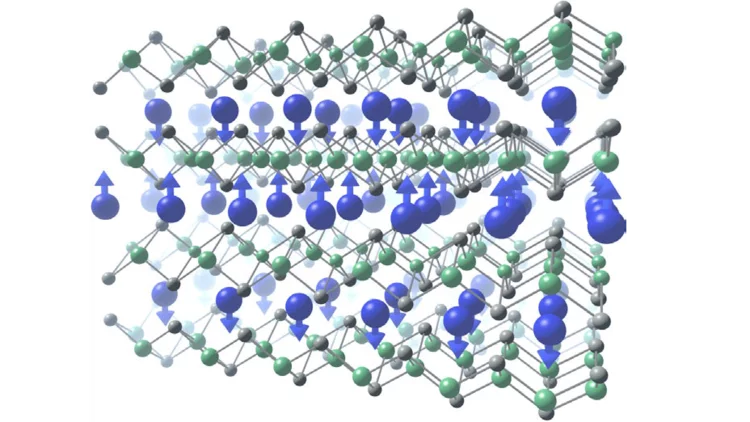
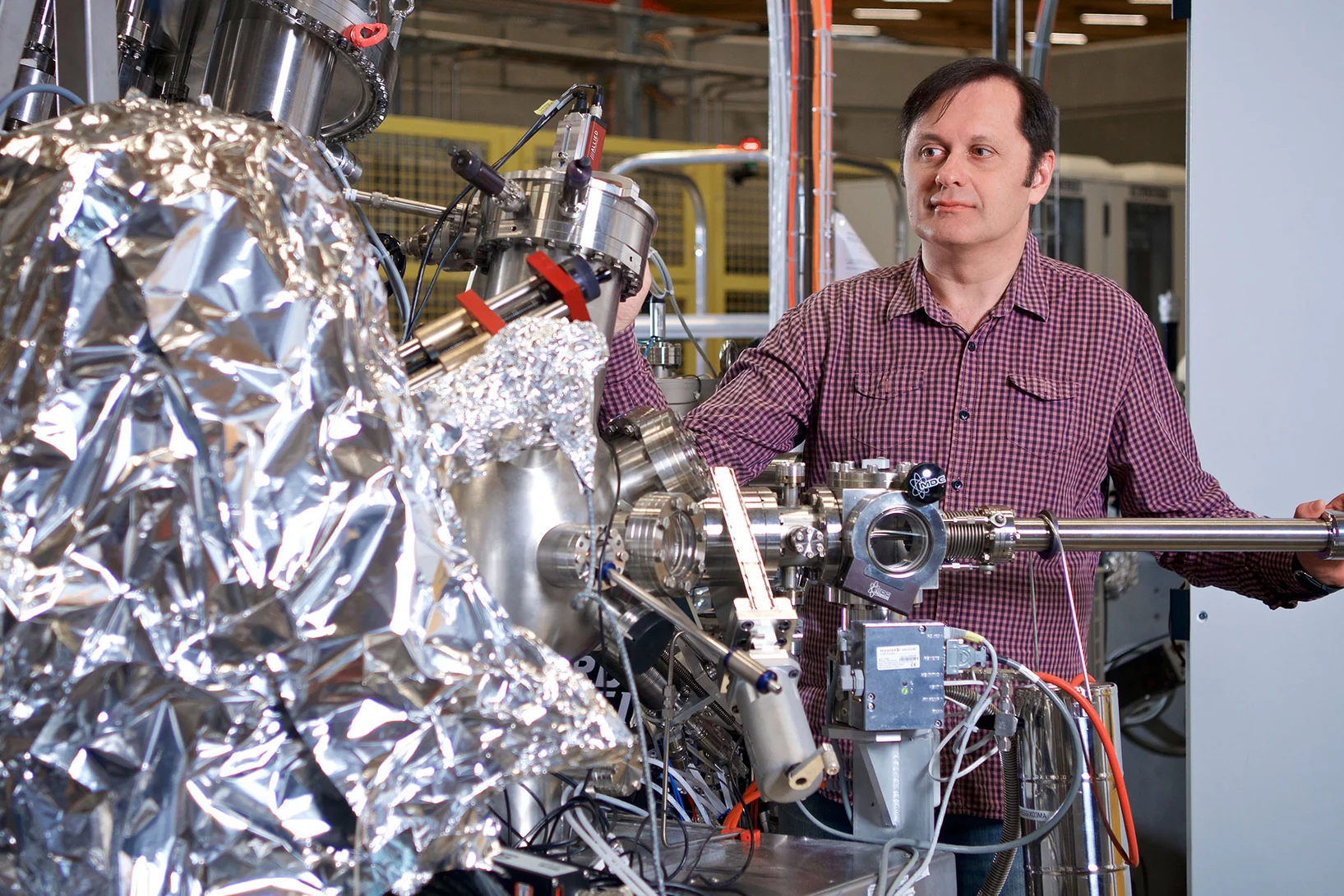
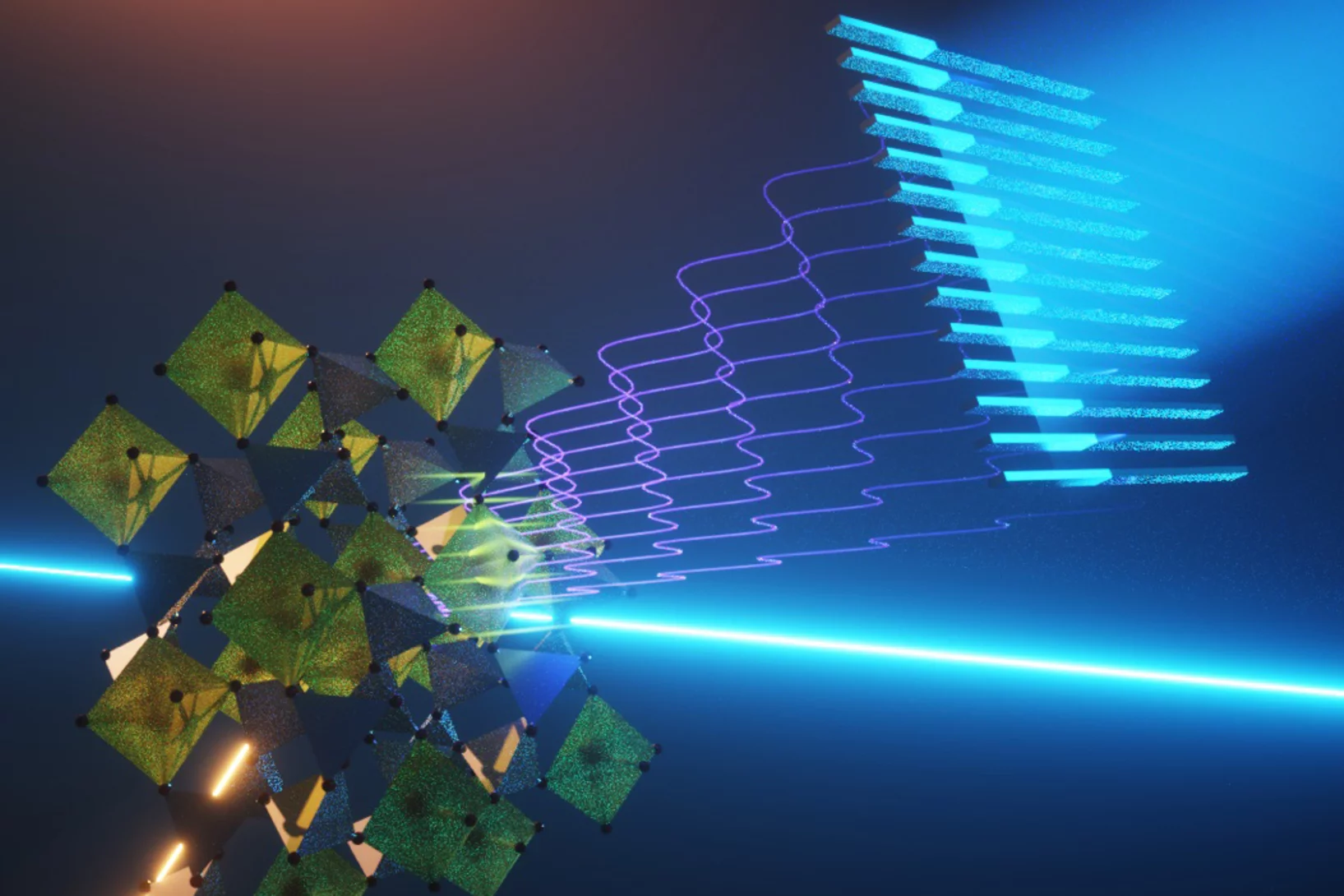
Strong modulation of carrier effective mass in WTe2 via coherent lattice manipulation
