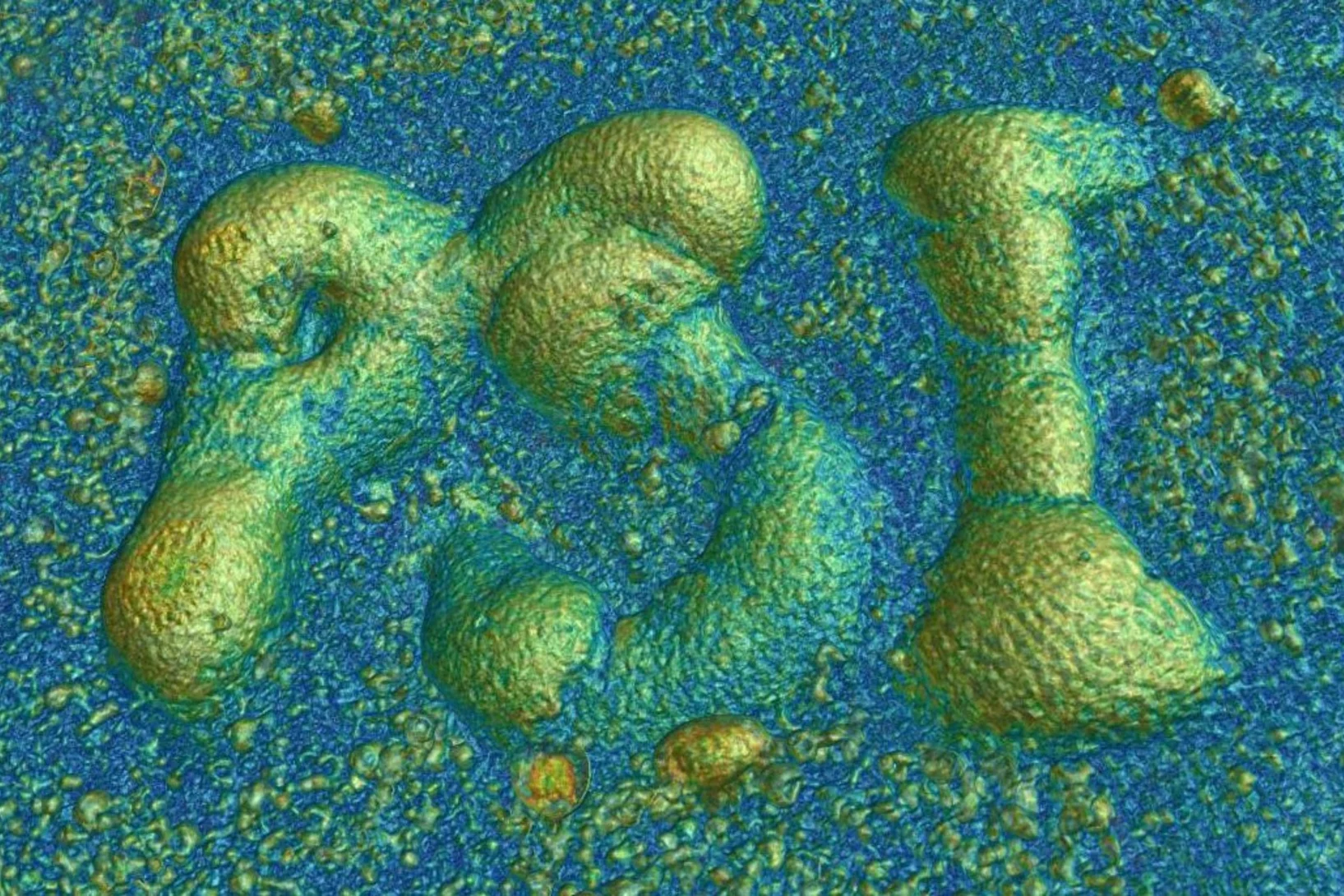
Skyrmion topology quantified in 3D
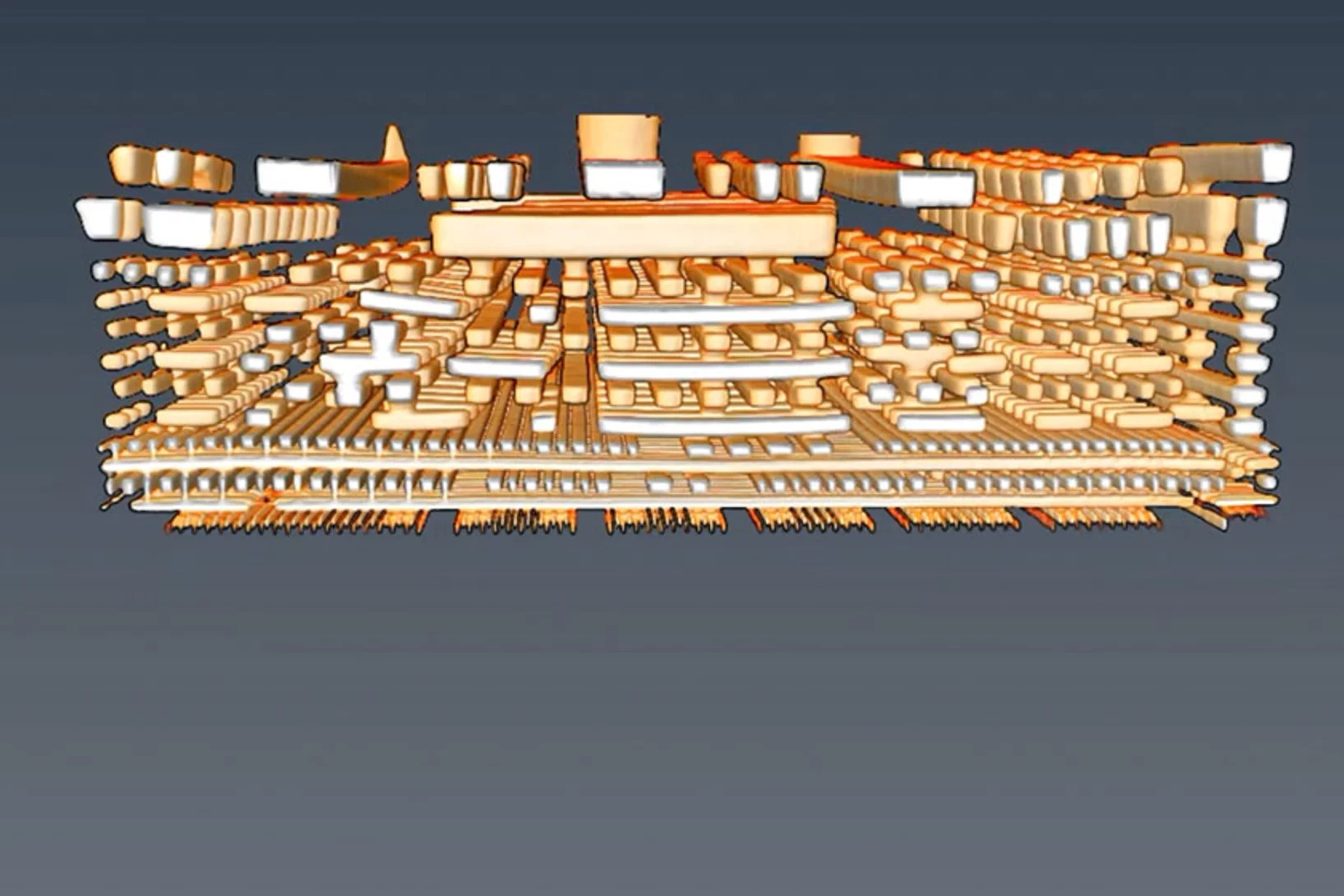
Researchers from an international collaboration between the United States of America and Switzerland have performed three-dimensional magnetic imaging of a magnetic skyrmion using soft X-ray laminography. This allowed for the investigation, in three dimensions, of the topological profile of the magnetic skyrmions.
