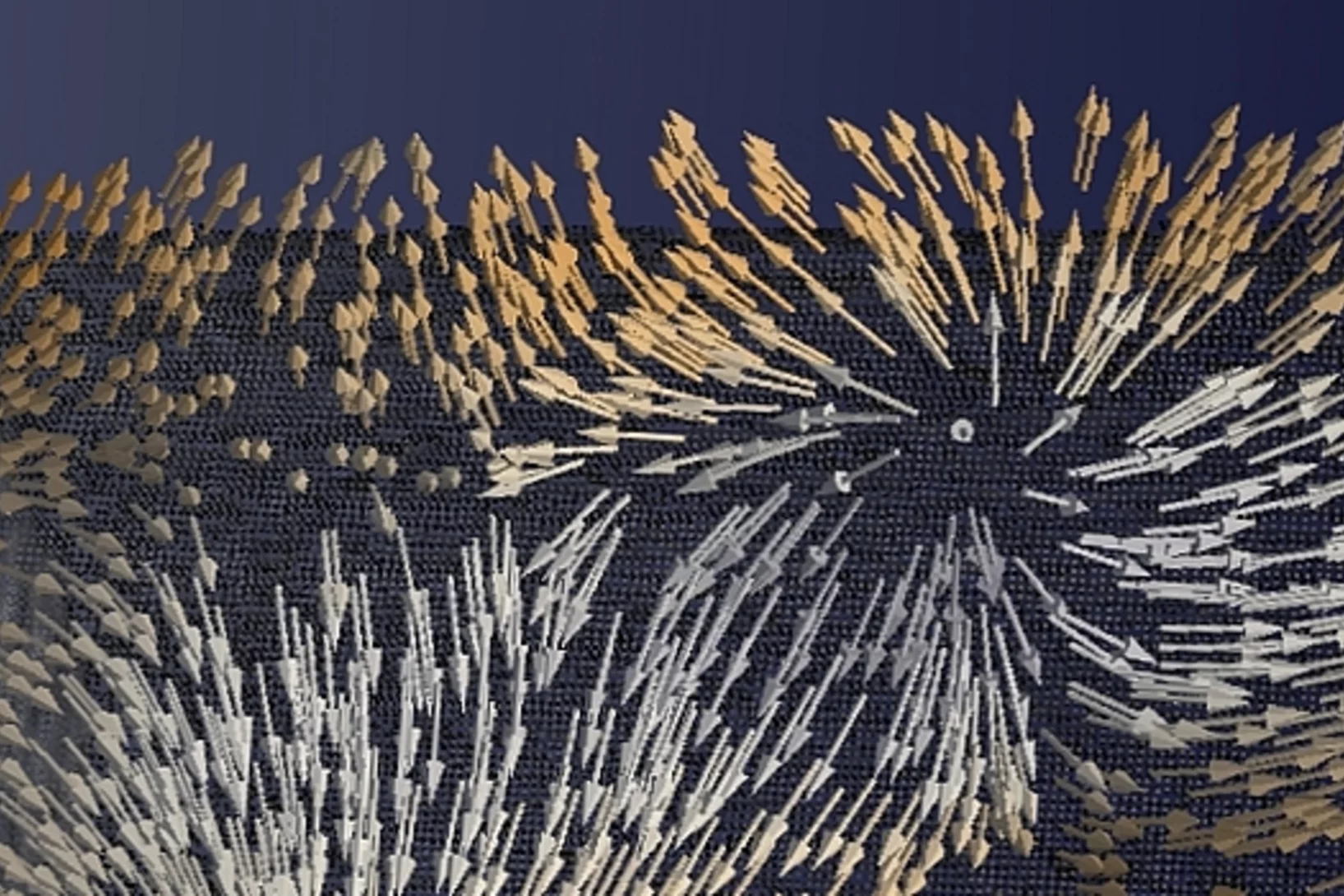
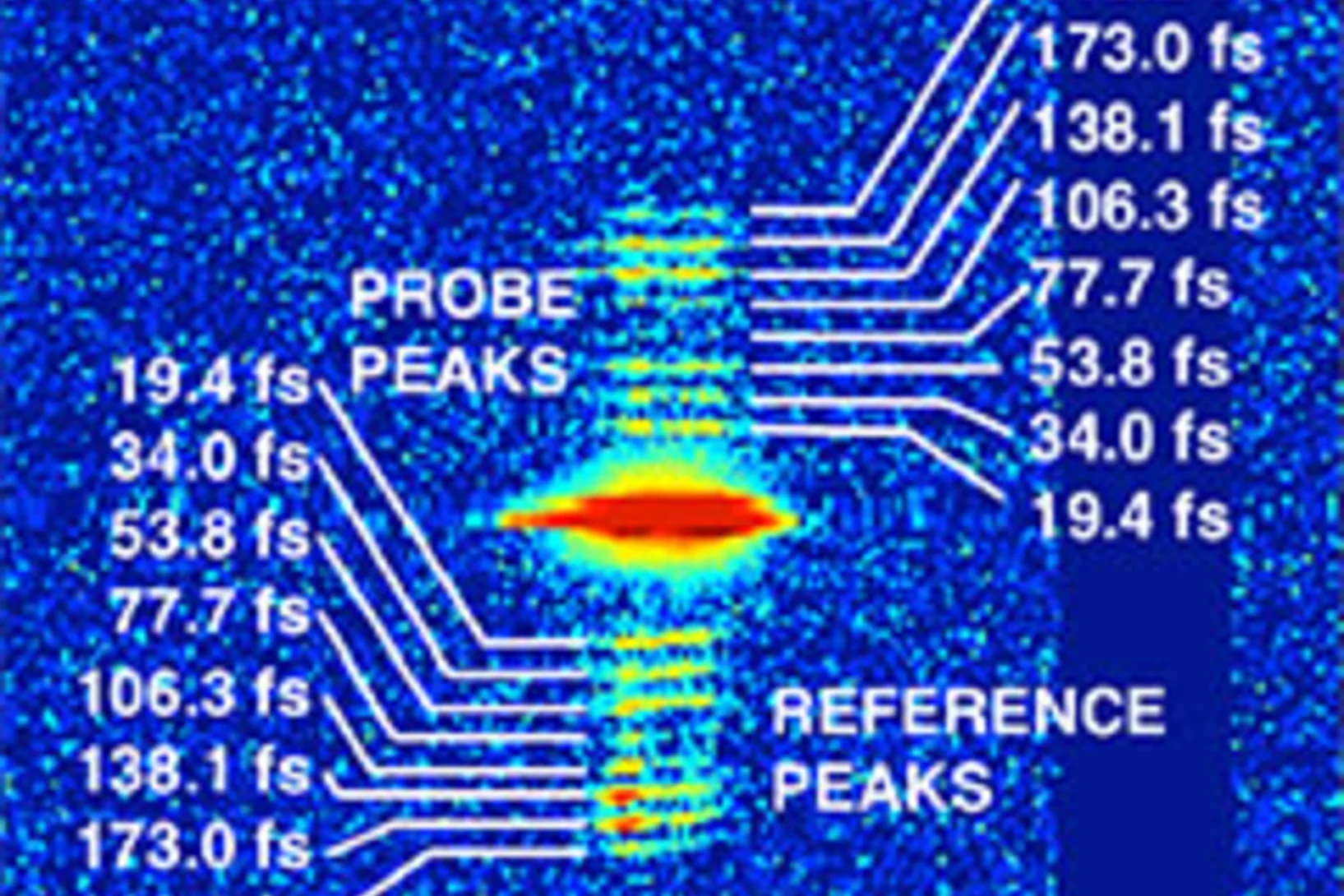
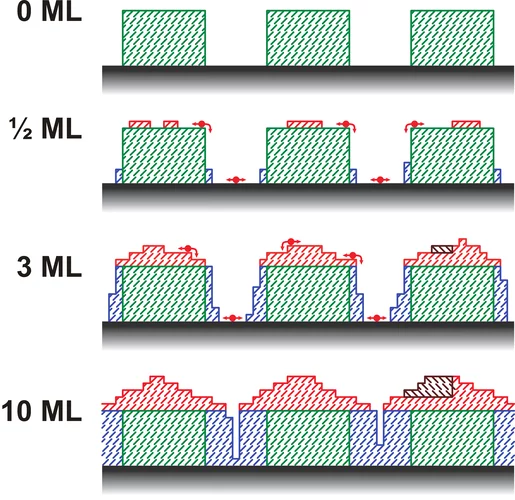
Demonstration of femtosecond X-ray pump X-ray probe diffraction on protein crystals
Our experiments, published in the September issue of Structural Dynamics, demonstrate the feasibility of time-resolved pump-multiprobe X-ray diffraction experiments on protein crystals