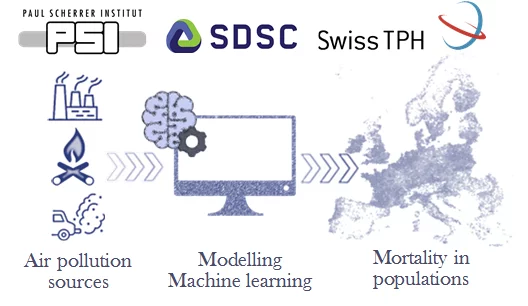
AURORA: from Air pollUtion souRces tO moRtAlity
The Laboratory of Atmospheric Chemistry has initiated innovative data-science-based modelling approaches to discover the most important pollution sources for human health
De l’hydrogène bleu peut protéger le climat
La clé: éviter les fuites.
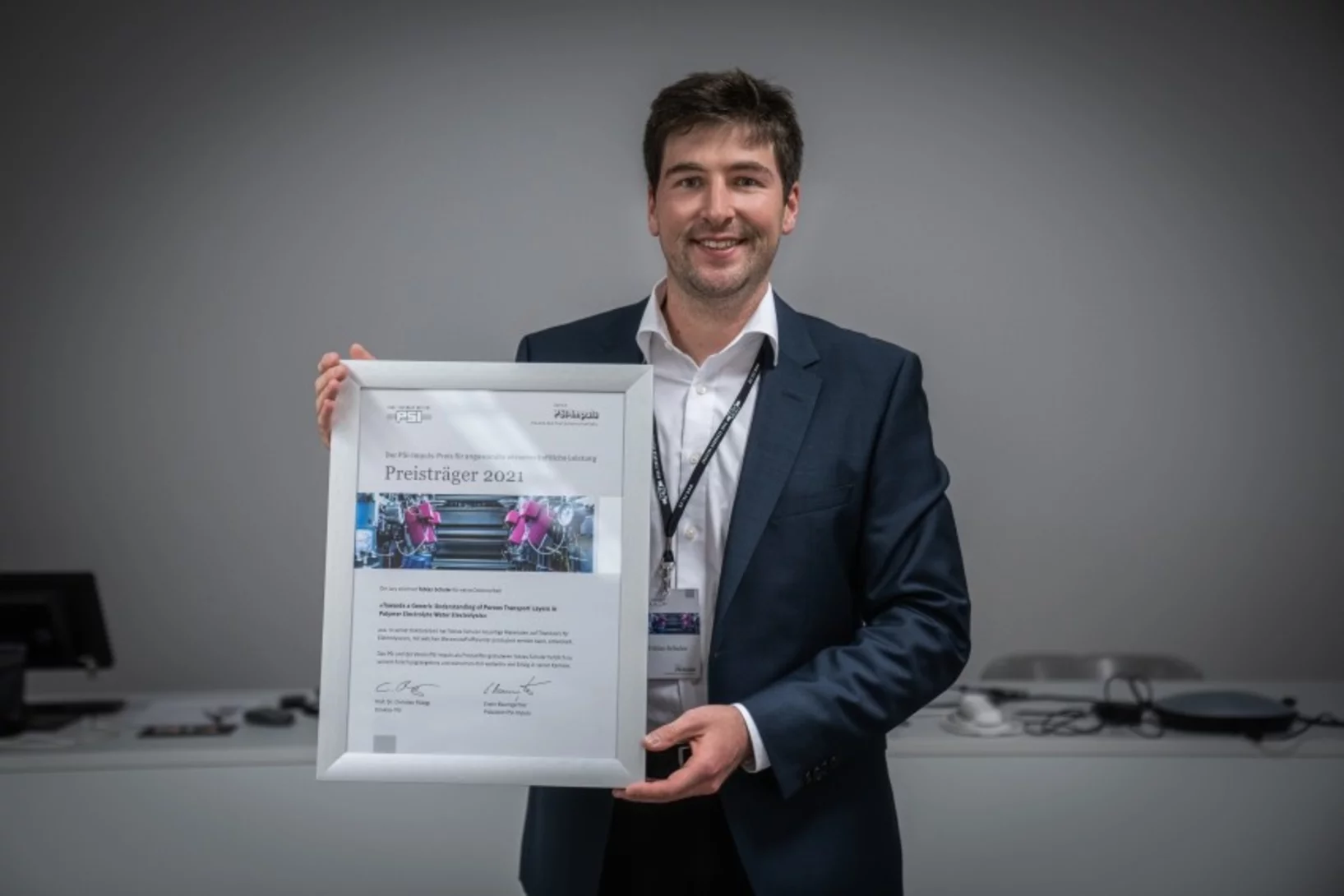
PSI Impuls Award Winner Tobias Schuler
On November 25th, Tobias Schuler was awarded the PSI Impuls Award for his doctoral thesis titled ‘Towards a Generic Understanding of Porous Transport Layers in Polymer Electrolyte Water Electrolysis’.