Unlocking the secrets of proteins
This year’s Nobel Prize in Chemistry goes to three researchers who have made a decisive contribution to cracking the code of proteins – important building blocks of life. However, developing applications from this knowledge, for example in medicine, requires research institutes such as PSI.
New Monochromators for SLS 2.0
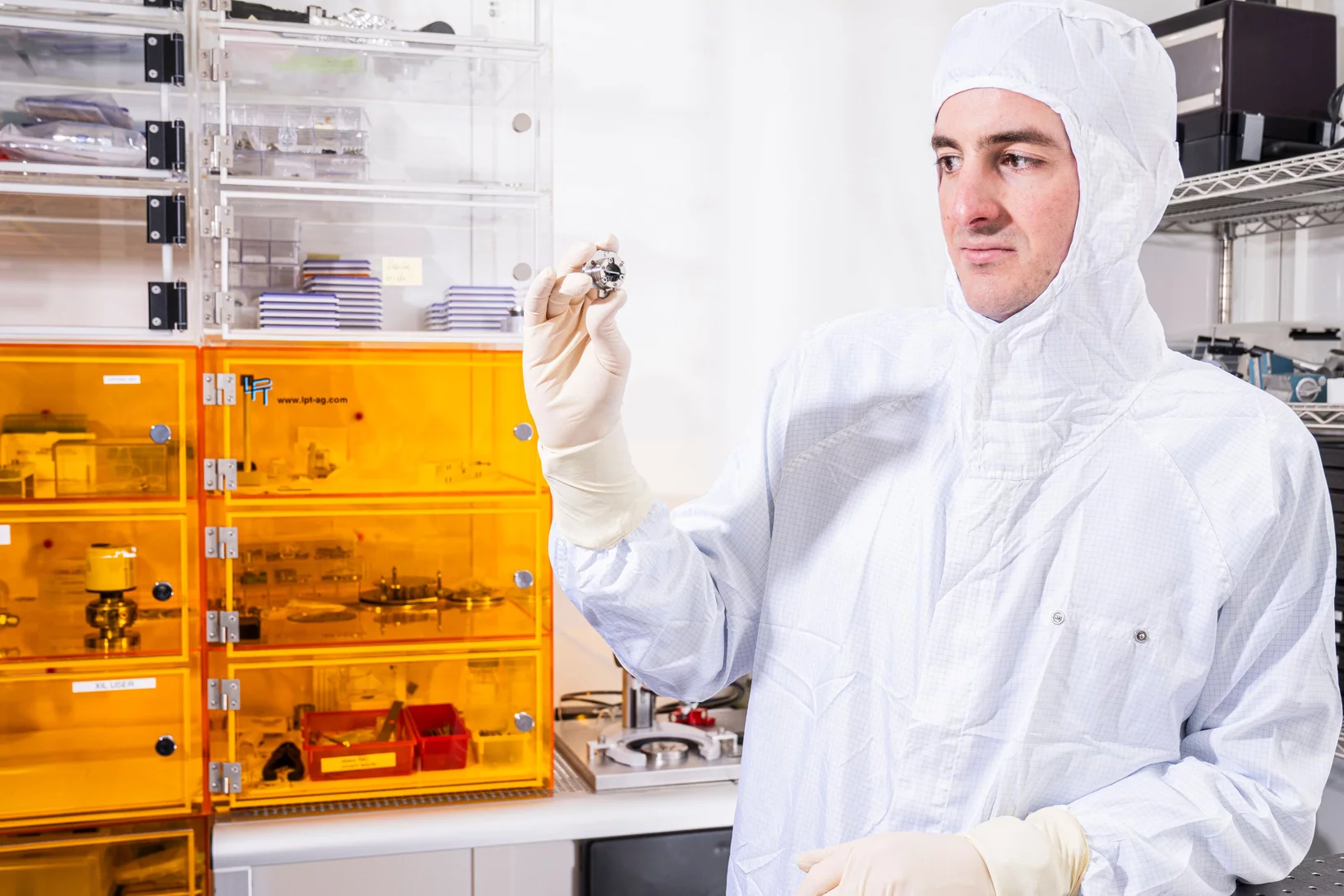
The brand-new monochromators that have been built by XDS Oxford for the hard X-ray beamlines at SLS 2.0 have now arrived. They were unpacked beginning of the week, and are currently being tested in our new lab space at Park Innovaare. These advanced instruments will play a crucial role in enhancing the beamline performance, ensuring superior precision and efficiency in the upcoming experiments.
Elusive multiferroicity in RNiO3 perovskites
In our recent paper we examined YNiO3 and proved that the RNiO3 type material known for its metal-insulator transition is in fact a type II multiferroic. We provide direct evidence of an electric-field-driven switch of the noncolliear magnetic state finally confirming the proposed type II multiferroic nature of YNiO3.
