SESAME beamline for tomography project (BEATS) is launched
On 1st January 2019, the European Horizon 2020 project BEAmline for Tomography at SESAME (BEATS) was launched with the objective to design, procure, construct and commission a beamline for hard X-ray full-field tomography at the SESAME synchrotron in Jordan. The European grant is worth 6 million euros and will span a four-year period from beginning 2019 to end 2022.
Dr Mirjam van Daalen appointed as Swiss ESFRI delegate
Dr. Mirjam van Daalen Chief of staff of the Photon Science Division, was mandated on the 1st of January 2019, by the State Secretariat for Education, Research and Innovation SERI as a member of the Swiss Delegation to the European Science Forum on Research Infrastructures ESFRI https://www.esfri.eu/.
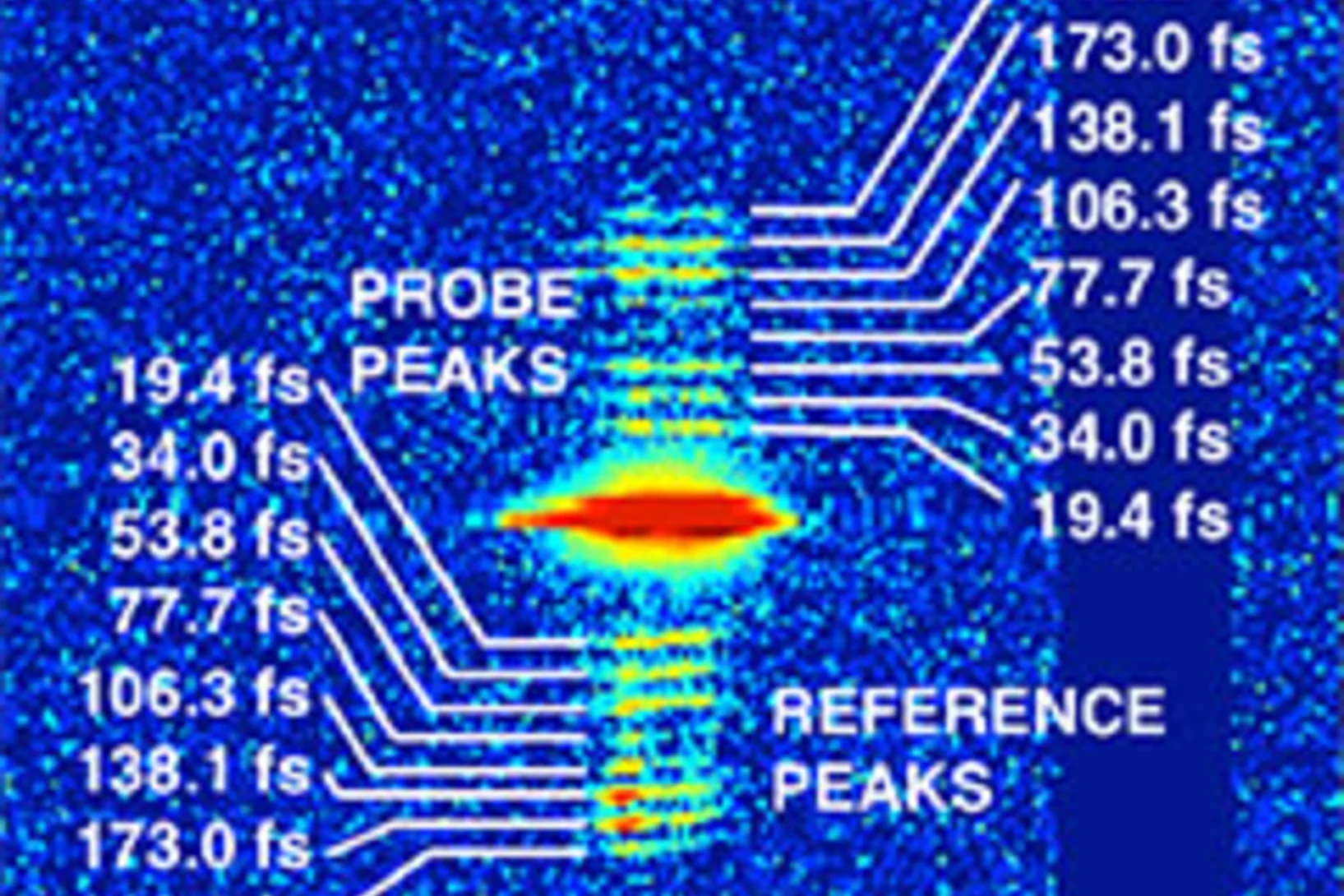
First femtosecond protein pump-probe measurements at SwissFEL
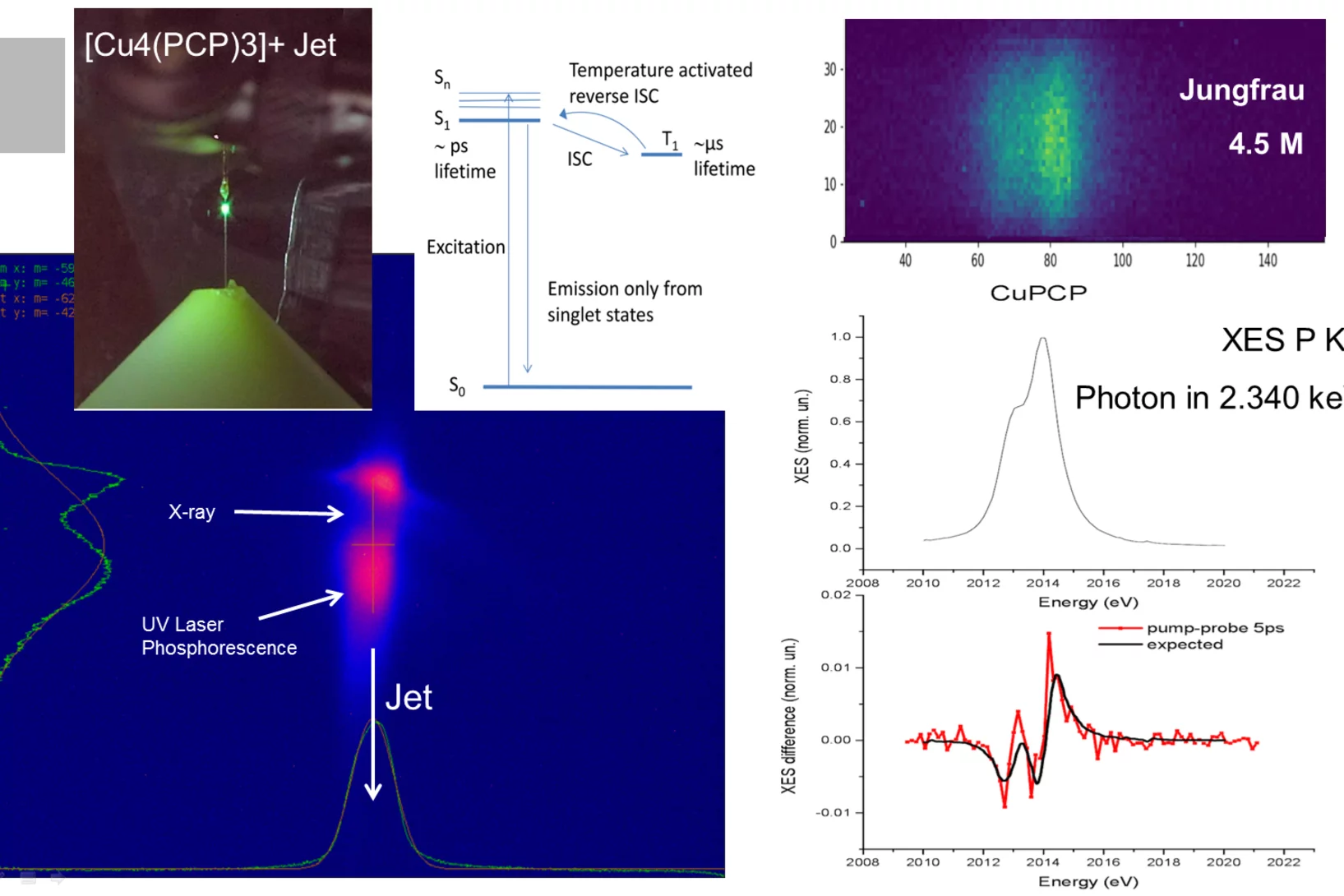
A major milestone in the commissioning of SwissFEL has been reached: the first pump-probe experiments on proteins have been successfully carried out. Crystals of several retinal-binding proteins were delivered in a viscous jet system and a femtosecond laser was used to start the isomerization reaction. Microsecond to sub-picosecond snapshots were then collected, catching the retinal proteins shortly after isomerization of the chromophore.
