Safety of currently operating light-water reactors, safety characteristics of future reactor concepts, and long-term safety of deep geological repositories for nuclear wastes are the main research topics at the PSI Center for Nuclear Engineering and Sciences.
Lab News & Scientific Highlights
“Magic” element challenges current model of nucleosynthesis
Surprising measurements lead to the discovery of an unknown process.
Cooperation in reactor research
Copenhagen Atomics and the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI have entered into a collaboration agreement on a thorium molten salt critical experiment.
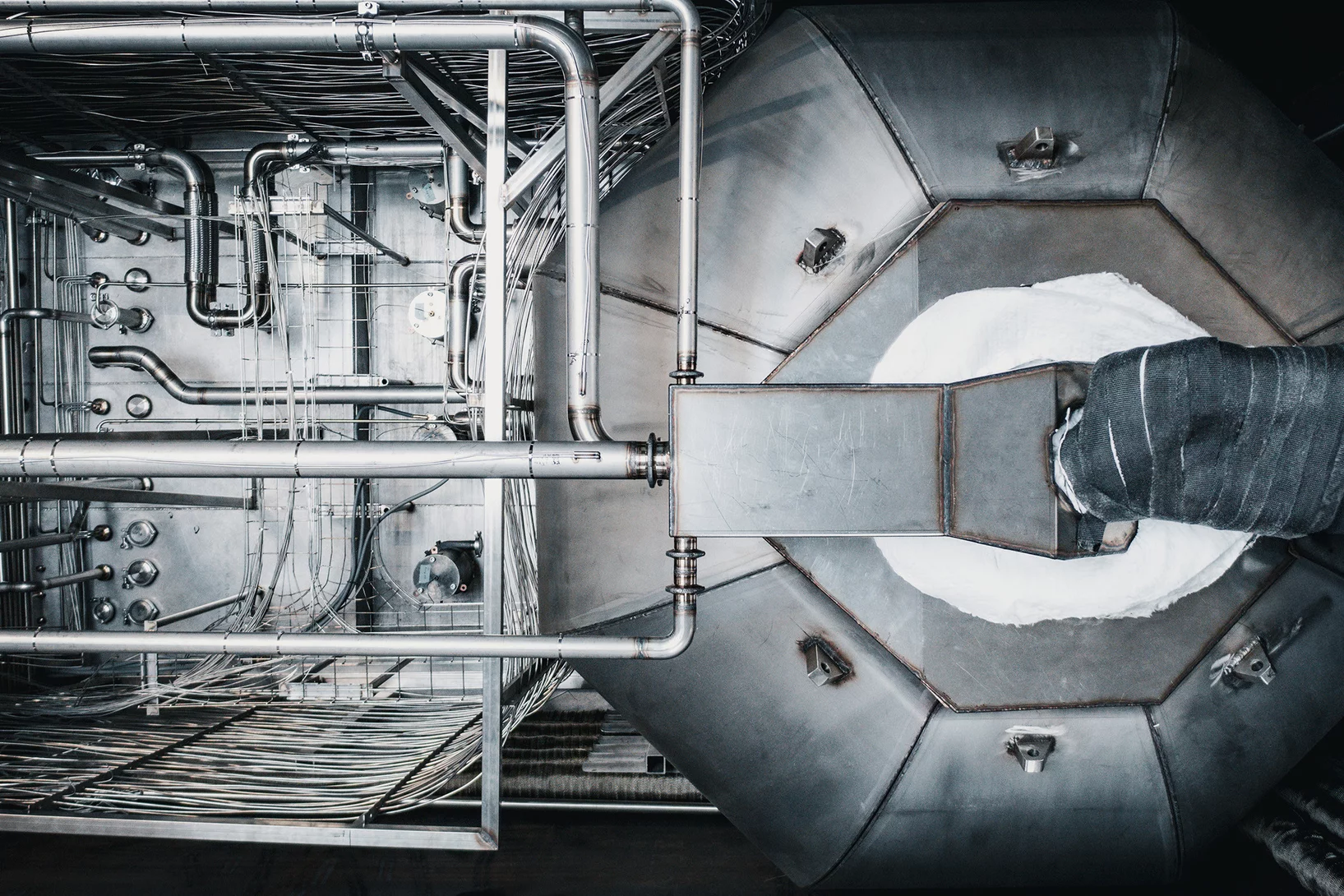
Breaking the Drops
For water-cooled nuclear reactors, a loss of coolant accident constitutes one of the key scenarios to be evaluated for the design of the plant and associated safety systems. Even if these accidents are not expected to occur at all during reactor lifetime, their potential consequences include the heat up of the fuel in the reactor core. For the recovery of the plant to safe conditions, safety systems are in place to inject water in order to reflood the core and to quench the high temperature fuel. The two-phase flow behaviour during this reflooding phase is extremely complex. In particular, the prediction of the behaviour of small liquid droplets generated as the quench front propagates upwards has a significant effect on the fuel temperatures in the upper regions of the reactor core. In collaboration with the US Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC), we have been working to improve our modelling of the droplet behaviour and their impact on key safety parameters.
Upcoming Events
Publications
-
Al-Yahia OS, Bernard M, Clifford I, Perret G, Bajorek S, Ferroukhi H
The influence of droplet breakup model on the prediction of reactor core parameters during reflood conditions
Nuclear Engineering and Design. 2024; 416: 112815 (16 pp.). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nucengdes.2023.112815
DORA PSI -
Albà A, Adelmann A, Münster L, Rochman D, Boiger R
Fast uncertainty quantification of spent nuclear fuel with neural networks
Annals of Nuclear Energy. 2024; 196: 110204 (8 pp.). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anucene.2023.110204
DORA PSI -
Alcayne V, Cano-Ott D, Garcia J, González-Romero E, Martínez T, Rada AP, et al.
A segmented total energy detector (sTED) optimized for (n, γ) cross-section measurements at n_TOF EAR2
Radiation Physics and Chemistry. 2024; 217: 111525 (11 pp.). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radphyschem.2024.111525
DORA PSI