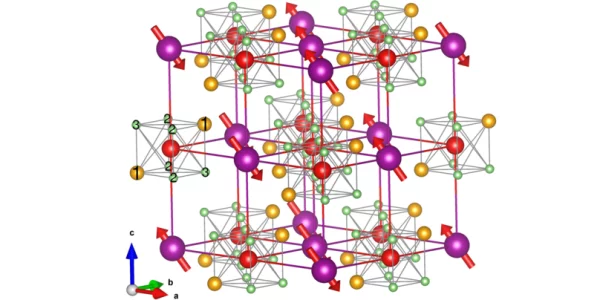
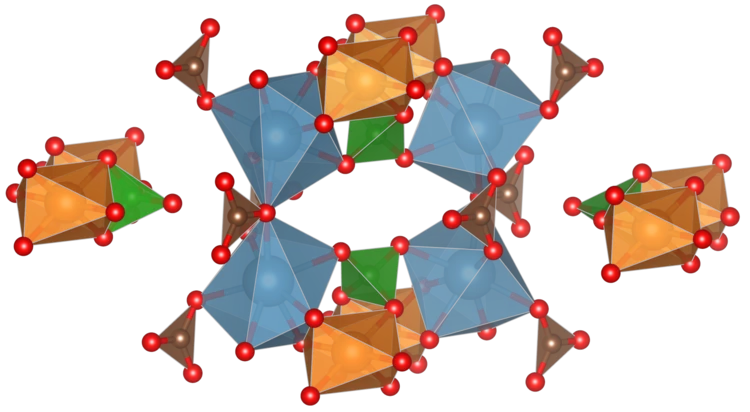
Mapping the ecosystem of Wannier Functions software
A new review article, just published in Reviews of Modern Physics and highlighted on the journal cover, provides a map to the vast landscape of software codes that allow researchers to calculate Wannier functions, and to use them for materials properties predictions. The authors, from all over Europe and the USA, include two PSI scientists. After providing readers with the theoretical foundations on Wannier functions and their calculation, together with intuitive graphical schematics to explain what Wannier functions are, the authors map the existing Wannier codes and the key applications.
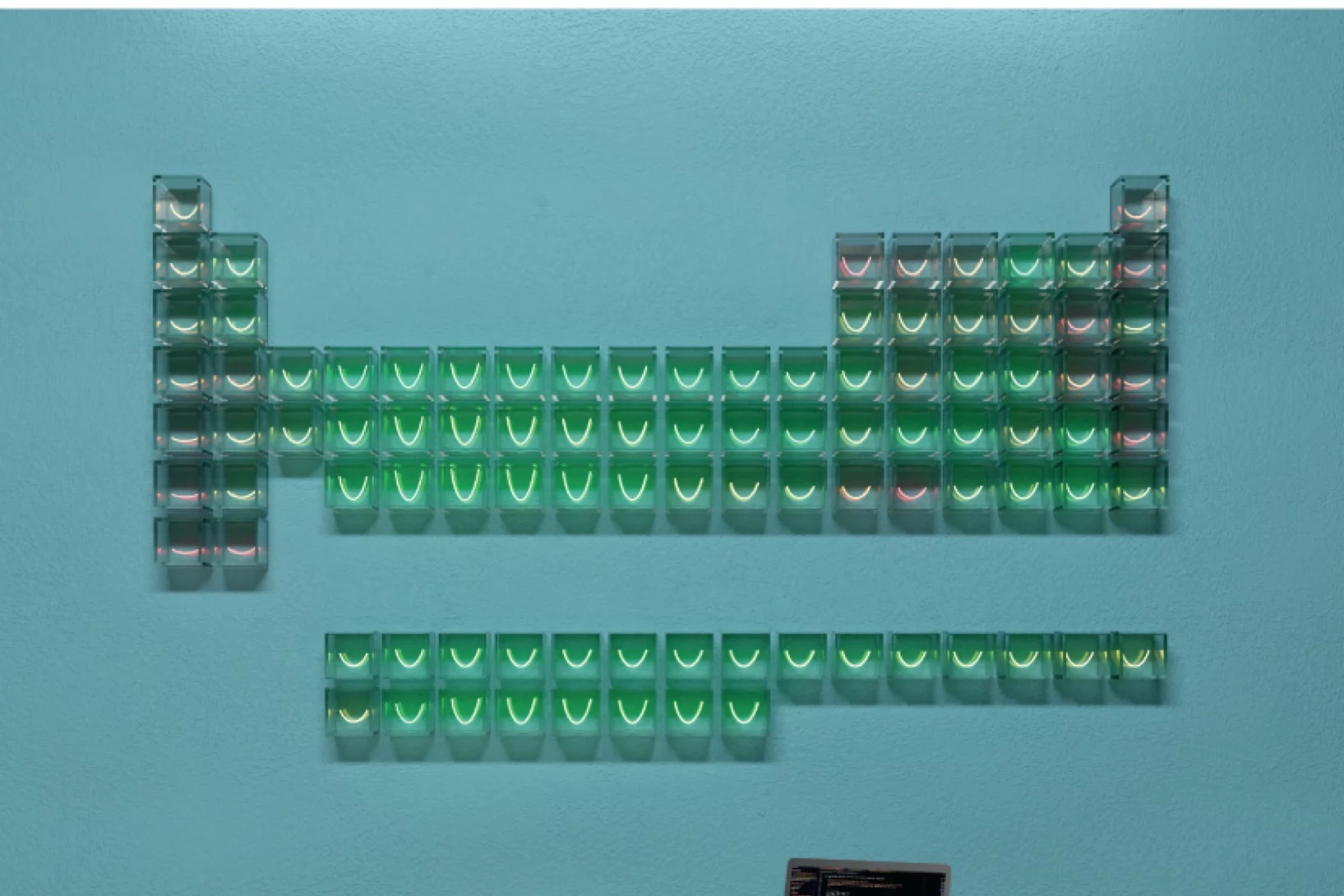
New widgets and extensions expand the OSSCAR platform for educational notebooks in materials science
In a new article published in Computer Physics Communications, the team of the Open Software Services for Classrooms and Research project (OSSCAR) describes how to create custom widgets and extensions that can be used in interactive notebooks to teach computational materials science. The article also introduces two new entries in OSSCAR: a widget to display an interactive periodic table that allows users to group elements into different states, and one to plot and visualize electronic band structures and density of states.
Computational marathon matches the efficiency of the AiiDA platform with the power of Switzerland Alps supercomputer
A group of researchers from the LMS lab at PSI has conducted a "hero run" on the new Swiss supercomputer, occupying it entirely for about 20 hours with calculations managed remotely by the AiiDA software tools. The run demonstrated the efficiency and stability of AiiDA, that could seamlessly fill the entire capacity of an exascale machine, as well as the performance of the Alps supercomputer, that has been just inaugurated. All the results will soon be published on the Materials Cloud.
International collaboration lays the foundation for future AI for materials via the OPTIMADE standard