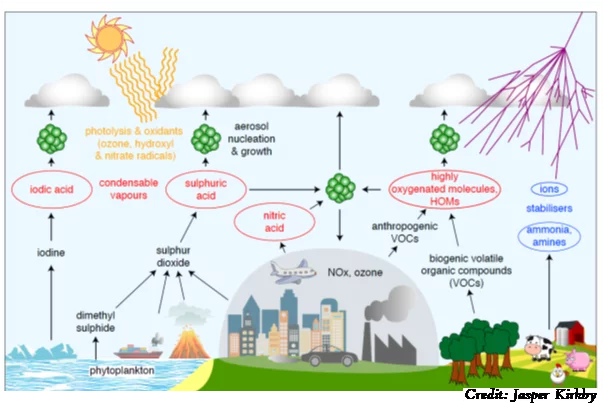
PSI maintains its leading role in the CLOUD experiment at CERN
The CLOUD experiment at CERN will be recreating particle formation in key regions of the globe to understand the effects of these particles on regional climates
Discovery of new chemistry on aerosol surfaces
In a study published in Science, ambient-pressure X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy reveals spontaneous redox chemistry at solvating particle surfaces.
Dioxyde de carbone peut devenir une ressource précieuse
Une nouvelle étude explore les méthodes qui permettent une utilisation efficace des émissions de CO2.
Take a deep breath. But how clean was the air?
The EU project, RI-URBANS, aims to improve air quality monitoring across Europe
Successful Ambizione Grant Applicant
Kaspar Dällenbach, Scientist at the Laboratory of Atmospheric Chemistry (LAC) at the Paul Scherrer Institute (PSI) was granted the Ambizione Grant 2020 with his project “Particulate air pollution sources in low-income megacities (PRESSING)”.
NET ZERO Day of the four RIs at Empa
Climate change is one of the biggest challenges humanity is facing. It requires an approach, in which competences and capacities in research are combined across Switzerland to develop solutions for a transformation of our society towards net zero CO2 emissions.
Successful Ambizione Grant Applicant
Alexander Muroyama, Postdoctoral Researcher at the Electrochemistry Laboratory (LEC) at the Paul Scherrer Institute has successfully applied for the Ambizione Grant 2020 with his project “A novel process for electrochemical direct-air capture of CO2”.
Successful Ambizione Grant applicant
Patrik Winiger, Research Grant Advisor and Project Manager at ETH Zurich, successfully applied for the Ambizione Grant 2020 with the project “Macromolecular Aerosols in the Cryosphere from the Arctic to the Alps – MACrAA”. The idea was developed together with the Laboratory for Atmospheric Chemistry (LAC) at PSI. The LAC is a global leader in aerosol analytics and source identification. They own and operate a unique laboratory infrastructure with various instruments and multiple aerosol simulation chambers available for researchers.
ReMaP – Current status of energy research
With its Energy Strategy 2050 Switzerland aims – beside other goals – to promote the use of domestic renewable energy and to develop the electricity power grid, which plays a decisive role in the upgrading of the system of electricity power supply. A lot of research needs to be done to achieve these ambitious goals. An important research project in this area is ReMaP and its status quo was presented at the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI on 28 September.
The ICE MEMORY program
As an international initiative, ICE MEMORY aims at collecting heritage ice cores from the world’s key endangered glaciers to store them under safe conditions and international governance in Antarctica for future generations of scientists.
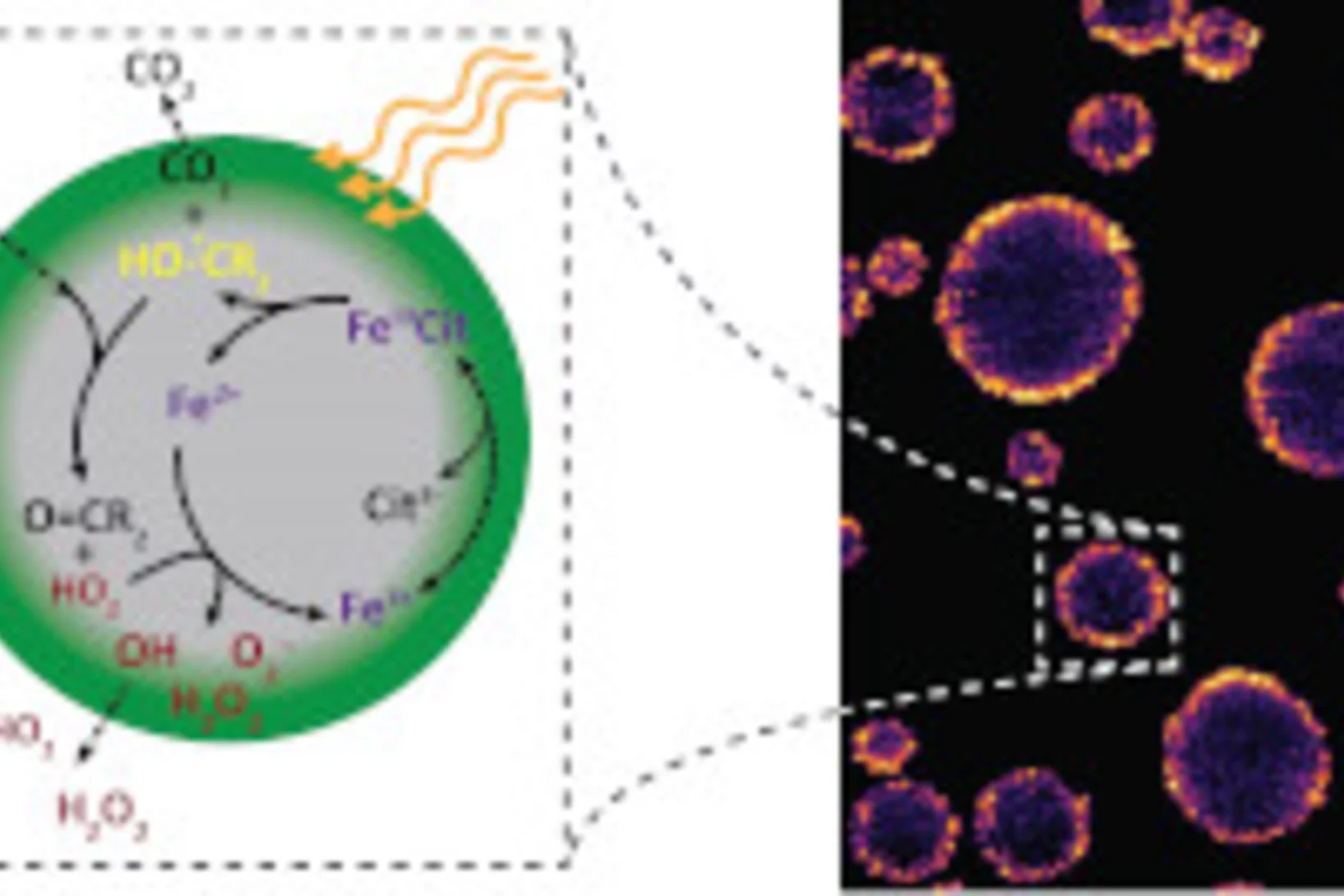
Looking inside airborne particles for the chemistry responsible for their adverse health effects.
