Bryan Benz awarded best talk at MNE 2024
Bryan Benz was awarded the conference’s best oral presentation at the 50th International Micro and Nano Engineering Conference (MNE 2024) for his talk entitled “High aspect ratio (1:500) silicon nanowires for force sensing”.
TOMCAT attends XNPIG2024, bags two awards
A TOMCAT delegation attended the 6th International Conference on X-ray and Neutron Phase Imaging with Gratings (XNPIG2024) held on 8-12 April, 2024 in Shenzhen, China. The team delivered a series of two invited talks and seven contributed talks, all of which were well-received by the conference attendees. Two team members were selected for their outstanding contributions: Simon Spindler was awarded one of the Best Poster Prizes for his recent work on “Diffraction Beamlets” while Stefano van Gogh was the co-recipient of the W.H.F. Talbot Award, in recognition of his outstanding PhD thesis.
Jisoo Kim receives PSI Thesis Medal 2023
Jisoo Kim receives the PSI Thesis Medal 2023. With this award, PSI recognises outstanding PhD theses, achieving a high degree of innovation and potentially leading to scientific breakthroughs. Jisoo holds a Master of Science from the Korean Advanced Institute of Science &Technology and defended his thesis entitled “Towards time-resolved X-ray scattering tensor tomography” at ETH Zürich.
Jisoo Kim bags the 2022 Werner Meyer-Ilse Award
Jisoo Kim was awarded the 2022 Werner Meyer-Ilse Memorial Award. The WMI Award is given to young scientists for exceptional contributions to the advancement of X-ray microscopy through either outstanding technical developments or applications, as evidenced by their presentation at the International Conference on X-ray Microscopy and supporting publications. Jisoo was awarded for his development of the method "Time-resolved x-ray scattering tomography for rheological studies", and is co-recipient of the award with Yanqi Luo from the Advanced Photons Source for her work on applications. The award was presented during the 15th International Conference on X-ray Microscopy XRM2022 hosted by the National Synchrotron Radiation Research Center (NSRRC) in Hsinchu, Taiwan on 19 - 24 June, 2022.
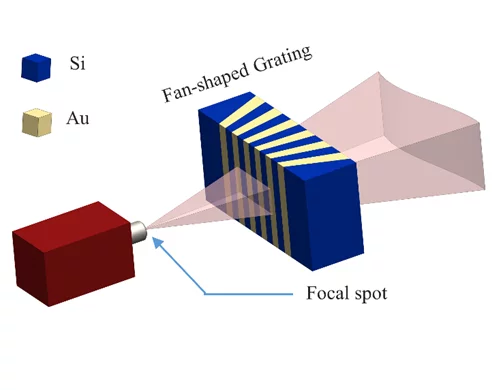
Broadening the field of view with a fan-shaped source grating
The orientation mismatch between the cone beam of an X-ray tube and the grating lines in a flat substrate remains a big challenge for laboratory grating-based X-ray interferometry, since it severely limits the imaging field of view. To solve this problem, we fabricated fan-shaped G0 source gratings by modulating the electric field during the deep reactive ion etching of silicon. With local electric field modulation in plasma we can etch high aspect ratio fan-shaped gratings that match the X-ray cone beam emission of a tube source. This new technology replaces the grating bending and allows a more compact design with larger field of view. Our work have recently been published in Applied Surface Science.
HERCULES students virtually at TOMCAT
In the framework of the HERCULES European School about Neutrons & Synchrotron Radiation for Science which is coordinated by the Université de Grenoble Alpes and took place on February 28 – April 1, 2022, we were pleased to virtually host 4 students for a hands-on session. During this practical on “Absorption and phase contrast X-ray tomographic microscopy”, the students had the chance to go, with the help of a jupyter notebook and the guidance of our team members Margaux Schmeltz and Christian Schlepütz, through different examples of tomographic reconstructions. They learnt about basic decisions and tradeoffs that have to be taken into account when planning to acquire tomographic imaging data, were introduced to some segmentation tools and even got to play with dynamic tomographic data!
