Charge Condensation and Lattice Coupling Drives Stripe Formation in Nickelates
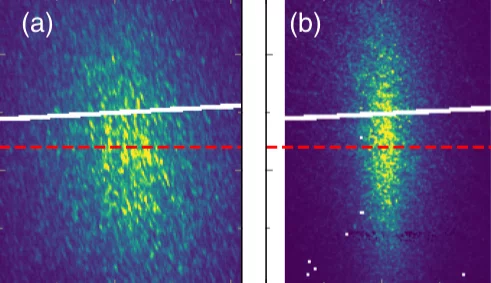
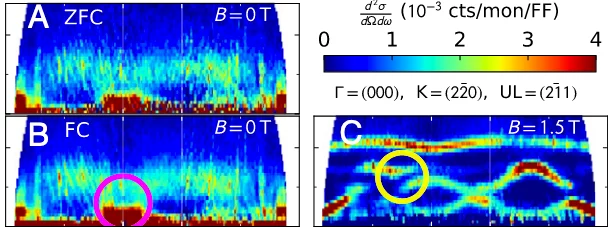
Revealing the predominant driving force behind symmetry breaking in correlated materials is sometimes a formidable task due to the intertwined nature of different degrees of freedom. This is the case for La2−xSrxNiO4+δ, in which coupled incommensurate charge and spin stripes form at low temperatures. Here, we use resonant x-ray photon correlation spectroscopy to study the temporal stability and domain memory of the charge and spin stripes in La2−xSrxNiO4+δ.
Frustration-driven magnetic fluctuations as the origin of the low-temperature skyrmion phase in Co7Zn7Mn6
Magnetic skyrmions in chiral cubic helimagnets, are stabilized by thermal fluctuations over a narrow region directly below the magnetic ordering temperature. Due to often being touted for use in applications, there is high demand to identify new mechanism that can expand the equilibrium skyrmion phases where these topological vortices may display an enhanced robustness against external perturbations, such as magnetic fields, due to a larger magnetic order parameter.
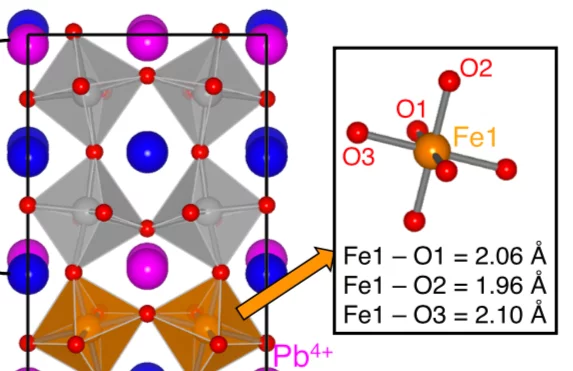
Observation of novel charge ordering and spin reorientation in perovskite oxide PbFeO3
PbMO3 (M = 3d transition metals) family shows systematic variations in charge distribution and intriguing physical properties due to its delicate energy balance between Pb 6s and transition metal 3d orbitals. However, the detailed structure and physical properties of PbFeO3 remain unclear. Herein, we reveal that PbFeO3 crystallizes into an unusual 2ap × 6ap × 2ap orthorhombic perovskite super unit cell with space group Cmcm.
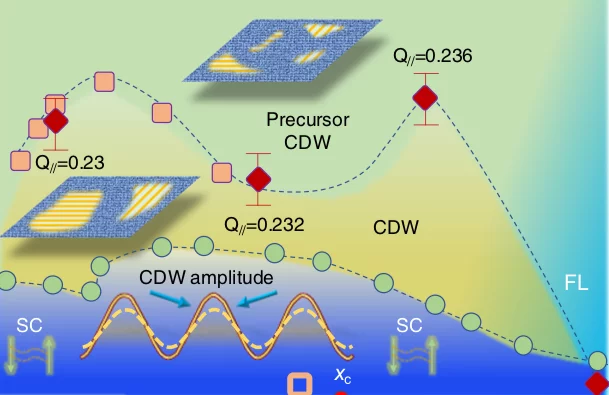
Charge density waves in cuprate superconductors beyond thecritical doping
The unconventional normal-state properties of the cuprates are often discussed in terms of emergent electronic order that onsets below a putative critical doping of xc≈0.19. Charge density wave (CDW) correlations represent one such order; however, experimental evidence for such order generally spans a limited range of doping that falls short of the critical value xc, leading to questions regarding its essential relevance. Here, we use X-ray diffraction to demonstrate that CDW correlations in La2−xSrxCuO4 persist up to a doping of at least x=0.21.
Strong Superexchange in a d^(9−δ) Nickelate Revealed by Resonant Inelastic X-Ray Scattering
The discovery of superconductivity in a d9−δ nickelate has inspired disparate theoretical perspectives regarding the essential physics of this class of materials. A key issue is the magnitude of the magnetic superexchange, which relates to whether cuprate-like high-temperature nickelate superconductivity could be realized. We address this question using Ni L-edge and O K-edge spectroscopy of the reduced d9−1/3 trilayer nickelates R4Ni3O8 (where R = La, Pr) and associated theoretical modeling.
