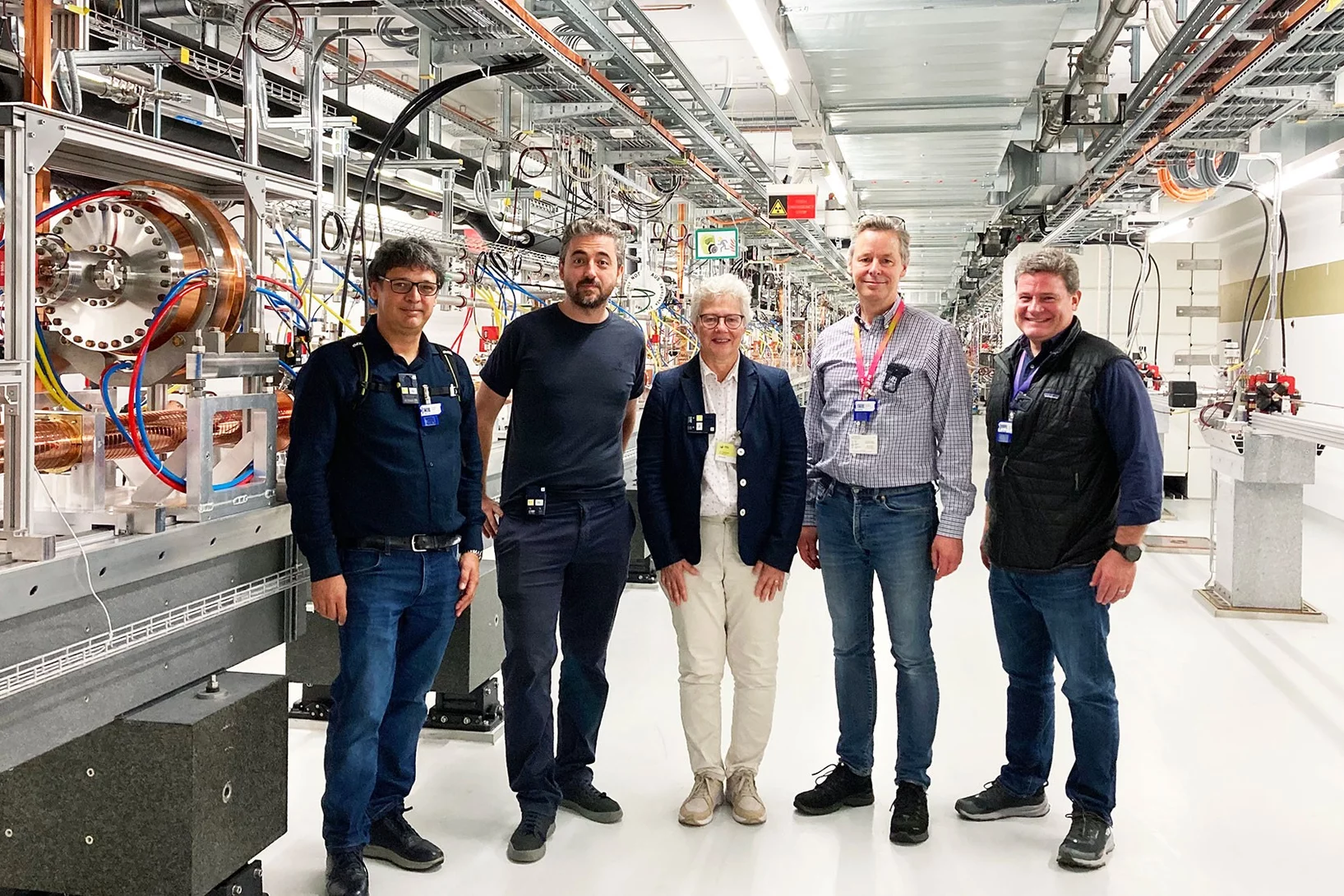
Nobel Prize winner Anne L’Huillier visits SwissFEL
X-ray free-electron lasers could unlock the next frontier in attosecond research
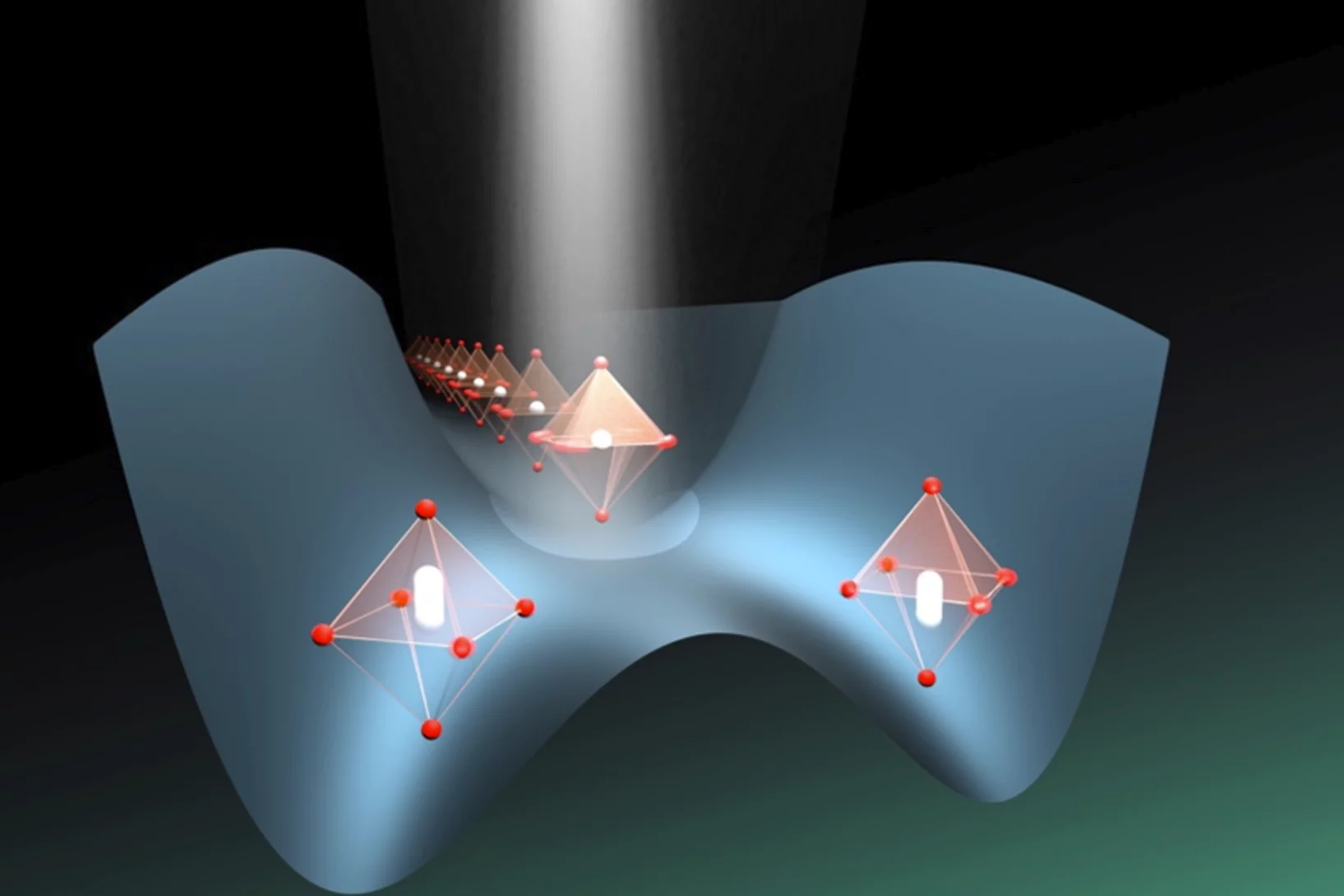
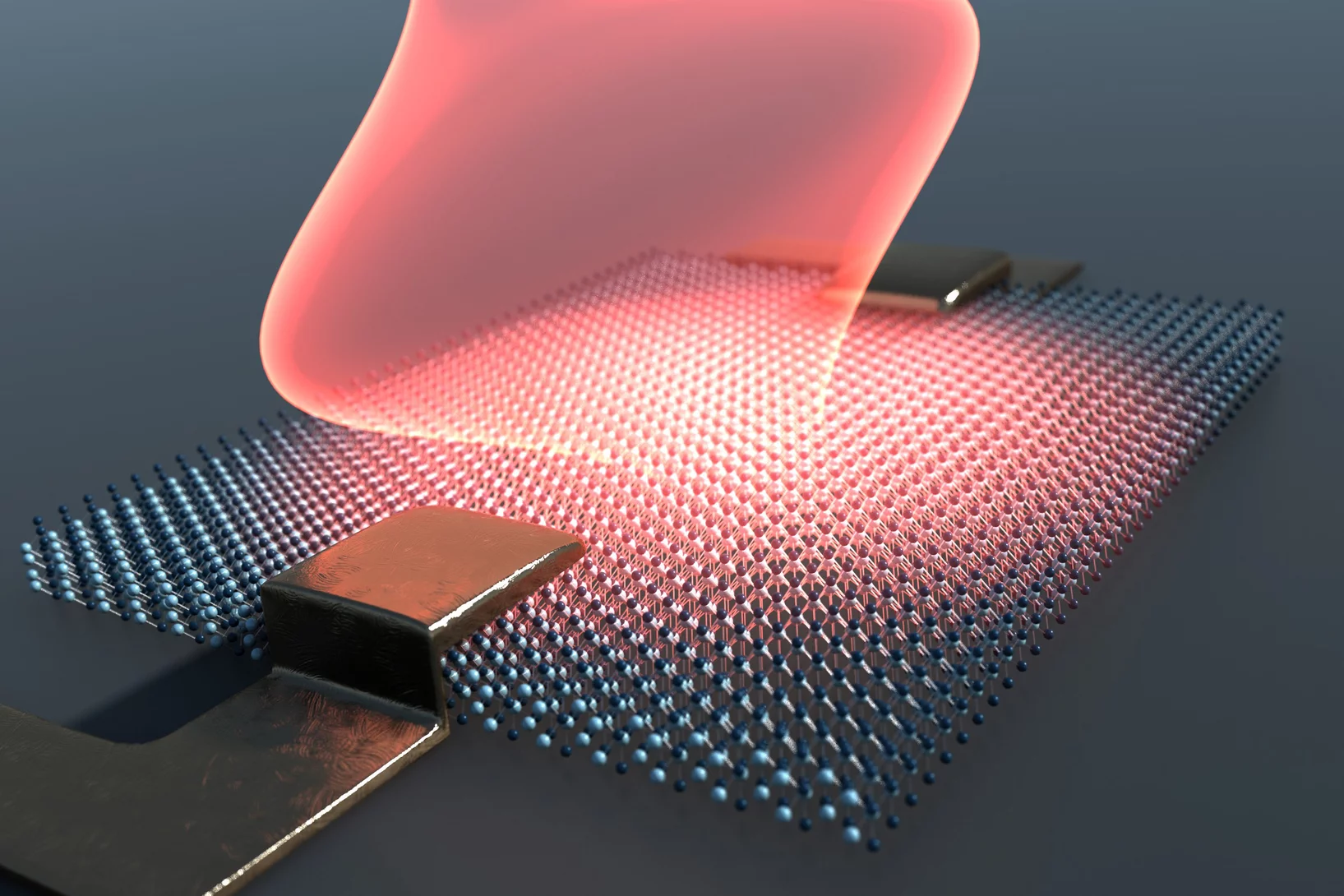
Controlling magnetic waves in a spin liquid
Scientists at the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI have shown that excitation of a spin liquid with intense THz pulses causes spins to appear and align within less than a picosecond. This induced coherent state causes a magnetic field to form inside the material, which is detected using ultrashort X-ray pulses at the X-ray Free Electron Laser SwissFEL.
Fundamentally different
Artificial intelligence is helping to evaluate an unimaginably vast amounts of data efficiently and exploit the facilities’ full potential for research.
Short x-ray pulses reveal the source of light-induced ferroelectricity
Ultrafast measurements of the fluctuating atomic positions in the quantum paraelectric SrTiO3 after mid-infrared light excitation, reveal details about the creation of the material’s ferroelectric state.