Researchers show that computer chips have the potential to become even smaller
Researchers at PSI reach unprecedented 5 nanometres half pitch resolution with EUV lithography.
New X-ray world record: Looking inside a microchip with 4 nanometre precision
Researchers at PSI have succeeded in imaging the spatial structure of a computer chip with a record resolution of 4 nanometres using X-rays.
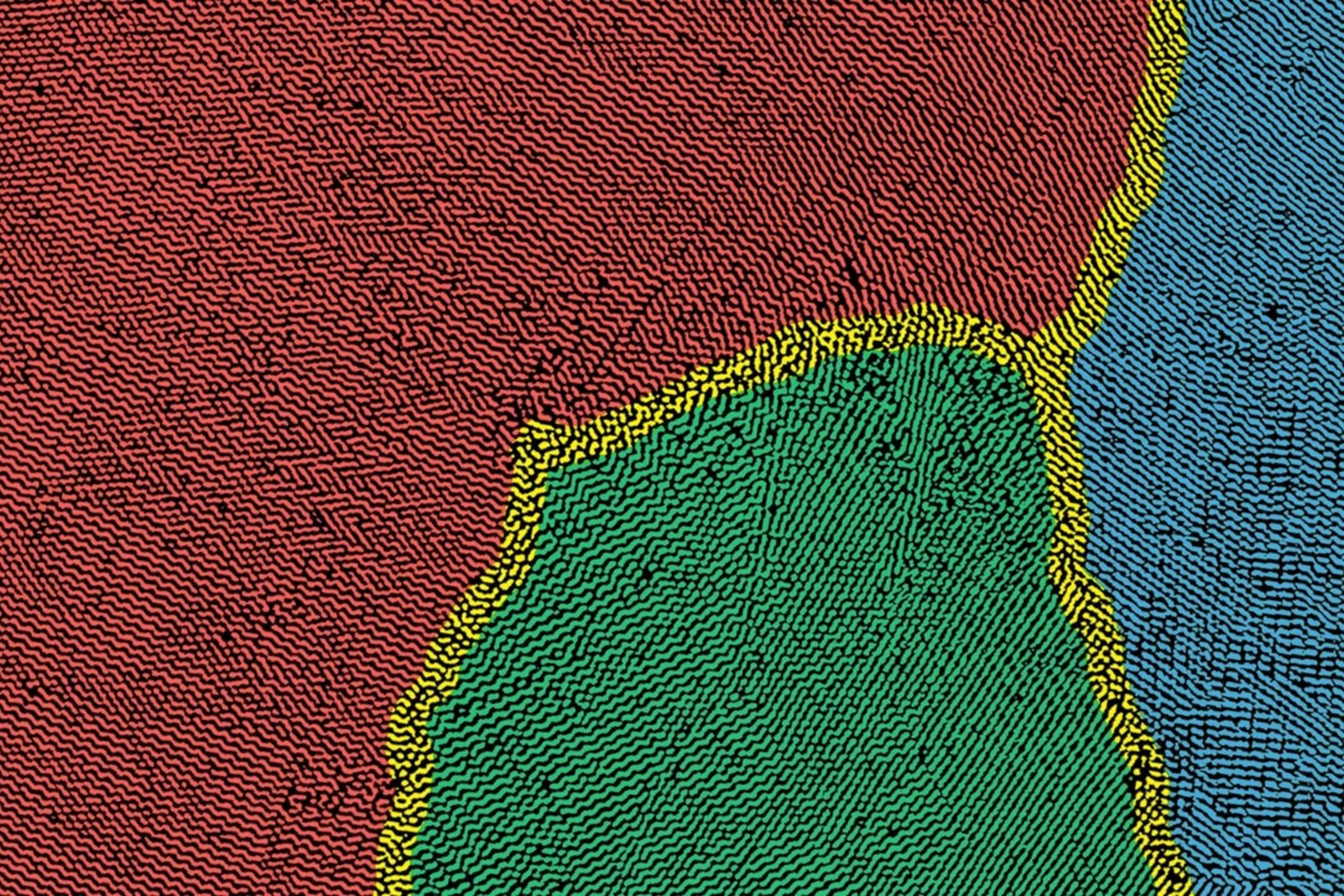
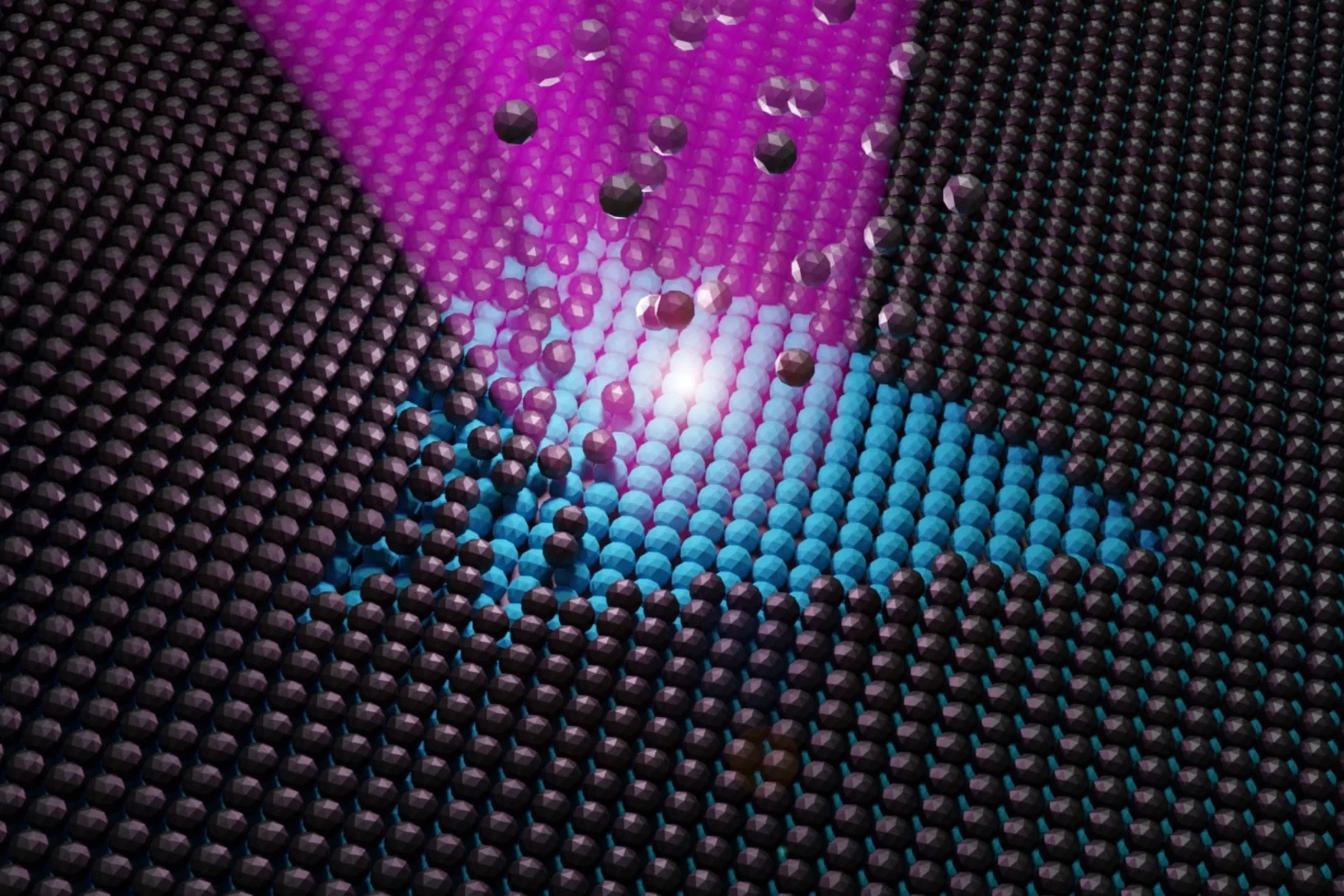
Nanoimaging Reveals Topological Textures in Nanoscale Crystalline Networks
X-ray nano-tomography reveals collective behavior in synthetic self-assembled nanostructures. The new method opens opportunities for the synthesis of photonic and plasmonic materials with improved long-range ordering.
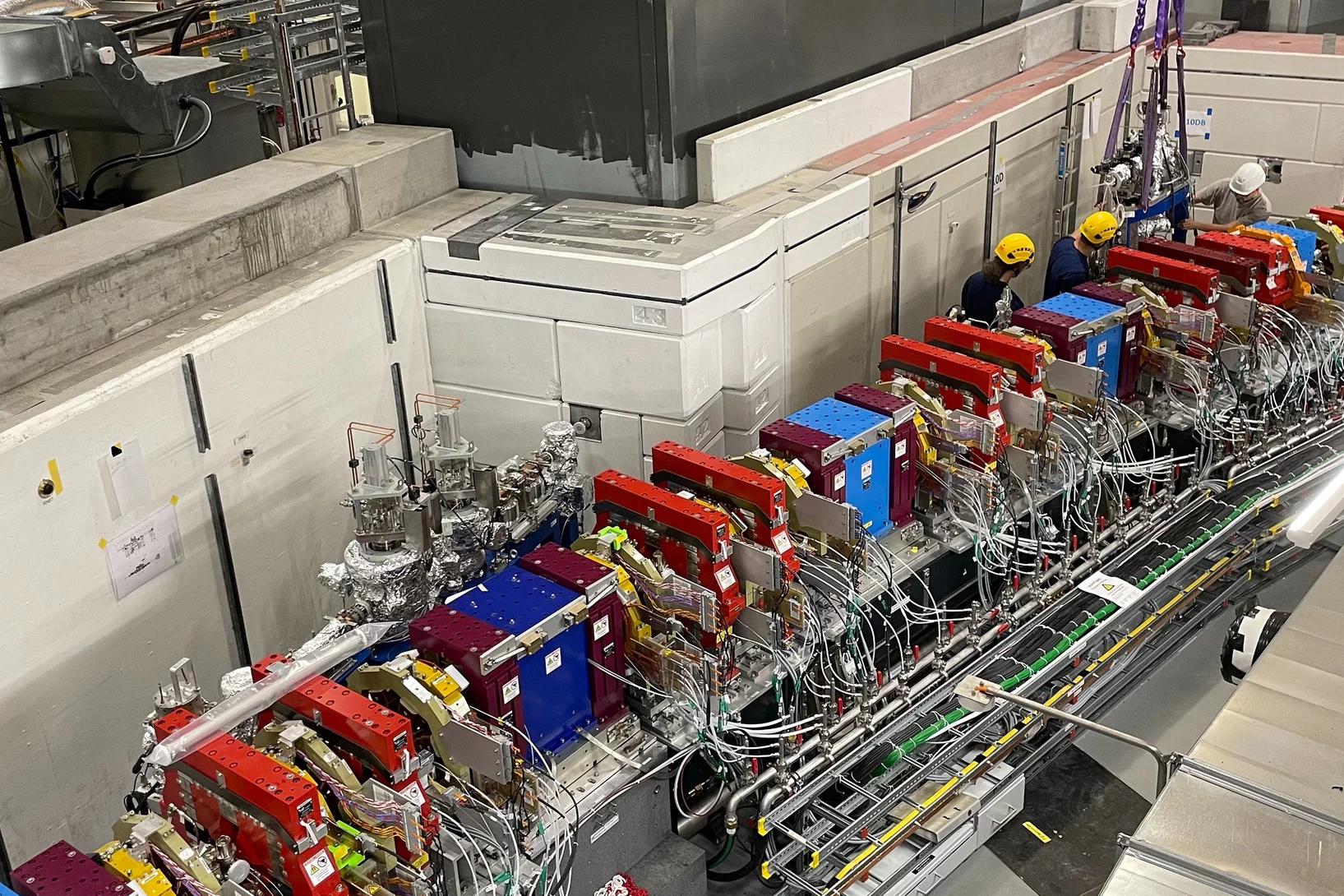
Installation of the first two front ends for the SLS2.0 completed
At the Swiss Light Source SLS of the Paul Scherrer Institute, another important step has been taken towards the completion of the SLS 2.0 upgrade project.