using a split-and-delay setup which was temporarily installed at the LCLS X-ray Free Electron Laser.
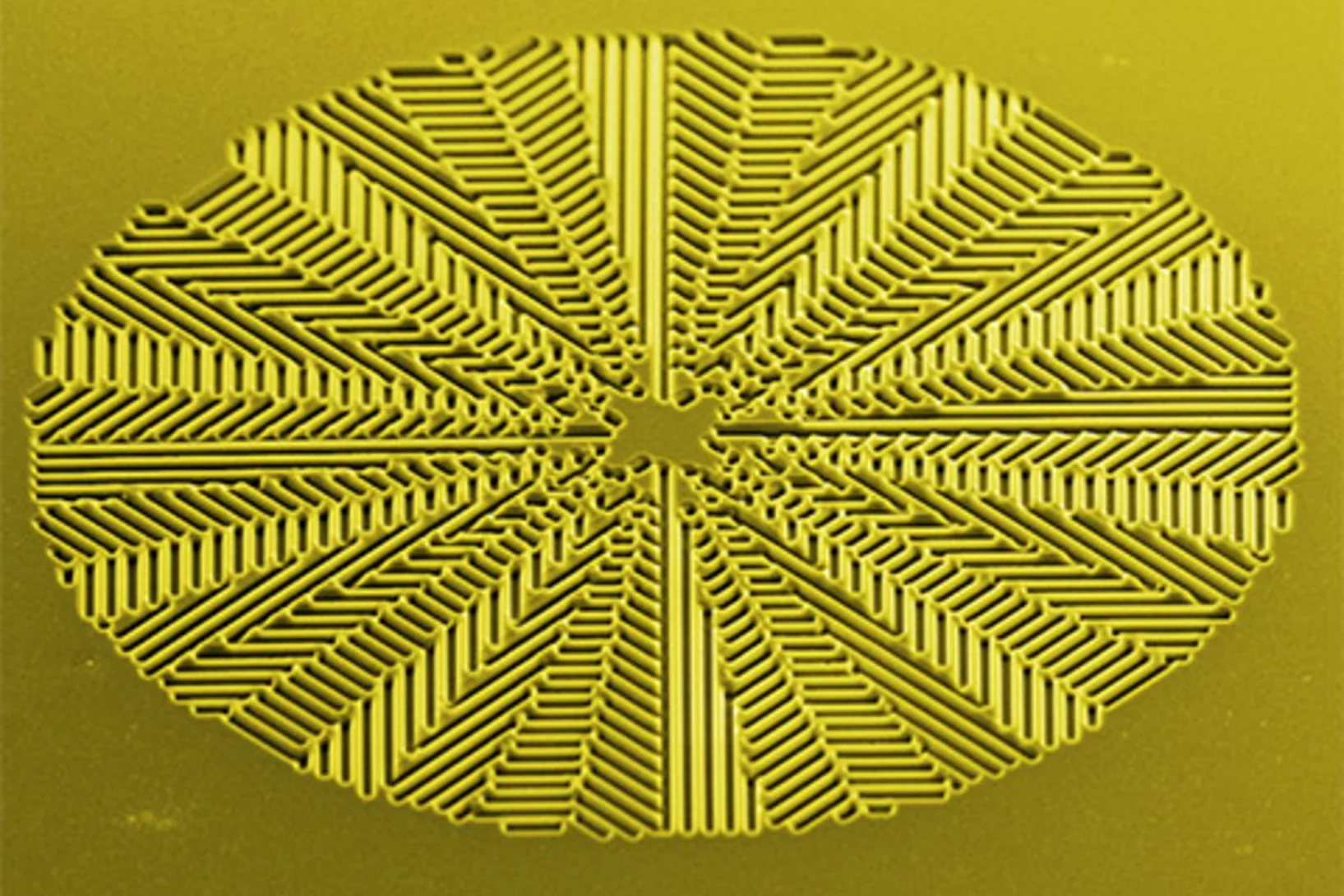
Diamond: a gem for micro-optics
Our image of a diamond structure was published on the cover page of the September 2018 issue of the journal "Materials Today". The corresponding paper reports on the nano-frabrication of micro-optical elements in diamond.
