Strong enhancement of s-wave superconductivity near a quantum critical point of Ca3Ir4Sn13
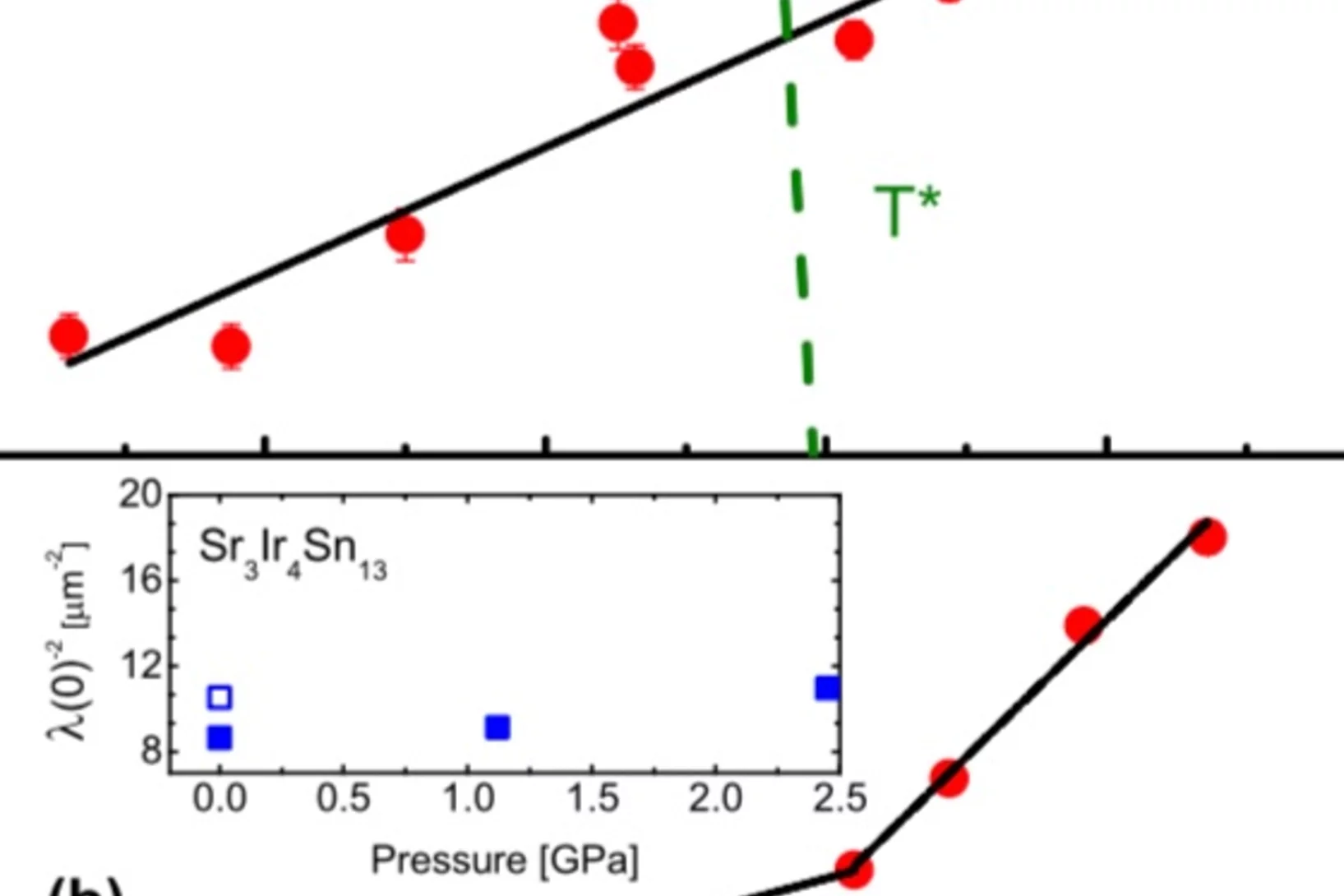
We report microscopic studies by muon spin rotation/relaxation as a function of pressure of the Ca3Ir4Sn13 and Sr3Ir4Sn13 cubic compounds, which are members of the (Ca1−xSrx)3Ir4Sn13 system displaying superconductivity and a structural phase transition associated with the formation of a charge density wave (CDW).
Direct evidence for a pressure-induced nodal superconducting gap in the Ba0.65Rb0.35Fe2As2 superconductor
The superconducting gap structure in iron-based high-temperature superconductors (Fe-HTSs) is non-universal. In contrast to other unconventional superconductors, in the Fe-HTSs both d-wave and extended s-wave pairing symmetries are close in energy. Probing the proximity between these very different superconducting states and identifying experi- mental parameters that can tune them is of central interest.
Intrinsic Paramagnetic Meissner Effect Due to s-Wave Odd-Frequency Superconductivity
In 1933, Meissner and Ochsenfeld reported the expulsion of magnetic flux - the diamagnetic Meissner effect - from the interior of superconducting lead. This discovery was crucial in formulating the Bardeen-Cooper-Schrieffer (BCS) theory of superconductivity. In exotic superconducting systems BCS theory does not strictly apply.
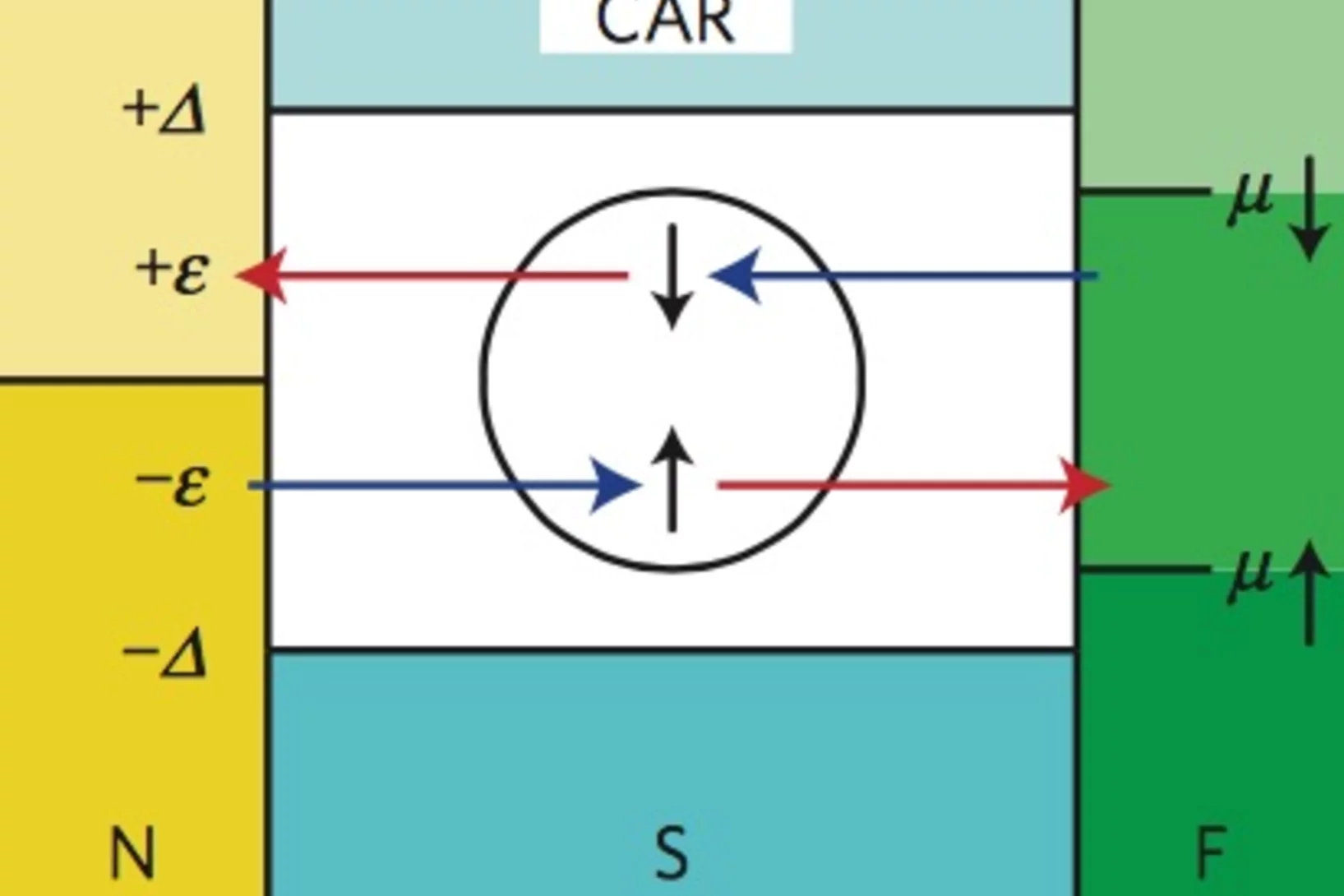
Remotely induced magnetism in a normal metal using a superconducting spin-valve
Superconducting spintronics has emerged in the past decade as a promising new field that seeks to open a new dimension for nanoelectronics by utilizing the internal spin structure of the superconducting Cooper pair as a new degree of freedom. Its basic building blocks are spin-triplet Cooper pairs with equally aligned spins, which are promoted by proximity of a conventional superconductor to a ferromagnetic material with inhomogeneous macroscopic magnetization.
