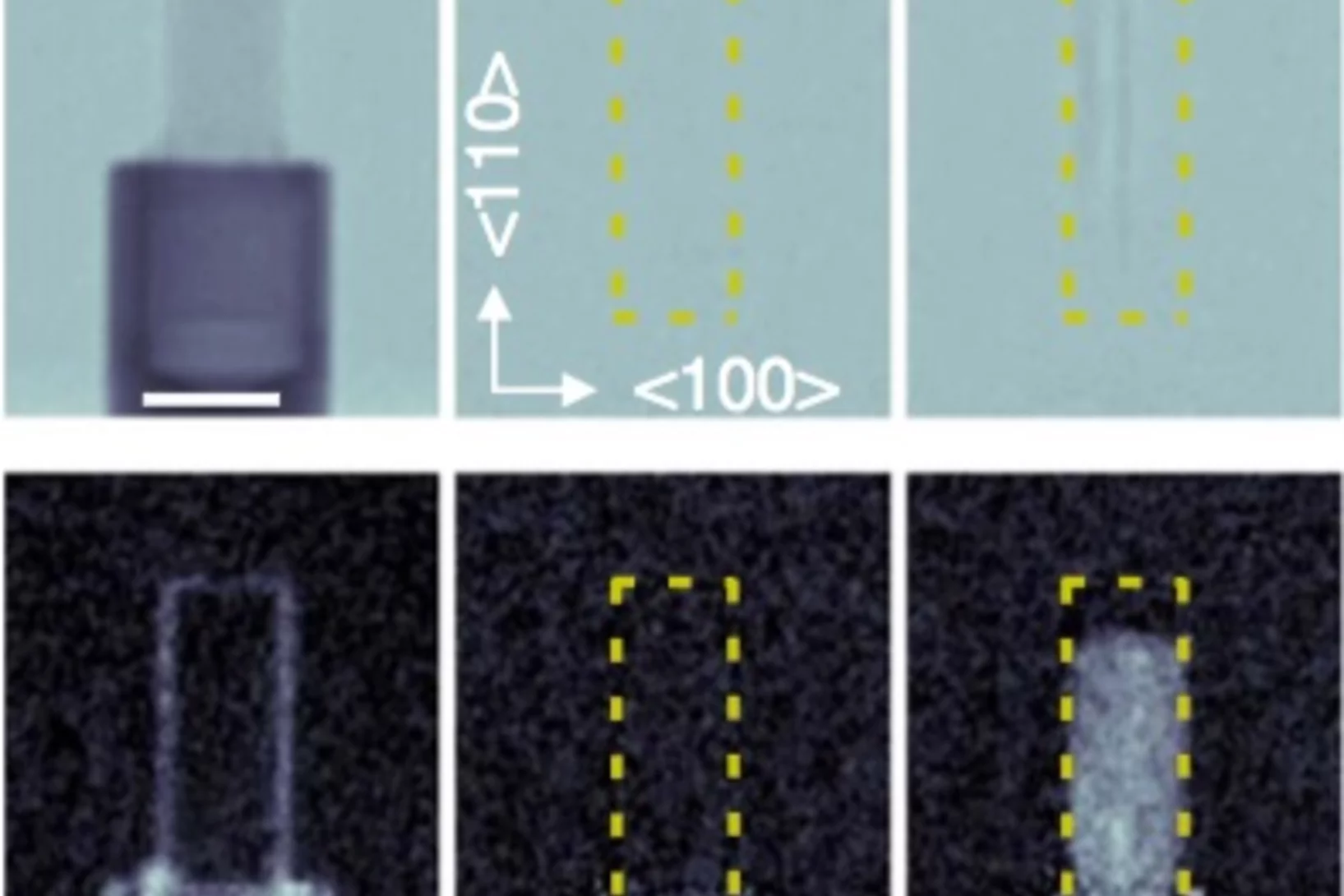
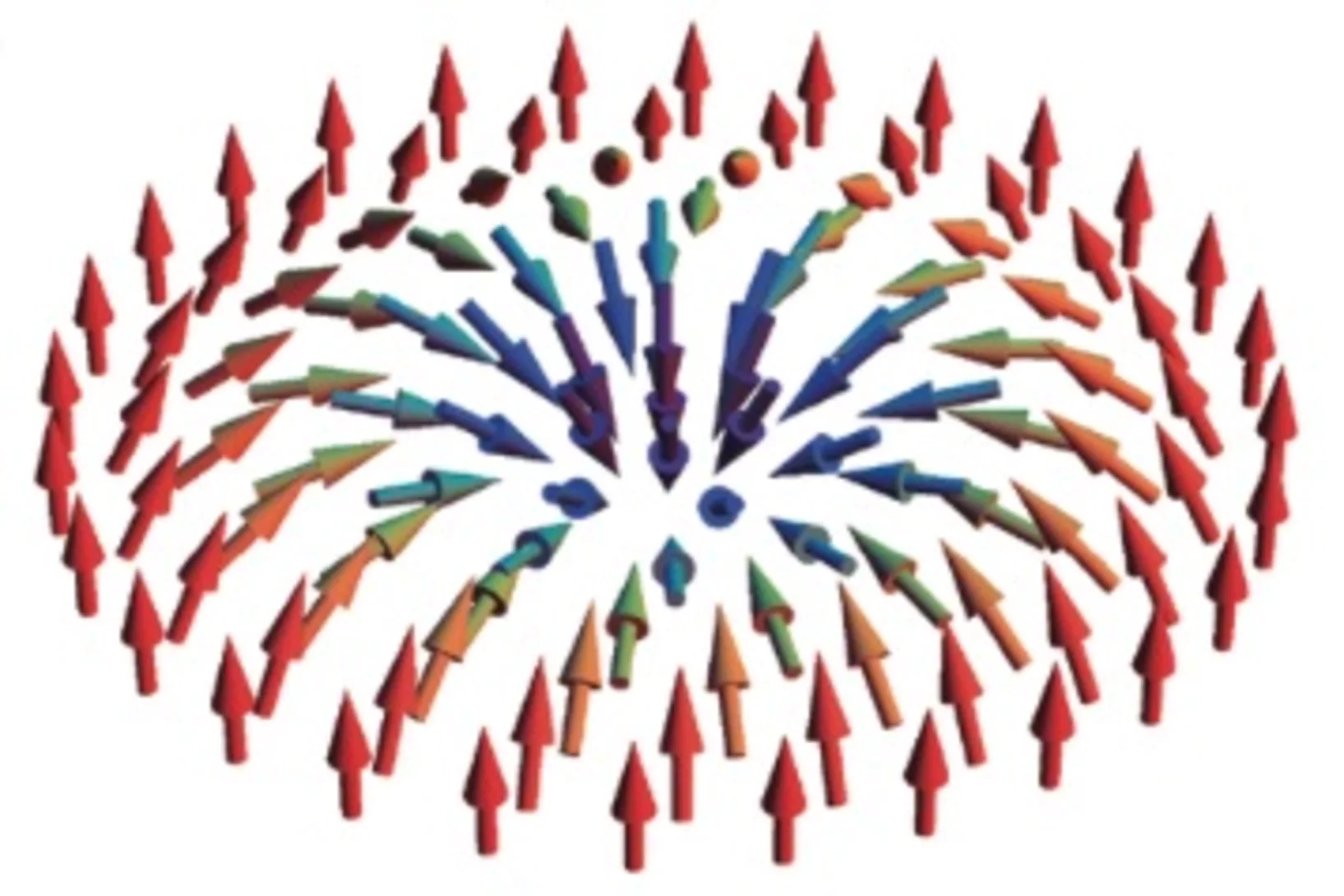
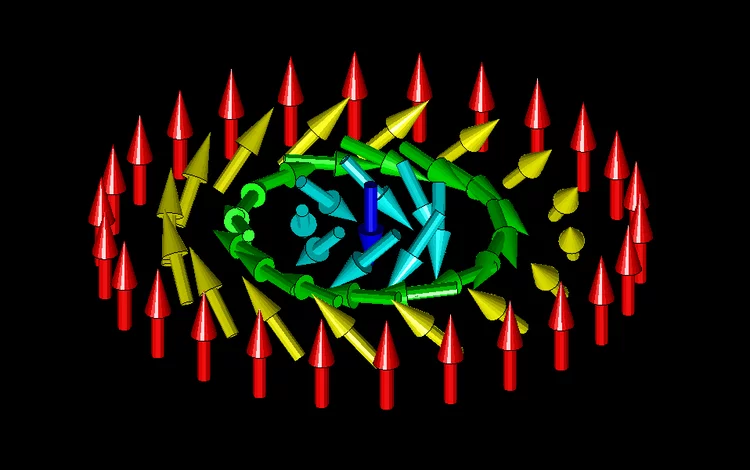
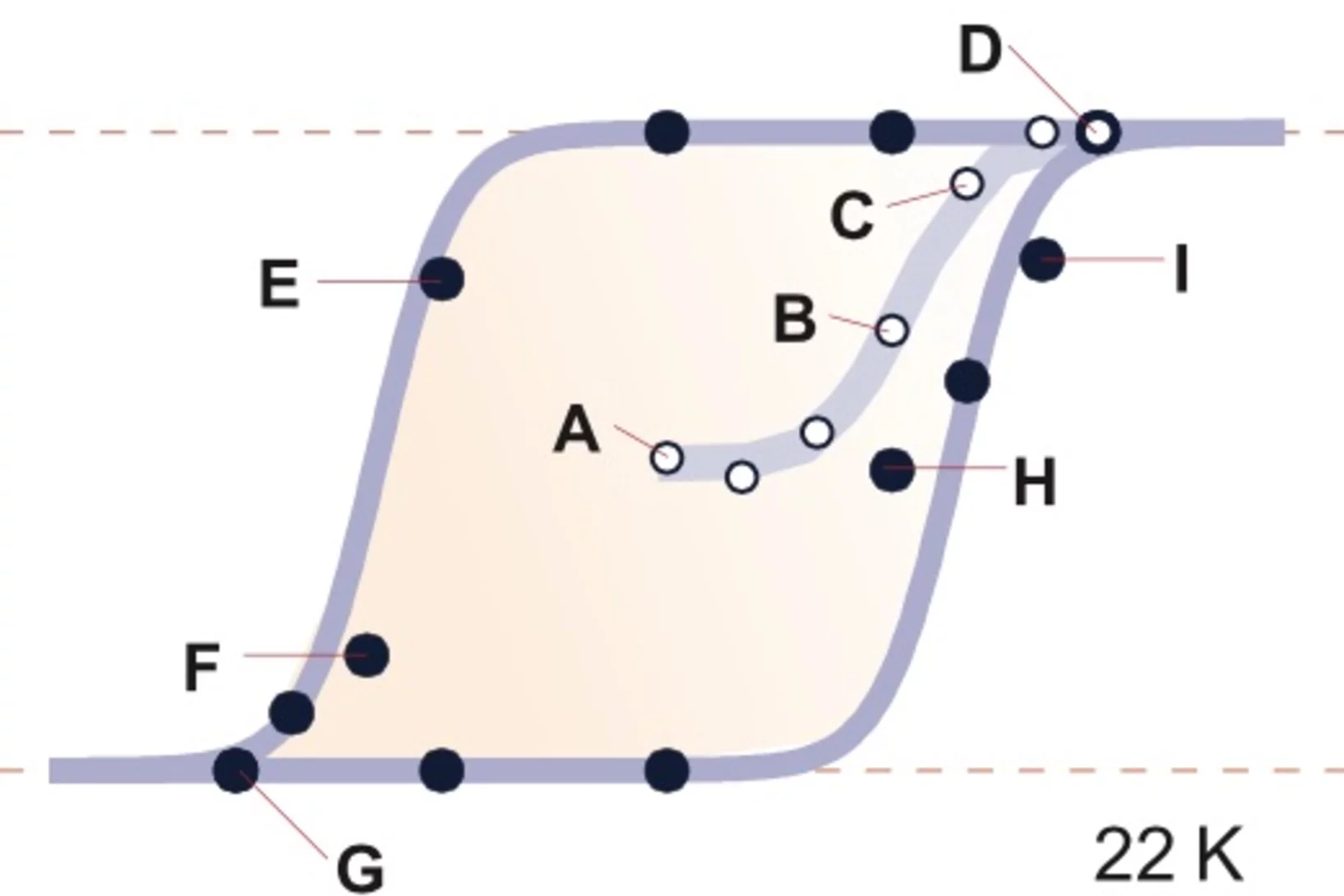
In-situ visualization of stress-dependent bulk magnetic domain formation by neutron grating interferometry
The efficiency of industrial transformers is directly influenced by the magnetic properties of high-permeability steel laminations (HPSLs). These laminations are coated by insulating layers, to reduce eddy-current losses in the transformer core. In addition, the coating induces favorable inter-granular tensile stresses that significantly influence the underlying magnetic domain structure.
