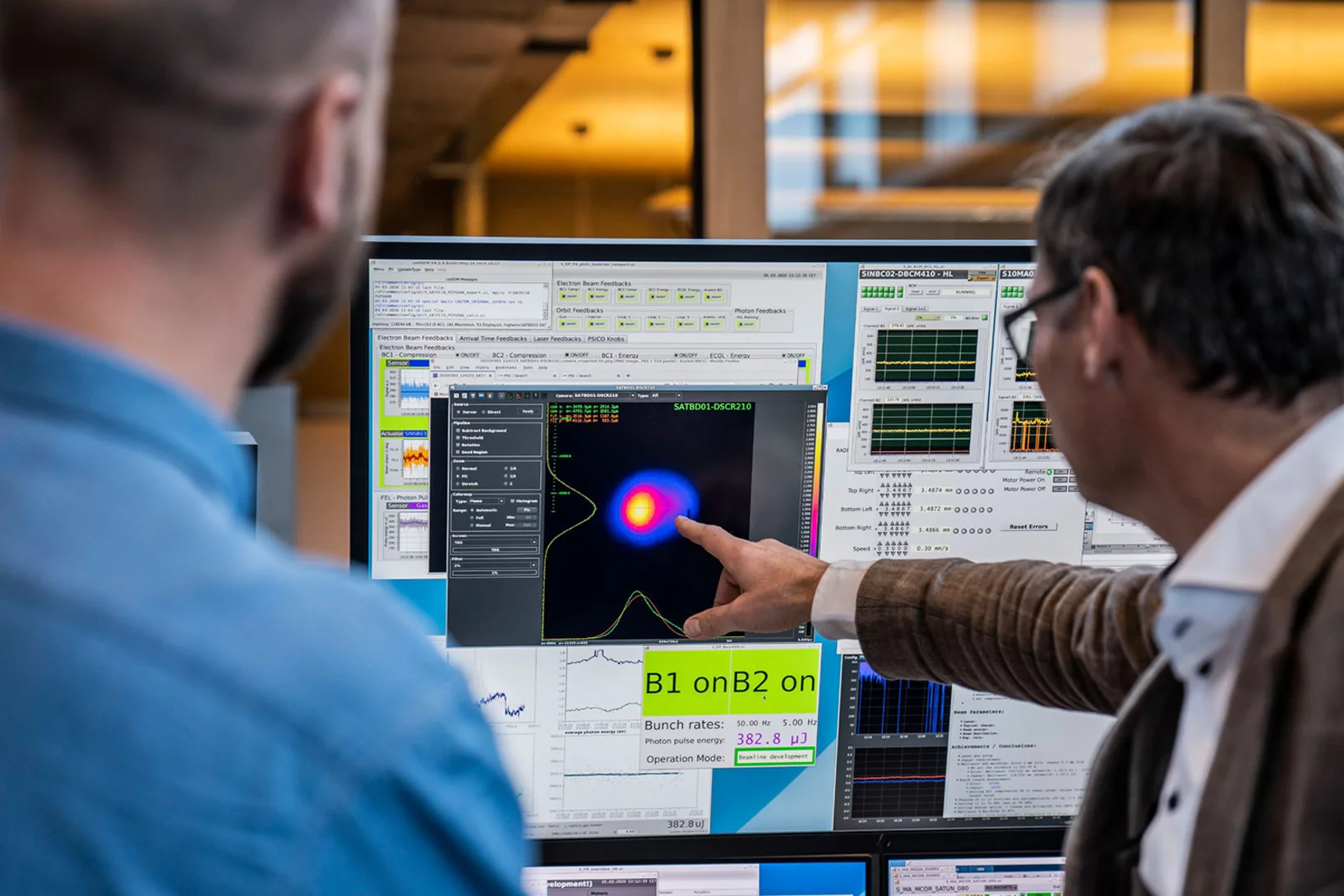
First light at Furka: The experiments can begin
The path to experiments that are unique in the world is now open.
No rose-coloured glasses here
Light is essential for life, and for researchers it is also a wonderful tool to better understand the structure of materials.
Growth in the data sciences
Another site for the Swiss Data Science Center will be established at PSI. This expansion is expected to give a further boost to the data sciences in Switzerland.
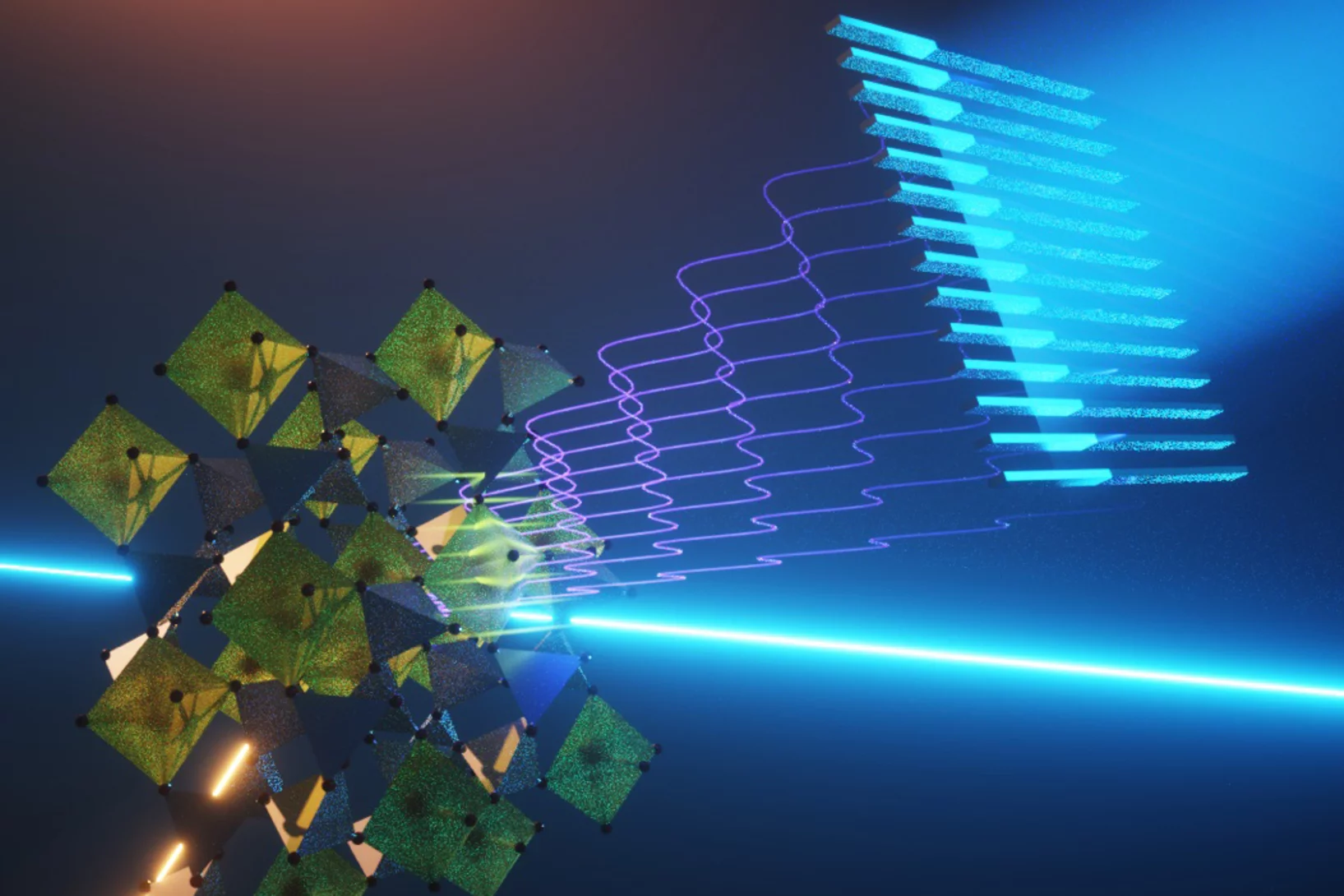
Uniquely sharp X-ray view
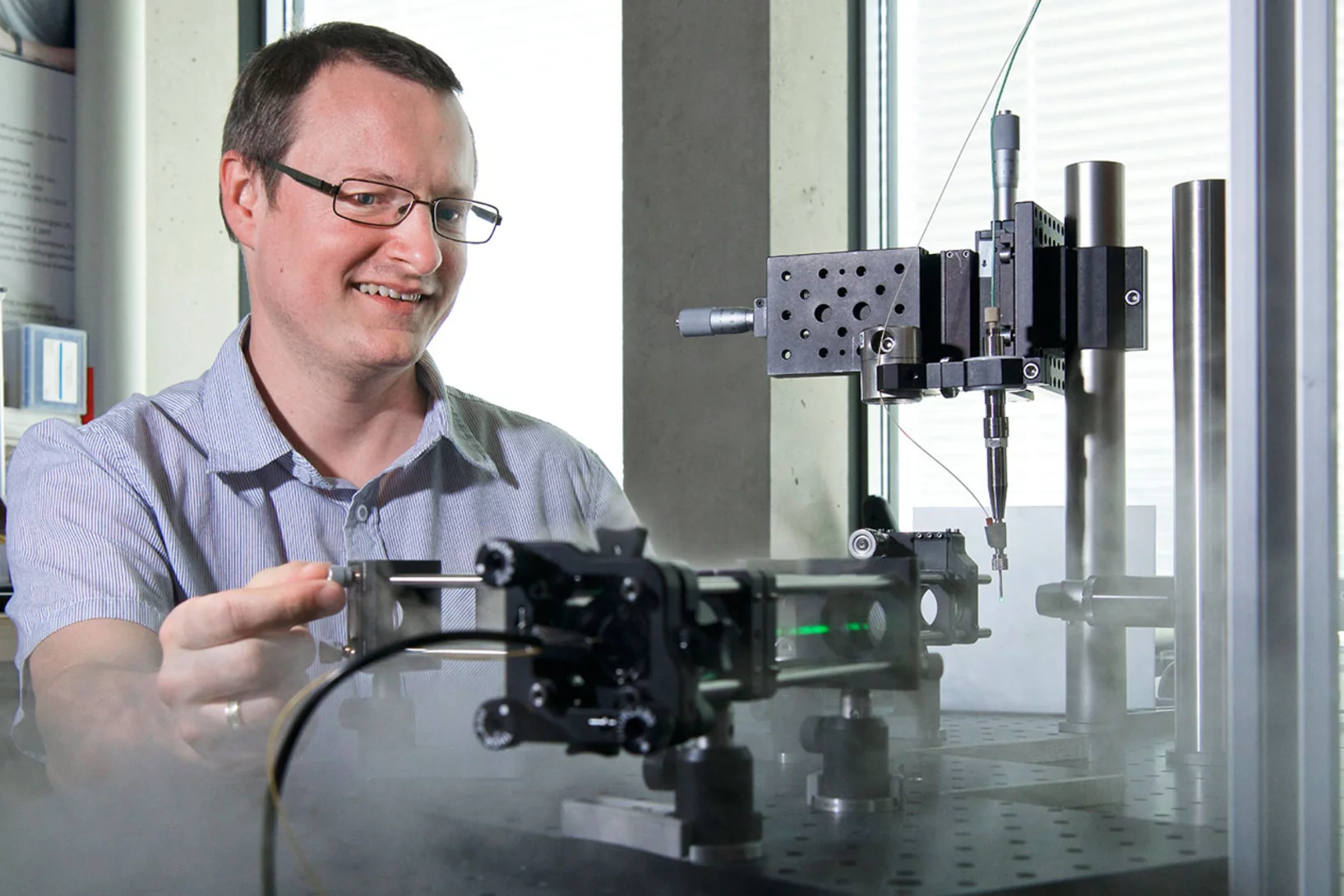
A new PSI method allows quantum-physical research on materials with the aid of X-ray lasers.
Compact and high-performance, like a Swiss Army knife