Decomposing Magnetic Dark-Field Contrast in Spin Analyzed Talbot-Lau Interferometry: A Stern-Gerlach Experiment without Spatial Beam Splitting
We have recently shown how a polarized beam in Talbot-Lau interferometric imaging can be used to analyze strong magnetic fields through the spin dependent differential phase effect at field gradients. While in that case an adiabatic spin coupling with the sample field is required, here we investigate a nonadiabatic coupling causing a spatial splitting of the neutron spin states with respect to the external magnetic field. This subsequently leads to no phase contrast signal but a loss of interferometer visibility referred to as dark-field contrast.
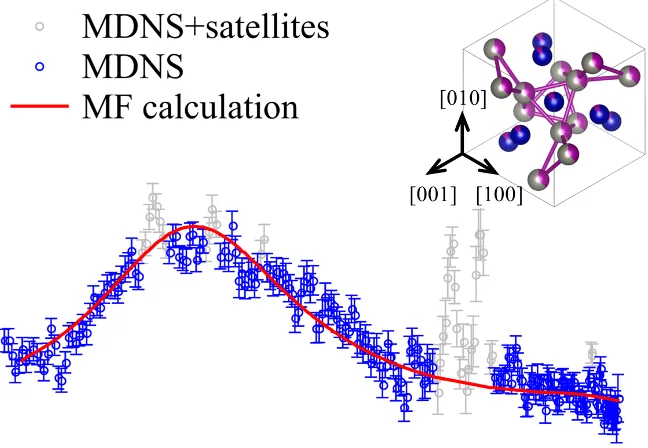
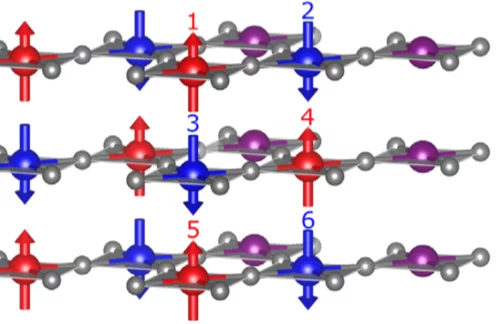
Interdependent scaling of long-range oxygen and magnetic ordering in nonstoichiometric Nd2NiO4.10
The interplay between oxygen and spin ordering for the low oxygen doped Nd2NiO4.10 has been investigated by single-crystal neutron diffraction. We find a coexistence of the magnetic order below TN with the 3D ordering of excess oxygen atoms, which has not been previously observed for the homologous nickelates. Moreover, the magnetic ordering modulation vectors are no longer independent and exactly follow the modulation vectors of the oxygen ordering.
Observation of plaquette fluctuations in the spin-1/2 honeycomb lattice
Quantum spin liquids are materials that feature quantum entangled spin correlations and avoid magnetic long-range order at T =0 K. Particularly interesting are two-dimensional honeycomb spin lattices where a plethora of exotic quantum spin liquids have been predicted. Here, we experimentally study an effective S = 1/2 Heisenberg honeycomb lattice with competing nearest and next-nearest-neighbour interactions.
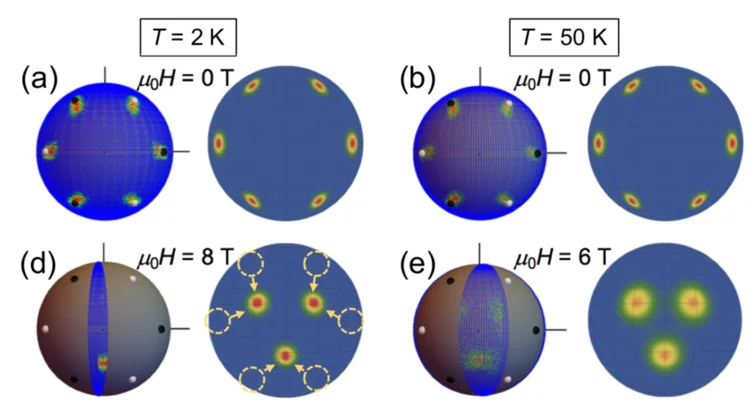
Particle-size dependent structural transformation of skyrmion lattice
Magnetic skyrmion is a topologically protected particle-like object in magnetic materials, appearing as a nanometric swirling spin texture. The size and shape of skyrmion particles can be flexibly controlled by external stimuli, which suggests unique features of their crystallization and lattice transformation process. Here, we investigated the detailed mechanism of structural transition of skyrmion lattice (SkL) in a prototype chiral cubic magnet Cu2OSeO3, by combining resonant soft X-ray scattering (RSXS) experiment and micromagnetic simulation...
Multiphase magnetism in Yb2Ti2O7
Quantum materials have properties that defy conventional theories of solids. Explaining these unusual properties is a frontier in physics, which promises both technological applications and fundamentally new states of matter. Yb2Ti2O7 is a center of attention in this work. While it becomes ferromagnetic at very low temperature, its excitation spectrum resembles that of a quantum spin liquid. We show using neutron scattering ...
Direct Observation of the Statics and Dynamics of Emergent Magnetic Monopoles in a Chiral Magnet
In the three-dimensional (3D) Heisenberg model, topological point defects known as spin hedgehogs behave as emergent magnetic monopoles, i.e., quantized sources and sinks of gauge fields that couple strongly to conduction electrons, and cause unconventional transport responses such as the gigantic Hall effect. We observe a dramatic change in the Hall effect upon the transformation of a spin hedgehog crystal in a chiral magnet MnGe through combined measurements of magnetotransport and small-angle neutron scattering (SANS).
