Neutron scattering techniques are highly versatile and powerful tools for studying the structure and dynamics of condensed matter. A wide scope of problems, ranging from fundamental to solid state physics and chemistry, and from materials science to biology, medicine and environmental science, can be investigated with neutrons. In addition to scattering, non-diffractive methods like imaging techniques allows for non-destructive inspection of materials and components, providing information on their internal structure, composition, and integrity with growing relevance also for industrial applications.
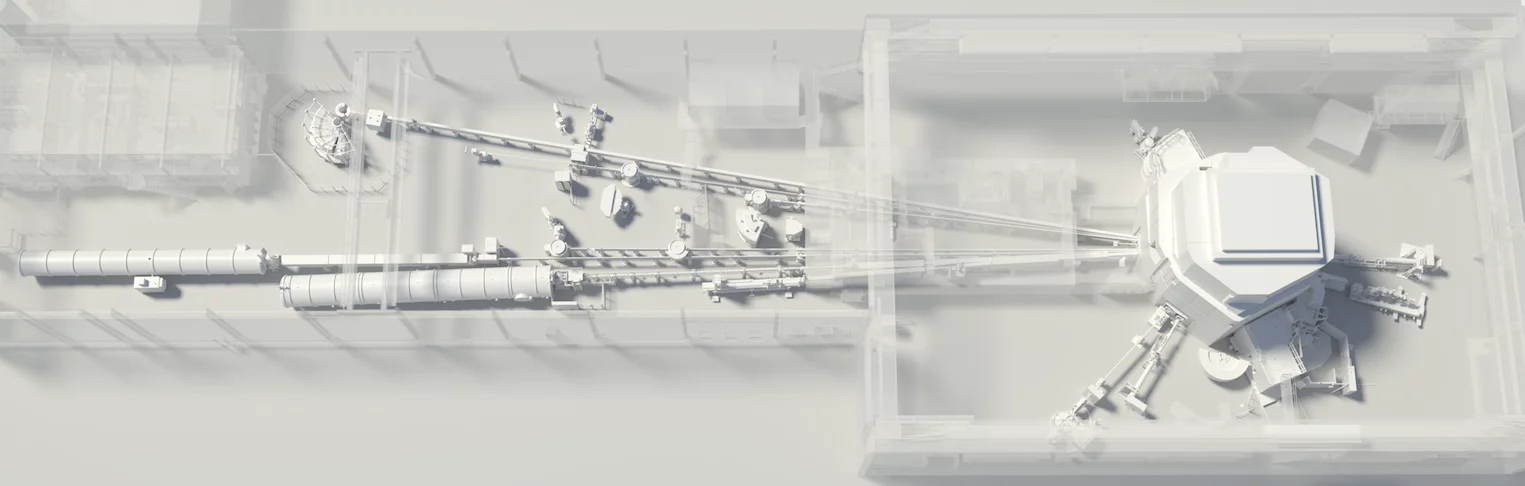
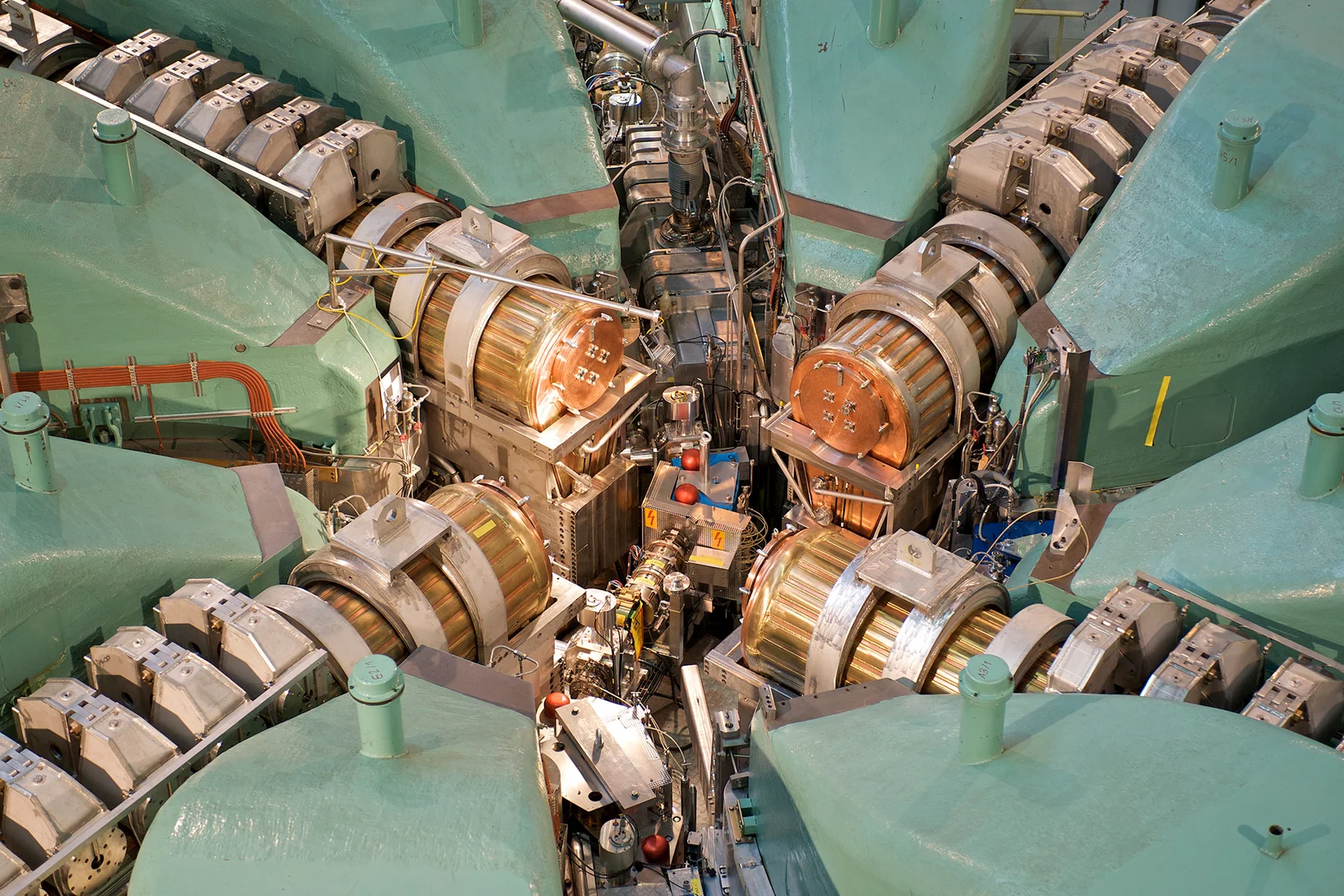
The spallation neutron source SINQ is a continuous source - the first and only one of its kind in the world - with a flux of about 1014 n/cm2/s. Beside thermal neutrons, a cold moderator of liquid deuterium (cold source) slows neutrons down and shifts their spectrum to lower energies. These neutrons have proved to be particularly valuable in materials research and in the investigation of biological substances.
SINQ operates as a user facility, meaning that scientists and research groups from around the world can apply for beamtime to conduct experiments using its various neutron instruments.
Latest News
The recent proposal deadline passed on 15 May 2025. The results of the evaluation have been published on 17 July.
The next call is planned for fall with a submission deadline on 15 January 2026.
Latest Scientific Highlights and News
Generating structured foam via flowing through a wire array