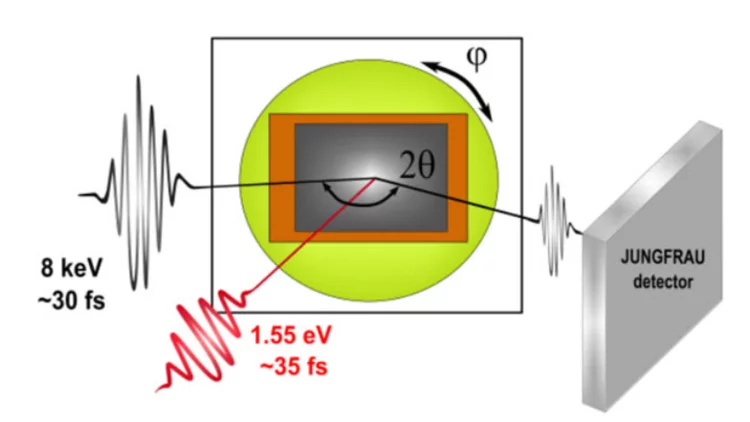
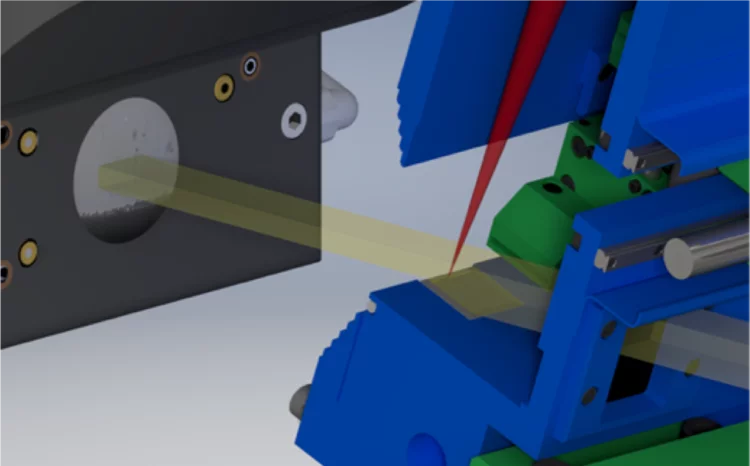
Schematic ultrafast surface diffraction setup used for monitoring the crystal lattice in multiple directions.
