Short film of a magnetic nano-vortex
Using a newly developed imaging method, researchers were able to visualise the magnetic structure inside a material with nanoscale resolution. They succeeded in creating a short "film" consisting of seven movie frames that shows, for the first time in 3D, how tiny vortices of the magnetisation deep within a material change over time.
Innovation Award on Synchrotron Radiation 2019 for the development of XFEL detectors using the adaptive gain principle
The Innovation Award on Synchrotron Radiation 2019 was given to the researchers Prof. Heinz Graafsma from Desy and Dr. Aldo Mozzanica and Dr. Bernd Schmitt both from the Paul Scherrer Institute. The three physicists were honored for their contributions to the development of detectors for XFEL applications based on the dynamic gain switching principle enabling simultaneously single photon resolution and a large dynamic range. The laudation was held by Prof. Edgar Weckert from Desy. The Synchrotron Radiation Innovation Award is sponsored by SPECS GmbH and BESTEC GmbH.
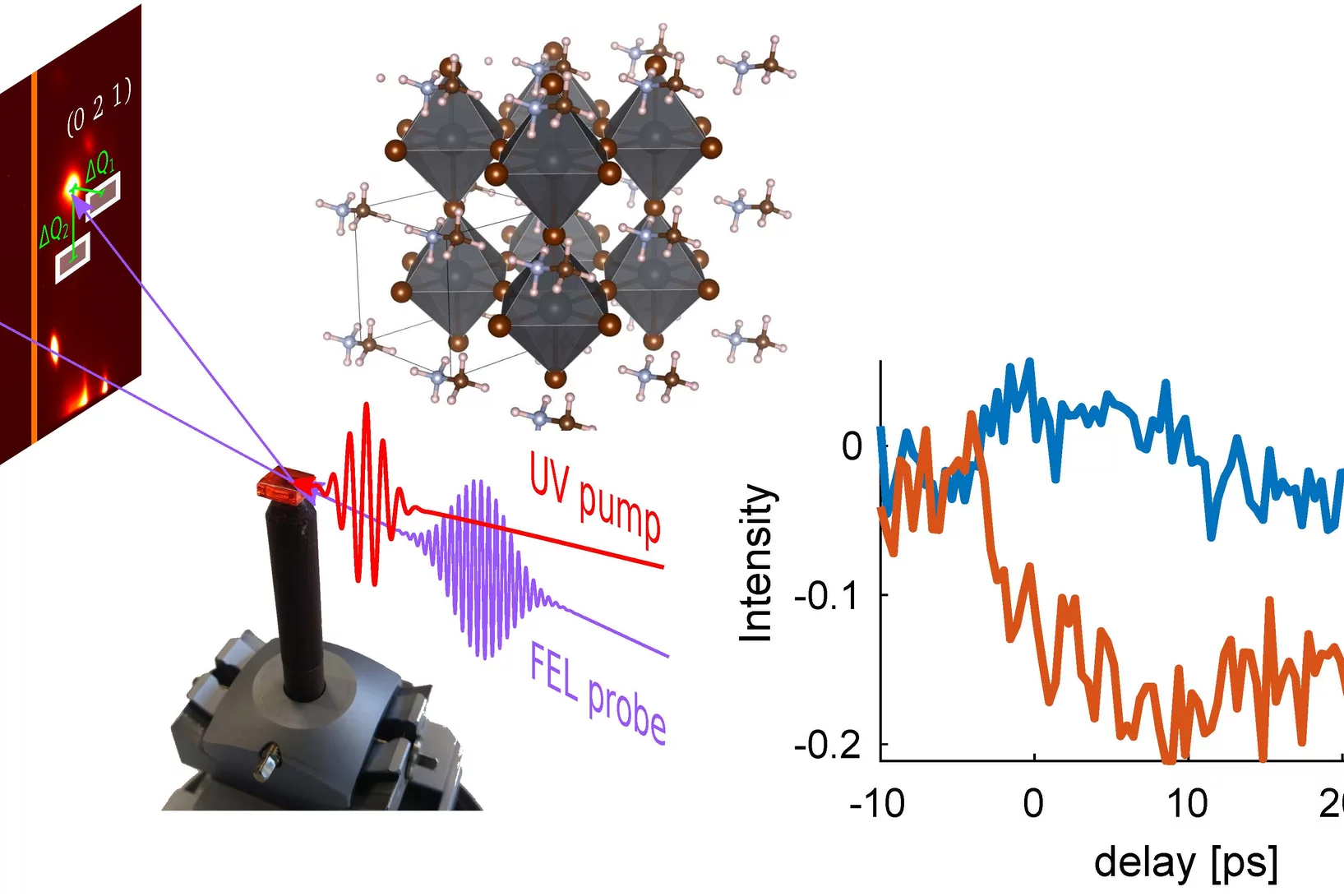
Ultrafast diffuse x-ray scattering of a hybrid perovskite crystal
Organic–inorganic ‘hybrid’ perovskites have recently gained attention as a low-cost alternative to silicon solar cells. However, many properties of these materials are still poorly understood. In particular, how imperfections in the crystals, which can be both static or dynamic, affect energy transport remains unclear.
More magnets, smoother curves: The SLS upgrade
The Swiss Light Source SLS is set to undergo an upgrade in the coming years: SLS 2.0. The renovation is made possible by the latest technologies and will create a large research facility that will meet the needs of researchers for decades to come.
A fast and precise look into fibre-reinforced composites
Researchers at the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI have developed a new process with which fibre-reinforced composite materials can be precisely X-rayed. This could help to develop better materials with novel properties.
New 6M€ European grant awarded to ExPaNDS to drive open access data
A new 6M€ grant is being launched for the Photon and Neutron Data Services (ExPaNDS) to come together and work under the European Open Science Cloud (EOSC). This ambitious project will create enormous opportunities for scientific communities, and through their findings for humankind worldwide. It aims to publish and map the data behind the thousands of successful published scientific papers generated by Europe’s Photon and Neutron Research Infrastructures (PaN RIs) – which every year create petabytes of data – and make it available to all.