2018 Innovation Award on Synchrotron Radiation
The Innovation Award on Synchrotron Radiation 2018 went to Dr. Christian David, also from the Paul Scherrer Institute, and to Prof. Alexei Erko, who recently moved from the HZB to the Institute for Applied Photonics (IAP) in Berlin-Adlershof.
EU bewilligt 14 Millionen für Schweizer Forschende
Ein Team mit drei Forschenden aus dem ETH-Bereich wurde mit einem prestigeträchtigen EU-Förderpreis ausgezeichnet. Heute erhielten sie den von der EU unterzeichneten Vertrag zur Bestätigung der ausserordentlich hohen Finanzierung in Höhe von 14 Millionen Euro. Damit werden sie Quanteneffekte untersuchen, die das Rückgrat der Elektronik der Zukunft bilden könnten.
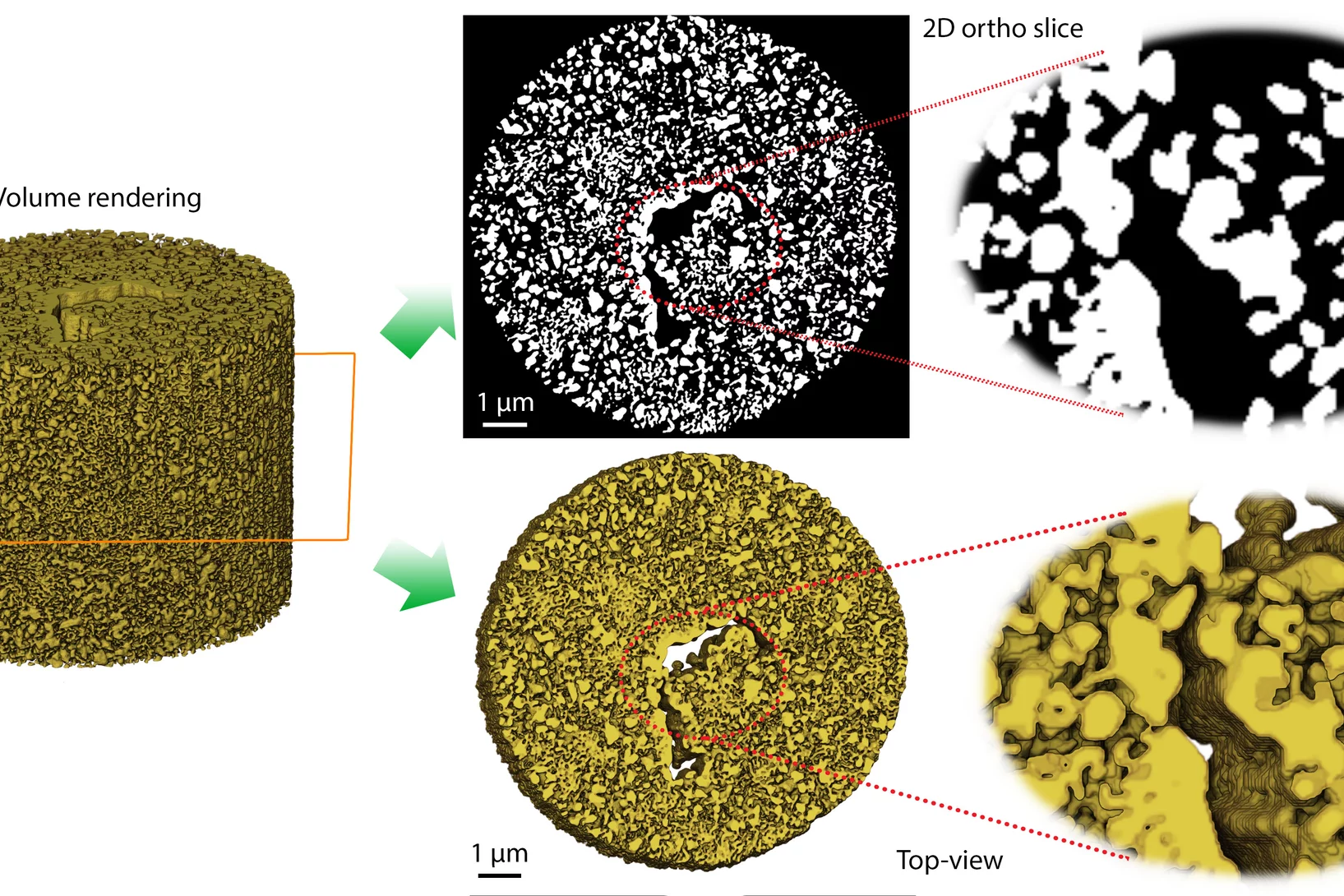
Helping chemists to understand degradation and stabilization of catalytic nanoporous gold structures
Catalytic materials are ubiquitously used in industrial processes to perform chemical reactions efficiently and in a sustainable manner. Nanoporous gold (npAu) is a monolithic sponge-like catalyst exhibiting a hierarchical structure with pores and connecting ligaments of typically 10 to 50 nm.
