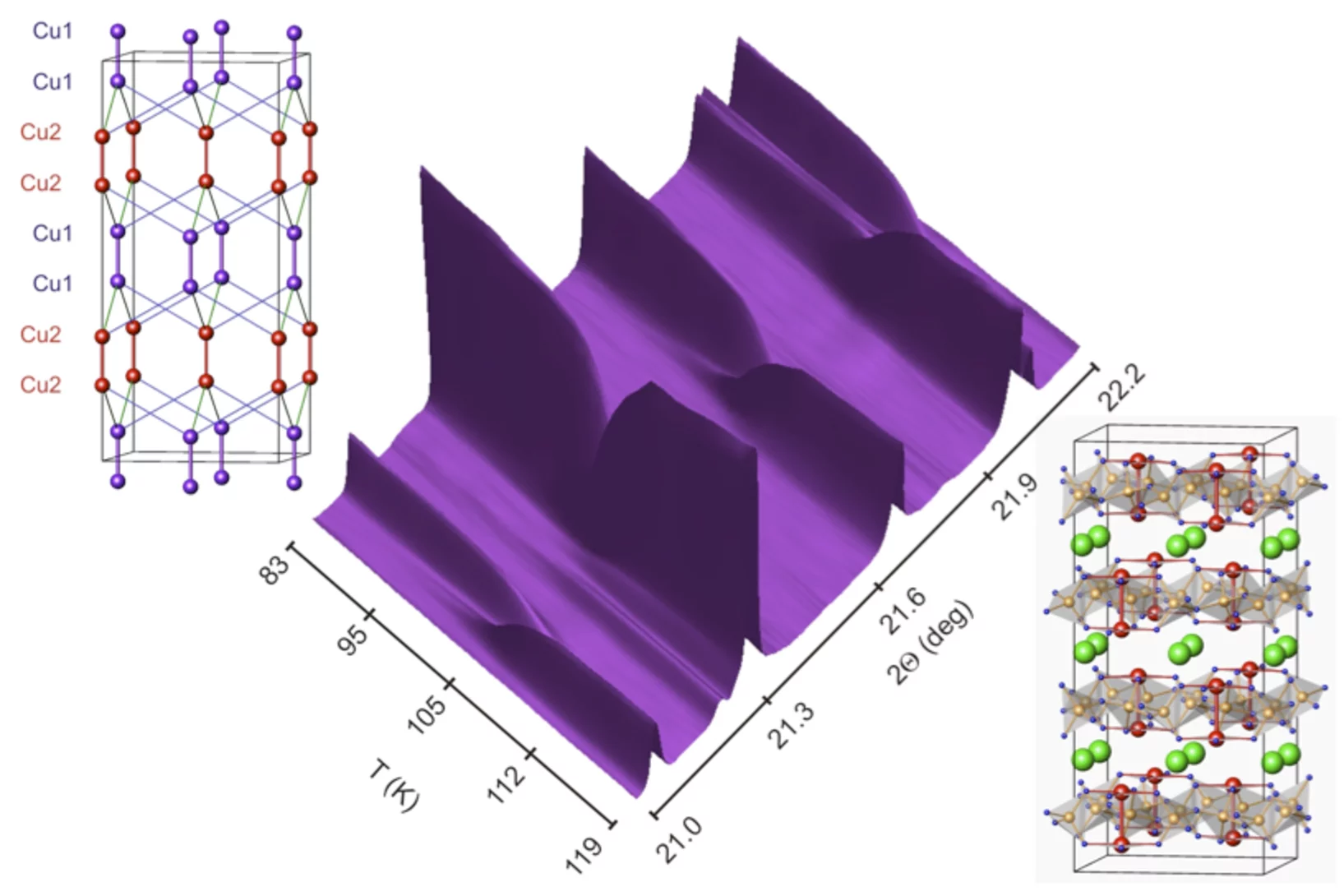
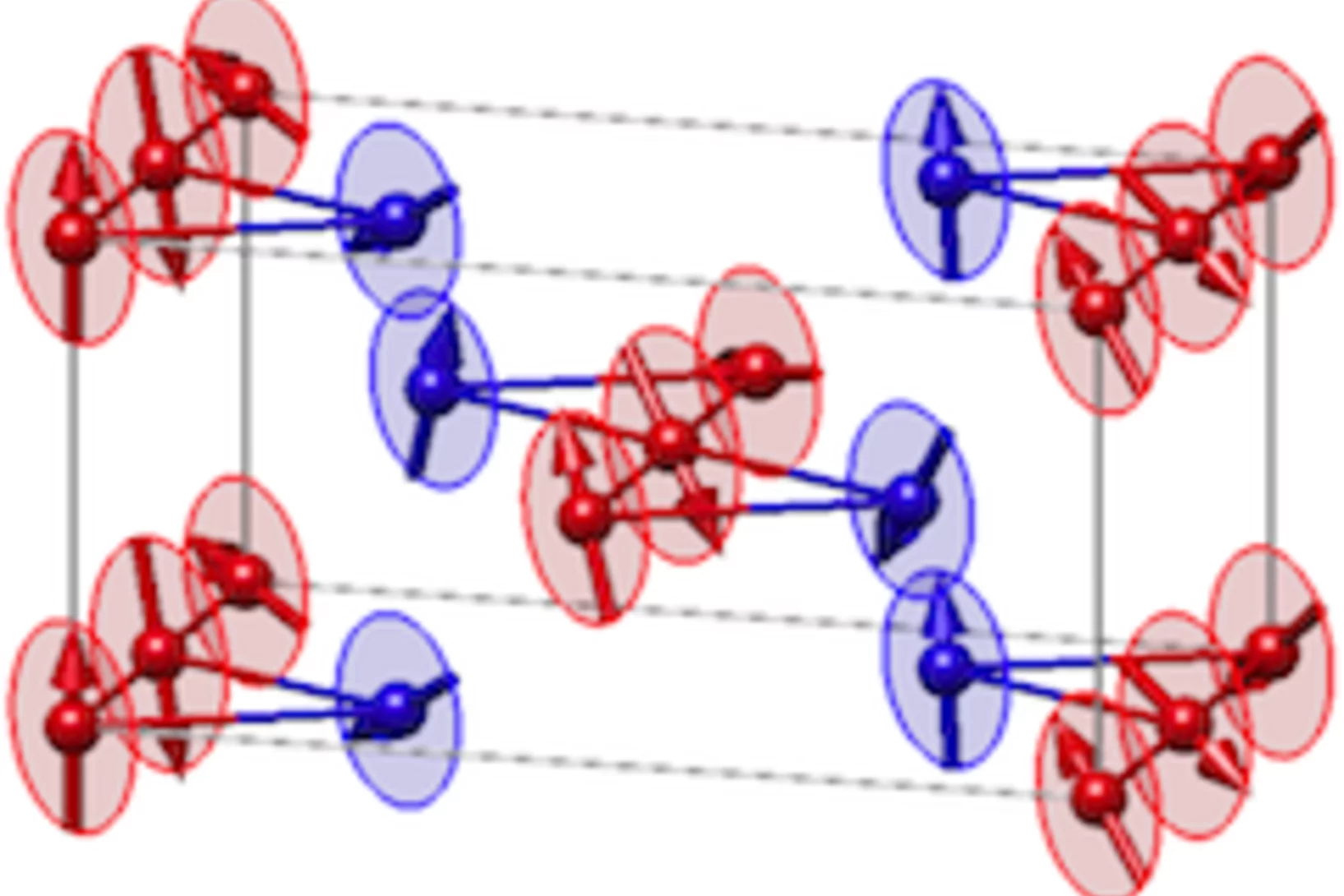
Two types of adjacent dimer layers in the low temperature phase of BaCuSi2O6
The interest in BaCuSi2O6 is motivated by its extraordinary phase diagram with field-induced Bose-Einstein condensation. Being a quantum paramagnet at zero magnetic field down to the lowest temperatures, the system displays a quantum phase transition into a magnetically ordered state at the critical value of magnetic field of ~23.5 T.