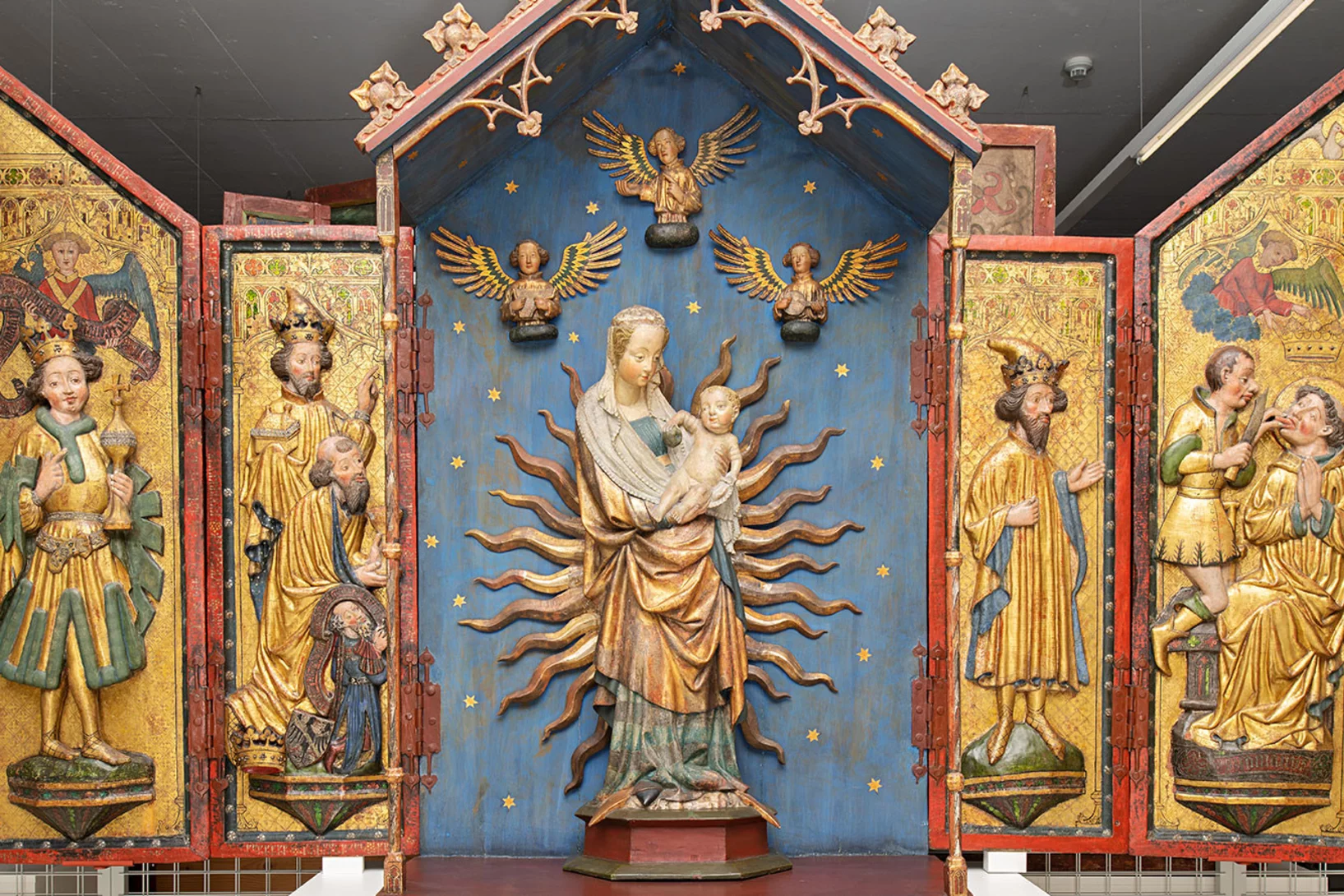
Nanomaterial from the Middle Ages
Unlocking the secrets of Zwischgold at PSI.
In situ alloying during additive manufacturing
In situ alloying is an effective method to engineer microstructures of additively manufactured Ti6Al4V3Fe alloys.
