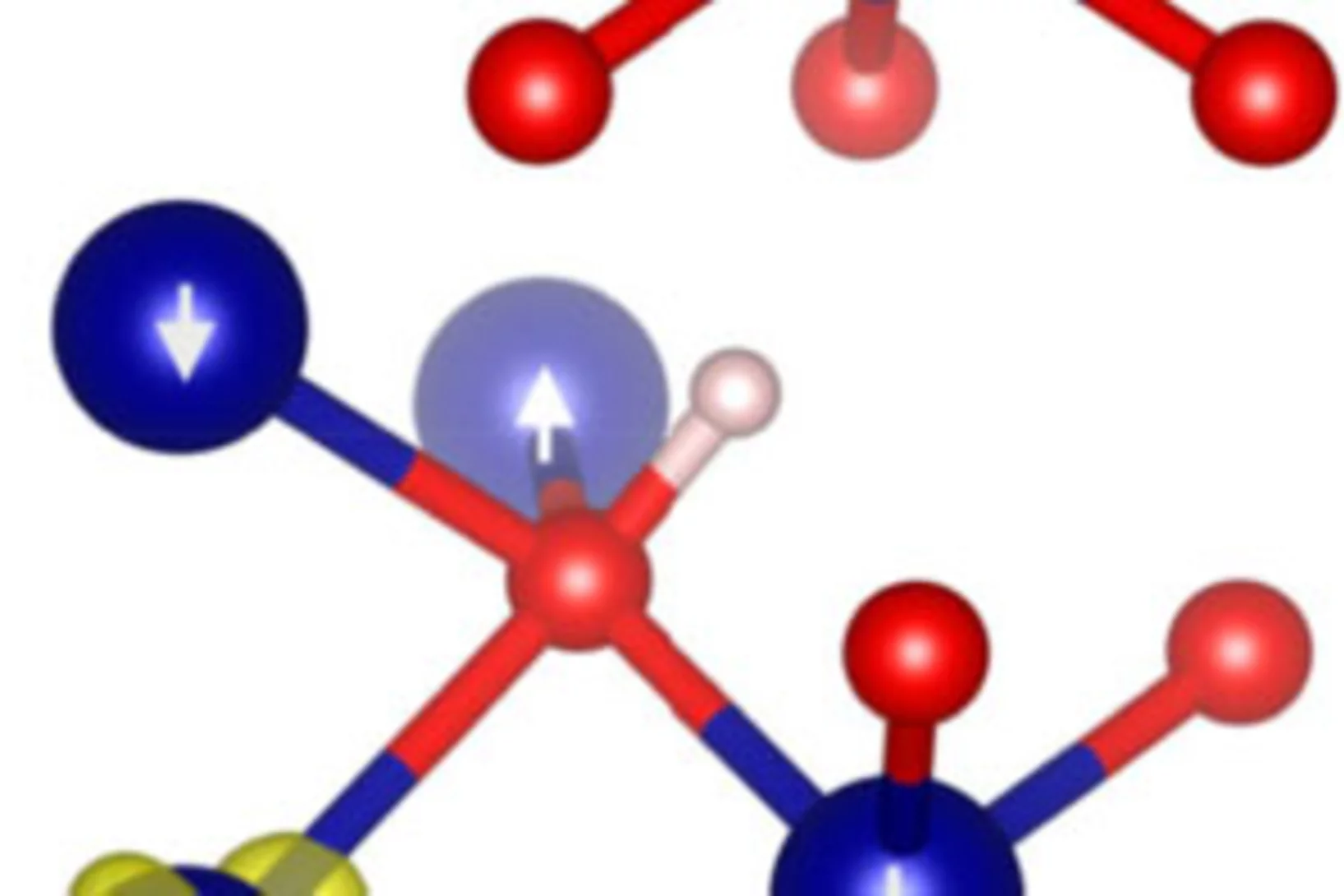
Observation of a Charge-Neutral Muon-Polaron Complex in Antiferromagnetic Cr2O3
We report a comprehensive muon spin rotation (μSR) study of the prototypical magnetoelectric antiferromagnet Cr2O3. We find the positively charged muon (μ+) occupies several distinct interstitial sites and displays a rich dynamic behavior involving local hopping, thermally activated site transitions, and the formation of a charge-neutral complex composed of a muon and an electron polaron.
