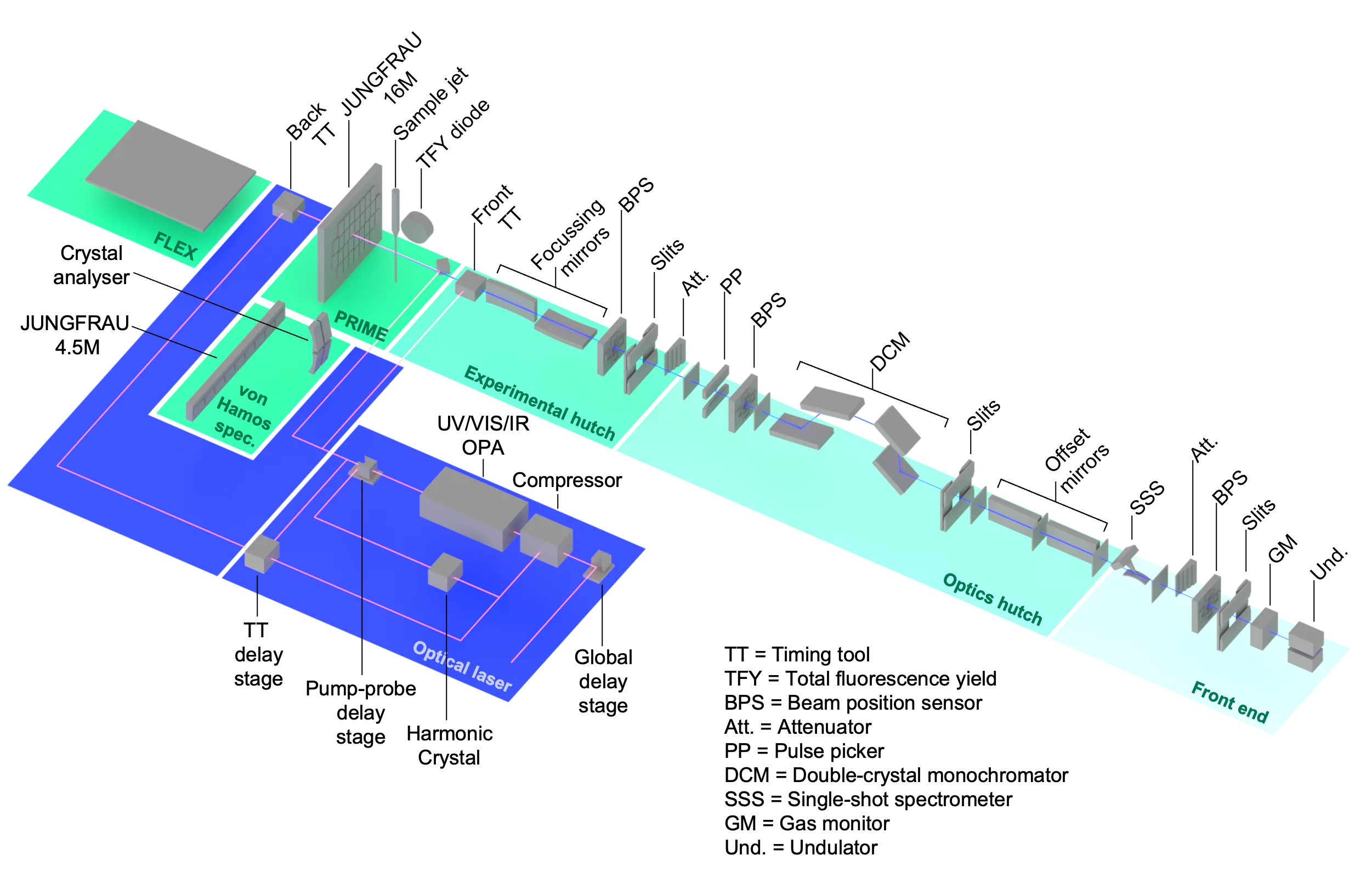
SwissFEL Alvra Experimental Station
Alvra specializes in measuring the ultrafast dynamics of photochemical and photobiological systems in solution, suspension, or crystals, using a variety of X-ray scattering and spectroscopic techniques. Alvra consists of two instruments: Alvra Prime and Alvra Flex. Prime is a helium/low vacuum atmosphere chamber designed to perform a range of techniques, including serial femtosecond crystallography (SFX), X-ray scattering (XDS), and X-ray absorption and emission spectroscopy (XAS, XES, and RIXS) over the full SwissFEL hard X-ray photon energy range of 2-13 keV. Flex is a versatile instrument designed to accommodate user experiments with an X-ray spectrometer that can be used for many different types of measurements, including inelastic X-ray scattering (IXS) and high energy resolution off-resonant spectroscopy (HEROS), as well as host user-provided setups. An overview of the Alvra design parameters can be found here and on the SwissFEL facility here. A user laboratory, to support chemistry and biology experiments is also available on-site. The summary of the lab infrastructure and equipment can be found here.