Marie-Christine Zdora joins the X-ray Tomography Group
The X-ray Tomography group welcomes Marie-Christine Zdora as a new member. In her role as translational X-ray imaging adjunct scientist, Marie will mainly work on phase-contrast and dark-field imaging focusing on the further development of these techniques towards their clinical translation. Before joining TOMCAT, Marie was a postdoc in the X-ray optics and applications group at the Laboratory for Micro- and Nanotechnology (LMN) at PSI, where she worked on the development of new X-ray optics as well as X-ray wavefront sensing. Prior to this position, she was a research fellow at the University of Southampton in the UK, where she made advances in X-ray speckle-based imaging using synchrotron and lab sources.
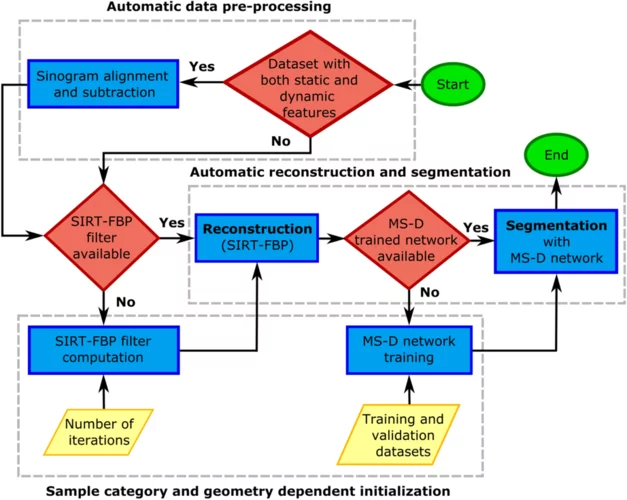
Deep learning based classification of dynamic processes in time-resolved X-ray tomographic microscopy
Time-resolved X-ray tomographic microscopy provides new opportunities in the volumetric investigation of dynamic processes. Full exploitation of these new capabilities is currently still hindered by the lack of efficient post-processing approaches capable of handling TBs of noisy datasets. A deep learning based reconstruction and classification algorithm designed to reconstruct and segment dynamic processes within a static matrix with high efficiency is a solution to this issue. In a paper published recently in Scientific Reports, we demonstrate the advantages of the proposed approach on dynamic, time-resolved fuel cell data, for which the current data post-processing pipeline heavily relies on manual labor, typically limiting the experimental plans to just a small range of the full parameter space.
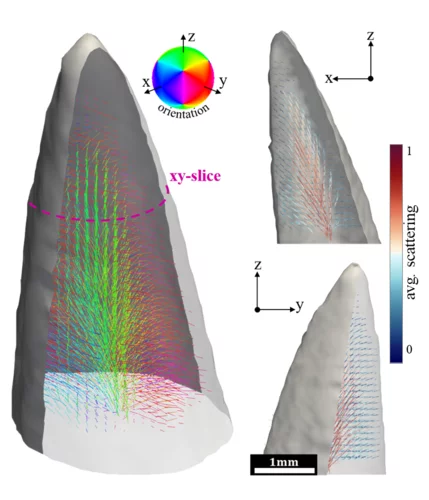
Fast acquisition protocol for X-ray scattering tensor tomography
X-ray scattering tensor tomography facilitates the investigation of the microstructural organization in statistically large sample volumes. Established acquisition protocols based on scanning small-angle X-ray scattering and X-ray grating interferometry inherently require long scan times even with high brilliance X-ray sources. Recent developments in X-ray circular diffractive optics enable fast single-shot acquisition of the sample scattering properties with 2D omnidirectional sensitivity. Researchers from the TOMCAT beamline at Paul Scherrer Institut have proposed simple yet inherently rapid acquisition protocols for X-ray scattering tensor tomography leveraging these new optical elements. Results from both simulation and experimental data, supported by a null space analysis, suggest that the proposed acquisition protocols are rapid and corroborate, providing sufficient information for the accurate volumetric reconstruction of the scattering properties. The proposed acquisition protocols will be the cornerstones for rapid inspection or time-resolved tensor tomography of the microstructural organization over an extended field of view. The work is published in Scientific Reports on 29 November 2021.
