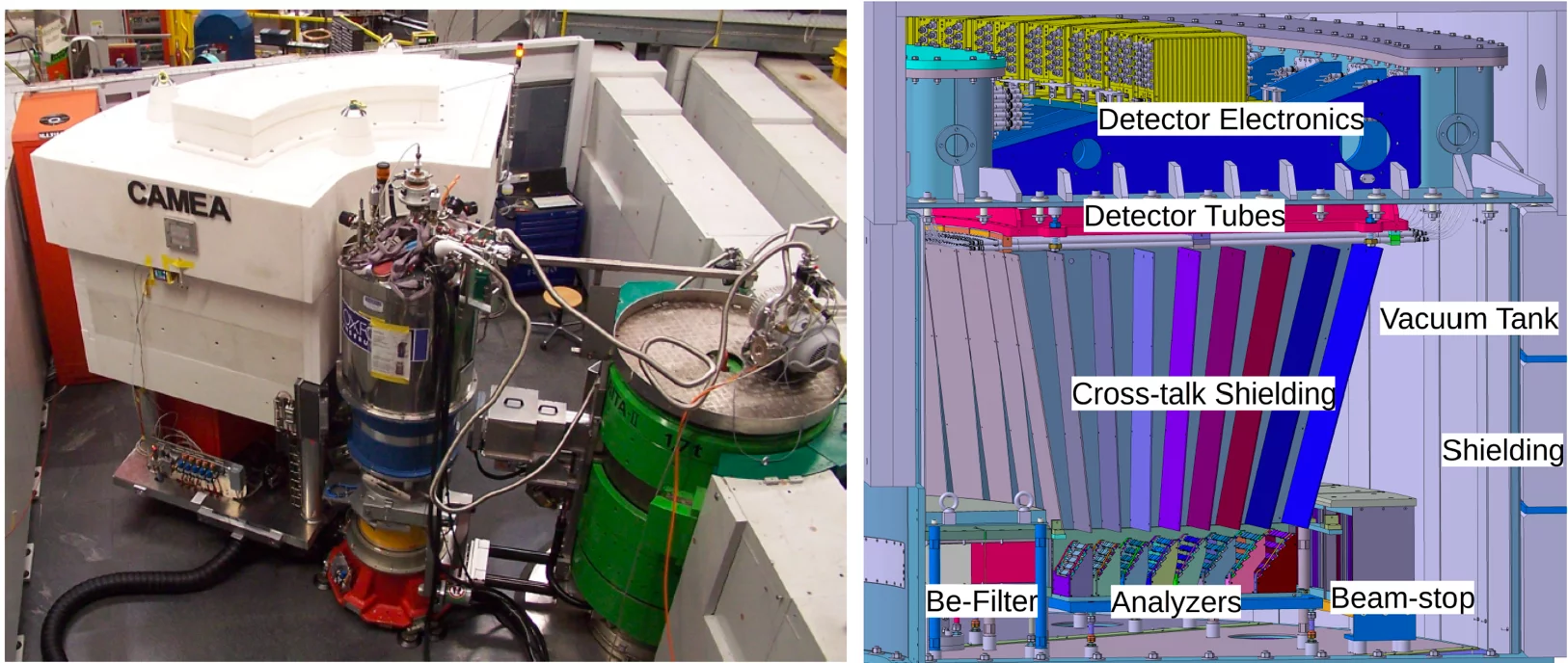
CAMEA is a multiplexing instrument, which benefits from the nearly perfect transmission of highly oriented pyrolytic graphite in a cold neutron beam. A series of eight upward scattering analyser arcs diffract the neutrons onto a detector array that consists of 104 position sensitive 3He tubes.
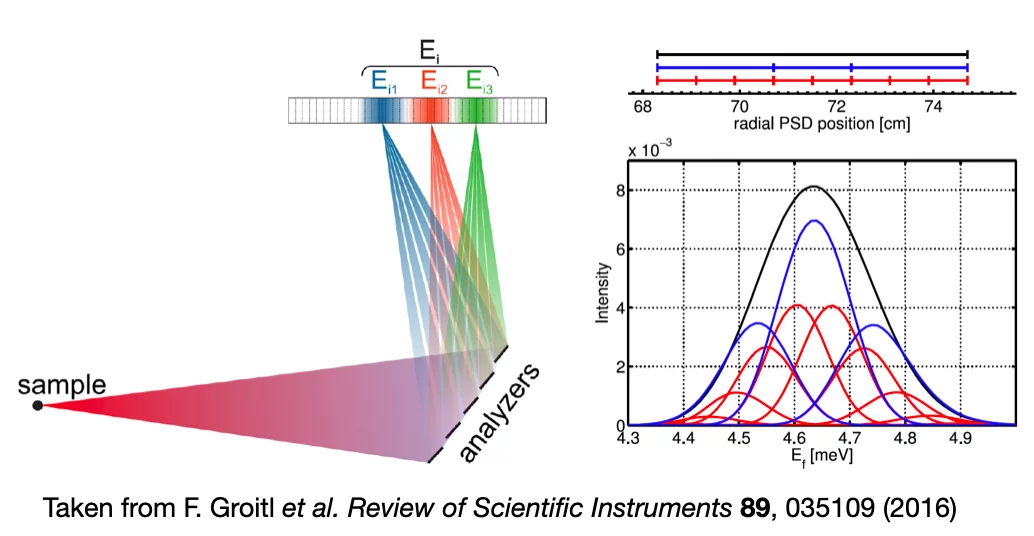
CAMEA uses the prismatic analyser concept that allows recording a range of energies for each analyser segment. The analysis software provides different binning options, helping to accommodate the needs of the user, i.e. maximising intensity or energy resolution.
