Complementary Response of Static Spin-Stripe Order and Superconductivity to Nonmagnetic Impurities in Cuprates
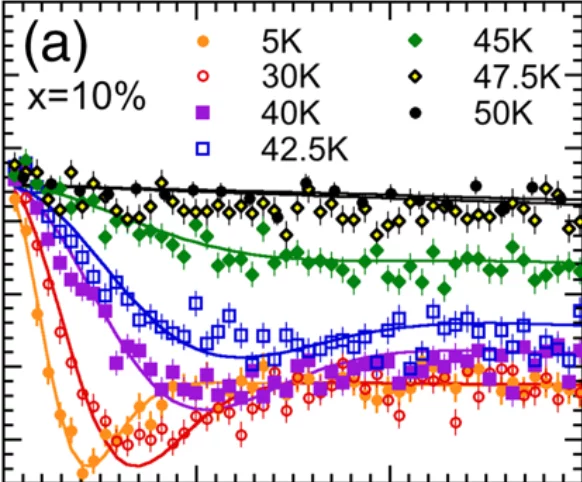
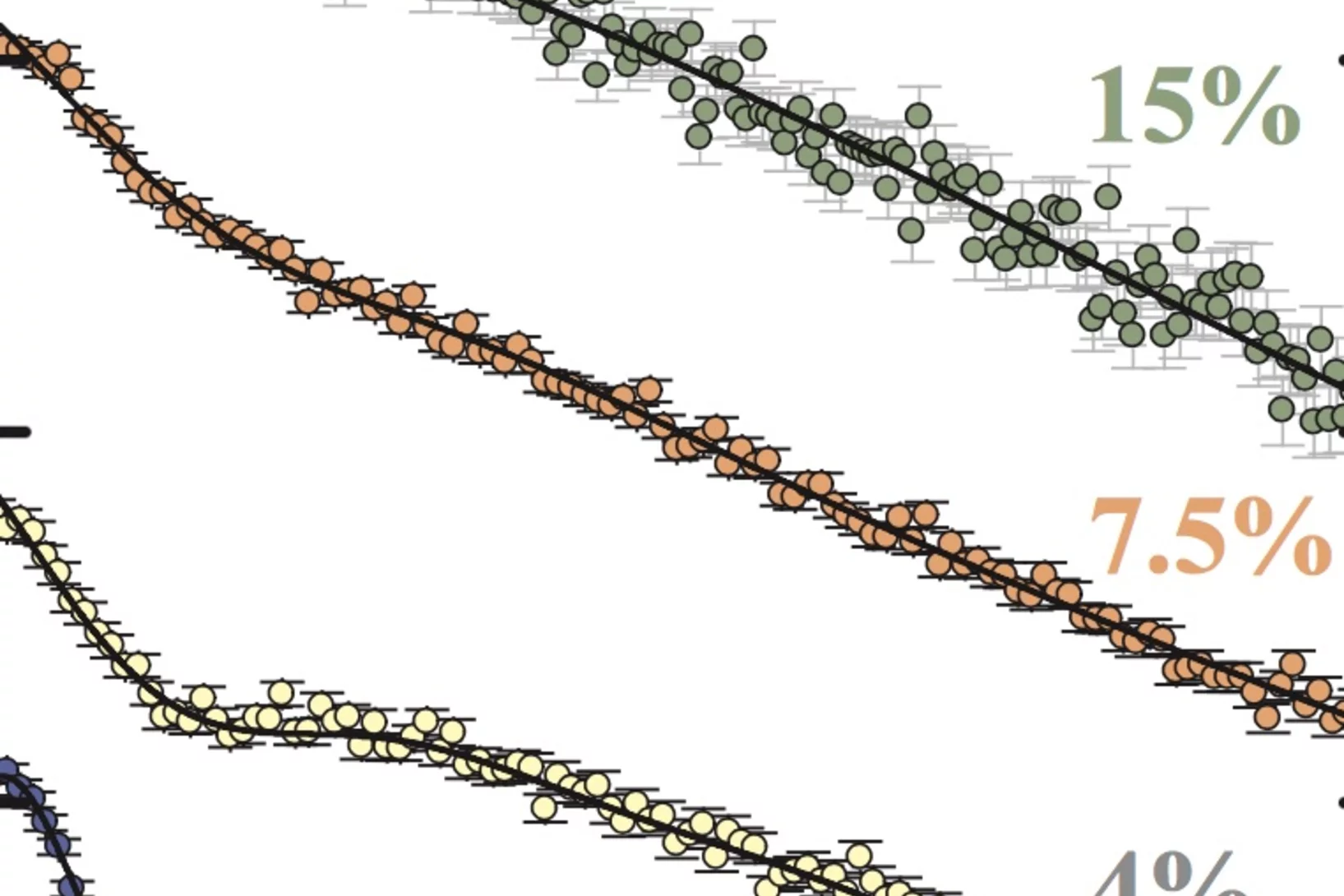
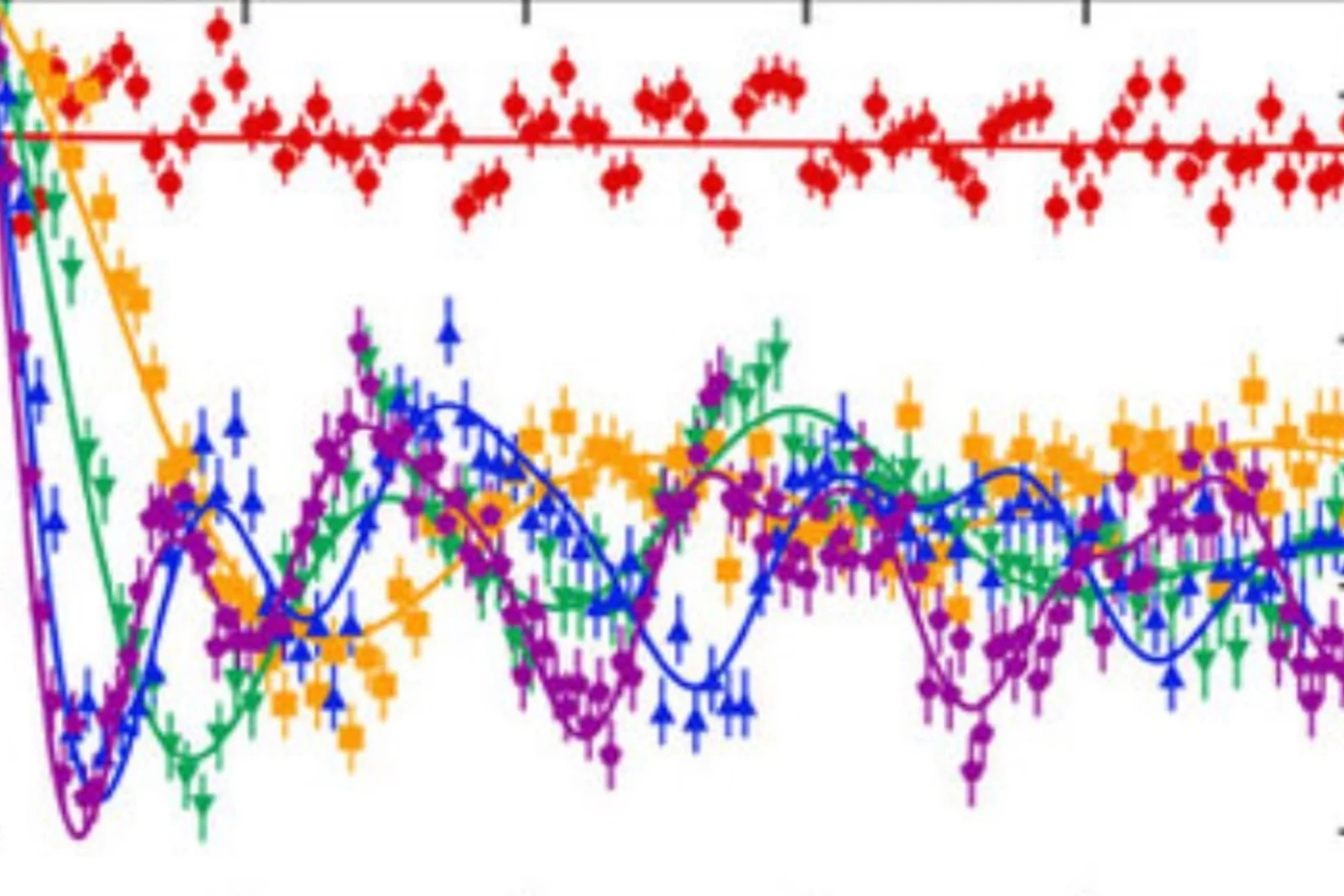
We report muon-spin rotation and neutron-scattering experiments on nonmagnetic Zn impurity effects on the static spin-stripe order and superconductivity of the La214 cuprates. Remarkably, it was found that, for samples with hole doping x ≈ 1/8, the spin-stripe ordering temperature Tso decreases linearly with Zn doping y and disappears at y ≈ 4%, demonstrating a high sensitivity of static spin-stripe order to impurities within a CuO2 plane.