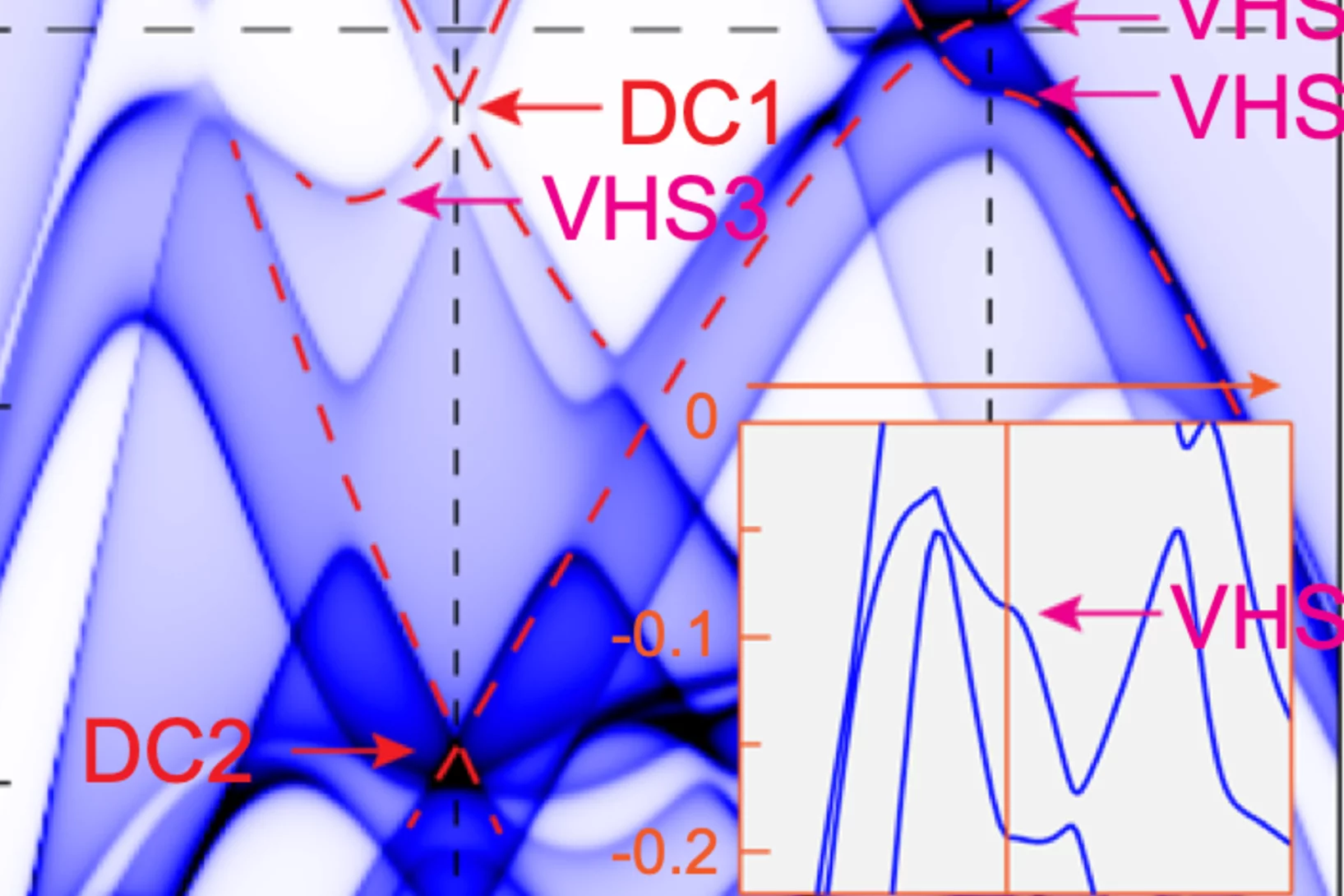
Phonon promoted charge density wave in topological kagome metal ScV6Sn6
Charge density wave (CDW) orders in vanadium-based kagome metals have recently received tremendous attention, yet their origin remains a topic of debate. The discovery of ScV6Sn6, a bilayer kagome metal featuring an intriguing √3 × √3 × √3 CDW order, offers a novel platform to explore the underlying mechanism behind the unconventional CDW. Here we combine ...