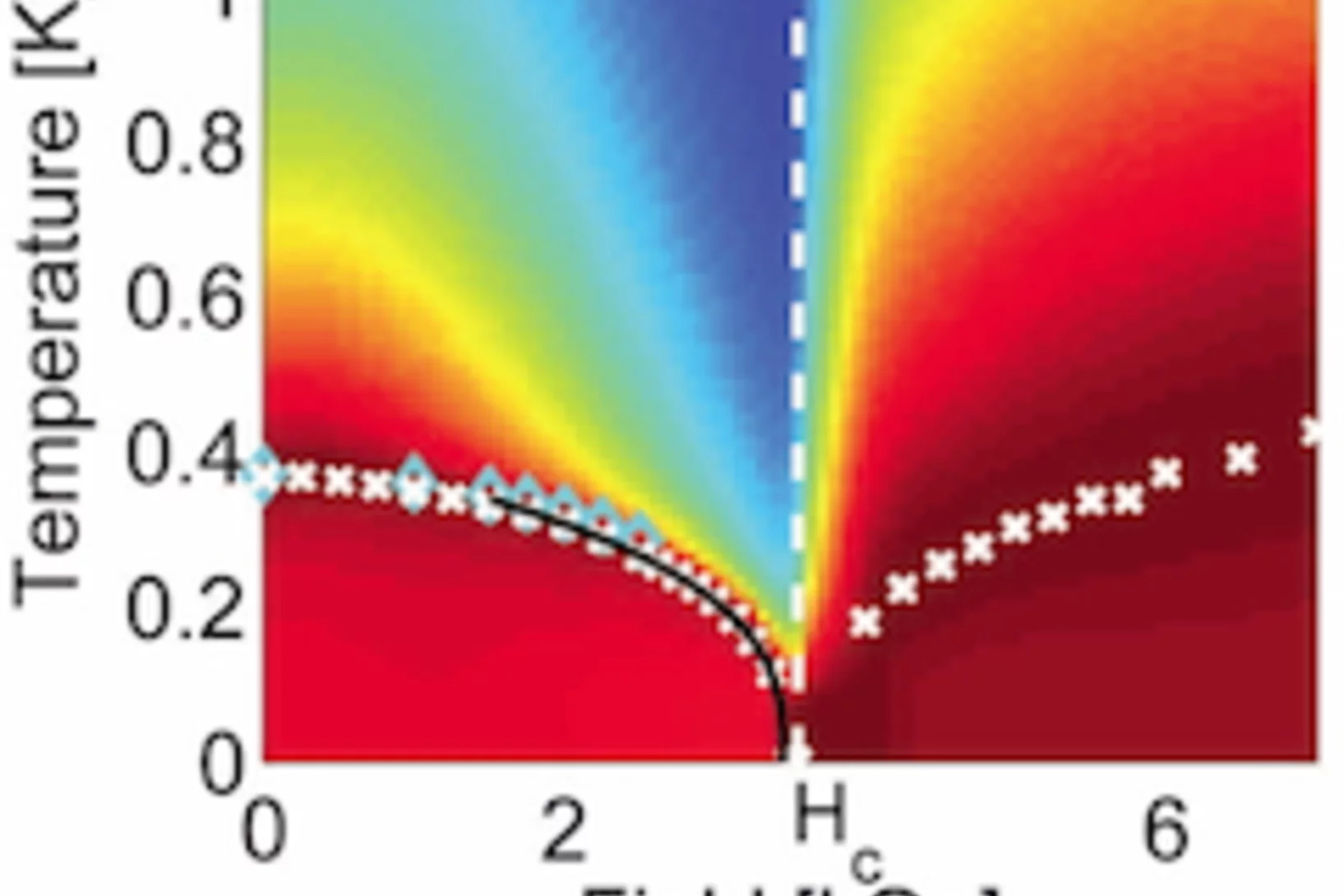
Dipolar Antiferromagnetism and Quantum Criticality in LiErF4
Magnetism has been predicted to occur in systems in which dipolar interactions dominate exchange. We present neutron scattering, specific heat, and magnetic susceptibility data for LiErF4, establishing it as a model dipolar-coupled antiferromagnet with planar spin-anisotropy and a quantum phase transition in applied field Hc|| = 4.0 ± 0.1 kilo-oersteds.