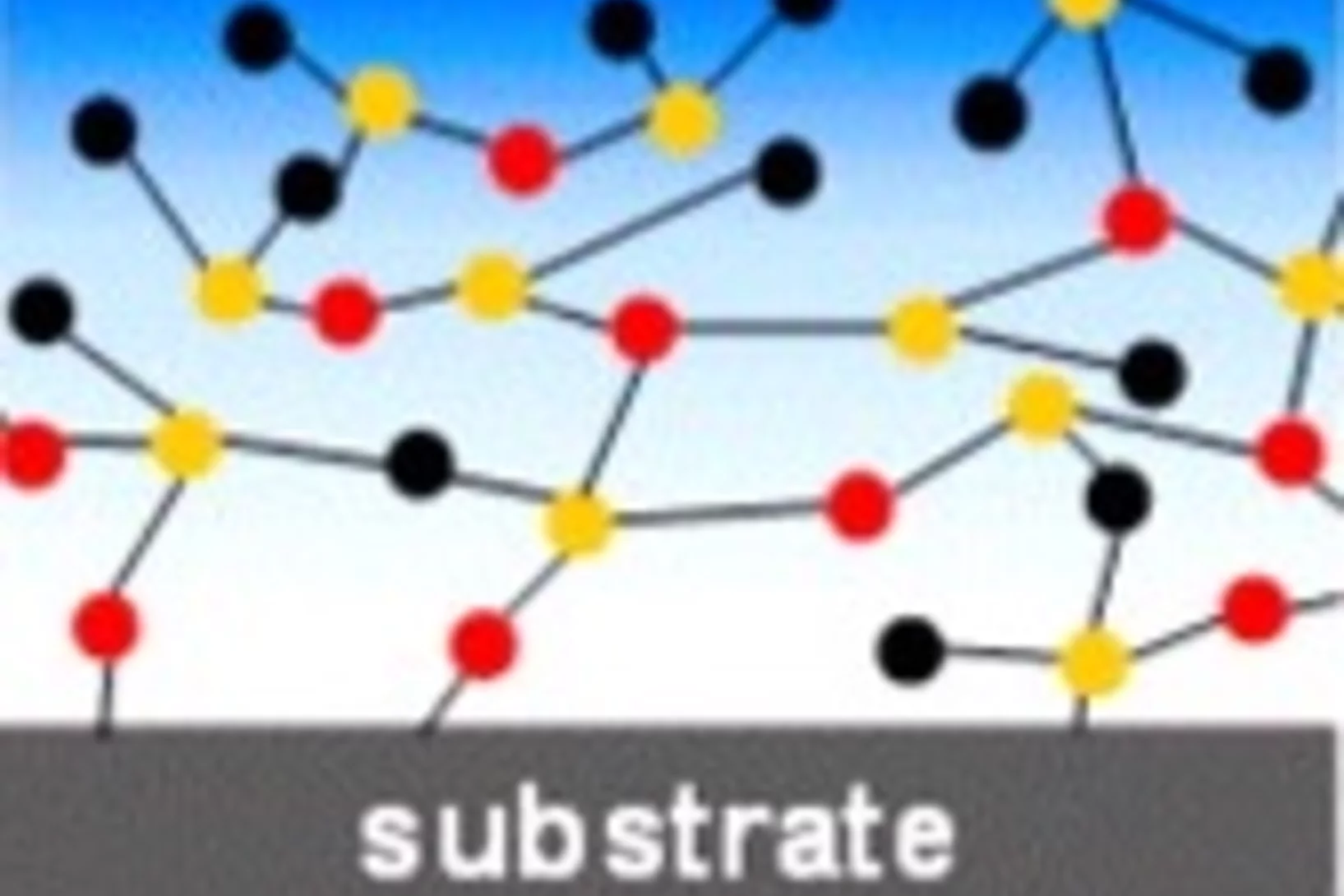
Stratified Micellar Multilayers - Toward Nanostructured Photoreactors
Polyelectrolyte multilayers (PEMs) with stratification of the internal structure were assembled from statistical amphiphilic copolyelectrolytes of opposite charges. These polyelectrolytes organize in aqueous solutions into micellar structures with fluoroalkyl and aromatic nanodomains, respectively, that were also preserved after deposition as thin films via layer-by-layer (LbL) electrostatic self-assembly.
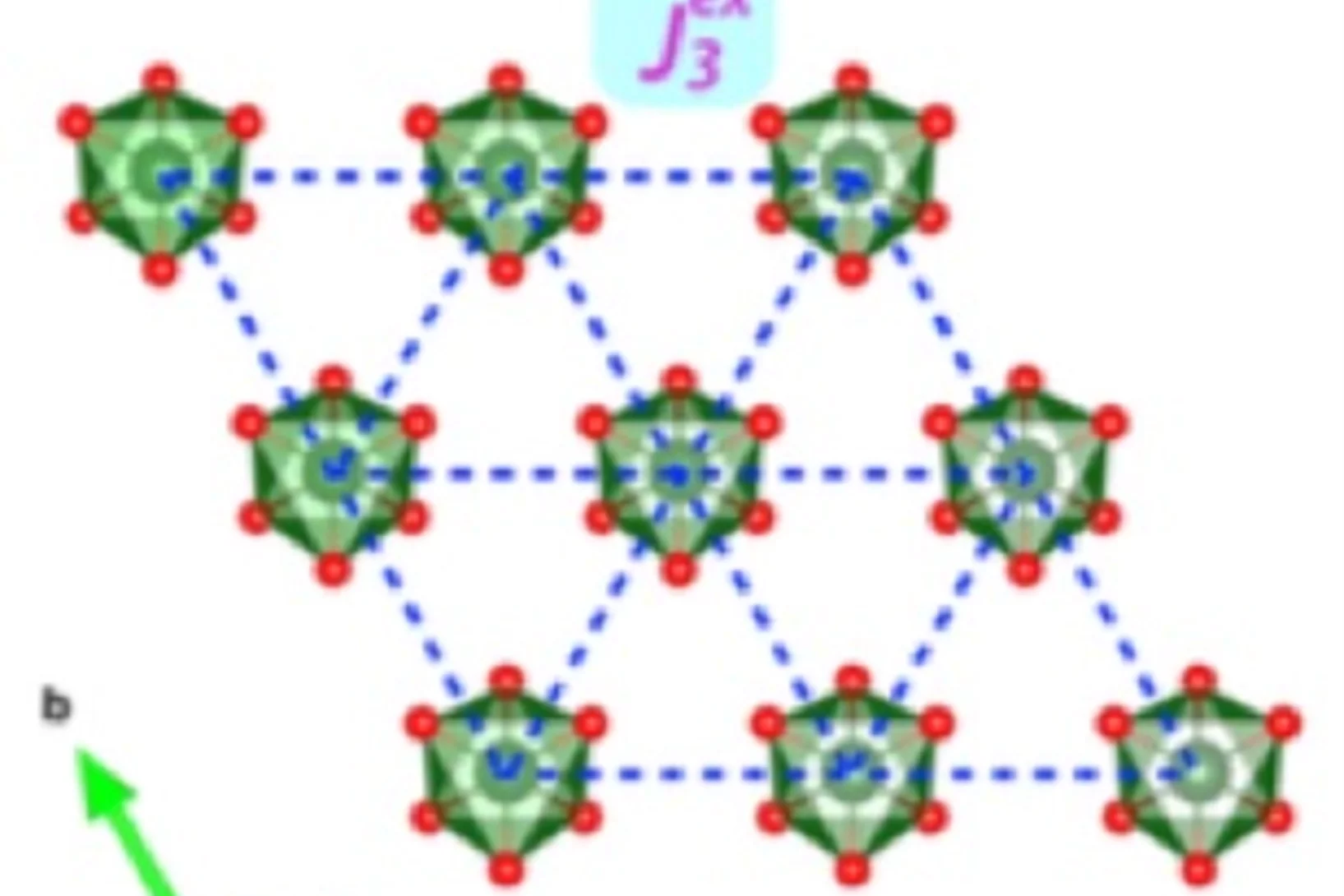
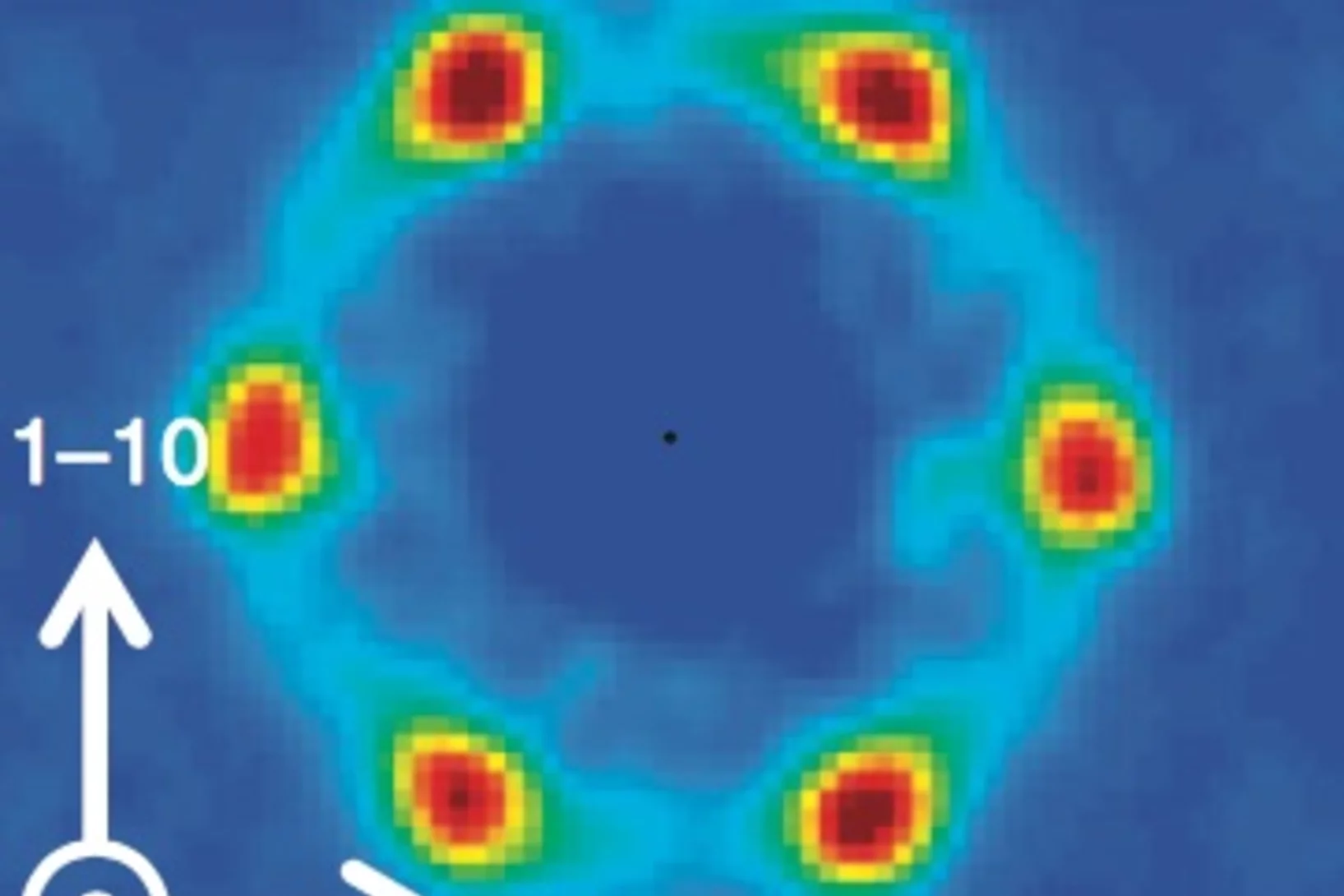
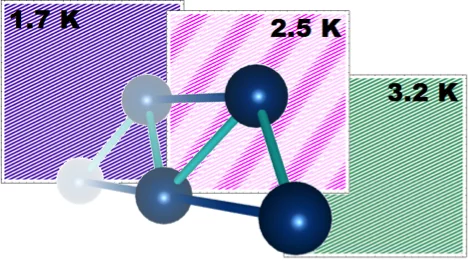
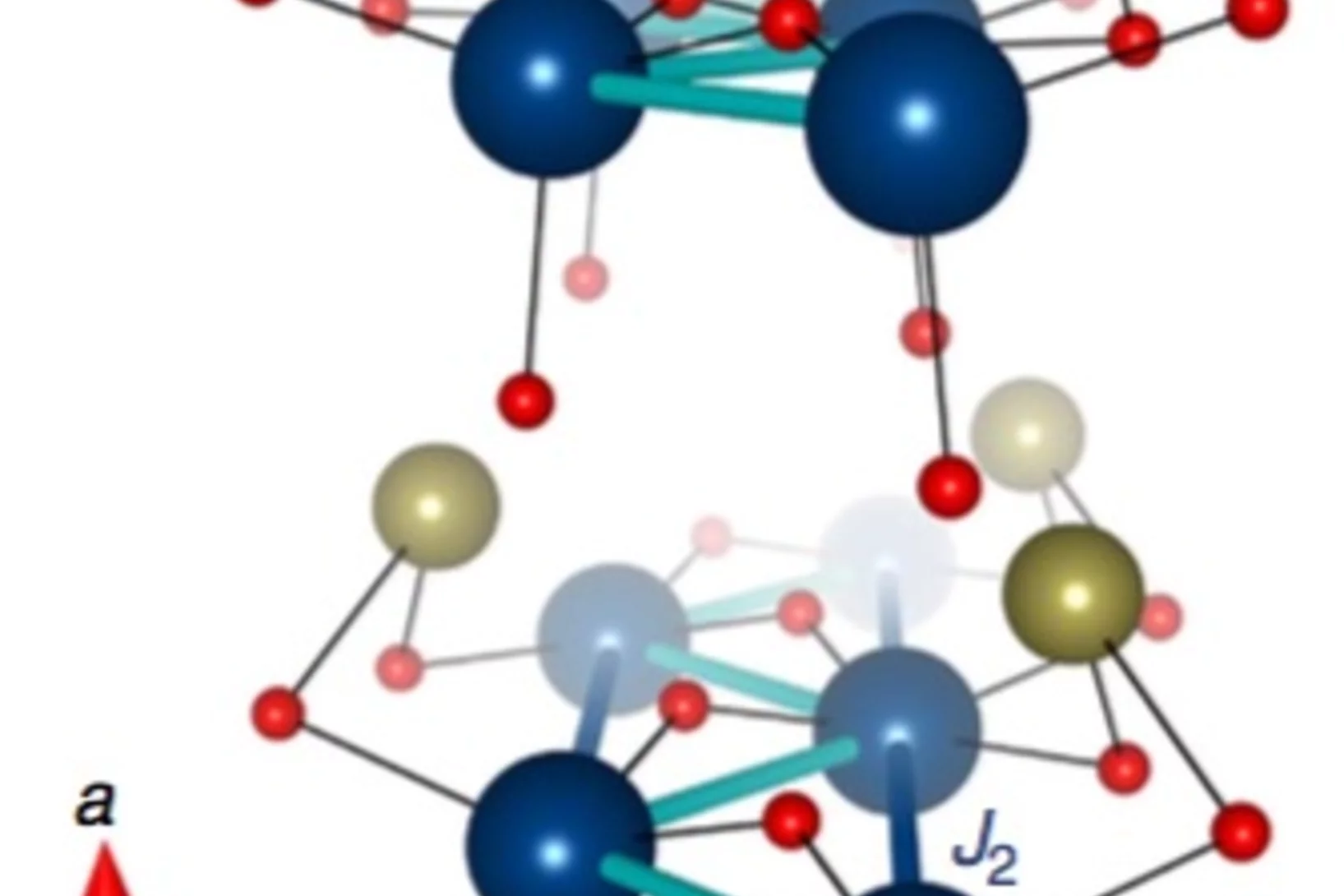
Origin of the Spin-Orbital Liquid State in a Nearly J=0 Iridate Ba3ZnIr2O9
