The PSI Center for Neutron and Muon Sciences uses neutrons and muons to explore and understand matter and materials.
Lab News & Scientific Highlights
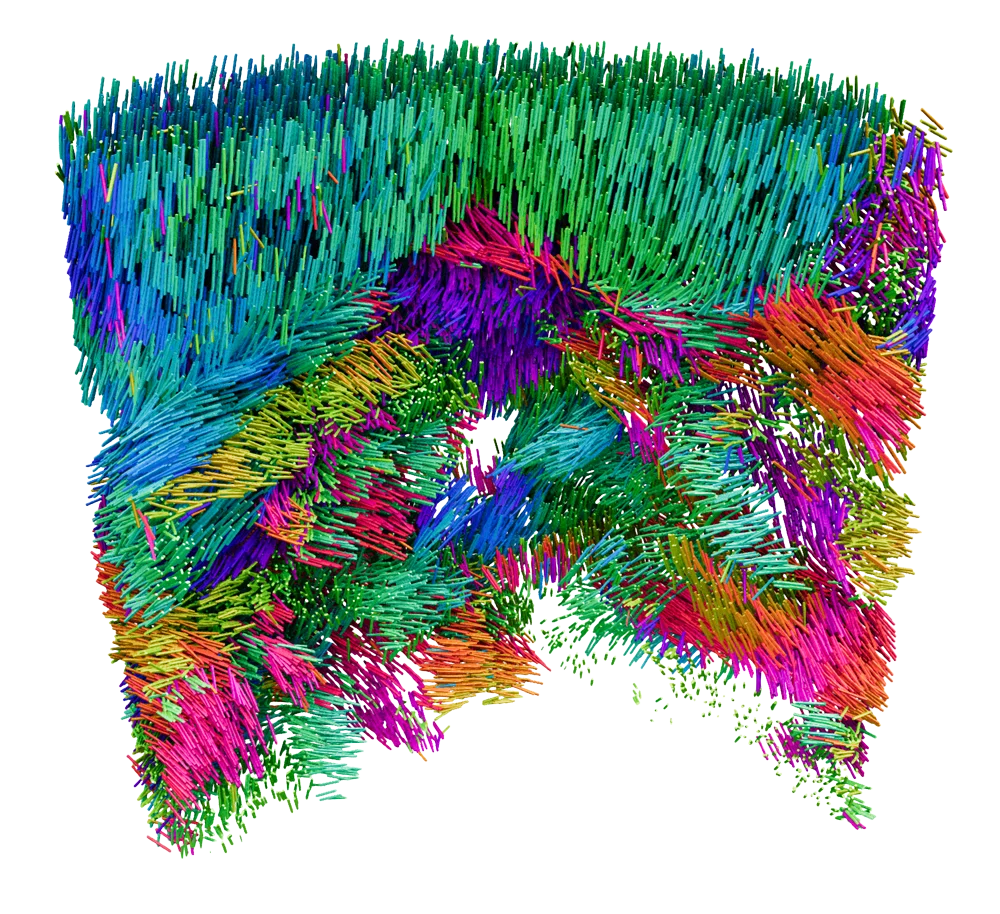
Anisotropic Skyrmion and Multi-q Spin Dynamics in Centrosymmetric Gd2PdSi3
Skyrmions are particlelike vortices of magnetization with nontrivial topology, which are usually stabilized by Dzyaloshinskii-Moriya interactions (DMI) in noncentrosymmetric bulk materials. Exceptions are centrosymmetric Gd- and Eu-based skyrmion-lattice (SL) hosts with zero DMI, where both the SL stabilization mechanisms and magnetic ground states remain controversial. We address these here by investigating both the static and dynamical spin properties ...