Chemical changes inside of breathable airborne particles can cause reactive oxygen species (ROS) and carbon centered radicals (CCRs) to form, which are harmful to our bodies and induce oxidative stress in lungs. Using X-ray spectromicroscopy at the PolLux beamline and mimicking the environmental and sunlit conditions aerosol particles experience in the atmosphere near the Earth Surface, it was recently found that highly viscous organic particles with low water content can attain high concentrations of ROS and CCRs that persist over long times. Natural particles like these will occur in ambient humidity below 60% and effectively trap ROS and CCRs inside that react when exposed to light.
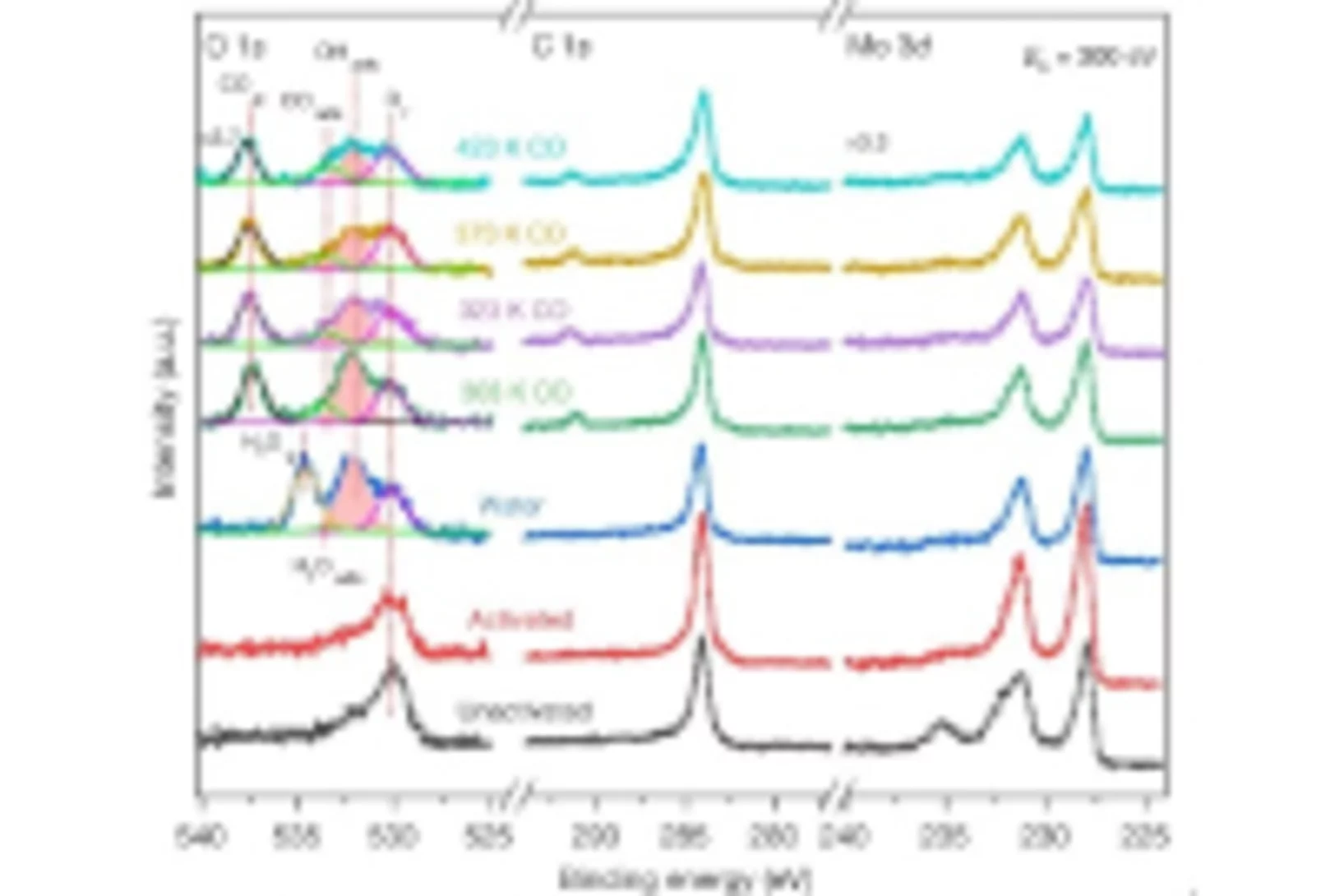
XPS allows in situ investigation of the solid-gas interface during a catalytic reaction
Platinum isolated atoms and clusters supported on molybdenum carbide have been characterized in situ by means of photoelectron spectroscopy. The presence of both species is essential to favor the stability, so that the catalysts displays high metal-normalized turnover number of 4,300,000 moles of hydrogen per mole of platinum during the water gas shift reaction.