EXCITE Summer School at TOMCAT
In the framework of the 15th EXCITE Summer School in Biomedical Imaging which took place in Zürich on 6-17 September 2021, we were pleased to host 8 students at the beamline for a hands-on session. During this practical on “Synchrotron based X-ray tomographic microscopy”, the students had the chance to see and learn about the beamline infrastructure, scan a few test samples, reconstruct the tomographic volumes and discuss different aspects of tomographic microscopy at a synchrotron.
The X-ray optics design and fabrication team has a new member
The X-ray Tomography group welcomes Craig Lawley as Postdoc in the X-ray optics design and fabrication team. He will contribute to developing the microfabrication process of hard X-ray gratings in silicon substrates suitable for preclinical testing with pitch size in the micrometer range and aspect ratio higher than 100.
TOMCAT welcomes on board two scientists
The X-ray Tomography group welcomes on board Mariana Verezhak and Goran Lovric as members of the TOMCAT beamline crew. They will both contribute to the further development and realization of TOMCAT 2.0 (S- and I-TOMCAT branches on SLS2.0).
Women in Engineering Materials highlights Dr. Lucia Romano's work
The paper "High aspect ratio grating microfabrication by Pt assisted chemical etching and Au electroplating” by Dr. Lucia Romano & coauthors has been highlighted in the "Women in Engineering Materials" Virtual Issue published on Advanced Engineering Materials. This Virtual Issue draws attention to outstanding works within Materials Science created under the lead of women as principal investigators.
Congratulations to Lucia and the x-ray optics design and fabrication team!
SLS 2.0 approved - TOMCAT 2.0 cleared for takeoff!
In December 2020 the Swiss parliament approved the Swiss Dispatch on Promotion of Education, Research and Innovation (ERI) for 2021 to 2024 which includes funding for the planned SLS 2.0 upgrade. The new machine will lead to significantly increased brightness, thus providing a firm basis for keeping the SLS and its beamlines state-of-the-art for the decades to come. The TOMCAT crew is very excited that the TOMCAT 2.0 plans (deployment of the S- and I-TOMCAT branches, see SLS 2.0 CDR, p. 353ff) have been included in the Phase-I beamline upgrade portfolio. These beamlines will receive first light right after the commissioning of the SLS 2.0 machine around mid 2025. A first milestone towards this goal has just been achieved, with the successful installation of the S-TOMCAT optics hutch during W1 of 2021. The TOMCAT scientific and technical staff would like to thank Mr. Nolte and his Innospec crew for delivering perfectly on schedule.
BEATS beamline scientist from SESAME synchrotron trains at TOMCAT
TOMCAT welcomes Gianluca Iori, beamline scientist from BEATS - the new beamline for tomography at the SESAME synchrotron in Jordan, to a 3-month training on beamline operations. Gianluca’s visit is part of the Staff Training (BEATS Work Package 2) organized for BEATS scientific staff and SESAME control engineers. BEATS is a European project, funded under the EU’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme and coordinated by the ESRF.
3 Post Docs and 1 PhD student join TOMCAT
The X-ray Tomography group welcomes Stefan Gstöhl (Post-Doc), Maxim Polikarpov (Post-Doc), Margaux Schmeltz (Post-Doc) and Aleksandra Ivanovic (PhD Student) as new members. The group also thank everybody who helped making it possible for our Post-Docs and PhD student to join PSI amidst the challenges brought by the COVID-19 pandemic.
