Here you find current and previous news from the PSI Center for Neutron and Muon Sciences.
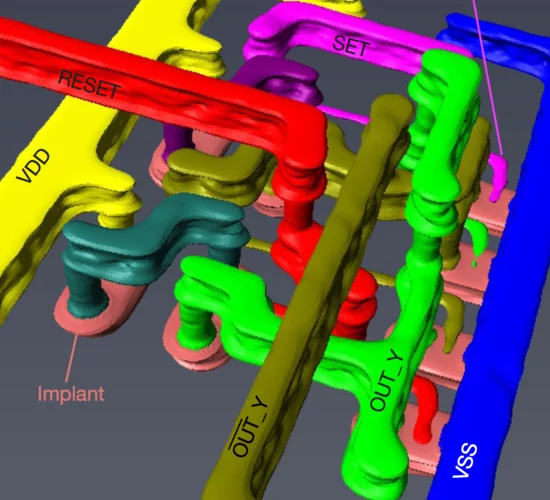
High-resolution non-destructive three-dimensional imaging of integrated circuits
Modern nanoelectronics has advanced to a point at which it is impossible to image entire devices and their interconnections non- destructively because of their small feature sizes and the complex three-dimensional structures resulting from their integration on a chip. This metrology gap implies a lack of direct feedback between design and manufacturing processes, and hampers quality control during production, shipment and use.
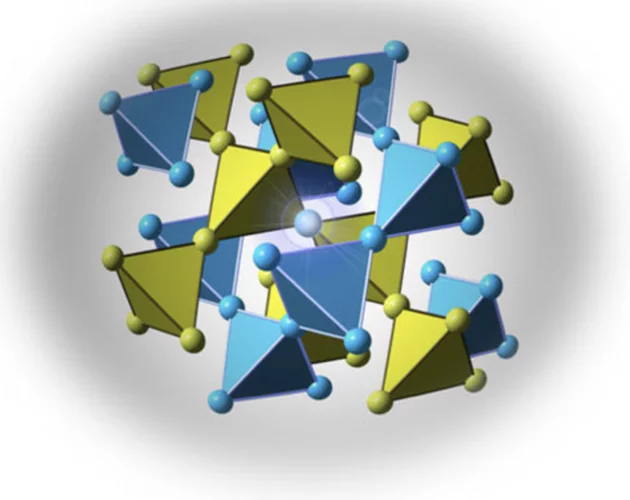
Ground state selection under pressure in the quantum pyrochlore magnet Yb2Ti2O7
A quantum spin liquid is a state of matter characterized by quantum entanglement and the absence of any broken symmetry. In condensed matter, the frustrated rare-earth pyrochlore magnets Ho2Ti2O7 and Dy2Ti2O7, so-called spin ices, exhibit a classical spin liquid state with fractionalized thermal excitations (magnetic monopoles).
Effects of Quantum Spin-1/2 Impurities on the Magnetic Properties of Zigzag Spin Chains
We investigate the effect of Co2+ (spin-1/2) impurities on the magnetic ground state and low-lying spin excitations of the quasione-dimensional spin-1/2 antiferromagnet SrCuO2 by means of neutron scattering, muon spin spectroscopy, and bulk (ac and dc) magnetic susceptibilities. We found that dilute Co doping induces an Ising-like anisotropy and enhances the magnetic ordering temperature rather significantly, but preserves the gapless nature of the spin excitations.
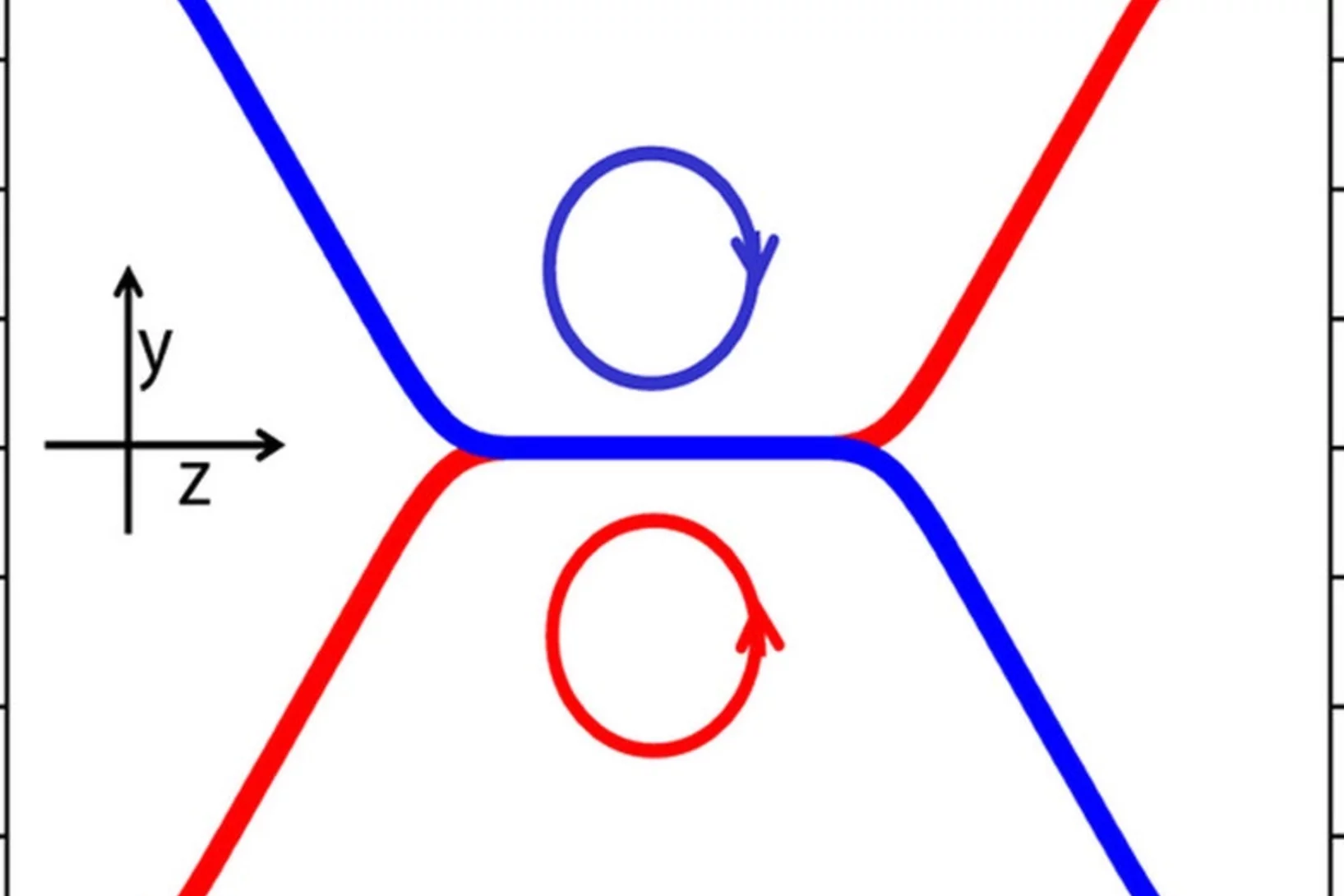
Distinct Evolutions of Weyl Fermion Quasiparticles and Fermi Arcs with Bulk Band Topology in Weyl Semimetals
The Weyl semimetal phase is a recently discovered topological quantum state of matter characterized by the presence of topologically protected degeneracies near the Fermi level. These degeneracies are the source of exotic phenomena, including the realization of chiral Weyl fermions as quasiparticles in the bulk and the formation of Fermi arc states on the surfaces.