Aerosol distribution in rooms and the importance of proper ventilation
Urs Baltensperger explains the background why it is absolutely necessary to wear masks in order to reduce the risk of beeing infected with Covid-19.
In the following you find the presentation and summary
Einfache Experimente zeigen: so gut schützen uns Masken und andere Materialien
Spätestens seit Corona ist der Maskengebrauch auch in der Schweiz im Alltag präsent. Doch wie gut können wir uns und andere mit verschieden Materialien vor kleineren und grösseren Partikeln schützen? Das alljährlich durchgeführte PSI Feriencamp bietet Kindern einen spannenden Einblick in die faszinierende Welt der Forschung. In diesem Jahr gingen Kinder an einer Projektstation genau dieser Frage nach. Dabei untersuchten sie, wie gut verschiedene Materialien die im Labor generierten Partikel zurückhalten. Es wurden Textilmasken (im Handel erhältlich, wiederverwendbar, nicht FFP2-zertifiziert), Chirurgenmasken (Einwegmasken, FFP2-zertifiziert), Teefilter, Kaffeefilter, Papiertaschentuch und WC-Papier getestet, und es wurde klar, Maske ist nicht gleich Maske.
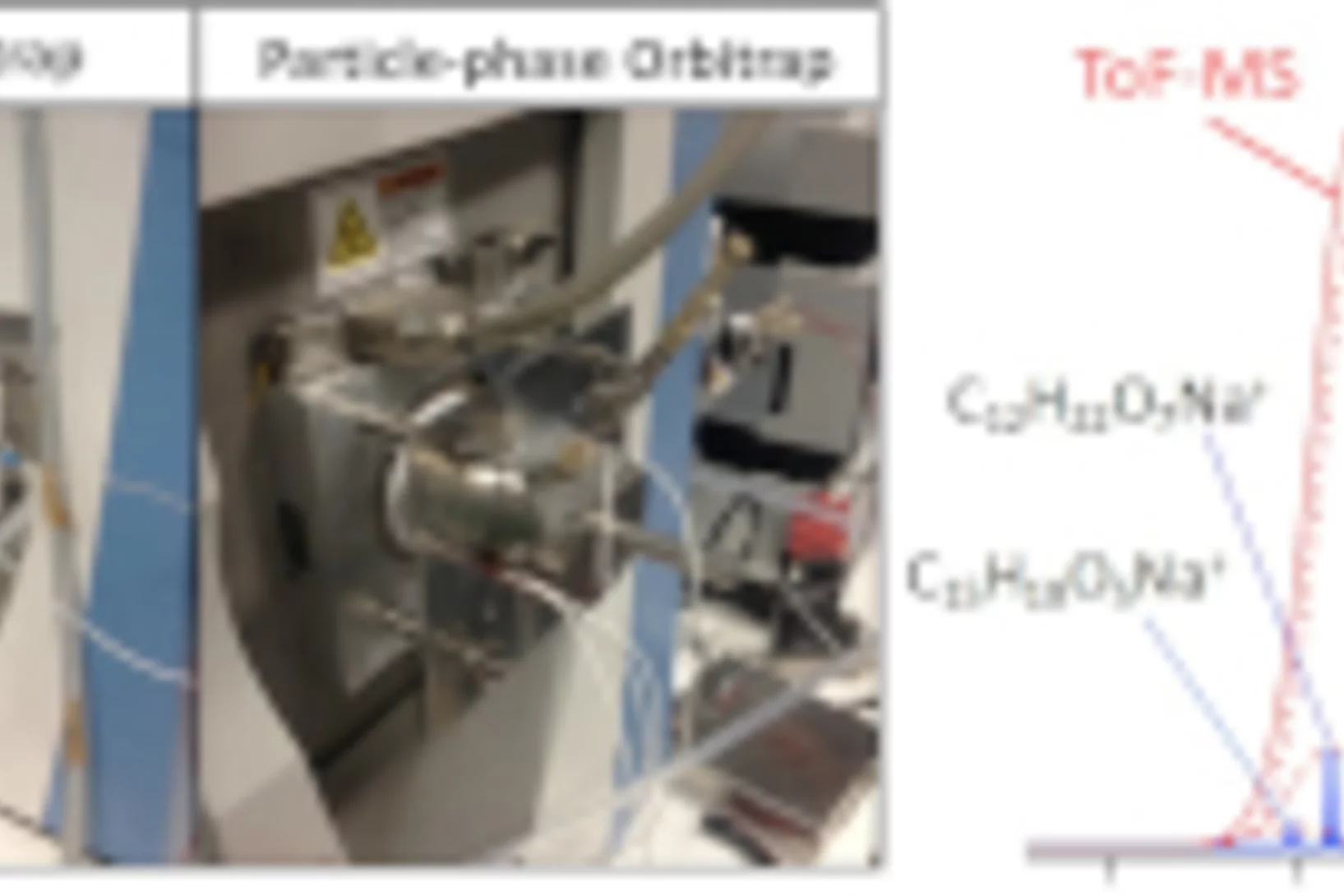
Online ultrahigh resolution mass spectrometry for the molecular analysis of the atmosphere
Atmospheric aerosols are considered the single largest uncertainty in assessing the human contribution to global warming and amongst the top five health risks worldwide. Our ability to investigate aerosol sources, their formation processes in the gas-phase, and their societal impacts is largely governed by our capability to measure their molecular constituents in real-time. Researchers at PSI have combined for the first time ultrahigh resolution mass spectrometry with high time resolution and sensitivity for the molecular analysis of aerosols.
