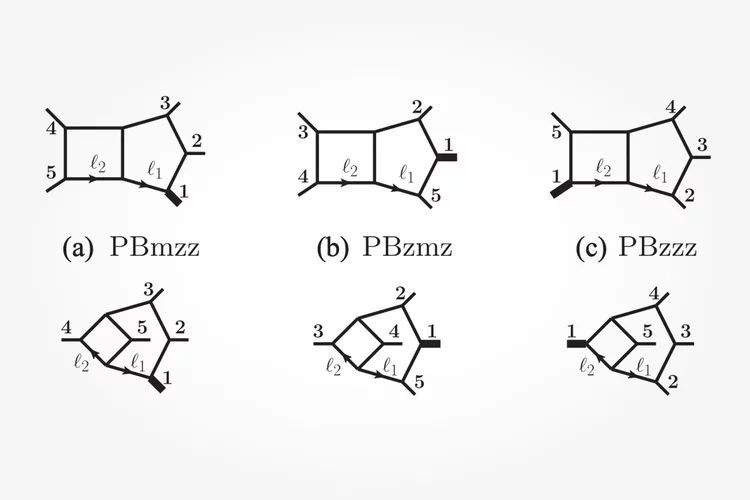
All Two-Loop Feynman Integrals for Five-Point One-Mass Scattering
We compute the complete set of two-loop master integrals for the scattering of four massless particles and a massive one. Our results are ready for phenomenological applications, removing a major obstacle to the computation of complete next-to-next-to-leading order QCD corrections to processes such as the production of a H/Z/W boson in association with two jets at the LHC. Furthermore ...
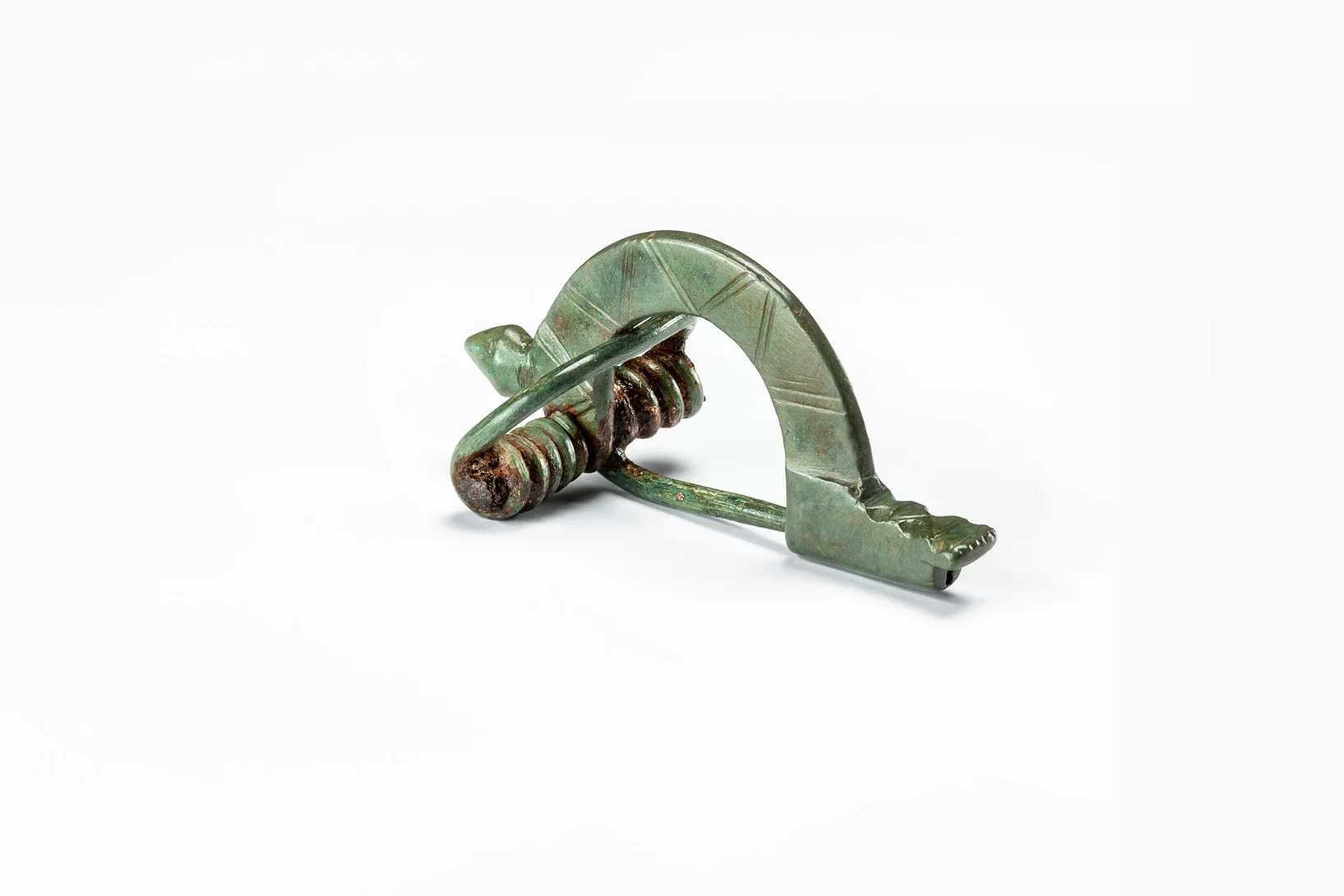
Muonic X-rays peer into brooch from Roman city
Using Muon Induced X-ray Emission, researchers could reveal the inner composition of a knob-bow fibula, excavated at Augusta Raurica in northern Switzerland.