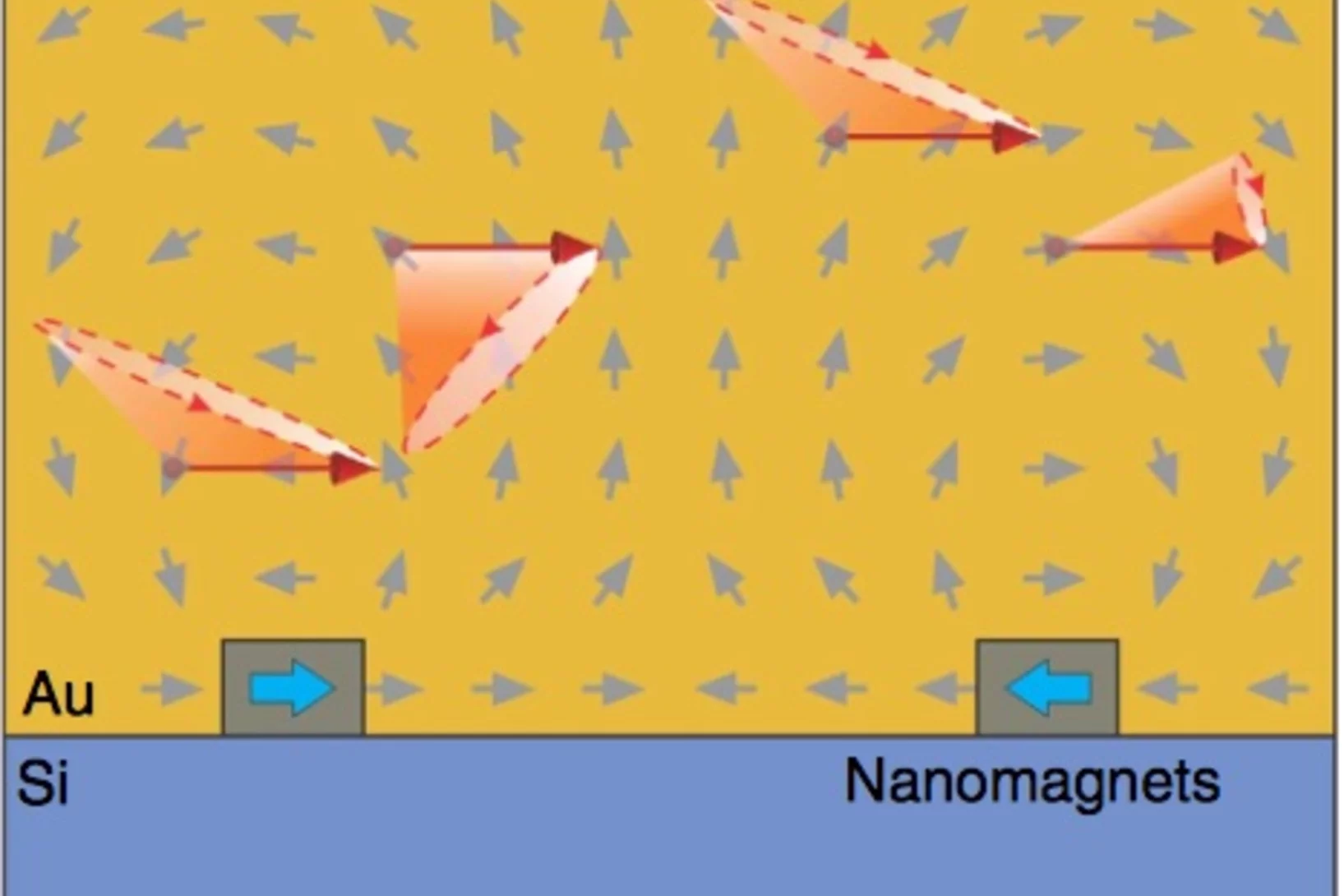
Thermodynamic phase transitions in a frustrated magnetic metamaterial
Materials with interacting magnetic degrees of freedom display a rich variety of magnetic behaviour that can lead to novel collective equilibrium and out-of-equilibrium phenomena. In equilibrium, thermodynamic phases appear with the associated phase transitions providing a characteristic signature of the underlying collective behaviour.
Pressure-induced electronic phase separation of magnetism and superconductivity in CrAs
The recent discovery of pressure (p) induced superconductivity in the binary helimagnet CrAs has raised questions on how superconductivity emerges from the magnetic state and on the mechanism of the superconducting pairing. In the present work the suppression of magnetism and the occurrence of superconductivity in CrAs were studied by means of muon spin rotation.
Candidate Quantum Spin Liquid in the Ce3+ Pyrochlore Stannate Ce2Sn2O7
We report the low-temperature magnetic properties of Ce2Sn2O7, a rare-earth pyrochlore. Our suscep- tibility and magnetization measurements show that due to the thermal isolation of a Kramers doublet ground state, Ce2Sn2O7 has Ising-like magnetic moments of ∼1.18 μB. The magnetic moments are confined to the local trigonal axes, as in a spin ice, but the exchange interactions are antiferromagnetic.