We show using detailed magnetic and thermodynamic studies and theoretical calculations that the ground state of Ba3ZnIr2O9 is a realization of a novel spin-orbital liquid state. Our results reveal that Ba3ZnIr2O9 with Ir5+ (5d4) ions and strong spin-orbit coupling (SOC) arrives very close to the elusive J 1⁄4 0 state but each Ir ion still possesses a weak moment.
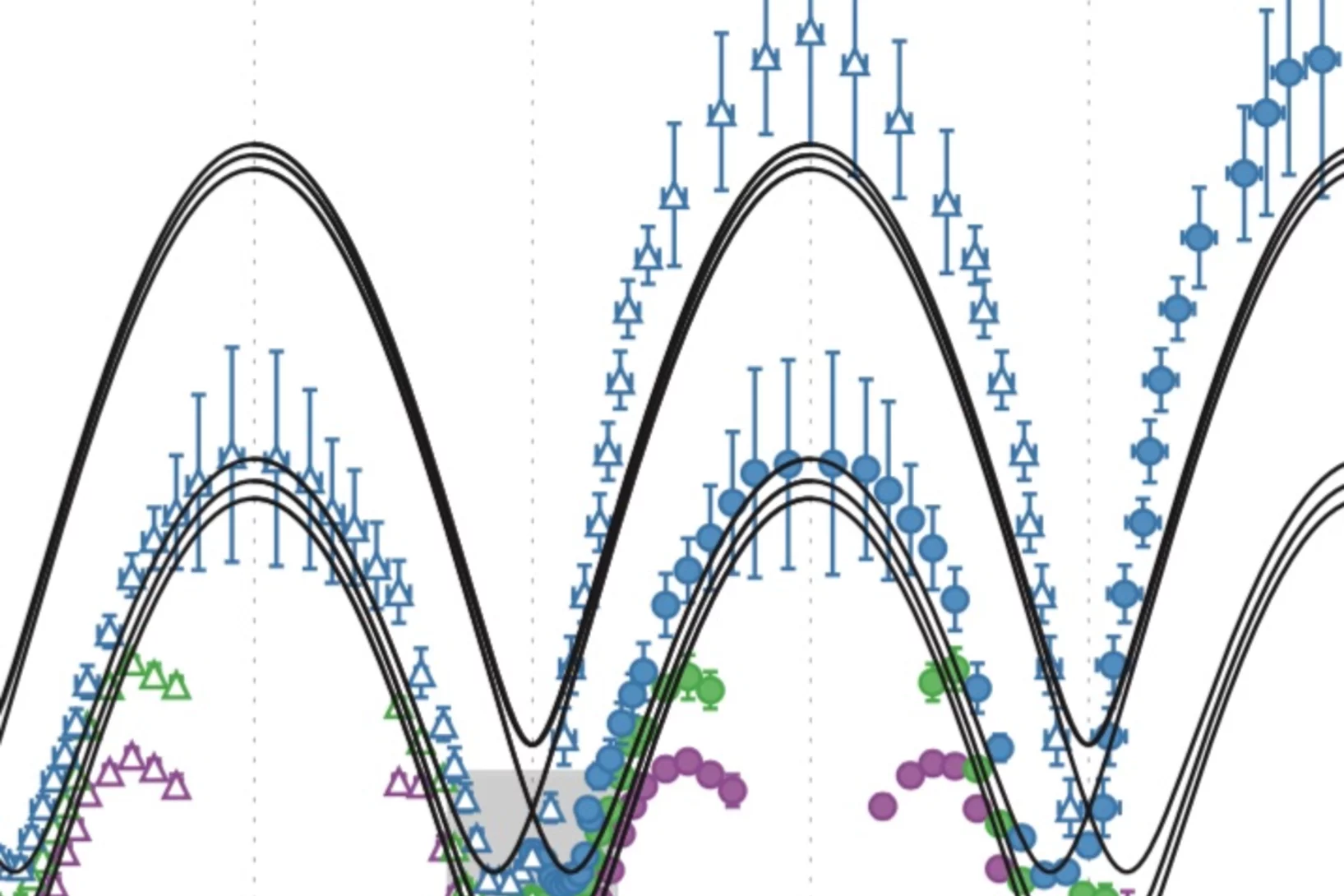
Quasiparticle-continuum level repulsion in a quantum magnet
When the energy eigenvalues of two coupled quantum states approach each other in a certain parameter space, their energy levels repel each other and level crossing is avoided. Such level repulsion, or avoided level crossing, is commonly used to describe the dispersion relation of quasiparticles in solids.