SwissFEL: a next generation tool for Attosecond Science
The 2023 Nobel Prize in Physics recognises attosecond science’s pioneers. Past and future, this field’s evolution is entwined with SwissFEL.
Repairing genetic damage with sunlight
An international research team at SwissFEL of PSI has discovered how an enzyme repairs DNA damage with the help of sunlight.
The secret life of an electromagnon
SwissFEL sheds light on how lattice and atomic spins jiggle together.
Bringing SwissFEL light to industrial users
High throughput experiments will enable new structural biology users to benefit from XFEL light.
Tender X-rays show how one of nature’s strongest bonds breaks
Short flashes of an unusual kind of X-ray light at SwissFEL and SLS bring scientists closer to developing better catalysts to transform the greenhouse gas methane into a less harmful chemical.
A compact gas attenuator for the SwissFEL ATHOS beamline realized using additive manufacturing
Gas attenuators are important devices providing accurate variation of photon intensity for soft X-ray beamlines. In the SwissFEL ATHOS beamline front-end the space is very limited and an innovative approach has been taken to provide attenuation of three orders of magnitude up to an energy of 1200 eV. Additive manufacturing of a differential pumping system vacuum manifold allowed a triple pumping stage to be realized in a space of less than half a meter. Measurements have shown that the response of the device is as expected from theoretical calculations.
An algorithm for sharper protein films
A newly developed algorithm allows measurements performed at X-ray free-electron lasers to be evaluated more efficiently.
The Hercules School visits PSI
20 international students visited PSI as part of the renowned Hercules School to learn about our state-of-the-art techniques and methodologies at our large scale facilities.
How vision begins
PSI scientists have discovered the very first step occurring in the eye when light hits the retina.
Using light to switch drugs on and off
PSI researchers record a molecular film of a cancer drug fitted with a photoswitch. This opens new insights for drug developers.
High-tech company VDL ETG: PSI’s new neighbour
The Dutch company VDL ETG has signed a rental agreement with Park Innovaare.
3.1 million in funding for new research projects at PSI
The PSI scientists Zurab Guguchia and Kirsten Schnorr are to receive grants totalling CHF 3.1 million from the Swiss National Science Foundation for ground-breaking projects.
Strong modulation of carrier effective mass in WTe2 via coherent lattice manipulation
Schematic ultrafast surface diffraction setup used for monitoring the crystal lattice in multiple directions.
A piece of PSI history sets off on a long journey
Off to new shores – a high-tech component is on its way from PSI to Australia by sea. In future, it will be deployed at the Australian Synchrotron in Melbourne.
Solving the unsolvable
PSI and ETH Zurich have founded the Quantum Computing Hub, where top researchers work together on concepts for quantum computers.
Athos just got even better
An ambitious upgrade at the soft X-ray beamline of the free electron laser SwissFEL opens up new experimental capabilities.
Faster and smarter
PSI is pooling its expertise regarding the evaluation of research data in the new research division Scientific Computing, Theory and Data.
New SwissFEL soft X-ray endstation welcomes first users
Maloja is go. First user experiments mark a double first, not only for the Maloja endstation but also for the second beamline of SwissFEL, Athos.
Hercules School 2022
PSI hosted again the Hercules School in March 2022. We had the pleasure to welcome 20 international PhD students, PostDocs and scientists to demonstrate our state-of-the-art techniques and methodologies at our large scale facilities, the Swiss Light Source (SLS), the Swiss Spallation Neutron Source (SINQ) and our free electron laser SwissFEL.
The wondrous world of light antennas
How light receptors can be used to specifically switch processes in cells on and off.
Opening the door to X-ray quantum optics
The 'perfect' X-ray beam-splitter: Researchers at SwissFEL have an ingenious solution to produce coherent copies of pulses, facilitating a realm of new X-ray techniques.