Beating the Stoner criterion using molecular interfaces
Only three elements are ferromagnetic at room temperature: the transition metals iron, cobalt and nickel. The Stoner criterion explains why iron is ferromagnetic but manganese, for example, is not, even though both elements have an unfilled 3d shell and are adjacent in the periodic table: according to this criterion, the product of the density of states and the exchange integral must be greater than unity for spontaneous spin ordering to emerge.
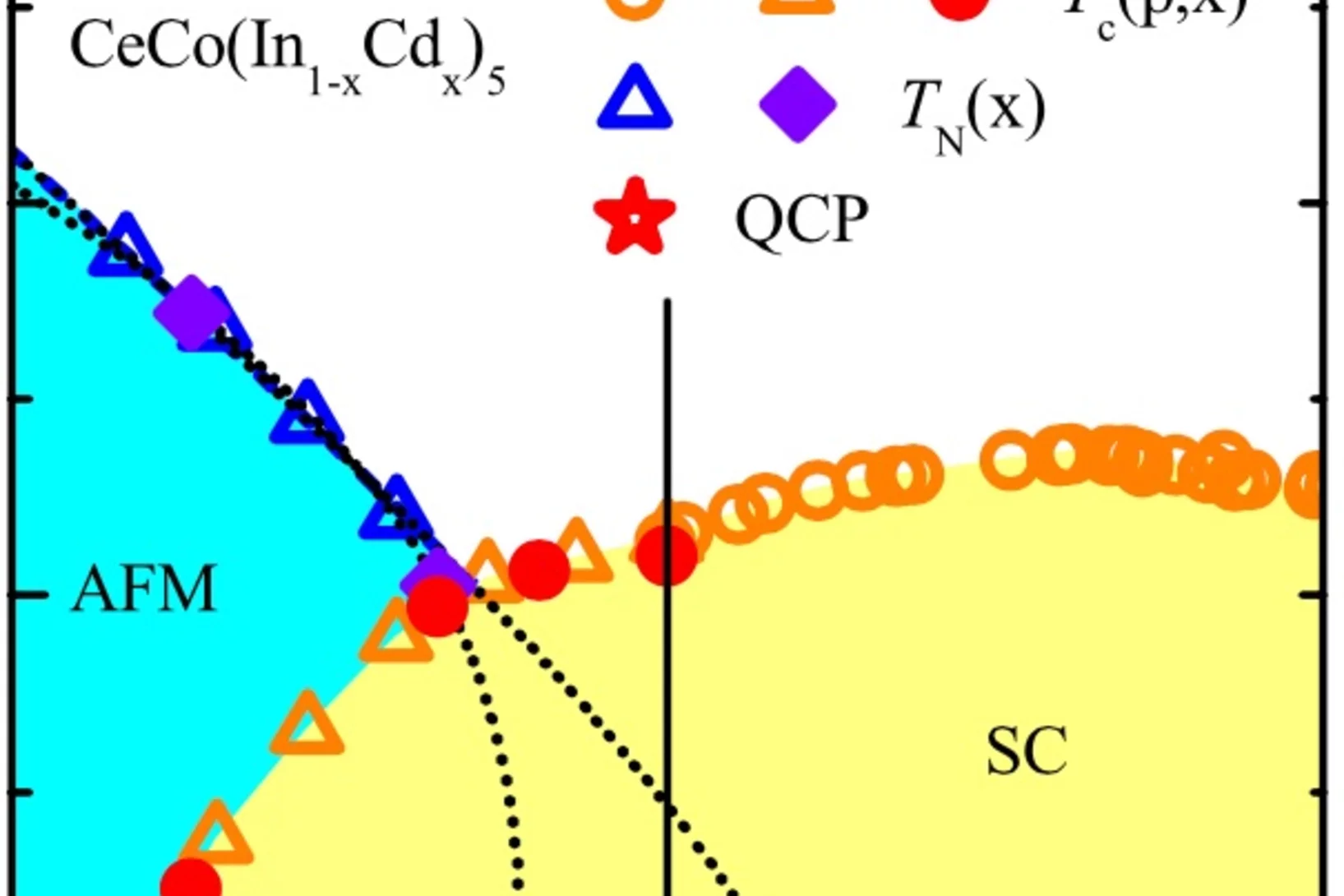
Evidence for Coexistence of Bulk Superconductivity and Itinerant Antiferromagnetism in the Heavy Fermion System CeCo(In1−xCdx)5
In the generic phase diagram of heavy fermion systems, tuning an external parameter such as hydrostatic or chemical pressure modifies the superconducting transition temperature. The superconducting phase forms a dome in the temperature-tuning parameter phase diagram, which is associated with a maximum of the superconducting pairing interaction. Proximity to antiferromagnetism suggests a relation between the disappearance of antiferromagnetic order and superconductivity.