Newly discovered rapid particle growth rates may be the answer to the mystery of aerosol formation in urban smog
Aerosols, suspended particles or droplets, play a key role in Earth’s atmosphere’s energy balance. They can also result in smog formation in cities, which leads to low visibility and serious health risks for the population. A recent study published in Nature outlines a newly discovered mechanism that may play a key role in the continued survival of particles in wintertime smog.
Around Antarctica in 90 days to study the pristine atmosphere
PSI researchers have designed and equipped a laboratory container for operation on research ships to undertake comprehensive studies of the chemistry and microphysics of the atmosphere. The floating laboratory was first deployed during the Antarctic Circumnavigation Expedition (ACE) with the aim of characterizing aerosol processes that are relevant for climate change in an atmosphere, which is hardly influenced by human emissions of air pollutants other than greenhouse gases.
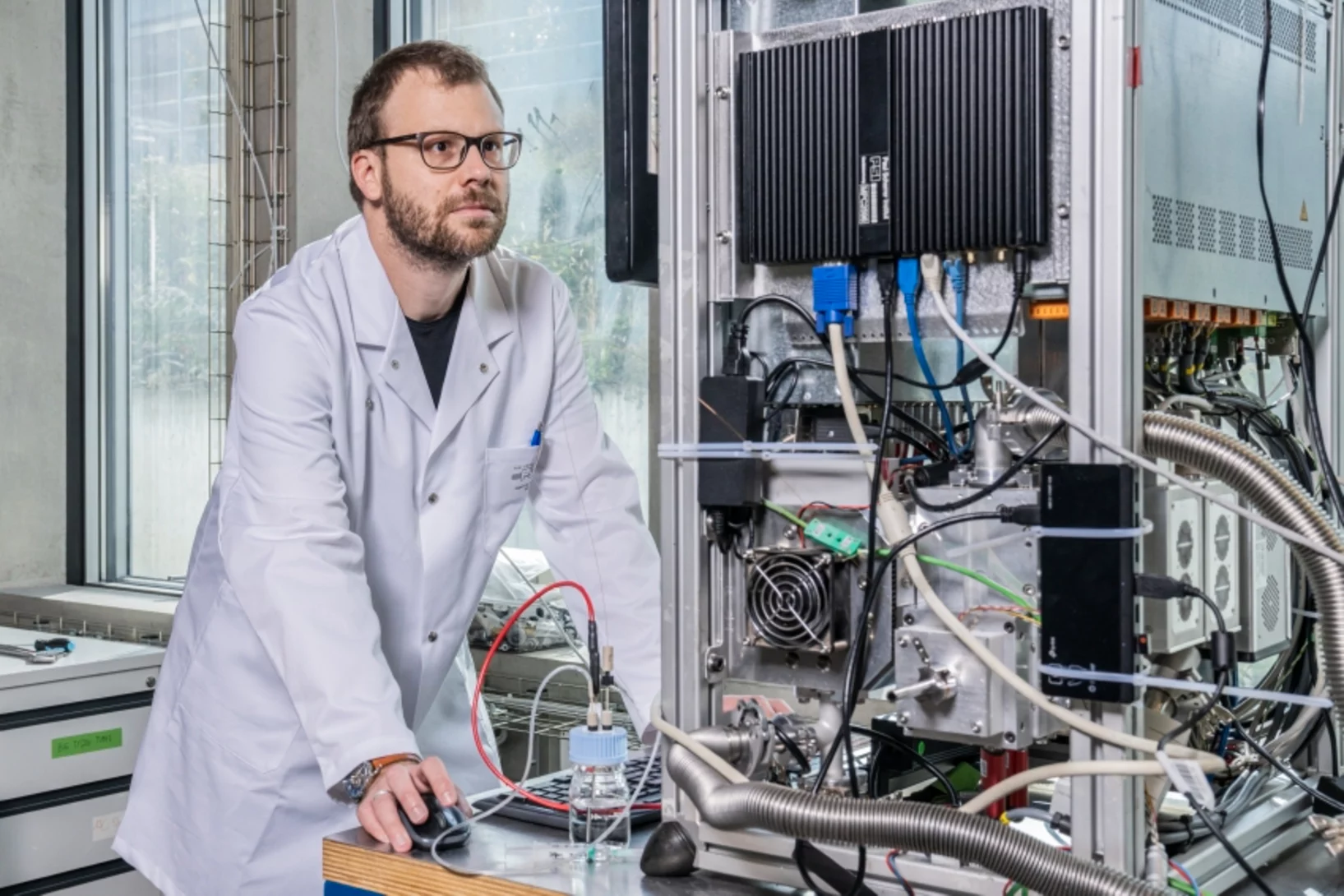
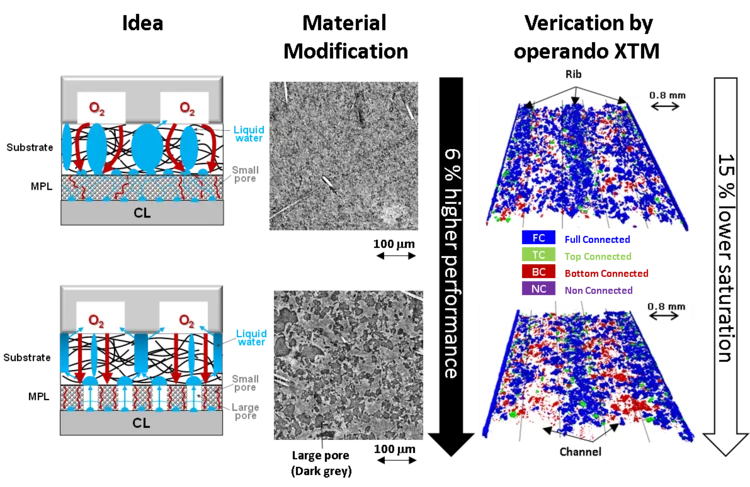
Fast operando X-ray tomographic microscopy improves polymer electrolyte fuel cells
Polymer electrolyte fuel cells (PEFC) are a key technology for the decarbonization of automotive mobility. In collaboration with Toyota, it is shown by dynamic, operando X-ray tomographic microscopy, how the liquid water saturation in modified gas diffusion layer materials is reduced.
The imaging data supports the understanding of the underlying mechanisms and explains improved cell performance. Novel instrumentation at the TOMCAT beamline further improves imaging time resolution and allows for scan times as short as 0.1 s.
