Show filters
Réparer de l’ADN endommagé avec la lumière du soleil
Les dommages infligés à l’ADN sont une cause du vieillissement, de la mort cellulaire et même du cancer. La capacité à réparer de l’ADN endommagé revêt donc une importance cruciale pour tous les organismes. Au SwissFEL du PSI, une équipe internationale de recherche vient d’étudier la manière dont la photolyase, une enzyme, utilise l’énergie de la lumière du soleil pour ce mécanisme de réparation.
Tender X-rays show how one of nature’s strongest bonds breaks
Short flashes of an unusual kind of X-ray light at SwissFEL and SLS bring scientists closer to developing better catalysts to transform the greenhouse gas methane into a less harmful chemical.
Utiliser la lumière pour activer et désactiver des médicaments
Des chercheurs du PSI tournent un film moléculaire d’un médicament anticancer doté d’un interrupteur. Cela ouvre de nouvelles perspectives pour les développeurs de substances actives.
How to get chloride ions into the cell
A molecular movie shot at PSI reveals the mechanism of a light-driven chloride pump
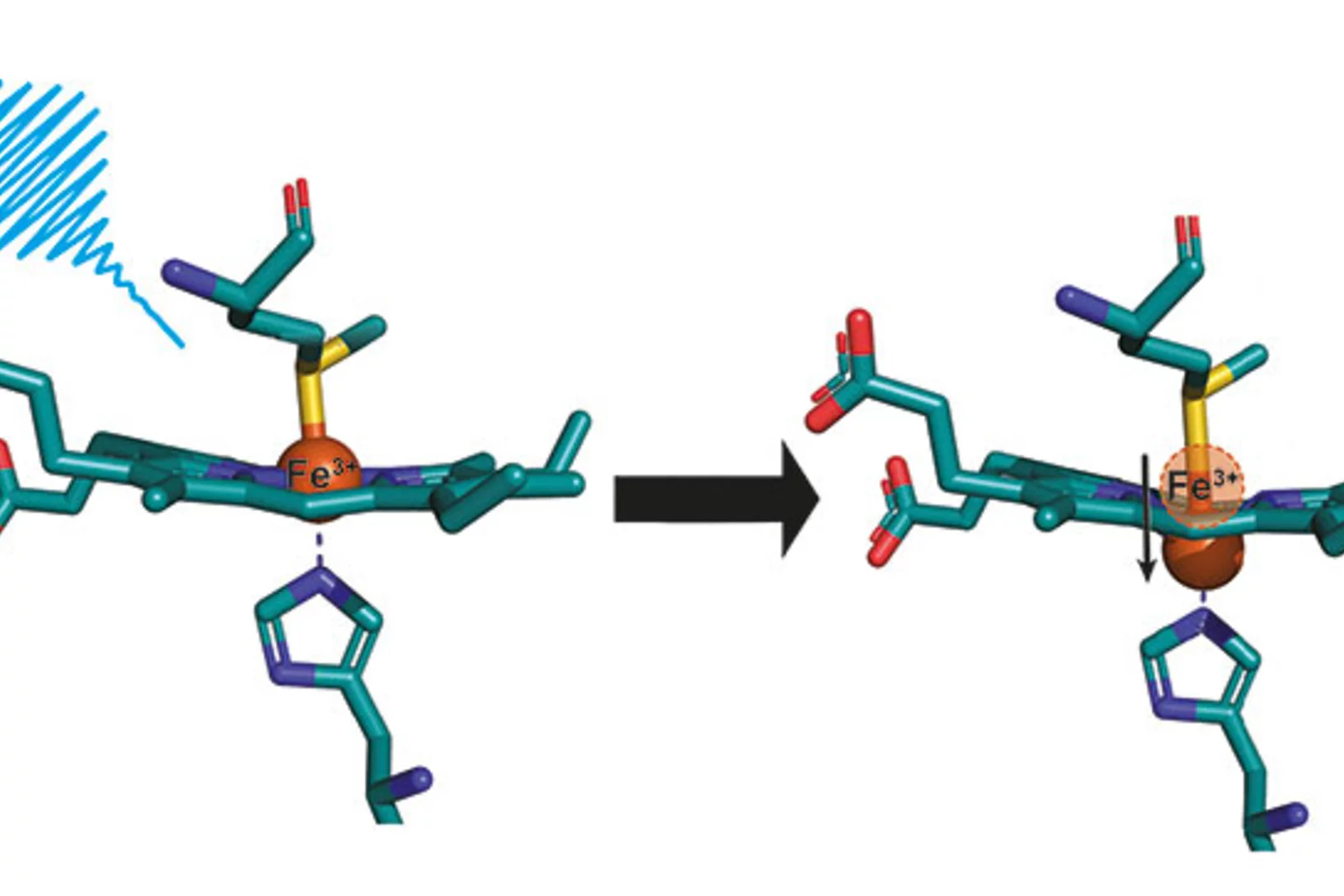
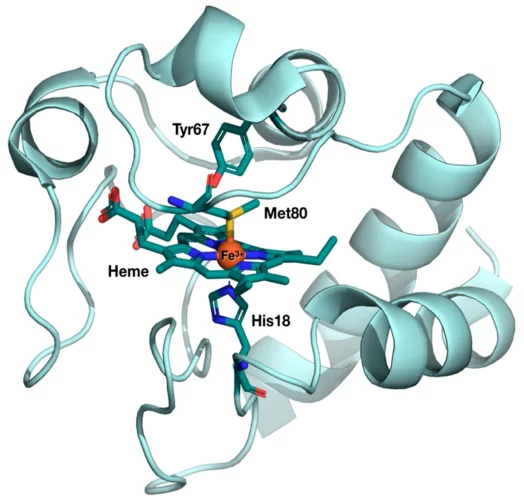
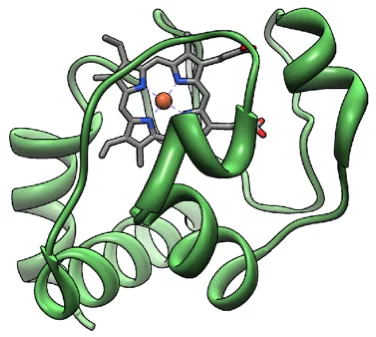
Déformation inattendue d’une protéine
Des chercheurs du PSI ont découvert un secret du cytochrome c, que cette protéine vitale avait bien gardé jusque-là. Des mesures au laser à rayons X à électrons libres SwissFEL ont mis en évidence des modifications structurelles que la science avait pourtant exclues pour ce type de biomolécules.