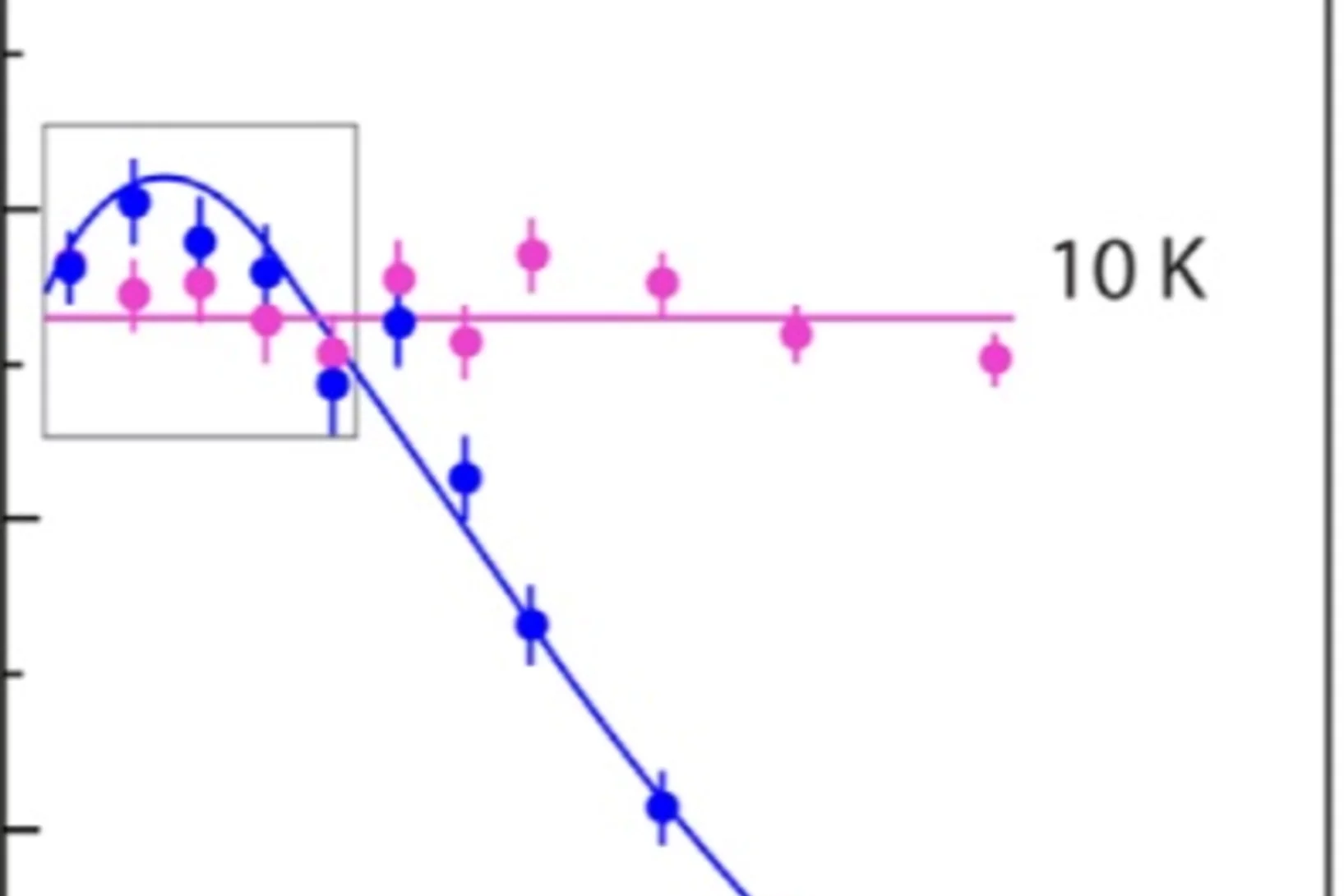
Mutual Independence of Critical Temperature and Superfluid Density under Pressure in Optimally Electron-Doped Superconducting LaFeAsO1−xFx
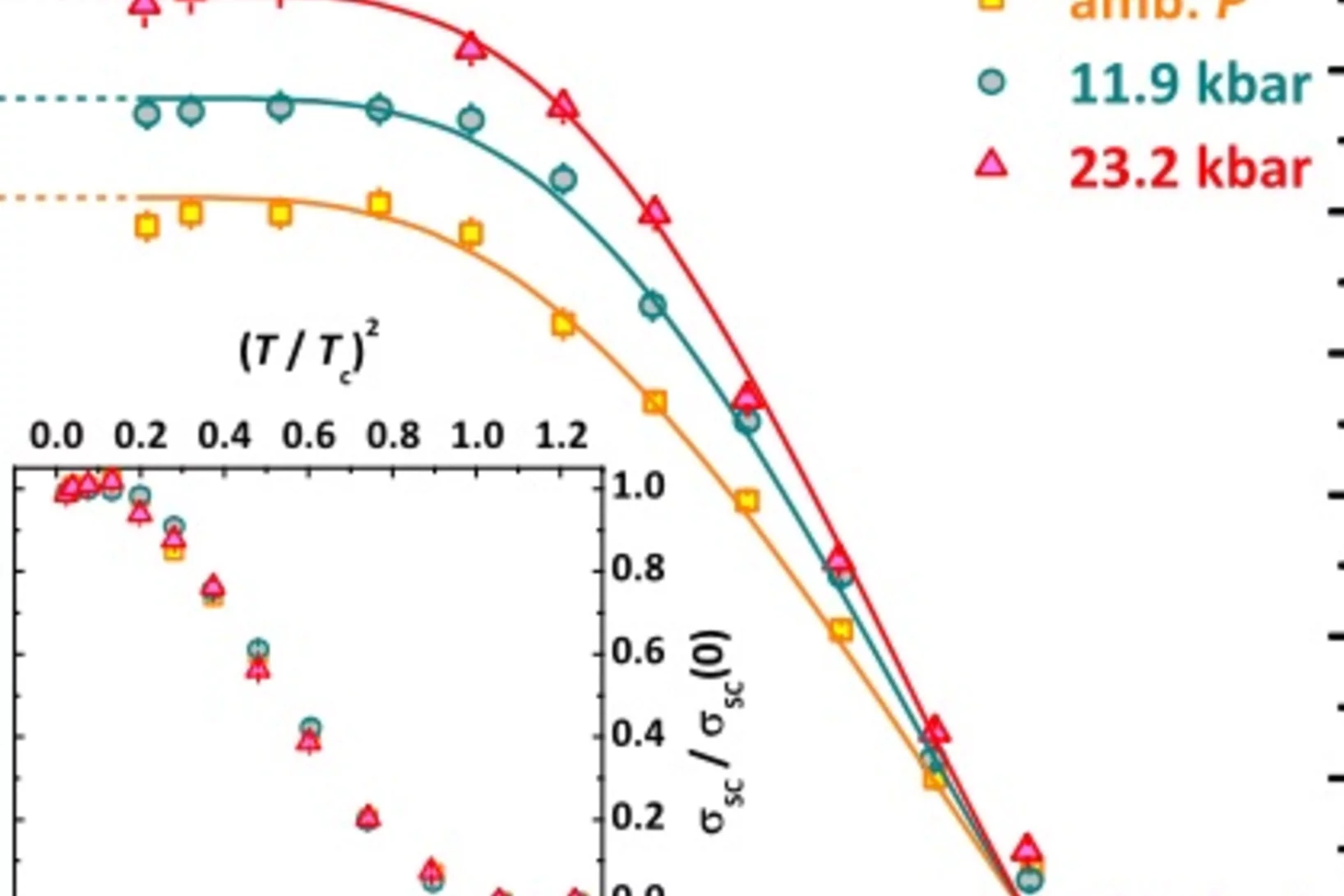
The superconducting properties of LaFeAsO1−xFx under conditions of optimal electron doping are investigated upon the application of external pressure up to ∼23 kbar. Measurements of muon-spin spectroscopy and dc magnetometry evidence a clear mutual independence between the critical temperature Tc and the low-temperature saturation value for the ratio ns/m* (superfluid density over effective band mass of Cooper pairs).
Controllable Broadband Absorption in the Mixed Phase of Metamagnets
Materials with broad absorption bands are highly desirable for electromagnetic filtering and processing applications, especially if the absorption can be externally controlled. Here, a new class of broadband-absorption materials is introduced. Namely, layered metamagnets exhibit an electromagnetic excitation continuum in the magnetic-field-induced mixed ferro- and antiferromagnetic phase.