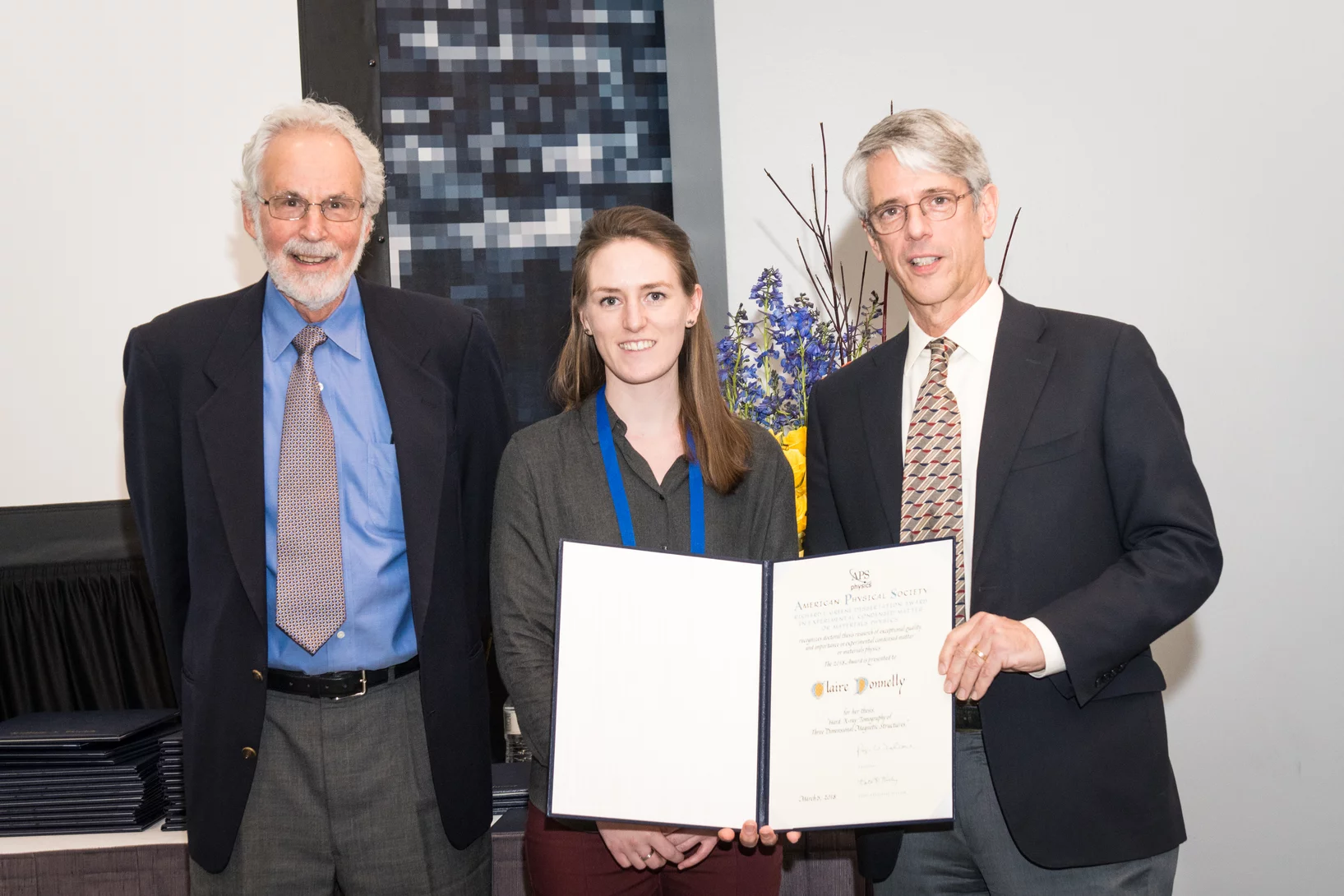
Claire Donnelly dissertation research awards
Claire Donnelly, Mesoscopic Systems (ETH Zurich - PSI), was awarded the COMSOL SPS Award in Computational Physics, the Werner Meyer-Ilse Memorial Award, the ETH Medal for an outstanding doctoral thesis, and the American Physical Society Richard L. Greene Dissertation Award.
Vers de nouveaux transistors de puissance
L'industrie de l'électronique attend d'un nouveau type de transistor de puissance en nitrure de gallium qu'il offre des avantages considérables par rapport aux transistors à haute fréquence qui sont utilisés aujourd'hui. Mais de nombreuses propriétés fondamentales du matériau ne sont pas encore connues. Pour la première fois, des chercheurs du PSI ont visionné un flux d'électrons dans le transistor en question. Pour ce faire, ils ont utilisé une des meilleures sources de rayons X mous au monde, qui se trouve à la Source de Lumière Suisse SLS du PSI.
MOOCs – a paradigm shift in education
In March 2018, the nine-week MOOC “Introduction to synchrotrons and x-ray free-electron lasers” (abbreviated to “SYNCHROTRONx”) came online via the edX provider of the École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL), created by Phil Willmott of the Swiss Light Source, Paul Scherrer Institute. “MOOC” is an acronym for “massive open online course”, a teaching platform started in the first decade of this century, which has become increasingly popular in the last five to six years. MOOCs have no limits to participation and are free. Some of the most popular MOOCs can attract many tens of thousands of participants. Even the most specialized subjects may have an initial enrollment of over a thousand, more than an order of magnitude larger than that typically found in traditional higher education. There were over 70 million MOOC enrollments covering nearly 10’000 subjects offered by the top five providers in 2017 alone!
Metteurs en scène avec missions additionnelles
Par rapport aux modèles actuels, les mémoires informatiques fabriquées à partir de certains matériaux novateurs devraient permettre d'enregistrer les informations beaucoup plus rapidement et dans un espace plus restreint, en consommant nettement moins d'énergie. Les séquences filmées au moyen du laser à rayons X montrent ce qui se passe au cœur de ces mémoires informatiques potentielles et comment optimiser les processus au cours desquels le matériau commute entre deux états.
Creation and deletion of isolated magnetic skyrmions via electrical currents
The writing and deletion of magnetic Skyrmions is a fundamental step towards the fabrication of memory devices based on this promising spin configuration. Researchers at the Korea Institute of Technology have demonstrated the writing and deleting of isolated magnetic Skyrmions at room temperature in ferrimagnetic multilayer superlattice stacks using electrical currents.
Fresnel Zone Plates with Zone Widths below 10 nm
The spot size of a Fresnel Zone Plate lens is mainly determined by the zone widths of its outermost zone. It is therefore essential to fabricate zone plates with structures as small as possible for high-resolution X-ray microscopy. Researchers at the Laboratory for Micro- and Nanotechnology at the PSI have now developed Fresnel zone plates with zone widths well below 10 nm, down to 6.4 nm. These lenses are capable of pushing resolution in X-ray microscopy to the single-digit regime.
LEAPS join forces with the European Commission to strengthen Europe’s leading role in science
“A world where European science is a catalyst for solving global challenges, a key driver for competitiveness and a compelling force for closer integration and peace through scientific collaboration.” This is the vision of LEAPS, League of European Accelerator-based Photon Sources, on which the LEAPS Strategy 2030 is based. Director Jean-David Malo, DG Research and Innovation, received the strategy today at the Bulgarian Presidency Flagship Conference on Research Infrastructures.
