In this work the spin dynamics of microstates in artificial spin ice (ASI) in Ni81Fe19 nanomagnets arranged in an interconnected kagome lattice has been investigated using microfocus Brillouin light scattering, broadband ferromagnetic resonance, magnetic force microscopy, x-ray photoemission electron microscopy, and micromagnetic simulations.
In this work the spin dynamics of microstates in artificial spin ice (ASI) in Ni81Fe19 nanomagnets arranged in an interconnected kagome lattice has been investigated using microfocus Brillouin light scattering, broadband ferromagnetic resonance, magnetic force microscopy, x-ray photoemission electron microscopy, and micromagnetic simulations.
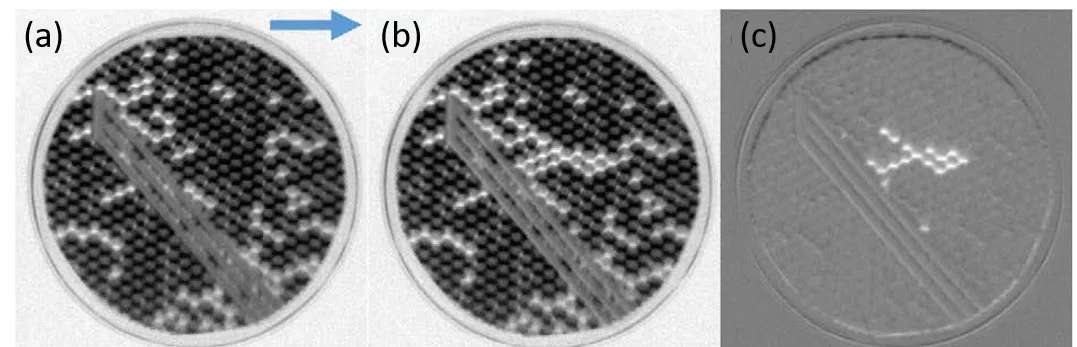
We experimentally reconfigure microstates in ASI using a 2D vector field protocol. To apply microwave-assisted switching an ultrahigh vacuum compatible, miniaturized voltage controlled oscillator (VCO) circuit was developed in a collaboration between PSI and EPFL. The circuit was mounted to the sample plate and enabled us to trigger in situ a magnetic reversal cascade within the sample (see Figure). This work provides an important step for the creation of avalanches inside the kagome ASI and reprogrammable magnonics based on ASIs. The research received funding by SNSF via project 163016.
Original Publication:
V. S. Bhat, S. Watanabe, K. Baumgaertl, A. Kleibert, M. A.W. Schoen, C. A. F. Vaz, and D. Grundler, Magnon Modes of Microstates and Microwave-Induced Avalanche in Kagome Artificial Spin Ice with Topological Defects, PHYSICAL REVIEW LETTERS 125, 117208 (2020)(https://doi.org/10.11032/PhysRevLett.125.117208)