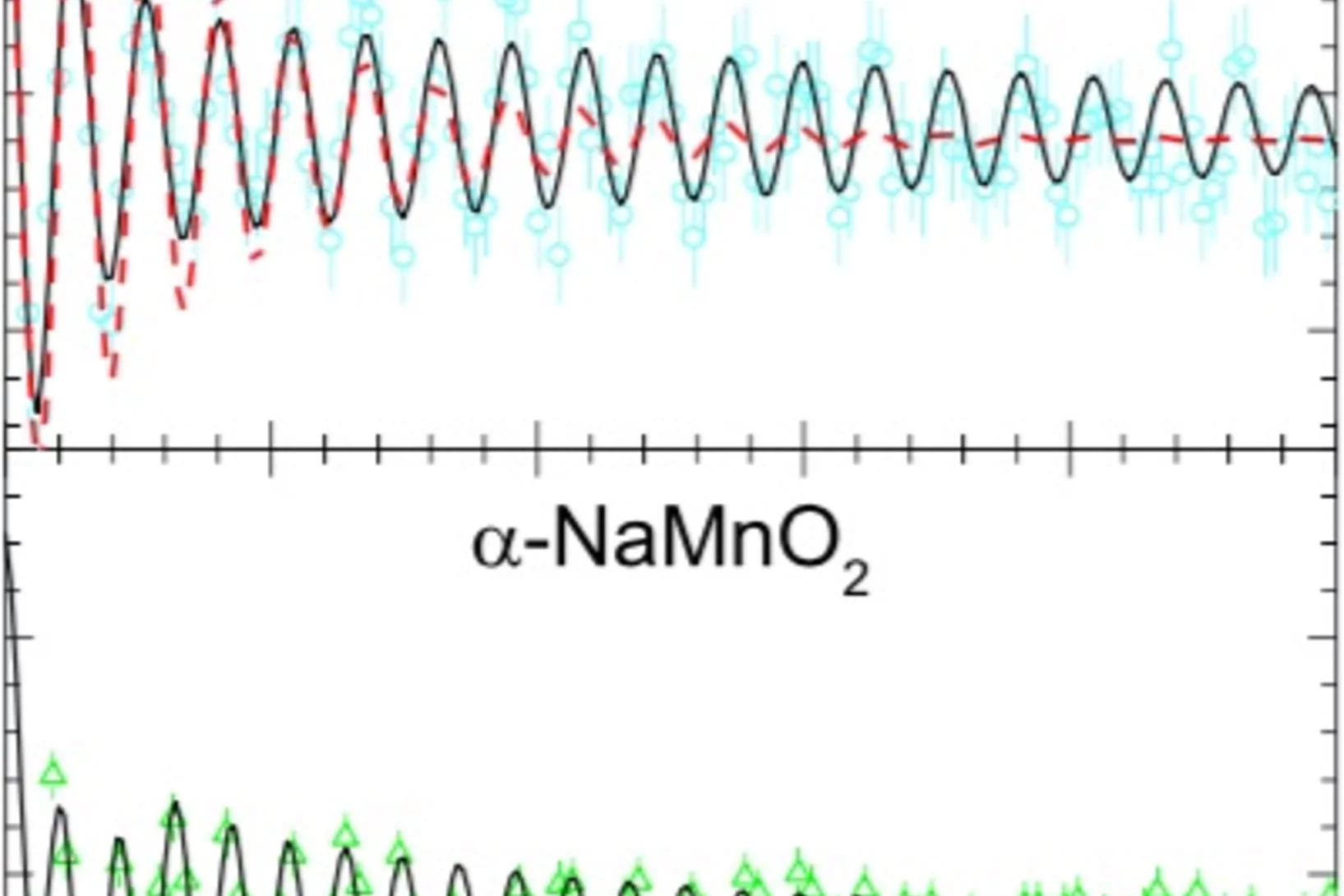
Magnetic inhomogeneity on a triangular lattice: the magnetic-exchange versus the elastic energy and the role of disorder
Inhomogeneity in the ground state is an intriguing, emergent phenomenon in magnetism. Recently, it has been observed in the magnetostructural channel of the geometrically frustrated α-NaMnO2, for the first time in the absence of active charge degrees of freedom. Here we report an in-depth numerical and local-probe experimental study of the isostructural sister compound CuMnO2 that emphasizes and provides an explanation for the crucial differences between the two systems.
Interfacial dominated ferromagnetism in nanograined ZnO: a μSR and DFT study
Diamagnetic oxides can, under certain conditions, become ferromagnetic at room temperature and therefore are promising candidates for future material in spintronic devices. Contrary to early predictions, doping ZnO with uniformly distributed magnetic ions is not essential to obtain ferromagnetic samples. Instead, the nanostructure seems to play the key role, as room temperature ferromagnetism was also found in nanograined, undoped ZnO.
Non-Fermi Liquid Behavior Close to a Quantum Critical Point in a Ferromagnetic State without Local Moments
A quantum critical point (QCP) occurs upon chemical doping of the weak itinerant ferromagnet Sc3.1In. Remarkable for a system with no local moments, the QCP is accompanied by non-Fermi liquid behavior, manifested in the logarithmic divergence of the specific heat both in the ferro-and the paramagnetic states, as well as linear temperature dependence of the low-temperature resistivity.
Muonium in Stishovite: Implications for the Possible Existence of Neutral Atomic Hydrogen in the Earth's Deep Mantle
Hydrogen in the Earth's deep interior has been thought to exist as a hydroxyl group in high-pressure minerals. We present Muon Spin Rotation experiments on SiO2 stishovite, which is an archetypal high-pressure mineral. Positive muon (which can be considered as a light isotope of proton) implanted in stishovite was found to capture electron to form muonium (corresponding to neutral hydrogen).
The phase diagram of electron-doped La2-xCexCuO4-δ
Superconductivity is a striking example of a quantum phenomenon in which electrons move coherently over macroscopic distances without scattering. The high-temperature superconducting oxides (cuprates) are the most studied class of superconductors, composed of two-dimensional CuO2 planes separated by other layers that control the electron concentration in the planes. A key unresolved issue in cuprates is the relationship between superconductivity and magnetism.
Competing superconducting and magnetic order parameters and field-induced magnetism in electron-doped Ba(Fe1-xCox)2As2
We have studied the magnetic and superconducting properties of Ba(Fe0.95Co0.05)2As2 as a function of temperature and external magnetic field using neutron scattering and muon spin rotation. Below the superconducting transition temperature the magnetic and superconducting order parameters coexist and compete. A magnetic field can significantly enhance the magnetic scattering in the superconducting state, roughly doubling the Bragg intensity at 13.5T.
