| Energy range | 250-1600 eV |
|---|---|
| Spectral resolution | >3000 |
| Polarization | Linear horizontal Circular (right/left) |
| Endstation | Scanning transmission x-ray microscopy (STXM) spatial resolution (focus size) < 40 nm, sample chamber vacuum (10-6 mbar) to 1 atm inert gas or He |
Current Highlights and News
Skyrmion topology quantified in 3D
Researchers from an international collaboration between the United States of America and Switzerland have performed three-dimensional magnetic imaging of a magnetic skyrmion using soft X-ray laminography. This allowed for the investigation, in three dimensions, of the topological profile of the magnetic skyrmions.
Spatially reconfigurable topological textures in freestanding antiferromagnetic nanomembranes
Researchers from the University of Oxford have imaged, through the use of the soft X-ray microscopy capabilities at the Swiss Light Source, spatially reconfigurable antiferromagnetic states in topologically rich free-standing nanomembranes
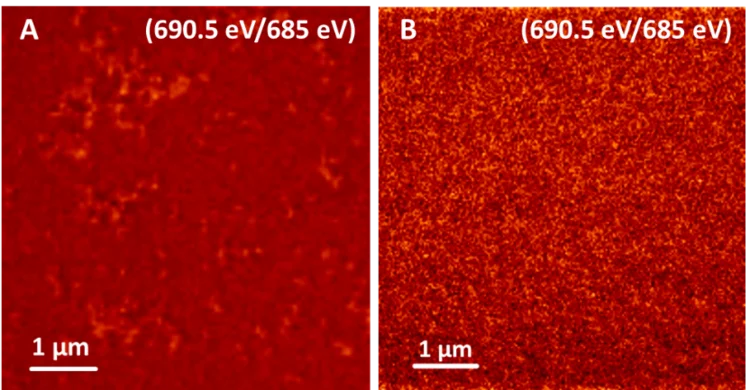
TEY-STXM confirms homogeneous doping of nanoparticles for non-fullerene organic solar cells
One of the challenges in modern research on the fabrication of non-fullerene acceptor based organic solar cells is the availability of very efficient hole transport layers (HTLs). A new approach that avoids mutual solubility issues is to deposit the HTL from a suspension of doped organic nanoparticles. Surface-sensitive TEY-STXM measurements at the PolLux beamline characterised the homogeneity of the dopant in the nanoparticles and develop efficient nanoparticle HTL materials for organic solar cells.