Making sense of the muon’s misdemeanours
An exotic atom called muonium could explain why muons won’t stick to the rules, believe researchers using the Swiss Muon Source at Paul Scherrer Institute PSI.
Upgraded pixel detector back in action at CERN
Built at Paul Scherrer Institute, the detector forms the heart of the CMS experiment. It is producing data again following an upgrade during the LHC shutdown.
The Running Bottom Quark Mass and the Higgs Boson
We present a new measurement of the bottom quark mass in the MS scheme at the renormalization scale of the Higgs boson mass from measurements of Higgs boson decay rates at the LHC: mb (mH) = 2.6 +0.36 -0.31 GeV. The measurement has a negligible theory uncertainty and excellent prospects to improve at the HL-LHC and a future Higgs factory.
Antiprotons in superfluid helium: a new way for sensitive measurements of antimatter
Scientists, publishing in Nature, have found that a hybrid antimatter-matter atom behaves in an unexpected way when submerged in superfluid helium.
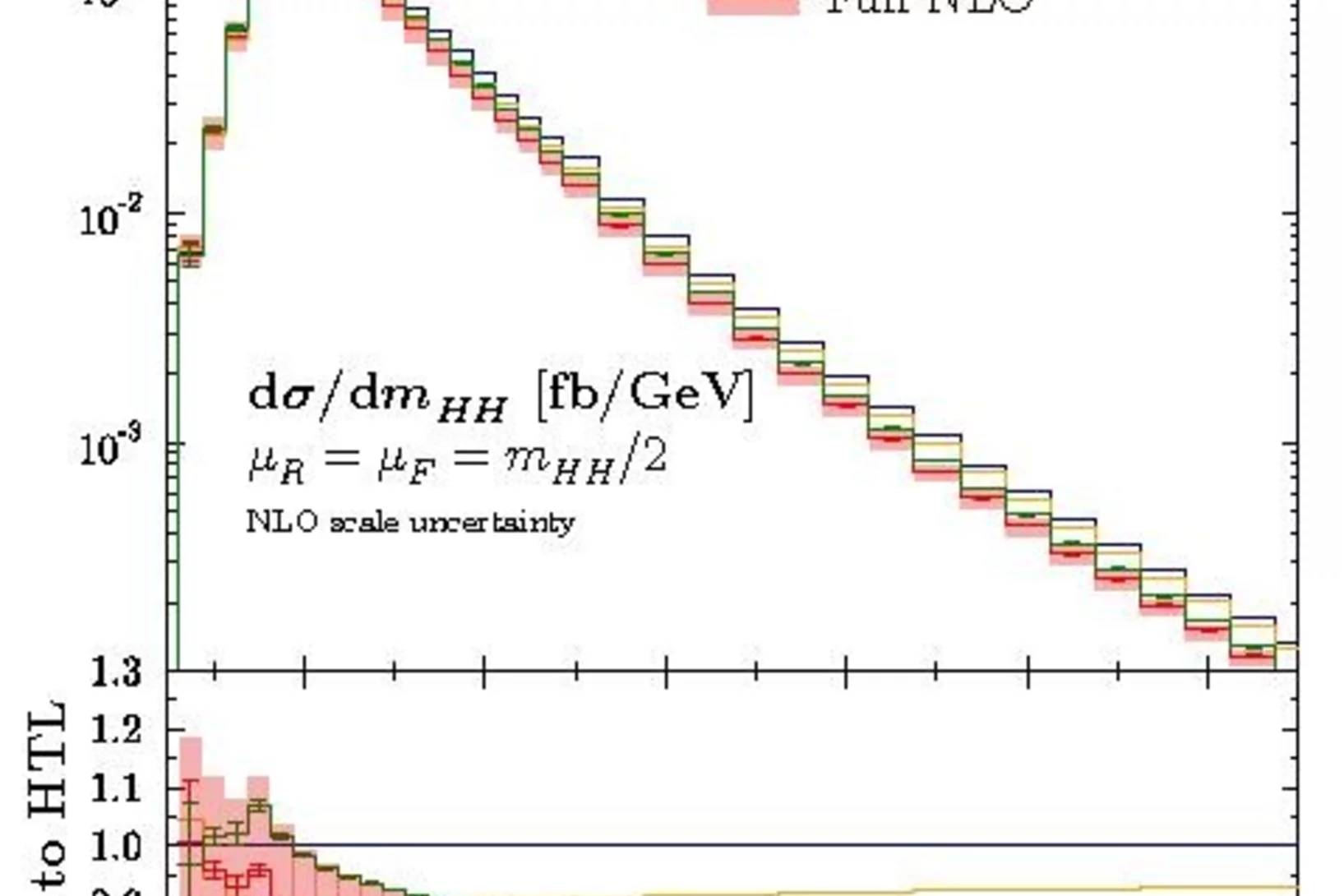
Higgs-boson pair production at LHC: reliable theoretical uncertainties
Researchers at PSI have refined the theoretical prediction for the pair production of Higgs bosons at the LHC and re-analized the related uncertainties resulting in sizable contributions neglected before. This process will be highly relevant at the high-luminosity run of the LHC to measure the Higgs potential directly.
