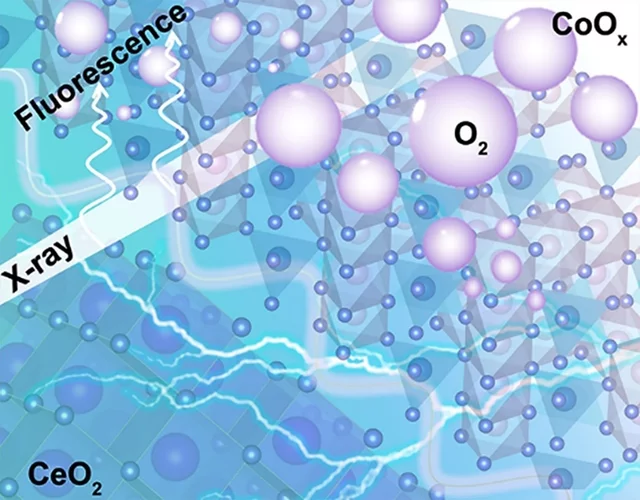
Insights into the superior oxygen evolution reaction activity of CoOx/CeO2 composite electrocatalyst
CeO2 significantly enhances the oxygen evolution reaction (OER) activity of CoOx, although the mechanism behind this synergy is still unclear. Here, operando hard X-ray absorption spectroscopy (hXAS) is applied to monitor the Co-K edge and Ce L3 edge in CoOx/CeO2 to shed light on the evolution of Co and Ce oxidation states during OER. In addition, ex situ soft XAS (sXAS) characterizations provide information on the irreversible surface-specific transformations of the Co L3 edge as well as the O K edge.
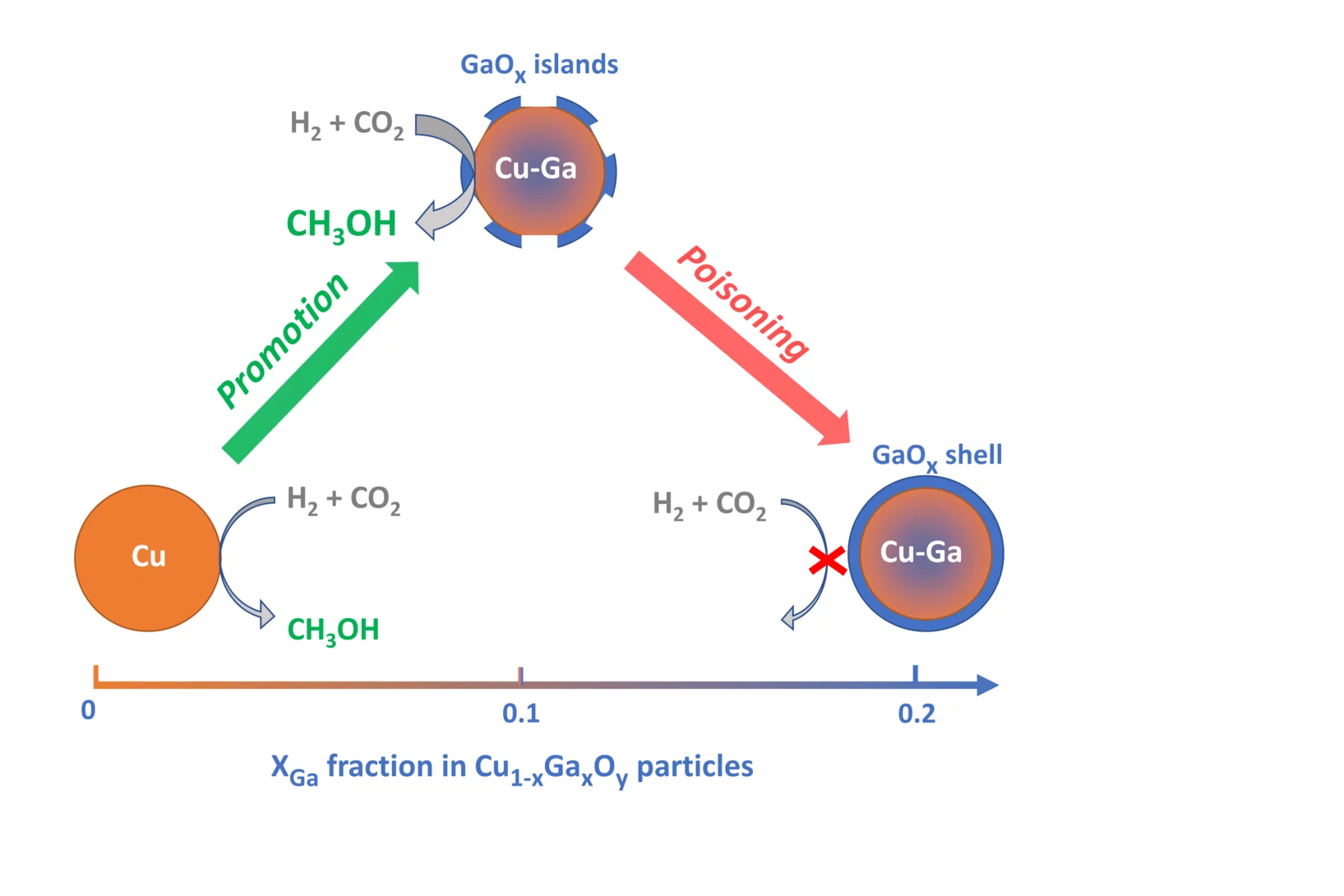
Promotion versus Poisoning in Copper–Gallium-Based CO2-to-Methanol Hydrogenation Catalysts
Cu–Ga-based CO2-to-methanol hydrogenation catalysts display a range of catalytic performance, depending on their preparation. Here, we investigated how the Ga/Cu ratio and Ga speciation affect the catalytic activity. Using surface organometallic chemistry, we prepared a series of silica-supported 3–6 nm Cu1–xGaxOy nanoparticles with a range of xGa. The materials display a volcano-type activity behavior, where methanol formation is promoted when xGa < 0.13–0.18 and is suppressed at higher values, indicating a poisoning of the catalysts. In situ X-ray absorption spectroscopy and in situ infrared spectroscopy helped to understand the structure-activity relationship.