The X-ray free-electron laser SwissFEL really is as high-performance and versatile as planned.
HERCULES SCHOOL 2021 AT PSI
During the week of March 15 – 19, we had the pleasure to welcome 20 international PhD students, PostDocs and assistant professors at PSI, taking part in the first virtual HERCULES SCHOOL on Neutrons & Synchrotron Radiation.
Watching receptor proteins changing shape
In our bodies, G protein-coupled receptors mediate countless processes. PSI researcher Ramon Guixà talks about how he brings those receptor molecules to life on the computer screen.
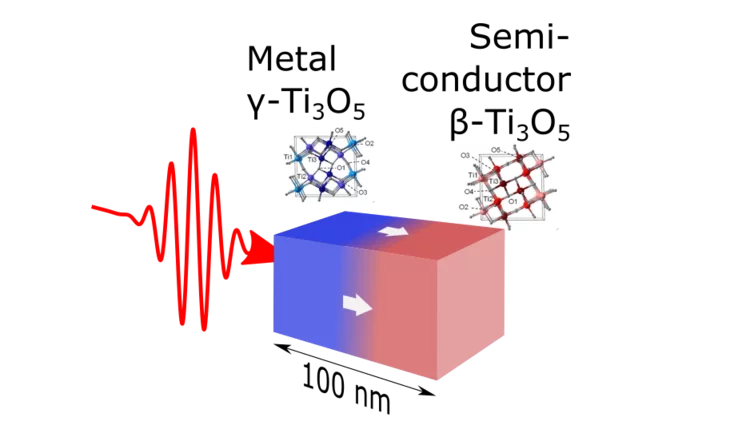
Conduction control in nanoparticles
Light induced propagation strain pulse, converting nanoparticles of Ti3O5 from semiconducting to metallic phase.
