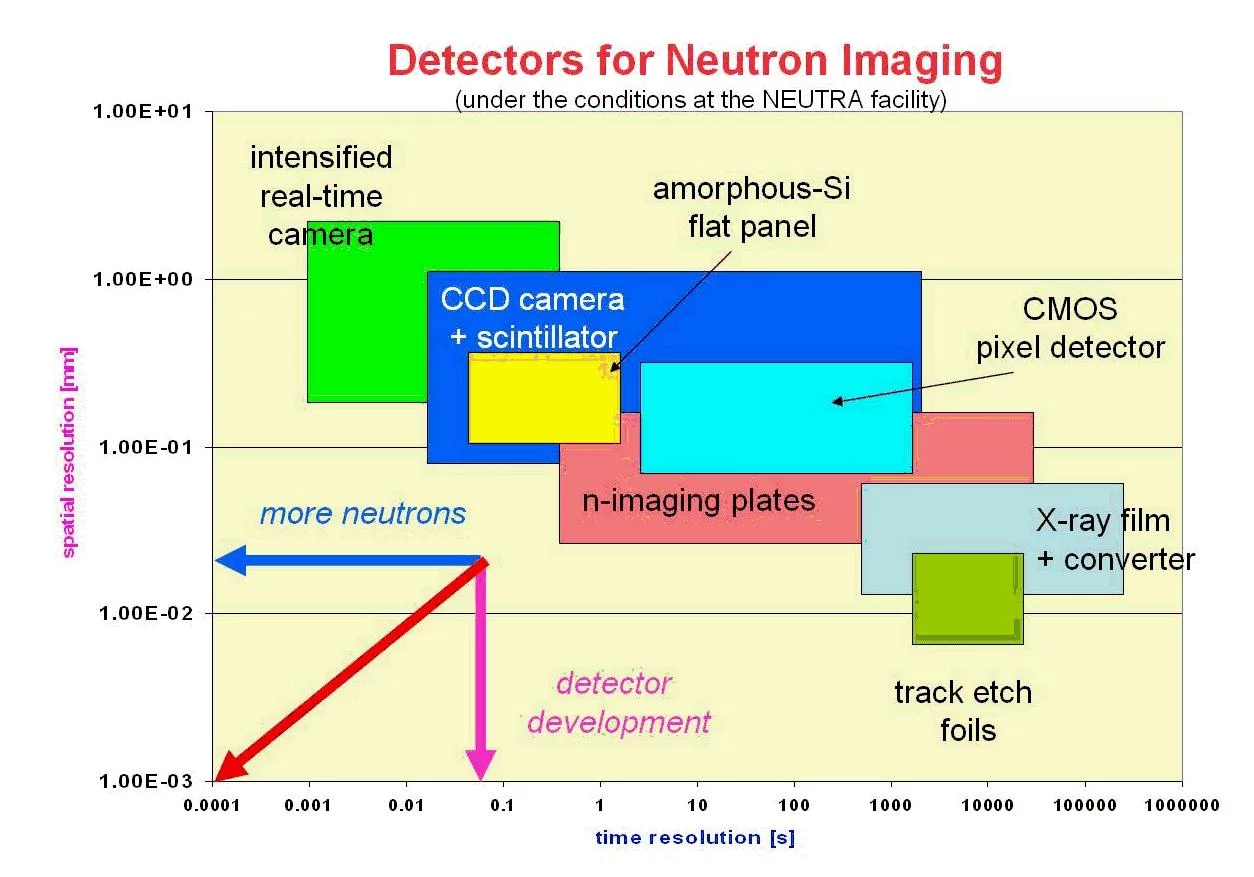
Detectors in use for Neutron Imaging (NI) purposes are those, which are able to measure the neutron field in two dimensions perpendicular to the beam direction. Therefore, the detector area should be in the order or larger than the beam cross-section. Further boundary conditions are the spatial and time dependent resolution of the detector, which can be very different among the existing detectors systems. An overview about these parameters is given for the most common systems in figure 8. The inherent detectors properties are mainly given by the detection process, which is a nuclear reaction initiated by the neutrons. The primary detection reactions for thermal neutrons are mainly neutron capture by an absorbing material emitting secondary radiation, which can be used as the real neutrons proof. This is why neutrons have no electric charge and cannot make ionization directly which is needed for the detection.