Research and tinkering – SwissFEL in 2019
The newest large research facility at the Paul Scherrer Institute, SwissFEL, has been completed. In January 2019 it began regular operation. Henrik Lemke, head of the SwissFEL Bernina research group, gives an interim report.
Preventing tumour metastasis
Researchers at the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI, together with colleagues from the pharmaceutical company F. Hoffmann-La Roche AG, have taken an important step towards the development of an active substance against the metastasis of certain cancers. Using the Swiss Light Source SLS, they deciphered the structure of a receptor that plays a crucial role in the migration of cancer cells.
Weyl fermions discovered in another class of materials
A particular variety of particles, the so-called Weyl fermions, had previously only been detected in certain non-magnetic materials. But now researchers at PSI have experimentally proved their existence for the first time in a specific paramagnetic material.
Molecular energy machine as a movie star
Using the Swiss Light Source SLS, PSI researchers have recorded a molecular energy machine in action and thus revealed how energy production at cell membranes works. For this purpose, they developed a new investigative method that could make the analysis of cellular processes significantly more effective than before.
First demonstration of a Germanium laser
Scientist at the Paul Scherrer Institut and ETH Zürich, with colleagues from CEA Grenoble, have demonstrated and characterized a technology that, for the first time, yields lasing from strained elemental Germanium. This achievement underlines PSI’s leading role in the development of Silicon-compatible laser light sources.
PSI School for Master Degree Students - Introducing Photons, Neutrons and Muons for Condensed Matter Physics and Materials Science
From 17 – 21 June 2019 the Neutron and Muon Division (NUM) and the Photon Science Division (PSD) of PSI hosted 18 Master Degree students of physics, chemistry, materials and interdisciplinary science, as well as nuclear engineering to provide an introduction to the characterization of materials with large scale facilities like SINQ, SμS, SLS and SwissFEL. The course taught a basic understanding of how photons, neutrons and muons interact with matter, and how this knowledge can be used to solve specific problems in materials research.