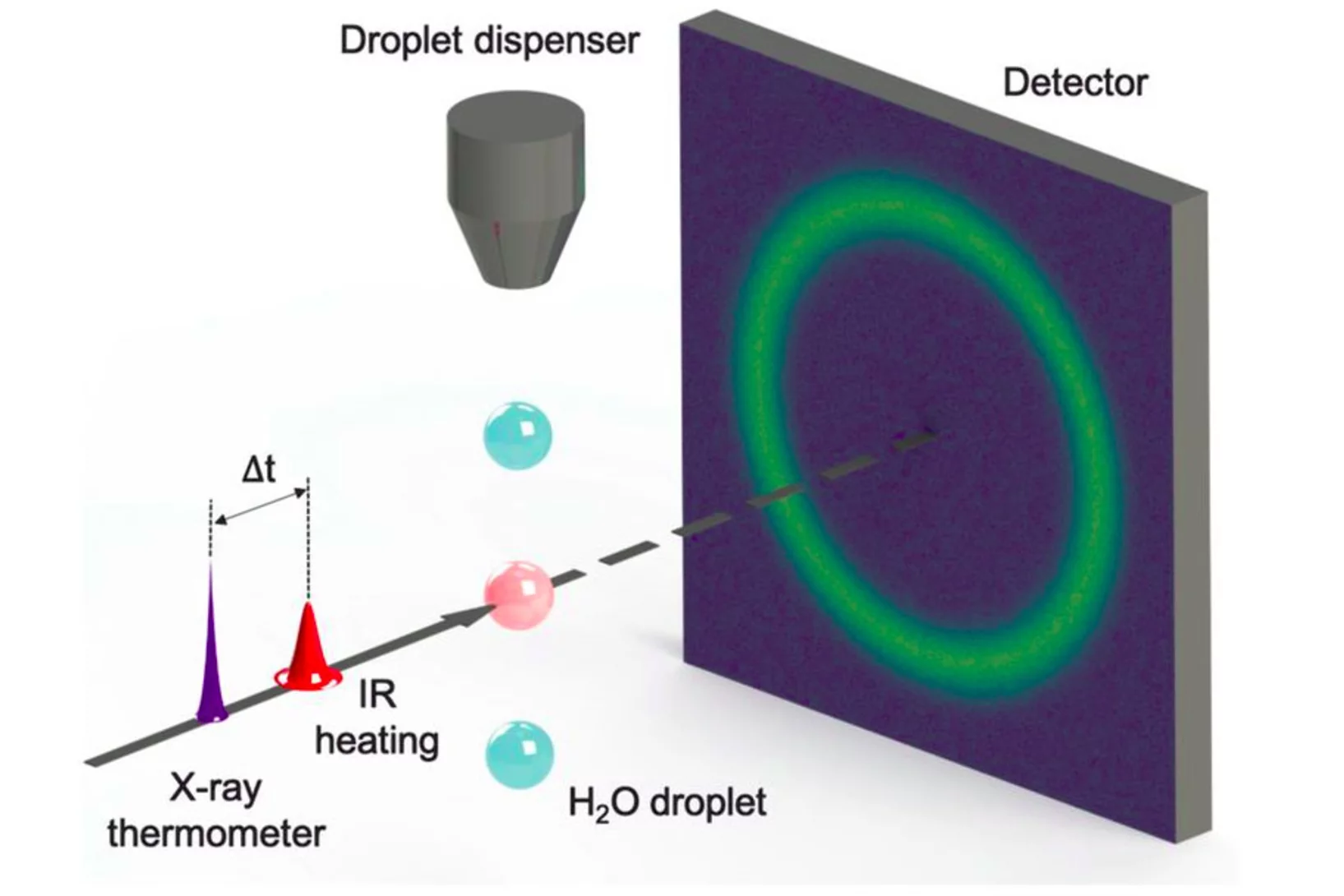
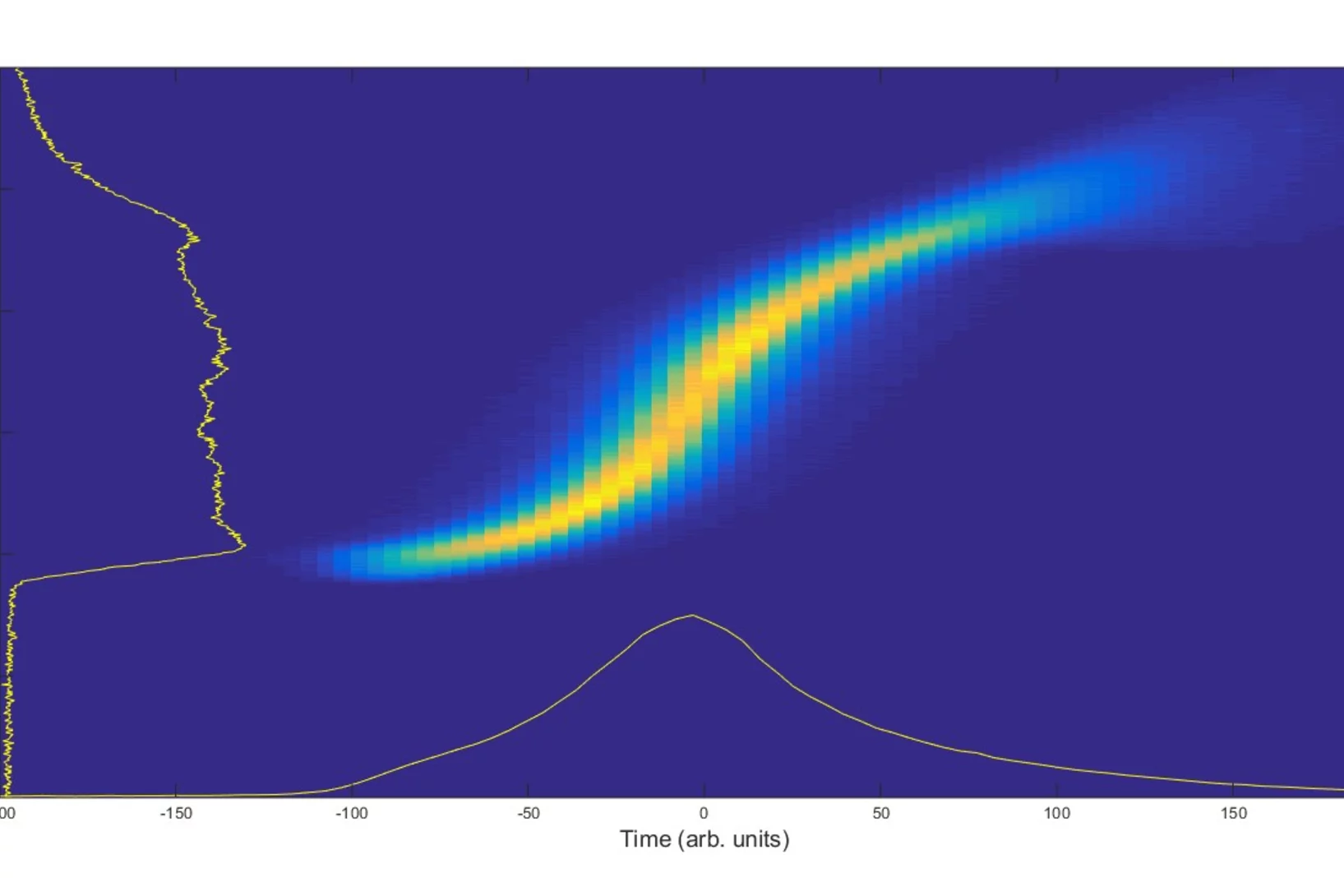
Ultrafast calorimetry of deeply supercooled water
FEL-based ultrafast calorimetry measurements show enhancement and maximum in the isobaric specific-heat.
