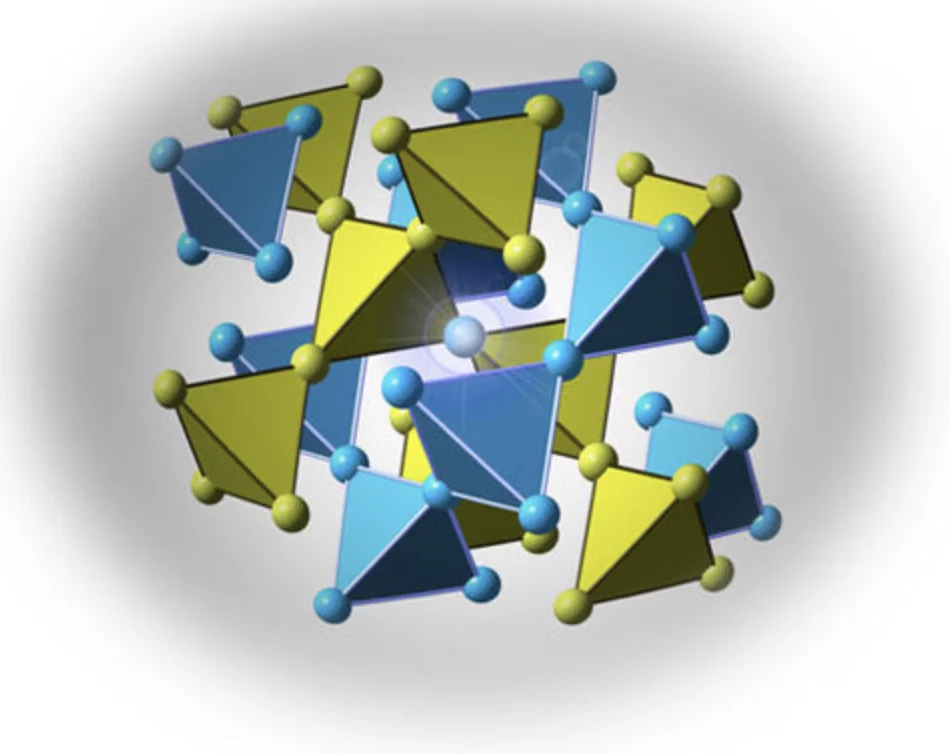
A quantum spin liquid is a state of matter characterized by quantum entanglement and the absence of any broken symmetry. In condensed matter, the frustrated rare-earth pyrochlore magnets Ho2Ti2O7 and Dy2Ti2O7, so-called spin ices, exhibit a classical spin liquid state with fractionalized thermal excitations (magnetic monopoles). Evidence for a quantum spin ice, in which the magnetic monopoles become long range entangled and an emergent quantum electrodynamics arises, seems within reach. The magnetic properties of the quantum spin ice candidate Yb2Ti2O7 have eluded a global understanding and even the presence or absence of static magnetic order at low temperatures is controversial. Here we show that sensitivity to pressure is the missing key to the low temperature behaviour of Yb2Ti2O7. By combining neutron diffraction and muon spin relaxation on a stoichiometric sample under pressure, we evidence a magnetic transition from a disordered, non-magnetic, ground state to a splayed ferromagnetic ground state.
Reference: E. Kermarrec et al, Nature Communications 8, 14810 (2017)
Read full article: here