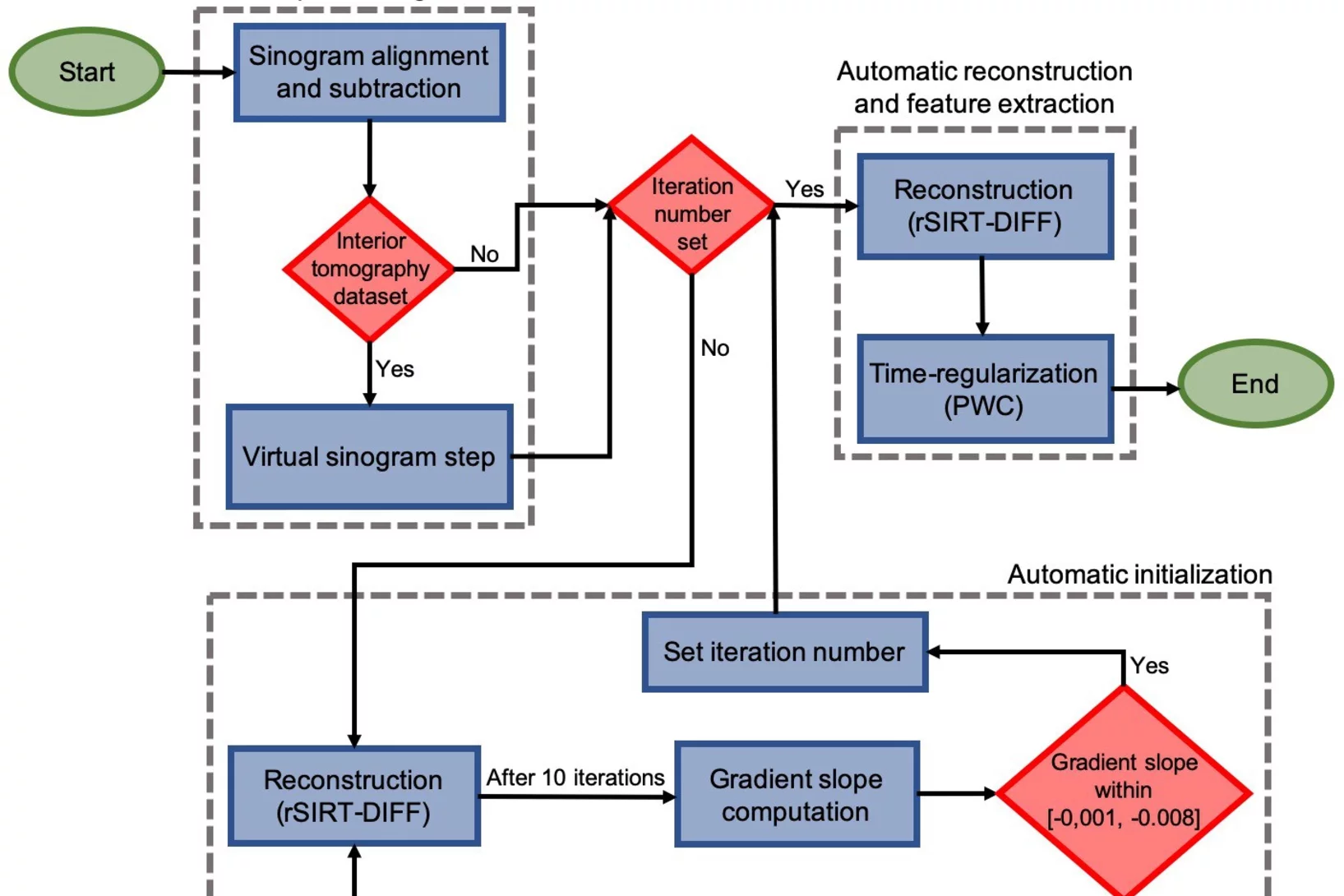
Automatic extraction of dynamic features from sub-second tomographic microscopy data
A fully automatized iterative reconstruction pipeline designed to reconstruct and segment dynamic processes within a static matrix has been developed at TOMCAT. The algorithm performance is demonstrated on dynamic fuel cell data where it enabled automatic extraction of liquid water dynamics from sub-second tomographic microscopy data. The work is published in Scientific Reports on 2 October 2020.
4 times compression factor for tomographic data feasible
In a recent study, TOMCAT has shown that lossy compression by a factor of at least 3 to 4 of raw acquisitions generally does not affect the reconstruction quality and that higher factors (six to eight times) can be achieved for tomographic volumes with a high signal-to-noise ratio as it is the case for phase-retrieved datasets. This finding is relevant to current challenges on large tomography data management and storage especially at synchrotron facilities. The results of this study was published in Journal of Synchrotron Radiation.