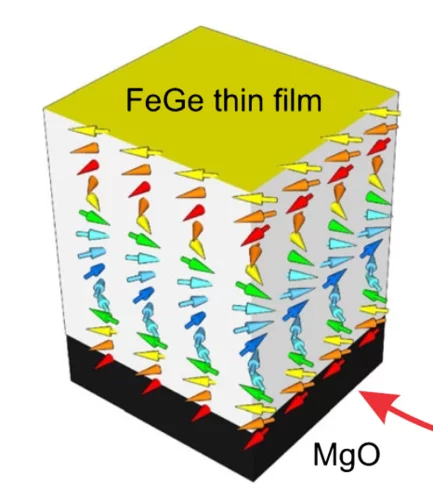
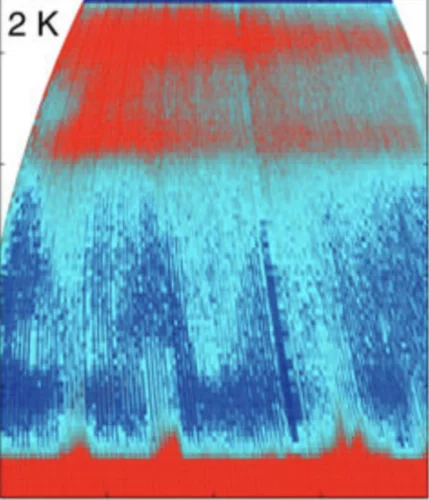
Room-temperature helimagnetism in FeGe thin films
Chiral magnets are promising materials for the realisation of high-density and low-power spintronic memory devices. For these future applications, a key requirement is the synthesis of appropriate materials in the form of thin films ordering well above room temperature. Driven by the Dzyaloshinskii-Moriya interaction, the cubic compound FeGe exhibits helimagnetism with a relatively high transition temperature of 278 K in bulk crystals.
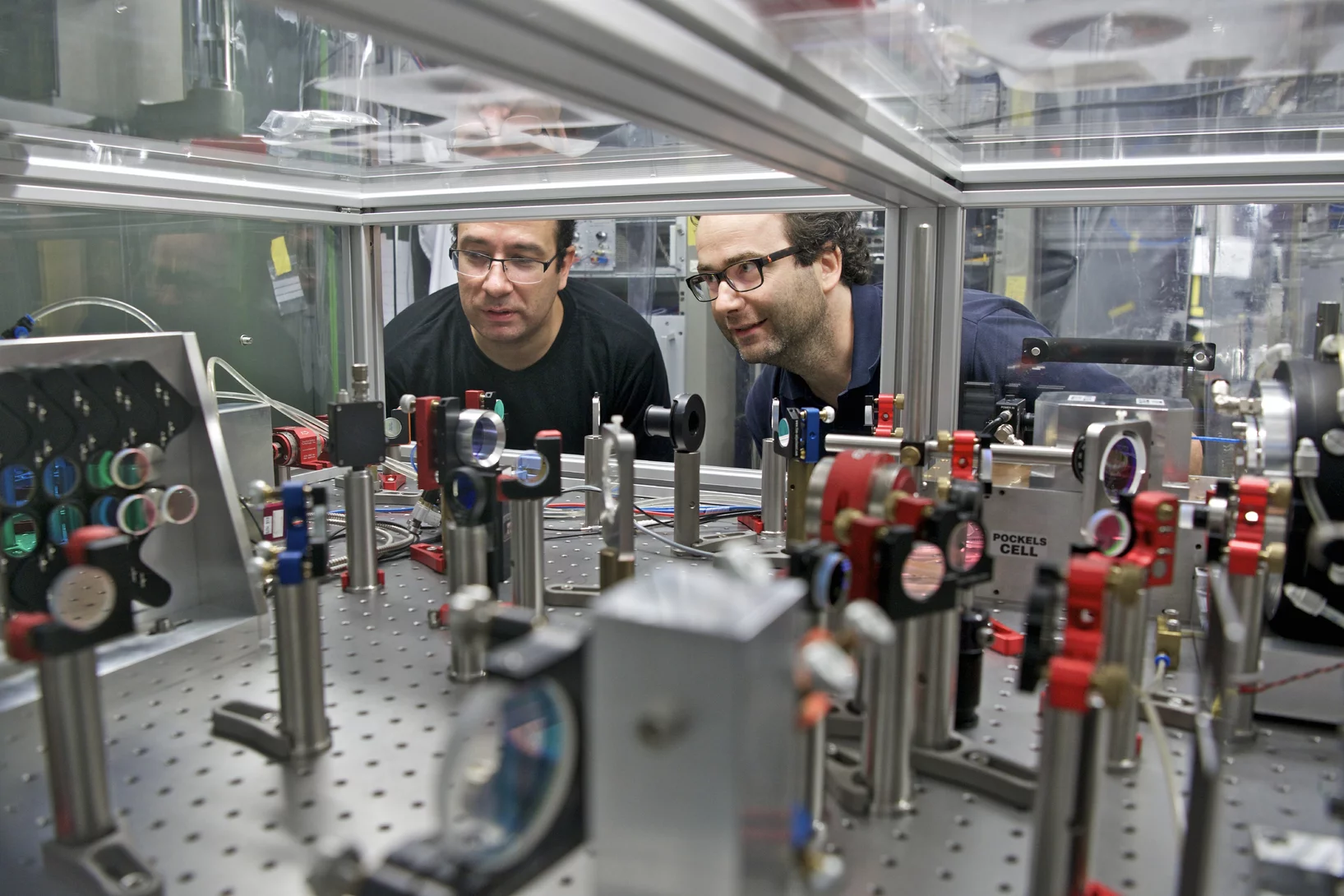
Silicon pixel barrel detector successfully installed in the CMS experiment
Middle of February the upgraded CMS silicon pixel barrel detector has been moved from PSI to CERN and was successfully installed in the CMS experiment.