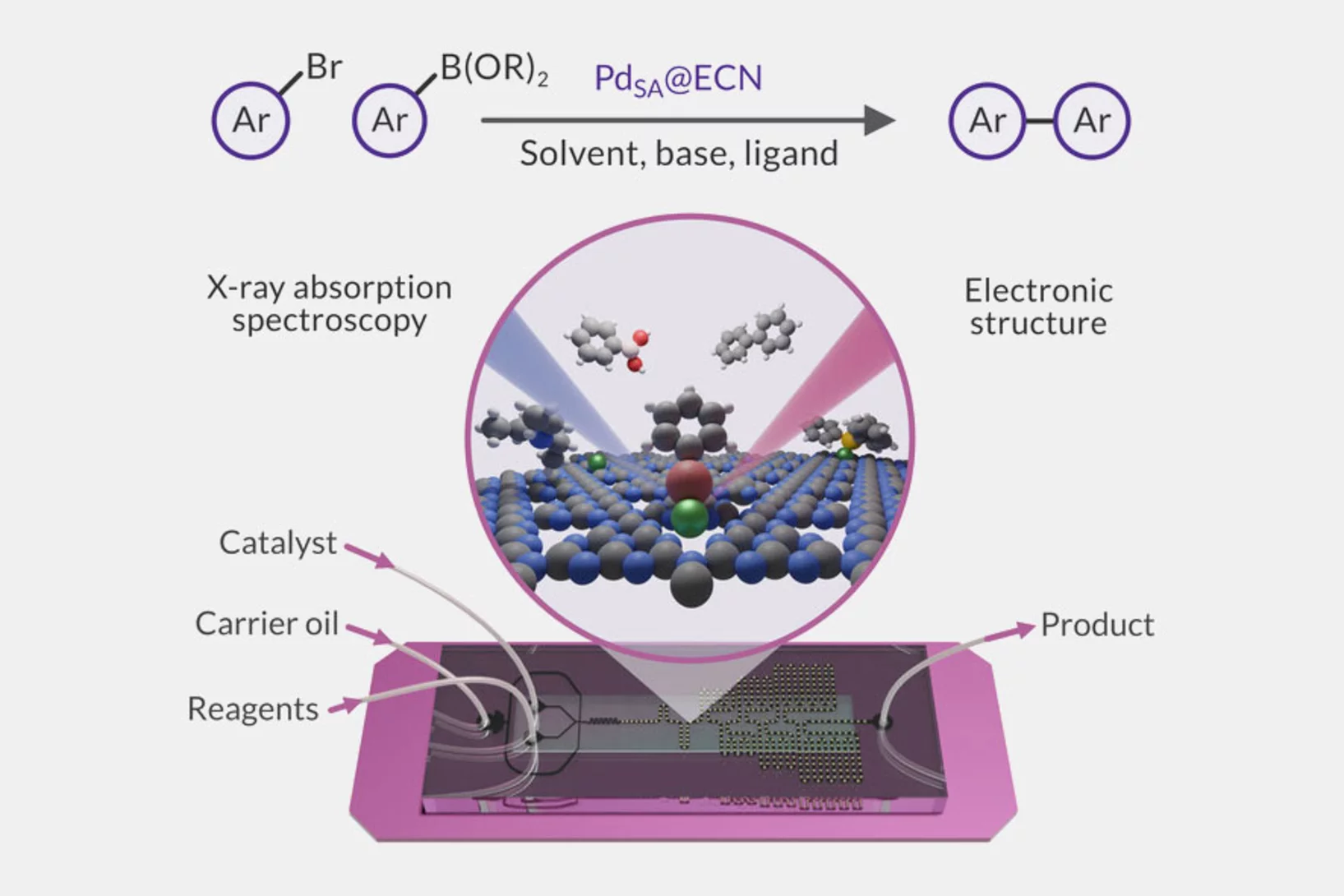
Microfluidic platform for in situ characterization of heterogenous catalysts
A deep understanding of active site architectures during surface-catalyzed reactions is a crucial step for the design of recyclable heterogeneous catalysts for organic synthesis. In this work, a droplet-based microfluidic setup was developed and applied to perform Suzuki-Miyaura coupling over heterogenous single-atom Pd-catalyst.
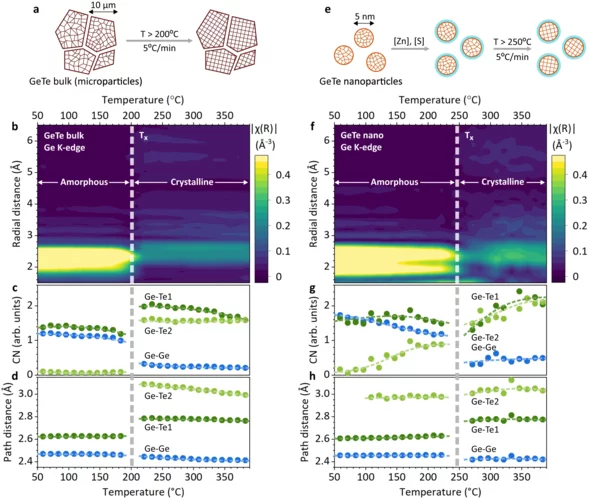
Unravelling the amorphous structure and crystallization mechanism of GeTe phase change memory materials
Here we use in-situ high-temperature x-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS) and theoretical calculations to quantify the amorphous structure of bulk and nanoscale GeTe. Based on XAS experiments, we develop a theoretical model of the amorphous GeTe structure, consisting of a disordered fcc-type Te sublattice and randomly arranged chains of Ge atoms in a tetrahedral coordination.