Nano-tourbillon doté d’une propriété bien particulière
Des chercheurs de l’Institut Paul Scherrer PSI ont établi pour la première fois l’existence de nano-tourbillons bien particuliers dans un matériau: des skyrmions antiferromagnétiques.
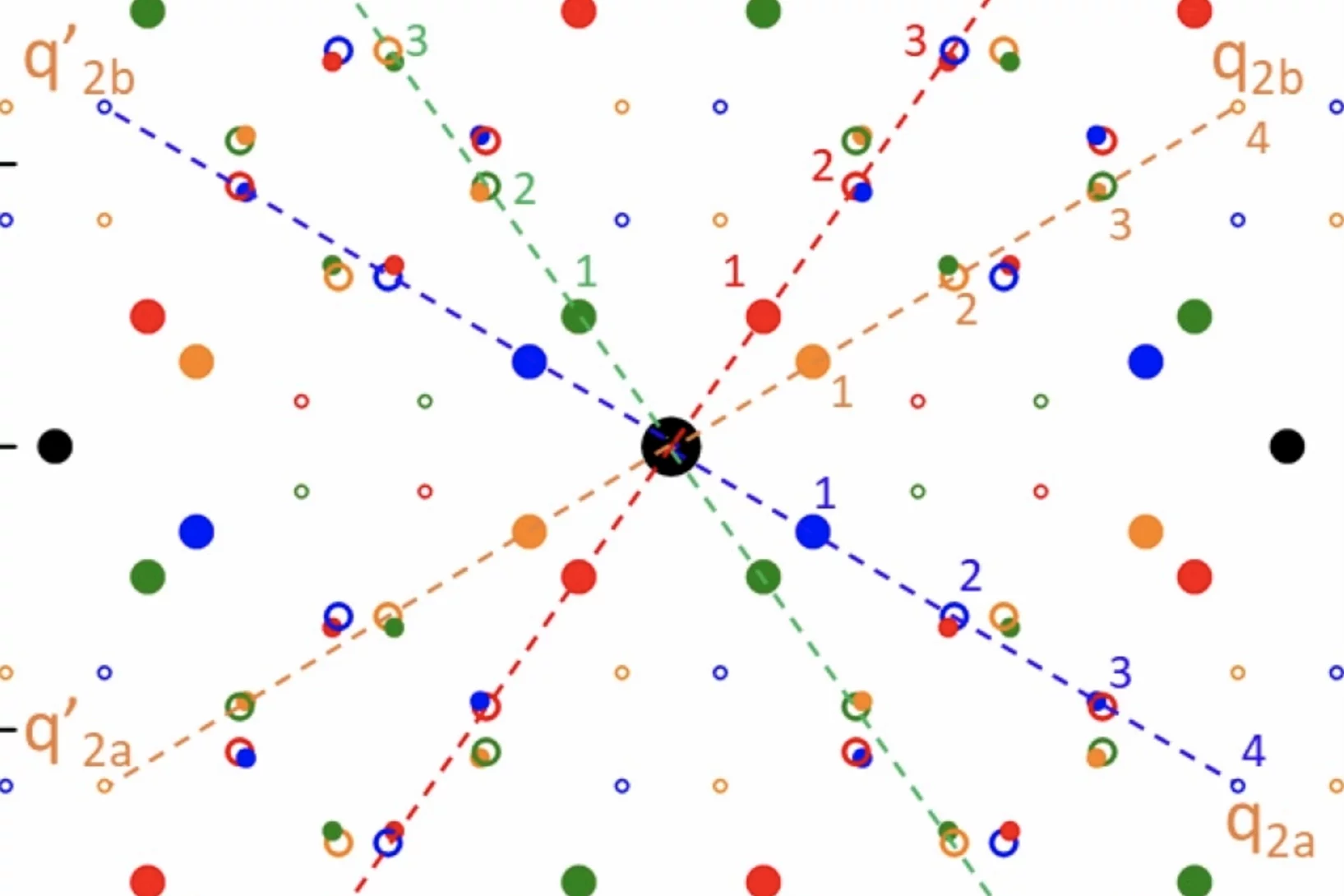
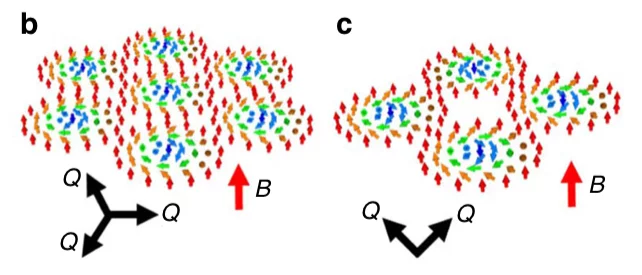
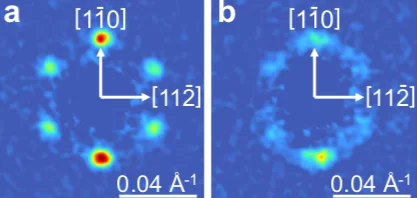
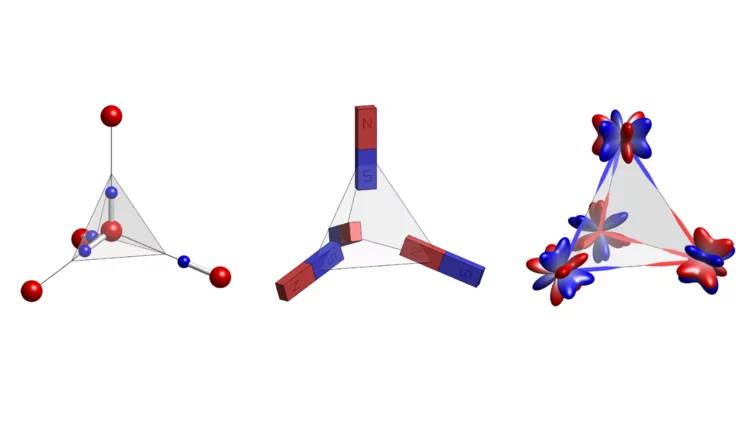
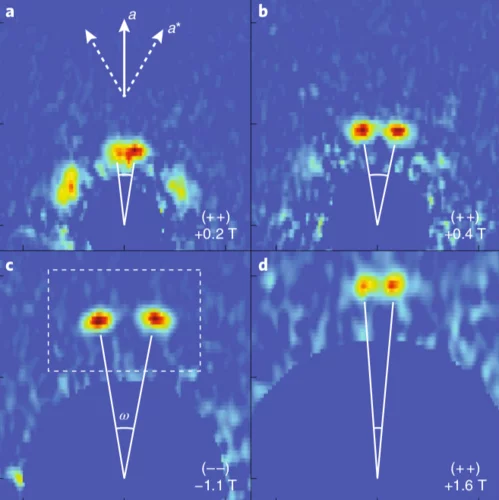
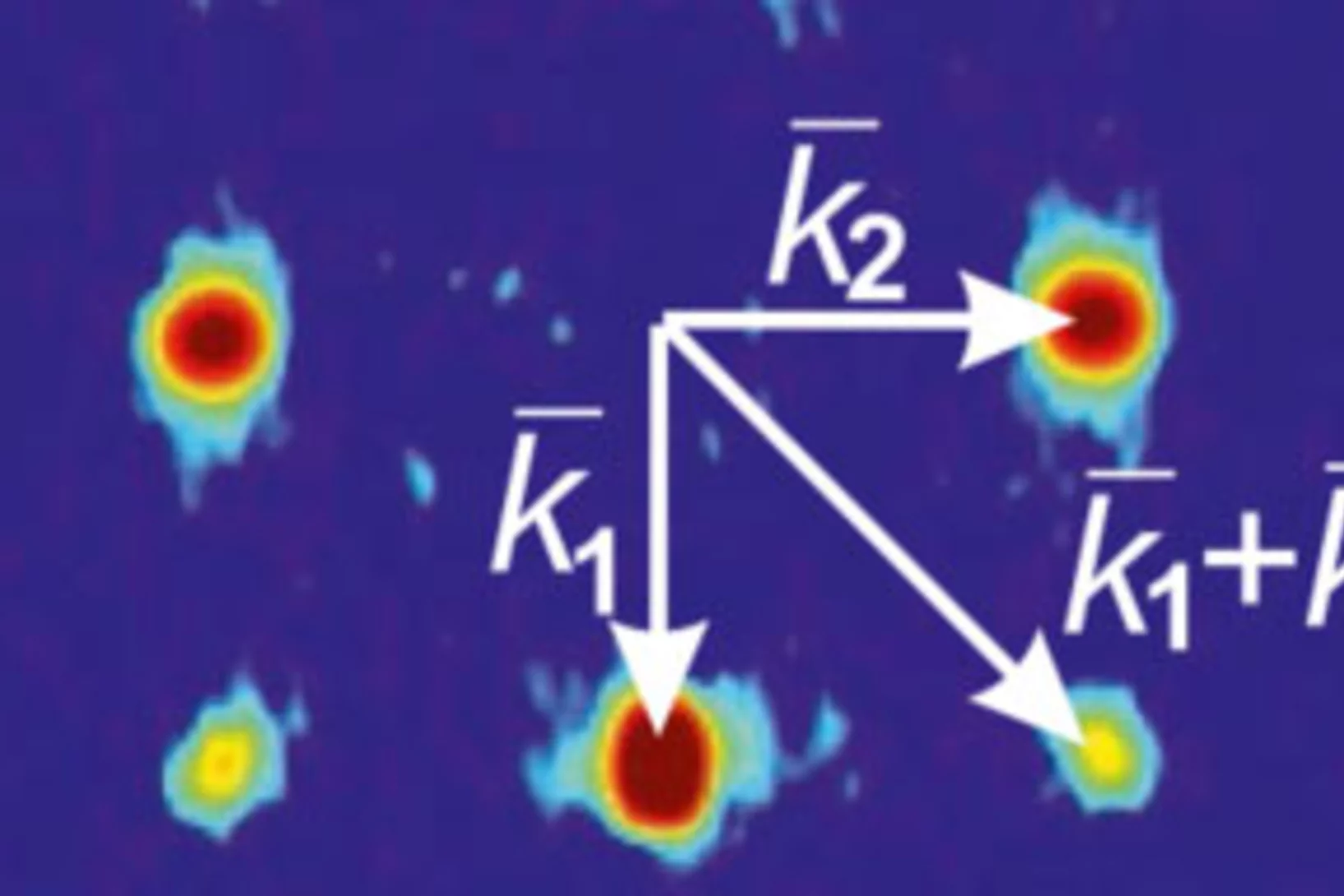
Fractional antiferromagnetic skyrmion lattice induced by anisotropic couplings
Magnetic skyrmions are topological solitons with a nanoscale winding spin texture that hold promise for spintronics applications. Skyrmions have so far been observed in a variety of magnets that exhibit nearly parallel alignment for neighbouring spins, but theoretically skyrmions with anti-parallel neighbouring spins are also possible. Such antiferromagnetic skyrmions may allow more flexible control than conventional ferromagnetic skyrmions. Here, by combining neutron scattering measurements and Monte Carlo simulations, we show that a fractional antiferromagnetic skyrmion lattice is stabilized in MnSc2S4 through anisotropic couplings.