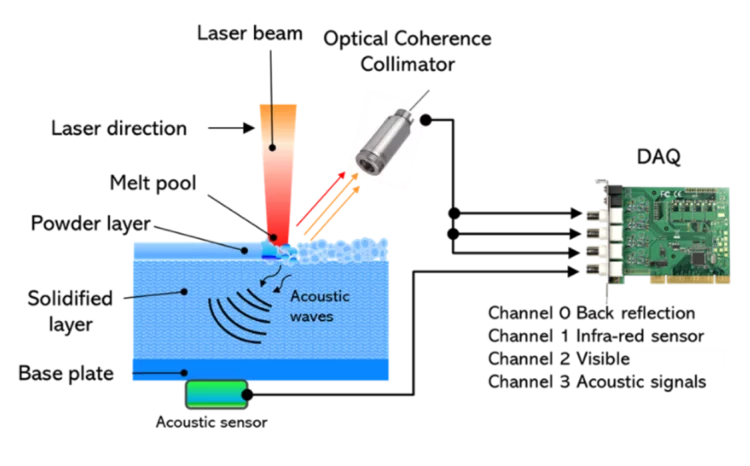
Deep learning-based monitoring of laser powder bed fusion processes
We present a novel monitoring strategy for 3D print processes that consists of developing and training a hybrid machine learning model that can classify regimes across different time scales based on heterogeneous sensing data.
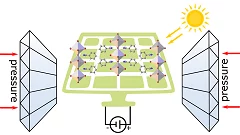
Mechanochromism of layered perovskites
The mechanochromism of hybrid 2D perovskites is probed at pressures compatible with practical applications
New SwissFEL soft X-ray endstation welcomes first users
Maloja is go. First user experiments mark a double first, not only for the Maloja endstation but also for the second beamline of SwissFEL, Athos.
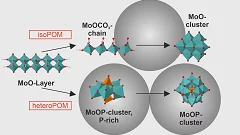
Direct mechanochemical synthesis of polyoxometalates
Polyoxomolybdates have been directly synthesized from basic reagents in a mechanochemical one-pot reaction.
Light amplification accelerates chemical reactions in aerosols
Aerosols in the atmosphere react to incident sunlight. This light is amplified in the interior of the aerosol droplets and particles, accelerating reactions. ETH and PSI researchers have now been able to demonstrate and quantify this effect and recommend factoring it into future climate models.
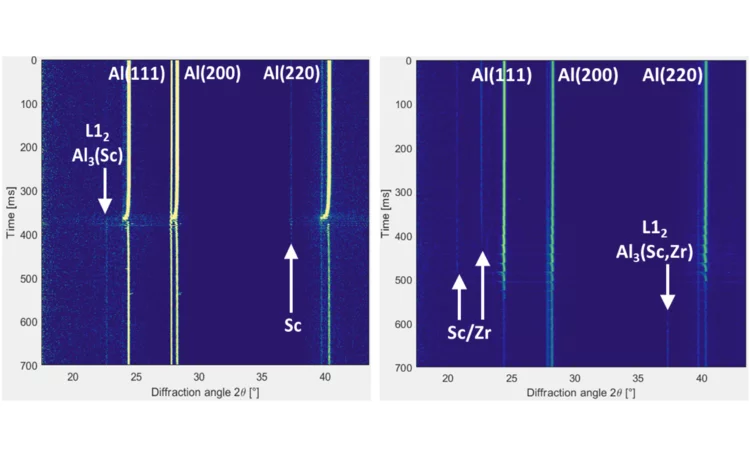
Thermal and phase evolution during laser powder bed fusion of Al-Sc-Zr elemental powder blends
The reaction of elemental scandium and zirconium powders with liquid aluminum is observed directly via operando X-ray diffraction during laser 3D printing. This work demonstrates that elemental blends can be used to create fine-grained crack-free Al-alloys and highlights the importance of feature size.
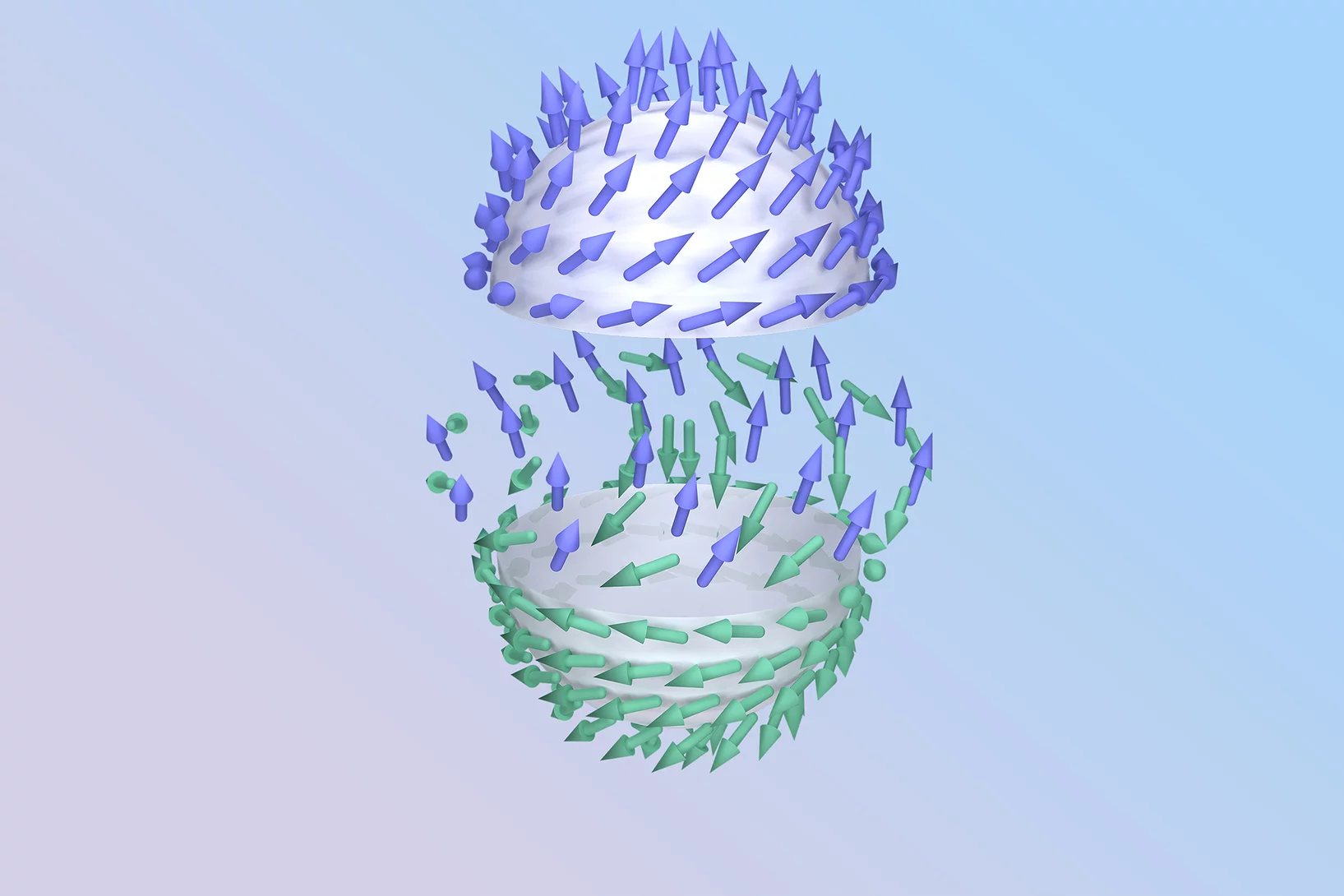
Into the fourth dimension: time-resolved soft X-ray laminography