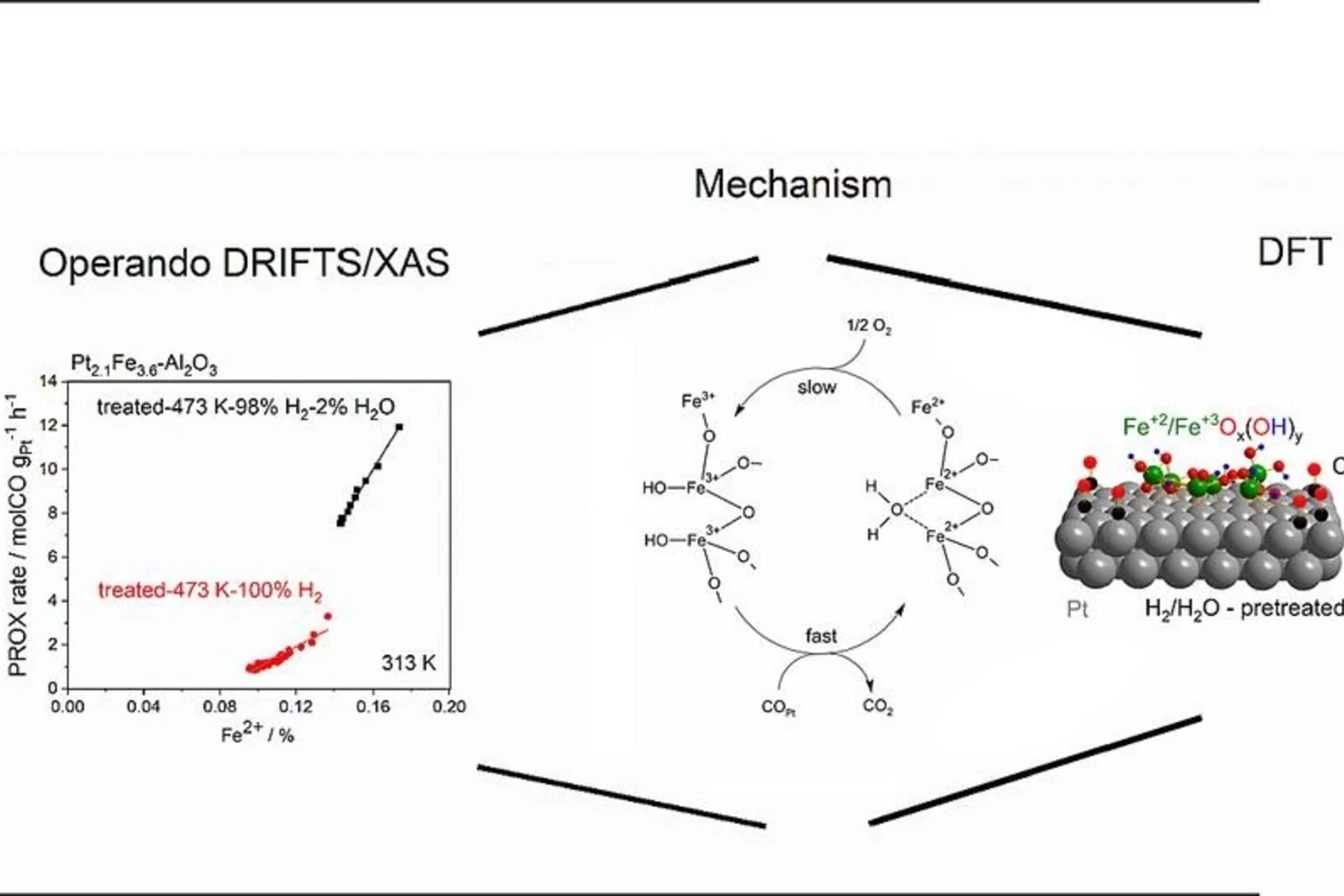
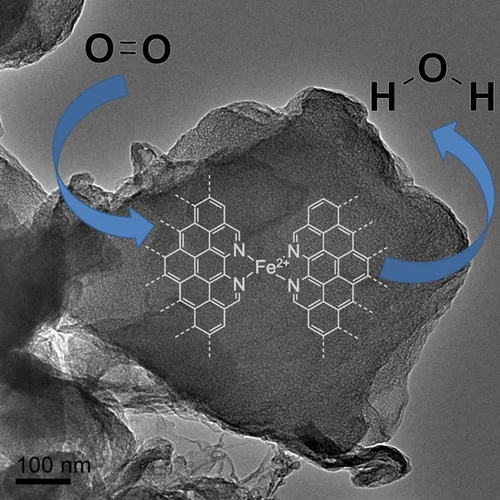
Water-assisted generation of catalytic interface: The case of interfacial Pt-FeOx(OH)y sites active in preferential carbon monoxide oxidation
Pt-FeOx(OH)y interface with enhanced activity for PROX is generated via strong metal-support interaction. Increase in the degree of hydroxylation of Pt-FeOx(OH)y interface enhances the rate of PROX mediated by active Fe2+ species.