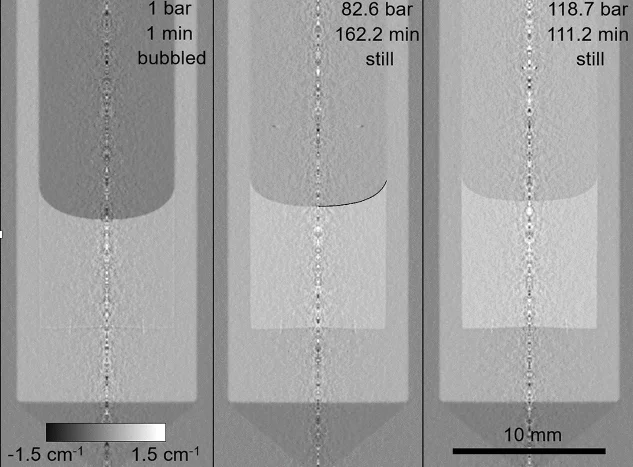
One-pot neutron imaging of surface phenomena, swelling and diffusion during methane absorption in ethanol and n-decane under high pressure
We study the gas diffusion in still liquids under gas high pressures. We demonstrate that the pressure-induced gas diffusion, liquid swelling and the liquid surface tension can be measured simultaneously in a one-pot experiment. The measurements are performed using the high-resolution neutron imaging in a non-tactile way. A major advantage of this new method is that the determination of surface tension necessitate no assumptions imposed on the properties of the liquid.
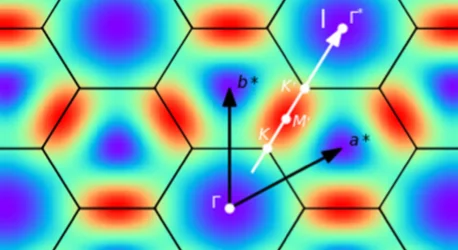
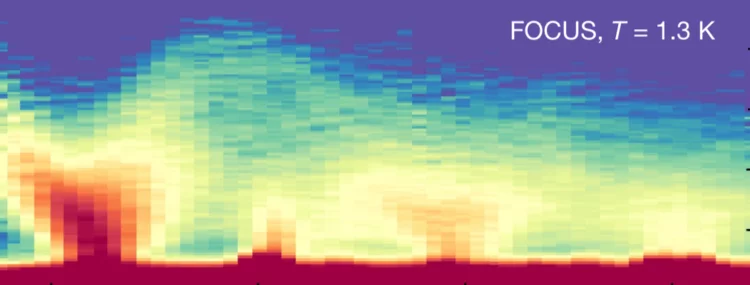
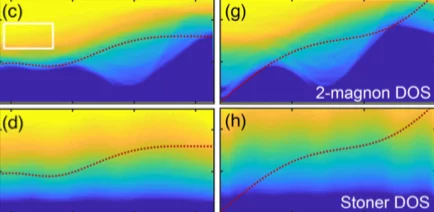
Momentum-Dependent Magnon Lifetime in the Metallic Noncollinear Triangular Antiferromagnet CrB2
Noncollinear magnetic order arises for various reasons in several magnetic systems and exhibits interesting spin dynamics. Despite its ubiquitous presence, little is known of how magnons, otherwise stable quasiparticles, decay in these systems, particularly in metallic magnets. Using inelastic neutron scattering, we examine the magnetic excitation spectra in a metallic noncollinear antiferromagnet CrB2, in which Cr atoms form a triangular lattice and display incommensurate magnetic order. Our data show intrinsic magnon damping ...
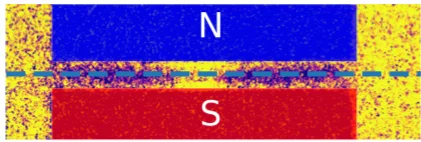
Macroscopic manifestation of domain-wall magnetism and magnetoelectric effect in a Néel-type skyrmion host
We report a magnetic state in GaV4Se8 which emerges exclusively in samples with mesoscale polar domains and not in polar mono- domain crystals. It is manifested by a sharp anomaly in the magnetic susceptibility and the magnetic torque, distinct from other anomalies observed also in polar mono-domain samples upon transitions between the cycloidal, the Néel-type skyrmion lattice and the ferromagnetic states.