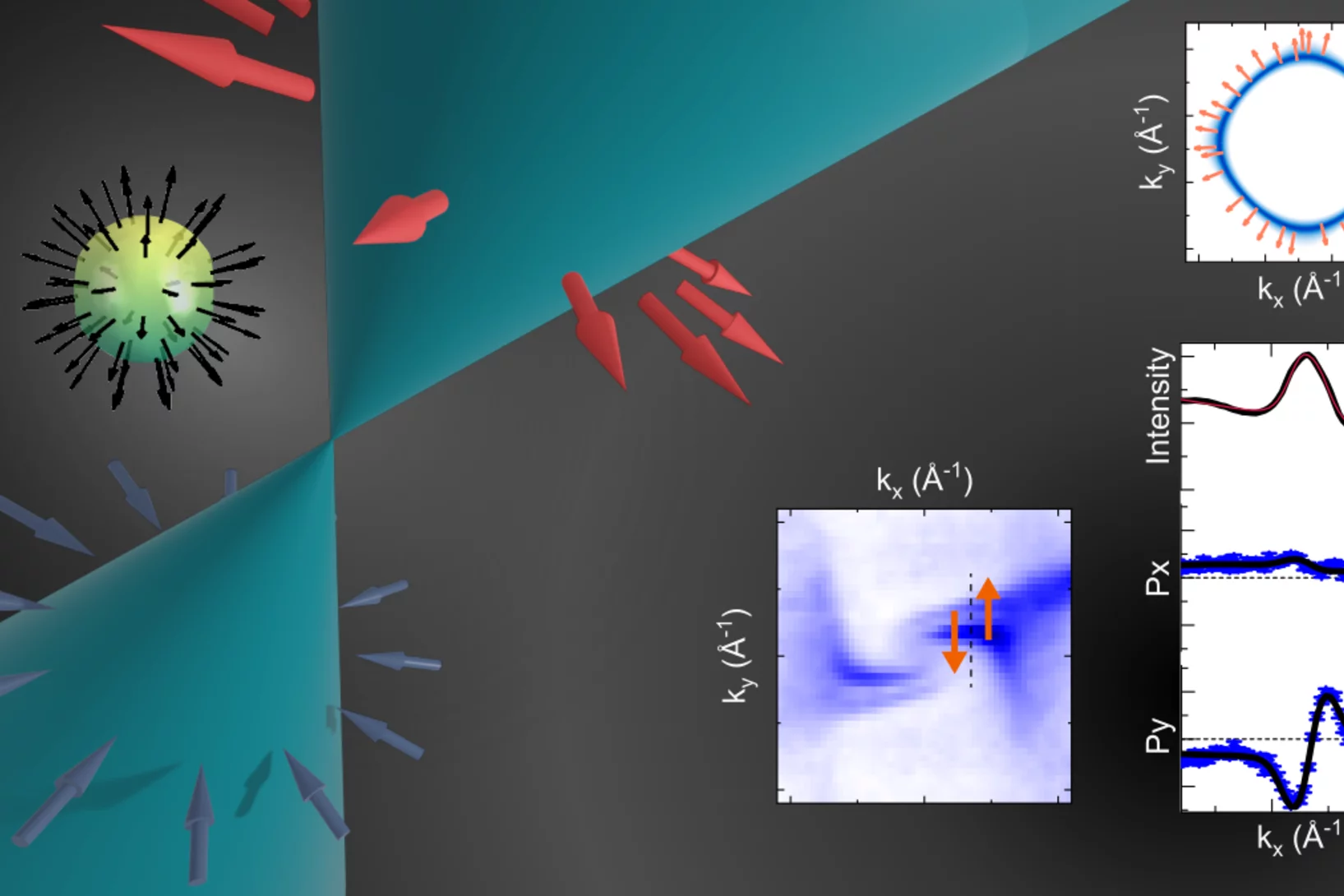
Weyl spin-momentum locking in a chiral topological semimetal
Spin–orbit coupling in noncentrosymmetric crystals leads to spin–momentum locking – a directional relationship between an electron’s spin angular momentum and its linear momentum. Isotropic orthogonal Rashba spin–momentum locking has been studied for decades, while its counterpart, isotropic parallel Weyl spin–momentum locking has remained elusive in experiments. Theory predicts ...
Fundamentally different
Artificial intelligence is helping to evaluate an unimaginably vast amounts of data efficiently and exploit the facilities’ full potential for research.
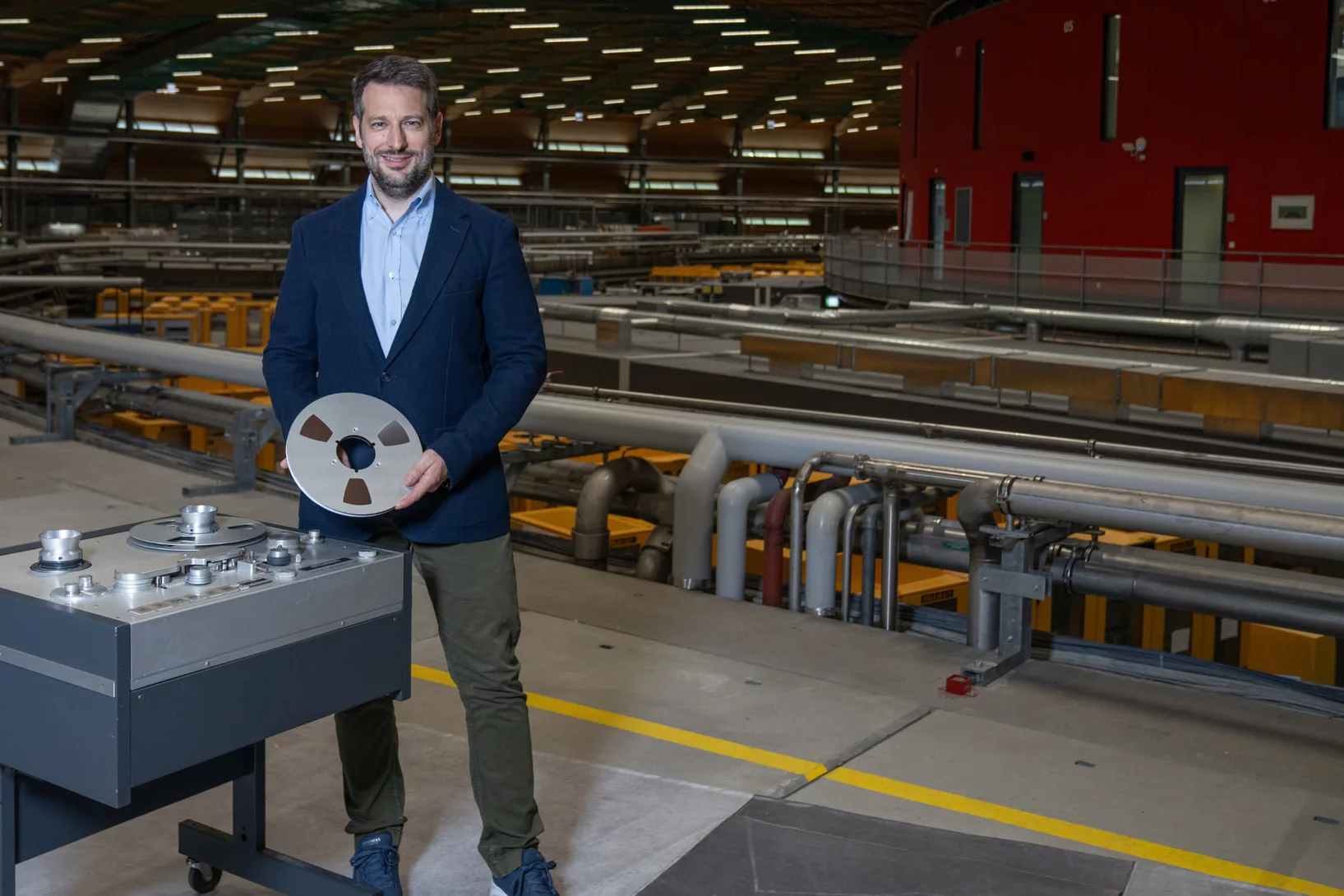
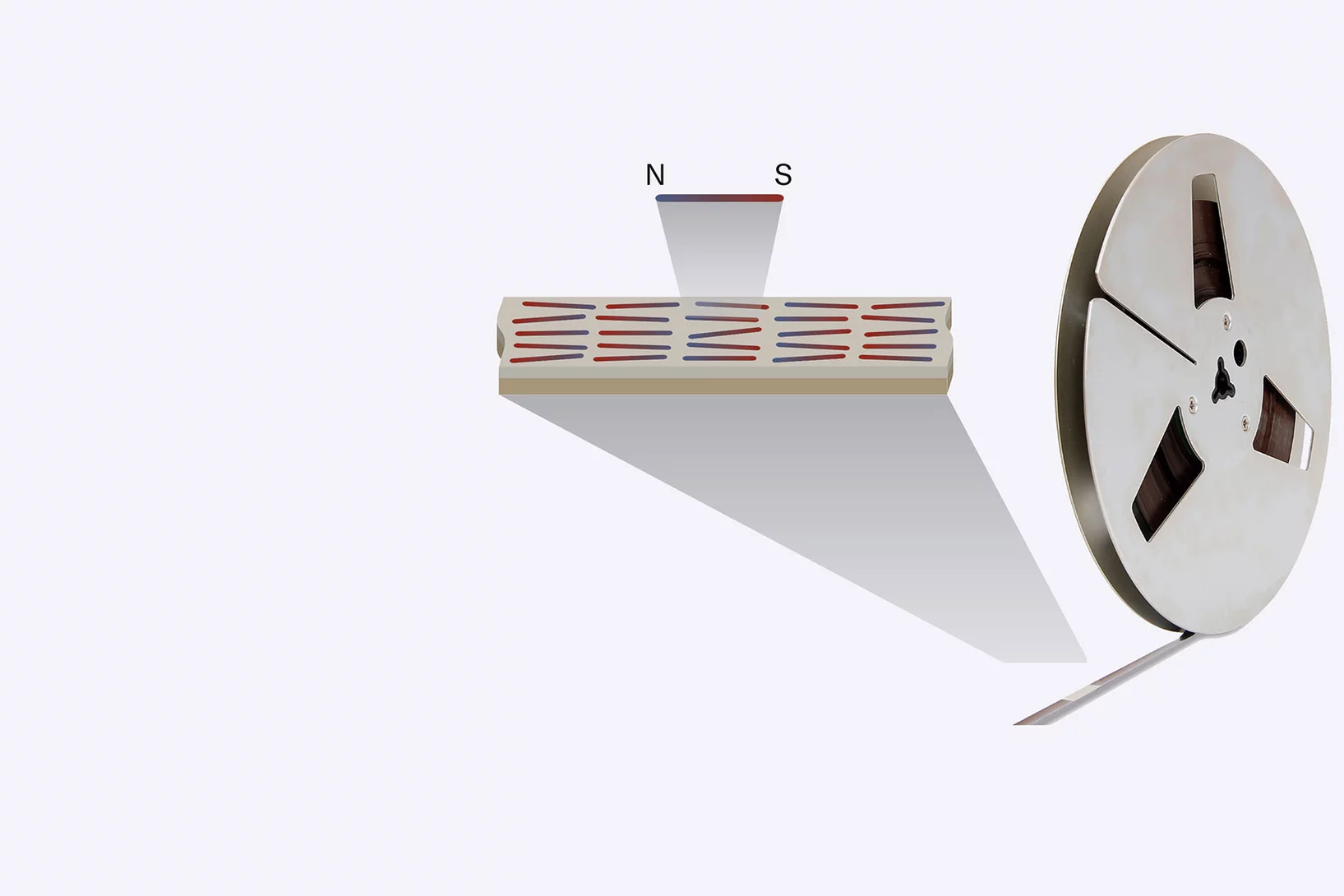
Rescuing music with X-rays
SLS plays the King of the Blues – B.B. King! In collaboration with the Montreux Jazz Digital Project, historic audio tapes are being digitised at PSI.
What will the SLS 2.0 upgrade mean for experiments?
Tighter beams, brighter light and extended photon energies open new experimental possibilities.
Making powerful lithium-air batteries suitable for everyday use
Chemical processes in lithium-air batteries revealed using neutron beams and synchrotron light.
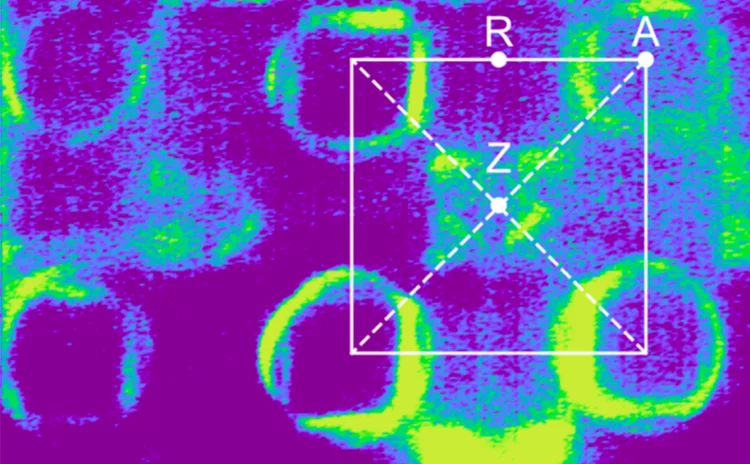
Flat-band hybridization between f and d states near the Fermi energy of SmCoIn5
