Duration: 2002-2004
Contact: Rolf Siegwolf,
Contact: Rolf Siegwolf,
Scope of project
- Quantification of the carbon fluxes with its driving variables and its components on the microscale
- Partitioning of the net ecosystem exchange rates on the ecosystem scale using the stable carbon and oxygen isotopes
- Characterization of the two ecosystem types under investigation (intensively used and abandoned grassland) with respect to their carbon and water vapor fluxes.
Changes in the NEE however, cannot be fully analyzed with this number alone. For the assessment of the variation in net carbon exchange due to an increase or decrease in the respiratory losses or carbon uptake rates, it is essential to quantify the carbon flux components. In an undisturbed ecosystem both carbon related key processes are in equilibrium. In the past five to ten years however, a decoupling of these two processes has globally been observed. So far the causes and possible consequences were not fully understood. Each of these CO2 flux components of the ecosystem has its specific isotopic signature. In analyzing the stable isotope ratios (13C/12C and 18O/16O) in the CO2 from the canopy, the atmosphere above the canopy, and the released CO2 from the soil (soil respiration), the ecosystem CO2 flux could be partitioned. Thus, in combination with the EC method, the sink and source strength of the different flux compartments could be quantified.
Field campaigns
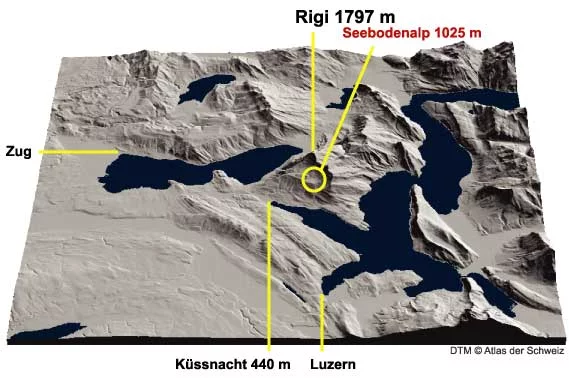
The experimental intensive studies took place on the Swiss study site in Seebodenalp. This site is located at the northwestern slope of Rigi, near Küssnacht, Canton Schwyz, close to a station of the Swiss Network for Air Pollution Monitoring (NABEL), where measurements have been made for more than ten years. Seebodenalp has an elevation of 1025 m asl, is relatively flat with a fetch of some 300 m in the main wind direction, and is well exposed towards westerly winds. It is easily accessible for maintenance and inspection. The Swiss site was equipped with standard Eddy Covariance instruments, i.e. a Solent Gill research ultrasonic anemometer and a LiCor 7500 open-path infrared gas analyzer. A full set of micrometeorological measurements complemented the EC measurements.
The isotope studies (EcF) were also carried out to a reduced extent on the other sites in Austria, Germany and Italy (spring, summer, and fall).
The isotope studies (EcF) were also carried out to a reduced extent on the other sites in Austria, Germany and Italy (spring, summer, and fall).
Funding
CARBOMONT was a joint project of the University of Innsbruck, Austria, the University of Bayreuth, Germany, the University of Tuscia, and the Centro di Ecologia Alpina, Trento, Italy, the Natural Environment Research Council, United Kingdom, the Centre for Geobiosphere Studies, Lund, Sweden, the University of Helsinki, Finland, the Foundation Centre for Environmental Studies of the Mediterranean, and the Paul Scherrer Institute, Switzerland.
CARBOMONT was funded by the European Commission under Framework Programme 5, Environment and Climate, Contract EVK2-CT2001-00125. PSI'S contribution was supported by the Swiss Federal Office for Education and Science, Grant 01.0319-1.
CARBOMONT was funded by the European Commission under Framework Programme 5, Environment and Climate, Contract EVK2-CT2001-00125. PSI'S contribution was supported by the Swiss Federal Office for Education and Science, Grant 01.0319-1.
Link
Publications
Journal Articles
Stakeholder Perceptions of the Impacts of Rural Funding Scenarios on Mountain Landscapes Across Europe.Bayfield, N., P. Barancok, M. Furger, M. Sebastià, G. Domínguez, M. Lapka, E. Cudlinova, L. Vescovo, D. Ganielle, A. Cernusca, U. Tappeiner, and M. Drösler, 2008
Ecosystems, 11, 1368-1382.
DOI: 10.1007/s10021-008-9197-1
Partitioning European grassland net ecosystem CO2 exchange into gross primary productivity and ecosystem respiration using light response function analysis.
Gilmanov, T. G., J. E. Soussana, L. Aires, V. Allard, C. Ammann, M. Balzarolo, Z. Barcza, C. Bernhofer, C. L. Campbell, A. Cernusca, A. Cescatti, J. Clifton-Brown, B. O. M. Dirks, S. Dore, W. Eugster, J. Fuhrer, C. Gimeno, T. Gruenwald, L. Haszpra, A. Hensen, A. Ibrom, A. F. G. Jacobs, M. B. Jones, G. Lanigan, T. Laurila, A. Lohila, G. Manca, B. Marcolla, Z. Nagy, K. Pilegaard, K. Pinter, C. Pio, A. Raschi, N. Rogiers, M. J. Sanz, P. Stefani, M. Sutton, Z. Tuba, R. Valentini, M. L. Williams, and G. Wohlfahrt, 2007
Agriculture Ecosystems & Environment, 121, 93-120.
DOI: 10.1016/j.agee.2006.12.008
Impact of past and present land-management on the C-balance of a grassland in the Swiss Alps.
Rogiers, N., F. Conen, M. Furger, R. Stöckli, and W. Eugster, 2008
Glob. Change Biol., 14, 2613-2625
DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2486.2008.01680.x
Effect of land management on ecosystem carbon fluxes at a subalpine grassland site in the Swiss Alps.
Rogiers, N., W. Eugster, M. Furger, and R. Siegwolf, 2005
Theor. Appl. Climatol., 80, 187-203
DOI: 10.1007/s00704-004-0099-7
Biotic, Abiotic, and Management Controls on the Net Ecosystem CO2 Exchange of European Mountain Grassland Ecosystems.
Wohlfahrt, G., M. Anderson-Dunn, M. Bahn, M. Balzarolo, F. Berninger, C. Campbell, A. Carrara, A. Cescatti, T. Christensen, S. Dore, W. Eugster, T. Friborg, M. Furger, D. Gianelle, C. Gimeno, K. Hargreaves, P. Hari, A. Haslwanter, T. Johansson, B. Marcolla, C. Milford, Z. Nagy, E. Nemitz, N. Rogiers, M. Sanz, R. Siegwolf, S. Susiluoto, M. Sutton, Z. Tuba, F. Ugolini, R. Valentini, R. Zorer, and A. Cernusca, 2008
Ecosystems, 11, 1338-1351
DOI: 10.1007/s10021-008-9196-2
Theses
Impact of site history and land-management on CO2 fluxes at a grassland in the Swiss Pre-Alps.Rogiers, N., 2005.
PhD Thesis, Institute of Geography, University of Bern, Switzerland, Bern, 175 pp.