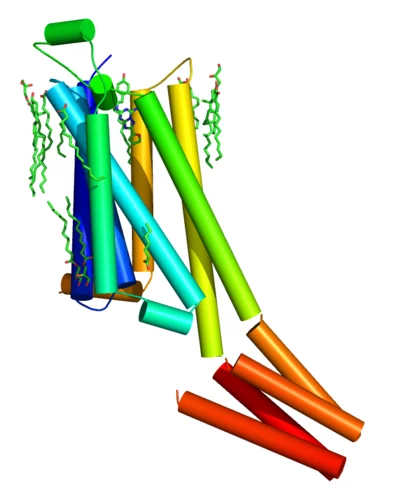
Advances in de novo protein structure determination using long-wavelength native-SAD phasing at SwissFEL
An international team of scientists from the Paul Scherrer Institute and members of the LeadXpro and Heptares pharmaceutical companies led by Karol Nass (Alvra group, SwissFEL) demonstrated a significant advancement in de novo protein structure determination at X-ray free-electron lasers. Their article, published recently in IUCrJ (DOI: 10.1107/S2052252520011379), describes structure determination of a membrane protein and an important drug target (A2A adenosine receptor) by native single-wavelength anomalous diffraction (native-SAD) at SwissFEL with up to ten fold reduction in the required number of indexed images.
Unraveling the structural dynamics of Heme proteins at SwissFEL
The results from the very first user experiment at SwissFEL have just been published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS). The measurements probed the electron transport properties of the cytochrome c protein, which is found in cellular mitochondria. The measurements show that when the Fe atom at the centre of the protein undergoes electronic excitation, for example when it gains or loses and electron, the active centre of the protein undergoes a doming structural rearrangement. This result raises interesting questions about how this structural change is involved in the electron transfer properties of cytochrome c.