HERCULES at the Swiss Light Source
In the week of March 18-23 PSI welcomes 20 PhD students and postdocs taking part in the HERCULES 2018 school on Neutron and Synchrotron Radiation. They will attend lectures and perform two days of practical courses at several beam lines of the Swiss Light Source.
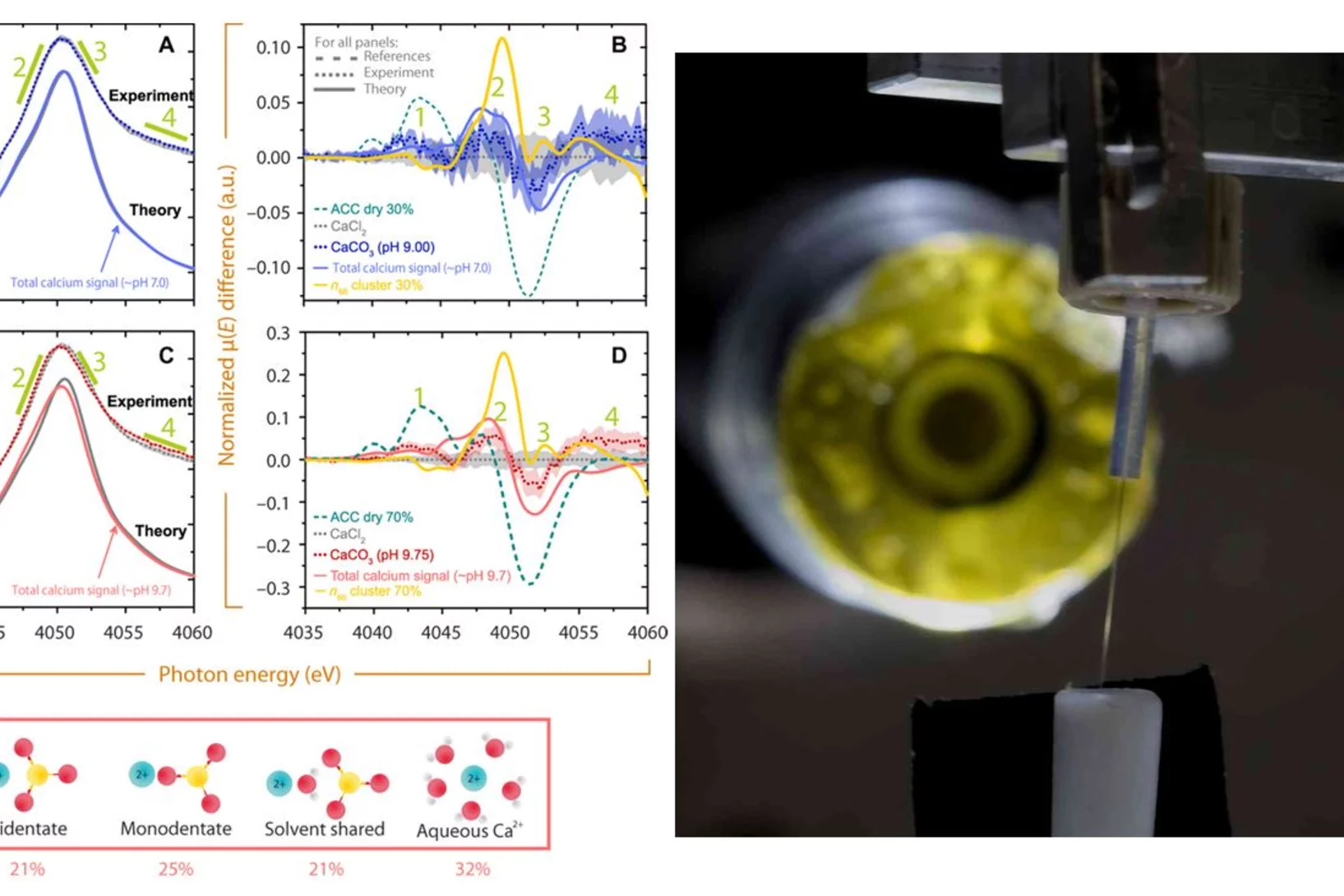
Are supersaturated calcium carbonate solutions classical or non-classical ?
Classical theory predicts that supersaturated carbonate solutions consist mostly of ions and ion pairs, with a small number of larger clusters present in the solution. The population of the different sized clusters in a solution is solely defined by the cluster’s size dependent Free Energy. If clusters are large enough they serve as nucleation germs for a new solid phase. The nucleation occurs once the surface free energy barrier posed by the new solid-liquid interface is overcome by the free energy win from bulk phase growth.
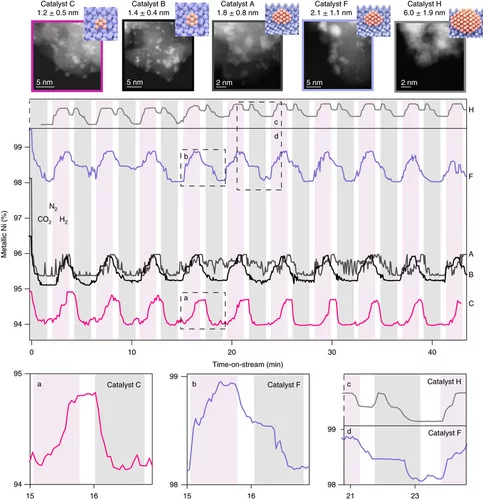
Unravelling structure sensitivity in CO2 hydrogenation over nickel
Using a unique set of well-defined silica-supported Ni nanoclusters (1–7 nm) and advanced characterization methods it was proved how structure sensitivity influences the mechanism of catalytic CO2 reduction, the nature of which has been long debated.