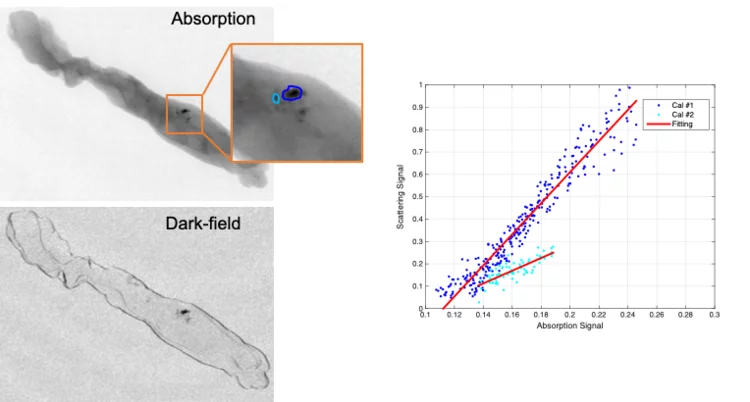
Looking into the hints of early breast cancer detection
Microcalcifications are the most important indicator in the diagnosis of early breast cancer. The team of X-ray tomography group, in collaboration with Kantonsspital Baden, has carried out a reader study to characterize microcalcifications non-invasively using grating interferometry. This study reveals a potential way to discriminate benign and malignant lesions at early stage.
A new etcher is just unpacked!
TOMCAT has a new etcher tool for the fabrication of very high aspect ratio gratings in silicon. The new SPTS Rapier system for silicon deep reactive ion etching just arrived and unpacked from the crate in front of the Laboratory of Micro and Nanotechnology at PSI! We thank the LMN technical staff for the support and the great job of moving in!
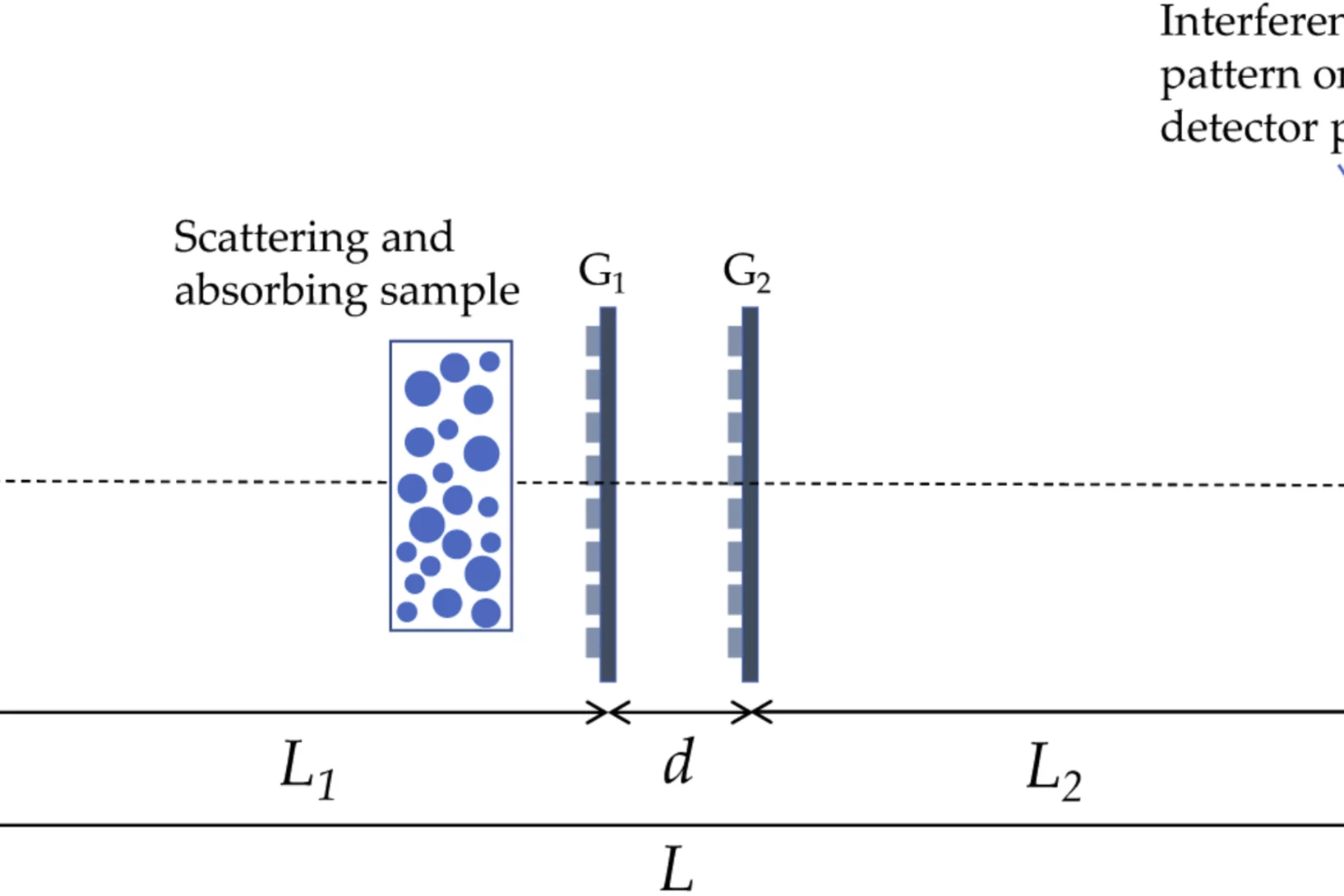
How to correct beam hardening effects in dual phase grating interferometry?