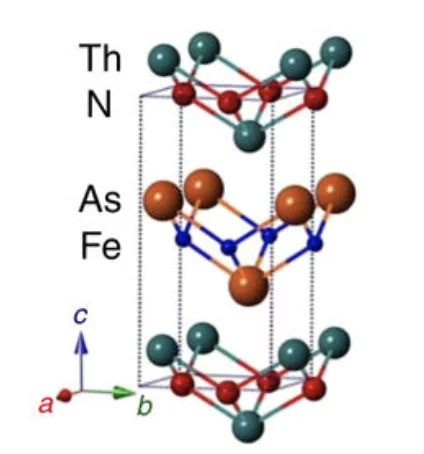
High-Tc superconductivity in undoped ThFeAsN
Unlike the widely studied ReFeAsO series, the newly discovered iron-based superconductor ThFeAsN exhibits a remarkably high critical temperature of 30 K, without chemical doping or external pressure. Here we investigate in detail its magnetic and superconducting properties via muon-spin rotation/relaxation and nuclear magnetic resonance techniques and show that ThFeAsN exhibits strong magnetic fluctuations, suppressed below ≈35 K, but no magnetic order.
Quantum Griffiths Phase Inside the Ferromagnetic Phase of Ni1-xVx
We study by means of bulk and local probes the d-metal alloy Ni1-xVx close to the quantum critical concentration, xc ≈ 11.6%, where the ferromagnetic transition temperature vanishes. The magnetization-field curve in the ferromagnetic phase takes an anomalous power-law form with a nonuniversal exponent that is strongly x dependent and mirrors the behavior in the paramagnetic phase.
Pressure-induced magnetic order in FeSe: A muon spin rotation study
The magnetic order induced by the pressure was studied in FeSe by means of muon spin rotation (μSR) technique.
Emergent magnetism at transition-metal-nanocarbon interfaces
Interfaces are critical in quantum physics, and therefore we must explore the potential for designer hybrid materials that profit from promising combinatory effects. In particular, the fine-tuning of spin polarization at metallo–organic interfaces opens a realm of possibilities, from the direct applications in molecular spintronics and thin-film magnetism to biomedical imaging or quantum computing.
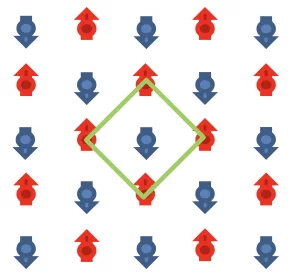
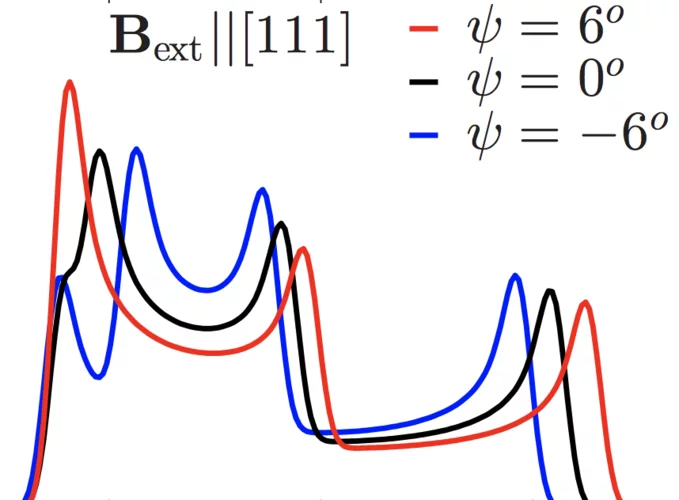
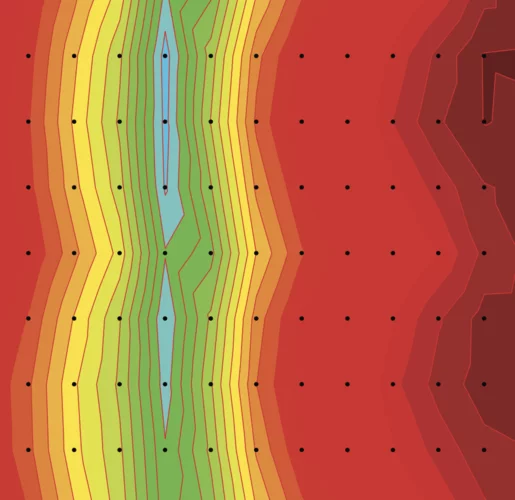
Unconventional magnetic order in the conical state of MnSi
In the temperature-magnetic field phase diagram, the binary metallic compound MnSi exhibits three magnetic phases below Tc ≈ 29K.An unconventional helicoidal phase is observed in zero field. At moderate field intensity a conical phase sets in. Near Tc, in an intermediate field range, a skyrmion lattice phase appears.
Magnetic states of MnP: muon-spin rotation studies
Muon-spin rotation data collected at ambient pressure (p) and at p = 2.42 GPa in MnP were analyzed to check their consistency with various low- and high-pressure magnetic structures reported in the literature. Our analysis con rms that in MnP the low-temperature and low-pressure helimagnetic phase is characterised by an increased value of the average magnetic moment compared to the high-temperature ferromagnetic phase.
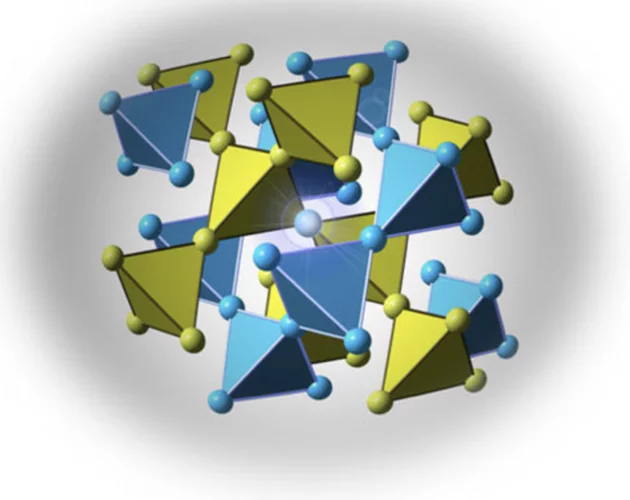
Ground state selection under pressure in the quantum pyrochlore magnet Yb2Ti2O7
A quantum spin liquid is a state of matter characterized by quantum entanglement and the absence of any broken symmetry. In condensed matter, the frustrated rare-earth pyrochlore magnets Ho2Ti2O7 and Dy2Ti2O7, so-called spin ices, exhibit a classical spin liquid state with fractionalized thermal excitations (magnetic monopoles).
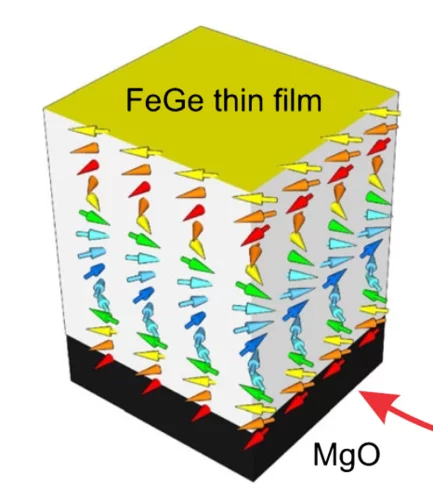
Room-temperature helimagnetism in FeGe thin films
Chiral magnets are promising materials for the realisation of high-density and low-power spintronic memory devices. For these future applications, a key requirement is the synthesis of appropriate materials in the form of thin films ordering well above room temperature. Driven by the Dzyaloshinskii-Moriya interaction, the cubic compound FeGe exhibits helimagnetism with a relatively high transition temperature of 278 K in bulk crystals.
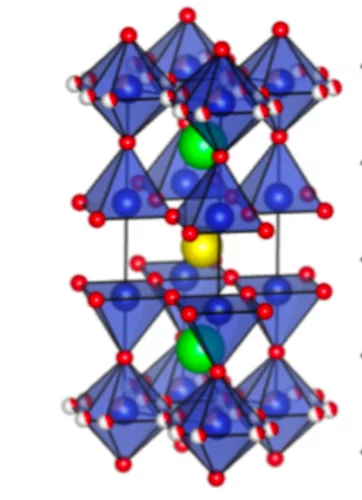
New magnetic phase in the nickelate perovskite TlNiO3
The RNiO3 perovskites are known to order antiferromagnetically below a material-dependent Néel temperature TN. We report experimental evidence indicating the existence of a second magnetically ordered phase in TlNiO3 above TN = 104K, obtained using nuclear magnetic resonance and muon spin rotation spectroscopy.