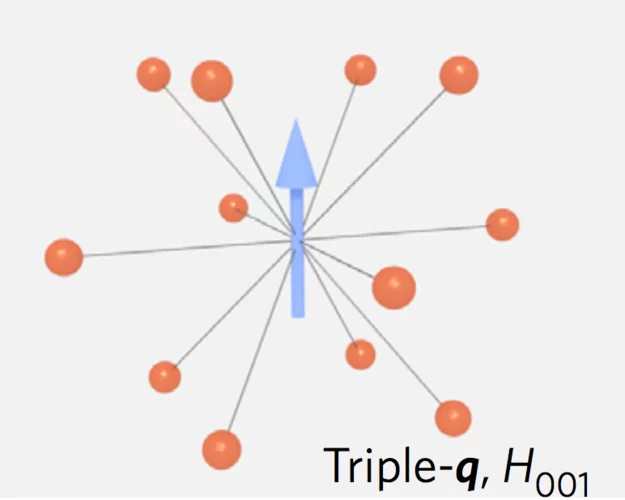
Spiral spin-liquid and the emergence of a vortex-like state in MnSc2S4
Spirals and helices are common motifs of long-range order in magnetic solids, and they may also be organized into more complex emergent structures such as magnetic skyrmions and vortices. A new type of spiral state, the spiral spin-liquid, in which spins fluctuate collectively as spirals, has recently been predicted to exist.
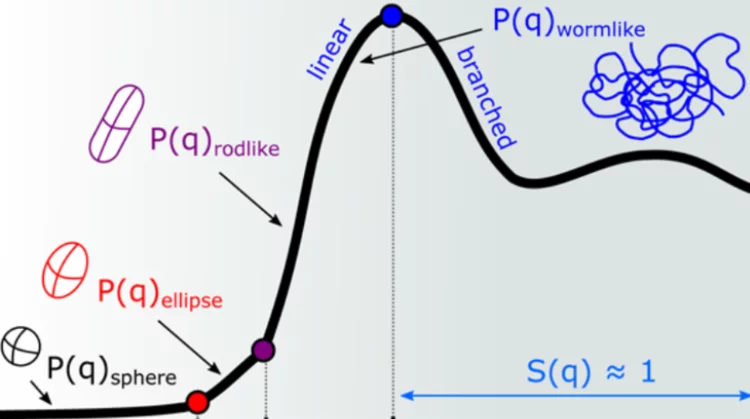
Intermicellar Interactions and the Viscoelasticity of Surfactant Solutions: Complementary Use of SANS and SAXS
In ionic surfactant micelles, basic interactions among distinct parts of surfactant monomers, their counterion, and additives are fundamental to tuning molecular self-assembly and enhancing viscoelasticity. Here, we investigate the addition of sodium salicylate (NaSal) to hexadecyltrimethylammonium chloride and bromide (CTAC and CTAB) and 1-hexadecylpyridinium chloride and bromide (CPyCl and CPyBr), which have distinct counterions and headgroup structures but the same hydrophobic tail.
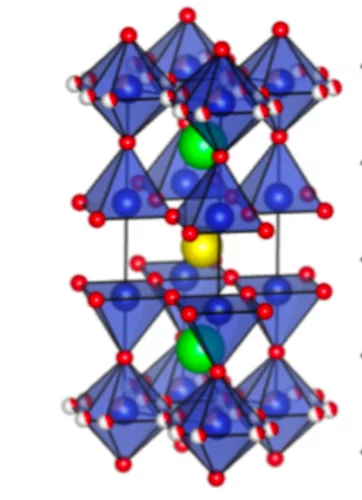
New magnetic phase in the nickelate perovskite TlNiO3
The RNiO3 perovskites are known to order antiferromagnetically below a material-dependent Néel temperature TN. We report experimental evidence indicating the existence of a second magnetically ordered phase in TlNiO3 above TN = 104K, obtained using nuclear magnetic resonance and muon spin rotation spectroscopy.
Magnetic Field Dependence of Excitations Near Spin-Orbital Quantum Criticality
The spinel FeSc2S4 has been proposed to realize a near-critical spin-orbital singlet (SOS) state, where entangled spin and orbital moments fluctuate in a global singlet state on the verge of spin and orbital order.