SwissFEL's First Call for Proposals
The first SwissFEL call for proposals took place, deadline for submission was the 15th of September. In this first call for proposals SwissFEL received overwhelming interest from the user community. A total of 47 proposals were submitted for the SwissFEL Alvra experimental station and 26 for the Bernina experimental station. The Proposal Review committee PRC took place on 18-19 October 2018.
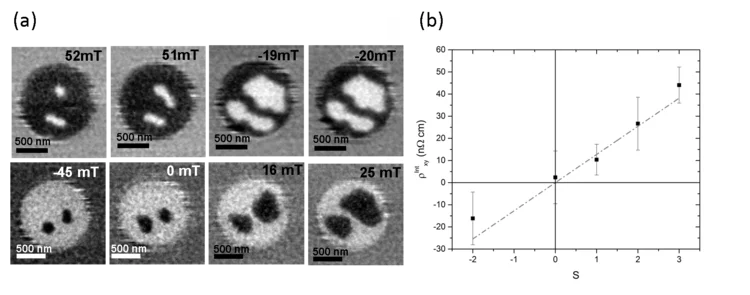
Discrete Hall contribution of magnetic skyrmions
The reliable electrical detection of magnetic skyrmions is of fundamental importance for the application of such topological magnetic quasi-particles for data storage devices. Researchers in a joint collaboration between the University of Leeds and the PolLux endstation have investigated the electrical detection of isolated magnetic skyrmions in applications-relevant nanostructured devices, observing the presence of a strong skyrmion-dependent contribution to the Hall resistivity.
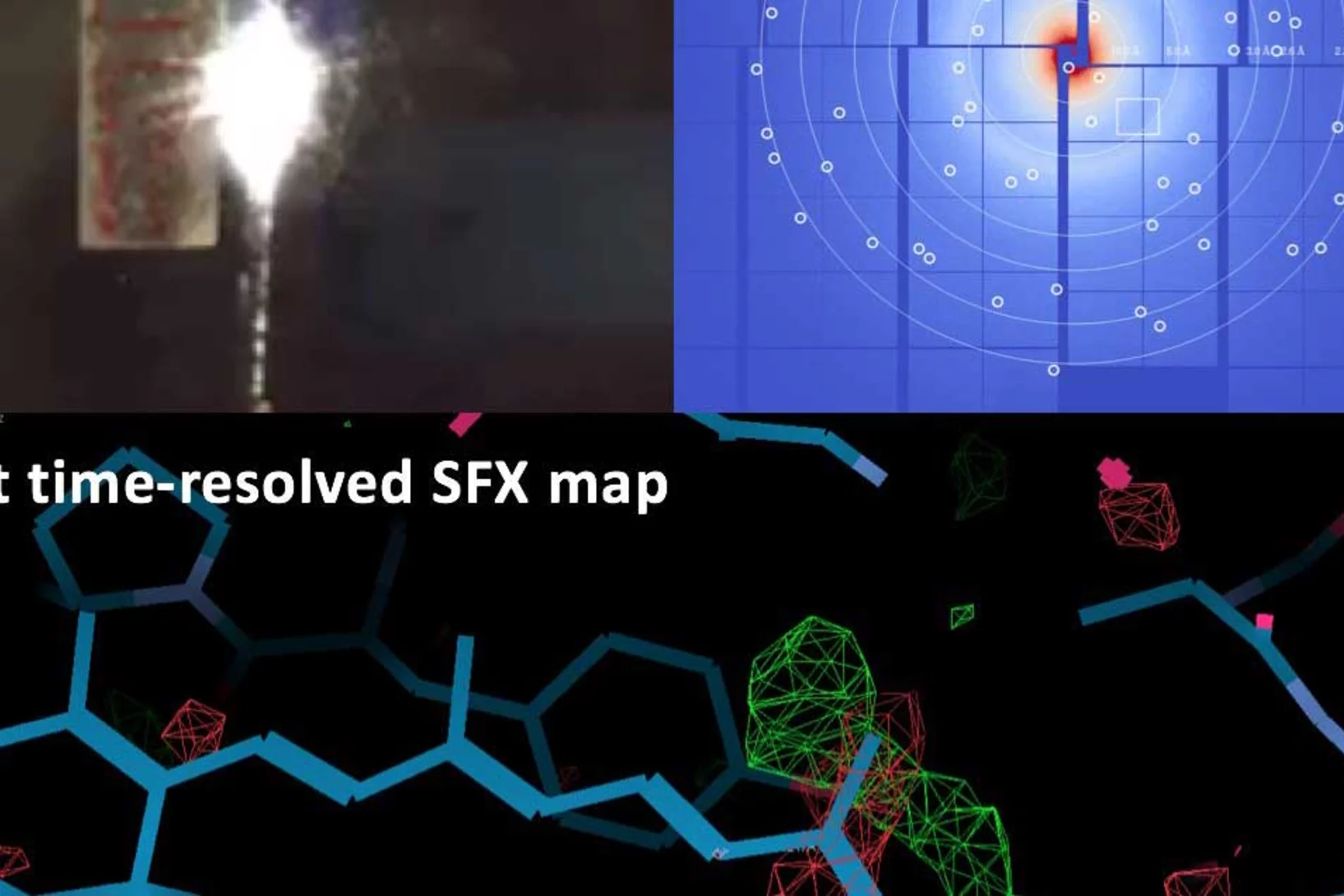
Demonstration of femtosecond X-ray pump X-ray probe diffraction on protein crystals
Our experiments, published in the September issue of Structural Dynamics, demonstrate the feasibility of time-resolved pump-multiprobe X-ray diffraction experiments on protein crystals using a split-and-delay setup which was temporarily installed at the LCLS X-ray Free Electron Laser.
Diamond: a gem for micro-optics
Our image of a diamond structure was published on the cover page of the September 2018 issue of the journal "Materials Today". The corresponding paper reports on the nano-frabrication of micro-optical elements in diamond.
Claire Donnelly dissertation research awards
Claire Donnelly, Mesoscopic Systems (ETH Zurich - PSI), was awarded the COMSOL SPS Award in Computational Physics, the Werner Meyer-Ilse Memorial Award, the ETH Medal for an outstanding doctoral thesis, and the American Physical Society Richard L. Greene Dissertation Award.