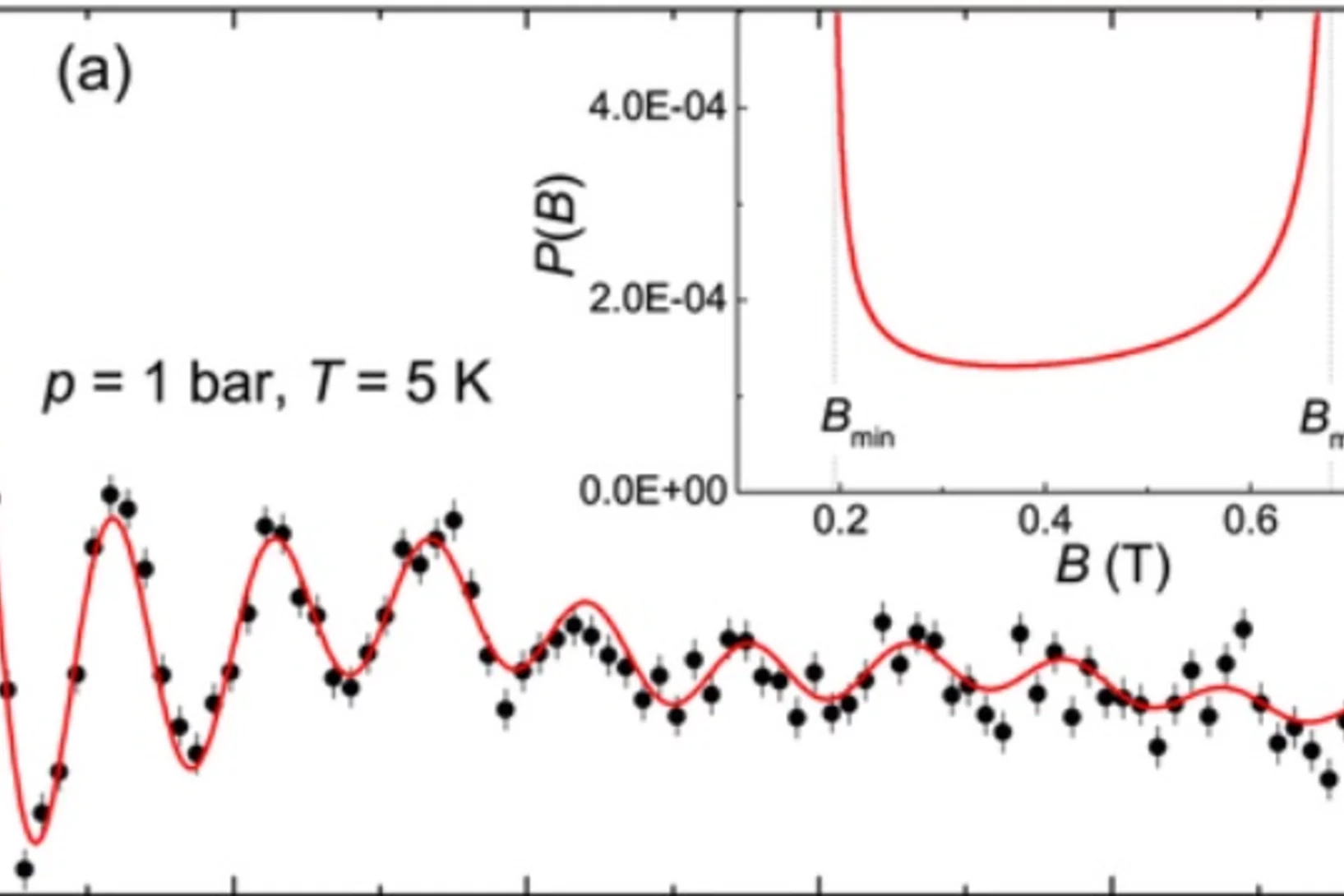
Dramatic pressure-driven enhancement of bulk skyrmion stability
The recent discovery of magnetic skyrmion lattices initiated a surge of interest in the scientic community. Several novel phenomena have been shown to emerge from the interaction of conducting electrons with the skyrmion lattice, such as a topological Hall-effect and a spin-transfer torque at ultra-low current densities.
Small-Angle Neutron Scattering Study of Interplay of Attractive and Repulsive Interactions in Nanoparticle-Polymer System
The phase behavior of nanoparticle (silica)−polymer (polyethylene glycol) system without and with an electrolyte (NaCl) has been studied. It is observed that nanoparticle−polymer system behaves very differently in the presence of electrolyte. In the absence of electrolyte, the nanoparticle−polymer system remains in one-phase even at very high polymer concentrations.
Mechanically Enhanced Liquid Interfaces at Human Body Temperature Using Thermosensitive Methylated Nanocrystalline Cellulose
The mechanical performance of materials at oil/water interfaces after consumption is a key factor affecting hydrophobic drug release. In this study, we methylated the surface of nanocrystalline cellulose (NCC) by mercerization and dimethyl sulfate exposure to produce thermosensitive biopolymers. These methylated NCC (metNCC) were used to investigate interfacial thermogelation at air/water and medium-chain triglyceride (MCT)/water interfaces at body temperature.
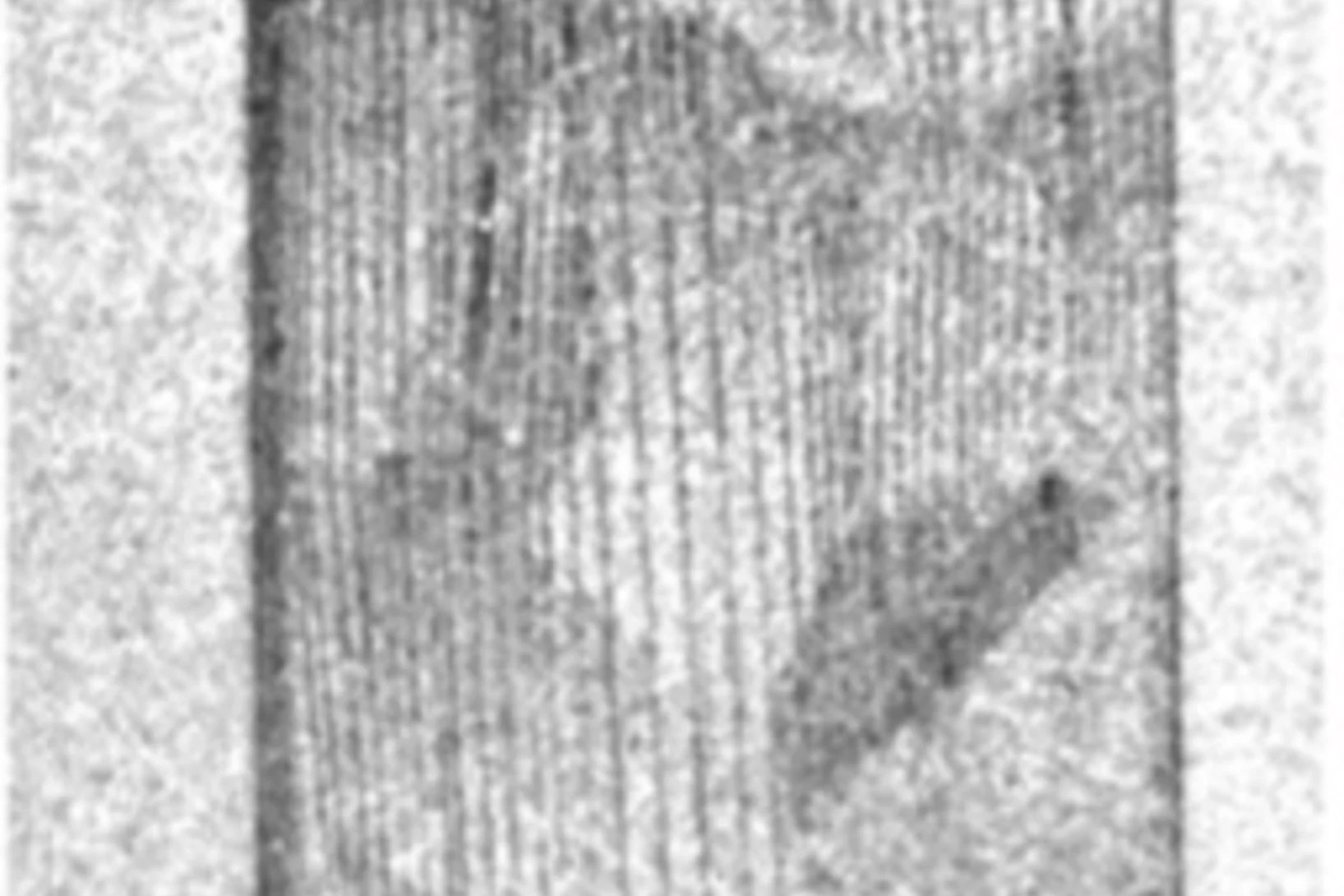