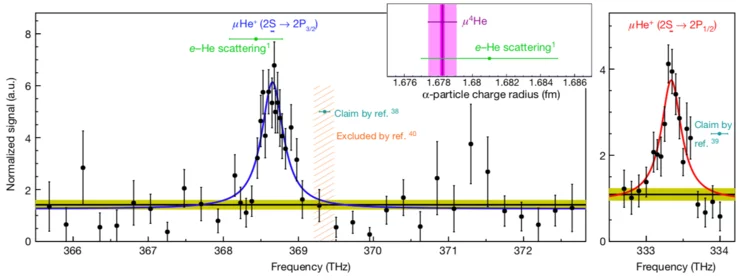
Size of helium nucleus measured more precisely than ever before
In experiments at the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI, an international research collaboration has measured the radius of the atomic nucleus of helium five times more precisely than ever before. The researchers are publishing their results today in the journal Nature.
Demonstration of Muon-Beam Transverse Phase-Space Compression
We demonstrate efficient transverse compression of a 12.5 MeV=c muon beam stopped in a helium gas target featuring a vertical density gradient and crossed electric and magnetic fields. The muon stop distribution extending vertically over 14 mm was reduced to a 0.25 mm size (rms) within 3.5 μs. The simulation including cross sections ...
Global Fit to Modified Neutrino Couplings and the Cabibbo-Angle Anomaly
Recently, discrepancies of up to 4σ between the different determinations of the Cabibbo angle were observed. In this context, we point out that this “Cabibbo-angle anomaly” can be explained by lepton flavor universality violating new physics in the neutrino sector. However, modified neutrino couplings to standard model gauge bosons also affect many other observables sensitive to lepton flavor universality violation, which have to be taken into account in order to assess the viability of this explanation.
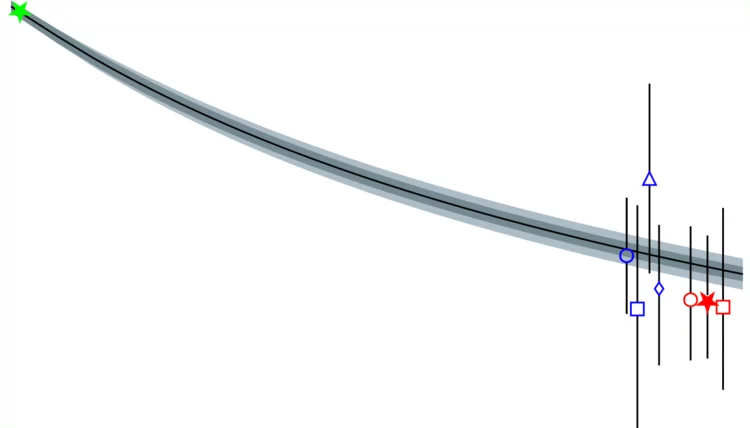
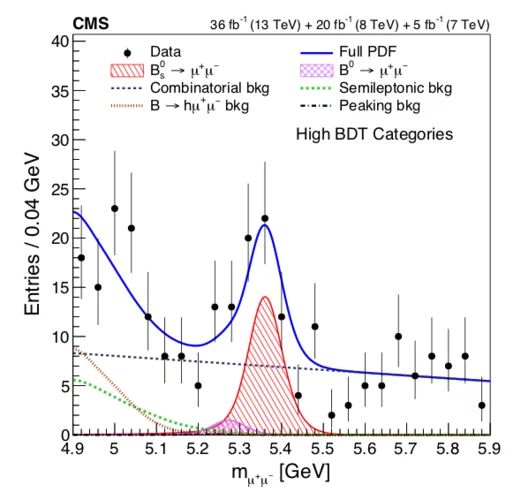
Measurement of properties of Bs0 → μ+μ− decays and search for B0 → μ+μ− with the CMS experiment
Results are reported for the B0s → μ+μ− branching fraction and effective lifetime and from a search for the decay B0 → μ+μ−. The analysis uses a data sample of proton-proton collisions accumulated by the CMS experiment in 2011, 2012, and 2016, with center-of-mass energies (integrated luminosities) of 7TeV (5fb−1), 8TeV (20fb−1),and 13TeV (36fb−1).
Detailed polarization measurements of the prompt emission of five gamma-ray bursts
Gamma-ray bursts (GRBs) are the strongest explosions in the Universe since the Big Bang. They are believed to be produced either in the formation of black holes at the end of massive star evolution or the merging of compact objects.
