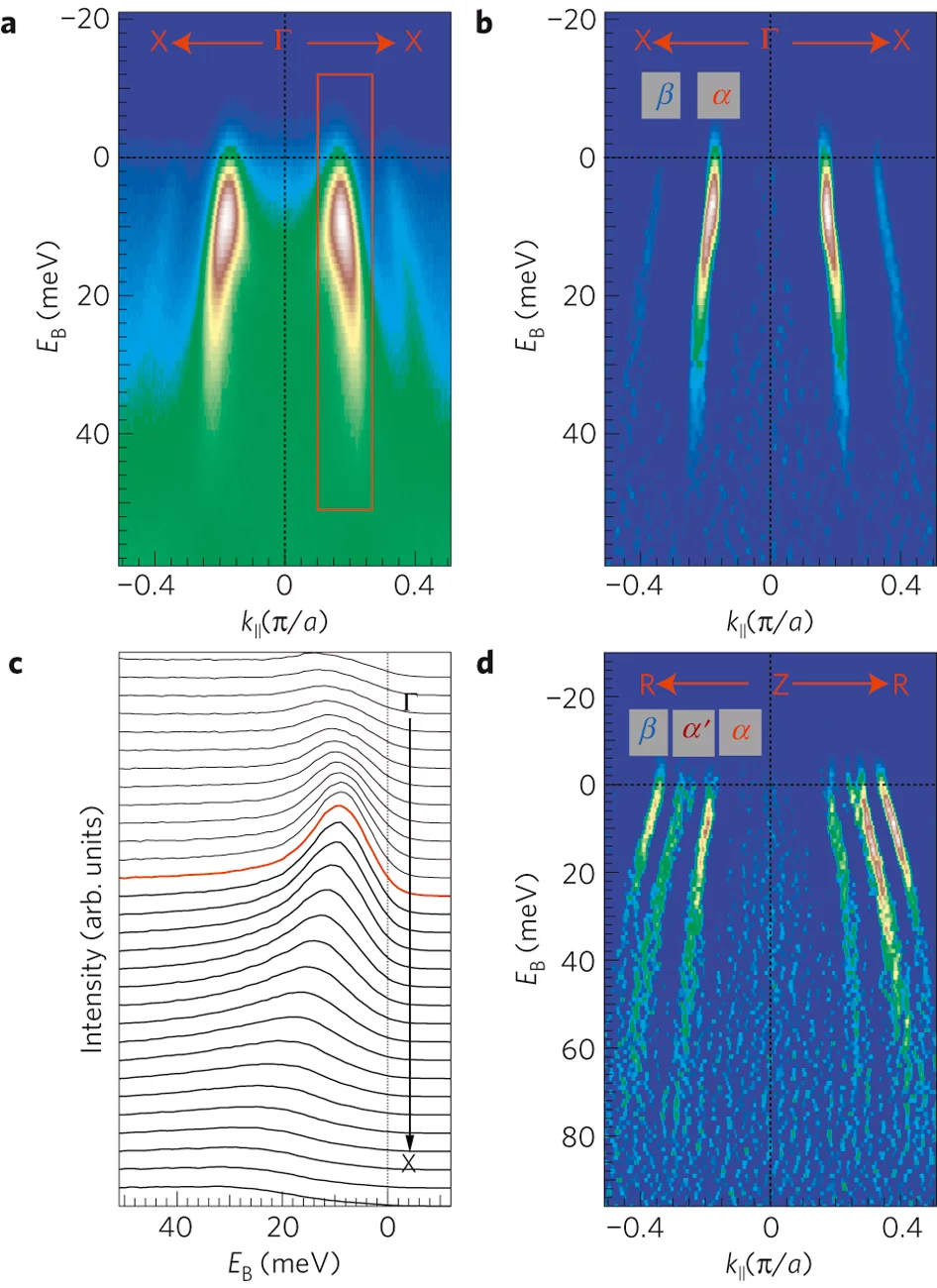
The iron-pnictide superconductors have a layered structureformed by stacks of FeAs planes from which the superconductivity originates. Given the multiband and quasi three-dimensional1 (3D) electronic structure of these high-temperature superconductors, knowledge of the quasi-3D superconducting (SC) gap is essential for understanding the superconducting mechanism. By using the kz capability of angle-resolved photoemission, we completely determined the SC gap on all five Fermi surfaces (FSs) in three dimensions on Ba0.6K0.4Fe2As2 samples. We found a marked kz dispersion of the SC gap, which can derive only from interlayer pairing. Remarkably, the SC energy gaps can be described by a single 3D gap function with two energy scales characterizing the strengths of intralayer Δ1 and interlayer Δ2 pairing. The anisotropy ratio Δ1/Δ2, determined from the gap function, is close to the c-axis anisotropy ratio of the magnetic exchange coupling Ja/Jab in the parent compound2. The ubiquitous gap function for all the 3D FSs reveals that pairing is short-ranged and strongly constrains the possible pairing force in the pnictides. A suitable candidate could arise from short-range antiferromagnetic fluctuations.
Reference
Reference
Facility: SLS
Paul Scherrer Institut, 5232 Villigen PSI, Switzerland
Email: ming.shi@psi.ch
Reference
Y-M. Xu, Y-B. Huang, X-Y. Cui, E. Razzoli, M. Radovic, M. Shi, G-F. Chen, P. Zheng, N-L. Wang, C-L. Zhang, P-C. Dai, J-P. Hu, Z. Wang & H. Ding, Nature Physics 7, 198 (2011), doi:10.1038/nphys1879Contact
Dr. Ming ShiPaul Scherrer Institut, 5232 Villigen PSI, Switzerland
Email: ming.shi@psi.ch