Efficient manufacturing methods could unlock foams with tailored, anisotropic properties. Conventional foam production methods rely on the self-arrangement of bubbles, typically leading to isotropic materials, or involve intricate additive layering processes. This study presents a simple, passive technique to modify the foam structure. A set of thin parallel wires ...
Hydration- and Temperature-Dependent Rotational Dynamics and Water Diffusion in Nanocellulose
Nanocellulose is a promising alternative to fossil-derived materials, but its development is hindered by a limited understanding of cellulose–water interactions. Herein, quasielastic neutron scattering (QENS) is used to investigate how hydration and temperature affect the localized rotations in cellulose nanocrystals (CNC) and the diffusion of mobile water. QENS reveals ...
Bright Monocompound Metal Halide Scintillator for Fast Neutron Radiography
Fast neutron imaging is a promising technique for visualizing objects containing dense, mixed light-and-heavy-elements materials, such as combustion engines, nuclear fuel assemblies, and fossils, where X-rays and thermal neutrons are ineffectiv. However, the limited efficiency of current detection technologies hinders their widespread adoption. Recoil proton detection ...
User Contacts
Office hours
Monday through Friday from 8:00-11:30 and 12:30-17:00
otherwise please contact us per email
User Office
Provides all information about user access to the PSI Large Research Facilities
DUO Login
Direct link to the Digital User Office