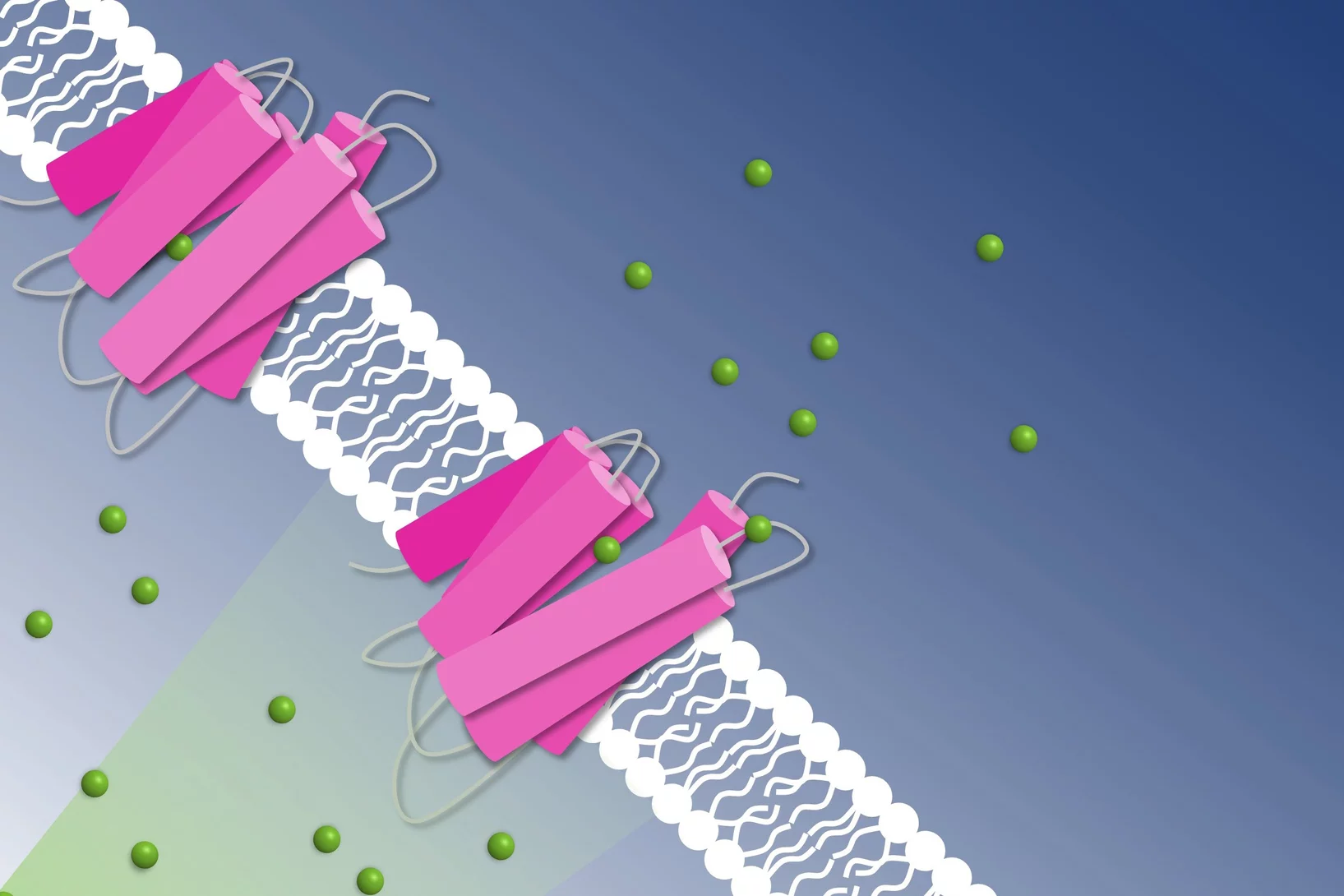
Elucidation du mécanisme d’une pompe à sodium contrôlée par la lumière
Des chercheurs de l’Institut Paul Scherrer PSI ont réussi une première: réaliser des prises de vue d’une pompe à sodium en action, plus précisément d’une pompe à sodium de cellules bactériennes contrôlée par la lumière. Ces éléments de connaissance sont prometteurs pour le développement de nouvelles méthodes dans le domaine de la neurobiologie. Pour leurs analyses, les chercheurs ont utilisé le nouveau laser à rayons X à électrons libres SwissFEL.