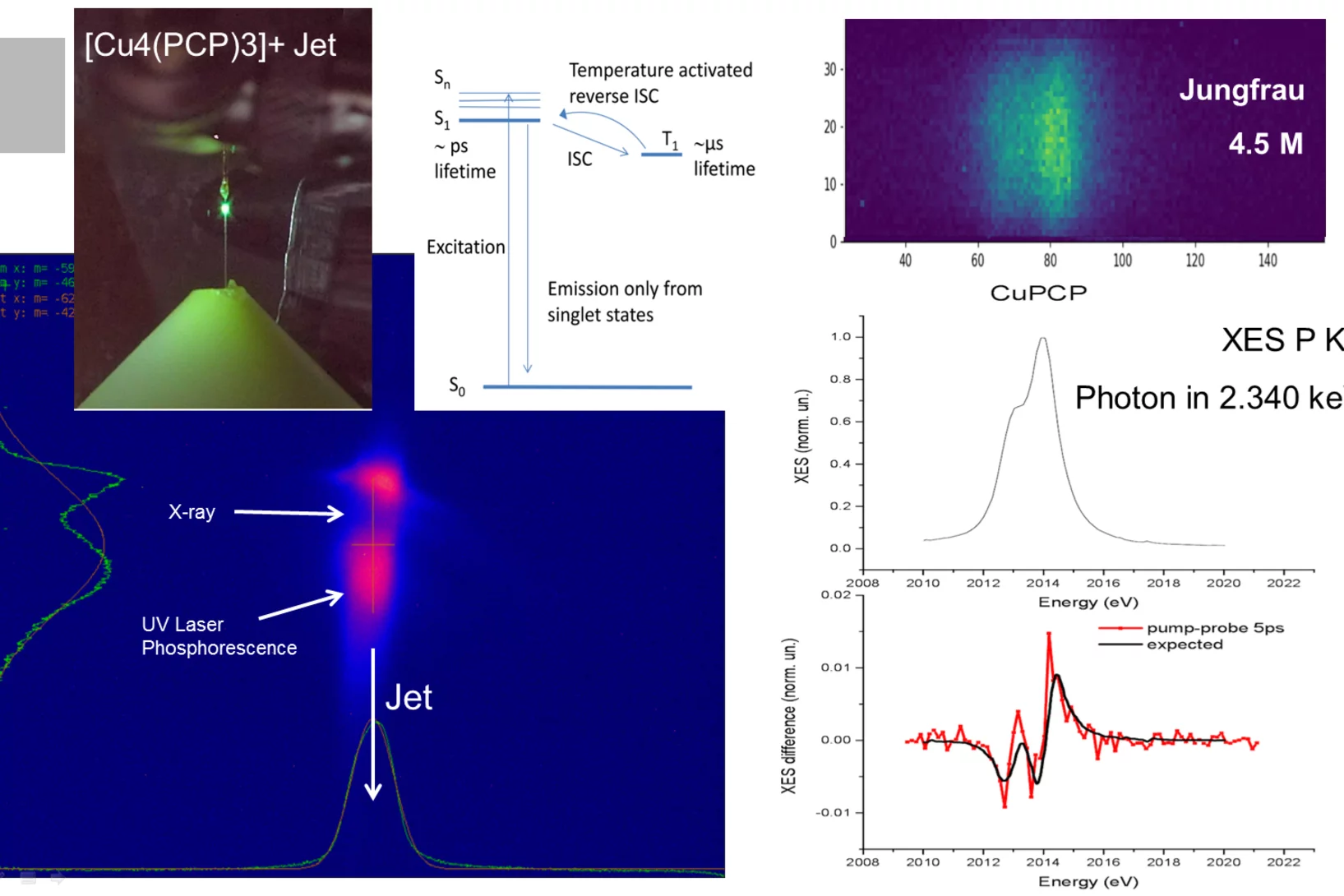
First Pilot Experiment at SwissFEL-Alvra: UV photo-induced charge transfer in OLED system
On the 17th of December 2017 SwissFEL saw its first pilot experiment in the Alvra experimental station of the SwissFEL ARAMIS beamline.
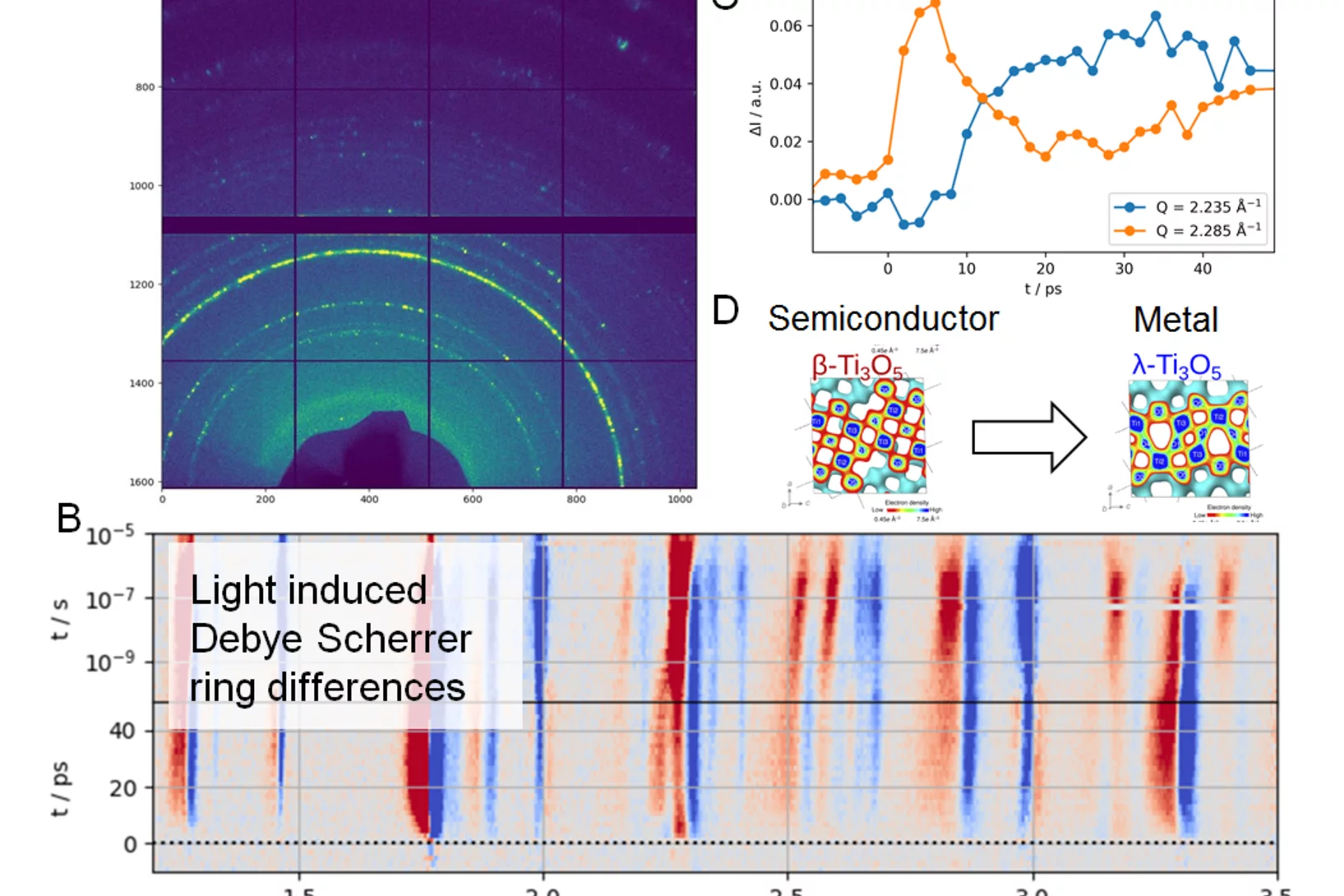
First time resolved Pilot Experiment by SwissFEL: Semiconductor to metal transition in Ti3O5 nanocrystals
On the 30th of November 2017 SwissFEL saw its first time resolved pilot experiment in the Bernina experimental station of the SwissFEL ARAMIS beamline. A team of scientists from the University of Rennes, ESRF and PSI, led by Marco Cammarata (Univ. Rennes) and Henrik Lemke (PSI), successfully started the experimental phase at SwissFEL.