Details of the program can be found at http://indico.psi.ch/event/PSImasterschool
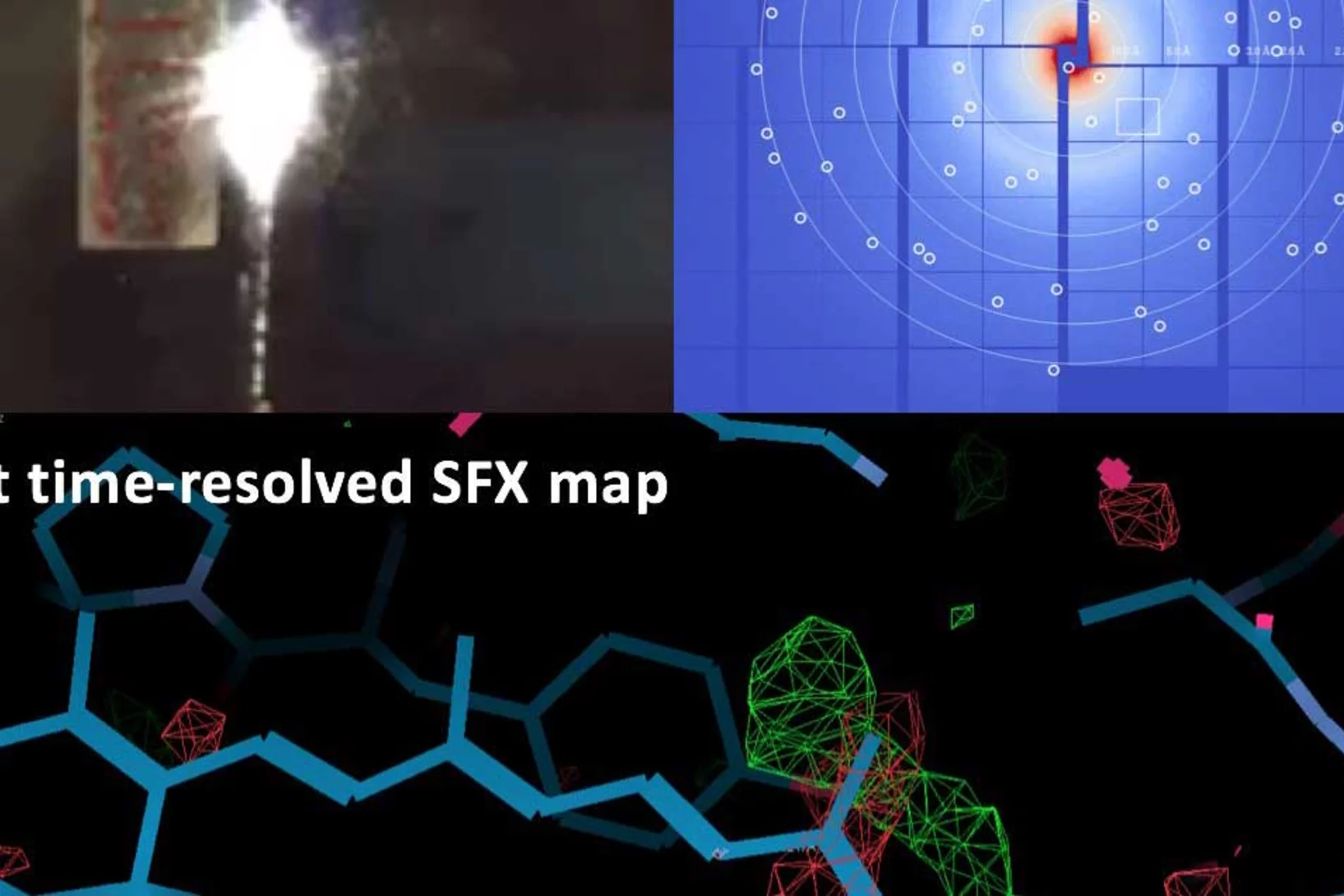
First serial femtosecond crystallography experiment using SwissFEL’s large bandwidth X-ray pulses
The typical mode of operation at XFEL facilities uses the so-called self-amplified spontaneous emission (SASE) process to generate the short, bright X-ray pulses. This mode of operation is stochastic in nature, causing some variance in intensity and spectrum on a shot-to-shot basis, which makes certain types of crystallographic measurements much more challenging.