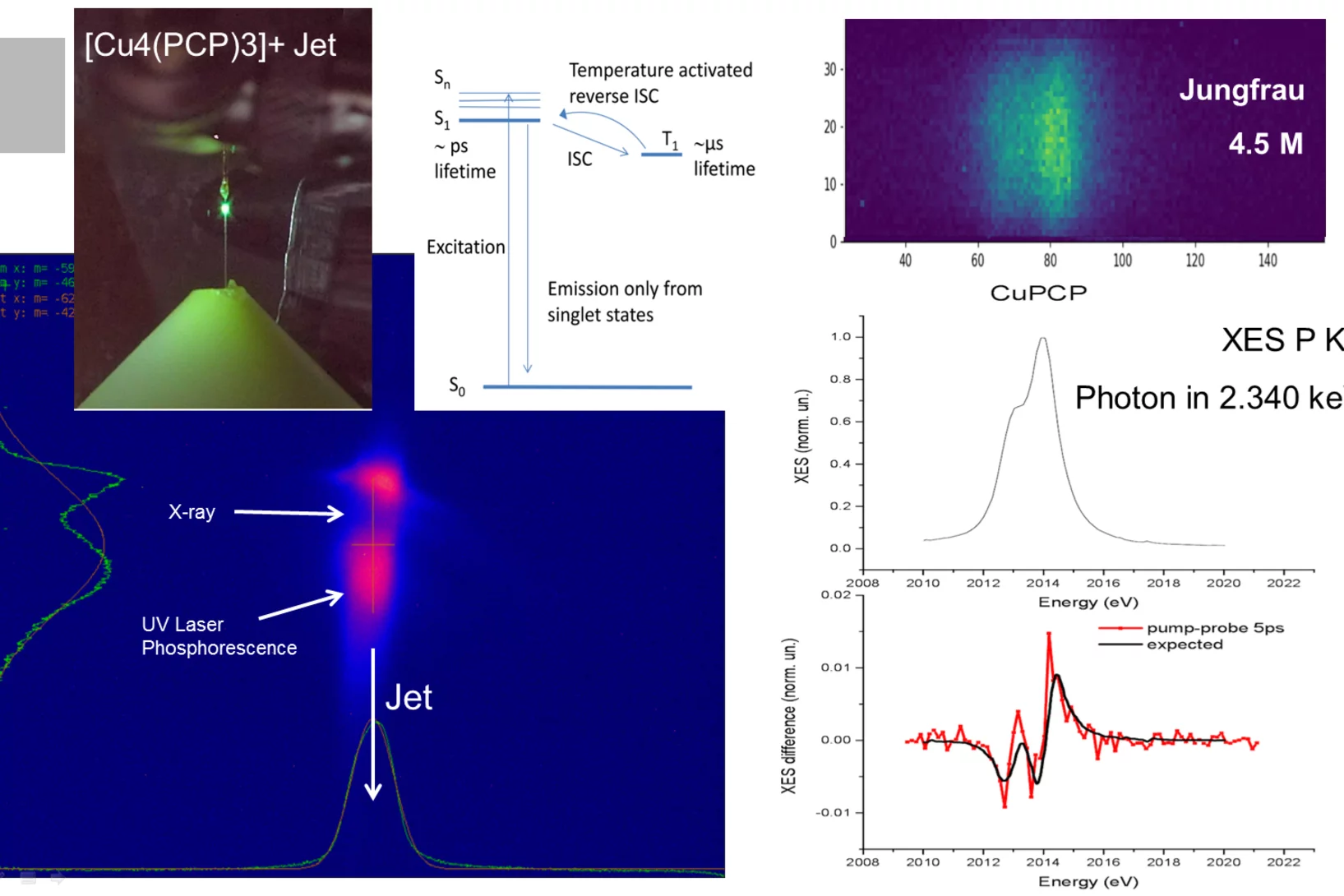
Publication of the very first Pilot experiment results from Alvra
The results from the first pilot experiment at Alvra have just been published in Nature Communications. The measurements probed the excited-state character of a Cu-P OLED complex using X-ray emission spectroscopy from the phosphorus atoms in the molecule.