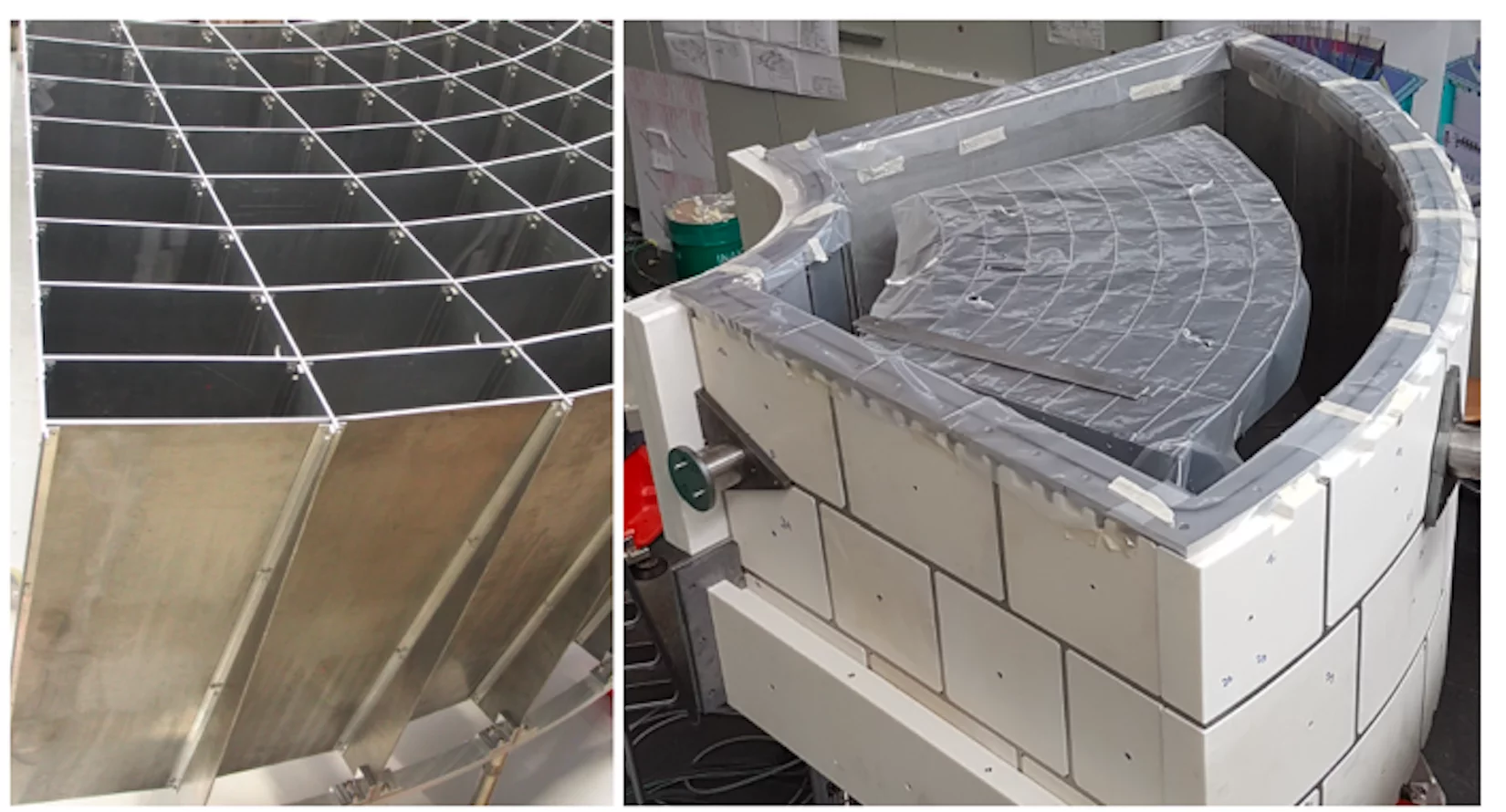
The background at CAMEA is kept at its minimum (0.3 counts/minute and detector) via an active shielding. The CAMEA unit sits in a vacuum tank (~10-7 mbar) that has a very low magnetic permeability (< 10-7 H/m). The tank is further dressed with Boralcan and 20 cm thick borated polyethylene blocks. The crosstalk between the different analyser is minimised through a 3 mm thick honeycomb structure made of Boralcan-dressed aluminium. Higher-order lambda contributions are suppressed by a Beryllium filter at the entrance of the spectrometer unit. The filter is combined with a radial collimator.
We refer to detailed description of the instrument design and performance .