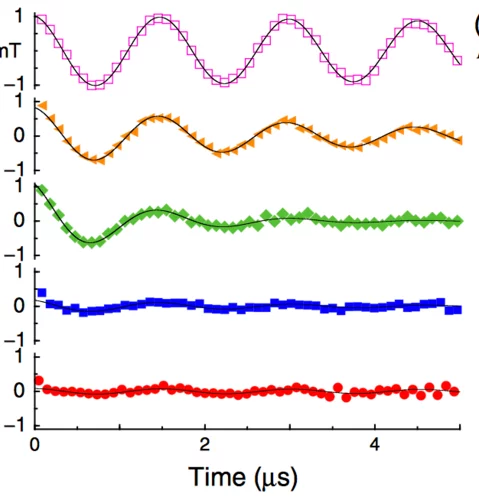
Probing current-induced magnetic fields in Au|YIG heterostructures with low-energy muon spin spectroscopy
We investigated the depth dependence of current-induced magnetic fields in a bilayer of a normal metal (Au) and a ferrimagnetic insulator (Yttrium Iron Garnet—YIG) by using low energy muon spin spectroscopy (LE-μSR). This allows us to explore how these fields vary from the Au surface down to the buried Au|YIG interface, which is relevant to study physics like the spin-Hall effect.
Full Elasticity Tensor from Thermal Diffuse Scattering
We present a method for the precise determination of the full elasticity tensor from a single crystal diffraction experiment using monochromatic X-rays. For the two benchmark systems calcite and magnesium oxide, we show that the measurement of thermal diffuse scattering in the proximity of Bragg reflections provides accurate values of the complete set of elastic constants.
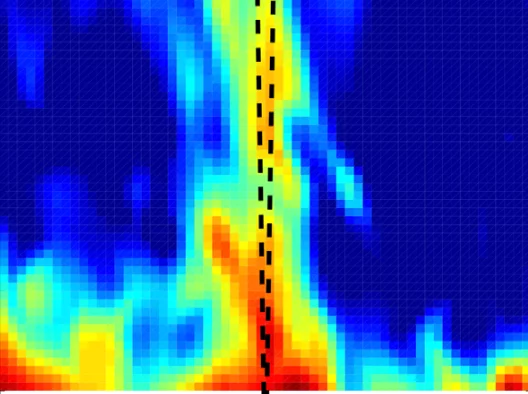
Suppression of magnetic excitations near the surface of the topological Kondo insulator SmB6
We present a detailed investigation of the temperature and depth dependence of the magnetic properties of the three-dimensional topological Kondo insulator SmB6, in particular, near its surface. We find that local magnetic field fluctuations detected in the bulk are suppressed rapidly with decreasing depths, disappearing almost completely at the surface.
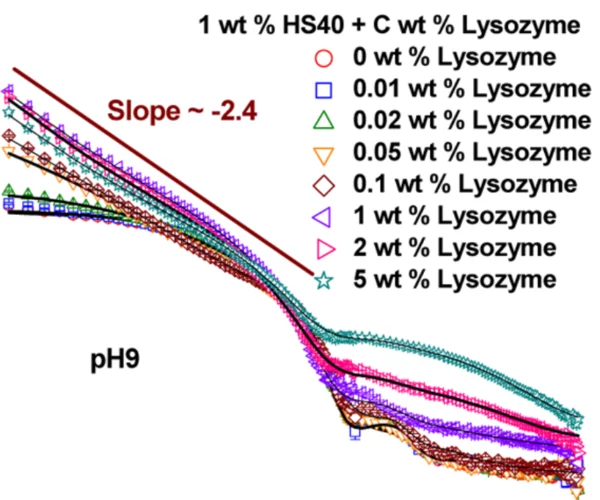
Structure and Interaction in the pH-Dependent Phase Behavior of Nanoparticle−Protein Systems
The pH-dependent structure and interaction of anionic silica nanoparticles (diameter 18 nm) with two globular model proteins, lysozyme and bovine serum albumin (BSA), have been studied. Cationic lysozyme adsorbs strongly on the nanoparticles, and the adsorption follows exponential growth as a function of lysozyme concentration, where the saturation value increases as pH approaches the isoelectric point (IEP) of lysozyme.