A la recherche du matériau électroluminescent du futur
A l’Institut Paul Scherrer PSI, des chercheurs ont scruté l’intérieur d’un matériau prometteur pour les diodes organiques électroluminescentes (OLED). Leurs conclusions contribueront au développement de matériaux électroluminescents à très bon rendement lumineux et peu coûteux à la fabrication.
First serial femtosecond crystallography experiment using SwissFEL’s large bandwidth X-ray pulses
The typical mode of operation at XFEL facilities uses the so-called self-amplified spontaneous emission (SASE) process to generate the short, bright X-ray pulses. This mode of operation is stochastic in nature, causing some variance in intensity and spectrum on a shot-to-shot basis, which makes certain types of crystallographic measurements much more challenging.
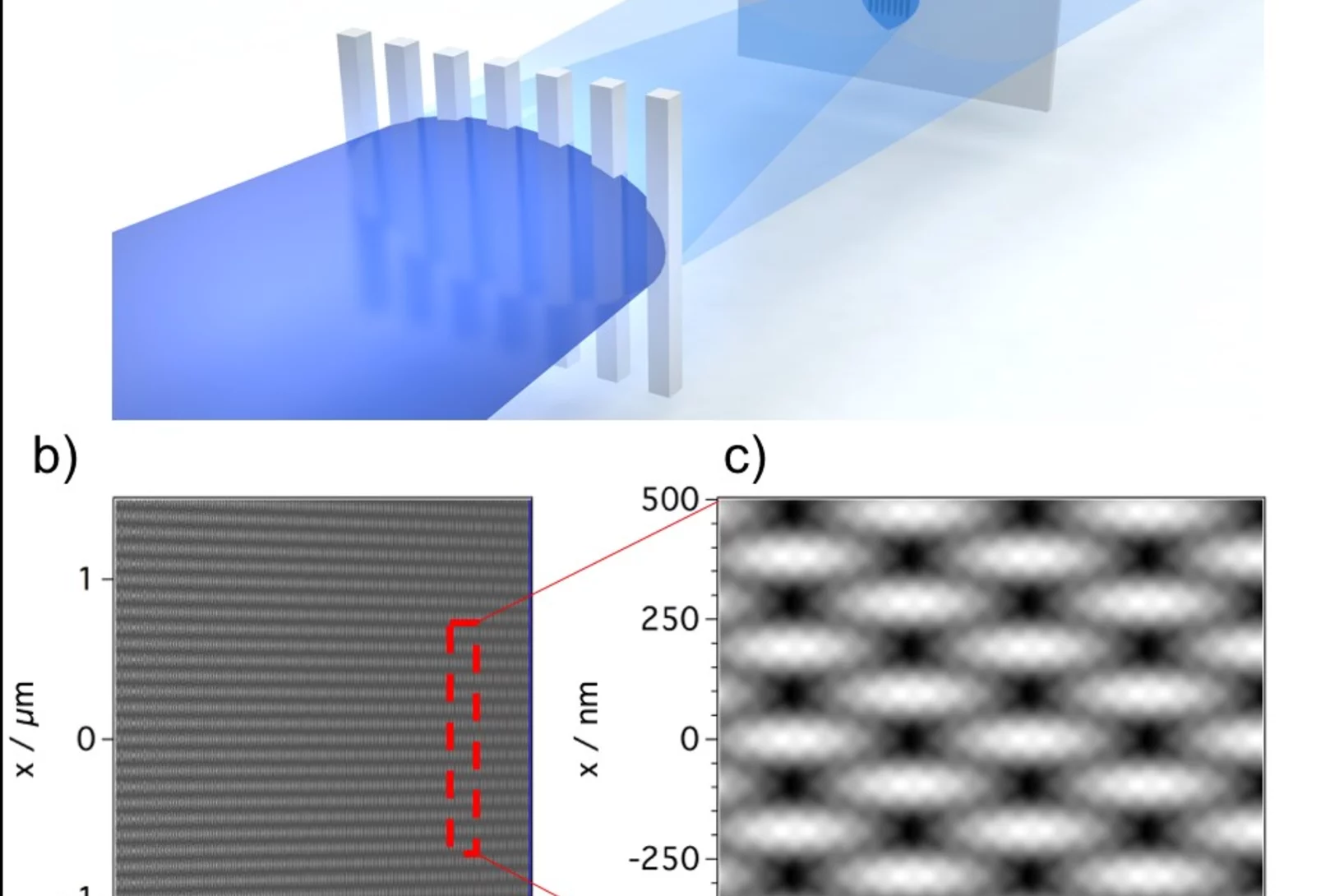
Towards X-ray Transient Grating Spectroscopy at SwissFEL
The high brilliance of new X-ray sources such as X-ray Free Electron Laser opens the way to non-linear spectroscopies. These techniques can probe ultrafast matter dynamics that would otherwise be inaccessible. One of these techniques, Transient Grating, involves the creation of a transient excitation grating by crossing X-ray beams on the sample. Scientists at PSI have realized a demonstration of such crossing by using an innovative approach well suited for the hard X-ray regime.
User operation at SwissFEL has begun