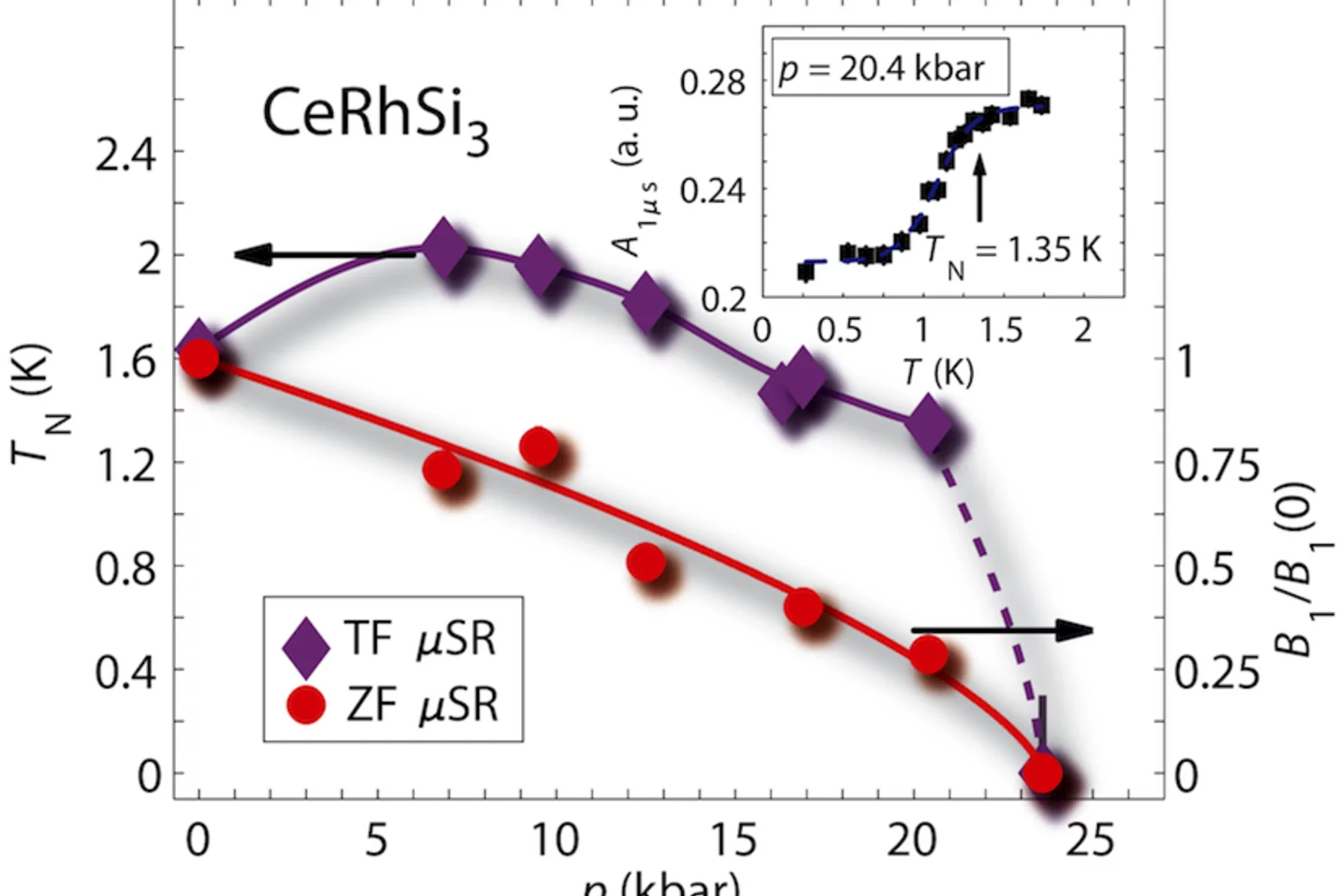
Direct observation of the quantum critical point in heavy fermion CeRhSi3
In many heavy fermion materials the quantum critical point is masked by superconductivity and it can only be detected by use of a local probe. In the noncentrosymmetric heavy fermion CeRhSi3 the ground state at ambient pressure is antiferromagnetically ordered and superconductivity sets in above 12 kbar coexisting with antiferromagnetism. We have unraveled a magnetic quantum critical point hidden deep inside the superconducting state of CeRhSi3.