Auf dem Weg zu neuen Leistungstransistoren
Von einem neuartigen Leistungstransistor aus Galliumnitrid verspricht sich die Elektronikindustrie erhebliche Vorteile gegenüber derzeit eingesetzten Hochfrequenztransistoren. Doch noch sind eine Vielzahl grundlegender Eigenschaften des Materials unbekannt. Forschende am Paul Scherrer Institut PSI haben nun erstmals den Elektronen im angesagten Transistor beim Fliessen zugeschaut. Sie nutzten dafür eine der weltweit besten Quellen für weiches Röntgenlicht an der Synchrotron Lichtquelle Schweiz des PSI.
MOOCs – a paradigm shift in education
In March 2018, the nine-week MOOC “Introduction to synchrotrons and x-ray free-electron lasers” (abbreviated to “SYNCHROTRONx”) came online via the edX provider of the École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL), created by Phil Willmott of the Swiss Light Source, Paul Scherrer Institute. “MOOC” is an acronym for “massive open online course”, a teaching platform started in the first decade of this century, which has become increasingly popular in the last five to six years. MOOCs have no limits to participation and are free. Some of the most popular MOOCs can attract many tens of thousands of participants. Even the most specialized subjects may have an initial enrollment of over a thousand, more than an order of magnitude larger than that typically found in traditional higher education. There were over 70 million MOOC enrollments covering nearly 10’000 subjects offered by the top five providers in 2017 alone!
Regisseure mit Zusatzaufgaben
Datenspeicher aus neuartigen Materialien sollen ermöglichen, Informationen auf kleinerem Raum viel schneller und energiesparender als bisher aufzuzeichnen. Filmaufnahmen mit dem Röntgenlaser zeigen, was im Inneren möglicher neuer Speichermedien passiert und wie sich die Prozesse, bei denen das Material zwischen zwei Zuständen wechselt, optimieren lassen.
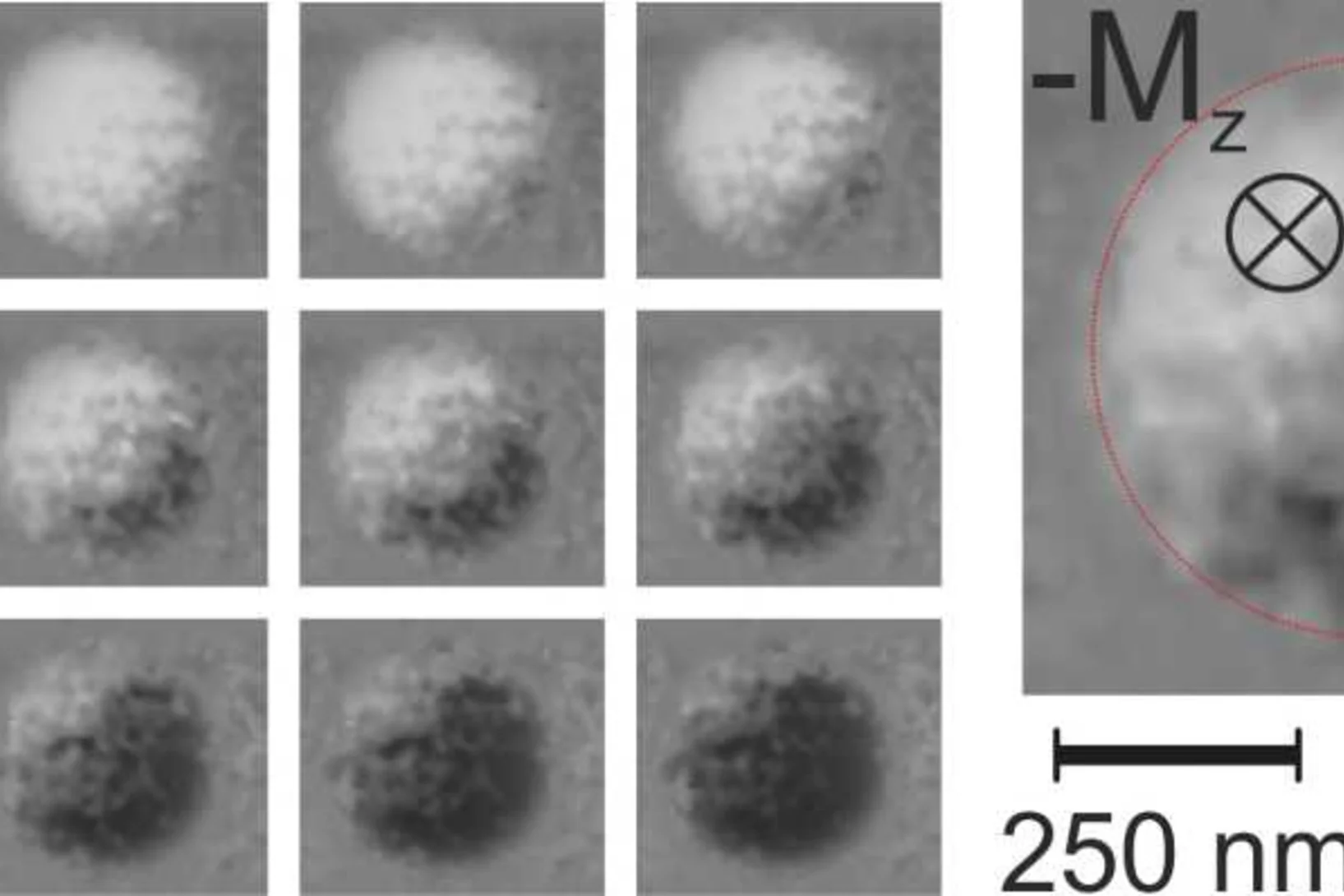
Creation and deletion of isolated magnetic skyrmions via electrical currents
The writing and deletion of magnetic Skyrmions is a fundamental step towards the fabrication of memory devices based on this promising spin configuration. Researchers at the Korea Institute of Technology have demonstrated the writing and deleting of isolated magnetic Skyrmions at room temperature in ferrimagnetic multilayer superlattice stacks using electrical currents.