A link between quantum magnetism and electronic band topology
Muon spin rotation experiments establish a quantitative link between the magnetic and topological electronic properties of the kagome magnet Co3Sn2S2 — and demonstrate effective ways for tuning these properties.
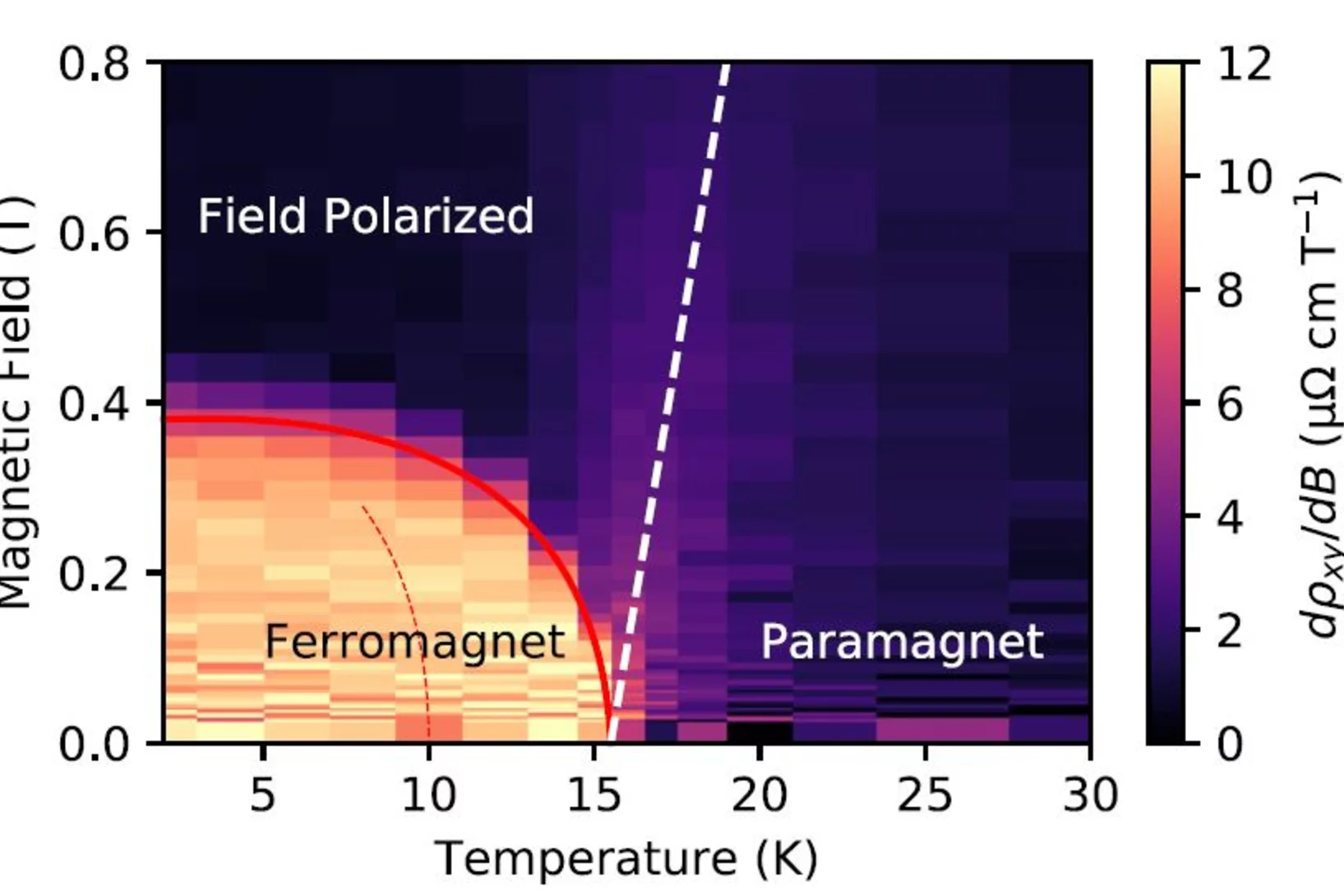
Tunable anomalous Hall conductivity through volume-wise magnetic competition in a topological kagome magnet
Magnetic topological phases of quantum matter are an emerging frontier in physics and material science. Along these lines, several kagome magnets have appeared as the most promising platforms. Here, we explore magnetic correlations in the kagome magnet Co3Sn2S2. Using muon spin-rotation, we present evidence for competing magnetic orders in the kagome lattice of this compound.