Combining time-resolved soft X-ray STXM imaging with magnetic laminography, researchers were able to investigate magnetization dynamics in a ferromagnetic microstructure resolved in all three spatial dimensions and in time. Thanks to the possibility of freely selecting the frequency of the excitation applied to the magnetic element, this technique opens the possibility to investigate resonant magneto-dynamical processes, such as e.g. magnetic vortex core gyration and switching, and spinwave emission.
A look into the magnetic future
PSI researchers are the first to observe a specific behaviour of magnetic ice.
Hercules School 2022
PSI hosted again the Hercules School in March 2022. We had the pleasure to welcome 20 international PhD students, PostDocs and scientists to demonstrate our state-of-the-art techniques and methodologies at our large scale facilities, the Swiss Light Source (SLS), the Swiss Spallation Neutron Source (SINQ) and our free electron laser SwissFEL.
Exchange scaling of ultrafast angular momentum transfer in 4f antiferromagnets
A novel approach to controlling the speed of magnetic processes has been found through resonant magnetic scattering in an antiferromagnetic Lanthanide intermetallics.
Direct observation of crack formation mechanisms with operando Laser Powder Bed Fusion X-ray radiography
Operando high-speed X-ray radiography experiments reveal the cracking mechanism during 3D laser printing of a Ni superalloy.
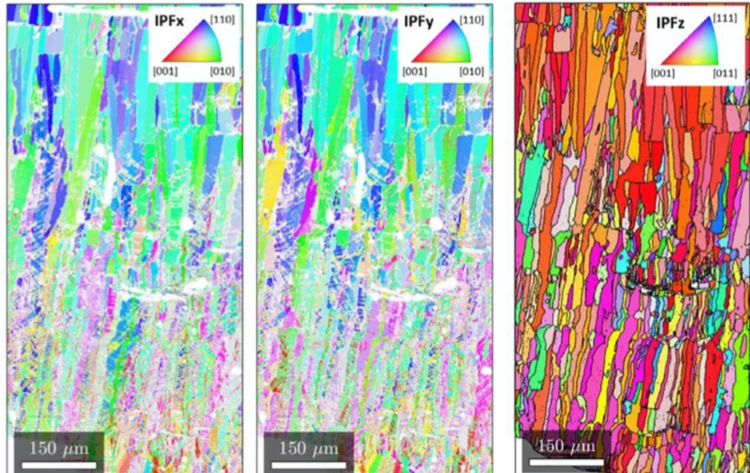
Understanding variant selection and texture in additively manufactured red-gold alloys
Synchrotron X-ray diffraction experiments reveal the presence of a non- negligible amount of tetragonal phase in 3D printed red-gold samples.
Semiconductors reach the quantum world
Boosted with superconductivity: Semiconductor technology can get a new twist by exploiting quantum effects in superconductors.