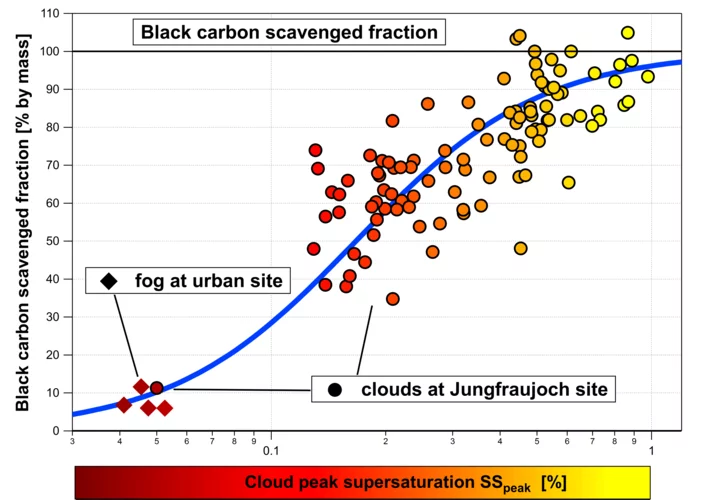
Cloud droplet formation on soot particles
PSI researchers went to the Jungfraujoch research station and applied in situ measurement techniques in real clouds to investigate the ability of soot particles to form cloud droplets. This is a key process determining the atmospheric life-cycle of soot particles, which are primarily emitted by combustion engines and which have a warming effect on climate by absorbing solar radiation.
A third dimension for the nanoscale
Researchers of the Laboratory for Catalysis and Sustainable Chemistry (LSK) from PSI have designed uneven probe supports, which reveal the hidden site of nanocrystals.
Their simple approach allows transmission electron microscopes (TEMs) complete access to the atomic structure of nanomaterials without the need for cumbersome experimental effort.
Giulia Stefenelli wins Swiss Aerosol Award 2019
Award conferred by SwissLung.org during the award ceremony in Berne, Switzerland
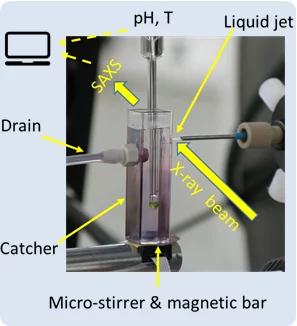
Matter before solid nucleation under synchrotron light
Investigation on early stage of solid formation from solution, before nucleation, have been carried out at PSI by small angle scattering technique using X-ray light from the Swiss Light Source SLS. The system under analysis was calcium carbonate, a model system archetype of several sparsely soluble inorganic materials and relevant in many field such as CO2 capturing and biomineralization. The experimental setup, the method, and developed theoretical framework can be applied to many other systems and made available for the entire scientific community.