New material with magnetic shape memory
PSI researchers have developed a material whose shape memory is activated through magnetism. Application areas for this new kind of composite material include, for example, medicine, space flight, electronics, and robotics.
New material also reveals new quasiparticles
Researchers at PSI have investigated a novel crystalline material at the Swiss Light Source SLS that exhibits electronic properties never seen before. Among other things, they were able to detect a new type of quasiparticle: so-called Rarita-Schwinger fermions.
HERCULES school 2019 at SLS
In the week of April 1-5 PSI welcomes 20 PhD students and postdocs taking part in the European HERCULES 2019 school on Neutron and Synchrotron Radiation. They will attend lectures and perform two days of practical courses at several beam lines of the Swiss Light Source.
A compass pointing West
Researchers at PSI have discovered a new phenomenon of magnetism with the help of the Swiss Light Source SLS. Certain groups of atoms behave like a compass pointing West. This could make computers much more powerful.
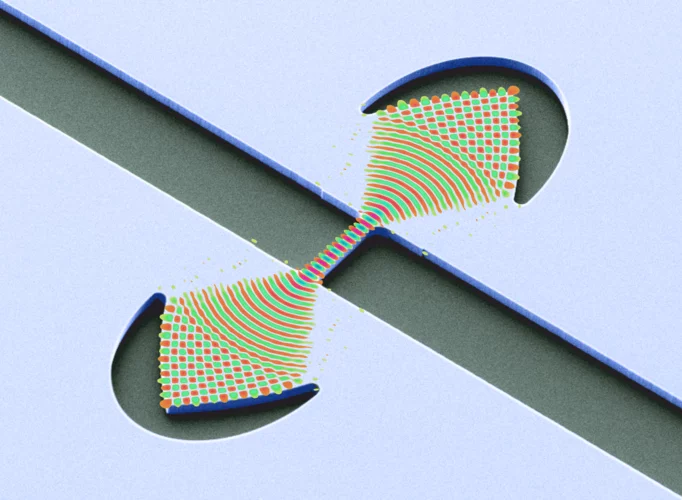
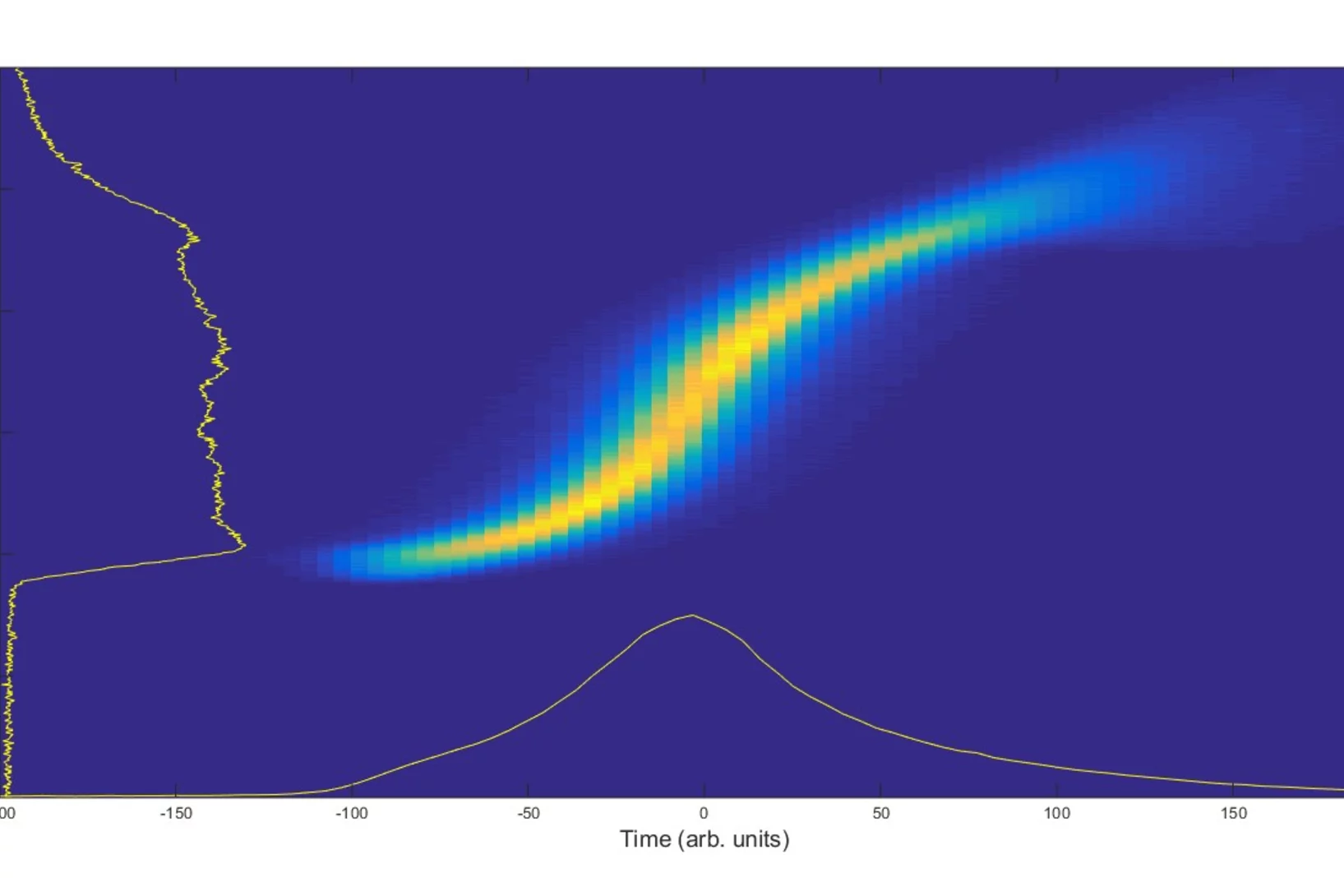
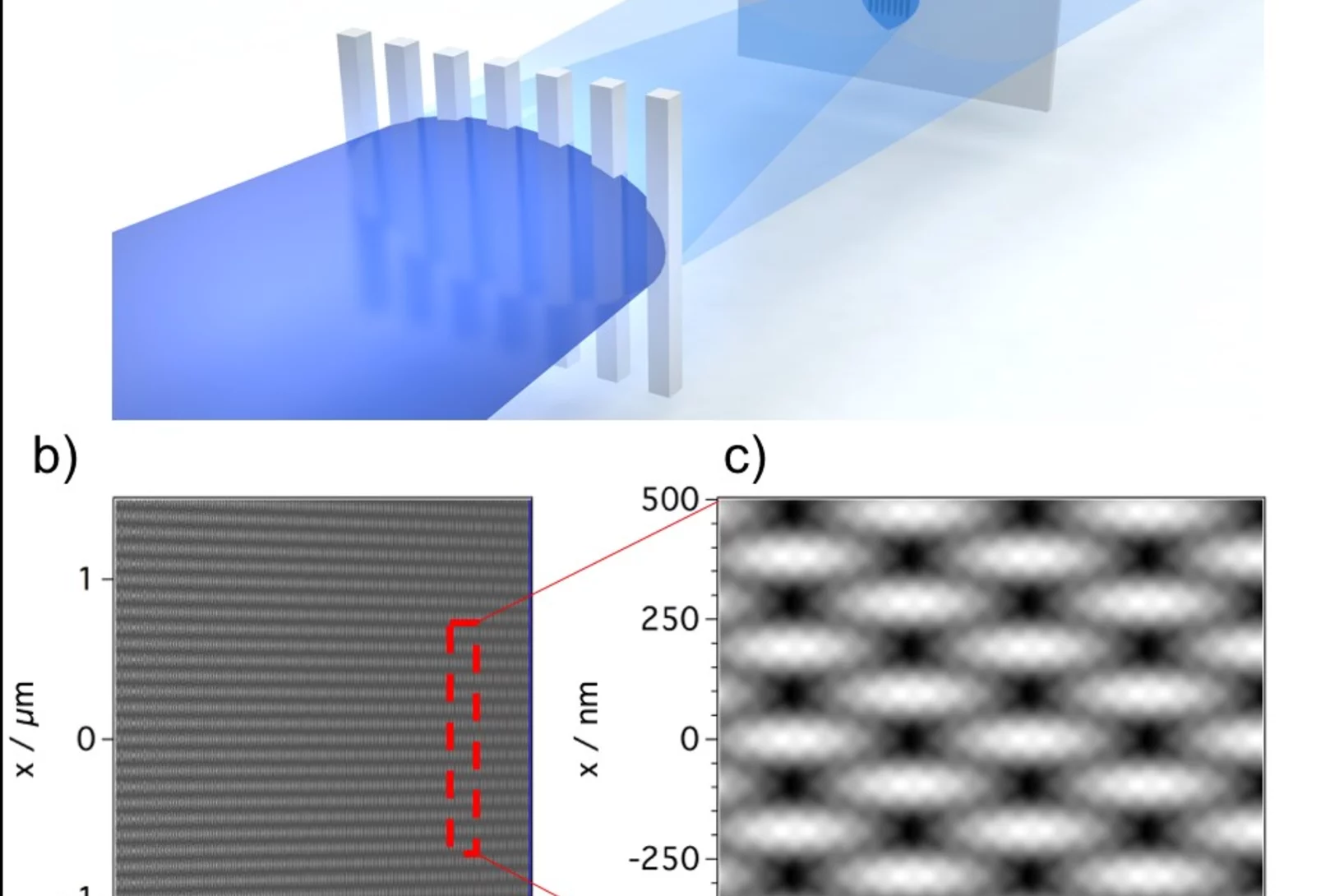
Towards X-ray Transient Grating Spectroscopy at SwissFEL
The high brilliance of new X-ray sources such as X-ray Free Electron Laser opens the way to non-linear spectroscopies. These techniques can probe ultrafast matter dynamics that would otherwise be inaccessible. One of these techniques, Transient Grating, involves the creation of a transient excitation grating by crossing X-ray beams on the sample. Scientists at PSI have realized a demonstration of such crossing by using an innovative approach well suited for the hard X-ray regime.
Watching electrons and switching bits on
Electronics should get smaller, faster, and above all more energy-efficient. These themes are also present in several research groups at PSI. From incremental improvements to complete rethinking – who is currently working on what?
Virtual lens improves X-ray microscopy
A method developed by PSI researchers makes X-ray images of materials even better. The researchers took a number of individual images while moving an optical lens. From these, with the help of computer algorithms, they generated one overall image.
Now it's time for something new
If you make electronic components smaller, they unfortunately get hotter. Also, we will soon reach the limit of technically feasible miniaturisation. At PSI, Gabriel Aeppli and Christian Rüegg are working on fundamentally new, physical solutions for better computers and data storage devices.