Thermal Control of Spin Excitations in the Coupled Ising-Chain Material RbCoCl3
We have used neutron spectroscopy to investigate the spin dynamics of the quantum (S=1/2) antiferromagnetic Ising chains in RbCoCl3. The structure and magnetic interactions in this material conspire to produce two magnetic phase transitions at low temperatures, presenting an ideal opportunity for thermal control of the chain environment. The high-resolution spectra we measure ...
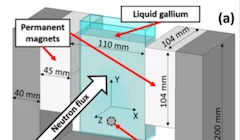
Phase boundary dynamics of bubble flow in a thick liquid metal layer under an applied magnetic field
We investigate argon bubble flow in liquid gallium within a container large enough to avoid wall effects. Flow with and without applied horizontal magnetic field is studied. We demonstrate the successful capture and quantification of the effects of applied magnetic field using dynamic neutron radiography and the previously developed and validated robust image processing pipeline, supported by the in silico reproduction of our experiment.
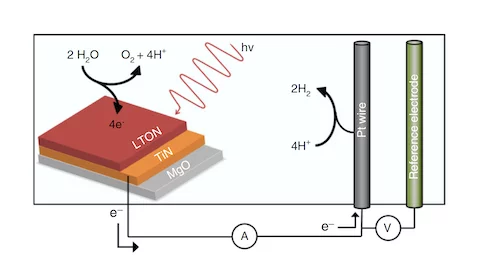
Zooming in on water splitting
Perovskite oxynitride materials can act as effective photocatalysts for water splitting driven by visible light. A combined neutron and x-ray study now provides unique insight into the underlying processes at the solid–liquid interface and highlights how solar-to-hydrogen conversion can be improved.
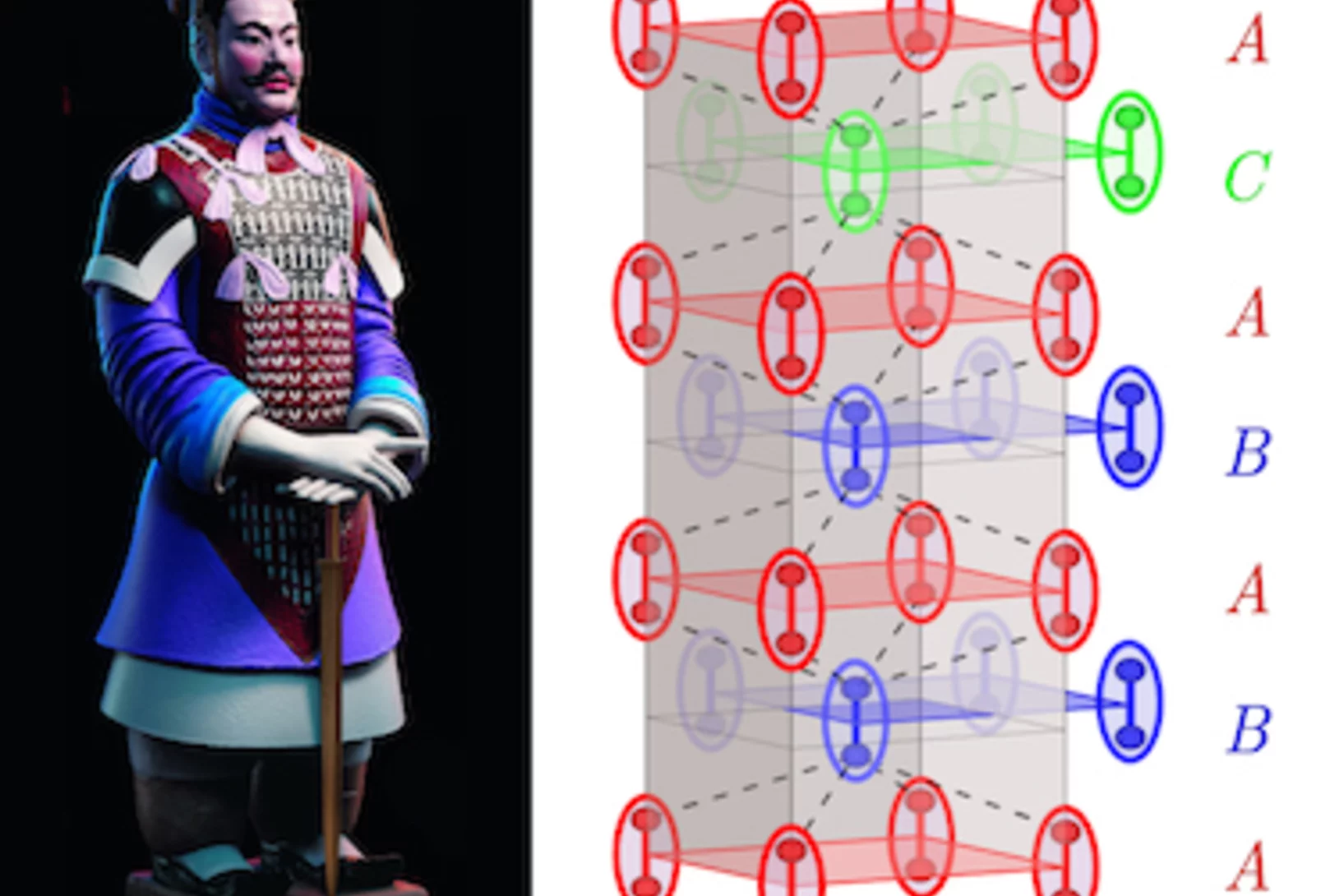
Understanding Quantum Critical Magnetism in Han Purple
The ancient purple pigment used to paint the terracotta warriors, BaCuSi2O6, is also a quantum magnetic material which consists of stacked Cu2+ bilayers hosting spin dimers. Magnetometry and NMR experiments have revealed puzzling critical phenomena at the quantum phase transition (QPT) caused by an applied magnetic field, which suggest that the universal behaviour of the system is not three- but only two-dimensional. By performing high-resolution neutron spectroscopy measurements .....