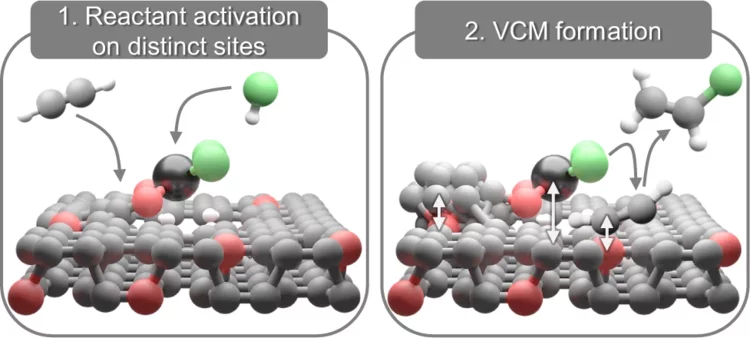
Evidence of bifunctionality of carbons and metal atoms in catalyzed acetylene hydrochlorination
Carbon supports are ubiquitous components of heterogeneous catalysts for acetylene hydrochlorination to vinyl chloride, from commercial mercury-based systems to more sustainable metal single-atom alternatives. Their potential co-catalytic role has long been postulated but never unequivocally demonstrated. Herein, combining operando X-ray absorption spectroscopy with other spectroscopic and kinetic analyses, we evidence the bifunctionality of carbons and metal sites (Pt, Au, Ru) in the acetylene hydrochlorination catalytic cycle.
Deciphering the Mechanism of Crystallization of UiO-66 Metal-Organic Framework
Zirconium-containing metal-organic framework (MOF) with UiO-66 topology is an extremely versatile material, which finds applications beyond gas separation and catalysis. By means of in situ time-resolved high-resolution mass spectrometry, Zr K-edge X-ray absorption spectroscopy, magic-angle spinning nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy, and X-ray diffraction it is showed that the nucleation of UiO-66 occurs via a solution-mediated hydrolysis of zirconium chloroterephthalates, whose formation appears to be autocatalytic.
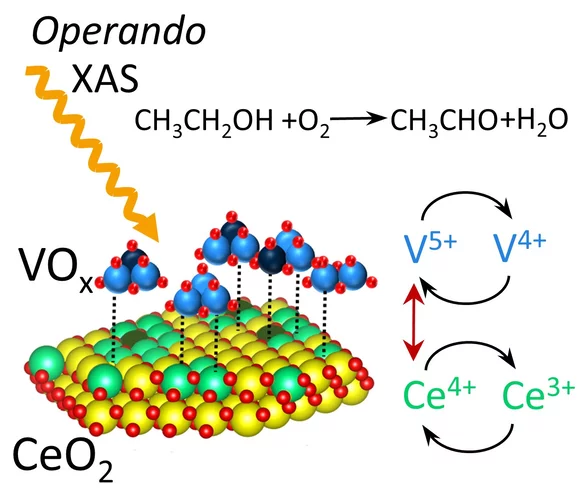
Activity Trend Origin of Ethanol Oxidative Dehydrogenation over VOx/CeO2
Using operando time-resolved X-ray absorption spectroscopy, we investigated the origin of volcano-shaped ethanol oxidative dehydrogenation activity trend of VOx/CeO2 catalysts as a function of VOx surface coverage. Vanadium and cerium synergistically change their oxidation states during the catalytic cycle. The catalytic activity correlates with the concentration of reversible Ce4+/3+species.
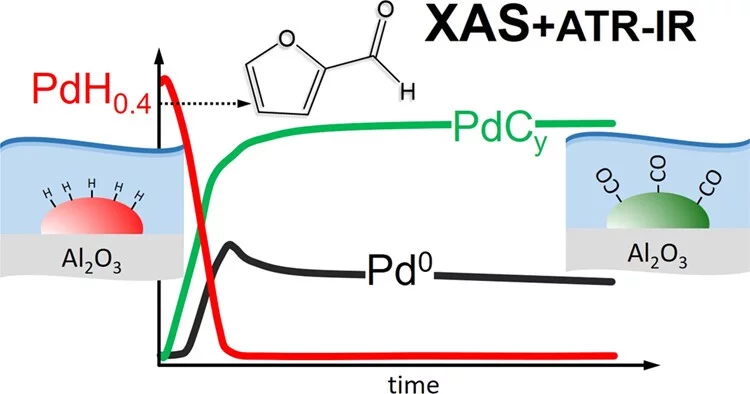
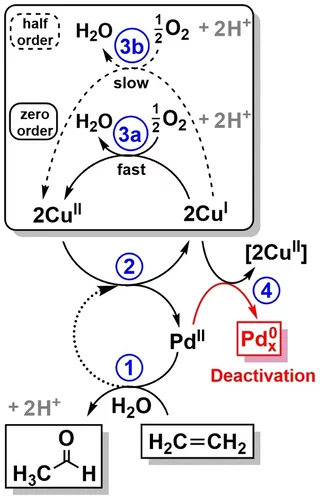
Preparation, Quantification, and Reaction of Pd Hydrides on Pd/Al2O3 in Liquid Environment
The ability to study in situ the formation and consumption of Pd hydrides (PdH) in liquid environments is a significant challenge hampering a deeper understanding of catalyzed liquid-phase hydrogenation reactions. Here, using quick scanning X-ray absorption spectroscopy (QEXAFS), we present a detailed kinetic study of Pd hydride formation and reactivity on Pd/Al2O3 in 2-propanol solvent.