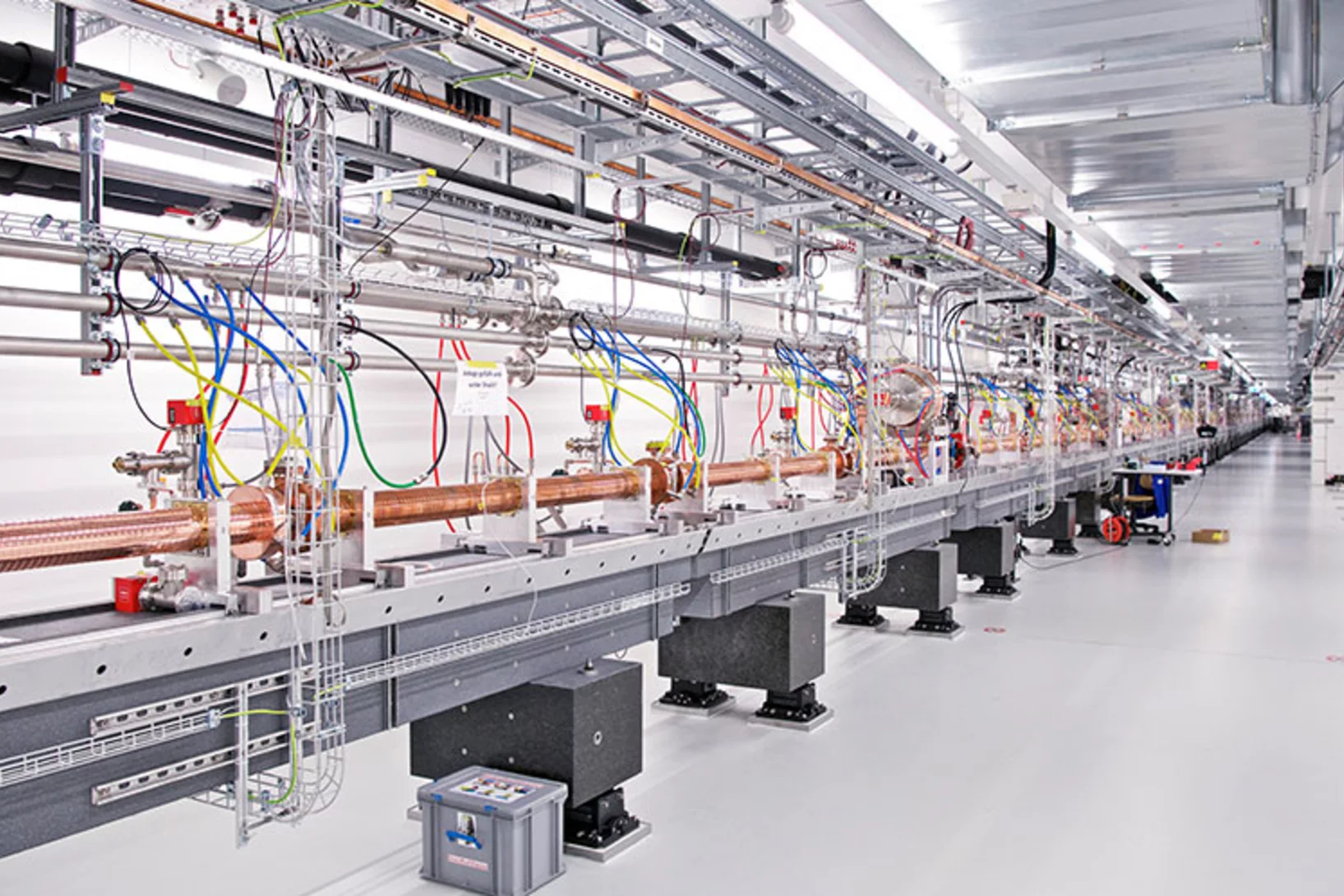
Milestone for the second beamline of SwissFEL
At the X-ray free-electron laser SwissFEL of the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI, the second beamline is currently being put into operation. With Athos, researchers want to understand how catalysts work or how biomolecules cause hereditary diseases.
SwissFEL: a perfect habitat for the black mortar bee
For the construction of the SwissFEL facility in 2013, around five hectares of forest were cleared and transformed into a new habitat for flora and fauna. Biologists and forest engineers have now assessed the results of the renaturization project and are excited about the progress to date.