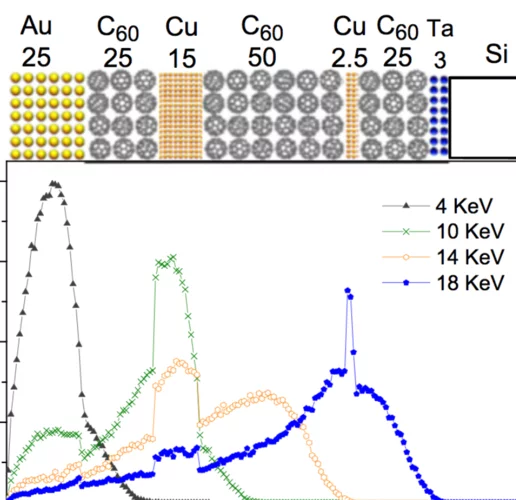
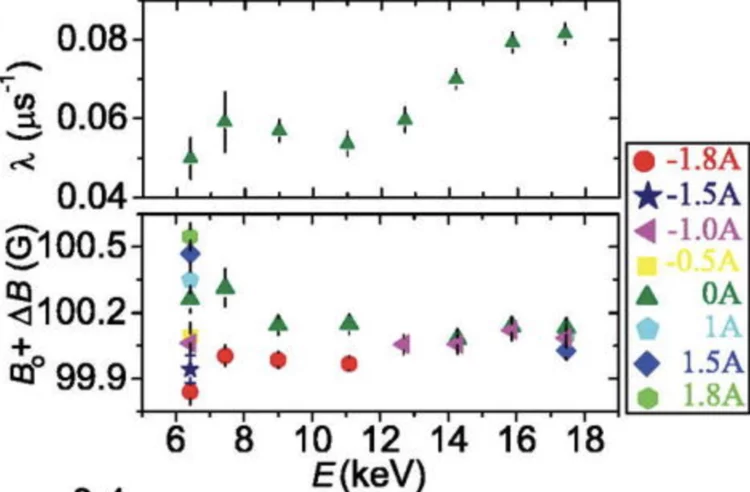
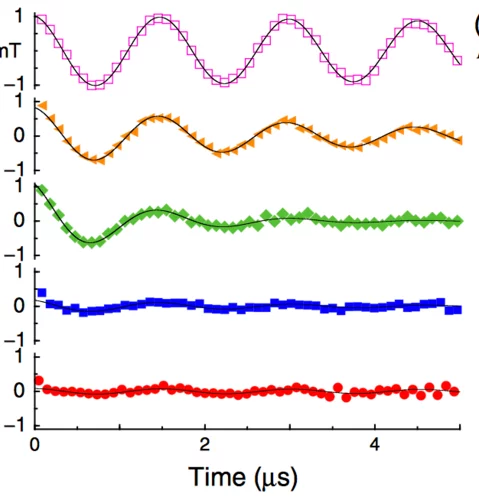
Probing current-induced magnetic fields in Au|YIG heterostructures with low-energy muon spin spectroscopy
We investigated the depth dependence of current-induced magnetic fields in a bilayer of a normal metal (Au) and a ferrimagnetic insulator (Yttrium Iron Garnet—YIG) by using low energy muon spin spectroscopy (LE-μSR). This allows us to explore how these fields vary from the Au surface down to the buried Au|YIG interface, which is relevant to study physics like the spin-Hall effect.
Suppression of magnetic excitations near the surface of the topological Kondo insulator SmB6
We present a detailed investigation of the temperature and depth dependence of the magnetic properties of the three-dimensional topological Kondo insulator SmB6, in particular, near its surface. We find that local magnetic field fluctuations detected in the bulk are suppressed rapidly with decreasing depths, disappearing almost completely at the surface.
Intrinsic Ferromagnetism in the Diluted Magnetic Semiconductor Co:TiO2
Here we present a study of magnetism in Co0.05Ti0.95O2−δ anatase films grown by pulsed laser deposition under a variety of oxygen partial pressures and deposition rates. Energy-dispersive spectrometry and transmission electron microscopy analyses indicate that a high deposition rate leads to a homogeneous microstructure, while a very low rate or postannealing results in cobalt clustering.
Bulk superconductivity at 84 K in the strongly overdoped regime of cuprates
By means of magnetization, specific heat, and muon-spin relaxation measurements, we investigate newly synthesized high-pressure oxidized Cu0.75Mo0.25Sr2YCu2O7.54, in which overdoping is achieved up to p ˜ 0.46 hole/Cu, well beyond the Tc-p superconducting dome of cuprates, where Fermi-liquid behavior is expected.
Effect of disorder on a pressure-induced z = 1 magnetic quantum phase transition
Pressure-induced ordering close to a z = 1 quantum-critical point is studied in the presence of bond disorder in the quantum spin system (C4H12N2)Cu2(Cl1−xBrx)6 (PHCX) by means of muon-spin rotation and relaxation.
Volume-wise destruction of the antiferromagnetic Mott insulating state through quantum tuning
RENiO3 (RE=rare-earth element) and V2O3 are archetypal Mott insulator systems. When tuned by chemical substitution (RENiO3) or pressure (V2O3), they exhibit a quantum phase transition (QPT) between an antiferromagnetic Mott insulating state and a paramagnetic metallic state. Because novel physics often appears near a Mott QPT, the details of this transition, such as whether it is first or second order, are important.
Physical realization of a quantum spin liquid based on a complex frustration mechanism
Unlike conventional magnets where the magnetic moments are partially or completely static in the ground state, in a quantum spin liquid they remain in collective motion down to the lowest temperatures. The importance of this state is that it is coherent and highly entangled without breaking local symmetries.
Iridates from the molecular side
New exotic phenomena have recently been discovered in oxides of paramagnetic Ir4+ ions, widely known as ‘iridates’. Their remarkable properties originate from concerted effects of the crystal field, magnetic interactions and strong spin-orbit coupling, characteristic of 5d metal ions.
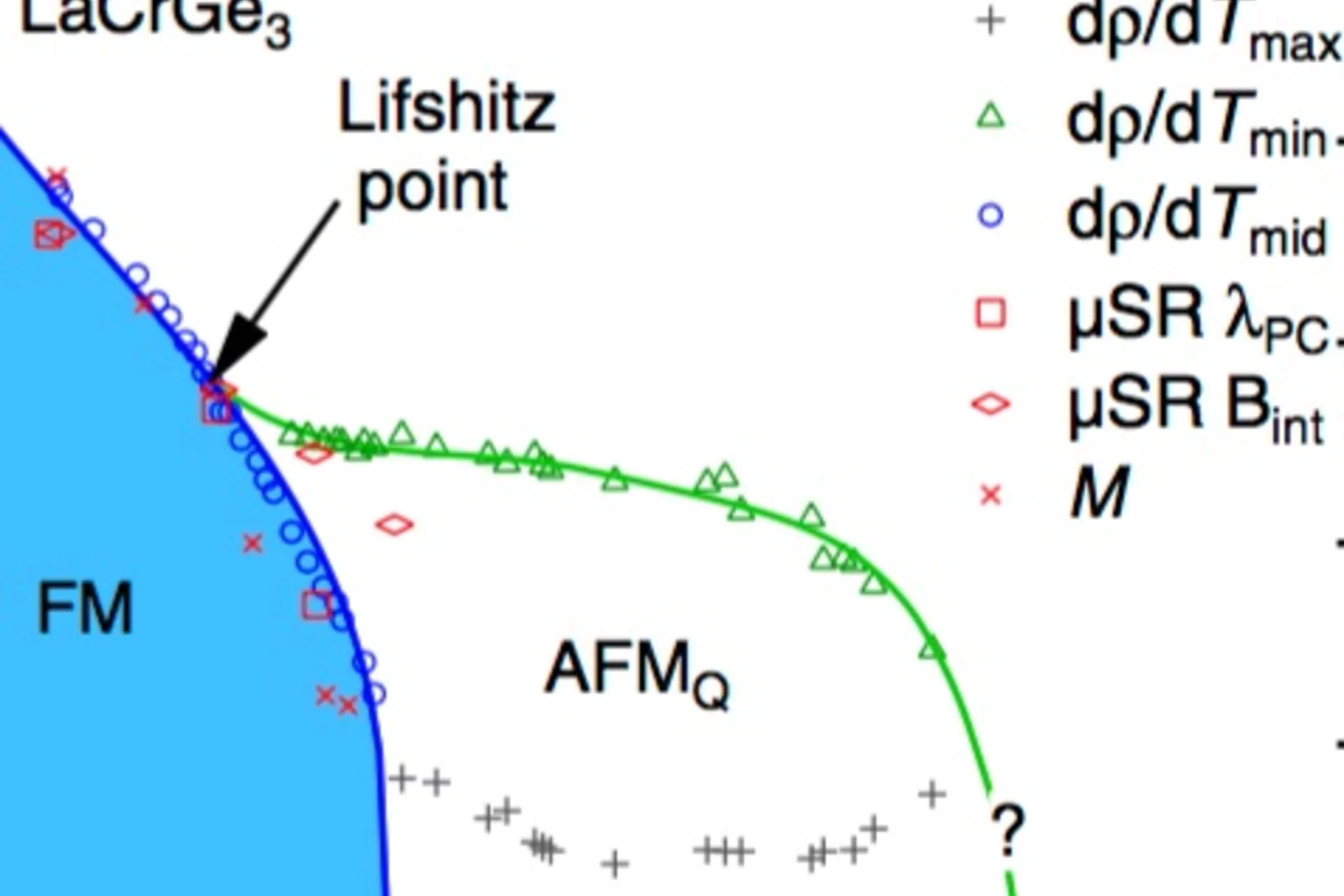
Ferromagnetic Quantum Critical Point Avoided by the Appearance of Another Magnetic Phase in LaCrGe3 under Pressure
The temperature-pressure phase diagram of the ferromagnet LaCrGe3 is determined for the first time from a combination of magnetization, muon-spin-rotation, and electrical resistivity measurements. The ferromagnetic phase is suppressed near 2.1 GPa, but quantum criticality is avoided by the appearance of a magnetic phase, likely modulated, AFMQ.