Spectroscopy vs. Electrochemistry: Catalyst Layer Thickness Effects on Operando/In Situ Measurements
Operando/in situ spectro-electrochemical studies often require high loadings and thick catalyst layers (CLs) leading to large ion- and mass-transport limitations. In this study we investigate PdH-formation in two Pd-catalysts with similar surface areas but drastically different morphologies. Our results unveil that the CL-thickness largely determines the PdH formation trends calling for the minimization of the CL-thickness in such experiments.
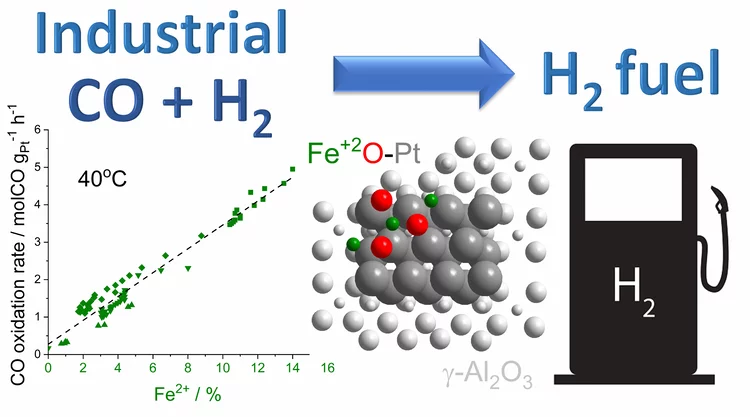
Platinum-Iron(II) Oxide Sites Directly Responsible for Preferential Carbon Monoxide Oxidation at Ambient Temperature: An Operando X-ray Absorption Spectroscopy Study
Operando X-ray absorption spectroscopy revealed a linear correlation between the amount of oxidic Fe2+ and the ambient temperature activity of Pt−FeOx preferential carbon monoxide oxidation catalysts. The hydrogen prereduction temperature and pressure determines the amount of active Fe2+ sites for alumina- and silica-supported Pt−Fe catalysts. Catalyst deactivation is linked with the oxidation of these sites.
Quantifying Photoinduced Polaronic and Thermal Distortions in Inorganic Lead Halide Perovskite Nanocrystals
The development of next-generation perovskite-based optoelectronic devices relies critically on the understanding of the interaction between charge carriers and the polar lattice in out-of-equilibrium conditions. While it has become increasingly evident for CsPbBr3 perovskites that the Pb–Br framework flexibility plays a key role in their light-activated functionality, the corresponding local structural rearrangement has not yet been unambiguously identified. In this work the photoinduced lattice changes were investigated using combination of time-resolved and temperature-dependent studies at Br K and Pb L3 X-ray absorption edges and ab initio simulations.
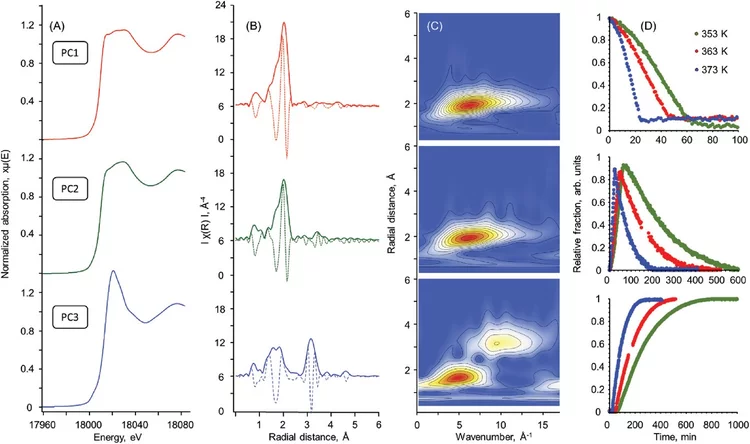
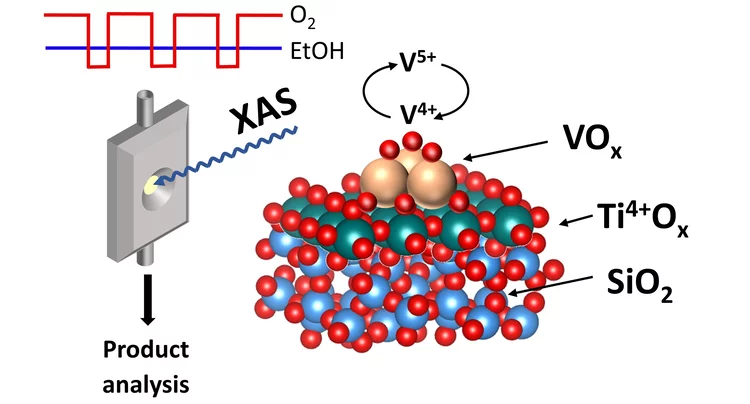
Redox Dynamics of Active VOx Sites Promoted by TiOx during Oxidative Dehydrogenation of Ethanol Detected by Operando Quick XAS
Operando time-resolved V and Ti K-edge X-ray absorption near-edge spectroscopy, coupled with a transient experimental strategy, quantitatively showed that the formation of acetaldehyde over 5% V2O5/15% TiO2/SiO2 is kinetically coupled to the formation of a V4+ intermediate, while the formation of V3+ is delayed and 10–70 times slower. The low-coordinated nature of various redox states of VOx species (V5+, V4+, and V3+) in the 5% V2O5/15% TiO2/SiO2 catalyst is confirmed using the extensive database of V K-edge XANES spectra of standards and specially synthesized molecular crystals.