Concurrent Operando Neutron Imaging and Diffraction Analysis Revealing Spatial Lithiation Phase Evolution in an Ultra-Thick Graphite Electrode
Energy-efficient, safe, and reliable Li-ion batteries (LIBs) are required for a wide range of applications. The introduction of ultra-thick graphite anodes, desired for high energy densities, meets limitations in internal electrode transport properties, leading to detrimental consequences. Yet, there is a lack of experimental tools capable of providing a complete view of local processes. Here, a multi-modal operando measurement approach is introduced, enabling quantitative spatio-temporal observations of Li concentrations and intercalation phases in ultra-thick graphite electrodes.
Neutron imaging and diffraction concurrently provide ...
YBa1−𝑥Sr𝑥CuFeO5 layered perovskites: An attempt to explore the magnetic order beyond the paramagnetic-collinear-spiral triple point
Layered perovskites of general formula AA'CuFeO5 are characterized by the presence of spiral magnetic phases whose ordering temperatures 𝑇spiral can be tuned far beyond room temperature by introducing modest amounts of Cu/Fe chemical disorder in the crystal structure. This rare property makes these materials prominent candidates to host multiferroicity and magnetoelectric coupling at temperatures suitable for applications. Moreover, it has been proposed that the highest 𝑇spiral value that can be reached in this structural family ( ∼400 K) corresponds to a paramagnetic-collinear-spiral triple point with potential to show exotic physics. Since generating high amounts of Cu/Fe disorder is experimentally difficult, the phase diagram region beyond the triple point has been barely explored. To fill this gap we investigate here eleven YBa1−𝑥Sr𝑥CuFeO5 solid solutions (0≤𝑥≤1 ), where we replace Ba with Sr with the aim of enhancing the impact of the experimentally available Cu/Fe disorder. Using a combination of bulk magnetization measurements, synchrotron x-ray and neutron powder diffraction we show that the spiral state with 𝐤𝑠=(1/2,1/2,1/2±𝑞) is destabilized beyond a critical Sr content, being replaced by a fully antiferromagnetic state with ordering temperature 𝑇coll2≥𝑇spiral and propagation vector 𝐤𝑐2=(1/2,1/2,0). Interestingly, both 𝑇spiral and 𝑇coll2 increase with 𝑥 with comparable rates. This suggests a common, disorder-driven origin for both magnetic phases, consistent with theoretical predictions.
Connection between f-electron correlations and magnetic excitations in UTe2
The detailed anisotropic dispersion of the low-temperature, low-energy magnetic excitations of the candidate spin-triplet superconductor UTe2 is revealed using inelastic neutron scattering. The magnetic excitations emerge from the Brillouin zone boundary at the high symmetry Y and T points and disperse along the crystallographic b-axis. In applied magnetic fields ...
Small-angle scattering interferometry with neutron orbital angular momentum states
Methods to prepare and characterize neutron helical waves carrying orbital angular momentum (OAM) were recently demonstrated at small-angle neutron scattering (SANS) facilities. These methods enable access to the neutron orbital degree of freedom which provides new avenues of exploration in fundamental science experiments as well as in material characterization applications.
However, ....
Fractional quasiparticles in three dimensions
Specific signatures of fractionalization have been observed in a three-dimensional system known as quantum spin ice.
Our Facilities
Recent CNM publications
-
Agarwal M, Zika A, Yücel M, Schweins R, Kohlbrecher J, Gröhn F
The role of light irradiation and dendrimer generation in directing electrostatic self-assembly
Polymers. 2025; 17(2): 170 (27 pp.). https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17020170
DORA PSI -
Arshad MS, Čoga L, Kovač J, Geue T, Cruz SMA, Kalin M
Understanding the role of tungsten species in diamond-like carbon coatings for enhanced interaction with ionic liquids
Tribology International. 2025; 201: 110220 (11 pp.). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2024.110220
DORA PSI -
Ferretto I, Sharma A, Kim D, Della Ventura NM, Michler J, Capek J, et al.
Effect of precipitates on martensite formation and shape memory effect of FeMnSi-based shape memory alloys fabricated by laser powder bed fusion
Materials Science and Engineering A: Structural Materials: Properties, Microstructure and Processing. 2025; 921: 147592 (18 pp.). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2024.147592
DORA PSI