We present high-quality angle-resolved photoemission (ARPES) and density functional theory calculations (DFT+U) of SmCoIn5. We find broad agreement with previously published studies of LaCoIn5 and CeCoIn5, confirming that the Sm 4f electrons are mostly localized. Nevertheless, our model is consistent with an additional delocalized Sm component, stemming from hybridization between the 4f electrons and the metallic bands at “hot spot” positions in the Brillouin zone.
Cause of clogged hypodermic needles discovered
Researchers at PSI and the ANAXAM technology transfer center have found the cause of clogging in prefilled syringes.
Phonon promoted charge density wave in topological kagome metal ScV6Sn6
Charge density wave (CDW) orders in vanadium-based kagome metals have recently received tremendous attention, yet their origin remains a topic of debate. The discovery of ScV6Sn6, a bilayer kagome metal featuring an intriguing √3 × √3 × √3 CDW order, offers a novel platform to explore the underlying mechanism behind the unconventional CDW. Here we combine ...
Extreme ultraviolet for scalable silicon quantum devices
Experiments at the Swiss Light Source (SLS) show the potential of extreme ultraviolet light (EUV) to make the building blocks of scalable quantum computers.
Observing laser-induced recrystallization
Synchrotron X-ray diffraction sheds light on laser-induced local recrystallization .
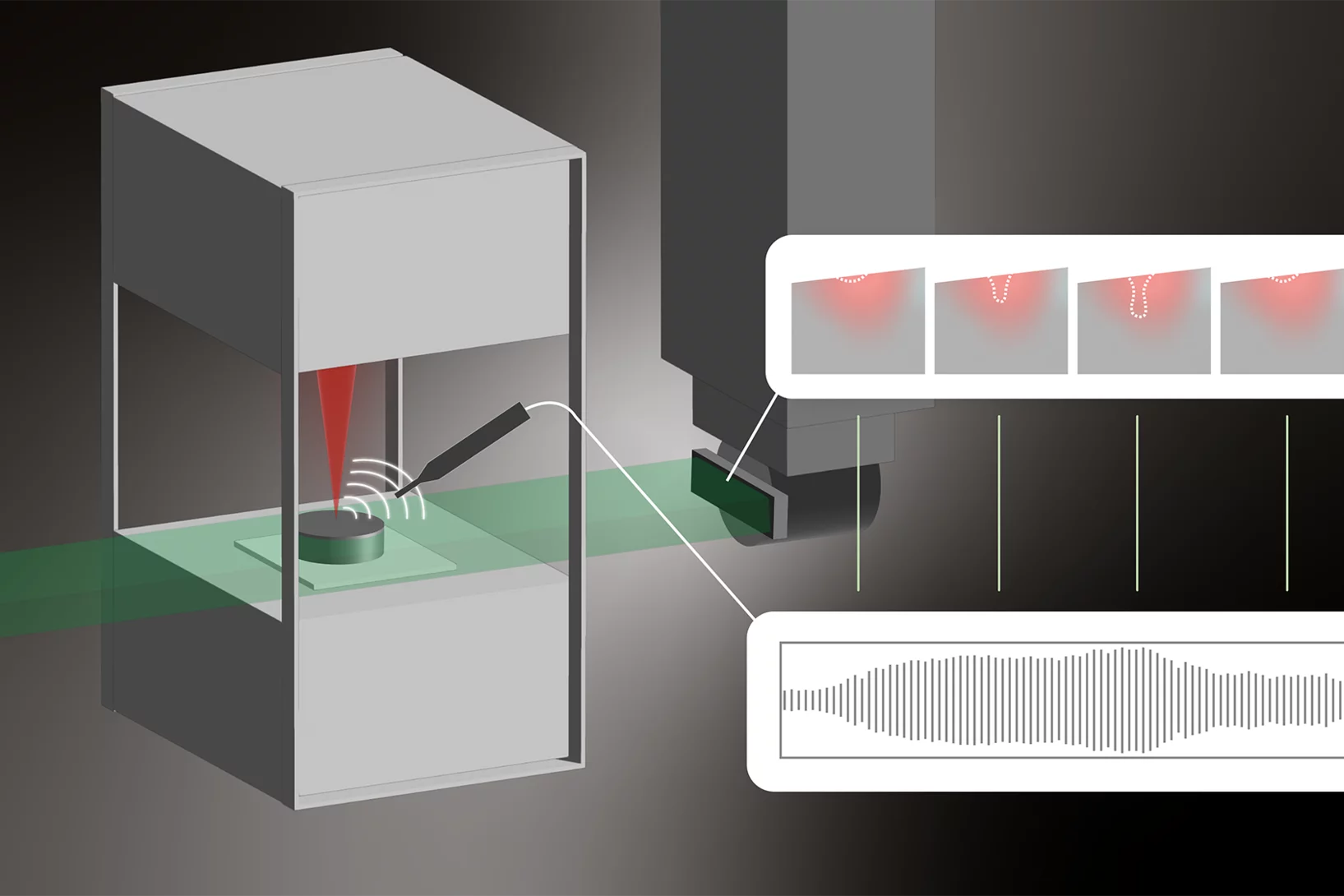
Listening for Defects as They Happen
Experiments at the Swiss Light Source SLS help resolve a long-standing debate surrounding metal 3D laser printing.