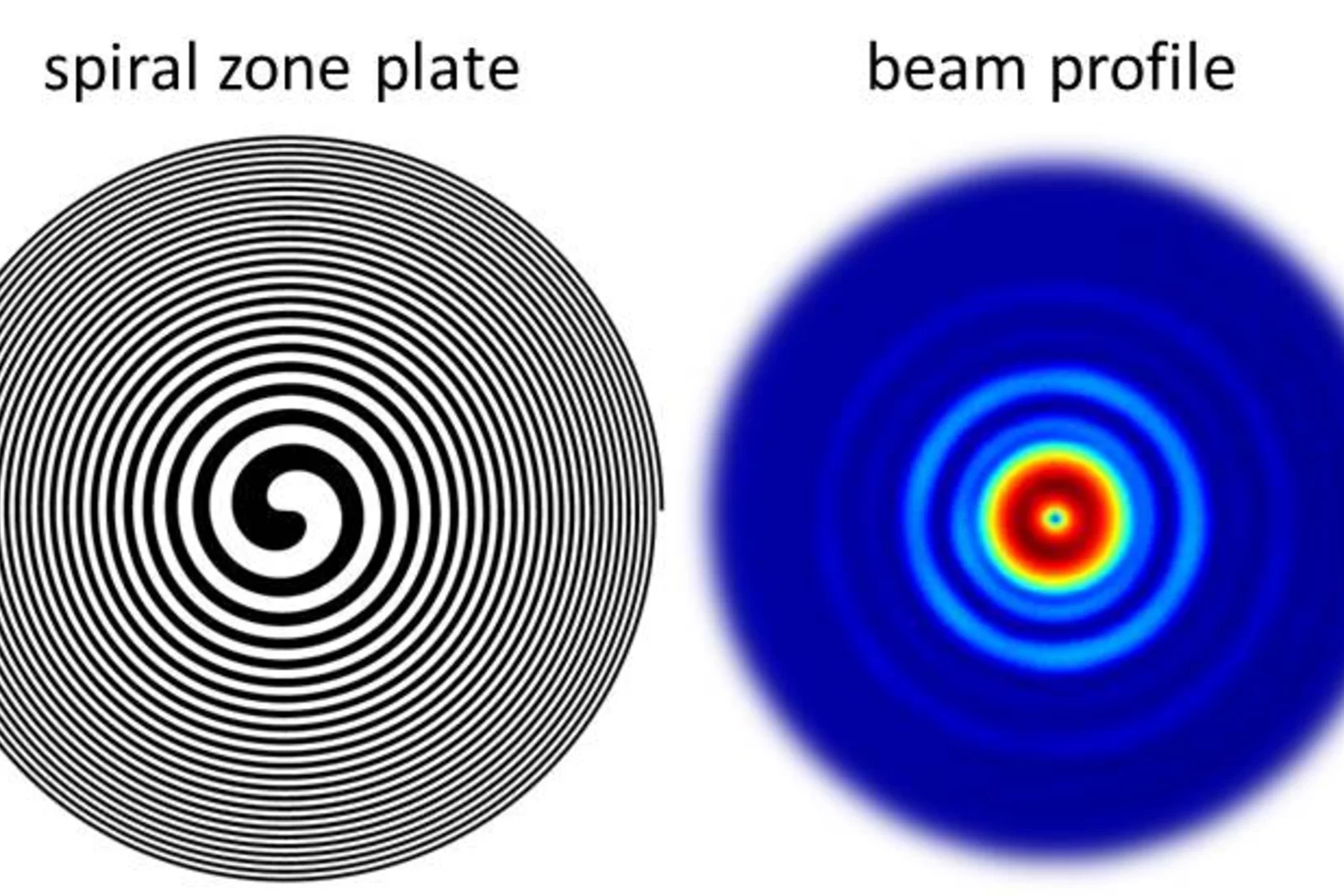
Extreme Ultraviolet Vortices at Free Electron Lasers
PSI scientists have developed tailored diffractive X-ray optics for a free electron laser that induces an optical vortex in extreme ultraviolet radiation. The experiment facilitates the first demonstration of orbital angular momentum in radiation created by a free electron laser in the extreme ultraviolet regime, with an extraordinary clean and defined wavefront. In a collaborative effort with researchers from the FERMI free electron laser in Trieste, Italy and from the University of Nova Gorica in Slovenia, the wavefront of the intense beams carrying an orbtial angular momentum was characterized. Furthermore, a method to characterize the footprint of a focused beam from a free electron laser was refined based on ablation imprints in polymers and subsequent treatment with organic solvents. In this way, the sensitivity of the imprint method could be enhanced to a dynamic range of three orders of magnitude in a single shot.
La spin-off du PSI GratXray remporte le Swiss Technology Award 2017
Une spin-off du PSI remporte le Swiss Technology Award 2017: la jeune entreprise GratXray développe une nouvelle méthode de diagnostic précoce du cancer du sein.
How ‘super-microscopes’ are changing the face of European science
13 November 2017 – Brussels – 16 organisations representing 19 light sources facilities across Europe gathered to launch the LEAPS initiative and signed an agreement to strengthen their collaboration, in the presence of Robert-Jan Smits, Director General for Research and Innovation (RTD) at the European Commission, and Giorgio Rossi, Chair of the European Strategy Forum on Research Infrastructures (ESFRI).
Magnetic structures take a new turn
The unexpected finding that in an ‘artificial spin ice’ magnetostatic energy can be transformed into directed rotation of magnetization provides fresh insights into such nano-patterned magnetic structures — and might enable novel applications in nanoscale devices.
First light in SwissFEL Experimental Station Bernina
Friday, October 20th, 2017, we brought the first light (wavelength 1.2 nm) into the experimental hutch of Bernina. The beam passed the Alvra endstation, went through the diagnostic devices and hit the diagnostic screen in front of the refocussing KB-system of Bernina. The upper picture shows the pink beam on the last diagnostic screen of the beamline. The lower left at the entrance of Bernina-hutch, 133 m downstream of the undulator. The lower right picture shows the beam centered in the alignment iris in front of the KB-system.
