Tailoring Novel Superconductivity
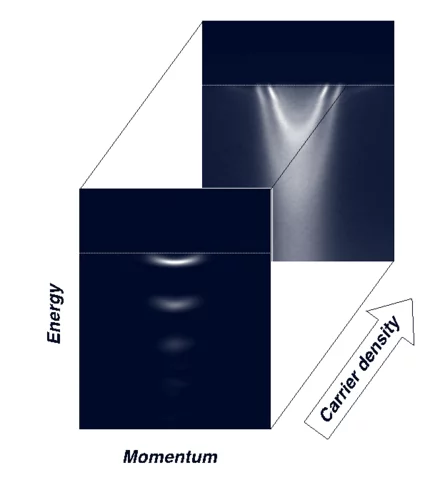
The Angle Resolved Photoemission Spectroscopy (ARPES) measurements performed on 2DEL at STO surface revealed that, at low carrier density, electrons are always accompanied by a quantized dynamic lattice deformation. Together with the electron, these phonon-cloud formed a new composite quasiparticle called Fröhlich polaron.
New particle could form the basis of energy-saving electronics
The Weyl fermion, just discovered in the past year, moves through materials practically without resistance. Now researchers are showing how it could be put to use in electronic components.
Slowed down current could point the way to energy-saving computers
Computers and other electronic devices account for a substantial portion of worldwide energy use. With today’s technologies, it is not possible to reduce this energy consumption significantly any further; chips in the energy-saving electronics of the future will hence have to be made from novel materials. Researchers at the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI have now found important clues in the search for such materials.
Observation of Fermi-Arc Spin Texture in TaAs
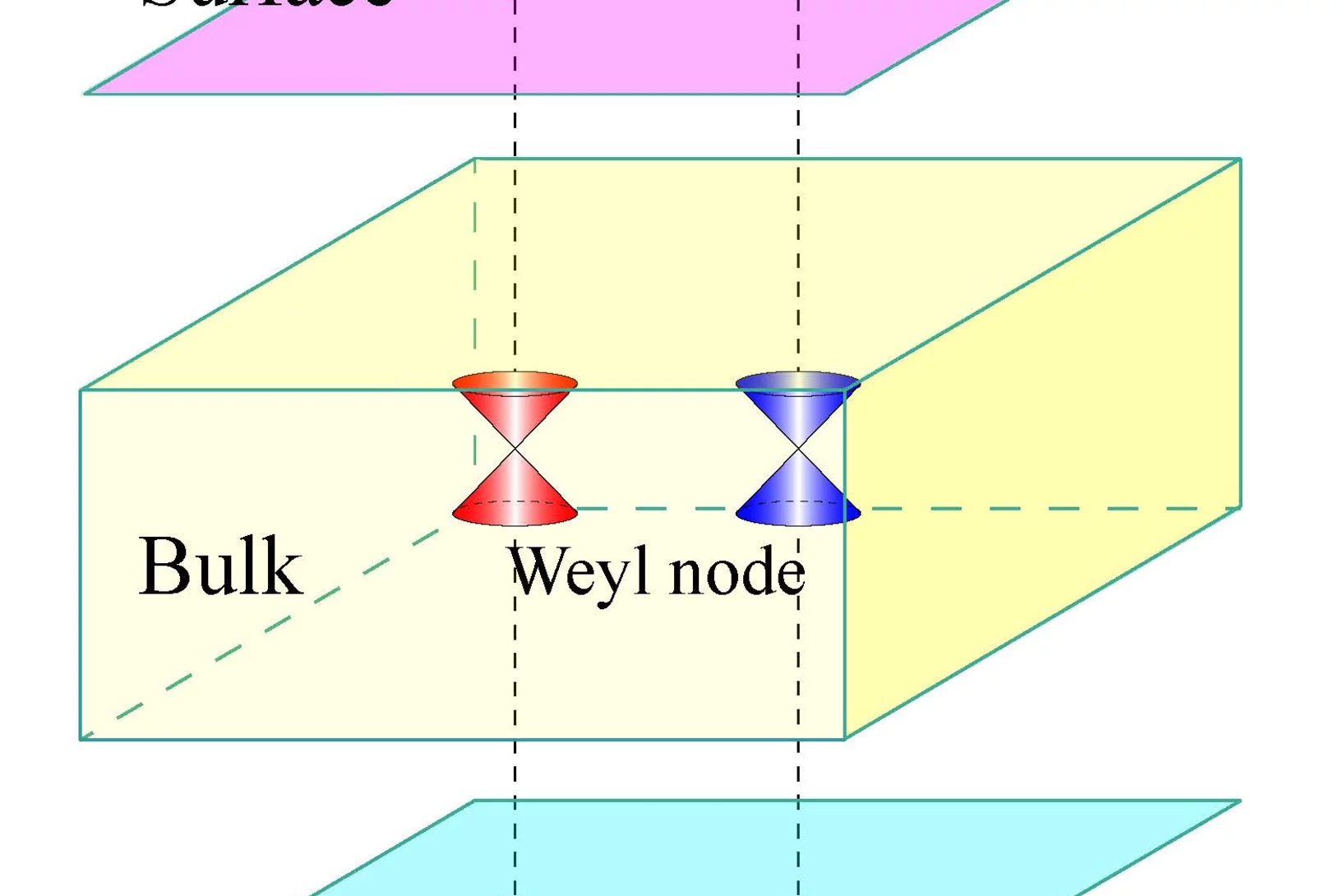
The study of nontrivial topological semimetals (TSM) is an emerging subject, providing a new frontier in topological aspects beyond insulators. Here, we have investigated the spin texture of surface Fermi arcs in the recently discovered Weyl semimetal TaAs using spin- and angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy. The experimental results demonstrate that the Fermi arcs are spin polarized. The measured spin texture fulfills the requirement of mirror and time-reversal symmetries and is well reproduced by our first-principles calculations, which gives strong evidence for the topologically nontrivial Weyl semimetal state in TaAs. The consistency between the experimental and calculated results further confirms the distribution of chirality of the Weyl nodes determined by first principles calculations.