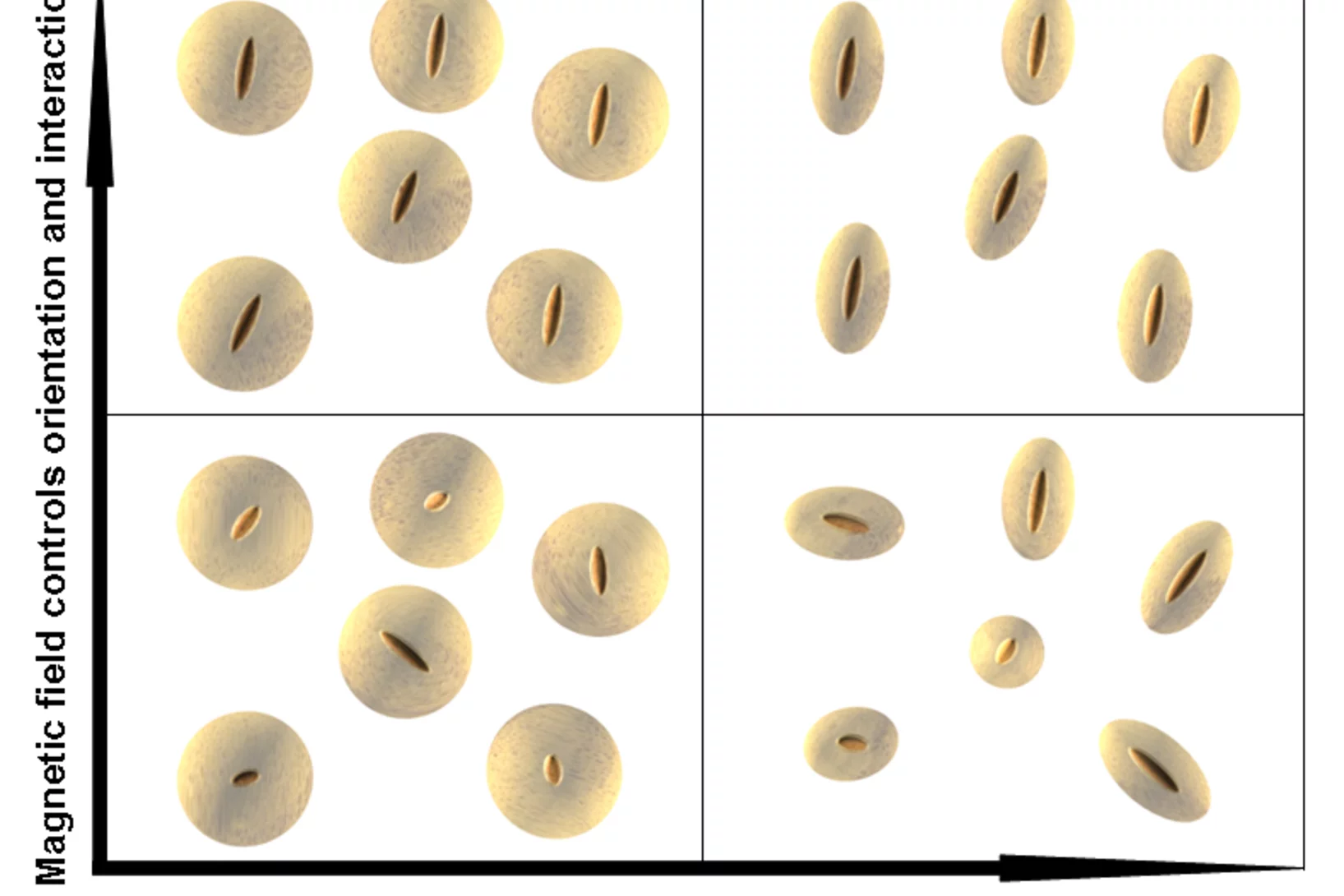
Ellipsoidal hybrid magnetic microgel particles with thermally tunable aspect ratios
We report on the synthesis and characterization of multiresponsive hybrid microgel particles. The particles consist of ellipsoidal silica-coated maghemite cores subsequently coated with thermoresponsive poly (N-isopropylacrylamide) (PNIPAM) shells. The PNIPAM shell enables the hybrid particle to alter its size and ratio of long to small axis with increasing temperature while the core morphology remains unchanged.
Directly coupled Ferromagnetism and Ferroelectricity in the Olivine Mn2GeO4
The olivine compound Mn2GeO4 is shown to feature both a ferroelectric polarization and a ferromagnetic magnetization that are directly coupled and point along the same direction. We show that a spin spiral generates ferroelectricity, and a canted commensurate order leads to weak ferromagnetism.
Direct Observation of Local Mn-Mn Distances in the Paramagnetic Compound CsMnxMg1-xBr3
We introduce a novel method for local structure determination with a spatial resolution of the order of 0.01 Å. It can be applied to materials containing clusters of exchange-coupled magnetic atoms. We use neutron spectroscopy to probe the energies of the cluster excitations which are determined by the interatomic coupling strength J.