Self-Diffusion in Amorphous Silicon
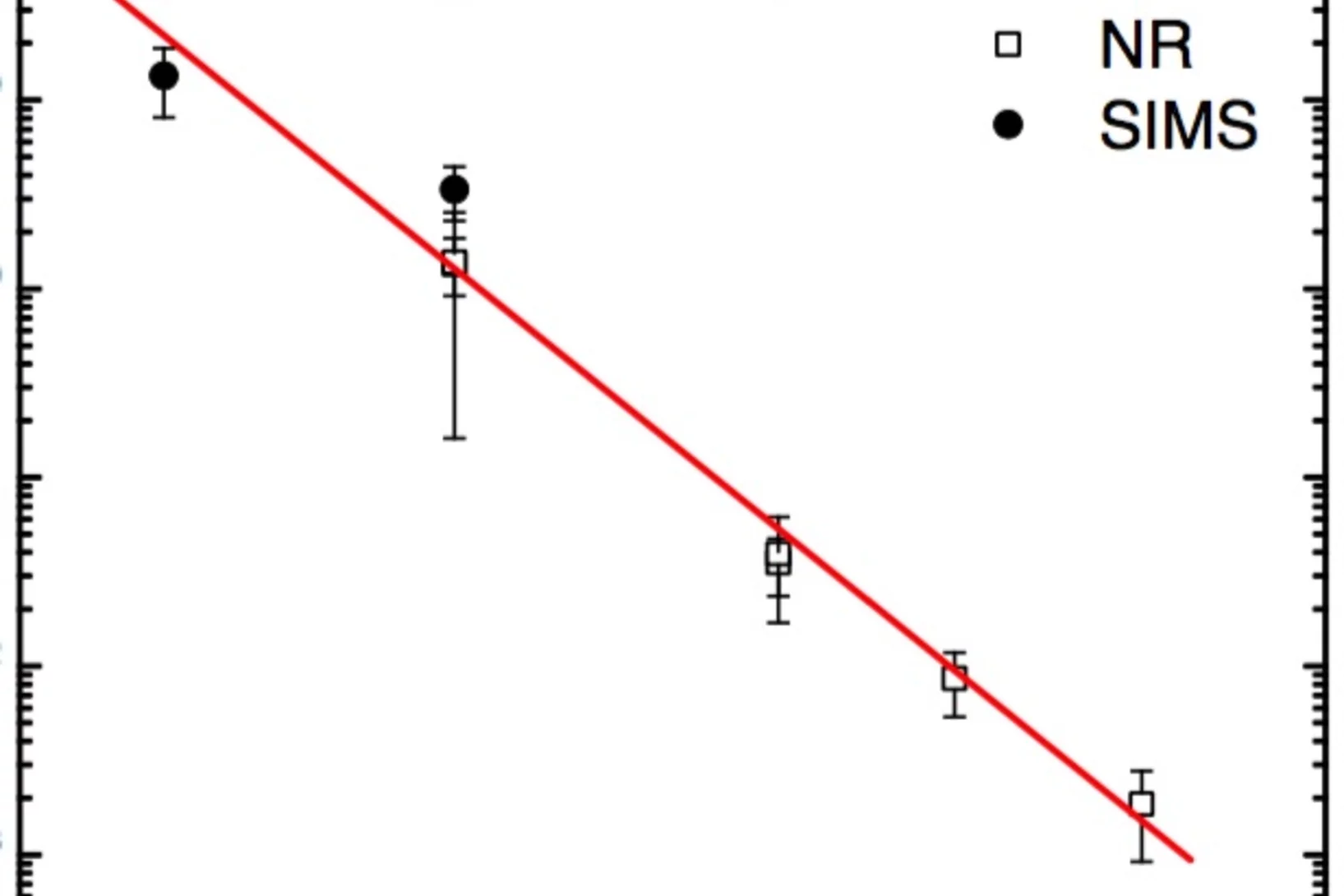
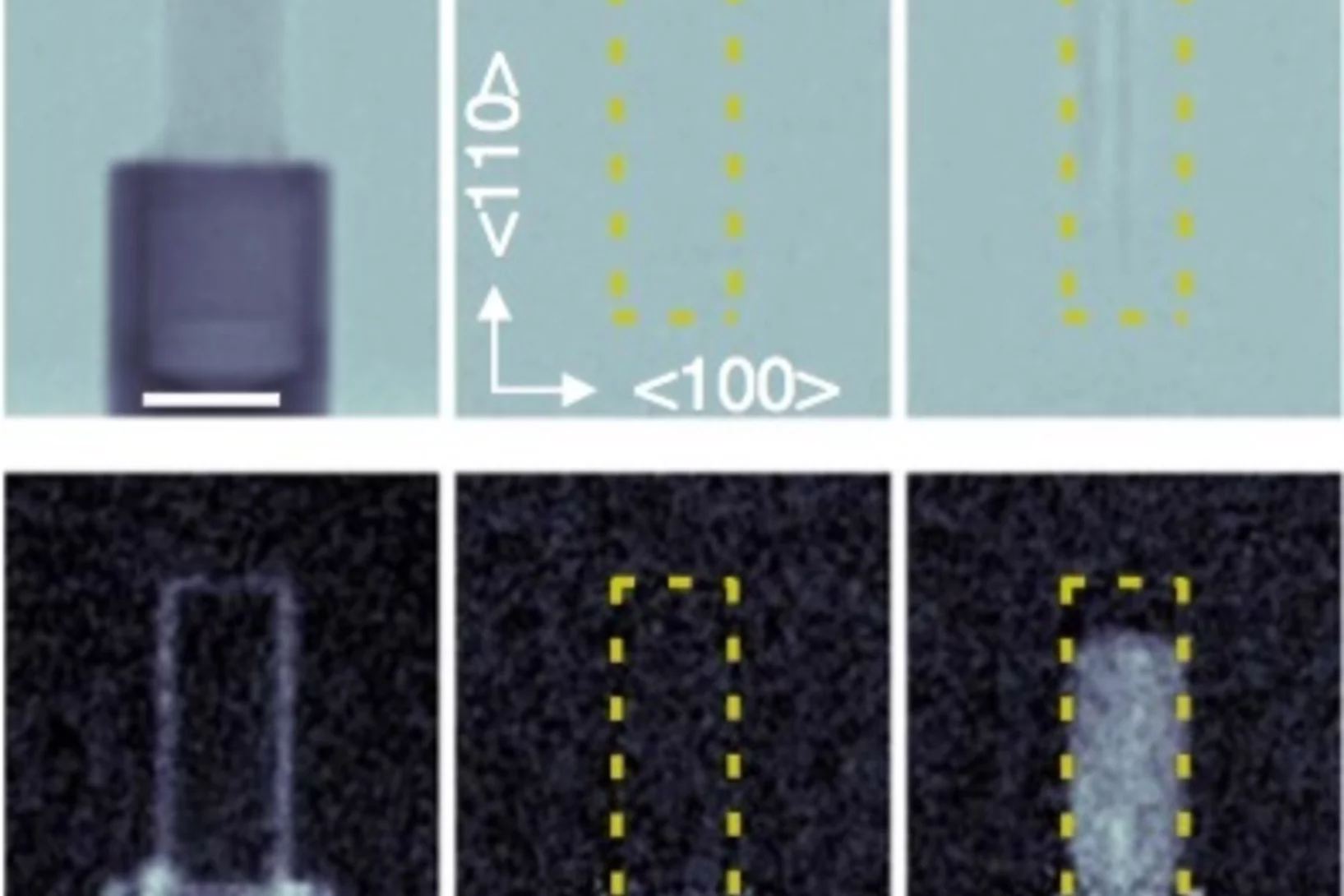
The present Letter reports on self-diffusion in amorphous silicon. Experiments were done on 29Si/natSi heterostructures using neutron reflectometry and secondary ion mass spectrometry. The diffusivities follow the Arrhenius law in the temperature range between 550 and 700°C with an activation energy of (4.4 ± 0.3) eV.
In-situ visualization of stress-dependent bulk magnetic domain formation by neutron grating interferometry
The performance and degree of efficiency of industrial transformers are directly influenced by the magnetic properties of high-permeability steel laminations (HPSLs). Industrial transformer cores are built of stacks of single HPSLs. While the insulating coating on each HPSL reduces eddy-current losses in the transformer core, the coating also induces favorable inter-granular tensile stresses that significantly influence the underlying magnetic domain structure.
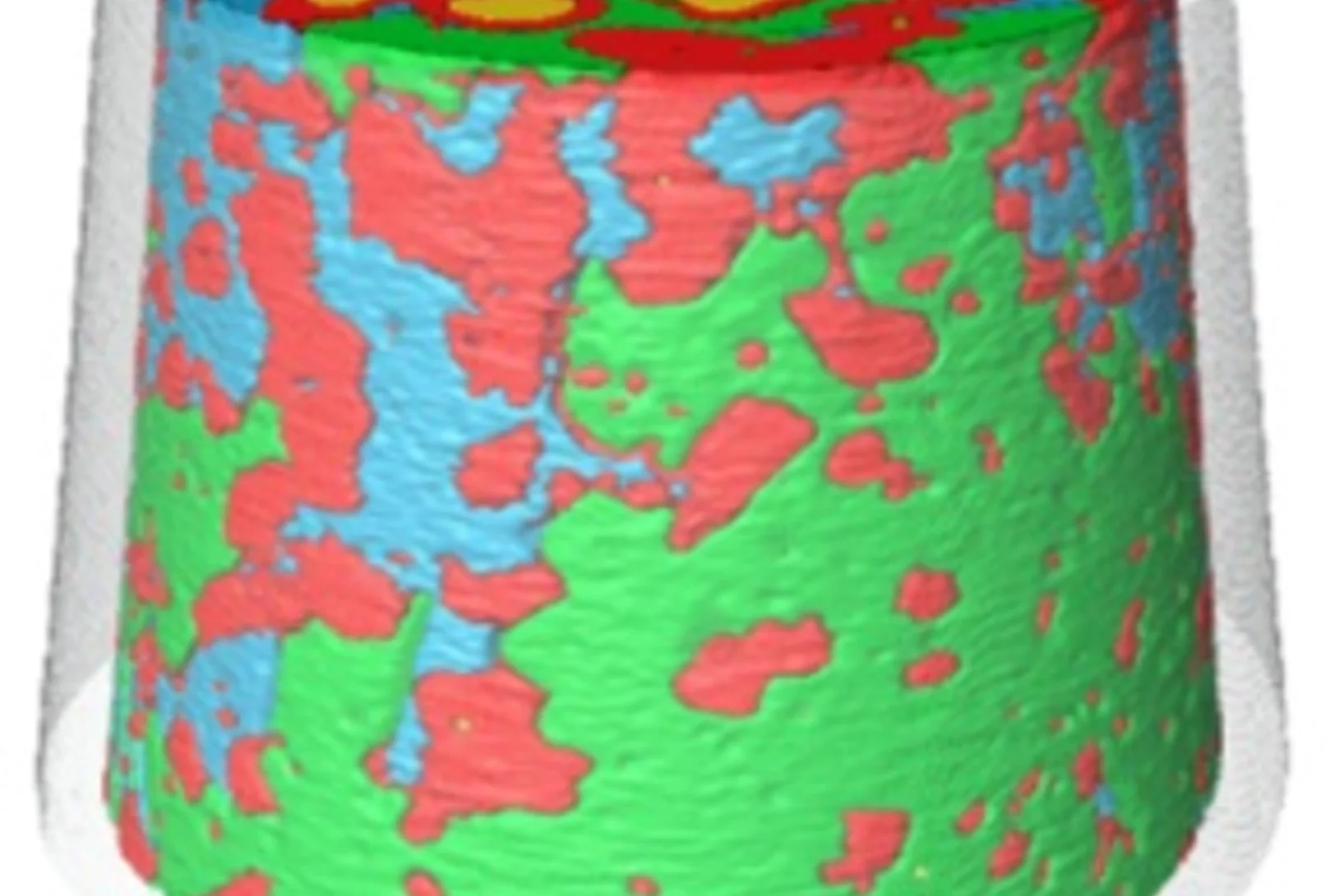
Nanostructure surveys of macroscopic specimens by small-angle scattering tensor tomography
The mechanical properties of many materials are based on the macroscopic arrangement and orientation of their nanostructure. This nanostructure can be ordered over a range of length scales. In biology, the principle of hierarchical ordering is often used to maximize functionality, such as strength and robustness of the material, while minimizing weight and energy cost.