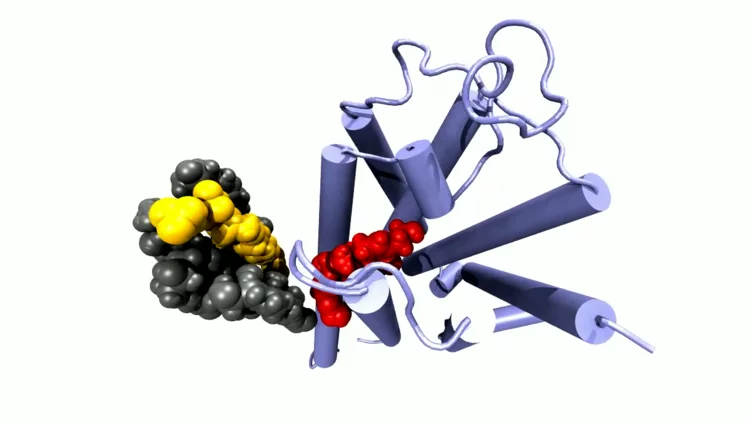
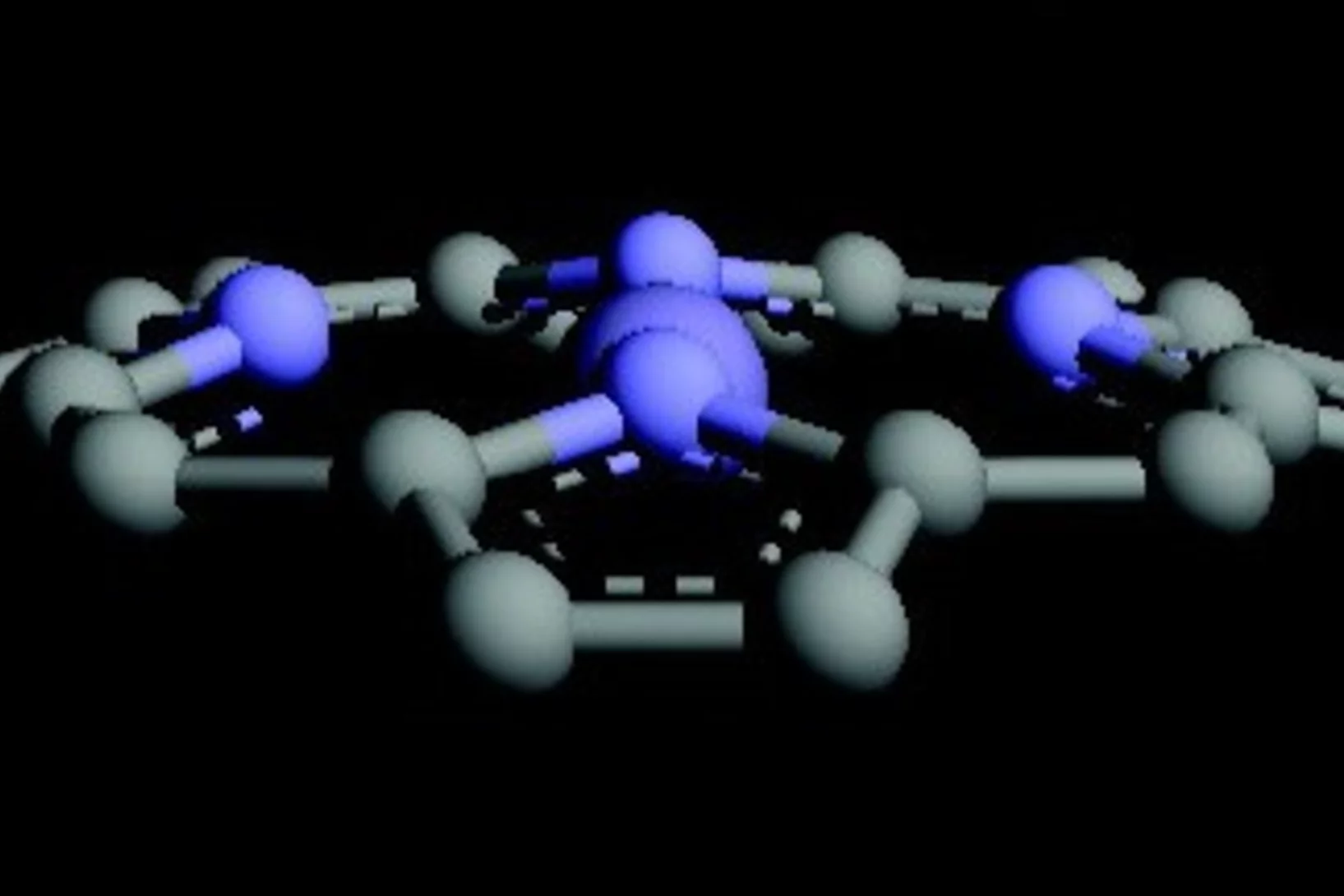
Spin cascade and doming in ferric hemes
In biology, structure and function are closely interwoven. A case in point is oxygen transport in the lungs, which relies on ferrous heme proteins adopting dome-like shapes.
First light in the SwissFEL Maloja endstation
The first endstation at the SwissFEL Athos soft X-ray branch is rapidly developing and on track for first experiments in 2021.
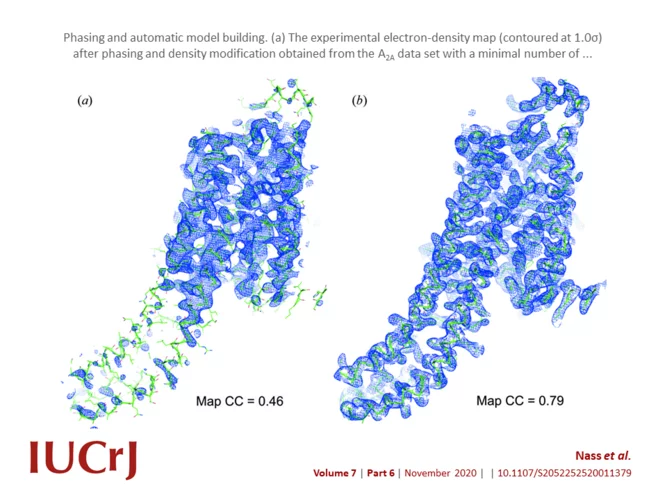
Advances in long-wavelength native phasing at X-ray free-electron lasers
Long-wavelength pulses from the Swiss X-ray free-electron laser (XFEL) have been used for de novo protein structure determination by native single-wavelength anomalous diffraction (native-SAD) phasing of serial femtosecond crystallography (SFX) data.
«Forschung online erleben»: Mittendrin statt nur dabei
Erstmals Live-Rundgang durch eine Grossforschungsanlage per Video-Stream. Am 9. September haben Interessierte exklusiv die Möglichkeit, sich von Experten des PSI durch den neuen Freie-Elektronen-Röntgenlaser SwissFEL führen zu lassen und zu erfahren, welche Rätsel der Materie und der Natur sich damit lösen lassen.
Elucidating the mechanism of a light-driven sodium pump
Researchers at the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI have succeeded for the first time in recording a light-driven sodium pump from bacterial cells in action. The findings promise progress in developing new methods in neurobiology. The researchers used the new X-ray free-electron laser SwissFEL for their investigations.
In search of the lighting material of the future
At the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI, researchers have gained insights into a promising material for organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs). This new understanding at the atomic level will help to develop new lighting materials that have higher light output and also are cost-efficient to manufacture.
Athos is making great strides
The new beamline at PSI's X-ray free-electron laser SwissFEL will soon be ready for action. In December, Athos delivered laser light for the first time − even sooner than expected, to the delight of the researchers responsible for its construction.