The most important detection reactions are (for thermal and cold neutrons):
3He + 1n → 3H + 1p + 0.77 MeV
6Li + 1n → 3H + 4He + 4.79 MeV
10B + 1n → ( 7%)7Li + 4He + 2.78 MeV
10B + 1n → (93%)7Li* + 4He + 2.30 MeV + γ (0.48 MeV)
155Gd + 1n → 156Gd + γ + conversion electrons (7.9 MeV)
157Gd + 1n → 158Gd + γ + conversion electrons (8.5 MeV)
113Cd + 1n → 114Cd + γ + conversion electrons
The further process for imaging in radiography based on the previous reactions is possible in different ways:
- by light excitation in a scintillator
- by blackening of a suited film
- by excitation of electronic (metastabile) states in a crystal (imaging plates)
- by creation of micro-traces in special foils (track-etch method)
- by charge separation in a semiconductor material
The following detector systems for radiography have been developed on the basis of the mentioned processes and are in use for different applications:
X-ray film in connection with converter foils from Gd, Dy, oder In. The excitation and blackening of the film is caused by gamma and beta radiation as well as by conversion electrons. | |
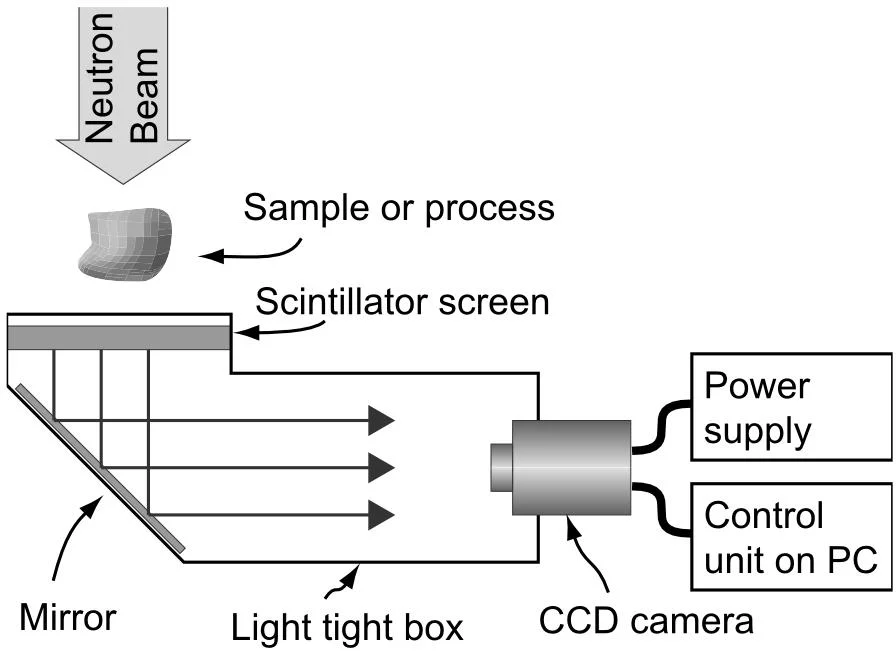
Highly light sensitive CCD camera detectors (cooled in most cases) looking onto the weak light emission from a neutron sensitive scintillator (Li-6 or Gd as neutron absorber). | |
By the use of image intensifiers, the light intensity can importantly be increased (as intensifier tubes or micro-channel plates). In this way, either less sensitive cameras can be applied or higher frame rates becomes possible. | |
Imaging Plates contain Gd as neutron absorber and BaFBr:Eu 2+ as the agent which provides the photoluminescence. A imaging plate scanner is extracting the latent image information as digitised data file from the plates by de-excitation caused by a laser signal. | |
Track-etch-foils are "scratched" by α-particles created in a capture reaction of B-10 with thermal neutrons. These very small tracks can be enlarged so much by chemical treatment (etching in an alkaline bath) that a macroscopic image occurs, which can be digitalized or optical enlarged by optical means. | |
Flat panels based on amorphous silicon can provide digital information directly and an optical magnification (as with cameras) is not necessary. However, thy have to be placed into the direct beam, which can cause some problems for long term use. |
A summary of important properties of radiography detectors is given below:
| Detector system for digital neutron imaging | X-ray film + transmission light scanner | Scintillator + CCD-camera | Imaging plates | amorphous silicon flat panel |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Max. spatial resolution (pixel size) [µm] | 20 - 50 | 20 - 500 | 25 - 100 | 127 - 750 |
| Typical exposure time for generation of good images | 5 min | 10 s | 20 s | 10s |
| Detector area (typical) | 18cm x 24cm | 25cm x 25cm | 20cm x 40cm | 30cm x 40cm |
| Number of pixels per line (optimal conditions) | 4000 | 2000 | 6000 | 1750 |
| Dynamic range | 102 (non-linear) | 105 (linear) | 105 (linear) | 103 (non-linear) |
| Digital format | 8 bit | 16 bit | 16 bit | 12 bit |