Exploring the role of structural distortions to obtain Cu photosensitizer with thousand times longer excited state lifetime
Cu diimine complexes present a noble metal free alternative to classical Ru, Re, Ir and Pt based photosensitizers in solution photochemistry, photoelectrochemical or dye-sensitized solar cells. Optimization of these dyes requires an understanding of factors governing the key photochemical properties: excited state lifetime and emission quantum yield. Using pump-probe XAS and DFT calculations we have explored the involvement of exciplex formation in the deactivation of the photoexcited state.
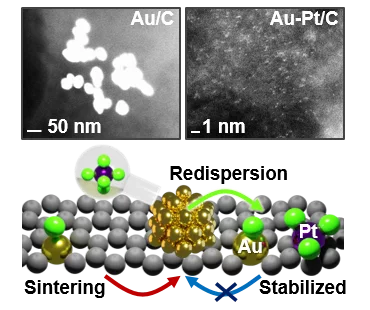
Sustainable Synthesis of Bimetallic Single Atom Gold-Based Catalysts with Enhanced Durability in Acetylene Hydrochlorination
Platinum chloride in aqueous solution promotes the dispersion of large gold nanoparticles (>70 nm) on carbon carriers into single atoms, forming bimetallic single-atom catalysts with improved resistance against sintering at temperatures up to 800 K and under the harsh reductive reaction conditions of acetylene hydrochlorination, leading to improved lifetime in this reaction. To rationalize these observations, this study, led by ETH Zurich, utilized X-ray adsorption spectroscopy conducted at the SuperXAS beamline of the SLS to provide insights into the degree of gold dispersion and the structure of the isolated metal sites in the bimetallic catalysts.
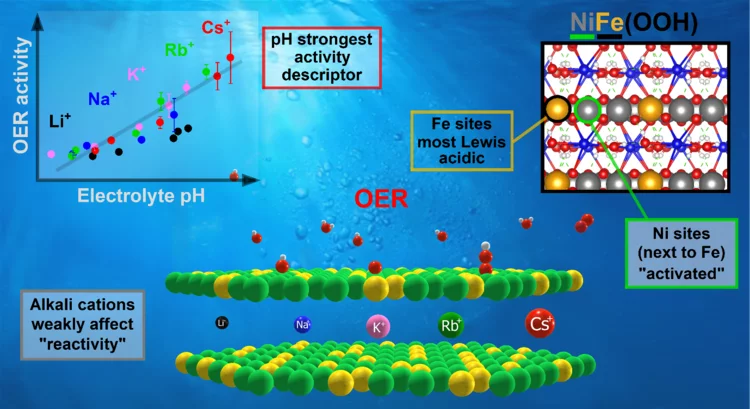
Key activity descriptors of nickel-iron oxygen evolution electrocatalysts in the presence of alkali metal cations
Ni-Fe oxyhydroxide is among the most active oxygen evolution electrocatalysts. Electrolyte alkali metal cations modify the activity and reaction intermediates, however, the exact mechanism is at question due to unexplained deviations from the cation size trend. Our X-ray absorption spectroelectrochemical results show that the OER activity follows the variations in .electrolyte pH rather than a specific cation. Our DFT-based reactivity descriptors confirm the conclusions of an indirect pH effect.
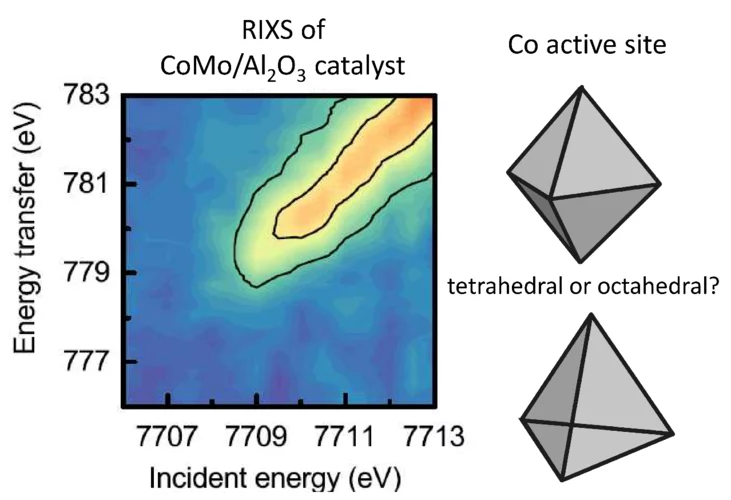
The structure of active sites of CoMo/Al2O3 catalysts determined by RIXS spectroscopy.
A fundamental understanding of the active sites in technical CoMo/ Al2O3 catalysts is crucial to improve the production of clean transportation fuels by hydrodesulfurization (HDS), which removes sulfur from fossil fuels. Sulfur dioxide, resulting from fossil fuel combustion, is one of the main causes for acid rain. In situ X-ray spectroscopic experiments at the SuperXAS beamline of the SLS provided insight in the structure and number of active sites (“Co−Mo−S”) in sulfided CoMo/ Al2O3 catalysts. When the Co to Mo ratio is less than 0.1, cobalt forms isolated sites on the MoS2 phase, where the cobalt promoter atoms are in centrosymmetric octahedral coordination with six-sulfur ligands.