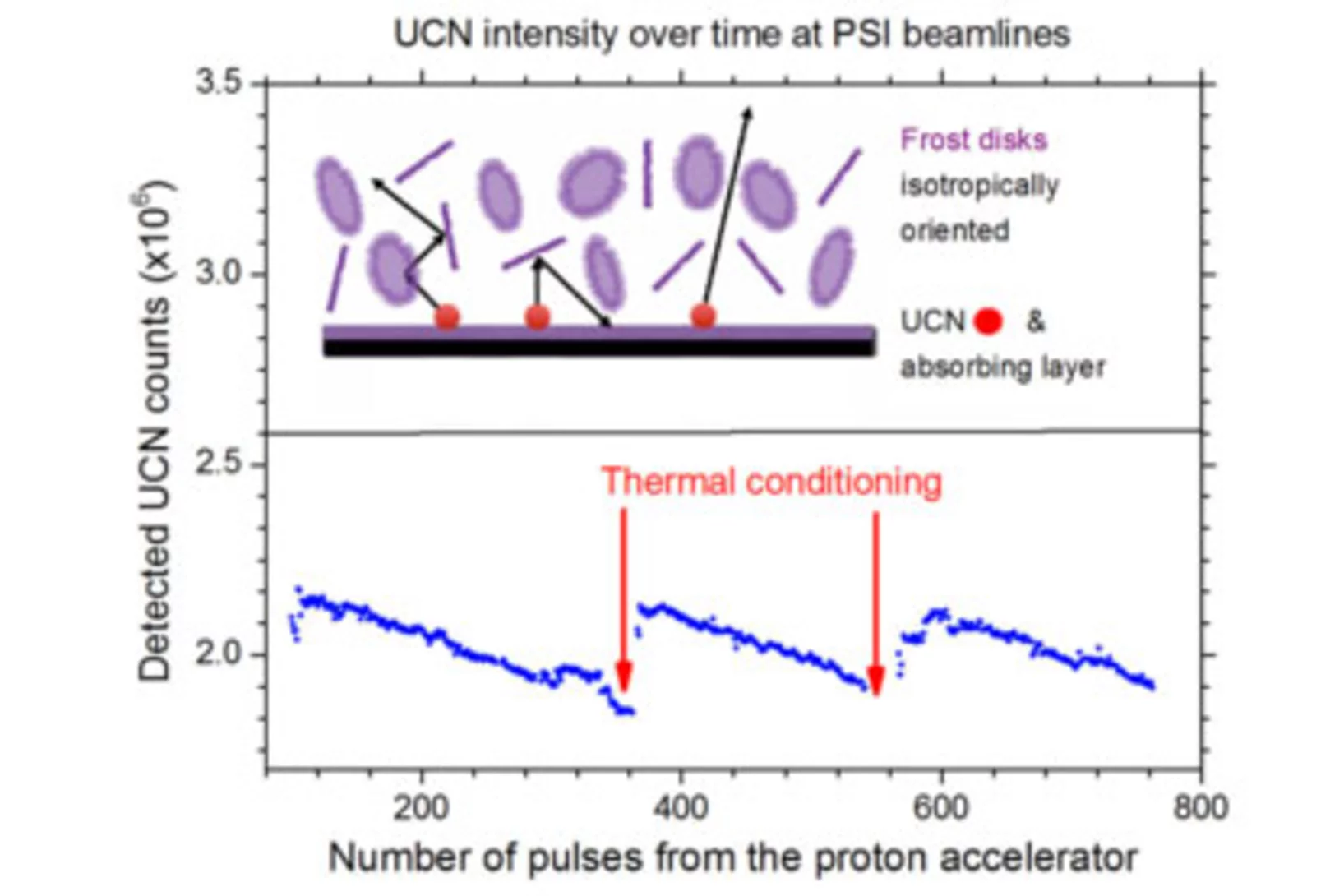
Solid deuterium surface degradation at ultracold neutron sources
Solid deuterium (sD2) is used as an efficient converter to produce ultracold neutrons (UCN). Itis known that the sD2 must be sufficiently cold, of high purity and mostly in its ortho-state in order to guarantee long lifetimes of UCN in the solid from which they are extracted into vacuum.
