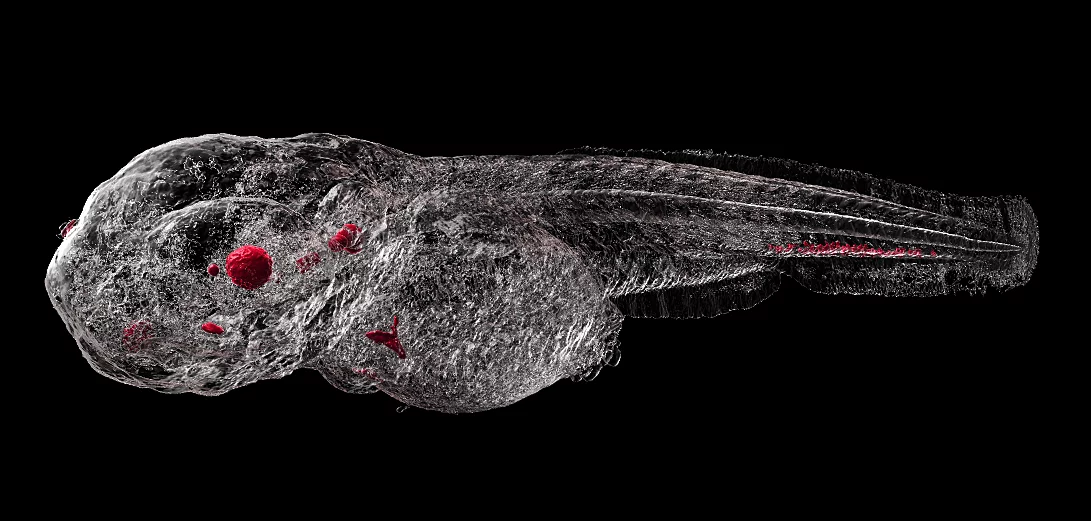
Metal-based nanoparticles are clinically used for diagnostic and therapeutic applications. After parenteral administration, they will distribute throughout different organs. Quantification of their distribution within tissues in the 3D space, however, remains a challenge owing to the small particle diameter.
In a study led by a team of researchers from the Pharmazentrum at University of Basel and the Paul Scherrer Institute, synchrotron radiation-based hard X-ray tomography (SRμCT) in absorption and phase contrast modes has been used for the localization of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (SPIONs) in soft tissues based on their electron density and X-ray attenuation. Biodistribution of SPIONs is studied using zebrafish embryos as a vertebrate screening model.
This label-free approach gives rise to an isotropic, 3D, direct space visualization of the entire 2.5 mm-long animal with a spatial resolution of around 2 µm. X-ray tomography is combined with physico-chemical characterization and cellular uptake studies to confirm the safety and effectiveness of protective SPION coatings.
The results were recently published in the journal Small and an artistic rendering of a 3D tomographic dataset is featured on journal cover for this issue.
Original Publication
Shedding light on metal-based nanoparticles in zebrafish by computed tomography with micrometer resolution
Cörek E, Rodgers G, Siegrist S, Einfalt T, Detampel P, Schlepütz CM, Sieber S, Fluder P, Schulz G, Unterweger H, Alexiou C, Müller B, Puchkov M & Huwyler J
Small 16(31), 2000746 (2020).
Project Website
News article at the Univeristy of Basel
https://www.unibas.ch/en/News-Events/News/Uni-Research/Tiny-fish-under-a-giant-camera.html
PSI Contact
Beamline Scientist, Swiss Light Source
Paul Scherrer Institut
Telephone: +41 56 310 4095
E-mail: christian.schlepuetz@psi.ch