Possible room-temperature signatures of unconventional 4f-electron quantum criticality in YbMn6Ge6−xSnx
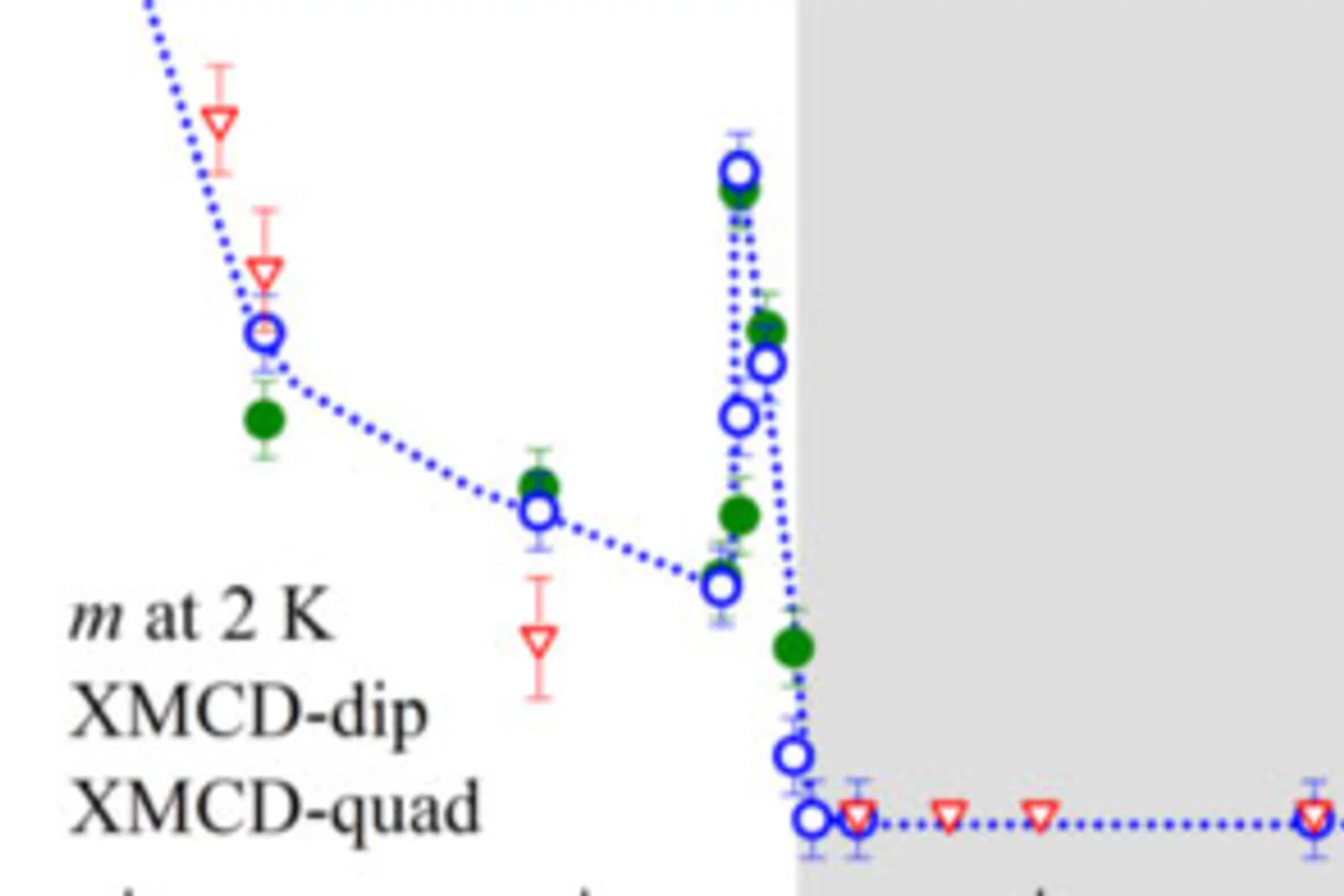
We investigate the Sn composition dependence of the Yb valence and local magnetization in YbMn6Ge6−xSnx (4.25 ≤x≤ 5.80) using x-ray absorption spectroscopy (XANES) and x-ray magnetic circular dichroism at the Yb L3 edge. In these materials, where Mn is ferromagnetically ordered, we observe a decrease of the Yb valence upon reducing the chemical pressure by Sn doping and a suppression of the Yb magnetic moment for strongly hybridized 4f states (ν ∼ 2.77).
Magnetism and anomalous transport in the Weyl semimetal PrAlGe: possible route to axial gauge fields
