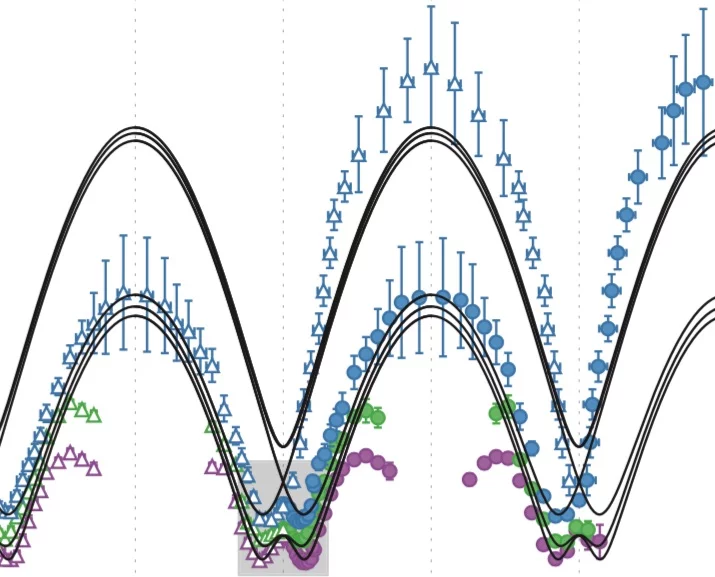
When the energy eigenvalues of two coupled quantum states approach each other in a certain parameter space, their energy levels repel each other and level crossing is avoided. Such level repulsion, or avoided level crossing, is commonly used to describe the dispersion relation of quasiparticles in solids. However, little is known about the level repulsion when more than two quasiparticles are present; for example, in a strongly interacting quantum system where a quasiparticle can spontaneously decay into a many-particle continuum. Here we show that even in this case level repulsion exists between a long-lived quasiparticle state and a continuum. In our fine-resolution neutron spectroscopy study of magnetic quasiparticles in the frustrated quantum magnet BiCu2PO6, we observe a renormalization of the quasiparticle dispersion relation due to the presence of the continuum of multi-quasiparticle states.
- About the CenterfermerAbout the Center
- Our Research
- Facilities
- SINQ: Swiss Spallation Neutron Source
- SμS: Swiss Muon Source
- CHRISP: Swiss Research Infrastructure for Particle Physics
- Scientific Advisory Committees
- Publications
- Jobs & Education