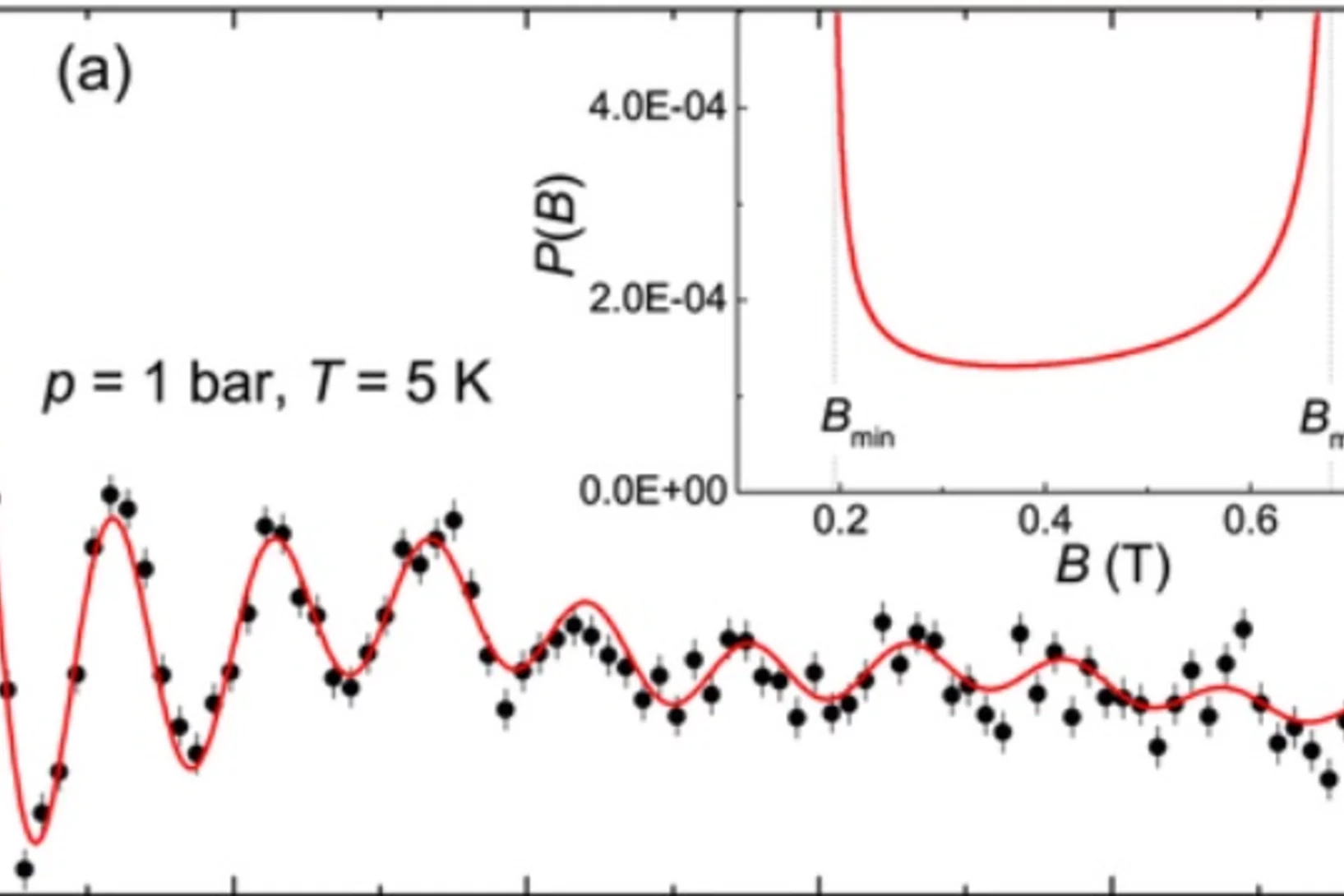
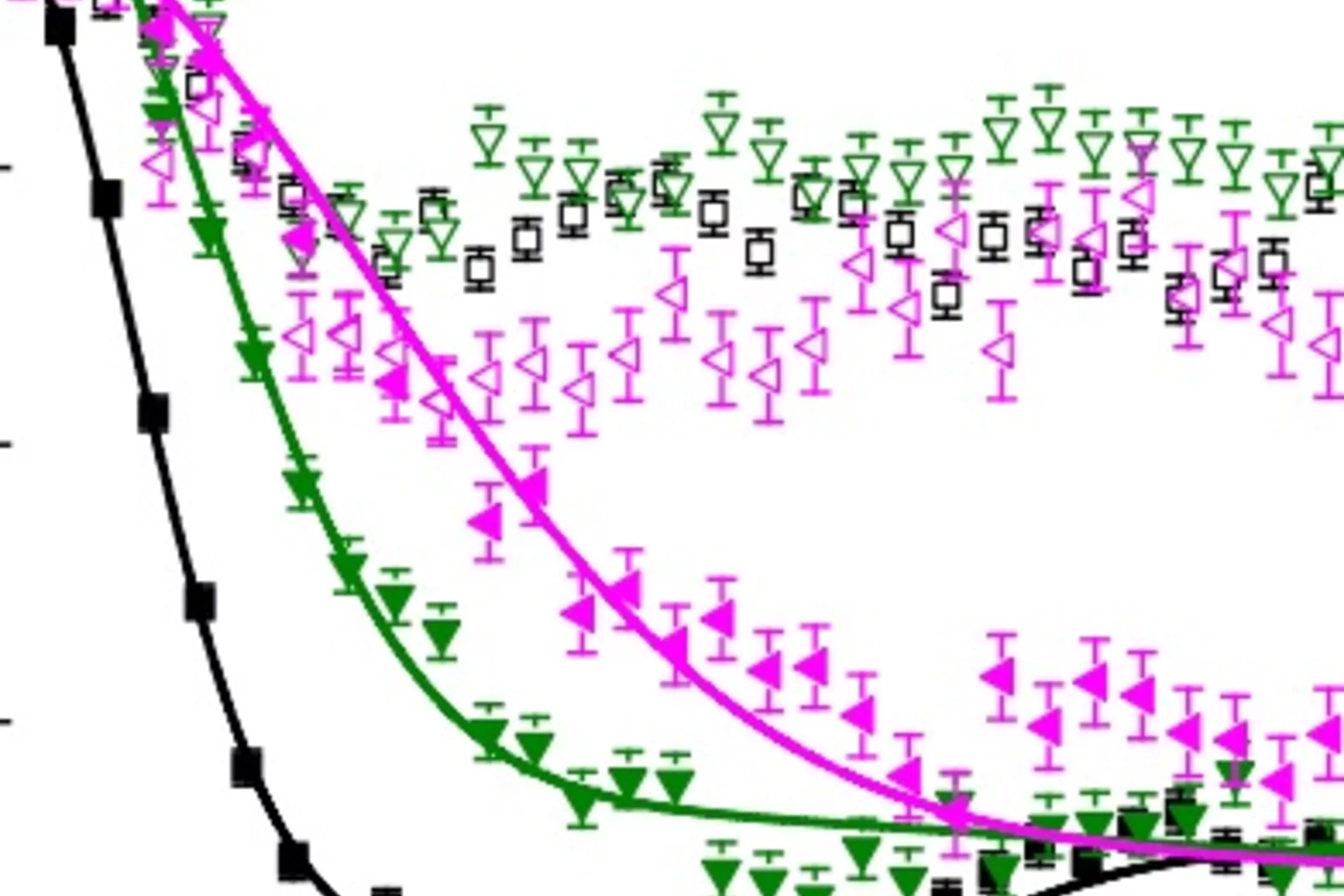
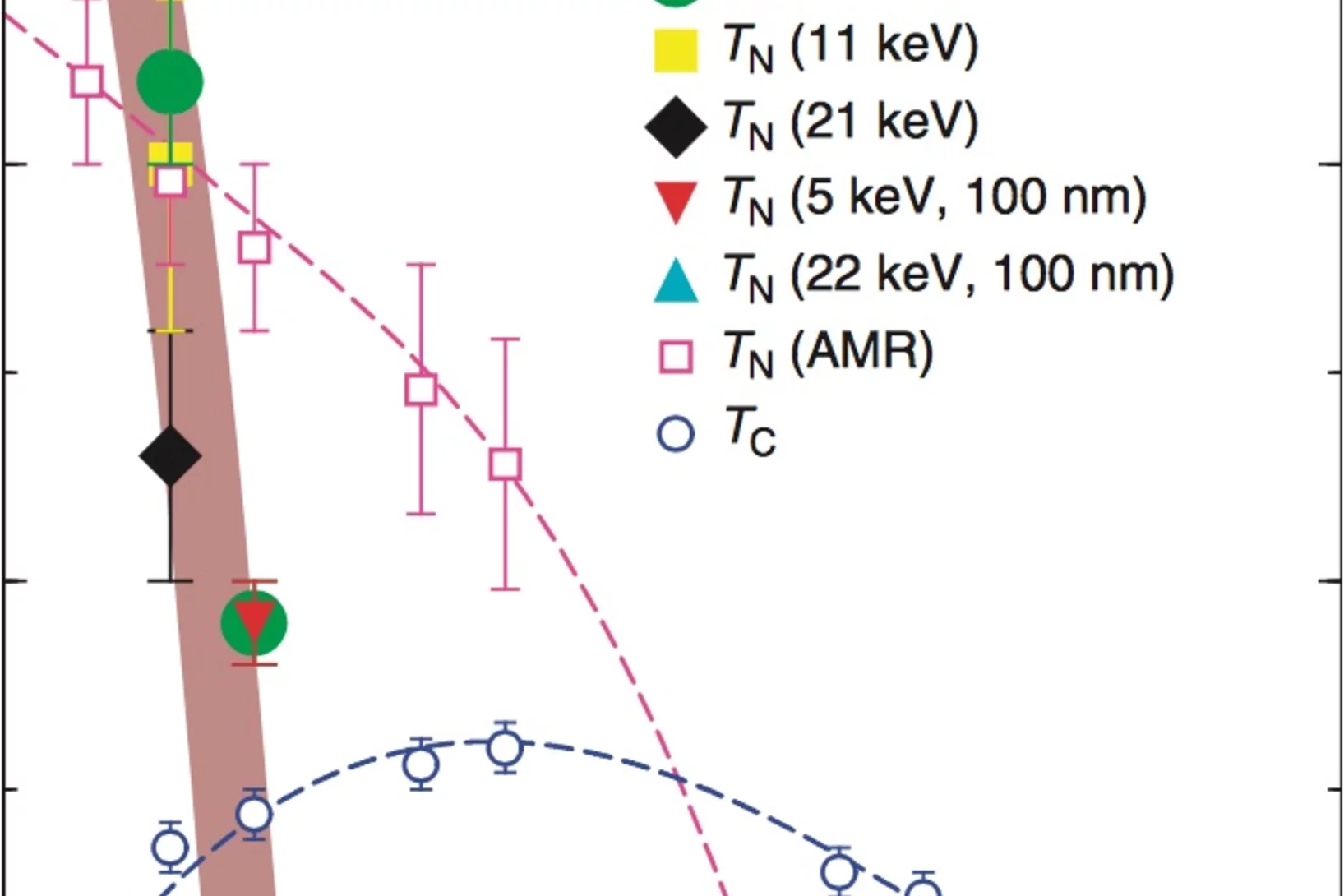
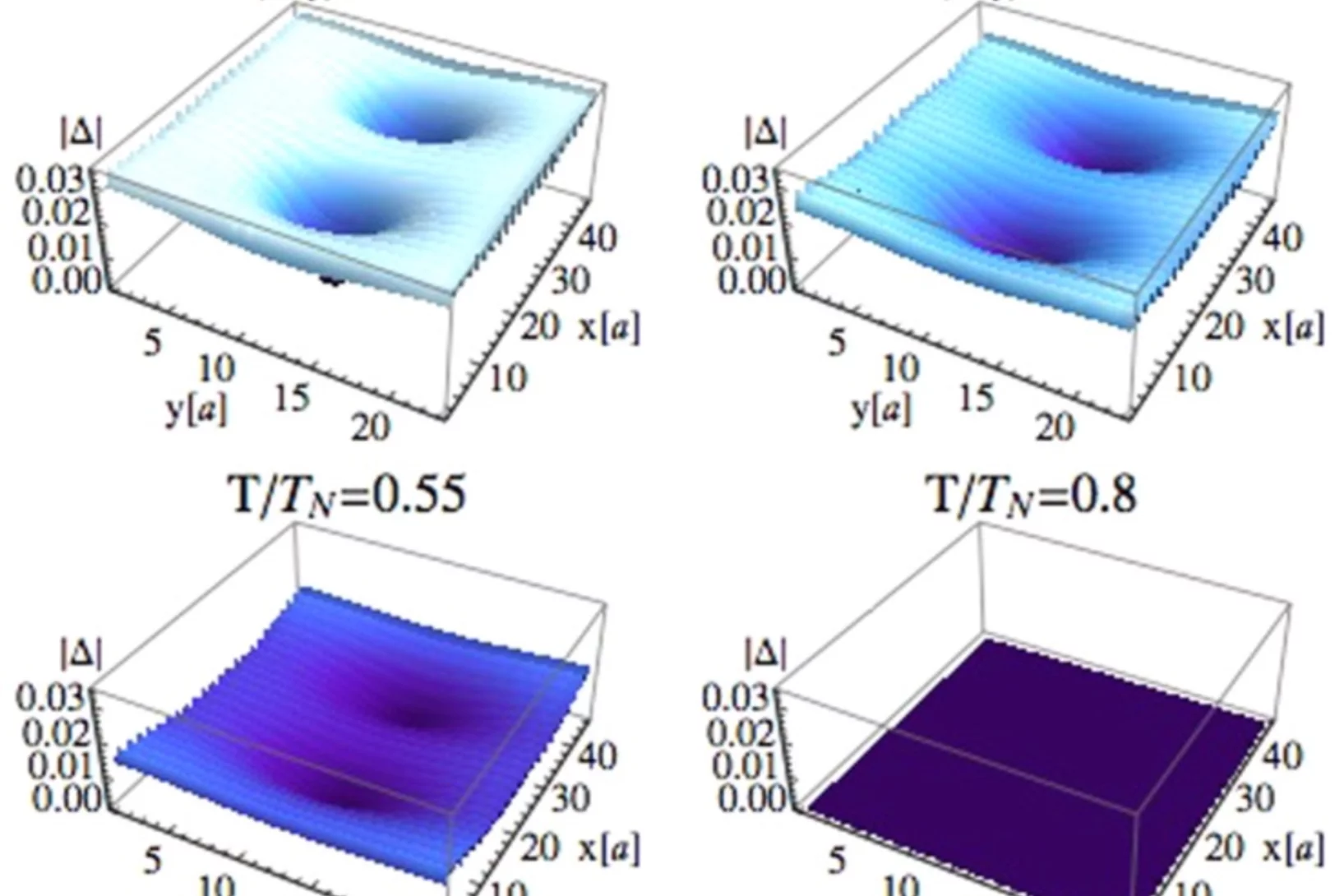
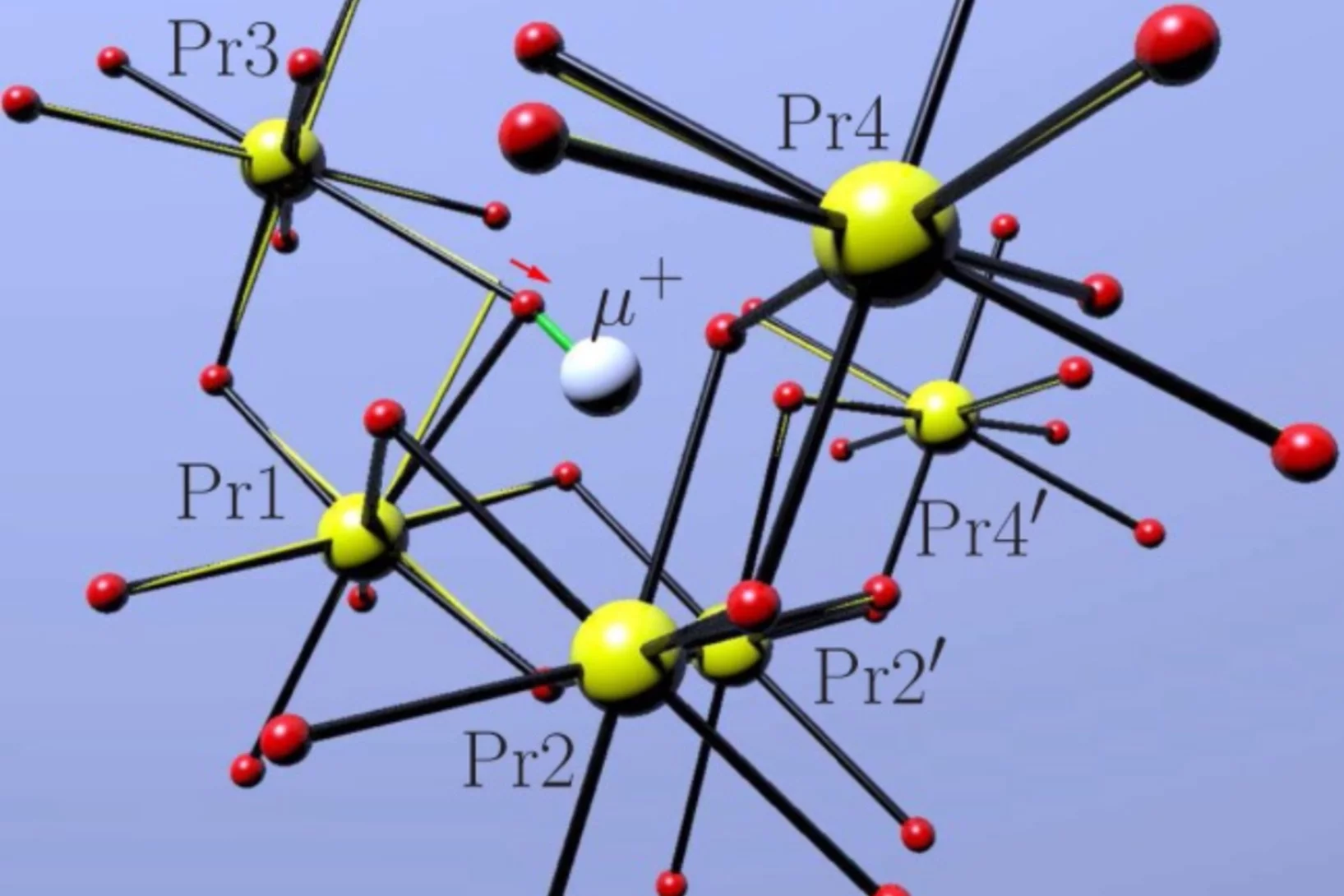
Anisotropic Local Modification of Crystal Field Levels in Pr-Based Pyrochlores: A Muon-Induced Effect Modeled Using Density Functional Theory