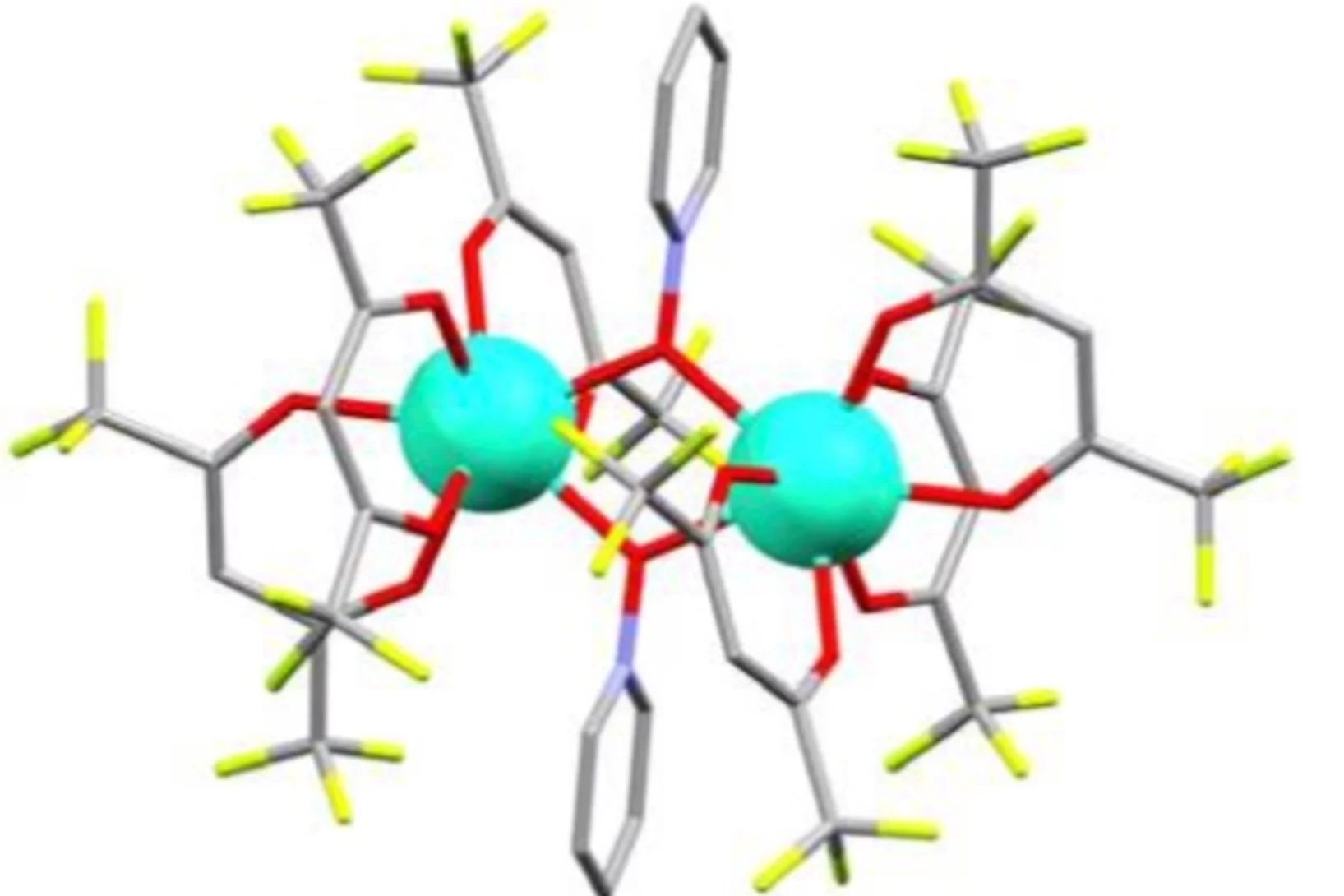
Robust Magnetic Properties of a Sublimable Single Molecule Magnet
The organization of single-molecule magnets (SMMs) on surfaces via thermal sublimation is a prerequisite for the development of future devices for spintronics exploiting the richness of properties offered by these magnetic molecules. However, a change in the SMM properties due to the interaction with specific surfaces is usually observed.
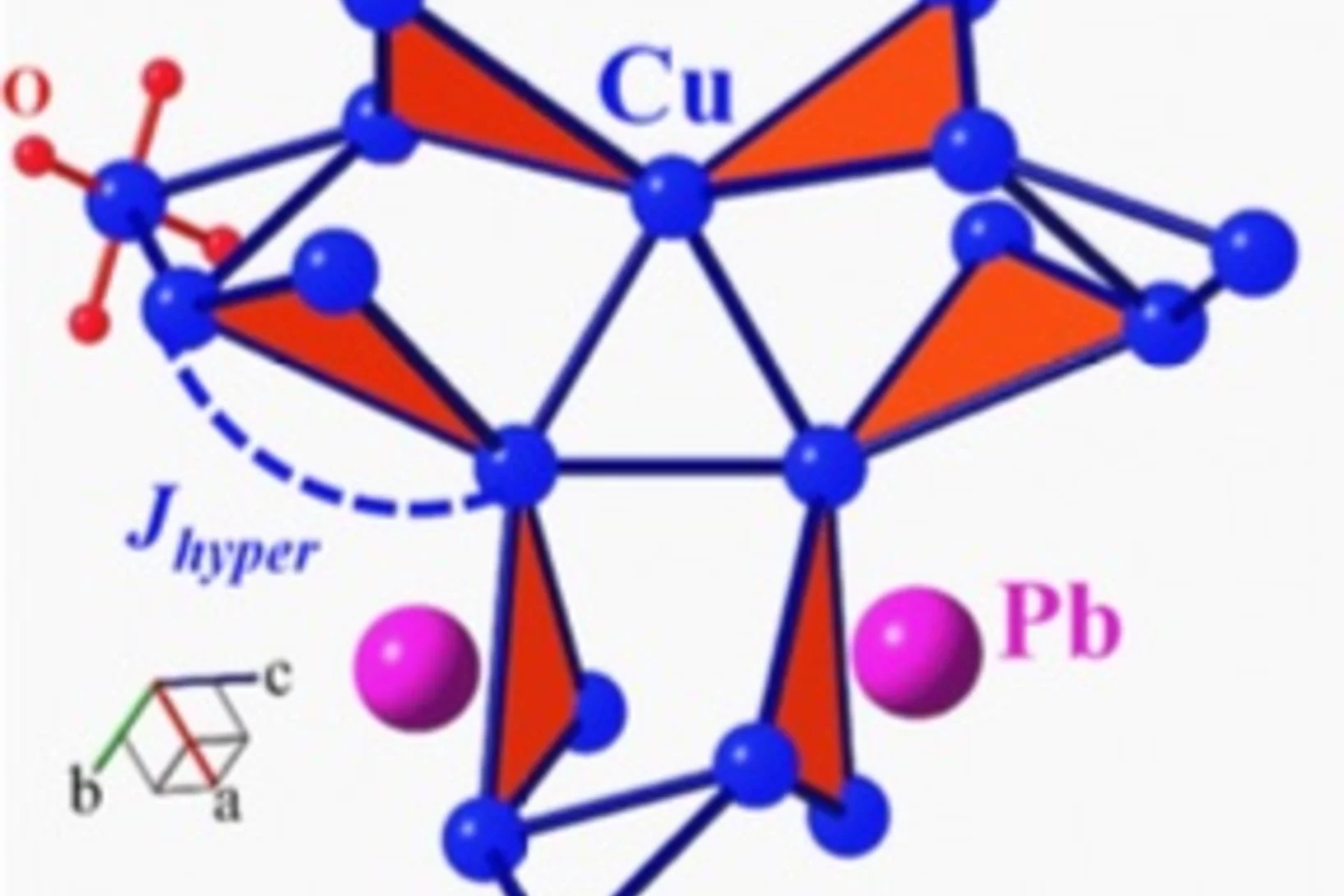
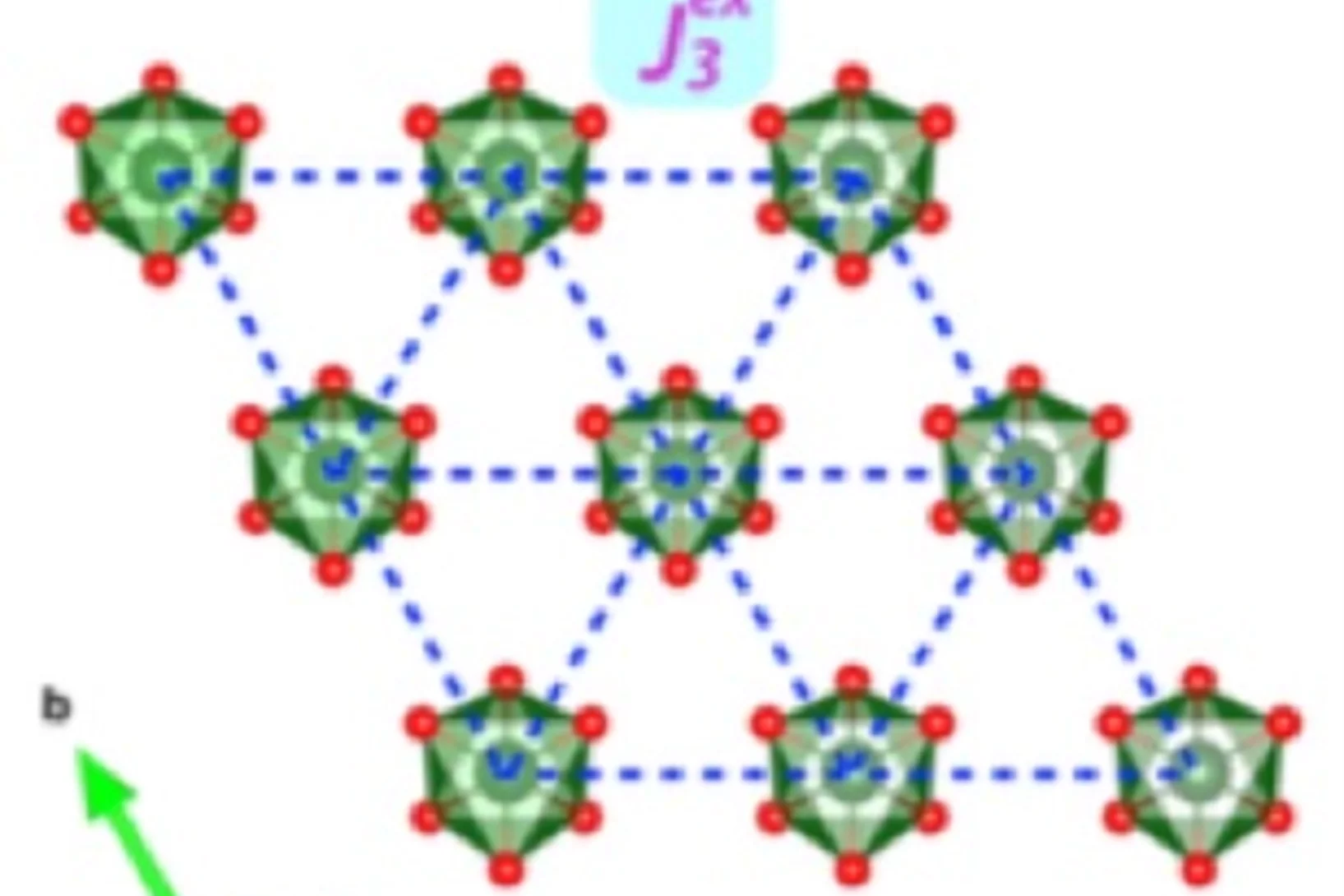
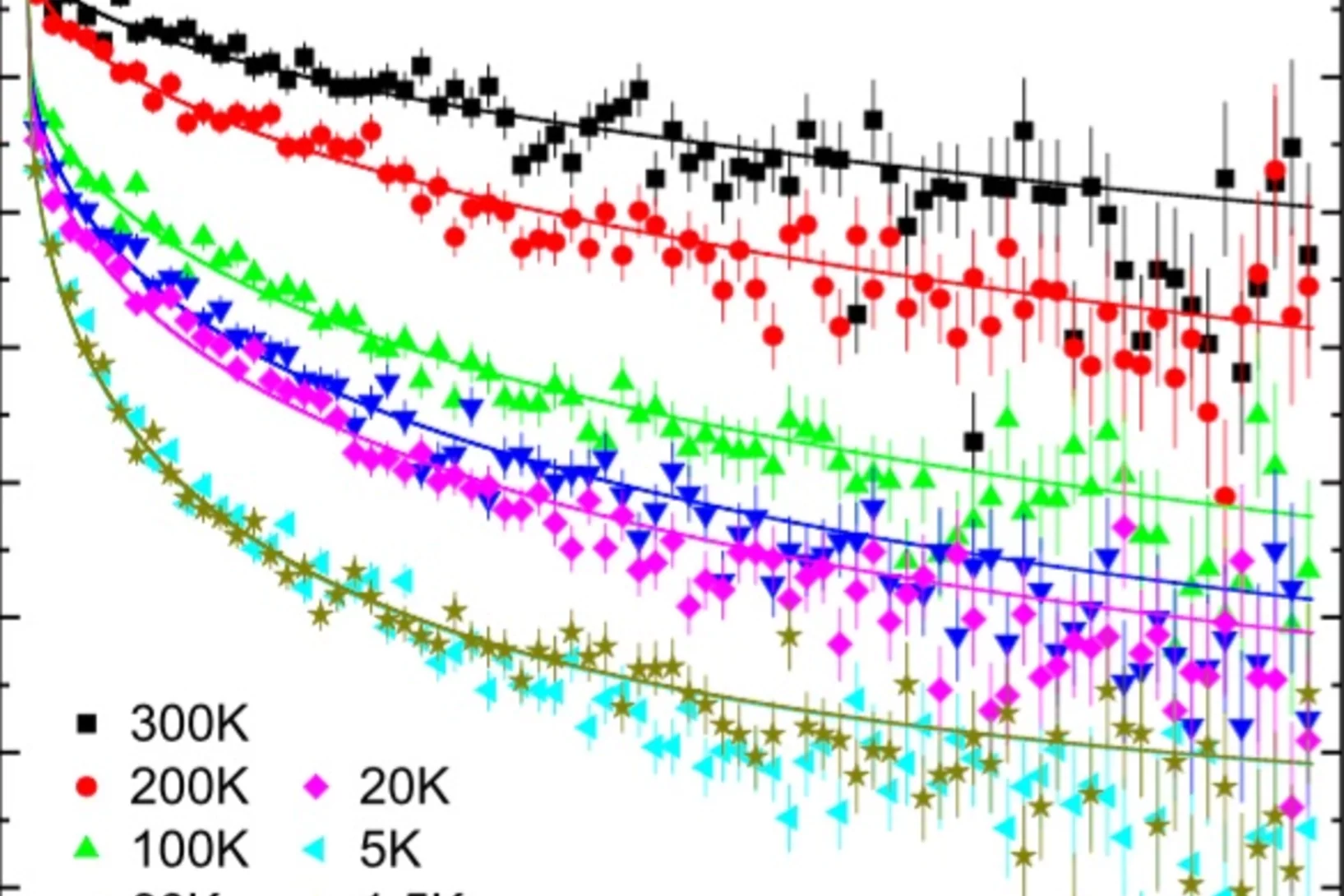
Spin Liquid State in the 3D Frustrated Antiferromagnet PbCuTe2O6: NMR and Muon Spin Relaxation Studies
PbCuTe2O6 is a rare example of a spin liquid candidate featuring a three-dimensional magnetic lattice. Strong geometric frustration arises from the dominant antiferromagnetic interaction that generates a hyperkagome network of Cu2+ ions although additional interactions enhance the magnetic lattice connectivity.
Origin of the Spin-Orbital Liquid State in a Nearly J=0 Iridate Ba3ZnIr2O9
We show using detailed magnetic and thermodynamic studies and theoretical calculations that the ground state of Ba3ZnIr2O9 is a realization of a novel spin-orbital liquid state. Our results reveal that Ba3ZnIr2O9 with Ir5+ (5d4) ions and strong spin-orbit coupling (SOC) arrives very close to the elusive J 1⁄4 0 state but each Ir ion still possesses a weak moment.