Research and tinkering – SwissFEL in 2019
The newest large research facility at the Paul Scherrer Institute, SwissFEL, has been completed. In January 2019 it began regular operation. Henrik Lemke, head of the SwissFEL Bernina research group, gives an interim report.
Molecular energy machine as a movie star
Using the Swiss Light Source SLS, PSI researchers have recorded a molecular energy machine in action and thus revealed how energy production at cell membranes works. For this purpose, they developed a new investigative method that could make the analysis of cellular processes significantly more effective than before.
PSI School for Master Degree Students - Introducing Photons, Neutrons and Muons for Condensed Matter Physics and Materials Science
From 17 – 21 June 2019 the Neutron and Muon Division (NUM) and the Photon Science Division (PSD) of PSI hosted 18 Master Degree students of physics, chemistry, materials and interdisciplinary science, as well as nuclear engineering to provide an introduction to the characterization of materials with large scale facilities like SINQ, SμS, SLS and SwissFEL. The course taught a basic understanding of how photons, neutrons and muons interact with matter, and how this knowledge can be used to solve specific problems in materials research.
Details of the program can be found at http://indico.psi.ch/event/PSImasterschool
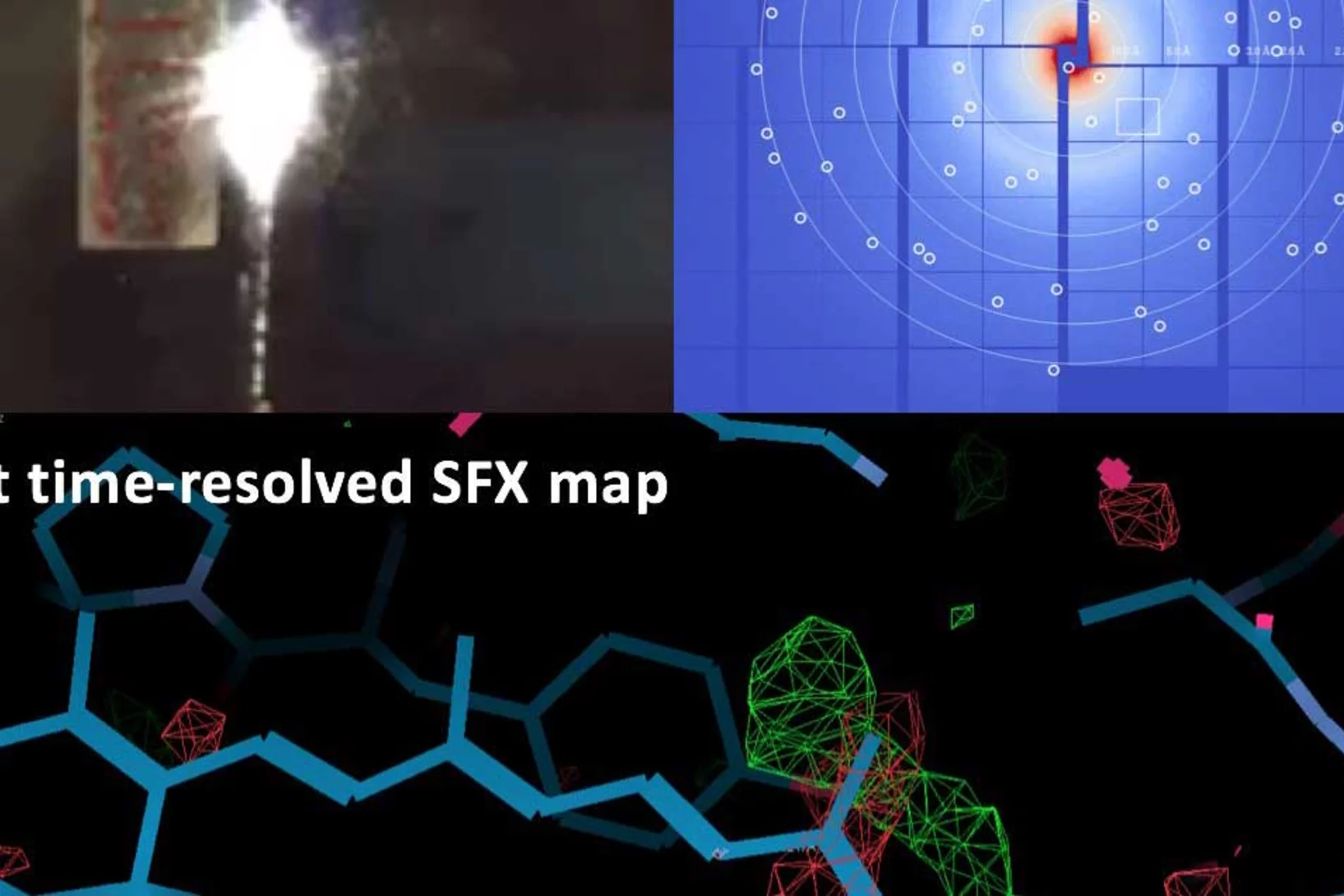
First serial femtosecond crystallography experiment using SwissFEL’s large bandwidth X-ray pulses
The typical mode of operation at XFEL facilities uses the so-called self-amplified spontaneous emission (SASE) process to generate the short, bright X-ray pulses. This mode of operation is stochastic in nature, causing some variance in intensity and spectrum on a shot-to-shot basis, which makes certain types of crystallographic measurements much more challenging.