Smart glass and music from SLS
Every year the PSI Founder Fellowship Programme supports new ideas for innovative applications with up to 150,000 Swiss francs.
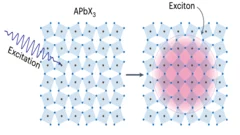
Excitons coupling to octahedral tilts in Pb nano-perovskites
Excitons coupling to octahedral tilts in Pb nano-perovskites
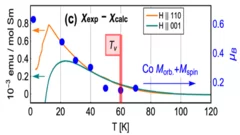
Crystal field rules heavy fermion delocalization in SmCoIn5
Crystal field rules heavy fermion delocalization
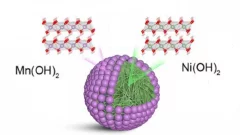
"Core-shell" cathodes for high performance Li-ion batteries
“Li-rich Ni-rich” core-shell particles are engineered as layered cathode materials for high energy Li-Ion batteries, including a controllable outer "Li-rich Mn-rich" shell improving cyclability.
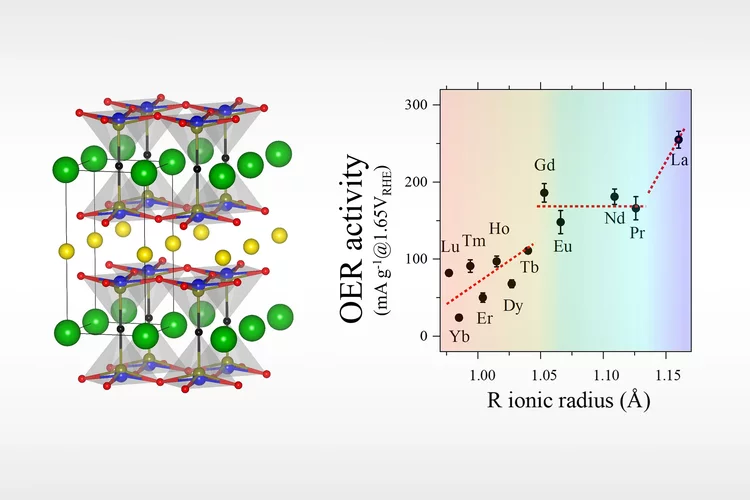
Cobalt-free layered perovskites RBaCuFeO5+d (R = 4f lanthanide) as electrocatalysts for the oxygen evolution reaction
Co oxides with perovskite-related structure are particularly promising, cost-effective OER catalysts. However, the increasing Co demand by the battery industry is pushing the search for Co-free alternatives. Here we investigate the potential of the Co-free layered perovskite family RBaCuFeO5+δ (R = 4f lanthanide), where we identify the critical structural and electronic variables leading to high OER catalytical performance. The employed methodology, based in the use of advanced neutron and X-ray synchrotron techniques combined with ab initio DFT calculations allowed to reveal LaBaCuFeO5+δ as new, promising Co-free electroctalyst. Moreover, we could show that this material can be industrially produced in nanocrystalline form. We believe that the reported results and methodology may contribute to the implementation of new technologies aimed to generate energy with lower carbon emissions, and can also inspire the scientific community in their search of other Co-free materials with good OER electrocatalytical properties.