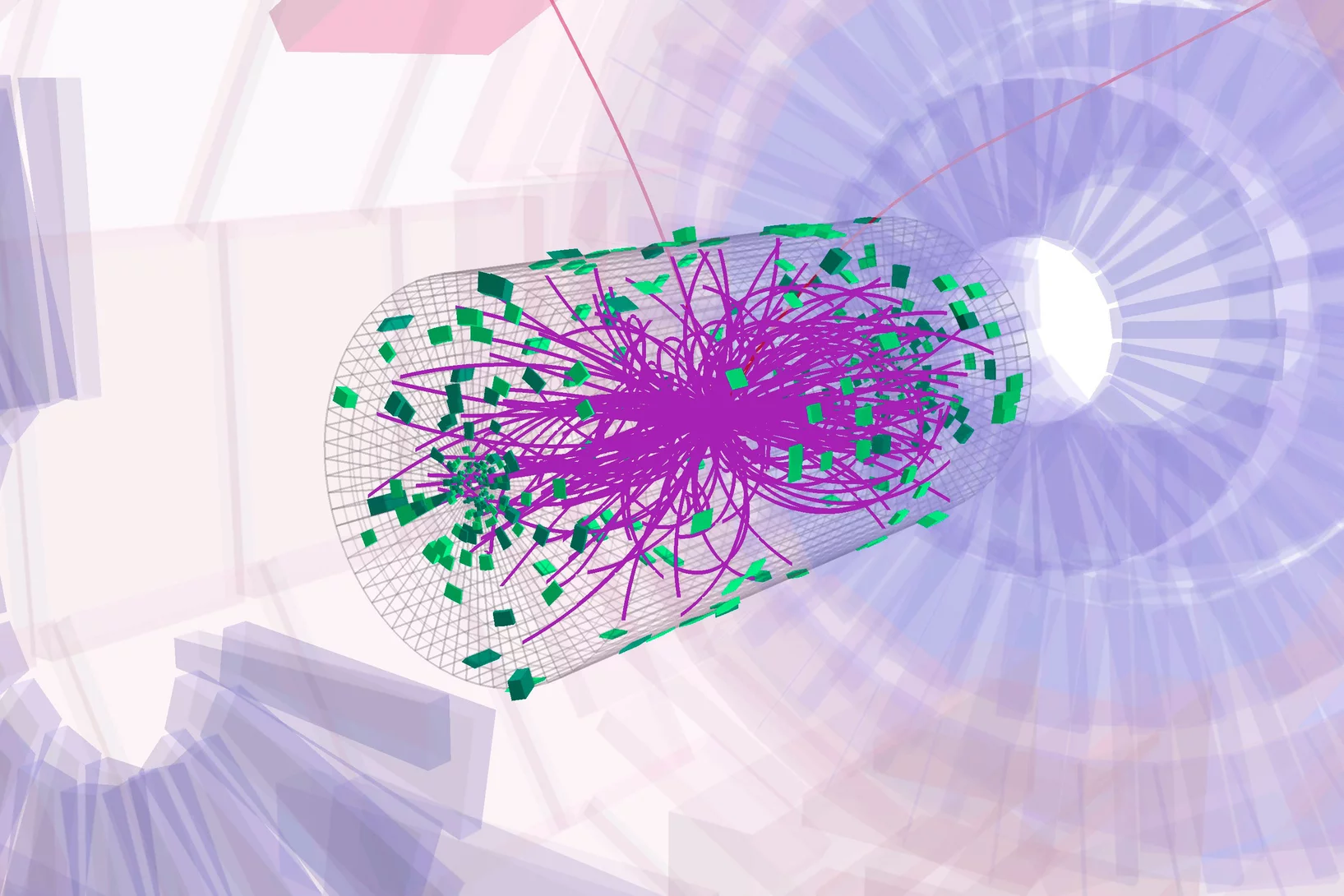
Observation of ttH Production
The observation of Higgs boson production in association with a top quark-antiquark pair is reported, based on a combined analysis of proton-proton collision data at center-of-mass energies of √s = 7,8, and 13 TeV, corresponding to integrated luminosities of up to 5.1, 19.7, and 35.9 fb-1, respectively. The data were collected with the CMS detector at the CERN LHC.
Searching for New Physics with b → sτ+τ-
In recent years, intriguing hints for the violation of lepton flavor universality (LFU) have been accumulated in semileptonic B decays, both in the charged-current transitions b → cl-ν-l (i.e., RD, RD∗, and RJ/Ψ and the neutral-current transitions b → sl+l- (i.e., RK and RK∗.
The Charpak-Ritz Prize 2018 is awarded to Roland Paul Horisberger
The Charpak-Ritz Prize 2018, jointly awarded by the French Physical Society and the Swiss Physical Society, has been bestowed to Roland Paul Horisberger for his numerous contributions to the development of precision silicon vertex detectors for particle physics experiments as well as for the application of these technologies in X-ray photon sciences.
Jean-Baptiste Mosset winner of PSI Founder Fellowship
Jean-Baptiste Mosset from the Laboratory of Particle Physics is the winner of a PSI Founder Fellowship and plans now to commercialise a neutron detector to spot plutonium and uranium. With his new technology, less expensive and more efficient neutron detectors could be developed. In the next 18 months, Mosset wants to further develop his prototype and find out if demand for this technology exists in industry.