Making the world go round - a look into the structure of a prominent heterogeneous catalyst
Fluid catalytic cracking catalysts, which are composite particles of hierarchical porosity, were examined using ptychographic X-ray tomography. These particles are essential to the conversion of crude oil into gasoline. Examination of catalysts at decreasing levels of catalytic conversion efficacy allowed the detection of possible deactivation causes.
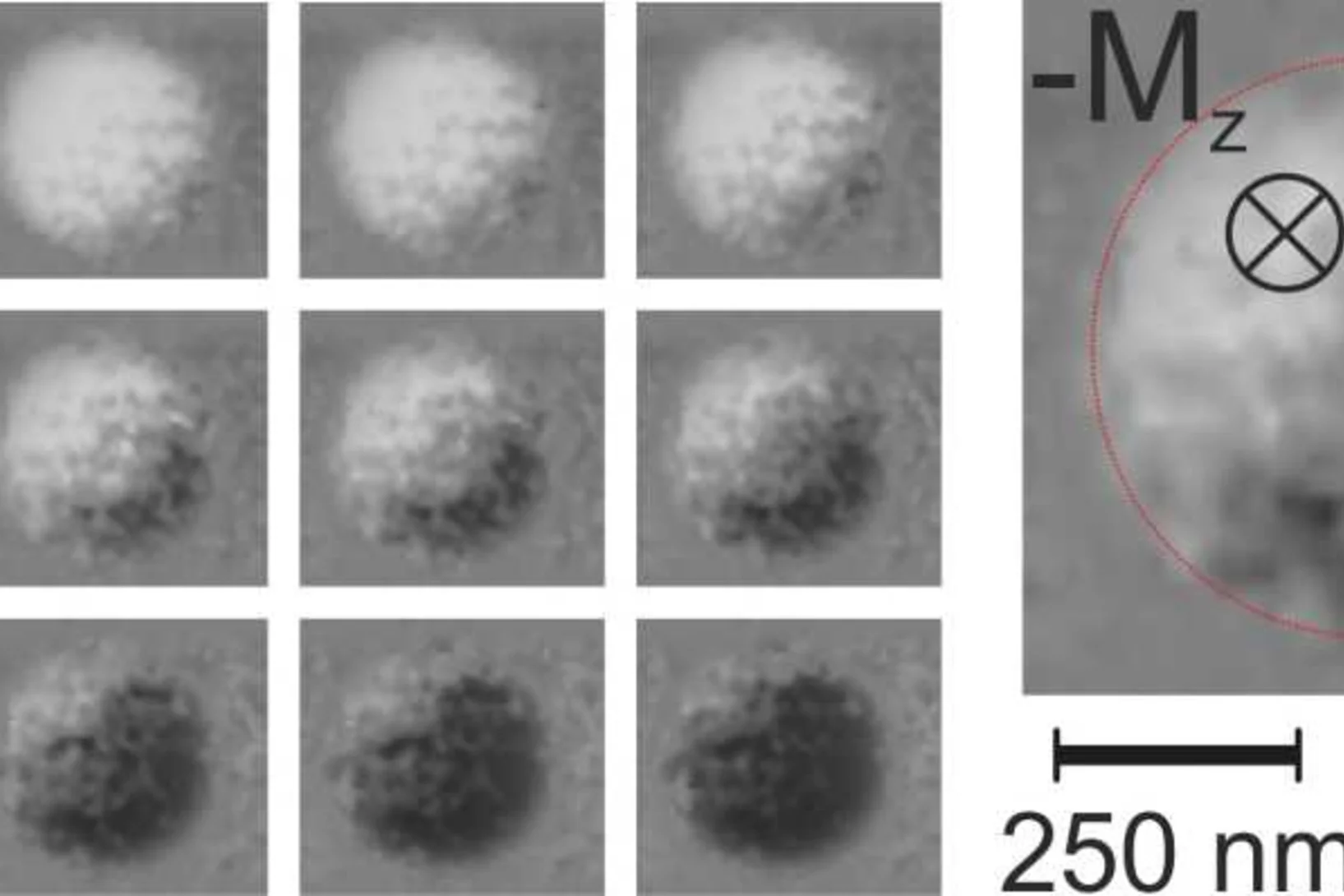
Time- and spatially-resolved magnetization dynamics driven by spin-orbit torques
Current-induced spin-orbit torques hold a great potential for manipulation of magnetization at ultrafast timescales. Researchers at ETH Zürich have demonstrated, using time-resolved STXM imaging at the Swiss Light Source, the influence of spin-orbit torques on the switching behaviour of Pt/Co/AlOx nanostructured elements.
Highly Crystalline C8-BTBT Thin-Film Transistors by Lateral Homo-Epitaxial Growth on Printed Templates
Highly crystalline thin films of organic semiconductors offer great potential for high-performance, low-cost flexible electronics. Researchers at IMEC Belgium have developed a new double-step thin film fabrication process that offers higher performance devices. Soft X-ray spectro-microscopy at the Swiss Light Source was used to prove that the increased performance comes from larger areas of material sharing the same molecular orientation.
L'atmosphère à la lumière des rayons X
Des chercheurs du PSI ont développé une chambre d’expérience où ils reconstituent certains processus qui se jouent dans l’atmosphère et peuvent étudier ces derniers avec une précision inégalée grâce à de la lumière de type rayons X issue de la SLS. Lors de leurs premières expériences, ils ont étudié la formation du brome, qui joue un rôle essentiel dans la dégradation de l’ozone dans les couches inférieures de l’atmosphère. A l’avenir, cette nouvelle chambre d’expérience sera également mise à disposition de chercheurs d’autres disciplines scientifiques.
ATHOS Conceptual Design Report (CDR)
The ATHOS Conceptual Design Report has recently been completed and describes the ATHOS project in detail. The CDR starts with a summary of the characteristics of the ATHOS undulator line. Especially the design parameters of the different ATHOS operation modes are explained and illustrated by simulation results. The core part of the report is a description of all key components, i.e. from the electron bunch extraction kicker down to the ATHOS experimental stations.
Dr. Nan Xu awarded SPS 2017 Prize in Condensed Matter Physics
The SPS 2017 Prize in Condensed Matter Physics, sponsored by IBM, has been awarded to Dr. Nan Xu for his excellent work on topological quantum states. Dr. Nan Xu is a joint postdoc of Paul Scherrer Institute (PSI) and the École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL).
A new RIXS analyzer scheme based on transmission zone plates
PSI scientists have developed a new type of X-ray optics that allows for analyzing the emission in resonant inelastic x-ray scattering (RIXS) experiments. The new approach combines the energy dispersion with imaging capabilities. In a collaborative effort with research groups from Göttingen and Hamburg, two new classes of RIXS experiments, energy mapping and RIXS imaging, have been demonstrated.