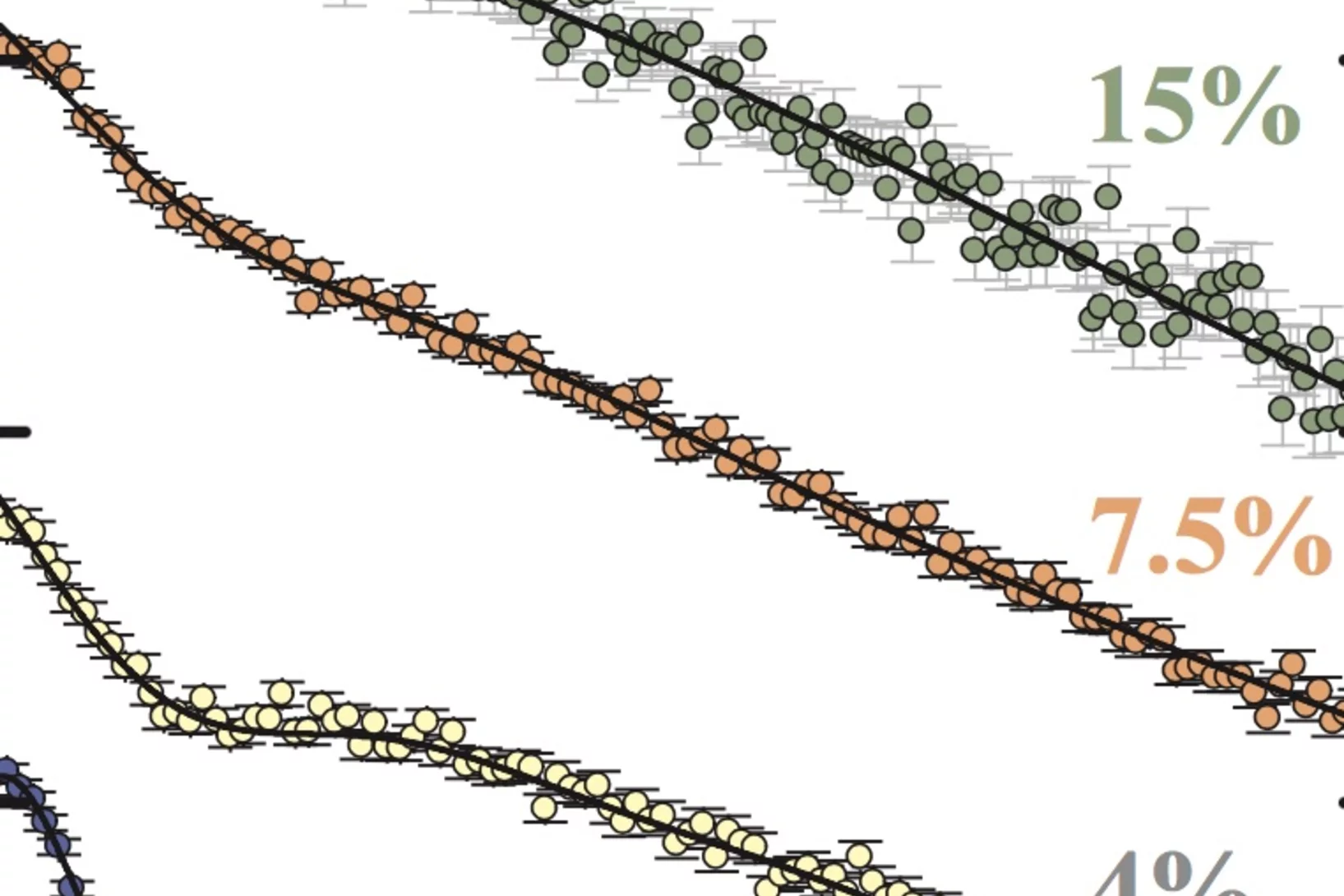
Tuning magnetic spirals beyond room temperature with chemical disorder
Frustrated magnets with spiral magnetic orders are of high current interest due to their potential for spintronics and low-power magnetoelectric devices. However, their low magnetic order temperatures (typically <100K) greatly restrict their fields of application. Researchers of PSI have demonstrated that the stability domain of the spiral phase in the perovskite YBaCuFeO5 can be enlarged by more than 150K through a controlled manipulation of the Fe/Cu chemical disorder.
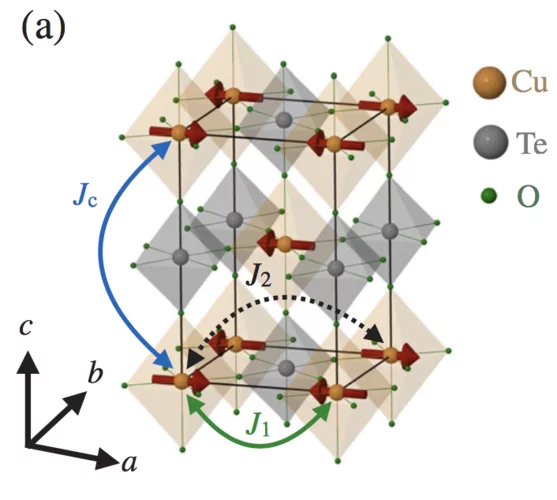
Magnetic Excitations and Electronic Interactions in Sr2CuTeO6: A Spin-1/2 Square Lattice Heisenberg Antiferromagnet
Sr2CuTeO6 presents an opportunity for exploring low-dimensional magnetism on a square lattice of S=1/2 Cu2+ ions. We employ ab initio multireference configuration interaction calculations to unravel the Cu2+ electronic structure and to evaluate exchange interactions in Sr2CuTeO6.
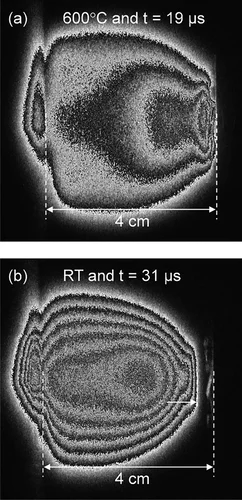
Pressure and temperature dependence of the laser-induced plasma plume dynamics
The influence of different background gases and substrate heating on the plasma plume dynamics from silver ablation is investigated by species selected time and space resolved imaging. The results provide a time-resolved understanding on how those process parameters affect the expansion: from a free expansion in vacuum with velocities exceeding 20'000 m/s to a very slow expansion in Ar at 1 × 10−1 mbar with arrival velocities of 280 m/s.
Electromagnon dispersion probed by inelastic X-ray scattering in LiCrO2
Lattice vibrations (phonons) in crystals are typically weakly interacting with the electronic and magnetic degrees of freedom, such as charge and spin fluctuations. Researchers of PSI together with collaborators from EPF Lausanne, Japan and USA discovered an unexpectedly strong coupling between lattice vibrations and spin fluctuations in the quantum magnet LiCrO2. The observed magnetoelastic waves or electromagnons carry both electric and magnetic dipole moment.
Intrinsic Ferromagnetism in the Diluted Magnetic Semiconductor Co:TiO2
Here we present a study of magnetism in Co0.05Ti0.95O2−δ anatase films grown by pulsed laser deposition under a variety of oxygen partial pressures and deposition rates. Energy-dispersive spectrometry and transmission electron microscopy analyses indicate that a high deposition rate leads to a homogeneous microstructure, while a very low rate or postannealing results in cobalt clustering.