Although muon spin relaxation is commonly used to probe local magnetic order, spin freezing, and spin dynamics, we identify an experimental situation in which the measured response is dominated by an effect resulting from the muon-induced local distortion rather than the intrinsic behavior of the host compound.
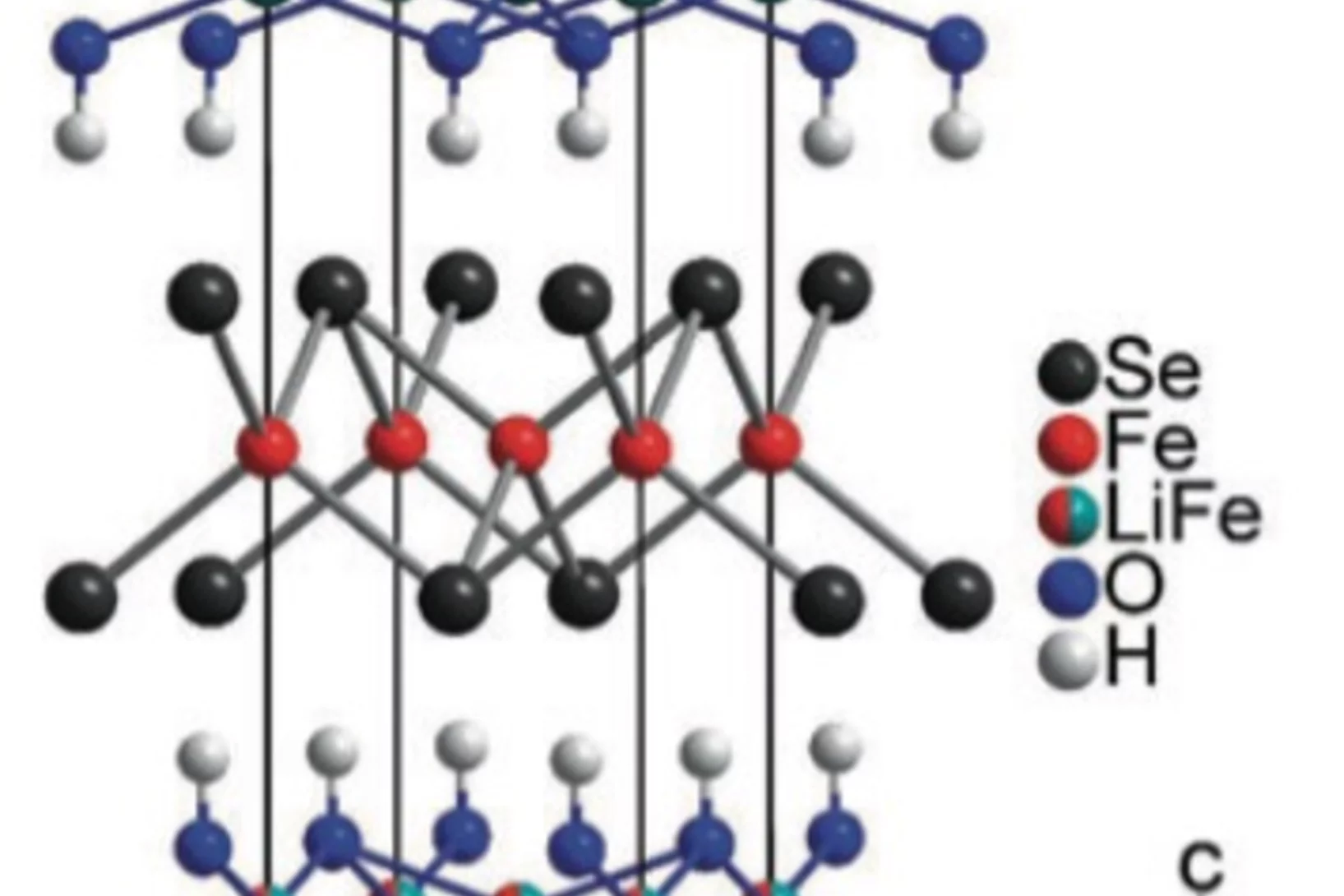
Coexistence of 3d-Ferromagnetism and Superconductivity in [(Li1-Fex)OH](Fe1-yLiy)Se
Superconducting [(Li1-xFex)OH](Fe1-yLiy)Se (x≈0.2, y≈0.08) was synthesized by hydrothermal methods and characterized by single-crystal and powder X-ray diffrac- tion. The structure contains alternating layers of anti-PbO type (Fe1-yLiy)Se and (Li1-xFex)OH. Electrical resistivity and magnetic susceptibility measurements reveal superconductivity at 43K.