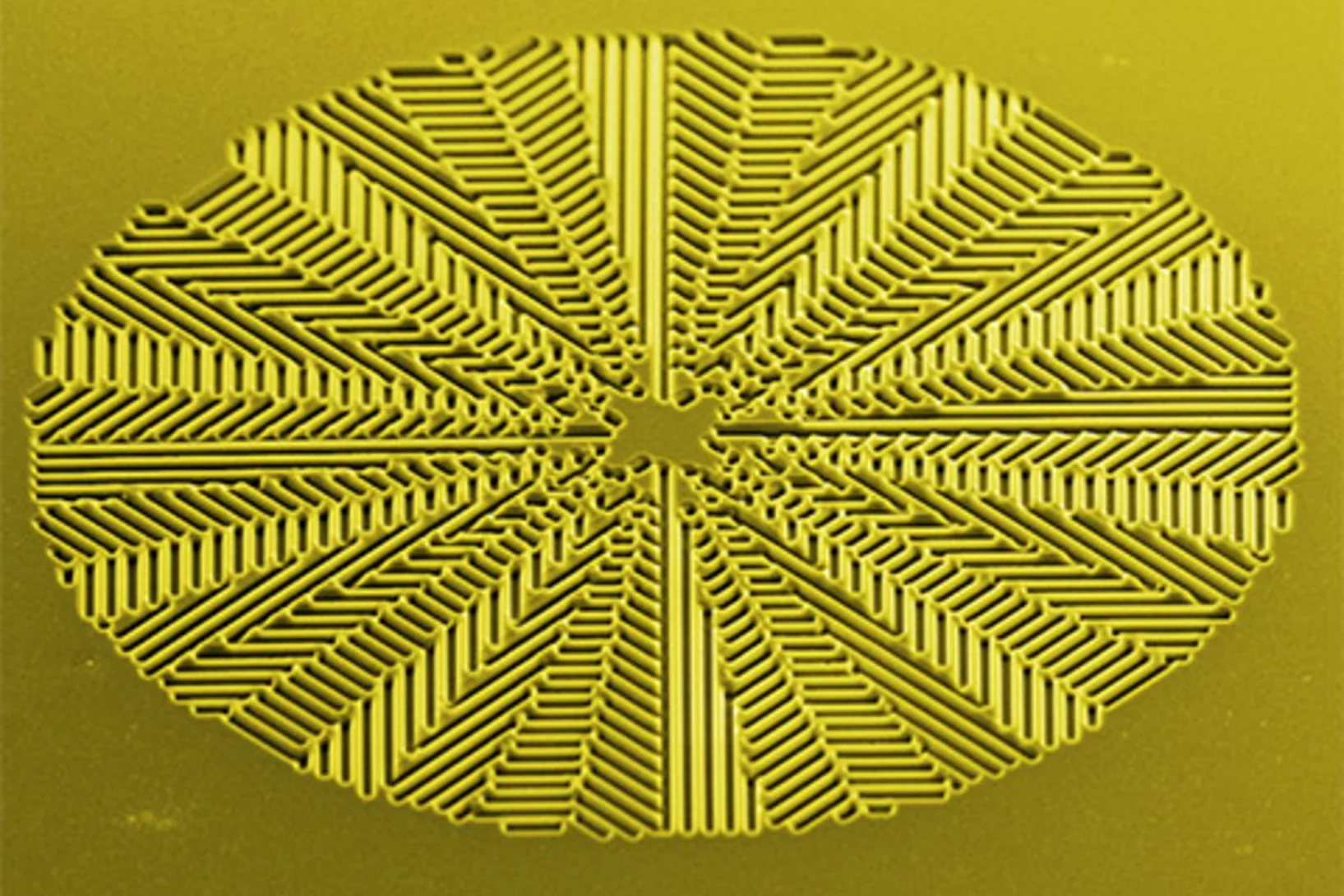
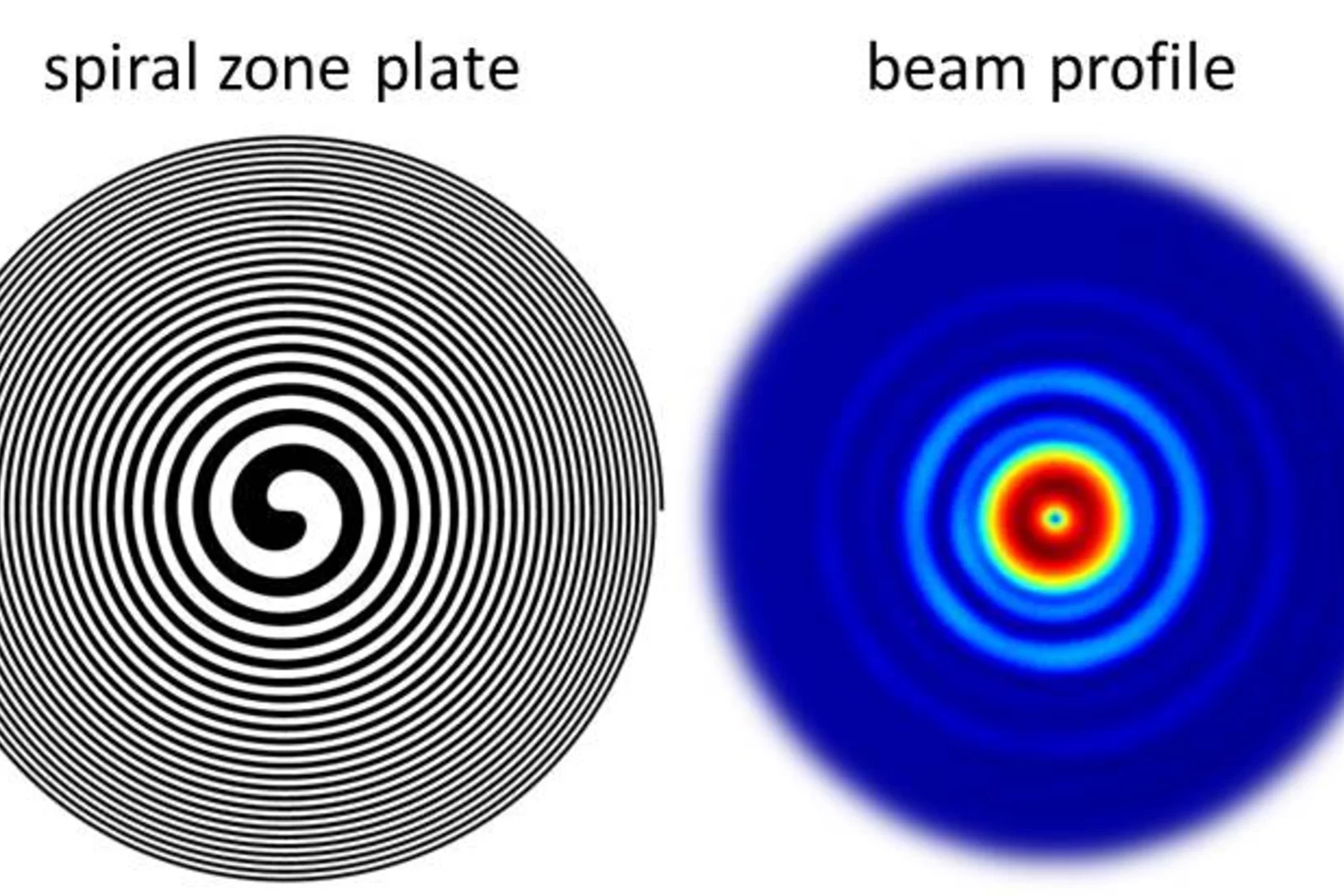
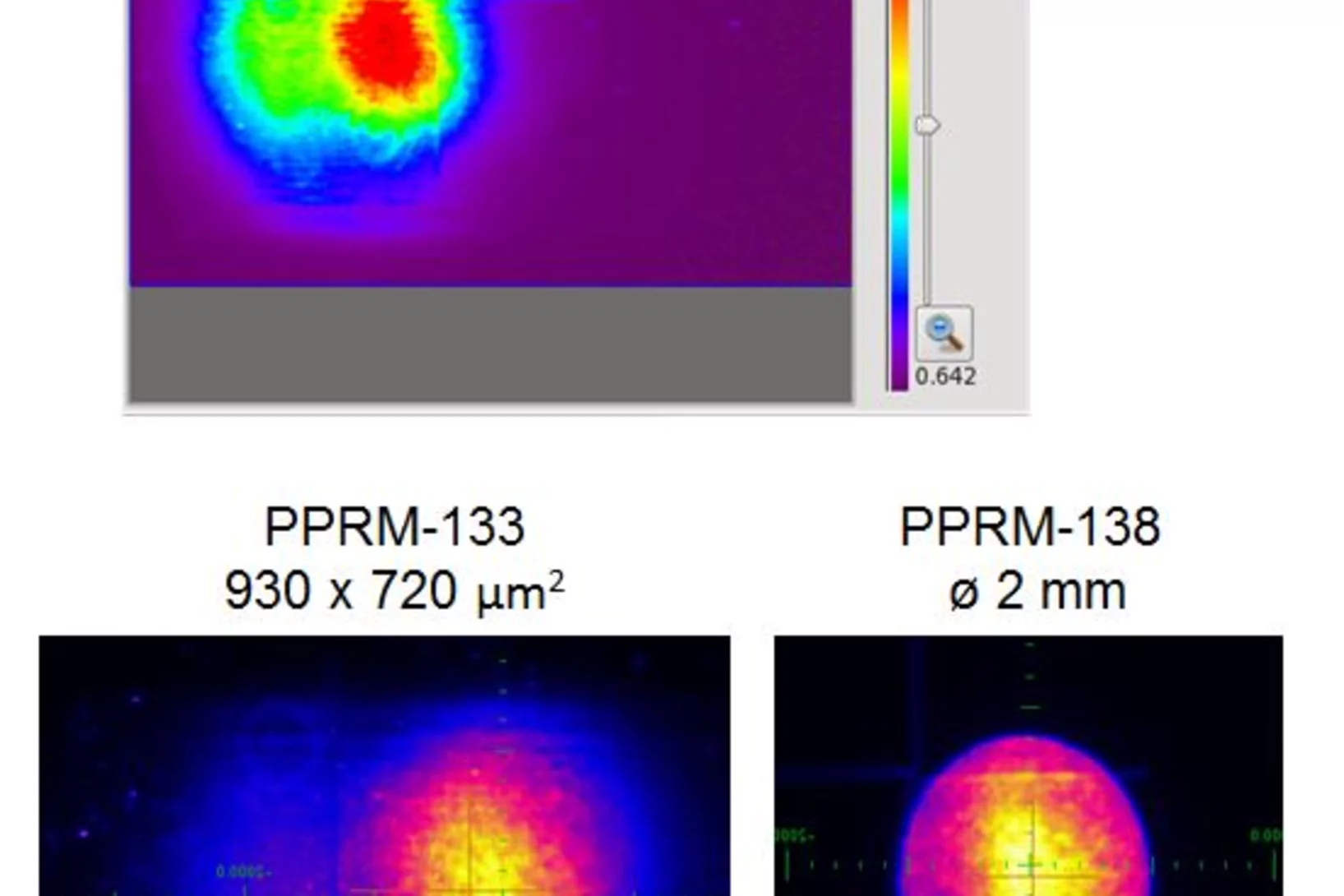
Fresnel Zone Plates with Zone Widths below 10 nm
The spot size of a Fresnel Zone Plate lens is mainly determined by the zone widths of its outermost zone. It is therefore essential to fabricate zone plates with structures as small as possible for high-resolution X-ray microscopy. Researchers at the Laboratory for Micro- and Nanotechnology at the PSI have now developed Fresnel zone plates with zone widths well below 10 nm, down to 6.4 nm. These lenses are capable of pushing resolution in X-ray microscopy to the single-digit regime.
LEAPS join forces with the European Commission to strengthen Europe’s leading role in science
“A world where European science is a catalyst for solving global challenges, a key driver for competitiveness and a compelling force for closer integration and peace through scientific collaboration.” This is the vision of LEAPS, League of European Accelerator-based Photon Sources, on which the LEAPS Strategy 2030 is based. Director Jean-David Malo, DG Research and Innovation, received the strategy today at the Bulgarian Presidency Flagship Conference on Research Infrastructures.
HERCULES at the Swiss Light Source
In the week of March 18-23 PSI welcomes 20 PhD students and postdocs taking part in the HERCULES 2018 school on Neutron and Synchrotron Radiation. They will attend lectures and perform two days of practical courses at several beam lines of the Swiss Light Source.