Electron’s cousin discovered after eighty-six-year search
In a series of experiments at the Swiss Light Source SLS, physicists from the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI have discovered a particle, the existence of which was predicted eighty-six years ago. It is a member of the particle family that also includes the electron, the carrier of electrical currents. The particle now discovered is massless and can exist only within a special class of materials known as Weyl semi-metals.
Fermi states and anisotropy of Brillouin zone scattering in the decagonal Al–Ni–Co quasicrystal
Quasicrystals (QCs) are intermetallic alloys where excellent long-range order coexists with lack of translational symmetry in one or more dimensions. These materials have a high potential in application as a material for a solar cells, hydrogen storage applications, heat insulating layers, and others.
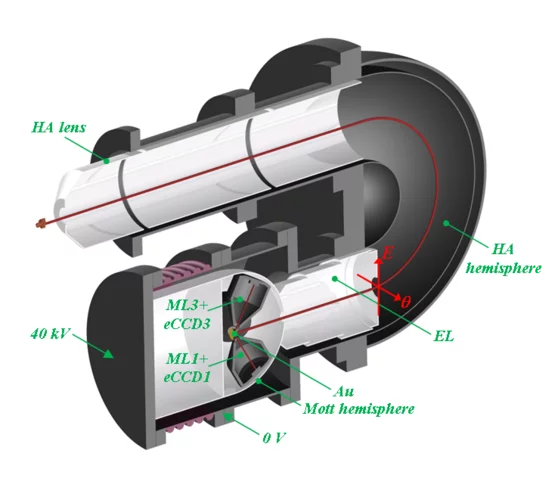
Concept of a multichannel spin-resolving electron analyzer based on Mott scattering
The spin of electron plays a crucial role in many physical phenomena, ranging from the obvious example of magnetism, via novel materials for spintronics applications, to high-temperature superconductivity. Spin- and angle-resolved photoelectron spectroscopy (SARPES) gives the most direct access to the spin aspects of the electronic structure, but the one-channel detection principle of all presently available SARPES spectrometers severely limits their efficiency. A team of Swiss and Russian scientists has developed a revolutionary concept of a multichannel electron spin detector based on Mott scattering as the spin selective process and imaging-type electron optics.
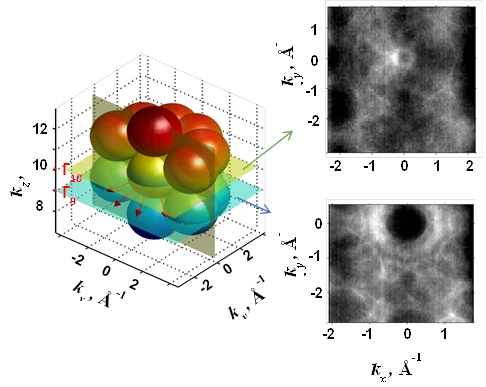
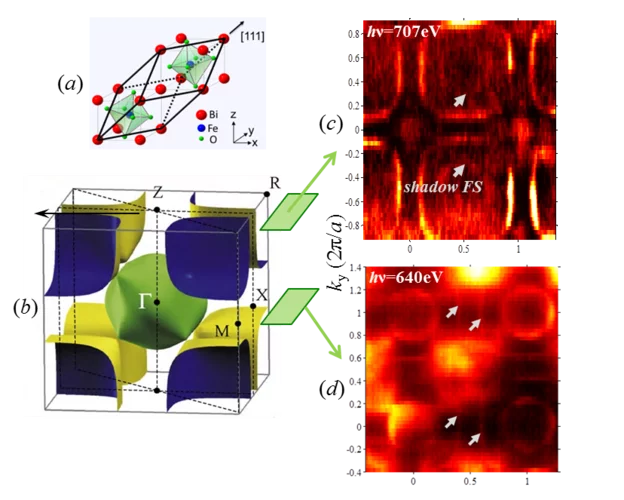
Fermi Surface of Three-Dimensional La1−xSrxMnO3 Explored by Soft-X-Ray ARPES: Rhombohedral Lattice Distortion and its Effect on Magnetoresistance
A research team led by scientists from the Swiss Light Source has for the first time established three-dimensional (3D) electronic structure of the perovskite compound La1−xSrxMnO3 connected with its colossal magnetoresistance. Instrumental for this study has been the use of the new experimental technique of soft-x-ray ARPES, available at the ADRESS beamline, with its intrinsically sharp definition of 3D electron momentum.