The first user experiment has taken place the the SwissFEL X-ray free electron laser, officially inaugurating it as the newest user facility at the Paul Scherrer Institute. The experiment, led by Camila Bacellar from EPFL, investigated ultrafast electron transfer dynamics in a protein to try to identify the charge density re-localization after the protein absorbs a photon of UV light. The experiment was performed using the Alvra Prime experimental station, taking advantage of the integrated von Hamos X-ray emission spectrometer to perform both X-ray absorption and emission measurements on the Fe atom, which is located at the centre of the protein.
First femtosecond protein pump-probe measurements at SwissFEL
A major milestone in the commissioning of SwissFEL has been reached: the first pump-probe experiments on proteins have been successfully carried out. Crystals of several retinal-binding proteins were delivered in a viscous jet system and a femtosecond laser was used to start the isomerization reaction. Microsecond to sub-picosecond snapshots were then collected, catching the retinal proteins shortly after isomerization of the chromophore.
SwissFEL's First Call for Proposals
The first SwissFEL call for proposals took place, deadline for submission was the 15th of September. In this first call for proposals SwissFEL received overwhelming interest from the user community. A total of 47 proposals were submitted for the SwissFEL Alvra experimental station and 26 for the Bernina experimental station. The Proposal Review committee PRC took place on 18-19 October 2018.
