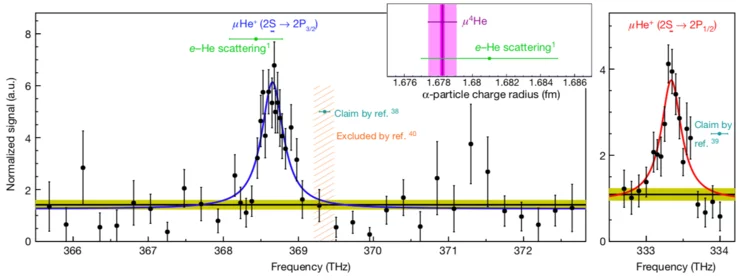
Size of helium nucleus measured more precisely than ever before
In experiments at the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI, an international research collaboration has measured the radius of the atomic nucleus of helium five times more precisely than ever before. The researchers are publishing their results today in the journal Nature.
A la recherche d’une nouvelle physique
L’accélérateur de protons à haute intensité HIPA permet à l’Institut Paul Scherrer PSI de produire des particules élémentaires pour élucider la structure de notre univers. Les chercheurs utilisent des pions, des muons et des neutrons pour vérifier la validité du modèle standard de la physique des particules.
Le travailleur de force du val Mesolcina
Aldo Antognini a la physique et la convivialité dans le sang. Aldo Antognini, chercheur au PSI, a reçu plus de 2 200 000 francs de l’UE pour sa nouvelle expérience. Son objectif: déterminer la répartition du magnétisme dans le proton. Pour y arriver, ce physicien des particules devra mettre ses talents scientifiques et techniques à contribution, mais aussi son entregent.
The deuteron too poses a mystery
The deuteron — one of the simplest atomic nuclei, consisting of just one proton and one neutron — is considerably smaller than previously thought. This finding was arrived at by an international research group that carried out experiments at the Paul Scherrer Institute, PSI. The new result is consistent with a 2010 study by the same group, in which the researchers measured the proton and found a significantly smaller value than previous research using different experimental methods.
Search for the lepton flavour violating decay μ+→e+γ with the full dataset of the MEG experiment
The final results of the search for the lepton flavour violating decay μ+→e+γ based on the full dataset collected by the MEG experiment at the Paul Scherrer Institut in the period 2009–2013 and totalling 7.5×1014 stopped muons on target are presented.
Muon polarization in the MEG experiment: predictions and measurements
The MEG experiment makes use of one of the world’s most intense low energy muon beams, in order to search for the lepton flavour violating process μ+→e+γ . We determined the residual beam polarization at the thin stopping target, by measuring the asymmetry of the angular distribution of Michel decay positrons as a function of energy. The initial muon beam polarization at the production is predicted to be Pμ=−1Pμ=−1 by the Standard Model (SM) with massless neutrinos.