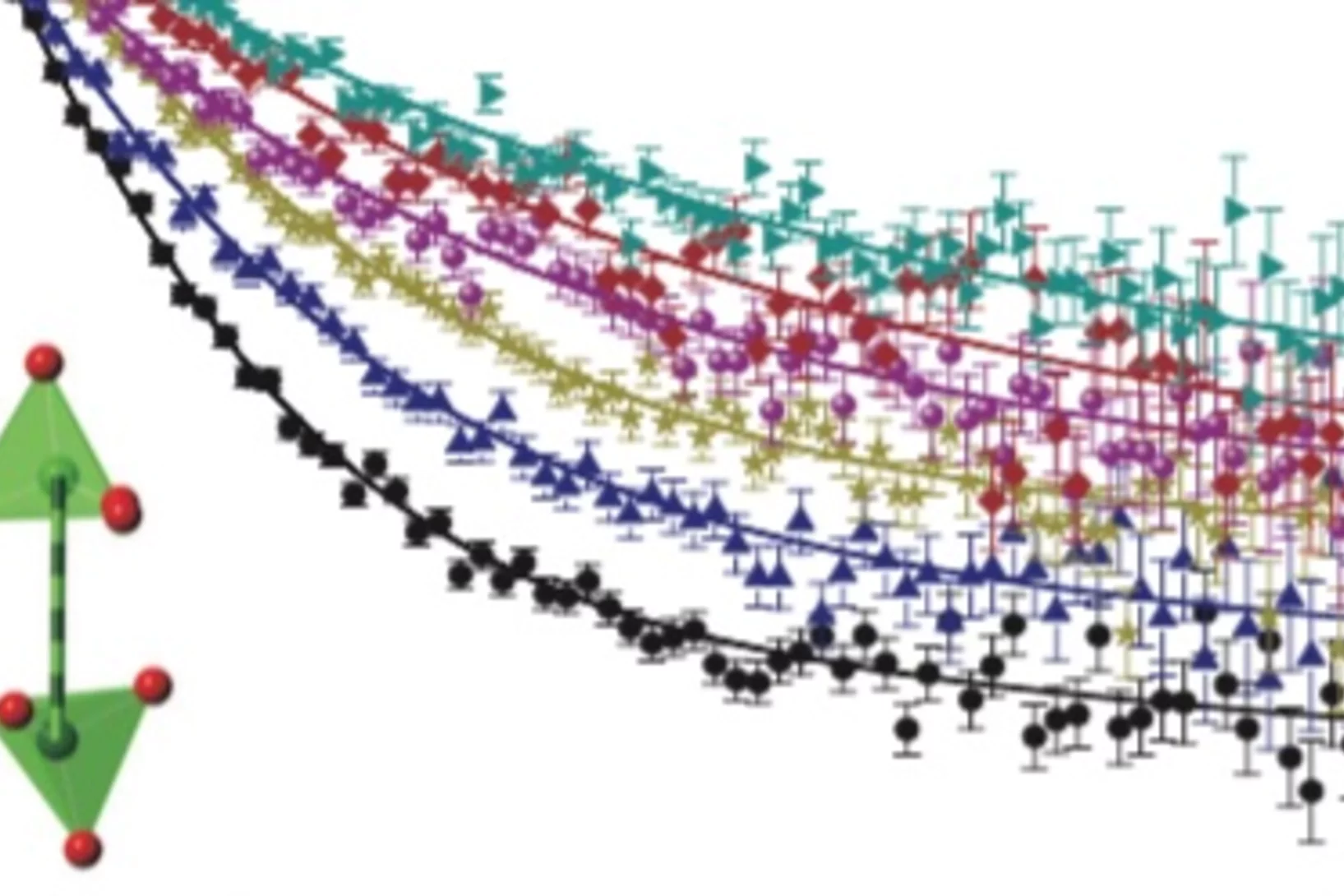
Coexistence of low-moment magnetism and superconductivity in tetragonal FeS and suppression of Tc under pressure
The family of iron-based superconductors has recently acquired a new member material, FeS. Theoretically, this compound has been shown to have electronic structure similar to that of the superconducting FeSe. However, contradictory ground states have been predicted for FeS. In this work, a collaboration of authors from Switzerland and Germany use muon spin rotation and relaxation to show that weak-moment magnetism microscopically coexists with bulk superconductivity.
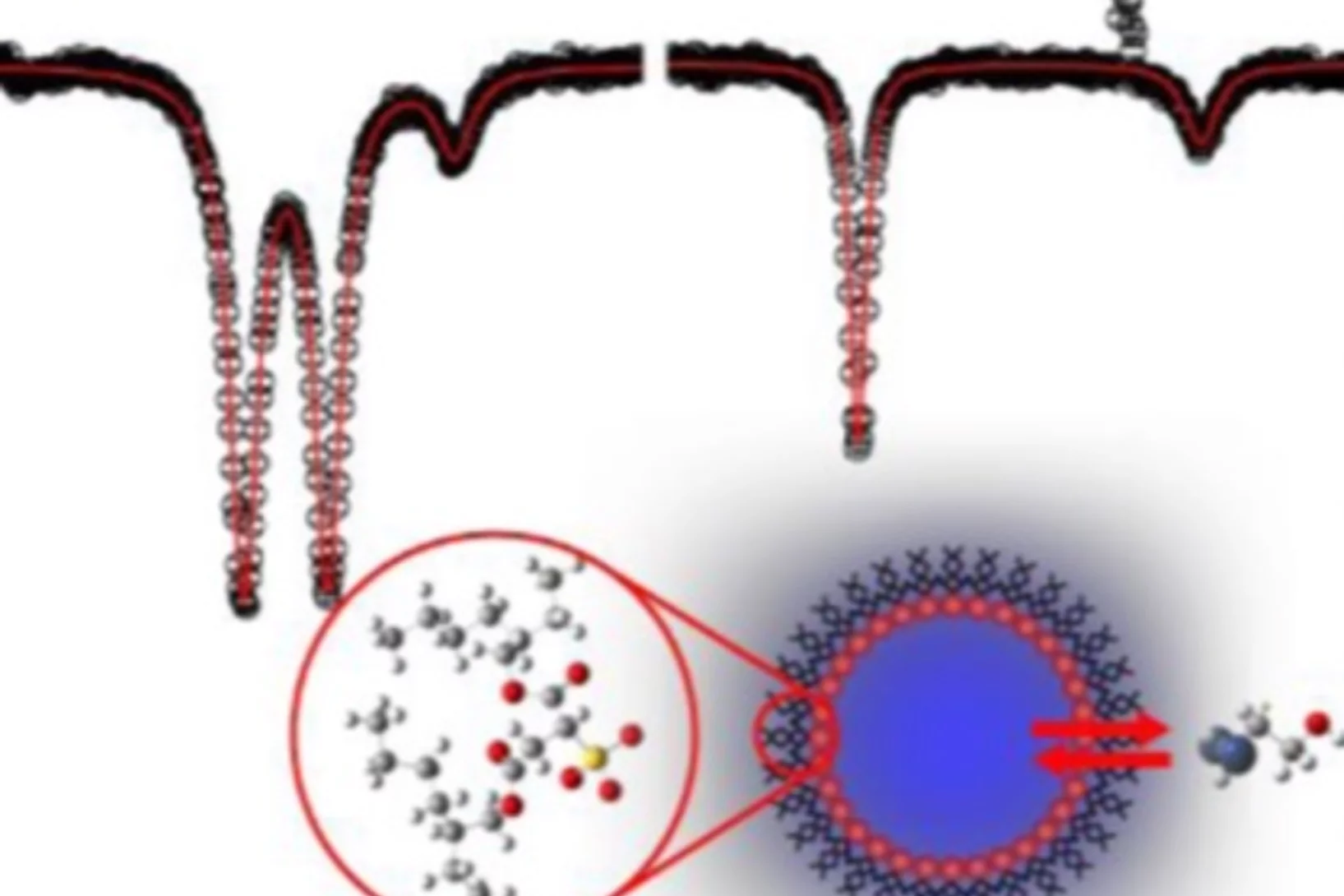
Rate of Molecular Transfer of Allyl Alcohol across an AOT Surfactant Layer Using Muon Spin Spectroscopy
The transfer rate of a probe molecule across the interfacial layer of a water-in-oil (w/o) microemulsion was investigated using a combination of transverse field muon spin rotation (TF-μSR), avoided level crossing muon spin resonance (ALC-μSR), and Monte Carlo simulations. Reverse micro-emulsions consist of nanometer-sized water droplets dispersed in an apolar solvent separated by a surfactant monolayer.