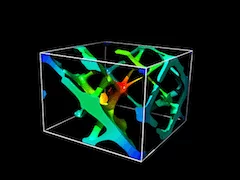
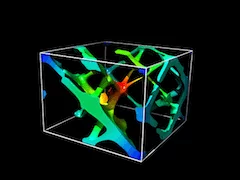
Visualizing the morphology of vortex lattice domains in a bulk type-II superconductor
Alike materials in the solid state, the phase diagram of type-II superconductors exhibit crystalline, amorphous, liquid and spatially inhomogeneous phases. The multitude of different phases of vortex matter has thence proven to act as almost ideal model system for the study of both the underlying properties of superconductivity but also of general phenomena such as domain nucleation and morphology.
Visualizing the morphology of vortex lattice domains in a bulk type-II superconductor
Alike materials in the solid state, the phase diagram of type-II superconductors exhibit crystalline, amorphous, liquid and spatially inhomogeneous phases. The multitude of different phases of vortex matter has thence proven to act as almost ideal model system for the study of both the underlying properties of superconductivity but also of general phenomena such as domain nucleation and morphology.
Response of Plasma-Polymerized Hexamethyldisiloxane Films to Aqueous Environments
Thin plasma polymer films were deposited in hexamethyldisiloxane (HMDSO) and HMDSO/O2 low-pressure discharges and their chemical structures analyzed using infrared (IR) spectroscopy and neutron reflectometry (NR). The (plasma-polymerized) ppHMDSO film exhibits hydrophobic, poly(dimethylsiloxane)-like properties, while the retention of carbon groups is reduced by O2 addition, yielding a more inorganic, hydrophilic ppSiOx film.
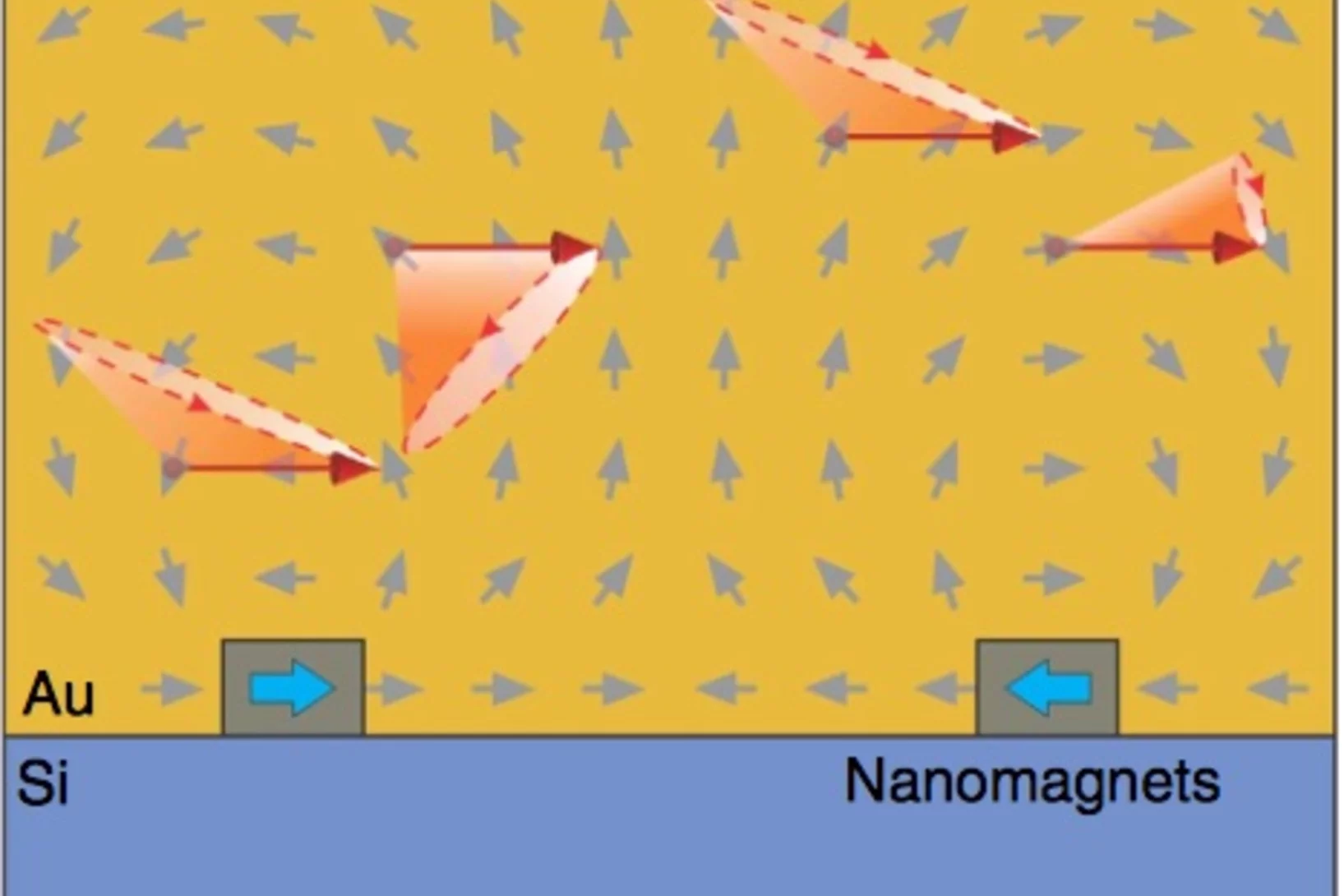
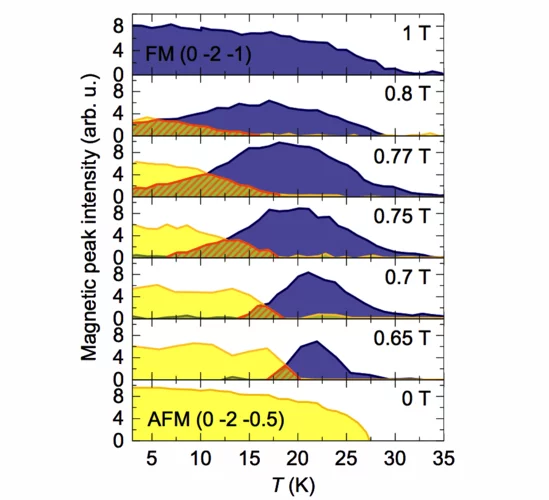
Thermodynamic phase transitions in a frustrated magnetic metamaterial
Materials with interacting magnetic degrees of freedom display a rich variety of magnetic behaviour that can lead to novel collective equilibrium and out-of-equilibrium phenomena. In equilibrium, thermodynamic phases appear with the associated phase transitions providing a characteristic signature of the underlying collective behaviour.
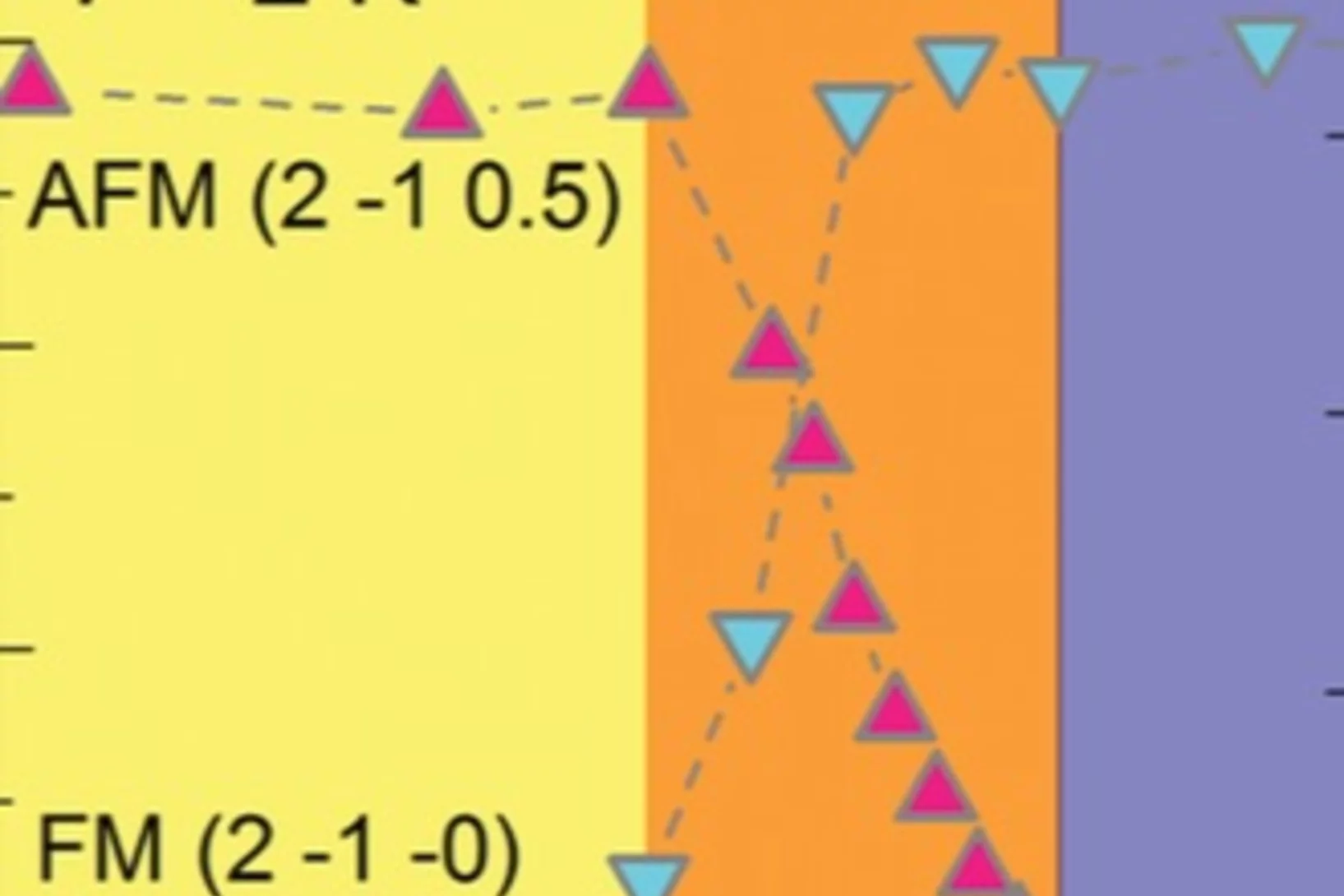
Pressure-induced electronic phase separation of magnetism and superconductivity in CrAs
The recent discovery of pressure (p) induced superconductivity in the binary helimagnet CrAs has raised questions on how superconductivity emerges from the magnetic state and on the mechanism of the superconducting pairing. In the present work the suppression of magnetism and the occurrence of superconductivity in CrAs were studied by means of muon spin rotation.