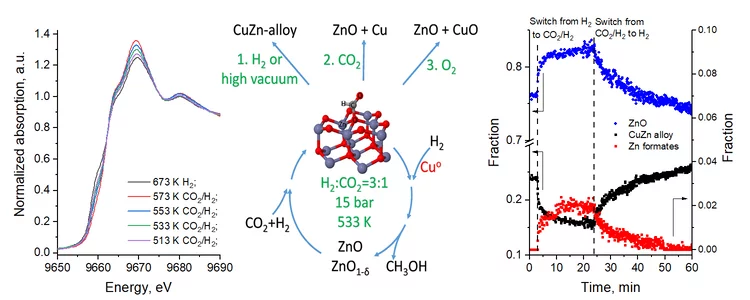
The unique interplay between copper and zinc during catalytic carbon dioxide hydrogenation to methanol
The nature of high activity of Cu/ZnO catalyst in methanol synthesis remains the subject of intensive debate. Here, the authors are revisiting carbon dioxide hydrogenation mechanism using high-pressure operando techniques.
Taking a snapshot of the triplet excited state of an OLED organometallic luminophore using X-rays
In this work, the complementarity of pump-probe experiments at SwissFEL (ALVRA endstation) and at synchrotrons (SuperXAS beamline of SLS and ID09 of ESRF) is used to investigate the triplet excited state of Cu OLED materials. Details about the charge transfer and structural rearrangements in the excited state of this material are revealed and obtained data can be used to verify computational methods for rational development of new OLED materials.
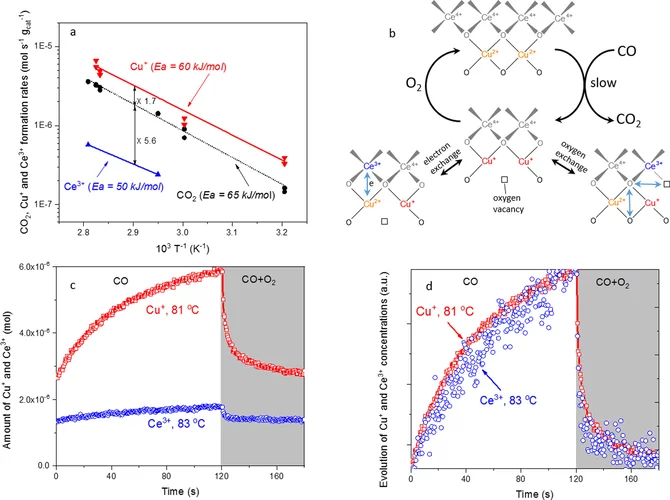
Elucidating the Oxygen Activation Mechanism on Ceria-Supported Copper-Oxo Species Using Time-Resolved X-ray Absorption Spectroscopy
We monitored the dynamic structure of the active sites in a catalyst containing highly dispersed copper-oxo species on ceria during low-temperature CO oxidation using time-resolved X-ray absorption spectroscopy. We quantitatively demonstrate that the CO oxidation mechanism below 90 °C involves an oxygen intermediate strongly bound to the active sites as well as the redox activity of Cu2+/Cu+ and Ce4+/Ce3+ couples.
Elucidating the mechanism of heterogeneous Wacker oxidation over Pd-Cu/zeolite Y by transient XAS
Unlike the homogeneous Wacker process, the understanding of the mechanism of the heterogeneous system has long remained to be superficial. Here the authors investigated the mechanism of heterogeneous Wacker oxidation over Pd-Cu/zeolite Y through transient XAS coupled with kinetic studies and chemometric analysis.
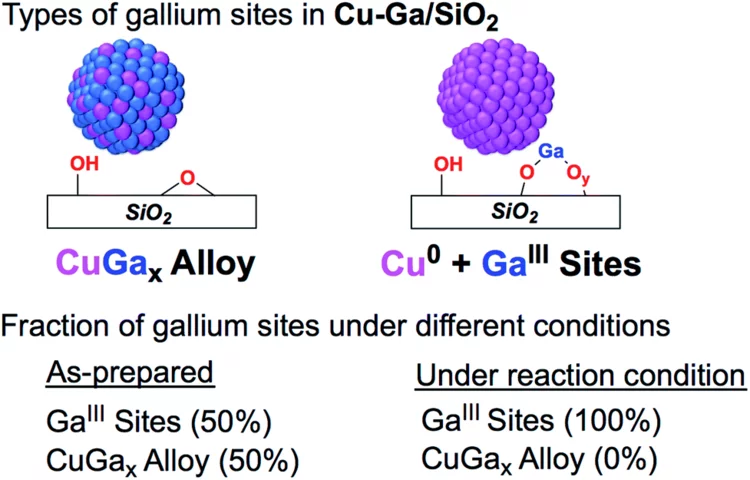
Enhanced CH3OH selectivity in CO2 hydrogenation using Cu-based catalysts generated via SOMC from GaIII single-sites
Small and narrowly distributed nanoparticles of copper alloyed with gallium supported on silica containing residual GaIII sites can be obtained via surface organometallic chemistry. This material is highly active and selective for CO2 hydrogenation to CH3OH. In situ X-ray absorption spectroscopy shows that gallium is oxidized under reaction conditions while copper remains as Cu0.
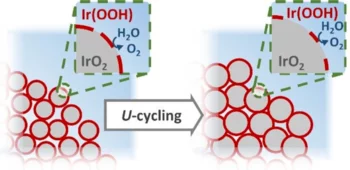
Operando X-ray Characterization of High Surface Area Iridium Oxides to Decouple their Activity Losses for the Oxygen Evolution Reaction
In order to clarify the mechanism behind this activity loss, in this study two high surface area iridium oxides were characterized under operando conditions using a novel setup that allows the quasi-simultaneous acquisition of anomalous small angle X-ray scattering (A-SAXS) and X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS) data.