Bulk superconductivity at 84 K in the strongly overdoped regime of cuprates
By means of magnetization, specific heat, and muon-spin relaxation measurements, we investigate newly synthesized high-pressure oxidized Cu0.75Mo0.25Sr2YCu2O7.54, in which overdoping is achieved up to p ˜ 0.46 hole/Cu, well beyond the Tc-p superconducting dome of cuprates, where Fermi-liquid behavior is expected.
The deuteron too poses a mystery
The deuteron — one of the simplest atomic nuclei, consisting of just one proton and one neutron — is considerably smaller than previously thought. This finding was arrived at by an international research group that carried out experiments at the Paul Scherrer Institute, PSI. The new result is consistent with a 2010 study by the same group, in which the researchers measured the proton and found a significantly smaller value than previous research using different experimental methods.
Structure and Conductivity of Epitaxial Thin Films of In-Doped BaZrO3‑Based Proton Conductors
Epitaxial thin films of the proton-conducting perovskite BaZr0.53In0.47O3−δH0.47−2δ, grown by pulsed laser deposition, were investigated in their hydrated and dehydrated conditions through a multitechnique approach with the aim to study the structure and proton concentration depth profile and their relationship to proton conductivity.
Effect of disorder on a pressure-induced z = 1 magnetic quantum phase transition
Pressure-induced ordering close to a z = 1 quantum-critical point is studied in the presence of bond disorder in the quantum spin system (C4H12N2)Cu2(Cl1−xBrx)6 (PHCX) by means of muon-spin rotation and relaxation.
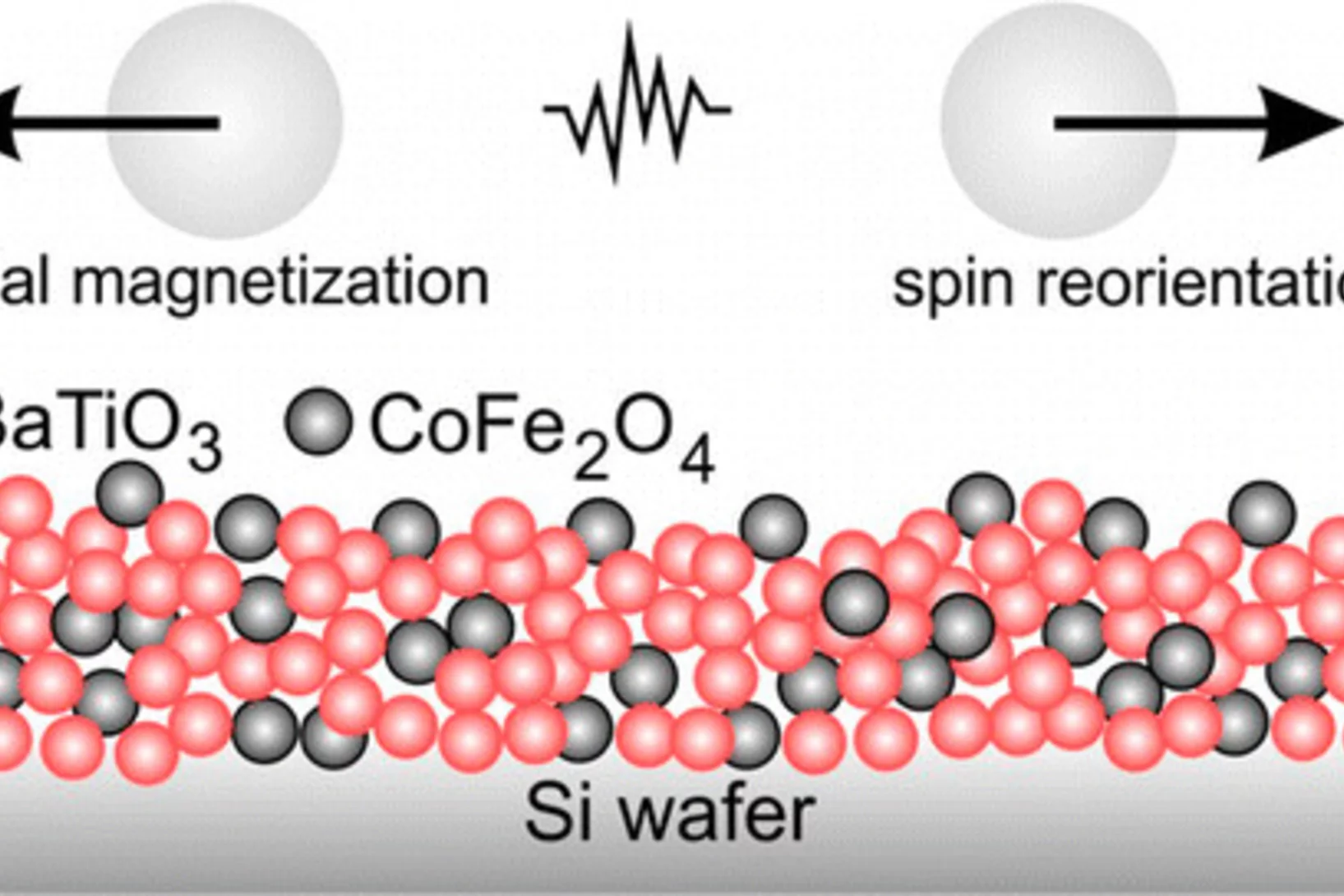
Nanoparticle-Based Magnetoelectric BaTiO3–CoFe2O4 Thin Film Heterostructures for Voltage Control of Magnetism
Multiferroic composite materials combining ferroelectric and ferromagnetic order at room temperature have great potential for emerging applications such as four-state memories, magnetoelectric sensors, and microwave devices.
Magnetodielectric detection of magnetic quadrupole order in Ba(TiO)Cu4(PO4)4 with Cu4O12 square cupolas
In vortex-like spin arrangements, multiple spins can combine into emergent multipole moments. Such multipole moments have broken space-inversion and time-reversal symmetries, and can therefore exhibit linear magnetoelectric (ME) activity. Three types of such multipole moments are known: toroidal; monopole; and quadrupole moments. So far, however, the ME activity of these multipole moments has only been established experimentally for the toroidal moment.