Alvra is currently in full-user operation mode, with both the Prime and Flex instruments commissioned at 100 Hz. A summary of the experimental station parameters follows
| Photon energy range | 2 – 13 keV (full SwissFEL Aramis photon energy range) |
| Beam profile | Measured focus 20 µm (FWHM) at 2 and 4.5 keV (defocussed beam also possible) |
| Measured focus 1.5 µm (FWHM) at 12 keV (defocussed beam also possible) | |
| Unfocused beam: 500 µm to 1 mm (FWHM) energy dependent | |
| Flexible KB mirrors can also provide an asymmetric focus | |
| Bandwidth | SASE 0.25% (pink beam), large bandwith availabe upon request (up to 2%) |
| Monochromatic: Si(111), Si(311) and InSb(111) | |
| Sample Environment | From vacuum (5 x 10-4 mbar) up to 800 mbar pressure (He or N2) |
| Sample delivery systems | Liquid jet for chemistry: |
| - Flat jet (100, 200 and 300 µm) with peristaltic pump | |
| - Round jet (25-200 µm) with HPLC or syringe pump | |
| LCP viscous injector (50-100 µm) | |
| GDVN injectors tested in chamber (user provided) | |
| Solid samples upon request | |
| Detectors and Spectrometers | 16M Jungfrau forward scattering detector at 10 cm distance (<1 Å resolution at 12.4 keV) |
| 4M Jungfrau forward scattering detector at 10 cm distance (1.5 Å resolution at 12.4 keV) | |
| 2 x 2 crystal von Hamos dispersive X-ray emission spectrometer (1-12.4 keV) | |
| APD and PIPS diodes for x-ray absorption measurements |
| Photon energy range | 6 – 13 keV |
| Beam profile | Flexible focus from 10 to >100 µm (FWHM) |
| Unfocused beam: ~1 x 1 mm2 (FWHM) energy dependent | |
| Bandwidth | SASE 0.5% (pink beam) |
| Monochromatic: Si(111), Si(311) and InSb(111) | |
| Sample Environment | Atmospheric conditions (in-air setup) |
| Sample delivery systems | Liquid jet for chemistry: |
| - Flat jet (100, 200 and 300 µm) with gear or peristaltic pump | |
| - Round jet (20-100 µm) with HPLC pump | |
| LCP viscous injector (50-100 µm) | |
| Solid samples | |
| Detectors and Spectrometers | 3 crystal von Hamos dispersive X-ray emission spectrometer with 1M Jungfrau detector |
| Diodes for x-ray absorption measurements |
| Primary pump source | 800 nm, 35 fs FWHM, 10 mJ (Ti:Sapphire) |
|---|---|
| Secondary pump sources | 240 nm – 2.5 micron (OPA with additional nonlinear conversion options). At present pulse energies at the sample location for 240-400 nm have been measured in the range of 10-30 µJ. We expect pulse energies of 150-500 µJ between 400 nm and 780 nm; 150-500 µJ between 1 µm and 2.5 µm. Pulse durations are expected to be approximately 50 fs fwhm. |
| Timing diagnostics | Alvra currently has two spectral encoding time-tools available, one pre and one post-interaction region. This approach has been demonstrated at several other facilities and works well for experiments that use the full SASE pulses at the full X-ray range of the endstation (2-12 keV) and for monochromatic experiments at the higher x-ray energies (>6 keV). |
News & Scientific Highlights
Réparer de l’ADN endommagé avec la lumière du soleil
Les dommages infligés à l’ADN sont une cause du vieillissement, de la mort cellulaire et même du cancer. La capacité à réparer de l’ADN endommagé revêt donc une importance cruciale pour tous les organismes. Au SwissFEL du PSI, une équipe internationale de recherche vient d’étudier la manière dont la photolyase, une enzyme, utilise l’énergie de la lumière du soleil pour ce mécanisme de réparation.
Tender X-rays show how one of nature’s strongest bonds breaks
Short flashes of an unusual kind of X-ray light at SwissFEL and SLS bring scientists closer to developing better catalysts to transform the greenhouse gas methane into a less harmful chemical.
Utiliser la lumière pour activer et désactiver des médicaments
Des chercheurs du PSI tournent un film moléculaire d’un médicament anticancer doté d’un interrupteur. Cela ouvre de nouvelles perspectives pour les développeurs de substances actives.
Contact
Group Leader and Beamline Scientist at Alvra