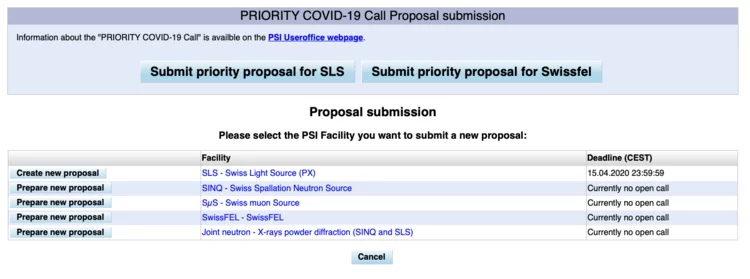
Priority access call for work on combating COVID-19 continues
On January 30th, 2020, the WHO declared the recent outbreak of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), a public health emergency of international concern. It declared that there is an urgent need to improve our understanding of the newly identified virus and its possible future evolution as well as to contain the spread; to develop precise diagnostics and treatment, and to improve the public health response and patient care.
The COVID priority access call continues and is still open in 2022.
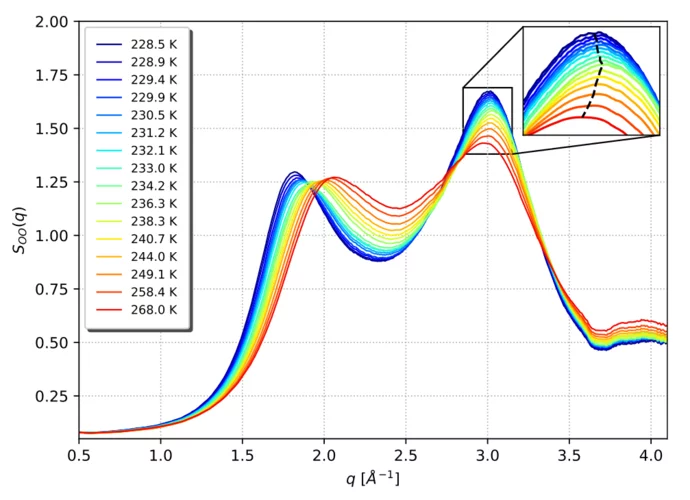
Anomalous temperature dependence of the experimental x-ray structure factor of supercooled water
Supercooled water scattering signals show an anolmalous structure factor temperature dependence suggesting decreasing density at lowering temperatures below 236 K (-37°C).
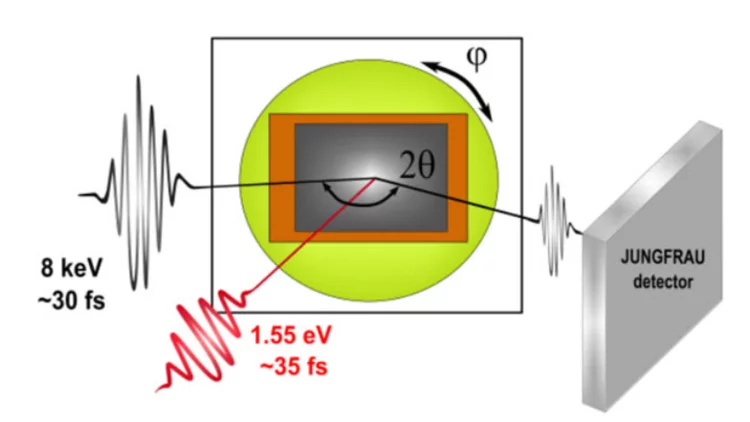
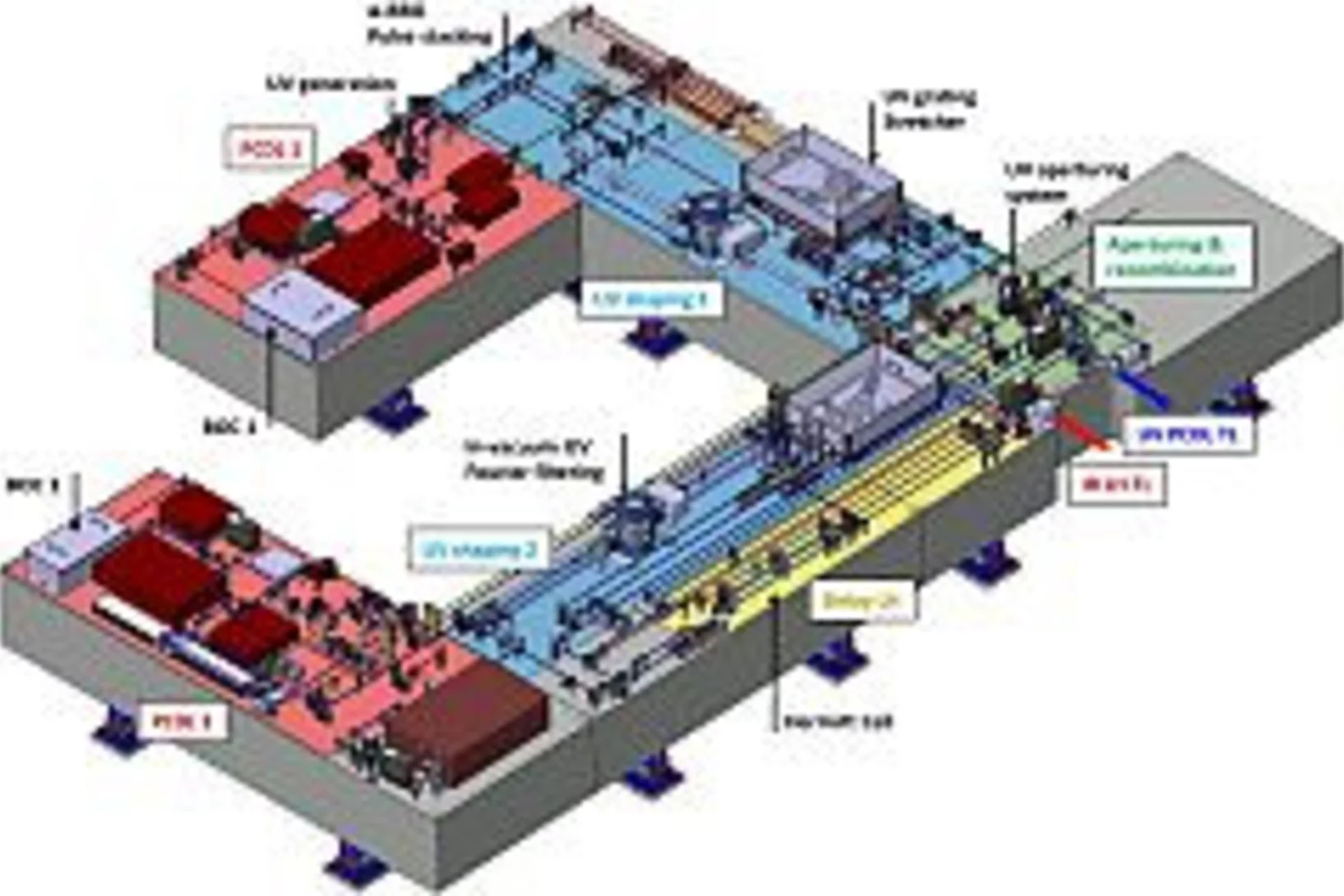
Overview of SwissFEL dual-photocathode laser capabilities and perspectives for exotic FEL modes