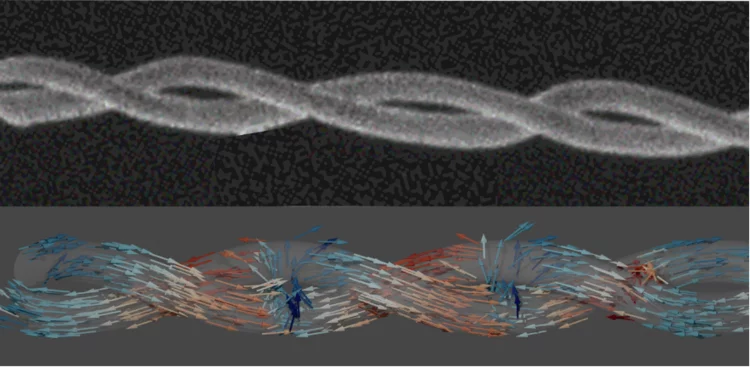
3D printed nanomagnets unveil a world of patterns in the magnetic field
Scientists have used state-of-the-art 3D printing and microscopy to provide a new glimpse of what happens when taking magnets to three-dimensions on the nanoscale – 1000 times smaller than a human hair.
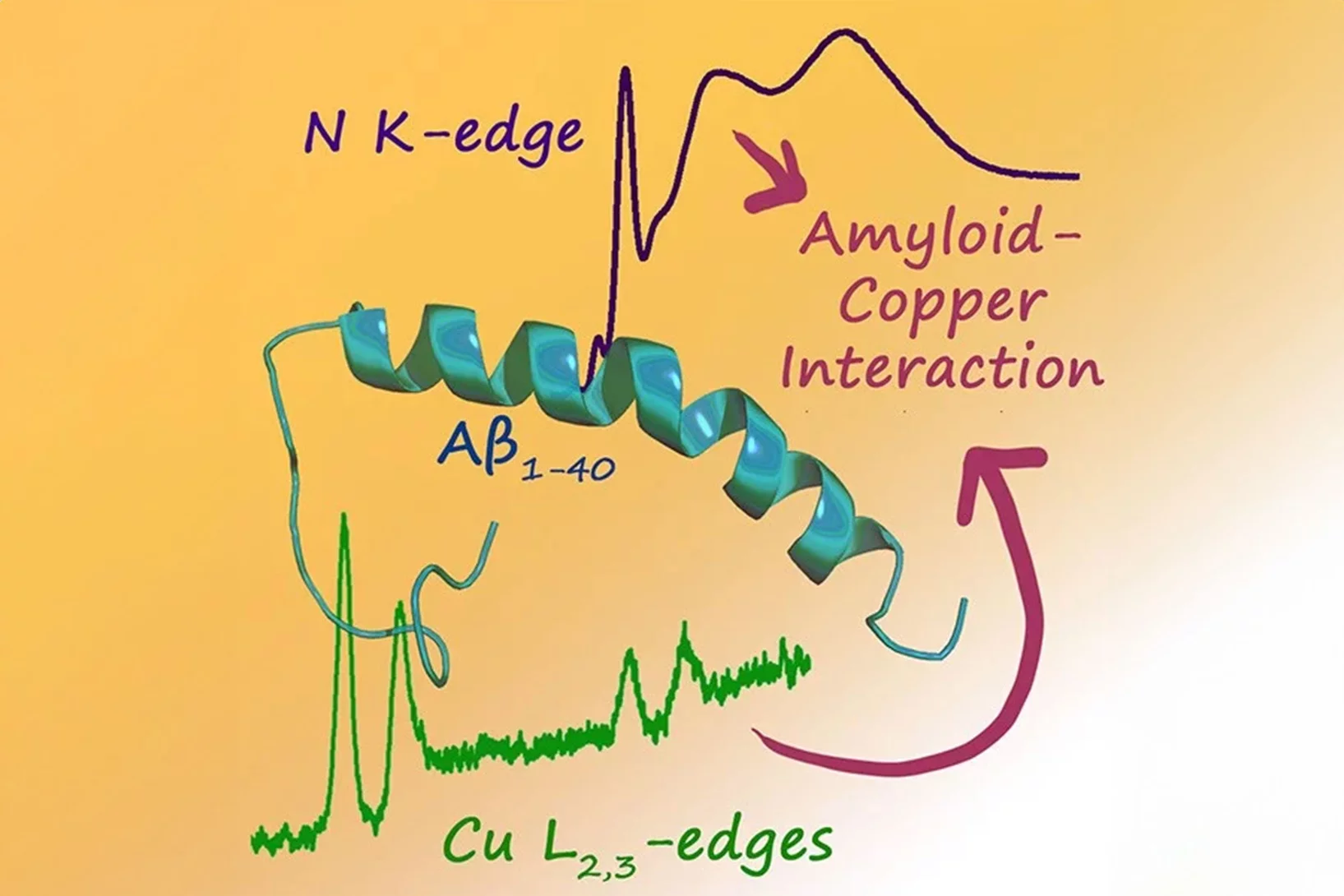
Fingerprint of Copper in Peptides Linked to Alzheimer's Disease
In an interdisciplinary project, researchers from the Laboratory of Nanoscale Biology in BIO and the Laboratory for Condensed Matter in PSD have revealed the reaction between the nitrogen atoms of the amyloid-beta peptide and copper/zinc ions by using soft X-ray absorption spectroscopy.