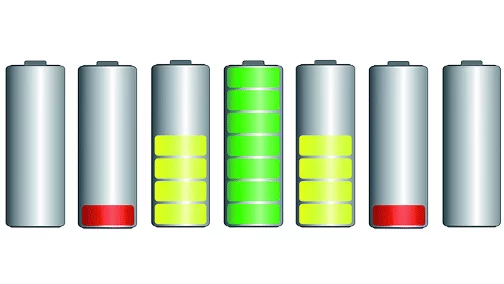
Batteries under the neutron stroboscope
The first application of stroboscopic neutron diffraction to studying lithium-ion batteries during operation establishes a new approach to unravelling the complex processes playing out in energy-storage materials.
Batteries under the neutron stroboscope
The first application of stroboscopic neutron diffraction to studying lithium-ion batteries during operation establishes a new approach to unravelling the complex processes playing out in energy-storage materials.
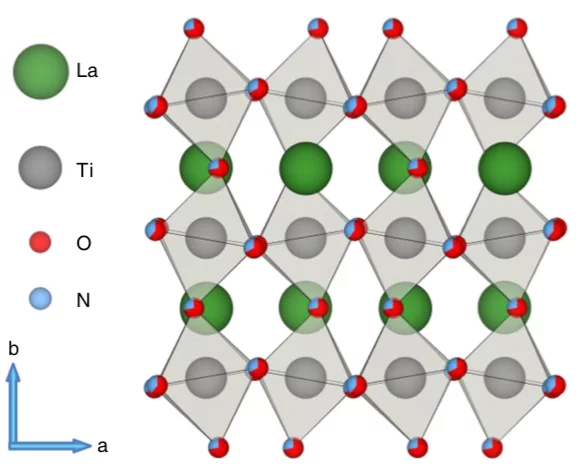
Examining the surface evolution of LaTiOxNy an oxynitride solar water splitting photocatalyst
LaTiOxNy oxynitride thin films are employed to study the surface modifications at the solid- liquid interface that occur during photoelectrocatalytic water splitting. Neutron reflectometry and grazing incidence x-ray absorption spectroscopy were utilised to distinguish between the surface and bulk signals, with a surface sensitivity of 3 nm.
Spin ice expands to higher orders
With experimental work demonstrating that the correlated ground state of the pyrochlore system Ce2Sn2O7 is a quantum liquid of magnetic octupoles, an international team led by PSI researcher Romain Sibille establishes a fundamentally new state of matter: higher-rank multipole ice.
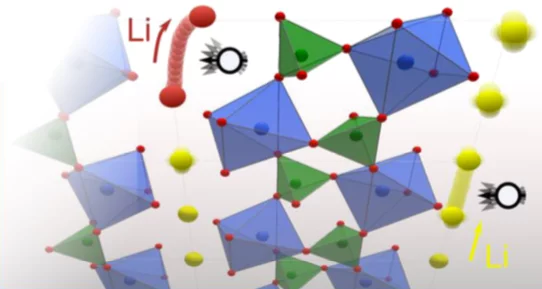
Quantifying Diffusion through Interfaces of Lithium-Ion Battery Active Materials
Detailed understanding of charge diffusion processes in a lithium-ion battery is crucial to enable its systematic improvement. Experimental investigation of diffusion at the interface between active particles and the electrolyte is challenging but warrants investigation as it can introduce resistances that, for example, limit the charge and discharge rates. Here, we show an approach to study diffusion at interfaces using muon spin spectroscopy.
Broken time-reversal symmetry in the topological superconductor UPt3
Topological properties of materials are of fundamental as well as practical importance. Of particular interest are unconven- tional superconductors that break time-reversal symmetry, for which the superconducting state is protected topologically and vortices can host Majorana fermions with potential use in quantum computing. However, in striking contrast to the unconventional A phase of superfluid 3He where chiral symmetry was directly observed, .....
Tunable anomalous Hall conductivity through volume-wise magnetic competition in a topological kagome magnet
Magnetic topological phases of quantum matter are an emerging frontier in physics and material science. Along these lines, several kagome magnets have appeared as the most promising platforms. Here, we explore magnetic correlations in the kagome magnet Co3Sn2S2. Using muon spin-rotation, we present evidence for competing magnetic orders in the kagome lattice of this compound.