Dr Yasin Ekinci elected as Fellow of SPIE
Dr. Yasin Ekinci, Head of the Advanced Lithography and Metrology Group and ad interim Head of the Laboratory for Micro and Nanotechnology, has been elected to the grade of Fellow of The International Society for Optics and Photonics (SPIE).
SESAME beamline for tomography project (BEATS) is launched
On 1st January 2019, the European Horizon 2020 project BEAmline for Tomography at SESAME (BEATS) was launched with the objective to design, procure, construct and commission a beamline for hard X-ray full-field tomography at the SESAME synchrotron in Jordan. The European grant is worth 6 million euros and will span a four-year period from beginning 2019 to end 2022.
Dr Mirjam van Daalen appointed as Swiss ESFRI delegate
Dr. Mirjam van Daalen Chief of staff of the Photon Science Division, was mandated on the 1st of January 2019, by the State Secretariat for Education, Research and Innovation SERI as a member of the Swiss Delegation to the European Science Forum on Research Infrastructures ESFRI https://www.esfri.eu/.
First femtosecond protein pump-probe measurements at SwissFEL
A major milestone in the commissioning of SwissFEL has been reached: the first pump-probe experiments on proteins have been successfully carried out. Crystals of several retinal-binding proteins were delivered in a viscous jet system and a femtosecond laser was used to start the isomerization reaction. Microsecond to sub-picosecond snapshots were then collected, catching the retinal proteins shortly after isomerization of the chromophore.
2018 Innovation Award on Synchrotron Radiation
The Innovation Award on Synchrotron Radiation 2018 went to Dr. Christian David, also from the Paul Scherrer Institute, and to Prof. Alexei Erko, who recently moved from the HZB to the Institute for Applied Photonics (IAP) in Berlin-Adlershof.