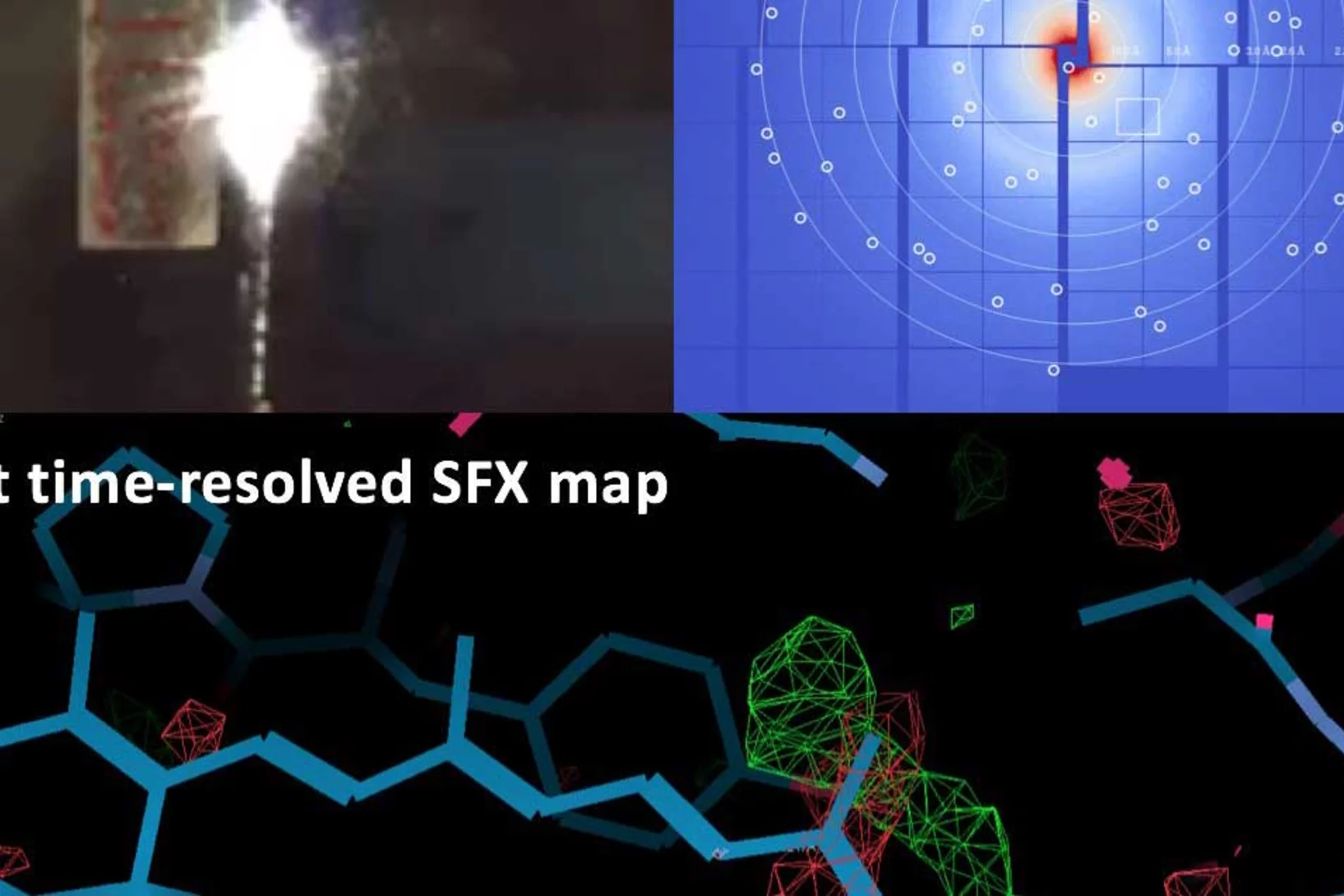
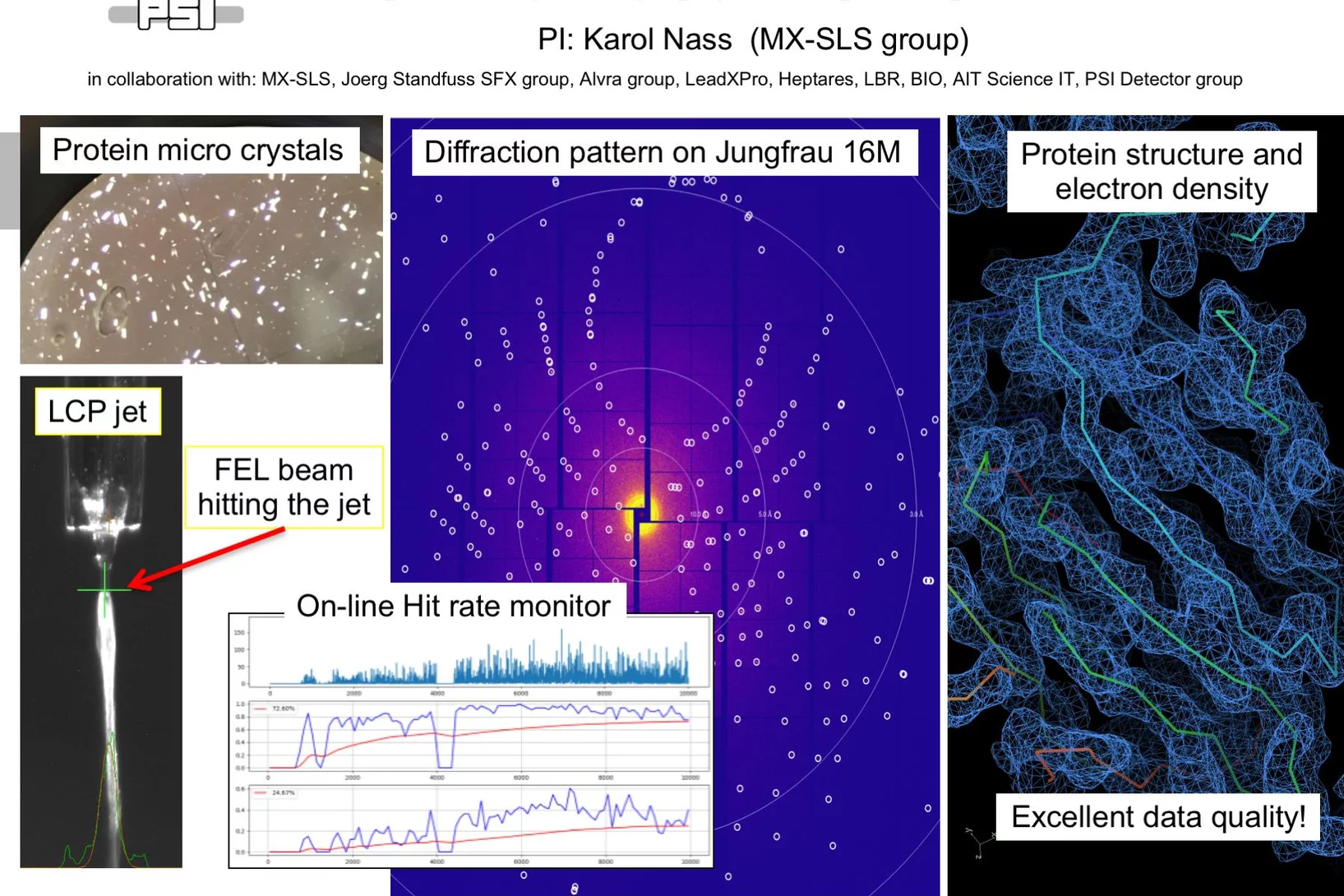
First serial femtosecond crystallography (SFX) pilot user experiment at SwissFEL
On the 7th to 12th of August 2018, a collaborative group of scientists from the Paul Scherrer Institute and members of the LeadXpro and Heptares pharmaceutical companies led by Karol Nass (PSI macromolecular crystallography MX-SLS group) performed the first serial femtosecond crystallography (SFX) pilot user experiment at the SwissFEL X-ray free electron laser (XFEL).
Hollywood en forêt de Würenlingen
Les chercheurs du PSI veulent utiliser le laser à rayons X SwissFEL pour réaliser des films qui présenteront des biomolécules en action. Ces productions montreront comment fonctionne notre œil ou quel est le mode d’action de nouveaux médicaments.
First Pilot Experiment at SwissFEL-Alvra: UV photo-induced charge transfer in OLED system
On the 17th of December 2017 SwissFEL saw its first pilot experiment in the Alvra experimental station of the SwissFEL ARAMIS beamline.
L’union fait la force
Décrypter les molécules au SwissFEL et à la SLSLes protéines sont un objet de recherche convoité, mais récalcitrant. Leur étude est aujourd’hui facilitée par une nouvelle méthode développée à l’aide d’un laser à rayons X à électrons libres comme le futur SwissFEL du PSI. Elle consiste à exposer à intervalles rapprochés de petits échantillons identiques de protéines à de la lumière de type rayons X. On contourne ainsi un problème majeur auquel la recherche sur les protéines s’est heurtée jusqu’ici: produire des échantillons de taille suffisante.