Realizing topological stability of magnetic helices in exchange-coupled multilayers for all-spin-based system
Topologically stabilized spin configurations like helices in the form of planar domain walls (DWs) or vortex-like structures with magnetic functionalities are more often a theoretical prediction rather than experimental realization. In this paper we report on the exchange coupling and helical phase characteristics within Dy-Fe multilayers. The magnetic hysteresis loops with temperature show an exchange bias field of around 1.0 kOe at 10 K.
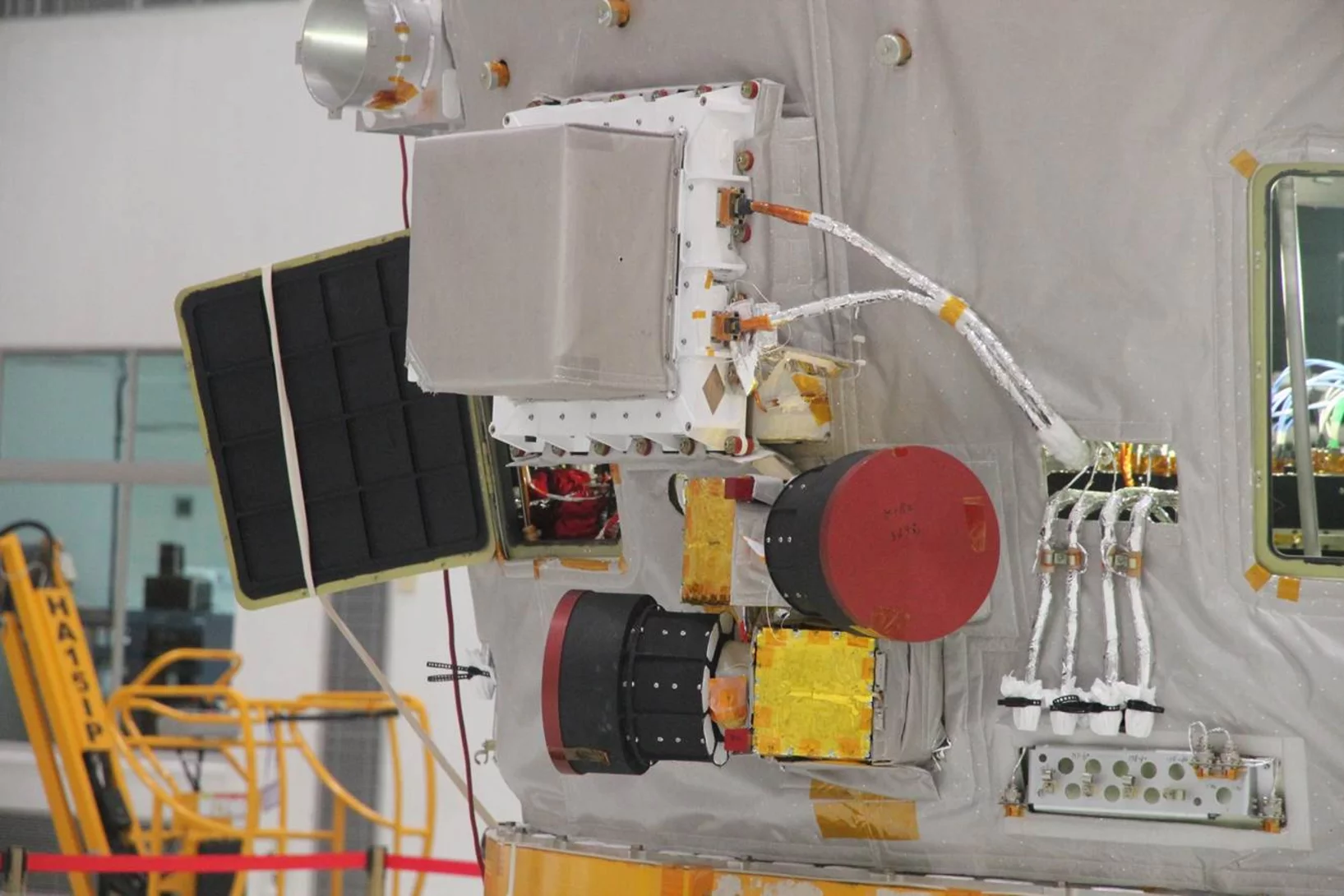
POLAR experiment successfully launched on Chinese spacecraft
The second Chinese space laboratory satellite Tian Gong 2 was successfully launched from the Jiuquan Satellite Launch Center on September 15th, 2016 at 22:04 BTC (UTC+8h). Among more than ten instruments onboard it also brought to space the only non-Chinese experiment POLAR - the hard X-ray polarimeter.