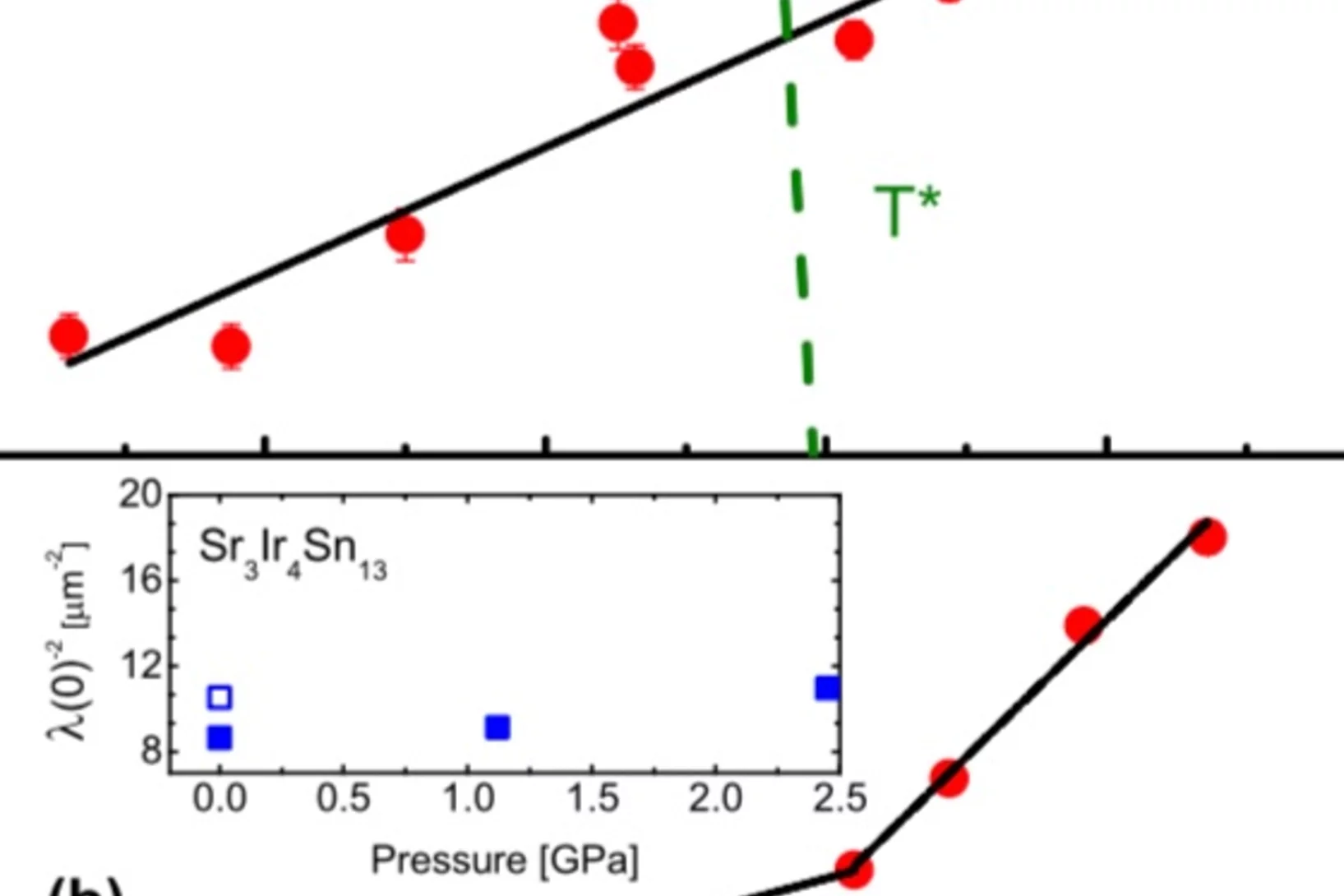
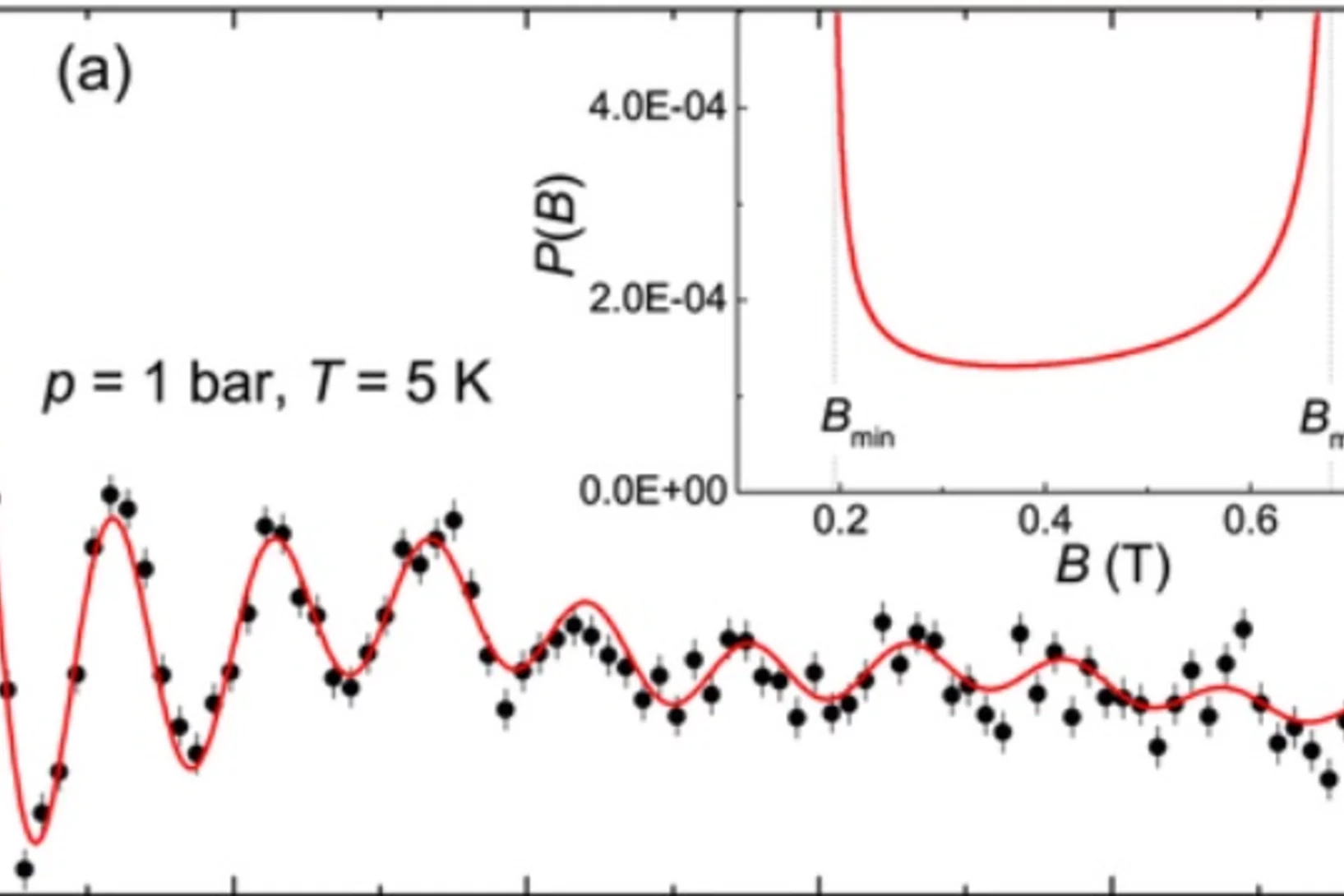
Strong enhancement of s-wave superconductivity near a quantum critical point of Ca3Ir4Sn13
We report microscopic studies by muon spin rotation/relaxation as a function of pressure of the Ca3Ir4Sn13 and Sr3Ir4Sn13 cubic compounds, which are members of the (Ca1−xSrx)3Ir4Sn13 system displaying superconductivity and a structural phase transition associated with the formation of a charge density wave (CDW).
Direct evidence for a pressure-induced nodal superconducting gap in the Ba0.65Rb0.35Fe2As2 superconductor
The superconducting gap structure in iron-based high-temperature superconductors (Fe-HTSs) is non-universal. In contrast to other unconventional superconductors, in the Fe-HTSs both d-wave and extended s-wave pairing symmetries are close in energy. Probing the proximity between these very different superconducting states and identifying experi- mental parameters that can tune them is of central interest.
Intrinsic Paramagnetic Meissner Effect Due to s-Wave Odd-Frequency Superconductivity
In 1933, Meissner and Ochsenfeld reported the expulsion of magnetic flux - the diamagnetic Meissner effect - from the interior of superconducting lead. This discovery was crucial in formulating the Bardeen-Cooper-Schrieffer (BCS) theory of superconductivity. In exotic superconducting systems BCS theory does not strictly apply.