Artificial intelligence (AI) is accelerating the development of new materials. A prerequisite for AI in materials research is large-scale use and exchange of data on materials, which is facilitated by a broad international standard. A major international collaboration including researchers from the LMS laboratory now presents an extended version of the OPTIMADE standard.
Eine mögliche Abkürzung
Maschinelles Lernen und künstliche Intelligenz gehören heute zum Handwerkszeug der meisten Forschenden am PSI. Diese Methoden verändern die Wissenschaft teilweise grundlegend.
"Magnetostriction-Driven Muon Localization in an Antiferromagnetic Oxide" published in Phys. Rev. Lett.
A study involving PSI scientists from the LMS lab, and just published in Physical Review Letters has found that in manganese oxide, a textbook antiferromagnetic material, the site of an implanted spin-polarized muon is not well identified, but can change due to a previously neglected effect: magnetostriction.
LMS paper featured on the cover of Nature Reviews Physics
Our paper "How to verify the precision of density-functional-theory implementations via reproducible and universal workflows" was featured on the January 2024 cover of the journal Nature Reviews Physics!
New post-doc position on high-throughput discovery in the MSD group
A new post-doc opportunity is open to join the MSD group to set up and maintain large scale materials discovery projects based on the workflow engine AiiDA.
These positions are funded by NCCR MARVEL, offering close collaboration opportunities with project partners such as the Swiss Supercomputer Center CSCS, and other institutions in Switzerland and Europe.
Deadline: December 10, 2023
New Nat. Rev. Phys. publication: A “gold standard” for computational materials science codes
A large consortium of scientists, coordinated by PSI researchers in the LMS laboratory, led the most comprehensive verification effort so far on computer codes for materials simulations, providing their colleagues with a reference dataset and a set of guidelines for assessing and improving existing and future codes.