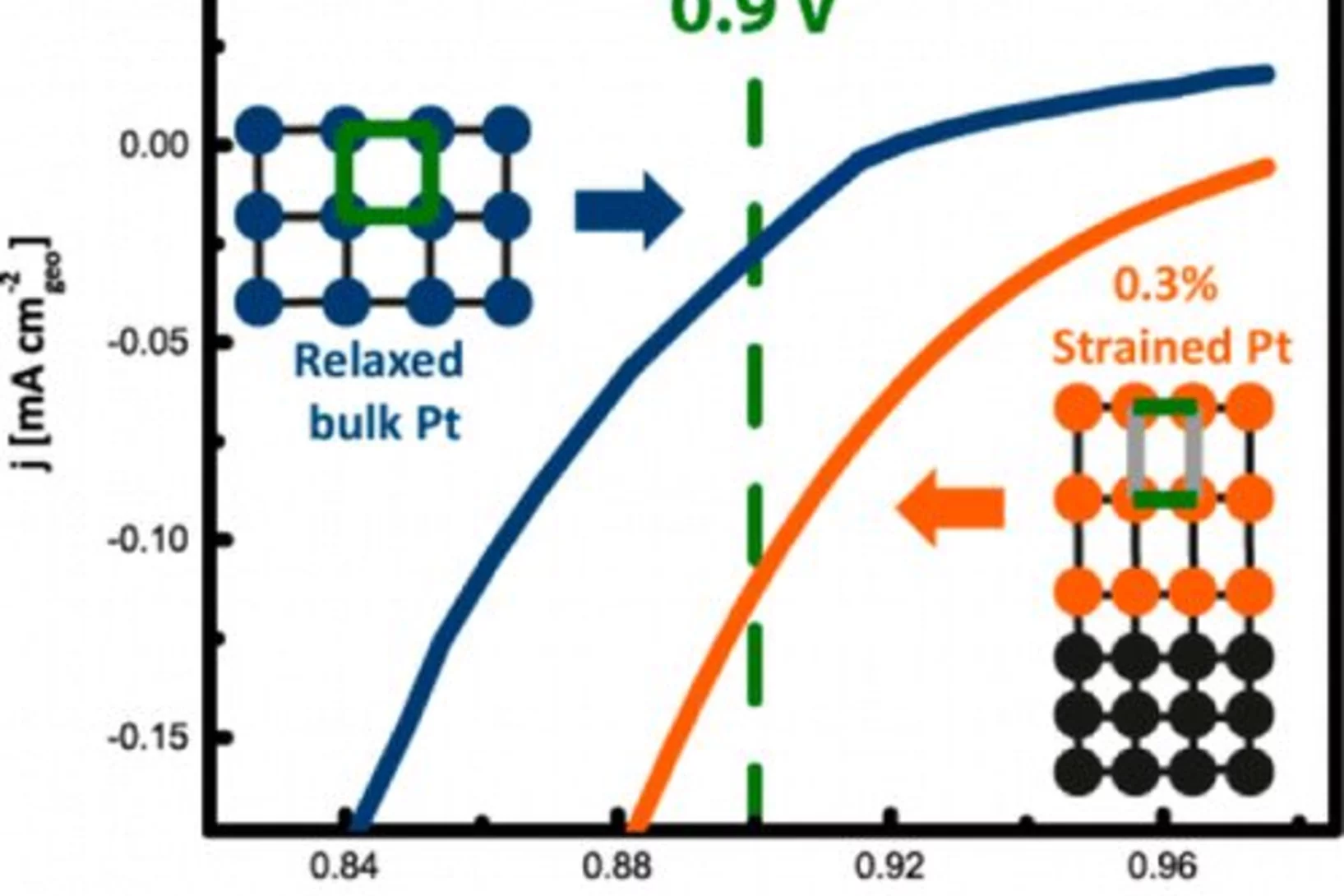
Investigating the Role of Strain toward the Oxygen Reduction Activity on Model Thin Film Pt Catalysts
Environmentally friendly energy conversion devices such as fuel cells are becoming more and more attractive. However, major impediments to large-scale application still arise on the material side, related to the cost and poor performance of the cathode catalyst. State-of-the-art electrocatalysts are all Pt-based materials, suffering from poor electrochemical oxygen reduction kinetics.
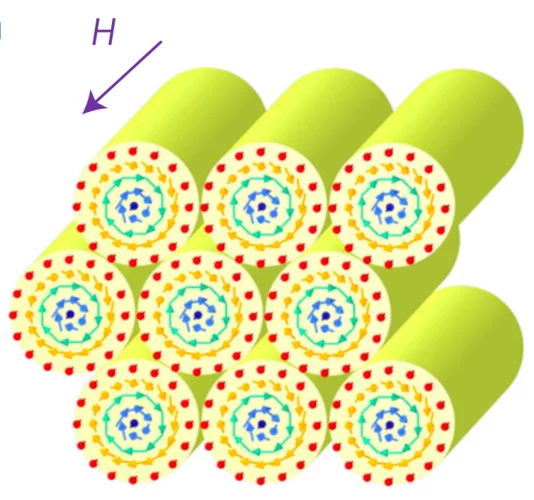
Robust metastable skyrmions and their triangular–square lattice structural transition in a high-temperature chiral magnet
Skyrmions, topologically protected nanometric spin vortices, are being investigated extensively in various magnets. Among them, many structurally chiral cubic magnets host the triangular-lattice skyrmion crystal (SkX) as the thermo- dynamic equilibrium state. However, this state exists only in a narrow temperature and magnetic-field region just below the magnetic transition temperature Tc, while a helical or conical magnetic state prevails at lower temperatures.
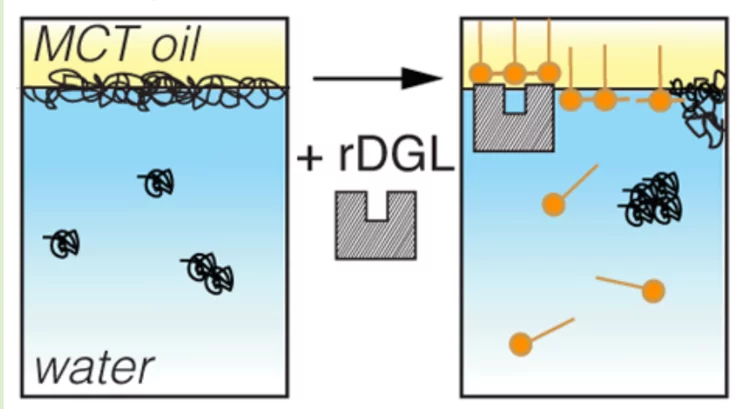
Blocking Gastric Lipase Adsorption and Displacement Processes with Viscoelastic Biopolymer Adsorption Layers
Delayed fat digestion might help to fight obesity. Fat digestion begins in the stomach by adsorption of gastric lipases to oil/water interfaces. In this study we show how biopolymer covered interfaces can act as a physical barrier for recombinant dog gastric lipase (rDGL) adsorption and thus gastric lipolysis.