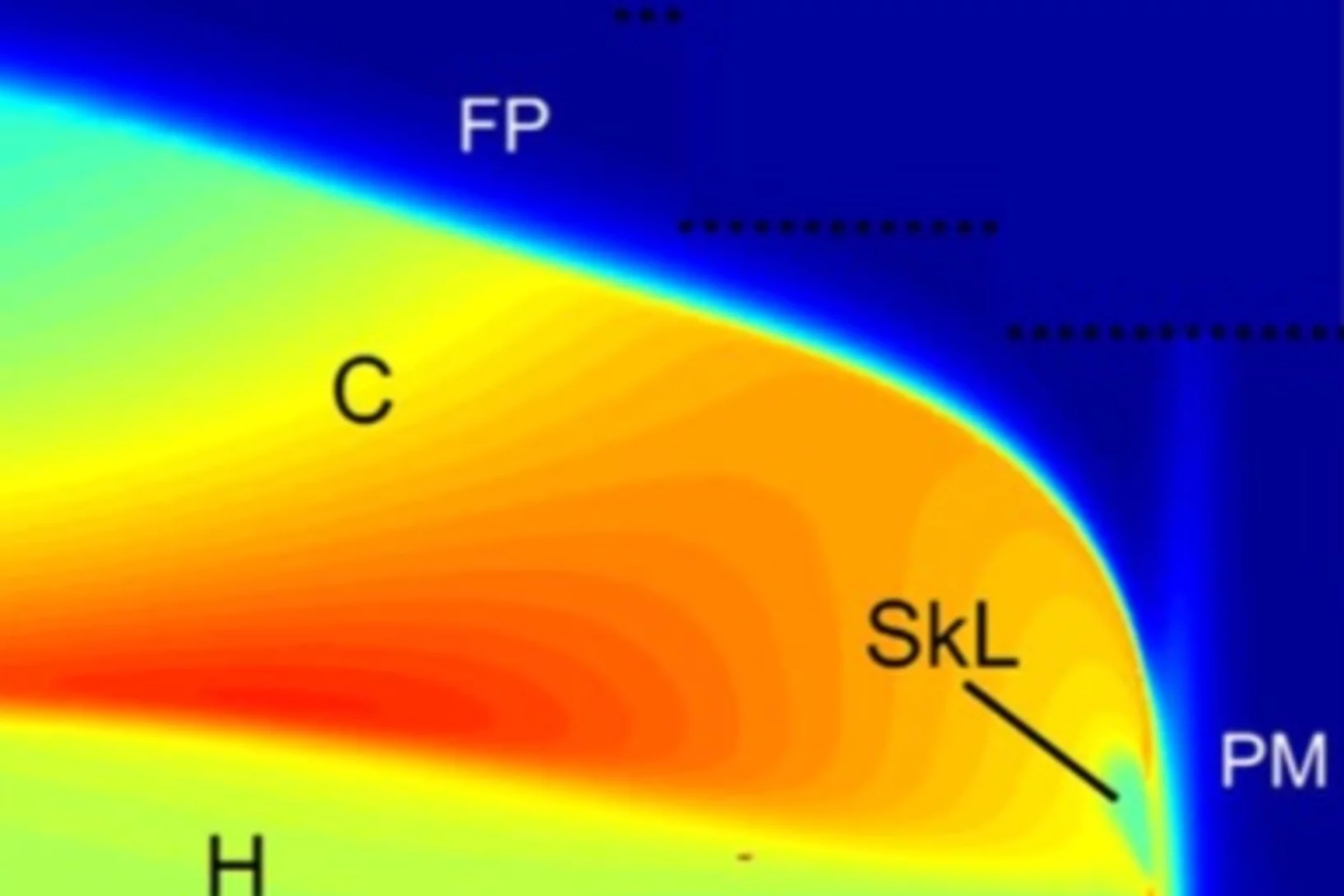
Néel-type skyrmion lattice with confined orientation in the polar magnetic semiconductor GaV4S8
Following the early prediction of the skyrmion lattice (SkL) - a periodic array of spin vortices - it has been observed recently in various magnetic crystals mostly with chiral structure. Although non-chiral but polar crystals with Cnv symmetry were identified as ideal SkL hosts in pioneering theoretical studies, this archetype of SkL has remained experimentally unexplored.
Lattice dynamics of α-cristobalite and the Boson peak in silica glass
This work marks a decisive step in the solution of the longstanding problem understanding the origin of the Boson peak in silica glass. The investigation by means of diffuse and inelastic x-ray scattering and lattice dynamics calculations from first principles allow for a direct comparison of the atomic motion in crystalline silica polymorphs and silica glass. The article was selected to illustrate the cover page of Journal of Physics: Condensed Matter, Vol. 27, Nr. 30.
Lattice dynamics of α-cristobalite and the Boson peak in silica glass
B. Wehinger et al., J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 27, 305401 (2015). This work marks a decisive step in the solution of the longstanding problem understanding the origin of the Boson peak in silica glass. The investigation by means of diffuse and inelastic x-ray scattering and lattice dynamics calculations from first principles allow for a direct comparison of the atomic motion in crystalline silica polymorphs and silica glass.
Candidate Quantum Spin Liquid in the Ce3+ Pyrochlore Stannate Ce2Sn2O7
We report the low-temperature magnetic properties of Ce2Sn2O7, a rare-earth pyrochlore. Our suscep- tibility and magnetization measurements show that due to the thermal isolation of a Kramers doublet ground state, Ce2Sn2O7 has Ising-like magnetic moments of ∼1.18 μB. The magnetic moments are confined to the local trigonal axes, as in a spin ice, but the exchange interactions are antiferromagnetic.
A new class of chiral materials hosting magnetic skyrmions beyond room temperature
Magnetic skyrmions are tiny, magnetic-spin vortices that can emerge in magnetic materials. Due to their nanometric size, skyrmions could be used to build extremely high density memory spintronics devices. However, stable skyrmions are not easy to find and control, and are usually only observed well below room temperature.
A new class of chiral materials hosting magnetic skyrmions beyond room temperature
Skyrmions, topologically protected vortex-like nanometric spin textures in magnets, have been attracting increasing attention for emergent electromagnetic responses and possible technological applications for spintronics. In particular, metallic magnets with chiral and cubic/tetragonal crystal structure may have high potential to host skyrmions that can be driven by low electrical current excitation.
Spin-stripe phase in a frustrated zigzag spin-1/2 chain
In strongly correlated electron systems periodic modulations on the nano-scale have typically been associated with competition between short- and long-range interactions, for example, between exchange and dipole-dipole interactions in the case of ferromagnetic thin films. Here we show that spin-stripe textures may develop also in antiferromagnets, where long-range dipole-dipole magnetic interactions are absent.
Spin-stripe phase in a frustrated zigzag spin-1/2 chain
Motifs of periodic modulations are encountered in a variety of natural systems, where at least two rival states are present. In strongly correlated electron systems, such behaviour has typically been associated with competition between short- and long-range interactions, for example, between exchange and dipole-dipole interactions in the case of ferromagnetic thin films.
Controllable Broadband Absorption in the Mixed Phase of Metamagnets
Combination of neutron scattering, muon spin relaxation, specific heat, ac and dc magnetization measurements, and electron magnetic resonance, reveals the ability of metamagnetic materials to absorb the electromagnetic radiation in an extremely broad frequency range.
Magnetoelectric domain control in multiferroic TbMnO3
The manipulation of domains by external fields in ferroic materials is of major interest for applications. In multiferroics with strongly coupled magnetic and electric order, however, the magnetoelectric coupling on the level of the domains is largely unexplored. We investigated the field-induced domain dynamics of TbMnO3 in the multiferroic ground state and across a first-order spin-flop transition.
Controllable Broadband Absorption in the Mixed Phase of Metamagnets
Materials with broad absorption bands are highly desirable for electromagnetic filtering and processing applications, especially if the absorption can be externally controlled. Here, a new class of broadband-absorption materials is introduced. Namely, layered metamagnets exhibit an electromagnetic excitation continuum in the magnetic-field-induced mixed ferro- and antiferromagnetic phase.