SwissFEL is a compact, high-brilliance, soft and hard X-ray Free Electron Laser (FEL) facility laser composed of two parallel beam lines seeded by a common linear accelerator (LINAC), and a two-bunch photo-injector. For the injector, an innovative dual-photocathode laser scheme has been developed based on state-of-the-art Ytterbium femtosecond laser systems. We just published an overview of the the SwissFEL Photo Cathode Drive Lasers (PCDL) performance, pulse shaping capabilities as well as the versatility of the systems, which allow many different modes of operation of SwissFEL [1]. The full control over the SwissFEL electron bunch properties via the unique architecture of the PCDL will enable in the future the advent of more advanced FEL modes; these modes are, but not restricted to, the generation of single or trains of sub-fs FEL pulses, multi-color FEL and finally the generation of fully coherent X-ray pulses via laser-based seeding.
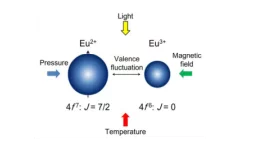
Ultrafast control of quantum materials
Using light to fundamentally change the properties of solids
Ultrafast electron localization
This experiment performed at SwissFEL shows how fast we can localize electrons out of an electron gas into correlated, well localized states of a material. It is based on a combined ultrafast x-ray absorption and diffraction experiment on an intermetallic system.