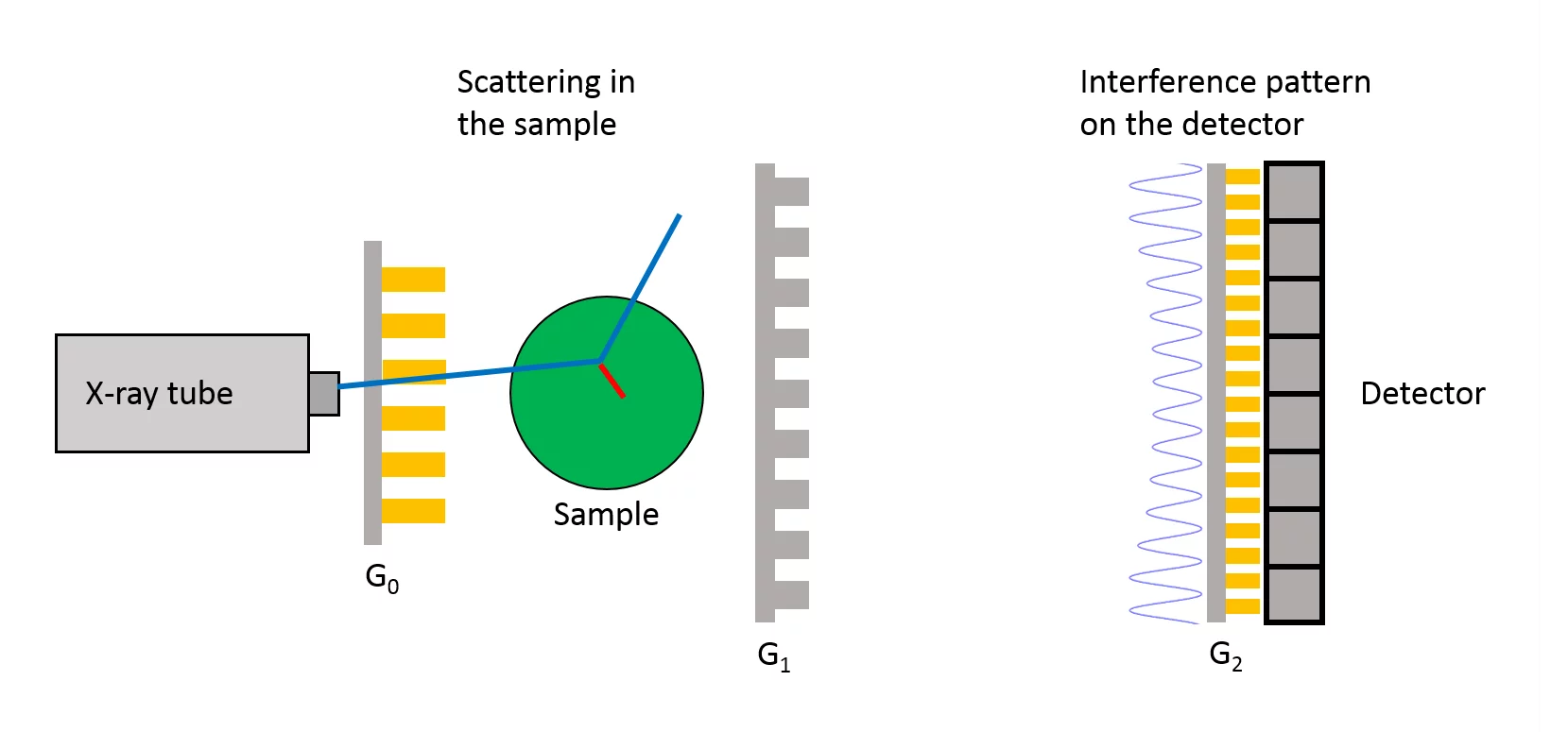
Simulations can aid the development process of clinical and non-clinical applications of X-ray grating interferometry (GI) with the estimation of patient and imaging relevant quantities like dose, spectra, image quality or visibility. Current state of the art simulation frameworks can either simulate interference patterns in case of wave propagation or scattering effects in the case of Monte Carlo. Even though, the potential of MC techniques to simulate interference patterns in GI setups has been demonstrated on smaller scales, there is no standard simulation framework capable of simultaneously including interference and scattering effects occurring in the imaging process of a clinical GI application.
Based on quantum mechanics a new GI Monte Carlo simulation framework for GI setups is developed in this work, with the aim to simulate scattering and interference phenomena within one framework. After a proof of principle on smaller scales with flat gratings, the algorithm will be extended for the simulation of clinically relevant volumes and extended to bent gratings. The use of Monte Carlo techniques opens additional opportunities for the simulation of GI devices like the use of incoherent sources, dose estimation or the impact of setup errors on performance.
References
- F. Pfeiffer, T. Weitkamp, O. Bunk, and C. David, Phase retrieval and differential phase-contrast imaging with low-brilliance x-ray sources, Nature physics 2, 258 (2006).
- . Pfeiffer, M. Bech, O. Bunk, P. Kraft, E. F. Eikenberry, C. Brönnimann, C. Grünzweig, and C. David, Hard-x-ray dark-field imaging using a grating interferometer, Nature materials 7, 134 (2008).
- S. A. Prahl, D. D. Duncan, and D. G. Fischer, Monte Carlo propagation of spatial coherence, in Biomedical Applications of Light Scattering III, Vol. 7187 (International Society for Optics and Photonics, 2009) p. 71870G.
- S. Peter, P. Modregger, M. K. Fix, W. Volken, D. Frei, P. Manser, and M. Stampanoni, Combining monte carlo methods with coherent wave optics for the simulation of phase-sensitive x-ray imaging, Journal of synchrotron radiation 21, 613 (2014).
-
P. Bartl, J. Durst, W. Haas, E. Hempel, T. Michel, A. Ritter, T. Weber, and G. Anton, Simulation of x-ray phase-contrast computed tomography of a medical phantom comprising particle and wave contributions, in Medical Imaging 2010: Physics of Medical Imaging, Vol. 7622 (International Society for Optics and Photonics, 2010) p.76220Q.
-
S. Cipiccia, F. A. Vittoria, M. Weikum, A. Olivo, and D. A. Jaroszynski, Inclusion of coherence in Monte Carlo models for simulation of x-ray phase contrast imaging, Optics express 22, 23480 (2014).
Collaboration
- Division of Medical Radiation Physics and Department of Radiation Oncology at Inselspital in Bern