Researchers at the X-ray tomography group have expanded the theoretical understanding of dual phase grating interferometry with polychromatic sources. As a result, beam hardening effects can be corrected and a real space correlation function of a sample can be retrieved in dark-field imaging. These are significant steps towards application of the method for the quantitative investigation of microstructures of materials and devices using dual phase grating interferometry. The results of the work were published in Optics Express on June 12, 2020.
Rapid 3D directional small-angle scattering imaging achieved at TOMCAT
Researchers from the TOMCAT beamline have developed a small-angle scattering tensor tomography method to visualize microscopic features within a macroscopic field of view with unprecedented data acquisition speed. The results of the study were published in Applied Physics Letters on April 1, 2020.
SNF funds dynamic X-ray imaging of the human auditory system in motion
In collaboration with clinicians from the Inselspital and engineers of the University Hospital of Bern, the X-Ray Tomography Group will be part of a new SNF project entitled “The Human Auditory System in Motion: Direct Observation of the Microfunction of Sound Transmission using Dynamic Phase-contrast X-ray Imaging”.
Towards dynamic feedback control during time-resolved CT at TOMCAT
Researchers from the CWI in Amsterdam and the TOMCAT beamline have developed and implemented a real-time CT reconstruction, visualisation, and on-the-fly analysis approach to monitor dynamic processes as they occur. With the processing of multiple sets of CT slices per second, this represents the next crucial step towards adaptive feedback control of time-resolved in situ tomographic experiments. The results of this study were published in Scientific Reports on December 5, 2019.
The X-ray Tomography Group welcomes Dr. Nazanin Samadi as Post Doc
Dr. Nazanin Samadi will help develop tools for comprehensive simulation of tomography beamline design and will contribute in the technical design report of the future TOMCAT 2.0 beamline upgrade. Before joining the group, she was a PhD student at the University of Saskatchewan in Canada.
Dr. Anne Bonnin got tenured
Congratulations to Dr. Anne Bonnin for having been tenured. Anne spent 2 years of post-doc and 4 years as beamline scientist at TOMCAT.
Dr. Jinqiu Xu joins the X-ray Tomography Group as Post Doc
Dr. Jinqiu Xu will work with the team developing X-ray phase contrast CT for breast cancer diagnosis. Before coming to PSI, she worked on CT reconstruction from incomplete data at Capital Normal University (Beijing, China).