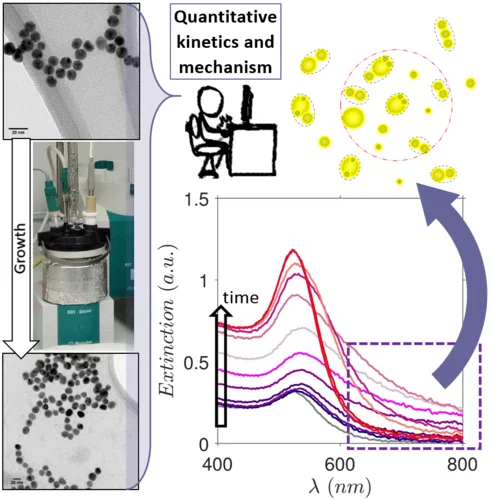
Kinetics and Mechanism of Metal Nanoparticle Growth via Optical Extinction Spectroscopy and Computational Modeling: The Curious Case of Colloidal Gold
An overarching computational framework unifying several optical theories to describe the temporal volution of gold nanoparticles (GNPs) during a seeded growth process is presented. To achieve this, we sed the inexpensive and widely available optical extinction spectroscopy, to obtain quantitative kinetic data. In situ spectra collected over a wide set of experimental conditions were regressed using the hysical model, calculating light extinction by ensembles of GNPs during the growth process. This model rovides temporal information on the size, shape, and concentration of the particles, and any electromagnetic interactions between them. Consequently, we were able to describe the mechanism of GNP growth and divide the process into distinct genesis periods. We provide explanations for several longstanding mysteries, e.g., the phenomena responsible for the purple-greyish hue during the early stages of GNP growth, the complex interactions between nucleation, growth and aggregation events, and a clear distinction between agglomeration and electromagnetic interactions. The presented theoretical formalism has been developed in a generic fashion so that it can readily be adapted to other nanoparticulate formation scenarios such as the genesis of various metal nanoparticles.
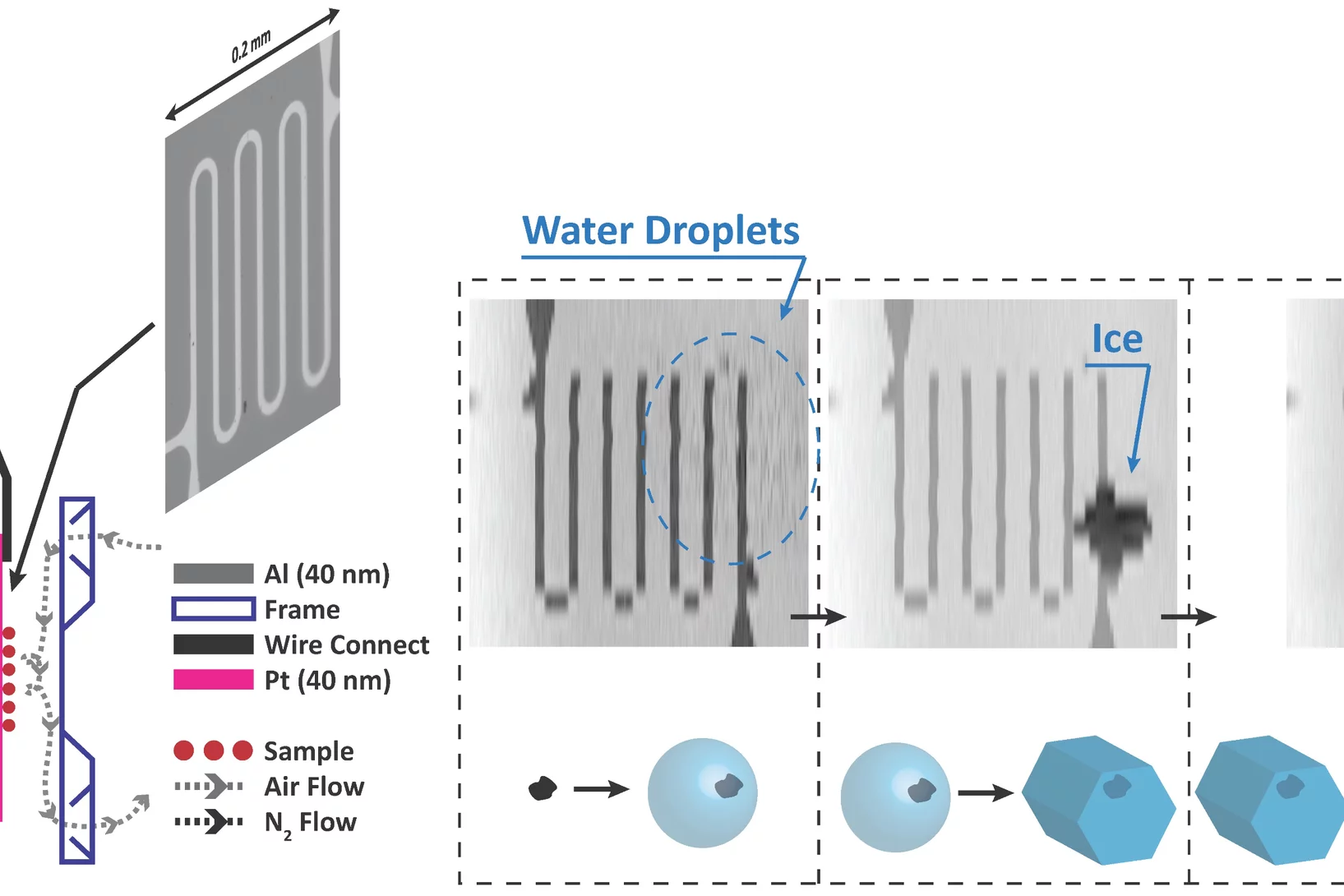
Chemically mapping ice forming particles
Scientists have just nucleated ice in an X-ray microscope for the first time and they created chemical maps of those responsible.