Possible room-temperature signatures of unconventional 4f-electron quantum criticality in YbMn6Ge6−xSnx
We investigate the Sn composition dependence of the Yb valence and local magnetization in YbMn6Ge6−xSnx (4.25 ≤x≤ 5.80) using x-ray absorption spectroscopy (XANES) and x-ray magnetic circular dichroism at the Yb L3 edge. In these materials, where Mn is ferromagnetically ordered, we observe a decrease of the Yb valence upon reducing the chemical pressure by Sn doping and a suppression of the Yb magnetic moment for strongly hybridized 4f states (ν ∼ 2.77).
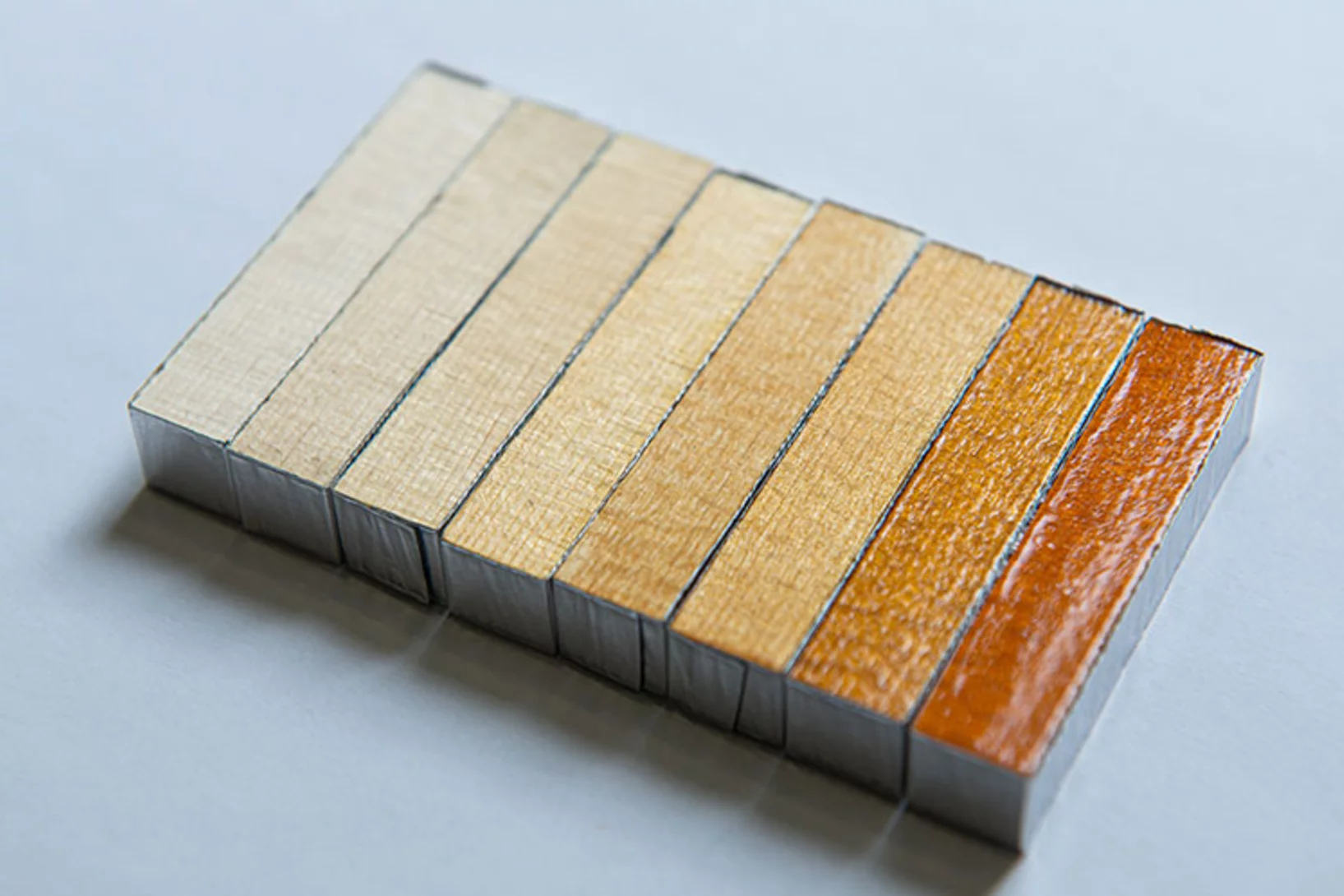
Les violons bien vernis jouent plus longtemps
Traditionnellement, on vernit les violons pour les protéger de l’humidité et des autres influences extérieures. Une équipe de scientifiques a analysé au PSI l’impact de l’application de différents produits sur l’instrument. Leur conclusion: en aucun cas on ne devrait se passer complètement de vernis.
Topological Magnetic Phase in the Candidate Weyl Semimetal CeAlGe
We report the discovery of topological magnetism in the candidate magnetic Weyl semimetal CeAlGe. Using neutron scattering we find this system to host several incommensurate, square-coordinated multi-k⃗ magnetic phases below TN. The topological properties of a phase stable at intermediate magnetic fields parallel to the c axis are suggested by observation of a topological Hall effect.