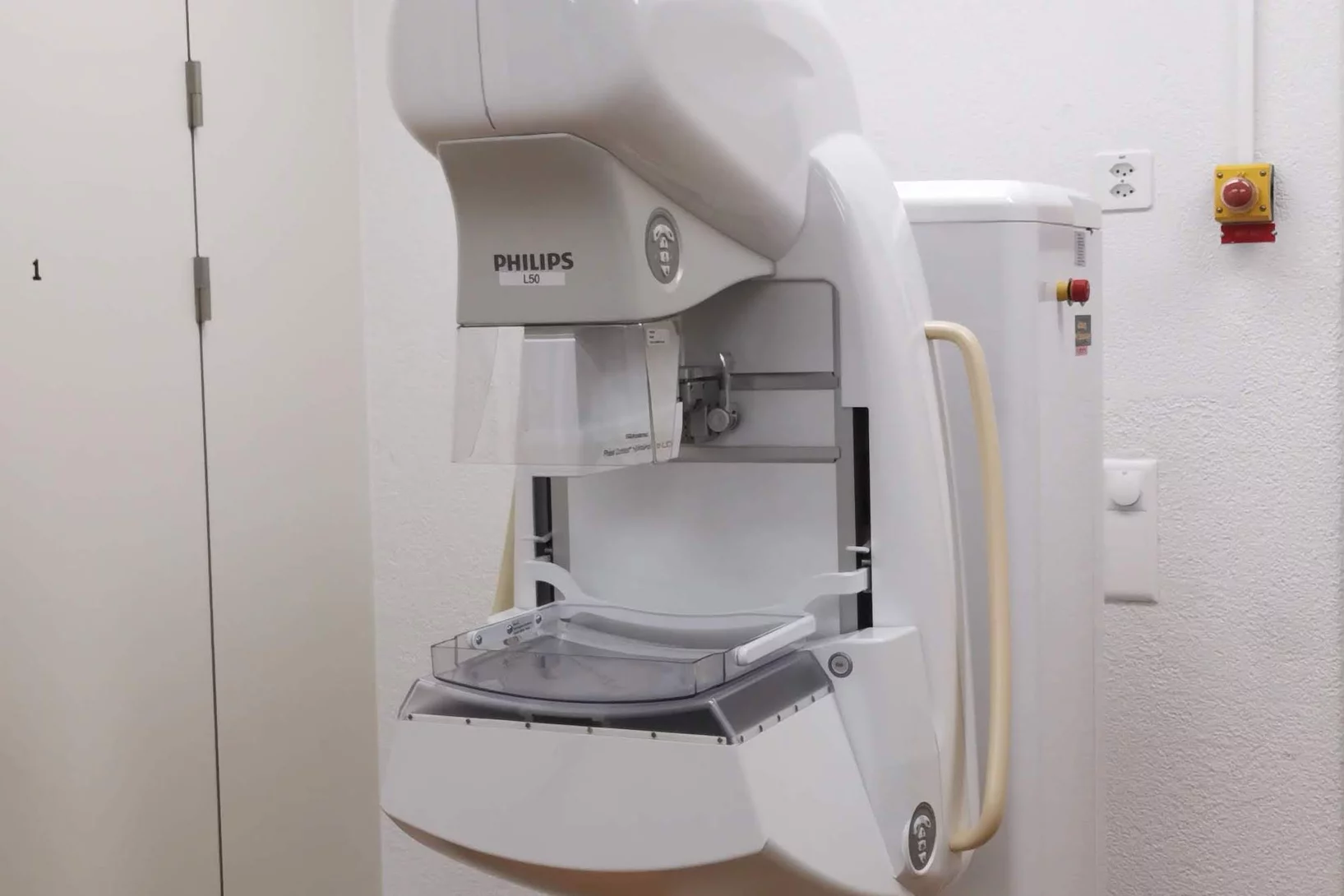
Towards clinical grating-interferometry mammography
The team of X-ray tomography group has developed the word-first clinical grating-interferometry mammography system in collaboration with Philips Research Hamburg, Kantonsspital Baden and Universitätspital Zurich. The novel imaging method shines a light on more accurate breast cancer detection. The prototype is installed at Universitätspital Zurich for clinical trial.
TOMCAT team hikes the UNESCO World Heritage Site Tectonic Arena Sardona
As summer tradition TOMCAT hikes in the Alps to enjoy fresh mountain air and have fun in each other's company. This year the TOMCAT team hikes in the UNESCO World Heritage Site Tectonic Arena Sardona.
High-numerical-aperture optics is key to ultra-fast tomographic microscopy
A novel high-numerical-aperture macroscope optics dedicated to high-temporal and high-spatial resolution X-ray tomographic microscopy is available at TOMCAT. Coupled with the in-house developed GigaFRoST camera, this highly efficient imaging setup enables tomographic microscopy studies at 20 Hz and beyond, opening up new possibilities in tomographic investigations of dynamic processes. A detailed characterization of the macroscope performance was published in Journal of Synchrotron Radiation on May 21, 2019.