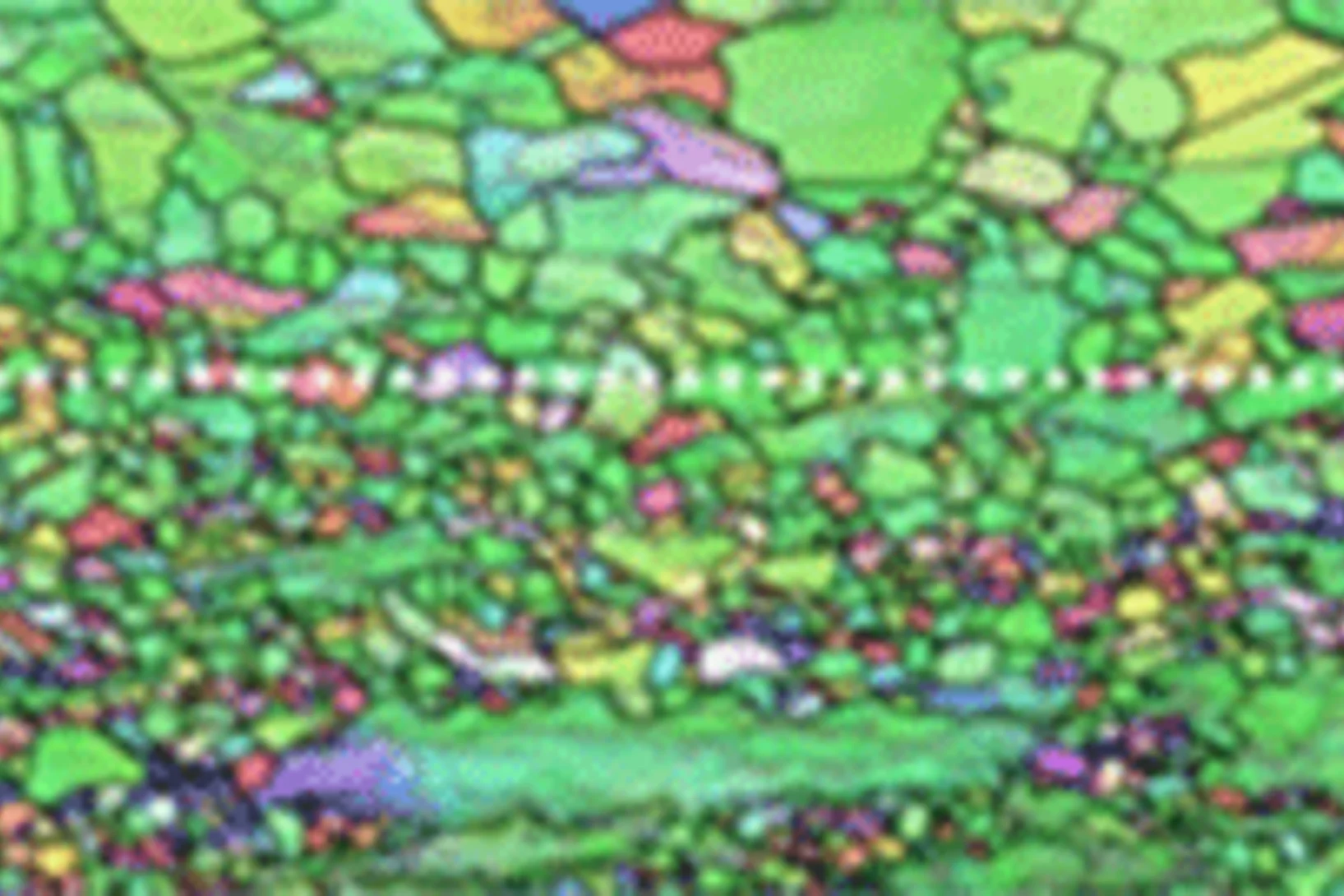
Additive manufacturing of alloys with programmable microstructure and properties
Using laser powder bed fusion (LPBF) technology, we devise special processing strategies to ‘program’ the thermal stability of the as-printed alloy, such that it is possible to decide, a priori, how the material’s microstructure will evolve upon heat treatment
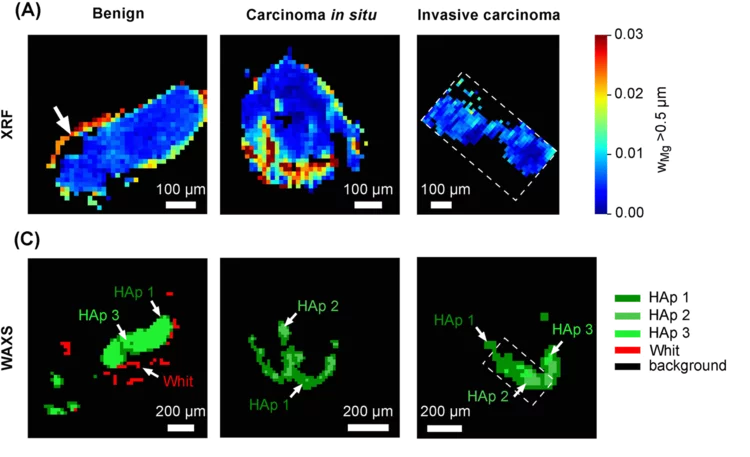
Whitlockite in mammary microcalcifications is not associated with breast cancer
Microcalcifications, small deposits of calcium-containing minerals that form in breast tissue, are often, but not always, a warning sign of breast cancer. The relationship between microcalcifications and cancer has not been fully understood thus far. Researchers discovered now that the relationship between microcalcifications and tumors seems to be linked to the presence of a particular mineral called whitlockite, which is rich in magnesium and is found in microcalcifications only in the absence of tumors.
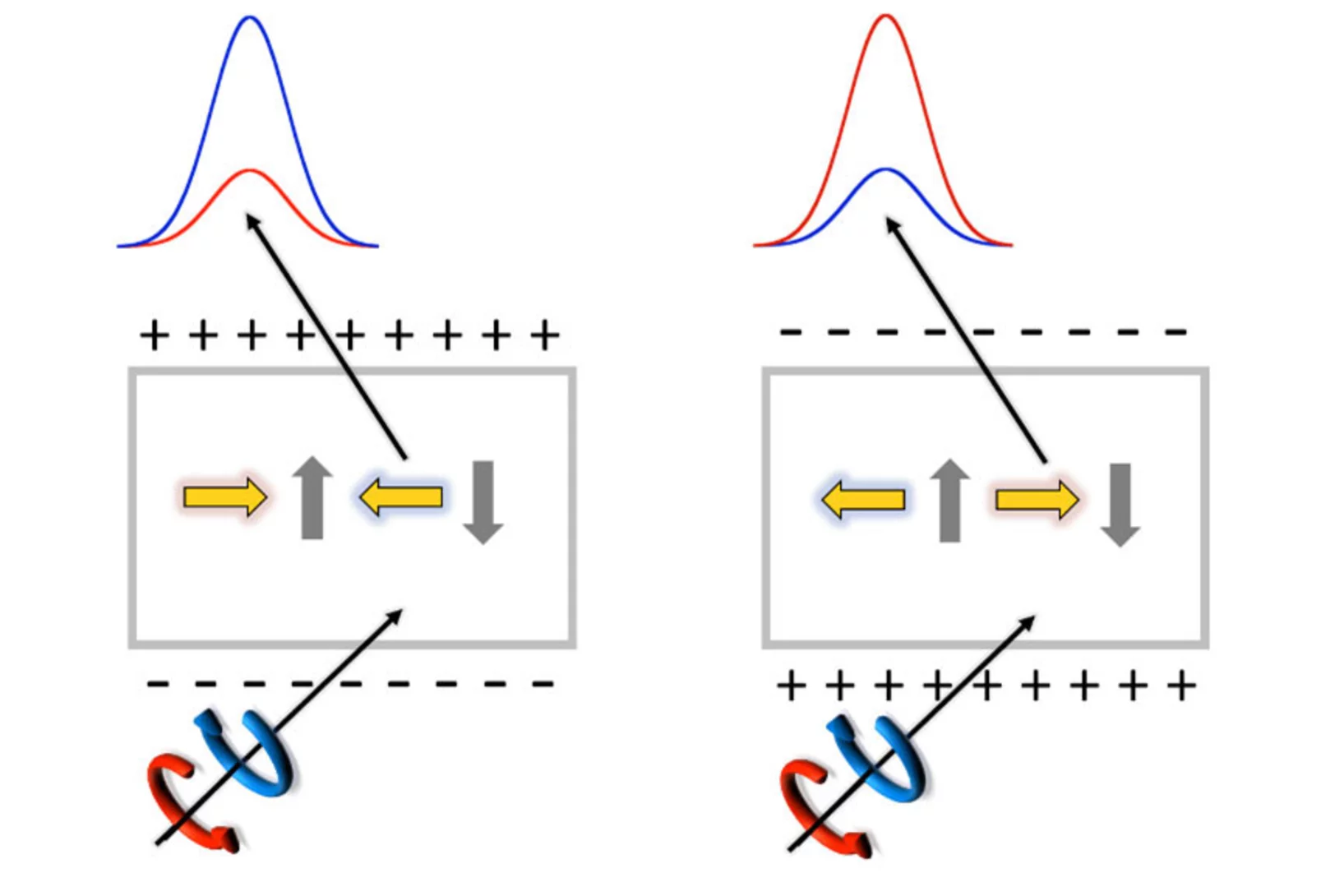
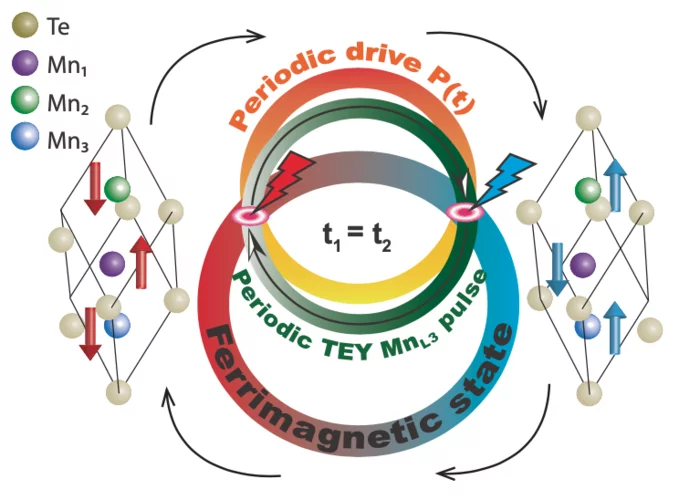
Efficient magnetic switching in a correlated spin glass
The interplay between spin-orbit interaction and magnetic order is one of the most active research fields in condensed matter physics and drives the search for materials with novel, and tunable, magnetic and spin properties. Here we report on a variety of unique and unexpected observations in thin multiferroic Ge1−xMnxTe films.
SLS 2.0: “Dark time” during the upgrade
The SLS is shutting down temporarily as it undergoes a major upgrade.
3D insights into an innovative manufacturing process
3D printing for creating complex shapes