Spin-based logic architectures provide nonvolatile data retention, near-zero leakage, and scalability, extending the technology roadmap beyond complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor logic. Architectures based on magnetic domain walls take advantage of the fast motion, high density, non-volatility and flexible design of domain walls to process and store information. Such schemes, however, rely on domain-wall manipulation and clocking using an external magnetic field, which limits their implementation in dense, large-scale chips.
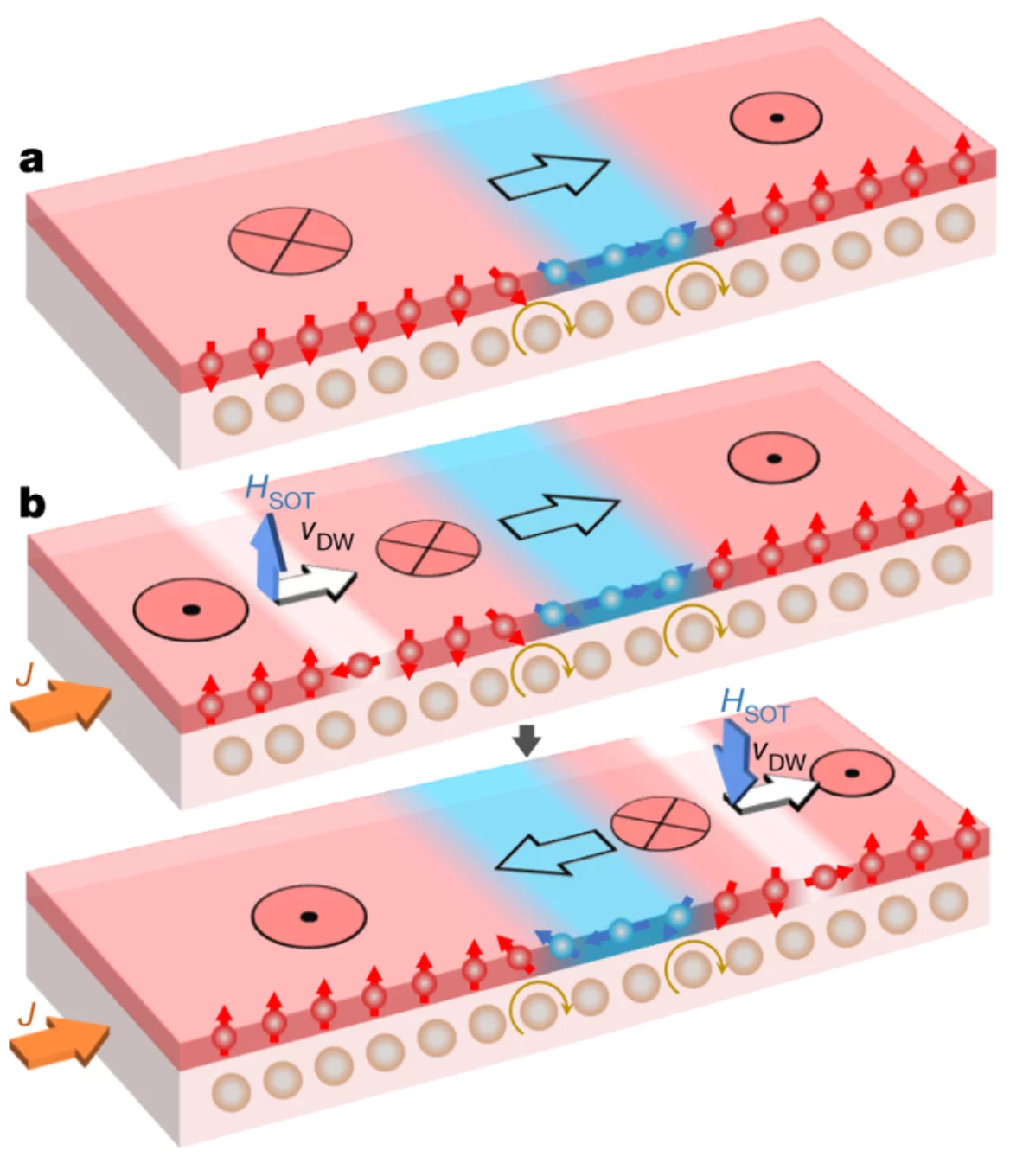
Here we demonstrate a method for performing all-electric logic operations and cascading using domain-wall racetracks. We exploit the chiral coupling between neighbouring magnetic domains induced by the interfacial Dzyaloshinskii–Moriya interaction, which promotes non-collinear spin alignment, to realize a domain-wall inverter, the essential basic building block in all implementations of Boolean logic. We then fabricate reconfigurable NAND and NOR logic gates, and perform operations with current-induced domain-wall motion. Finally, we cascade several NAND gates to build XOR and full adder gates, demonstrating electrical control of magnetic data and device interconnection in logic circuits. Our work provides a viable platform for scalable all-electric magnetic logic, paving the way for memory-in-logic applications.
Facility: SLS
Reference: Z. Luo et al, Nature 579, 214 (2020)
Read full article: here