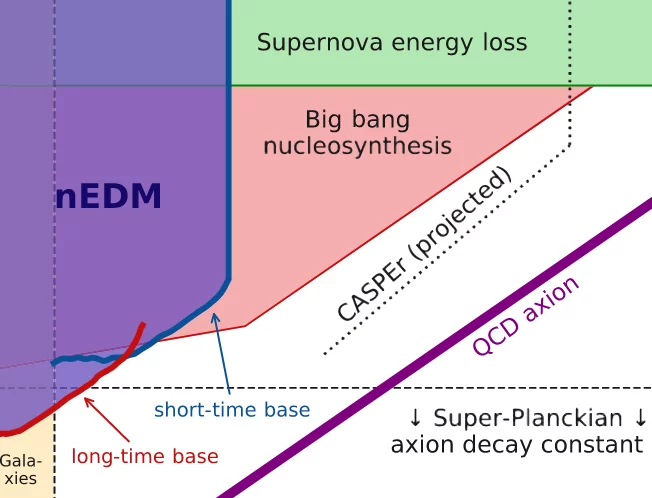
Search for Axionlike Dark Matter through Nuclear Spin Precession in Electric and Magnetic Fields
We report on a search for ultralow-mass axionlike dark matter by analyzing the ratio of the spin-precession frequencies of stored ultracold neutrons and 199Hg atoms for an axion-induced oscillating electric dipole moment of the neutron and an axion-wind spin-precession effect. No signal consistent with dark matter is observed for the axion mass range 10-24 ≤ ma ≤ 10-17eV.
Commissioning and first performance studies of the new CMS pixel detector
In the previous months the new CMS pixel detector was brought into operation. The detector was moved from PSI to CERN and installed in February, followed by an intensive period of commissioning and calibration. This process mostly involved the adjustment of many operational parameters which influence the detector performance, e.g.
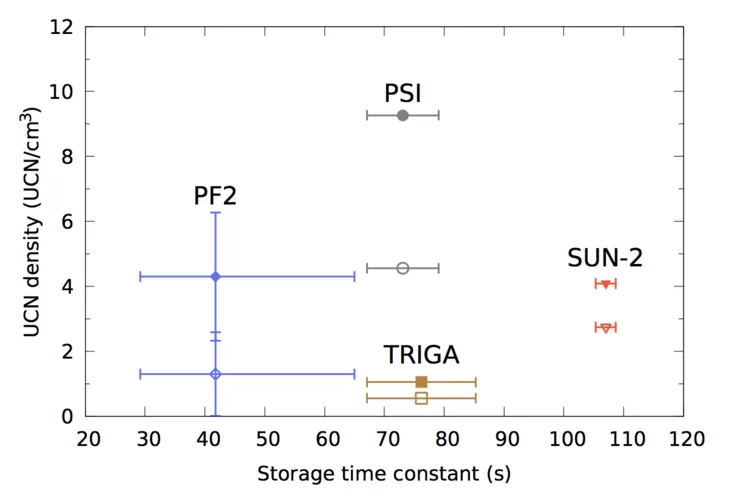
Comparison of ultracold neutron sources for fundamental physics measurements
Ultracold neutrons (UCNs) are key for precision studies of fundamental parameters of the neutron and in searches for new charge-parity-violating processes or exotic interactions beyond the Standard Model of particle physics. The most prominent example is the search for a permanent electric-dipole moment of the neutron (nEDM). We have performed an experimental comparison of the leading UCN sources currently operating.
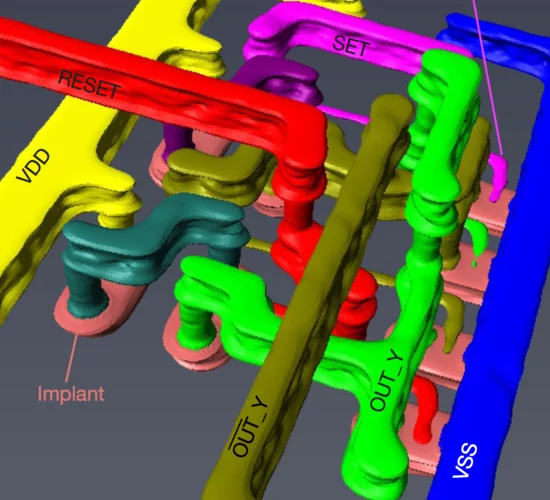
High-resolution non-destructive three-dimensional imaging of integrated circuits
Modern nanoelectronics has advanced to a point at which it is impossible to image entire devices and their interconnections non- destructively because of their small feature sizes and the complex three-dimensional structures resulting from their integration on a chip. This metrology gap implies a lack of direct feedback between design and manufacturing processes, and hampers quality control during production, shipment and use.
Silicon pixel barrel detector successfully installed in the CMS experiment
Middle of February the upgraded CMS silicon pixel barrel detector has been moved from PSI to CERN and was successfully installed in the CMS experiment.
The deuteron too poses a mystery
The deuteron — one of the simplest atomic nuclei, consisting of just one proton and one neutron — is considerably smaller than previously thought. This finding was arrived at by an international research group that carried out experiments at the Paul Scherrer Institute, PSI. The new result is consistent with a 2010 study by the same group, in which the researchers measured the proton and found a significantly smaller value than previous research using different experimental methods.