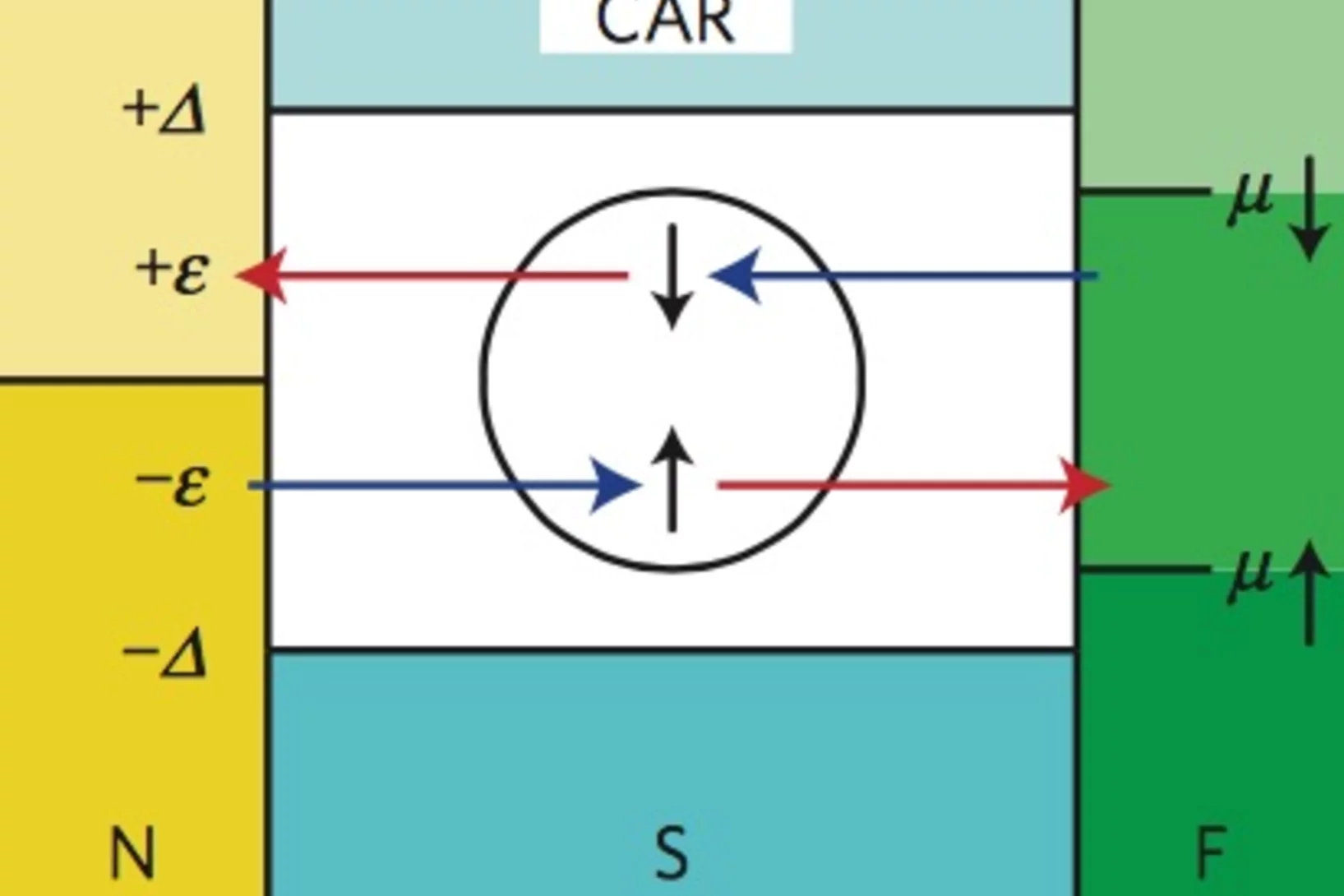
Remotely induced magnetism in a normal metal using a superconducting spin-valve
Superconducting spintronics has emerged in the past decade as a promising new field that seeks to open a new dimension for nanoelectronics by utilizing the internal spin structure of the superconducting Cooper pair as a new degree of freedom. Its basic building blocks are spin-triplet Cooper pairs with equally aligned spins, which are promoted by proximity of a conventional superconductor to a ferromagnetic material with inhomogeneous macroscopic magnetization.
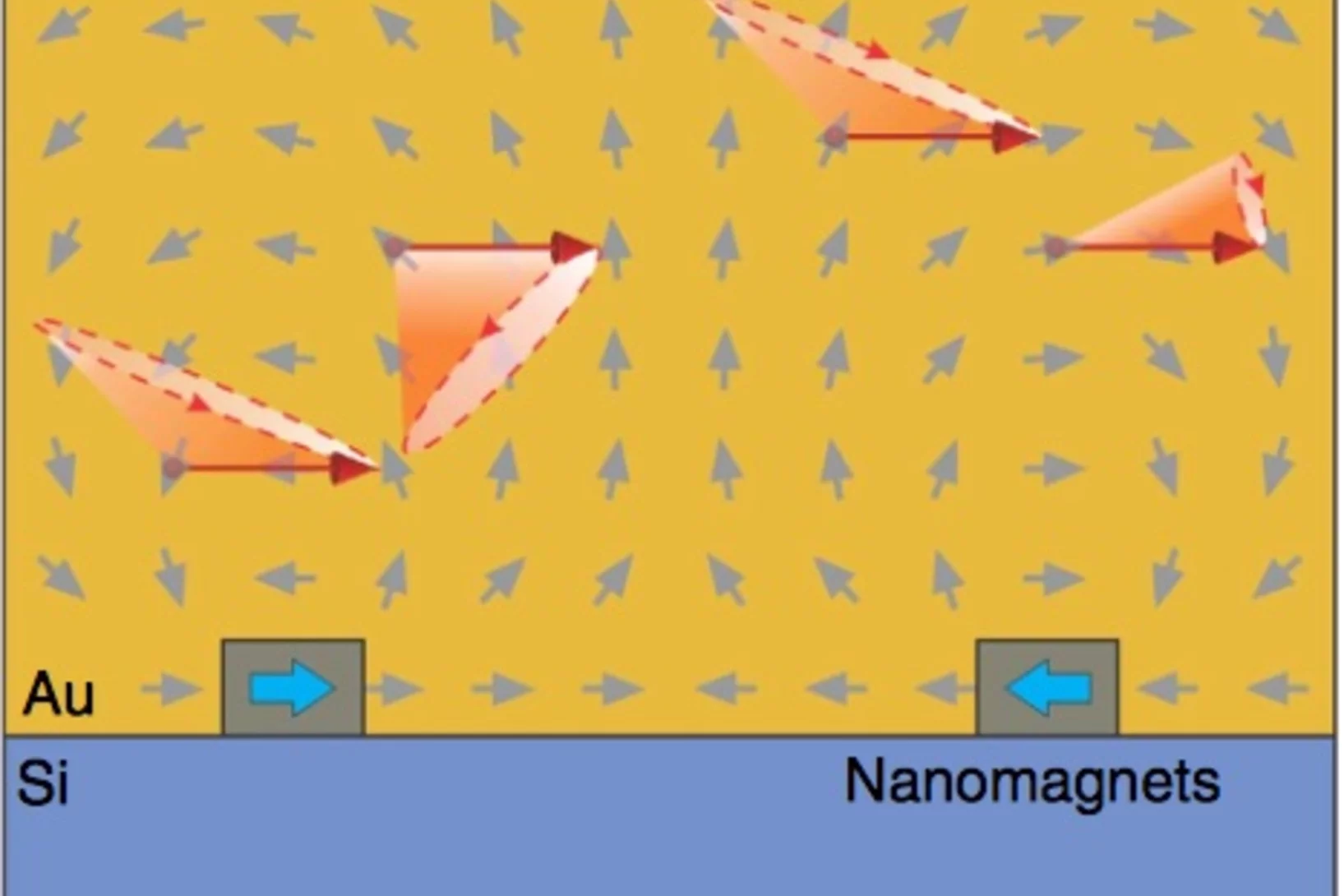
Thermodynamic phase transitions in a frustrated magnetic metamaterial
Materials with interacting magnetic degrees of freedom display a rich variety of magnetic behaviour that can lead to novel collective equilibrium and out-of-equilibrium phenomena. In equilibrium, thermodynamic phases appear with the associated phase transitions providing a characteristic signature of the underlying collective behaviour.
Pressure-induced electronic phase separation of magnetism and superconductivity in CrAs
The recent discovery of pressure (p) induced superconductivity in the binary helimagnet CrAs has raised questions on how superconductivity emerges from the magnetic state and on the mechanism of the superconducting pairing. In the present work the suppression of magnetism and the occurrence of superconductivity in CrAs were studied by means of muon spin rotation.