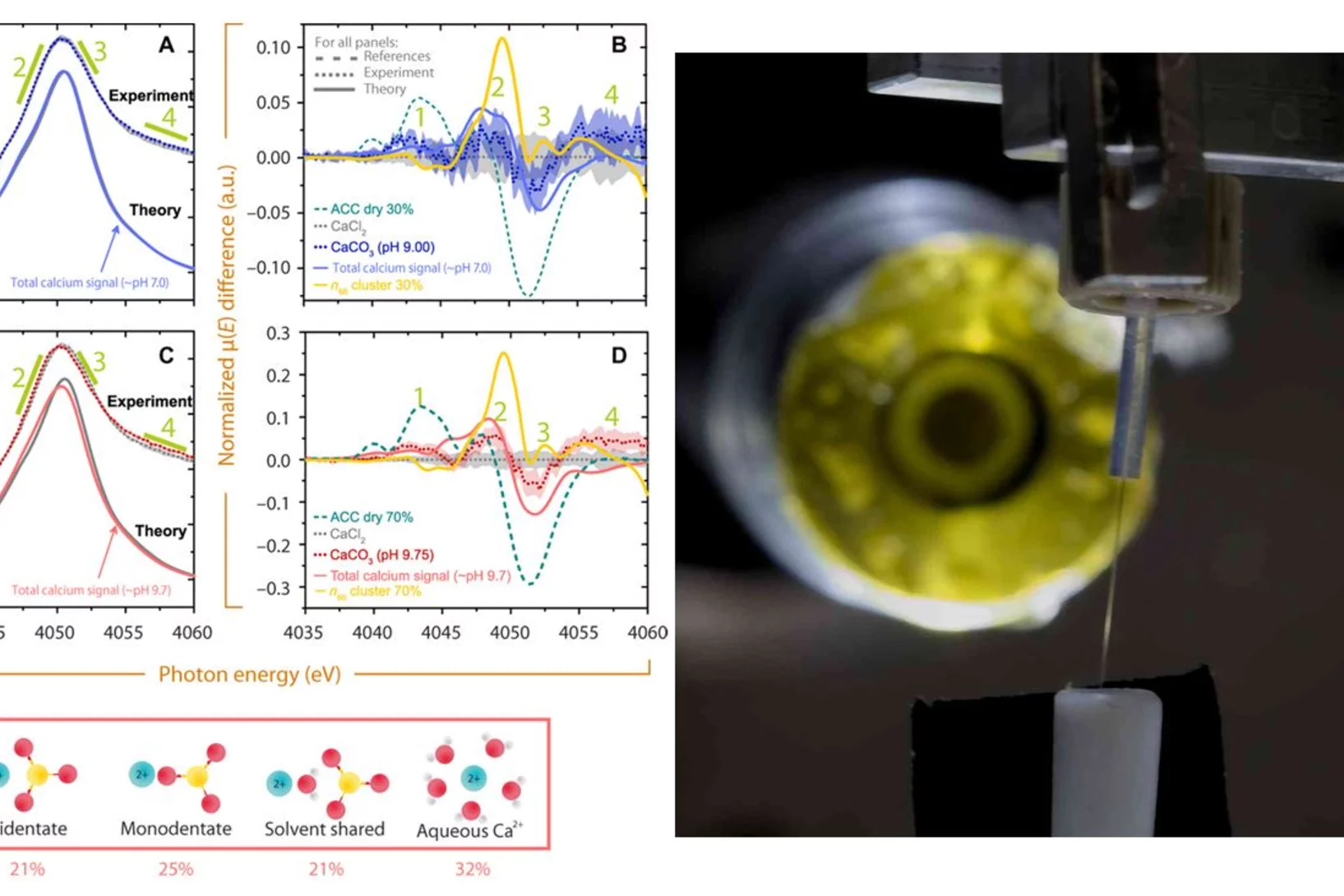
Are supersaturated calcium carbonate solutions classical or non-classical ?
Classical theory predicts that supersaturated carbonate solutions consist mostly of ions and ion pairs, with a small number of larger clusters present in the solution. The population of the different sized clusters in a solution is solely defined by the cluster’s size dependent Free Energy. If clusters are large enough they serve as nucleation germs for a new solid phase. The nucleation occurs once the surface free energy barrier posed by the new solid-liquid interface is overcome by the free energy win from bulk phase growth.
Unravelling structure sensitivity in CO2 hydrogenation over nickel
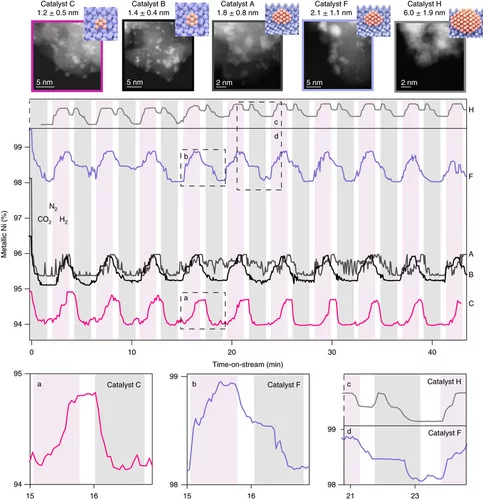
Using a unique set of well-defined silica-supported Ni nanoclusters (1–7 nm) and advanced characterization methods it was proved how structure sensitivity influences the mechanism of catalytic CO2 reduction, the nature of which has been long debated.
First Pilot Experiment at SwissFEL-Alvra: UV photo-induced charge transfer in OLED system
On the 17th of December 2017 SwissFEL saw its first pilot experiment in the Alvra experimental station of the SwissFEL ARAMIS beamline.
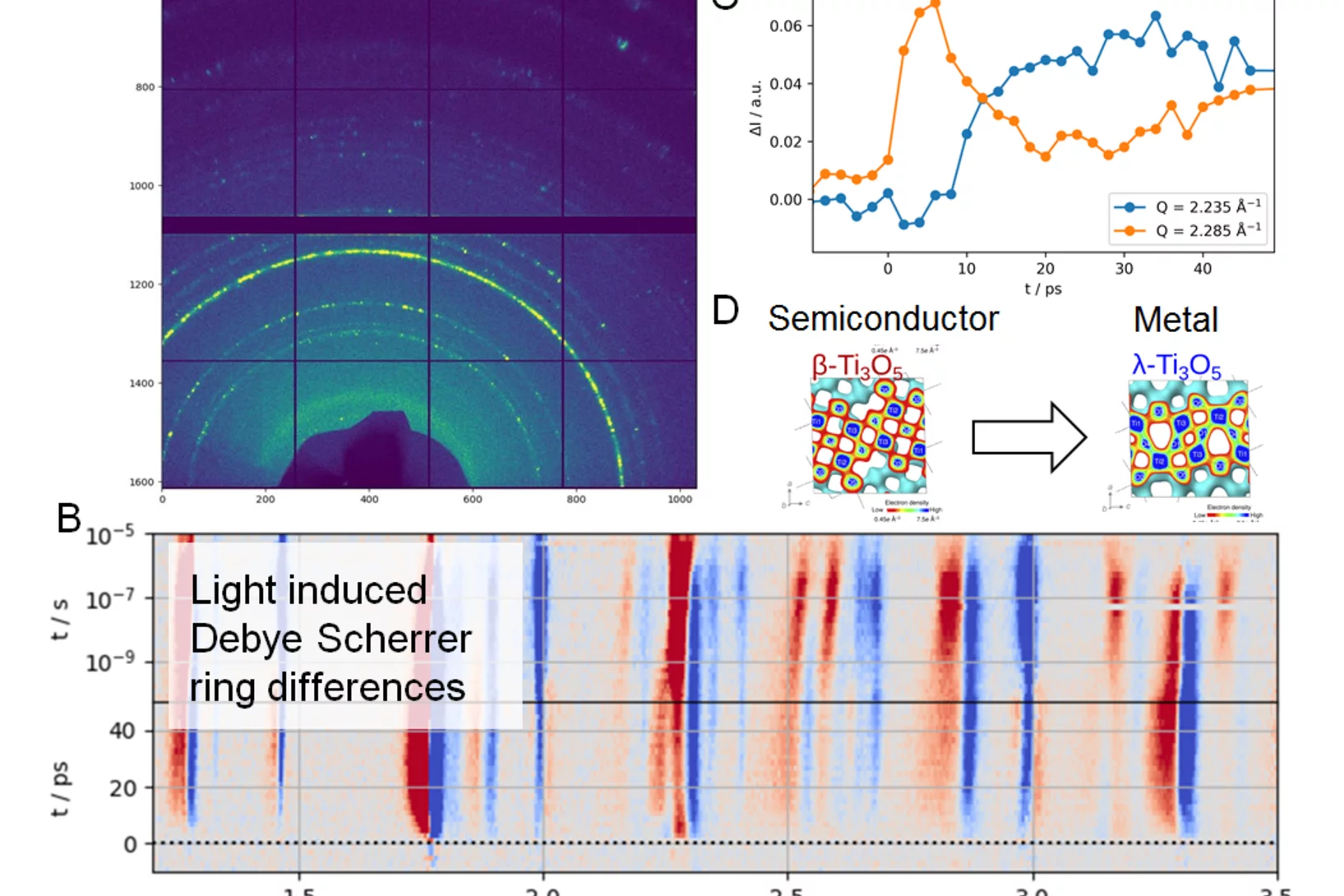
First time resolved Pilot Experiment by SwissFEL: Semiconductor to metal transition in Ti3O5 nanocrystals
On the 30th of November 2017 SwissFEL saw its first time resolved pilot experiment in the Bernina experimental station of the SwissFEL ARAMIS beamline. A team of scientists from the University of Rennes, ESRF and PSI, led by Marco Cammarata (Univ. Rennes) and Henrik Lemke (PSI), successfully started the experimental phase at SwissFEL.
Extreme Ultraviolet Vortices at Free Electron Lasers
PSI scientists have developed tailored diffractive X-ray optics for a free electron laser that induces an optical vortex in extreme ultraviolet radiation. The experiment facilitates the first demonstration of orbital angular momentum in radiation created by a free electron laser in the extreme ultraviolet regime, with an extraordinary clean and defined wavefront. In a collaborative effort with researchers from the FERMI free electron laser in Trieste, Italy and from the University of Nova Gorica in Slovenia, the wavefront of the intense beams carrying an orbtial angular momentum was characterized. Furthermore, a method to characterize the footprint of a focused beam from a free electron laser was refined based on ablation imprints in polymers and subsequent treatment with organic solvents. In this way, the sensitivity of the imprint method could be enhanced to a dynamic range of three orders of magnitude in a single shot.
PSI-Spin-off GratXray
gewinnt Swiss Technology Award 2017
Ein Spin-off aus dem PSI hat den diesjährigen Swiss Technology Award erhalten: Das junge Unternehmen “GratXray” entwickelt eine neue Methode zur Früherkennung von Brustkrebs.