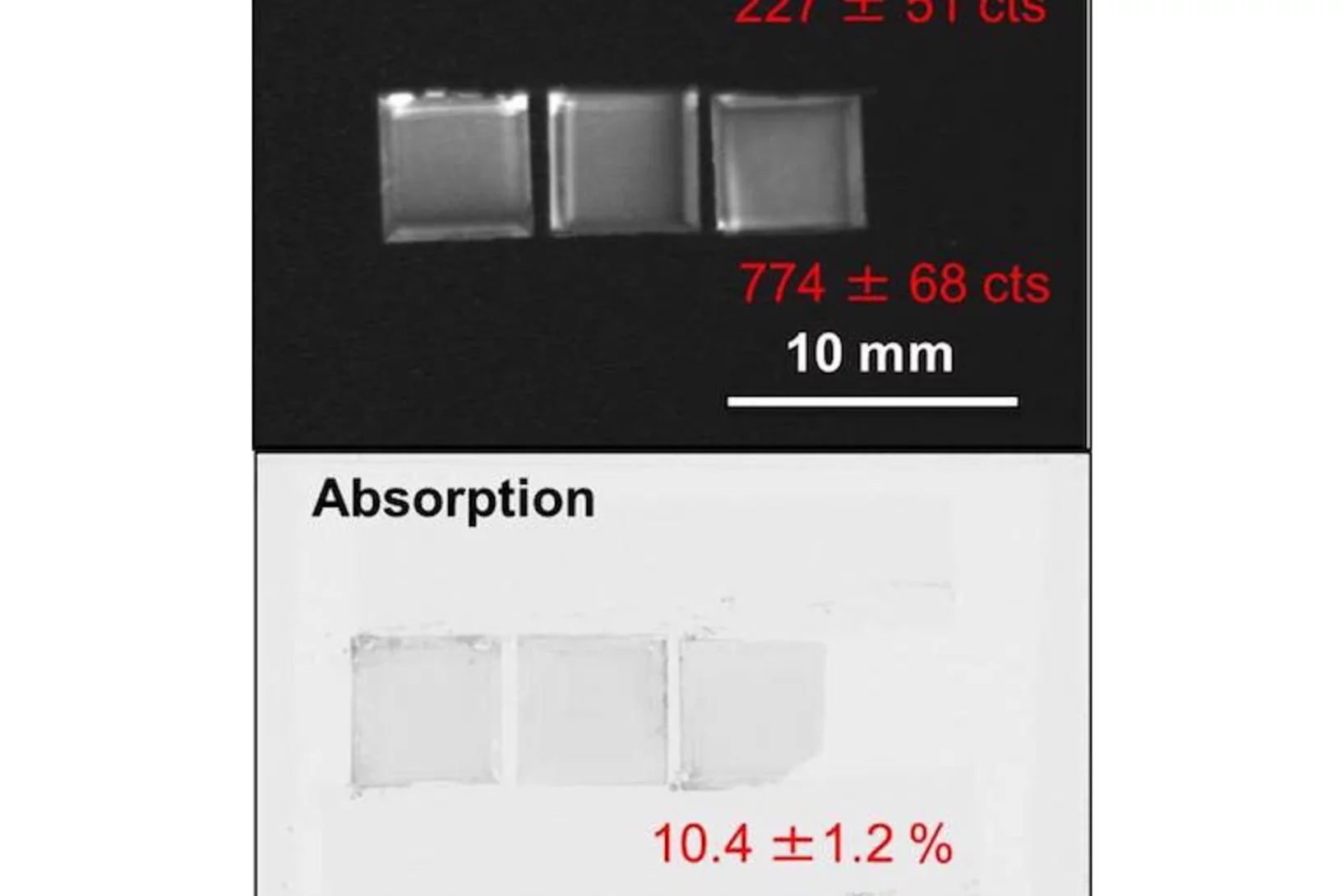
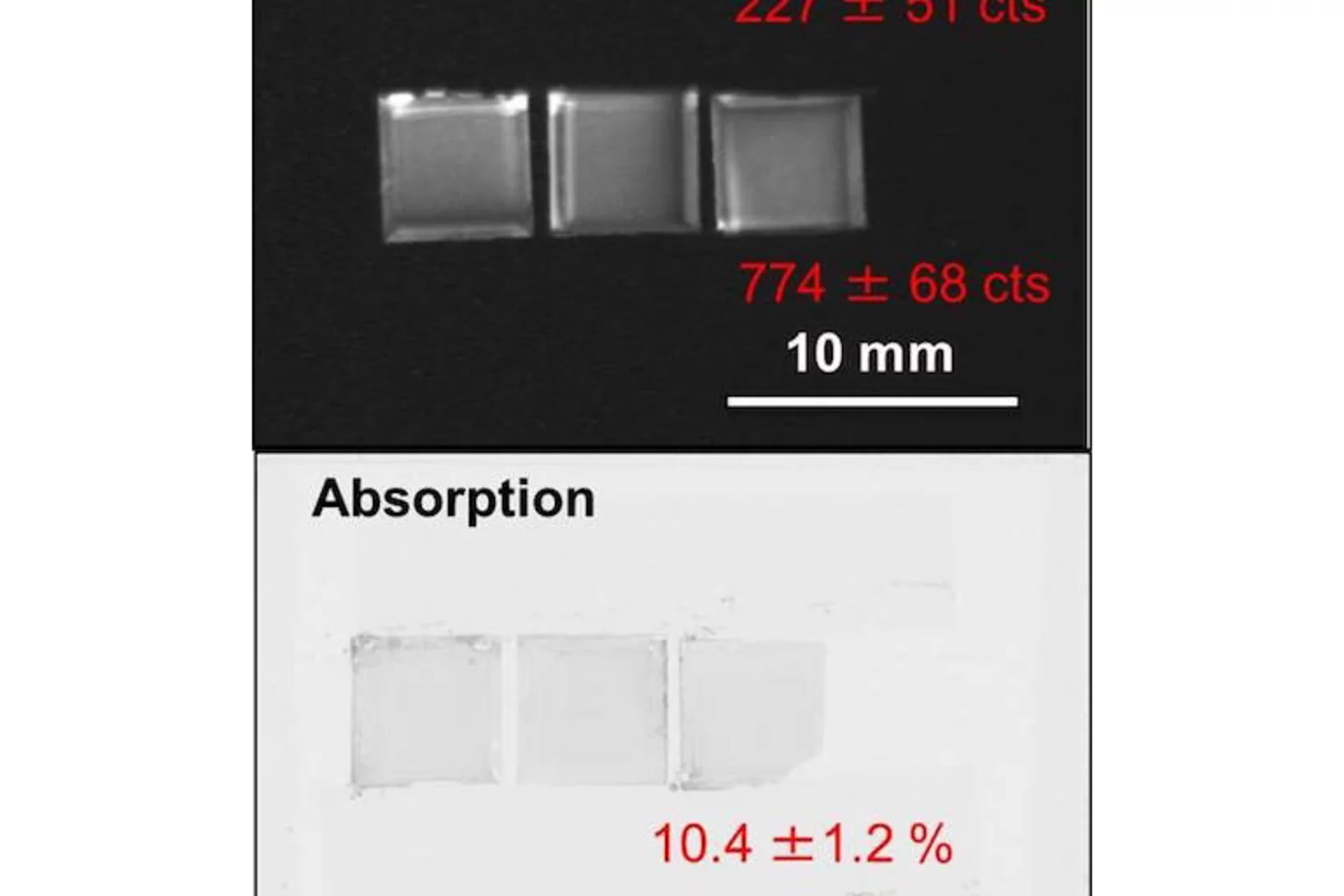
Isotopically-enriched gadolinium-157 oxysulfide scintillator screens for the high-resolution neutron imaging
High-resolution neutron imaging (Neutron Microscope project) requires highly efficient scintillator screens. Our aim is to achieve sub-5µm spatial resolution. Here, we demonstrate the feasibility of the production of isotopically-enriched gadolinium oxysulfide scintillator screens for the high spatial-resolution neutron imaging. Approximately 10 g of 157Gd2O2S:Tb was produced in the form of fine powder (the level of 157Gd enrichment above 88%).
Isotopically-enriched gadolinium-157 oxysulfide scintillator screens for the high-resolution neutron imaging
High-resolution neutron imaging (Neutron Microscope project) requires highly efficient scintillator screens. Our aim is to achieve sub-5µm spatial resolution. Here, we demonstrate the feasibility of the production of isotopically-enriched gadolinium oxysulfide scintillator screens for the high spatial-resolution neutron imaging. Approximately 10 g of 157Gd2O2S:Tb was produced in the form of fine powder (the level of 157Gd enrichment above 88%).
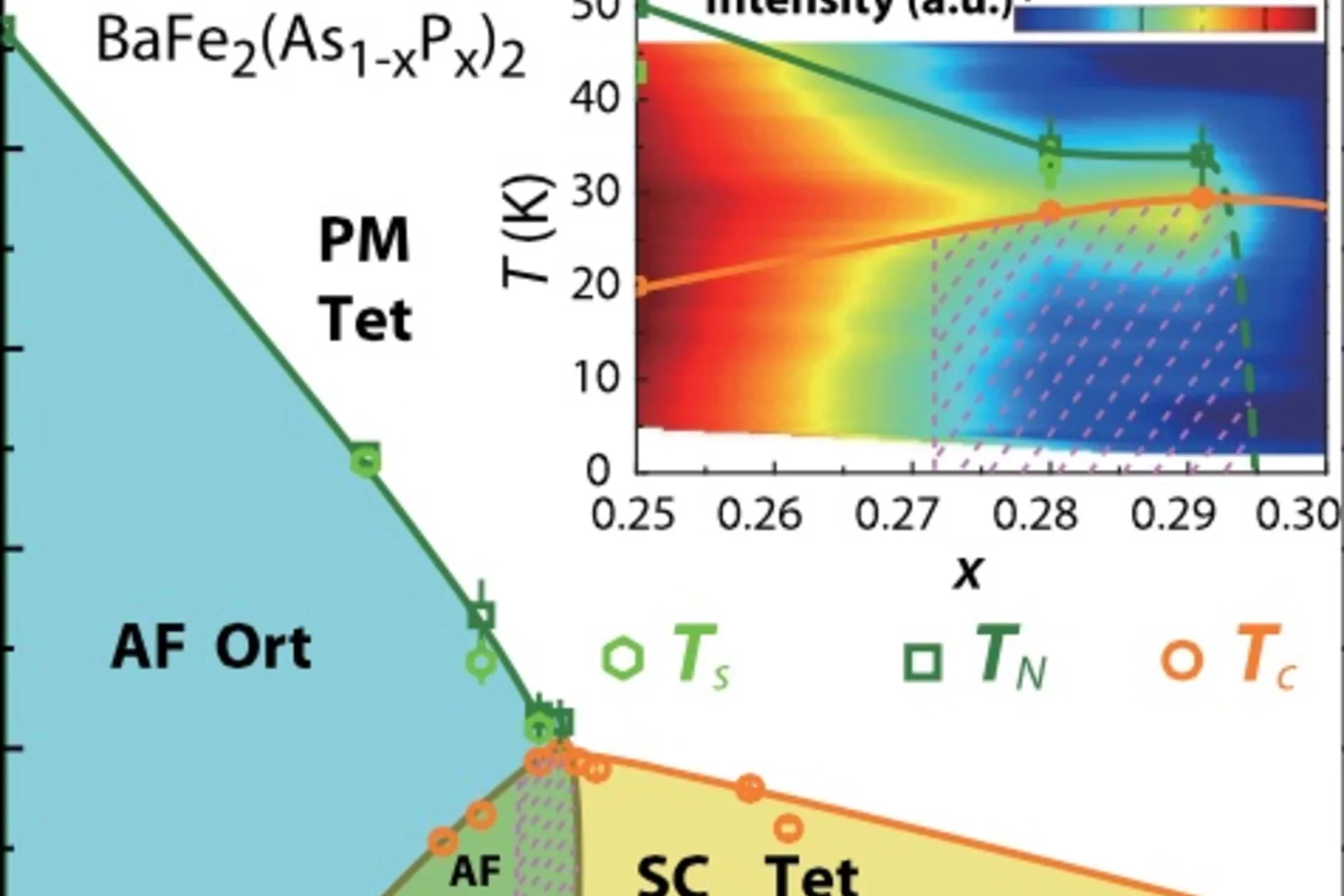
Structural and Magnetic Phase Transitions near Optimal Superconductivity in BaFe2(As1-xPx)2
We use nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR), high-resolution x-ray, and neutron scattering studies to study structural and magnetic phase transitions in phosphorus-doped BaFe2(As1-xPx)2. Previous transport, NMR, specific heat, and magnetic penetration depth measurements have provided compelling evidence for the presence of a quantum critical point (QCP) near optimal superconductivity at x=0.3.
Mass Density and Water Content of Saturated Never-Dried Calcium Silicate Hydrates
Calcium silicate hydrates (C-S-H) are the most abundant hydration products in ordinary Portland cement paste. Yet, despite the critical role they play in determining mechanical and transport properties, there is still a debate about their density and exact composition. Here, the site-specific mass density and composition of C-S-H in hydrated cement paste are determined with nanoscale resolution in a nondestructive approach.