In magnetic Weyl semimetals, where magnetism breaks time-reversal symmetry, large magnetically sensitive anomalous transport responses are anticipated that could be useful for topological spintronics. The identification of new magnetic Weyl semimetals is therefore in high demand, particularly since in these systems Weyl node configurations may be easily modified using magnetic fields. Here we explore experimentally the magnetic semimetal PrAlGe, and unveil a direct correspondence between easy-axis Pr ferromagnetism and anomalous Hall and Nernst effects.
Topological Magnetic Phase in the Candidate Weyl Semimetal CeAlGe
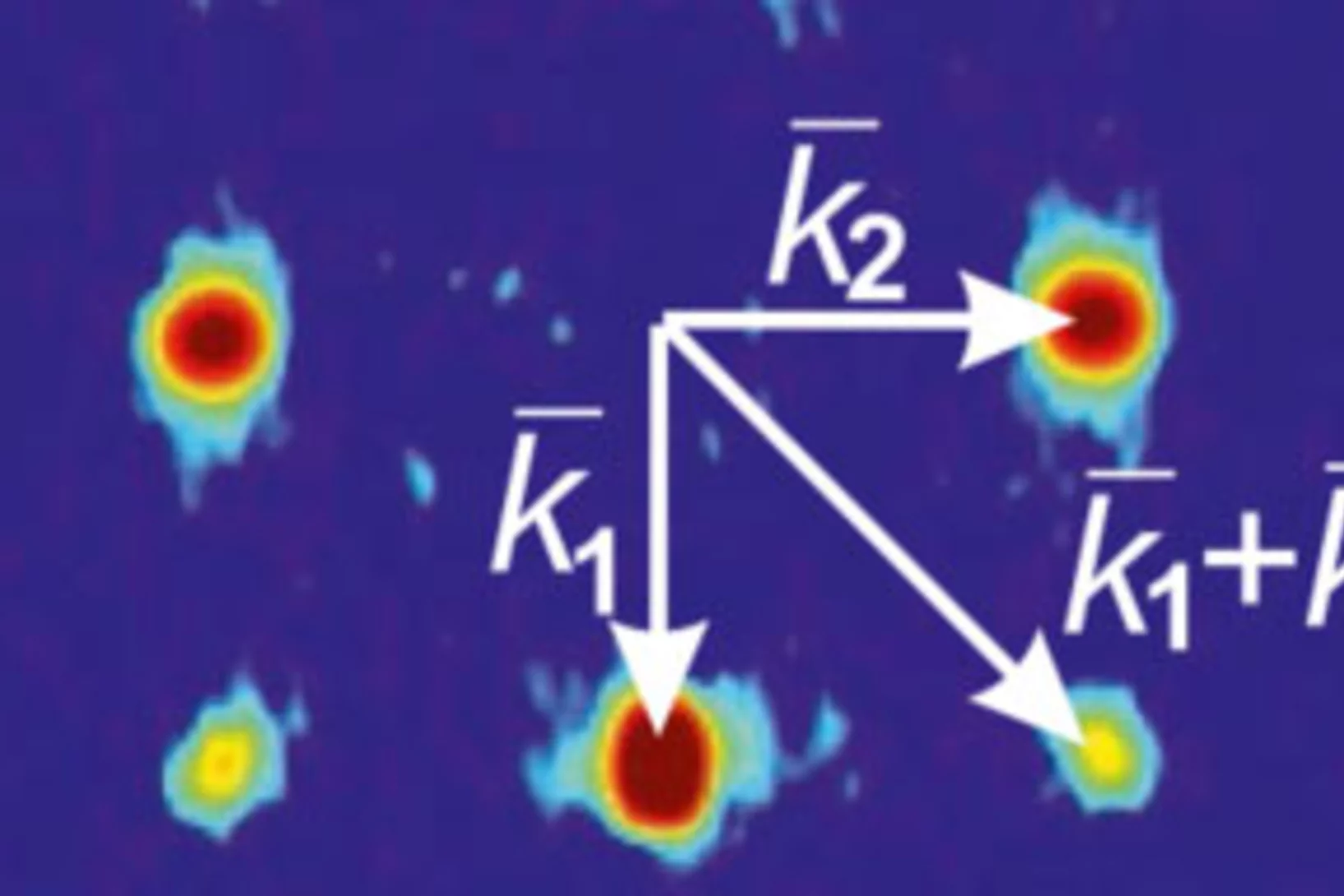
We report the discovery of topological magnetism in the candidate magnetic Weyl semimetal CeAlGe. Using neutron scattering we find this system to host several incommensurate, square-coordinated multi-k⃗ magnetic phases below TN. The topological properties of a phase stable at intermediate magnetic fields parallel to the c axis are suggested by observation of a topological Hall effect.
Determination and evaluation of the nonadditivity in wetting of molecularly heterogeneous surfaces
Every folded protein presents an interface with water that is composed of domains of varying hydrophilicity/-phobicity. Many simulation studies have highlighted the nonadditivity in the wetting of such nanostructured surfaces in contrast with the accepted theoretical formula that is additive. We present here an experimental study on surfaces of identical composition but different organization of hydrophobic and hydrophilic domains.