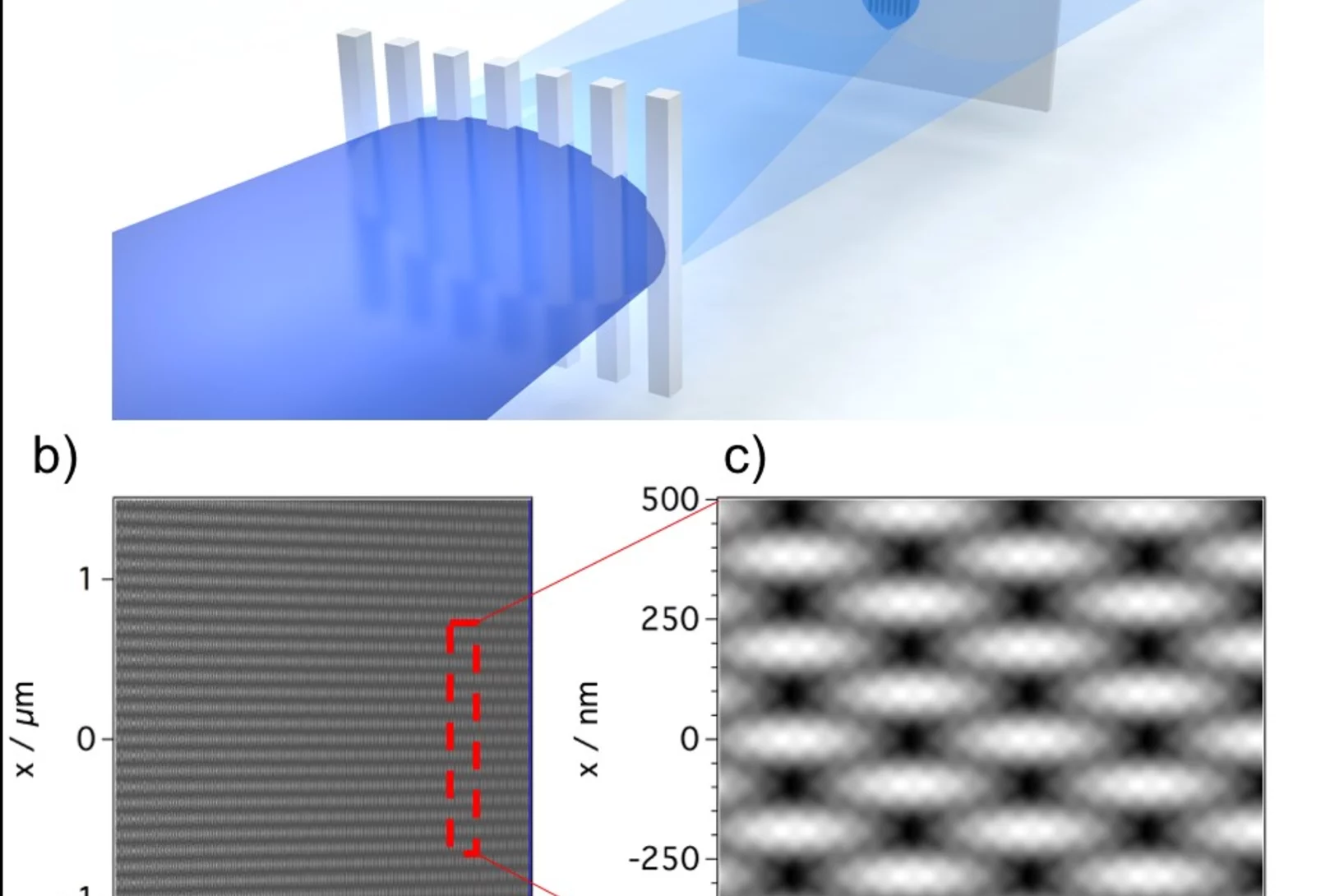
Towards X-ray Transient Grating Spectroscopy at SwissFEL
The high brilliance of new X-ray sources such as X-ray Free Electron Laser opens the way to non-linear spectroscopies. These techniques can probe ultrafast matter dynamics that would otherwise be inaccessible. One of these techniques, Transient Grating, involves the creation of a transient excitation grating by crossing X-ray beams on the sample. Scientists at PSI have realized a demonstration of such crossing by using an innovative approach well suited for the hard X-ray regime.
First femtosecond protein pump-probe measurements at SwissFEL
A major milestone in the commissioning of SwissFEL has been reached: the first pump-probe experiments on proteins have been successfully carried out. Crystals of several retinal-binding proteins were delivered in a viscous jet system and a femtosecond laser was used to start the isomerization reaction. Microsecond to sub-picosecond snapshots were then collected, catching the retinal proteins shortly after isomerization of the chromophore.
EU grants 14 million to Swiss Researchers
A team with three researchers from the ETH Domain has been awarded a prestigious EU grant. Today, they received the contract signed by the EU confirming the extraordinary 14 million euros funding. With it, they will investigate quantum effects which could become the backbone of future electronics.
SwissFEL's First Call for Proposals
The first SwissFEL call for proposals took place, deadline for submission was the 15th of September. In this first call for proposals SwissFEL received overwhelming interest from the user community. A total of 47 proposals were submitted for the SwissFEL Alvra experimental station and 26 for the Bernina experimental station. The Proposal Review committee PRC took place on 18-19 October 2018.
Bernina status first summer shutdown
The summer shutdown was used to install more missing hardware. With the new components the Bernina instrument will be already very close to the full design capabilities when the exciting time of user experiments will begin in 2019.
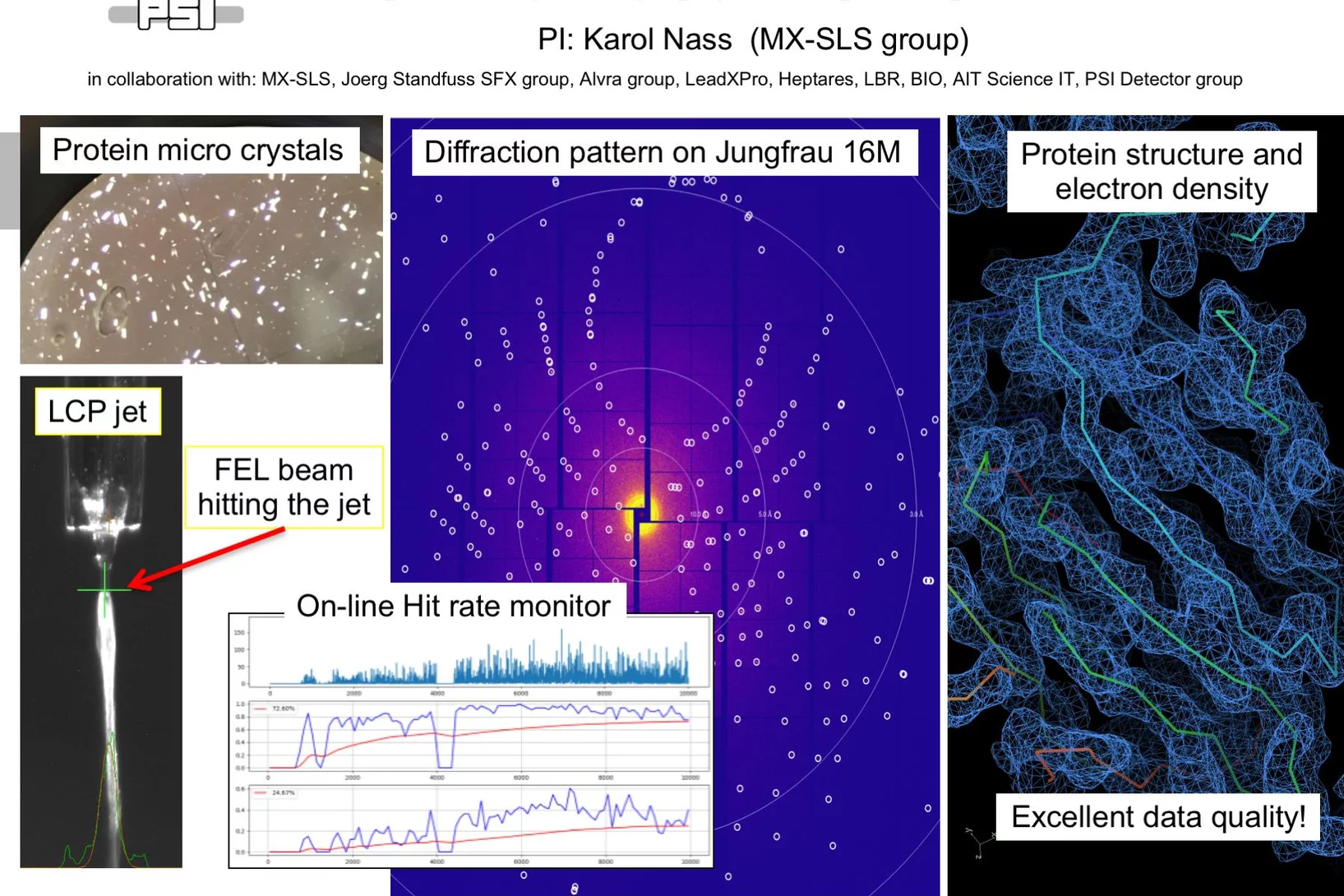
First serial femtosecond crystallography (SFX) pilot user experiment at SwissFEL
On the 7th to 12th of August 2018, a collaborative group of scientists from the Paul Scherrer Institute and members of the LeadXpro and Heptares pharmaceutical companies led by Karol Nass (PSI macromolecular crystallography MX-SLS group) performed the first serial femtosecond crystallography (SFX) pilot user experiment at the SwissFEL X-ray free electron laser (XFEL).