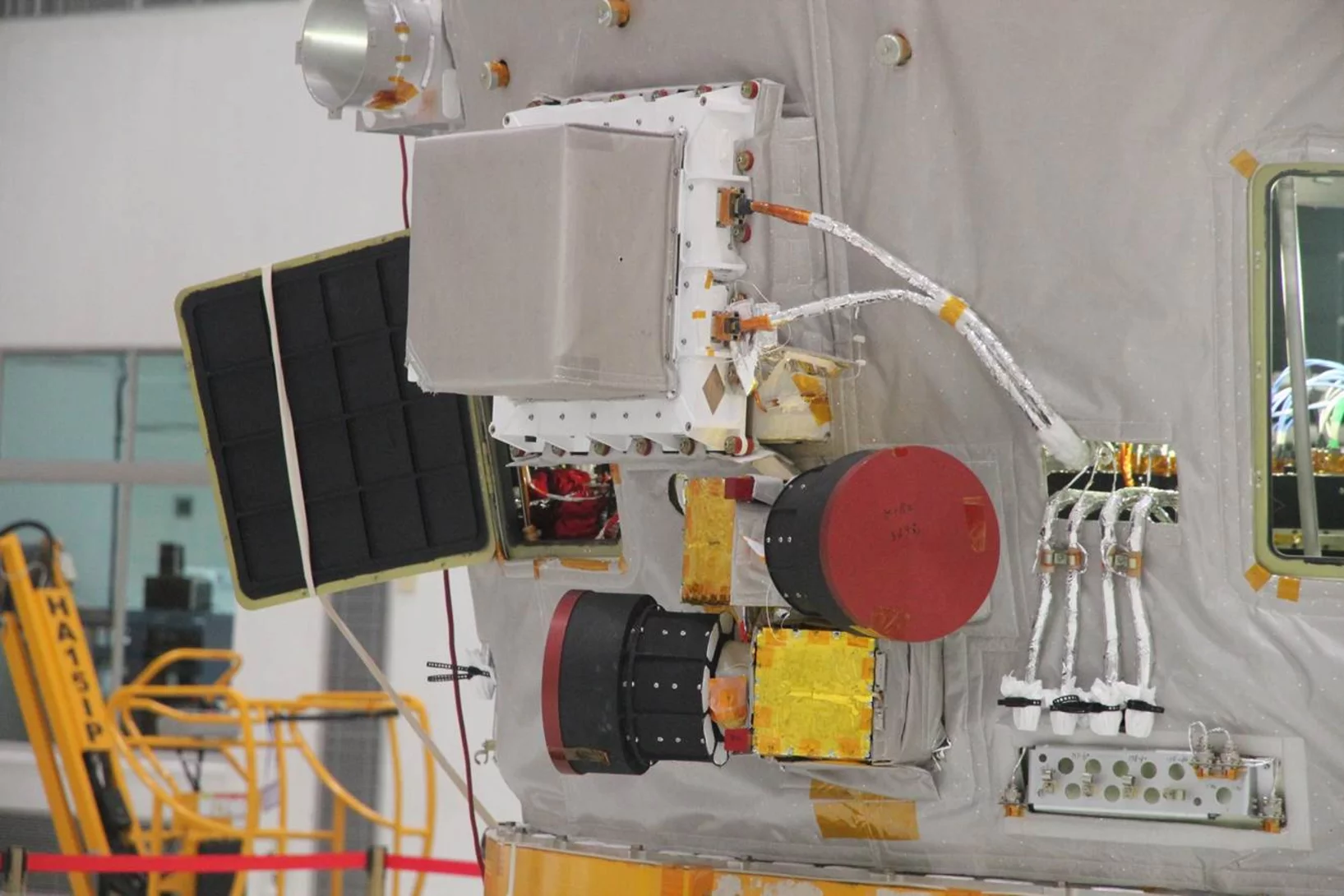
POLAR experiment successfully launched on Chinese spacecraft
The second Chinese space laboratory satellite Tian Gong 2 was successfully launched from the Jiuquan Satellite Launch Center on September 15th, 2016 at 22:04 BTC (UTC+8h). Among more than ten instruments onboard it also brought to space the only non-Chinese experiment POLAR - the hard X-ray polarimeter.
Search for the lepton flavour violating decay μ+→e+γ with the full dataset of the MEG experiment
The final results of the search for the lepton flavour violating decay μ+→e+γ based on the full dataset collected by the MEG experiment at the Paul Scherrer Institut in the period 2009–2013 and totalling 7.5×1014 stopped muons on target are presented.
POLAR detector developed at the PSI flies into orbit with a Chinese space mission
Researchers working with Wojciech Hajdas at the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI have developed a detector called POLAR. This instrument is expected to search out and investigate so-called gamma ray bursts coming from the depths of the universe. Gamma ray bursts are eruptions of high-energy light that despite being extremely strong remain, up to now, only poorly understood.
Muon polarization in the MEG experiment: predictions and measurements
The MEG experiment makes use of one of the world’s most intense low energy muon beams, in order to search for the lepton flavour violating process μ+→e+γ . We determined the residual beam polarization at the thin stopping target, by measuring the asymmetry of the angular distribution of Michel decay positrons as a function of energy. The initial muon beam polarization at the production is predicted to be Pμ=−1Pμ=−1 by the Standard Model (SM) with massless neutrinos.