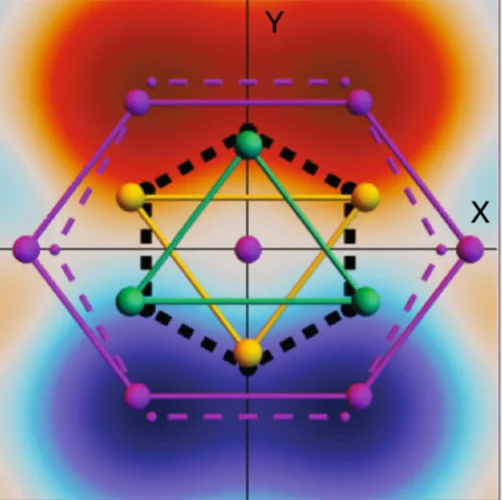
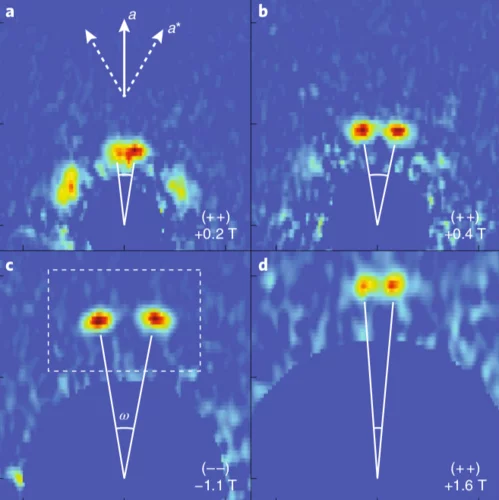
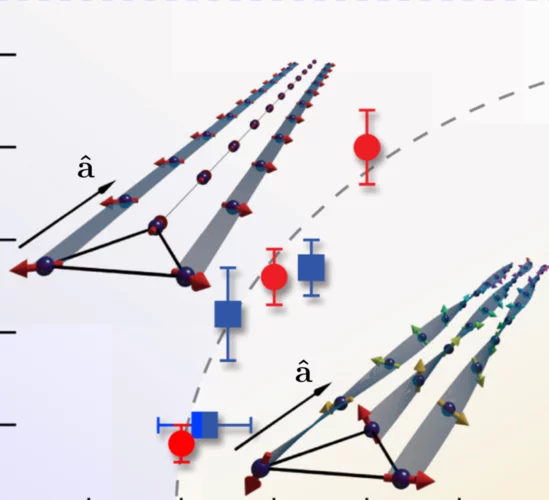
Field-induced double spin spiral in a frustrated chiral magnet
Magnetic ground states with peculiar spin textures, such as magnetic skyrmions and multifunctional domains are of enormous interest for the fundamental physics governing their origin as well as potential applications in emerging technologies. Of particular interest are multiferroics, where sophisticated interactions between electric and magnetic phenomena can be used to tailor several functionalities.
The multi-layered physics of layered superconductors
Muon spin rotation experiments provide unique microscopic insight into the superconductivity and magnetism of transition metal dichalcogenides — and reveal complex and unconventional patterns, hinting towards a common mechanism for and electronic origin of ‘unconventional’ superconductivity.
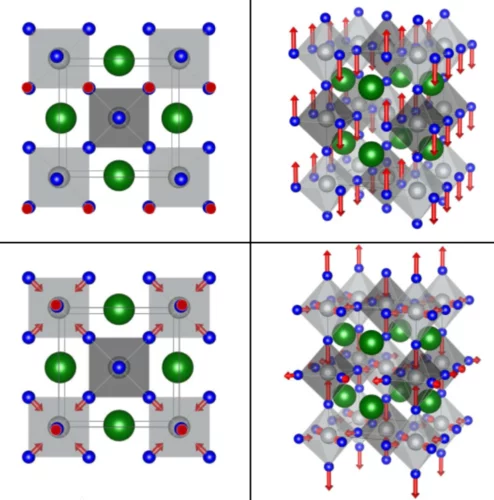
Distortion mode anomalies in bulk PrNiO3: Illustrating the potential of symmetry-adapted distortion mode analysis for the study of phase transitions
The origin of the metal-to-insulator transition (MIT) in RNiO3 perovskites with R = trivalent 4f ion has challenged the condensed matter research community for almost three decades. A drawback for progress in this direction has been the lack of studies combining physical properties and accurate structural data covering the full nickelate phase diagram. Here we focus on a small region close to the itinerant limit (R = Pr, 1.5K < T < 300K), where we investigate the gap opening and the simultaneous emergence of charge order in PrNiO3.