2018 Highly Cited Researchers
Three LAC researchers were highly cited in 2018.
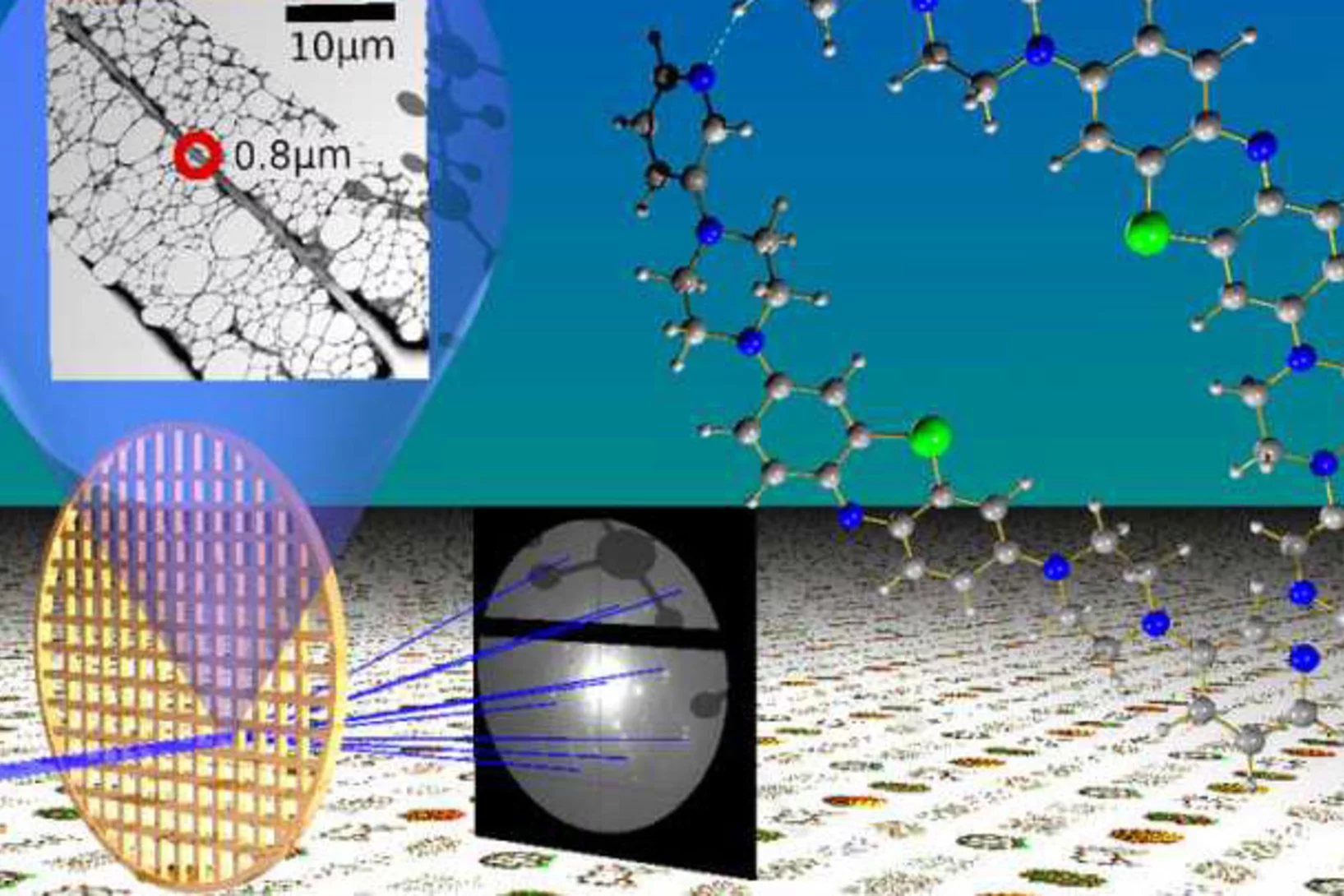
Breakthrough - electron crystallography for everyone
Recent advances in electron crystallography published in Angewandte Chemie and highlighted by Science, Chemical & Engineering News and ScienceNews!Under the lead of LSK member, "Rapid structure determination of microcrystalline molecular compounds using electron diffraction", published in Angewandte Chemie International Edition https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/anie.201811318 has attracted great attention in the chemistry community.
Les causes de la fin du Petit Âge glaciaire au milieu du XIXe siècle
Au cours de la première moitié du XIXe siècle, une série de fortes éruptions volcaniques dans les Tropiques a provoqué temporairement un refroidissement global du climat terrestre. Le fait que les glaciers ont progressé pendant la phase finale du Petit Âge glaciaire, avant de reculer à nouveau, était un phénomène naturel. C’est ce qu’ont montré des chercheurs du PSI au moyen de carottes de glace.