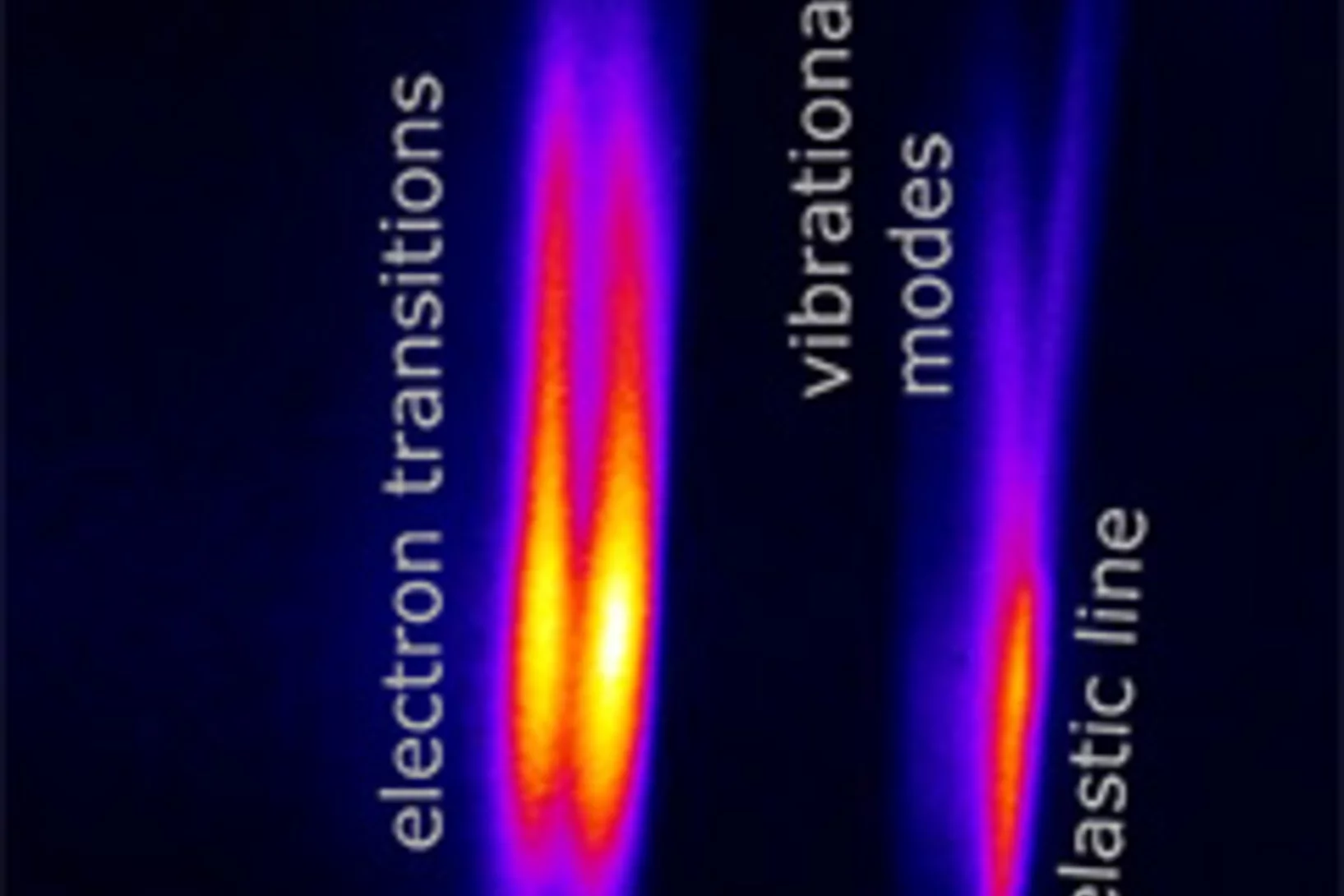
Single-shot Monitoring of Ultrafast Processes via X-ray Streaking at a Free Electron Laser
The advent of x-ray free electron lasers has extended the unique capabilities of resonant x-ray spectroscopy techniques to ultrafast time scales. Here, in collaboration between researchers from PSI, Sorbonne Universités, HASYLAB/DESY, Synchrotron SOLEIL, CNRS, and Uppsala University, we report on a novel experimental method that allows retrieving with a single x-ray pulse the time evolution of an ultrafast process, not only at a few discrete time delays, but continuously over an extended time window.
Plongée dans un aimant
Pour la première fois, des chercheurs ont réussi à visualiser les directions de l'aimantation dans un objet magnétique tridimensionnel. Les plus petits détails de leur visualisation mesuraient moins d'un dixième de millième de millimètre. Un type de motif exceptionnel est ressorti dans la structure qu'ils ont fait apparaître: des singularités magnétiques appelées points de Bloch, jusque-là connues uniquement en théorie.
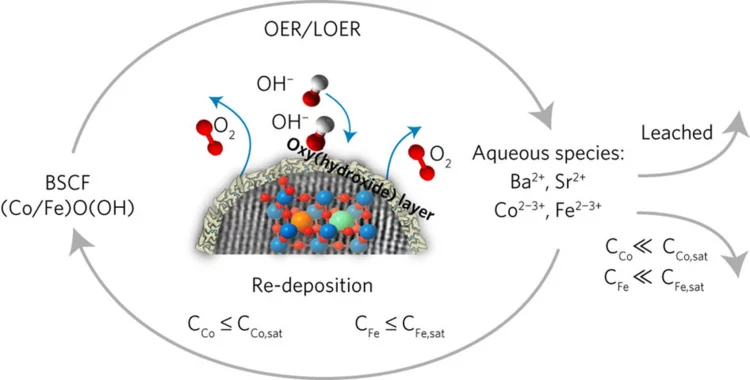
Nanomaterial helps store solar energy: efficiently and inexpensively
By combining a scalable cutting-edge synthesis method with time-resolved X-ray absorption spectroscopy measurements, it was possible to capture the dynamic local electronic and geometric structure during realistic operando conditions for highly active OER perovskite nanocatalysts.
Understanding the reaction mechanism in lignin catalytic fast pyrolysis
Lignin is a major constituent of plants, and may be used as a precursor for fuels and fine chemicals. Catalytic fast pyrolysis of lignin is one of the most promising approaches. By using vacuum ultraviolet synchrotron radiation and threshold photoelectron spectroscopy we could identify elusive intermediates, which are responsible for the formation of phenol and benzene and could thus tackle this reaction mechanism. Mechanistic understanding could enable targeted improvement of production methods in the future, beyond the currently used "cook-and-look" approach.