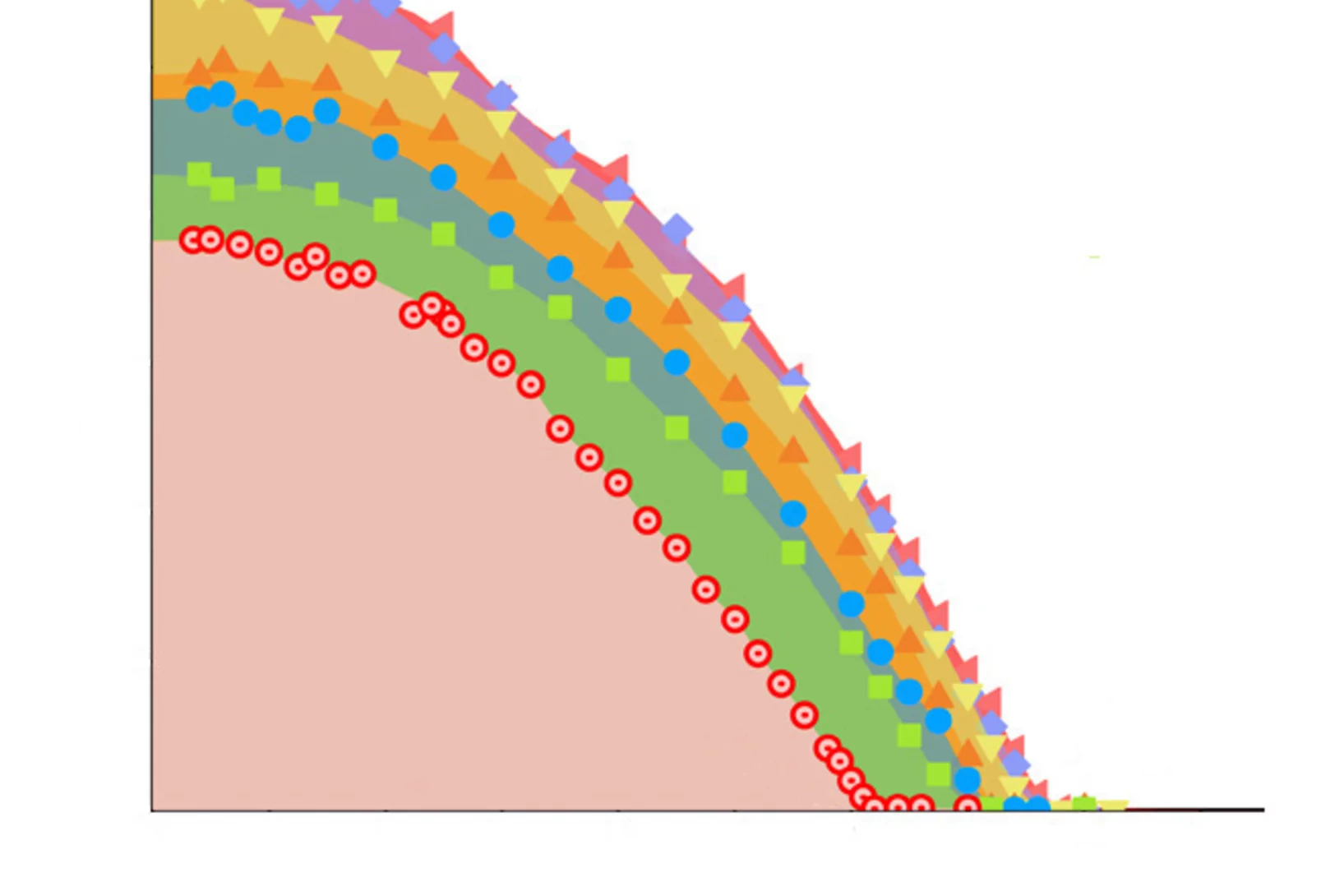
Pinning down the proximate Kitaev spin liquid
A study of the extended Kitaev model on the honeycomb lattice that factors in Kitaev, Heisenberg and off-diagonal symmetric interactions provides both a definitive answer on proximate Kitaev states and an essential guide to the physics of candidate Kitaev materials.