HERCULES school 2019 at SLS
In the week of April 1-5 PSI welcomes 20 PhD students and postdocs taking part in the European HERCULES 2019 school on Neutron and Synchrotron Radiation. They will attend lectures and perform two days of practical courses at several beam lines of the Swiss Light Source.
Structural selectivity of supported Pd nanoparticles for catalytic NH3 oxidation resolved using combined operando spectroscopy
The link between Pd nanoparticle structure and surface reactivity for NH3 abatement was found using operando X-ray absorption fine structure spectroscopy, diffuse reflectance infrared Fourier-transformed spectroscopy and on-line mass spectrometry.
Fe-Based O2-Reduction Catalysts Synthesized Using Na2CO3 as a Pore-Inducing Agent
This work presents a new approach for synthesizing Fe-based oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) catalysts using sodium carbonate (Na2CO3) as an inexpensive but effective pore-inducing agent offering microporosity control.
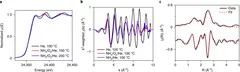
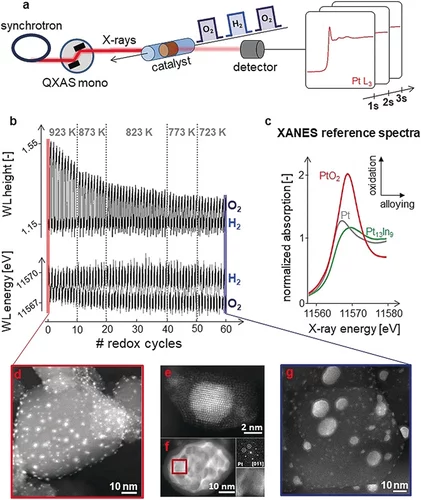
Kinetics of Lifetime Changes in Bimetallic Nanocatalysts Revealed by Quick X‐ray Absorption Spectroscopy
The different reaction steps involved in repeated Pt13In9 segregation‐alloying are identified by XAS and kinetically characterized at the single‐cycle level.
The SLS congratulates Ronald Frahm for receiving the IXAS outstanding achievement Award 2018
The highest award of the international X-ray absorption spectroscopy (IXAS) society, the Edward Stern Outstanding Achievement Award, was presented to Prof. Ronald Frahm during the tri-annual IXAS meeting in Kraków, Poland in July 2018.
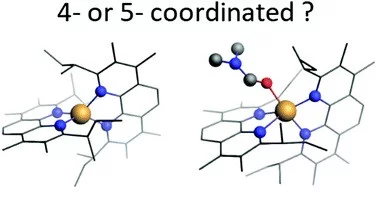
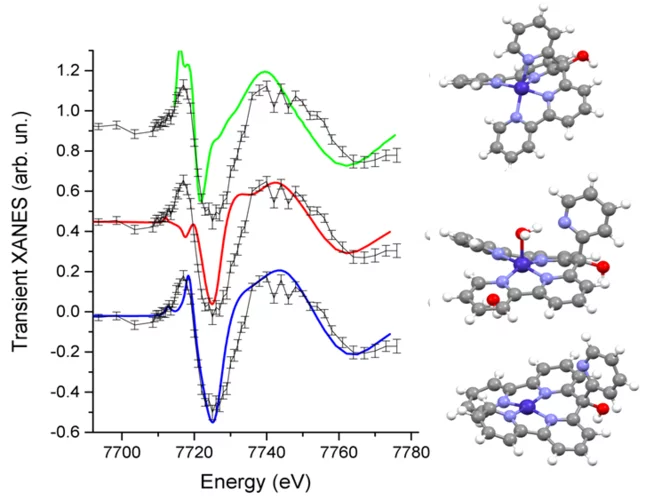
Structure of the Co(I) Intermediate of a Cobalt Pentapyridyl Catalyst for Hydrogen Evolution Revealed by Time‐Resolved X‐ray Spectroscopy
The mechanism of hydrogen evolution by cobalt polypyridyls catalysts is investigated. Pump-probe X‐ray absorption spectra measured at SuperXAS in the microsecond time range indicate that the pendant pyridine dissociates from the cobalt in the intermediate Co(I) state. This opens the possibility for pyridinium to act as an intramolecular proton donor, which can be used for the development of efficient catalysts.
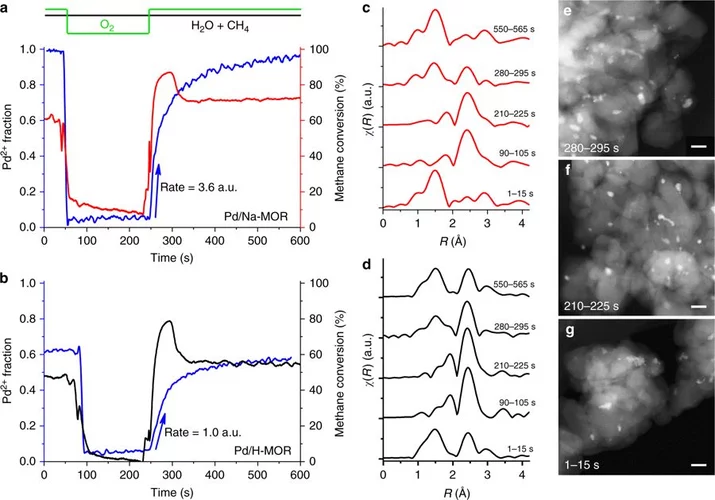
Stable complete methane oxidation over palladium based zeolite catalysts
Using targeted synthesis and in situ characterization a palladium catalyst with improved stability against sintering during methane oxidation was prepared.