EU grants 14 million to Swiss Researchers
A team with three researchers from the ETH Domain has been awarded a prestigious EU grant. Today, they received the contract signed by the EU confirming the extraordinary 14 million euros funding. With it, they will investigate quantum effects which could become the backbone of future electronics.
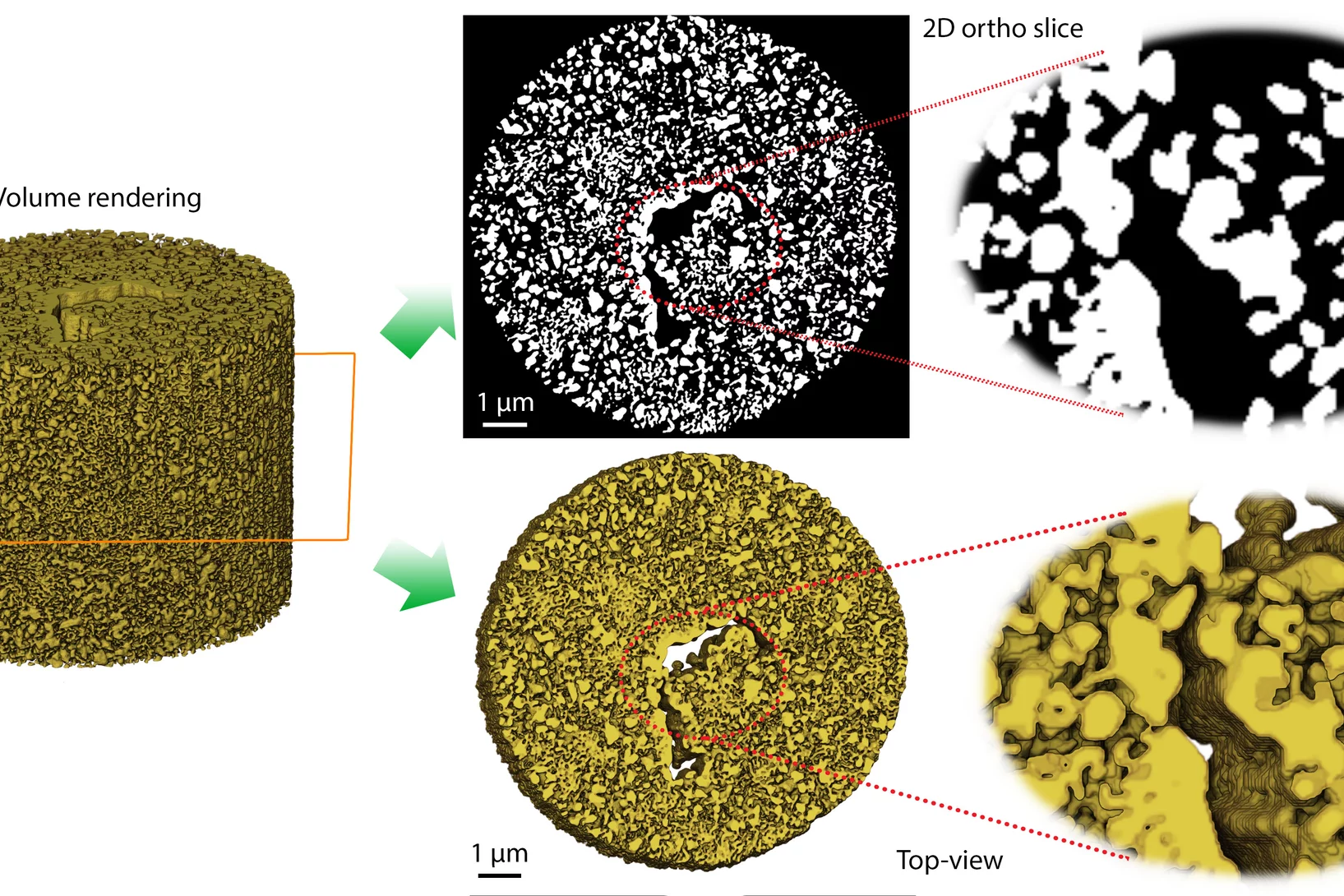
Helping chemists to understand degradation and stabilization of catalytic nanoporous gold structures
Catalytic materials are ubiquitously used in industrial processes to perform chemical reactions efficiently and in a sustainable manner. Nanoporous gold (npAu) is a monolithic sponge-like catalyst exhibiting a hierarchical structure with pores and connecting ligaments of typically 10 to 50 nm.
SwissFEL's First Call for Proposals
The first SwissFEL call for proposals took place, deadline for submission was the 15th of September. In this first call for proposals SwissFEL received overwhelming interest from the user community. A total of 47 proposals were submitted for the SwissFEL Alvra experimental station and 26 for the Bernina experimental station. The Proposal Review committee PRC took place on 18-19 October 2018.
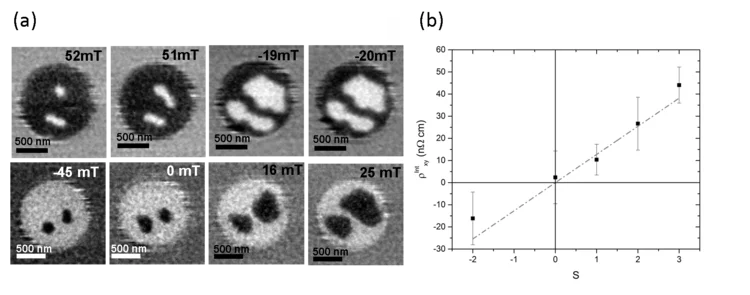
Discrete Hall contribution of magnetic skyrmions
The reliable electrical detection of magnetic skyrmions is of fundamental importance for the application of such topological magnetic quasi-particles for data storage devices. Researchers in a joint collaboration between the University of Leeds and the PolLux endstation have investigated the electrical detection of isolated magnetic skyrmions in applications-relevant nanostructured devices, observing the presence of a strong skyrmion-dependent contribution to the Hall resistivity.