Ground-breaking technology development recognised
PSI researchers win the international Innovation Award on Synchrotron Radiation for 3D mapping of nanoscopic details in macroscopic specimens, such as bone.
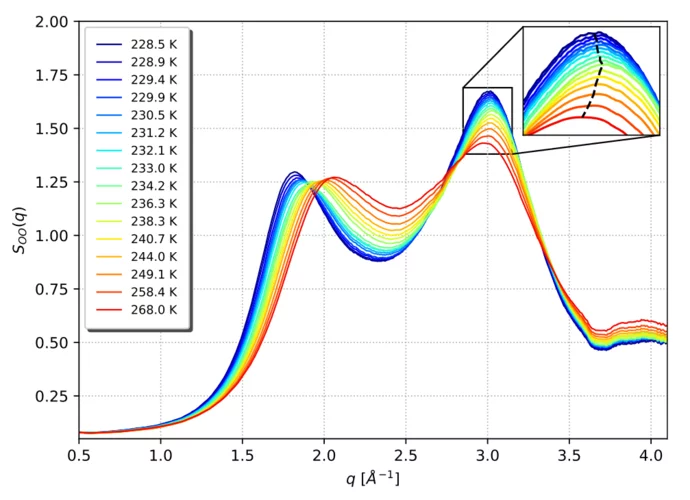
Anomalous temperature dependence of the experimental x-ray structure factor of supercooled water
Supercooled water scattering signals show an anolmalous structure factor temperature dependence suggesting decreasing density at lowering temperatures below 236 K (-37°C).
Ultrafast electron localization
This experiment performed at SwissFEL shows how fast we can localize electrons out of an electron gas into correlated, well localized states of a material. It is based on a combined ultrafast x-ray absorption and diffraction experiment on an intermetallic system.
Exploring the practical benefits of exotic materials
Niels Schröter receives an award from the Swiss Physical Society (SPG).
Creating novel quantum phases via the heterostructure engineering
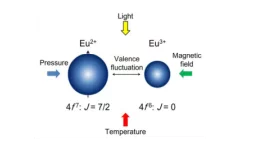
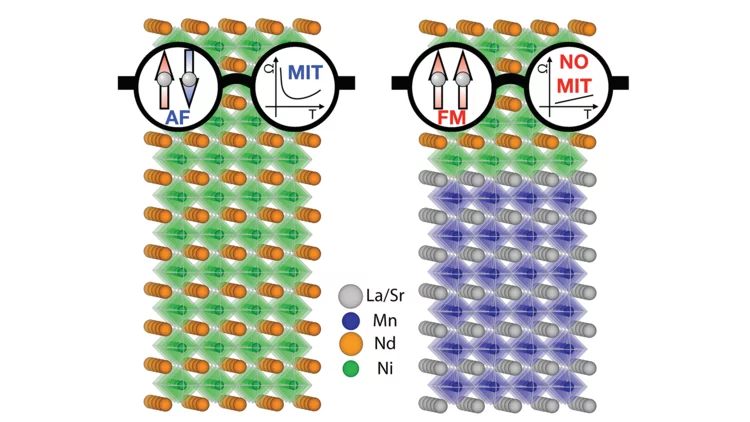
Within this synergetic collaboration, PSI scientists have investigated the correlation between magnetic and electronic ordering in NdNiO3 by tuning its properties through proximity to a ferromagnetic manganite layer. The main outcome is that the stray magnetic field from the manganite layer causes a novel ferromagnetic-metallic (FM-M) phase in NNO. This work demonstrates the utilization of heterostructure engineering for creating novel quantum phases.
Understanding the physics in new metals
Together with international colleagues, PSI researchers have now been able to make correlated metals more readily usable for applications in superconductivity, data processing, and quantum computers.
Magnetic nanoworld
At PSI, researchers come across exotic phenomena such as frustrated magnets and nano-vortices, which may one day enable better data storage.
Uniquely sharp X-ray view
A new PSI method allows quantum-physical research on materials with the aid of X-ray lasers.
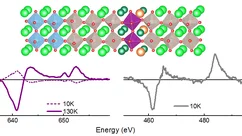
Hindering the magnetic dead layer in manganites
The authors demonstrate the stability of ferromagnetic order of one unit cell thick optimally doped manganite (La0.7Ba0.3MnO3, LBMO) epitaxially grown between two layers of SrRuO3 (SRO). LBMO shows ferromagnetism even above SRO Tc. Density Functional Theory calculations help understand the reasons behind this interesting result.
HERCULES SCHOOL 2021 AT PSI
During the week of March 15 – 19, we had the pleasure to welcome 20 international PhD students, PostDocs and assistant professors at PSI, taking part in the first virtual HERCULES SCHOOL on Neutrons & Synchrotron Radiation.