How ‘super-microscopes’ are changing the face of European science
13 November 2017 – Brussels – 16 organisations representing 19 light sources facilities across Europe gathered to launch the LEAPS initiative and signed an agreement to strengthen their collaboration, in the presence of Robert-Jan Smits, Director General for Research and Innovation (RTD) at the European Commission, and Giorgio Rossi, Chair of the European Strategy Forum on Research Infrastructures (ESFRI).
Magnetic structures take a new turn
The unexpected finding that in an ‘artificial spin ice’ magnetostatic energy can be transformed into directed rotation of magnetization provides fresh insights into such nano-patterned magnetic structures — and might enable novel applications in nanoscale devices.
First light in SwissFEL Experimental Station Bernina
Friday, October 20th, 2017, we brought the first light (wavelength 1.2 nm) into the experimental hutch of Bernina. The beam passed the Alvra endstation, went through the diagnostic devices and hit the diagnostic screen in front of the refocussing KB-system of Bernina. The upper picture shows the pink beam on the last diagnostic screen of the beamline. The lower left at the entrance of Bernina-hutch, 133 m downstream of the undulator. The lower right picture shows the beam centered in the alignment iris in front of the KB-system.
Time- and spatially-resolved magnetization dynamics driven by spin-orbit torques
Current-induced spin-orbit torques hold a great potential for manipulation of magnetization at ultrafast timescales. Researchers at ETH Zürich have demonstrated, using time-resolved STXM imaging at the Swiss Light Source, the influence of spin-orbit torques on the switching behaviour of Pt/Co/AlOx nanostructured elements.
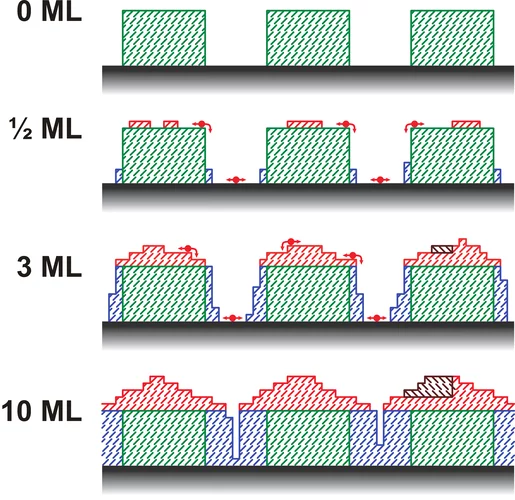
Making the world go round - a look into the structure of a prominent heterogeneous catalyst
Fluid catalytic cracking catalysts, which are composite particles of hierarchical porosity, were examined using ptychographic X-ray tomography. These particles are essential to the conversion of crude oil into gasoline. Examination of catalysts at decreasing levels of catalytic conversion efficacy allowed the detection of possible deactivation causes.
Highly Crystalline C8-BTBT Thin-Film Transistors by Lateral Homo-Epitaxial Growth on Printed Templates
Highly crystalline thin films of organic semiconductors offer great potential for high-performance, low-cost flexible electronics. Researchers at IMEC Belgium have developed a new double-step thin film fabrication process that offers higher performance devices. Soft X-ray spectro-microscopy at the Swiss Light Source was used to prove that the increased performance comes from larger areas of material sharing the same molecular orientation.