MOOCs – a paradigm shift in education
In March 2018, the nine-week MOOC “Introduction to synchrotrons and x-ray free-electron lasers” (abbreviated to “SYNCHROTRONx”) came online via the edX provider of the École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL), created by Phil Willmott of the Swiss Light Source, Paul Scherrer Institute. “MOOC” is an acronym for “massive open online course”, a teaching platform started in the first decade of this century, which has become increasingly popular in the last five to six years. MOOCs have no limits to participation and are free. Some of the most popular MOOCs can attract many tens of thousands of participants. Even the most specialized subjects may have an initial enrollment of over a thousand, more than an order of magnitude larger than that typically found in traditional higher education. There were over 70 million MOOC enrollments covering nearly 10’000 subjects offered by the top five providers in 2017 alone!
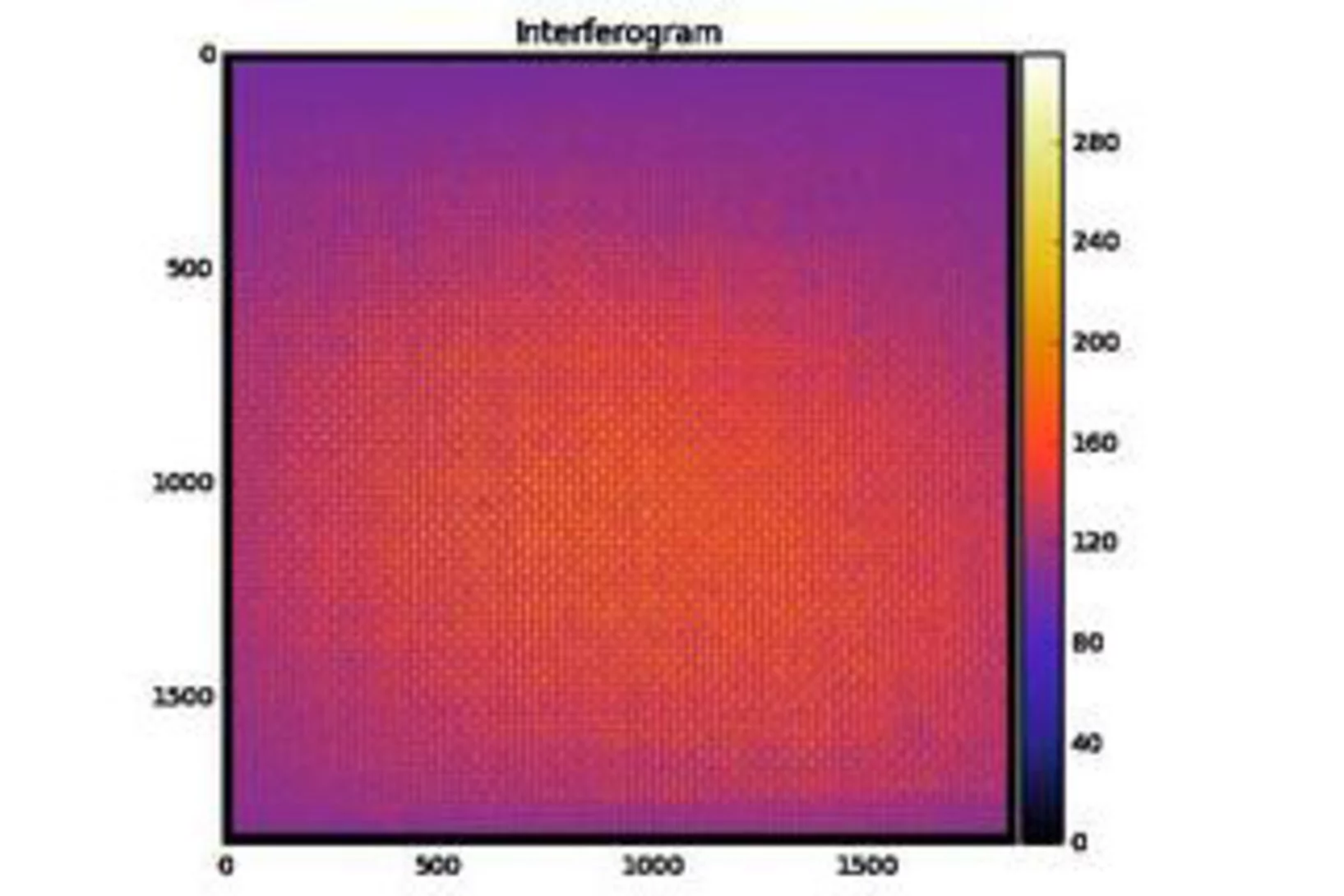
A first glance at the SwissFEL x-rays wave-front
X-ray Free Electron Lasers (XFELs) combine the properties of synchrotron radiation (short wavelengths) and laser radiation (high lateral coherence, ultrashort pulse durations). These outstanding machines allow to study ultra-fast phenomena at an atomic level with unprecedented temporal resolution for answering the most intriguing open questions in biology, chemistry and physics.