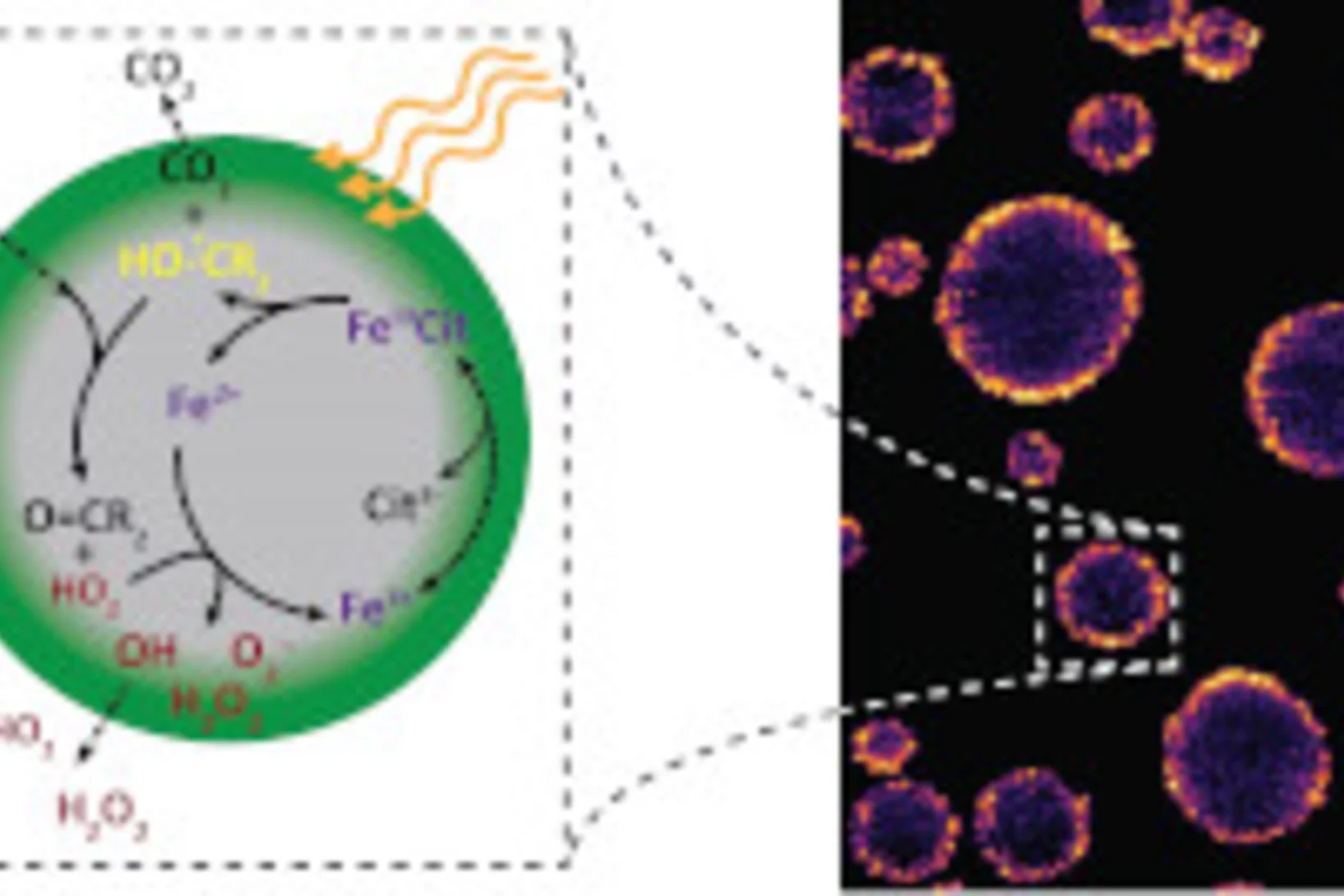
Looking inside airborne particles for the chemistry responsible for their adverse health effects.
Chemical changes inside of breathable airborne particles can cause reactive oxygen species (ROS) and carbon centered radicals (CCRs) to form, which are harmful to our bodies and induce oxidative stress in lungs. Using X-ray spectromicroscopy at the PolLux beamline and mimicking the environmental and sunlit conditions aerosol particles experience in the atmosphere near the Earth Surface, it was recently found that highly viscous organic particles with low water content can attain high concentrations of ROS and CCRs that persist over long times. Natural particles like these will occur in ambient humidity below 60% and effectively trap ROS and CCRs inside that react when exposed to light.
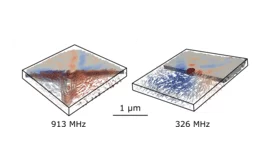
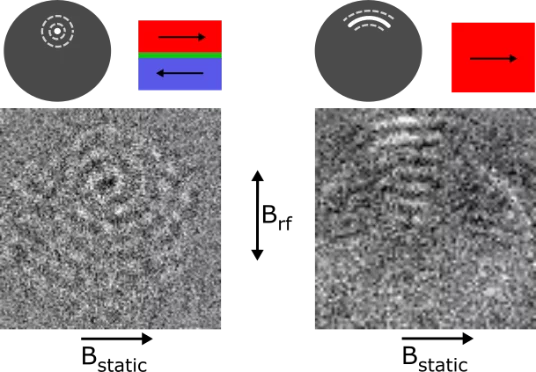
Spin-wave emission from vortex cores under static magnetic bias fields
Employing time-resolved STXM imaging, researchers investigated the emission of spin waves from a magnetic vortex core. By applying static magnetic fields, the control of both the shape of the vortex core and of the spatial profile of the emitted spin waves could be demonstrated, allowing for the fabrication of field-tunable spin wave focusing elements.