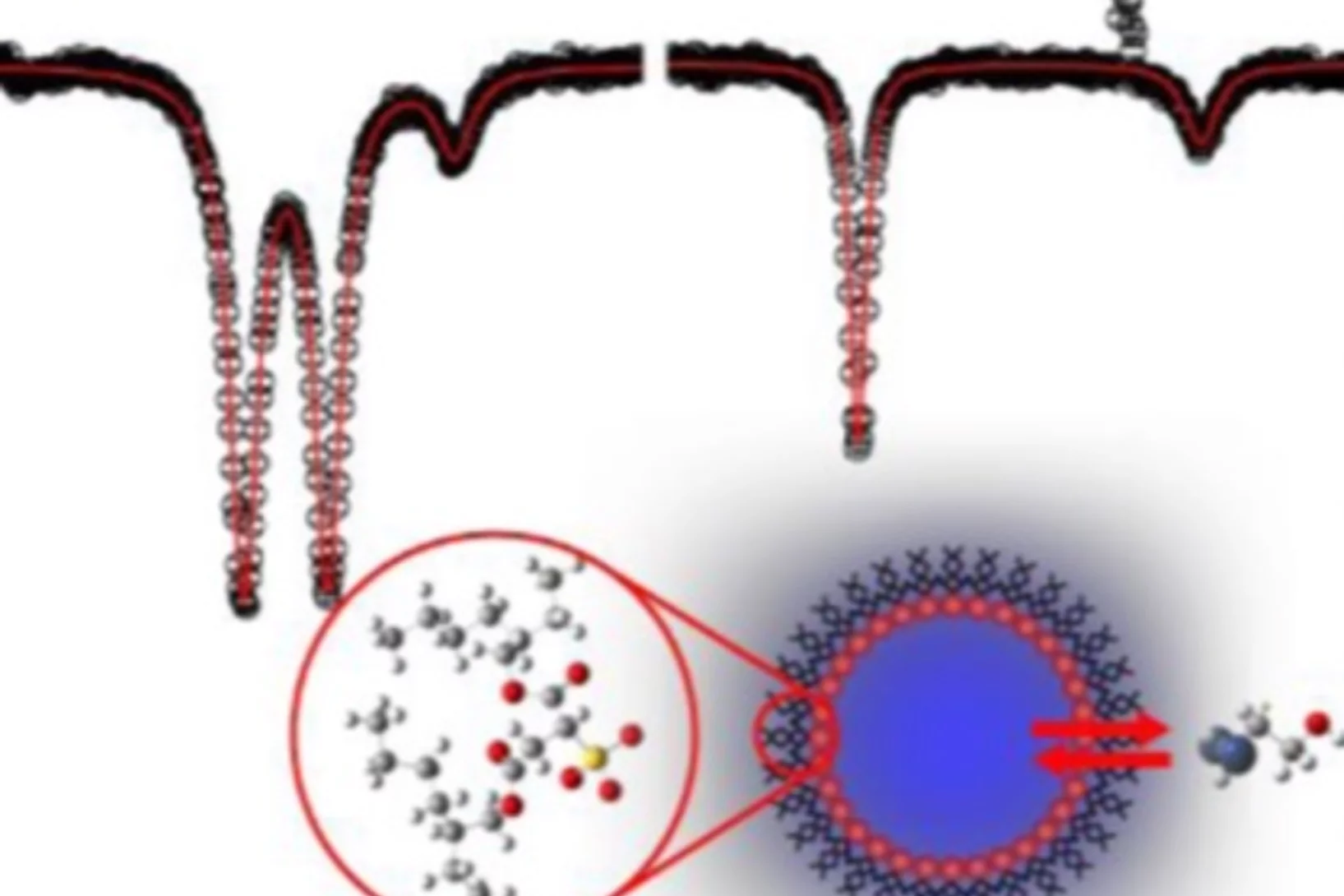
Rate of Molecular Transfer of Allyl Alcohol across an AOT Surfactant Layer Using Muon Spin Spectroscopy
The transfer rate of a probe molecule across the interfacial layer of a water-in-oil (w/o) microemulsion was investigated using a combination of transverse field muon spin rotation (TF-μSR), avoided level crossing muon spin resonance (ALC-μSR), and Monte Carlo simulations. Reverse micro-emulsions consist of nanometer-sized water droplets dispersed in an apolar solvent separated by a surfactant monolayer.
Observation of Gravitationally Induced Vertical Striation of Polarized Ultracold Neutrons by Spin-Echo Spectroscopy
We describe a spin-echo method for ultracold neutrons (UCNs) confined in a precession chamber and exposed to a |B0| = 1μT magnetic field. We have demonstrated that the analysis of UCN spin-echo resonance signals in combination with knowledge of the ambient magnetic field provides an excellent method by which to reconstruct the energy spectrum of a confined ensemble of neutrons.
Constraining interactions mediated by axion-like particles with ultracold neutrons
We report a new limit on a possible short range spin-dependent interaction from the precise measurement of the ratio of Larmor precession frequencies of stored ultracold neutrons and 199Hg atoms confined in the same volume. The measurement was performed in a ∼1μT vertical magnetic holding field with the apparatus searching for a permanent electric dipole moment of the neutron at the Paul Scherrer Institute.