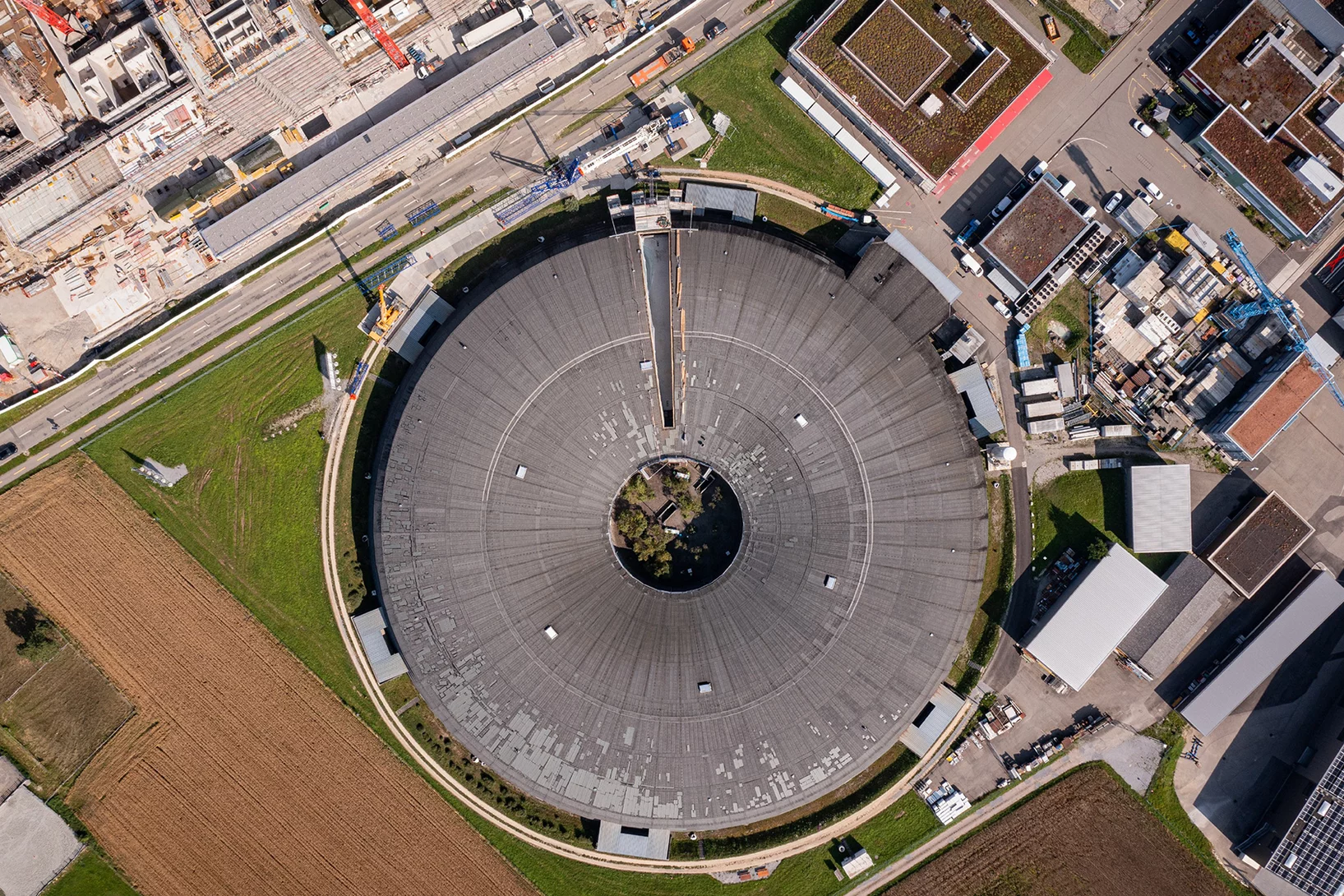
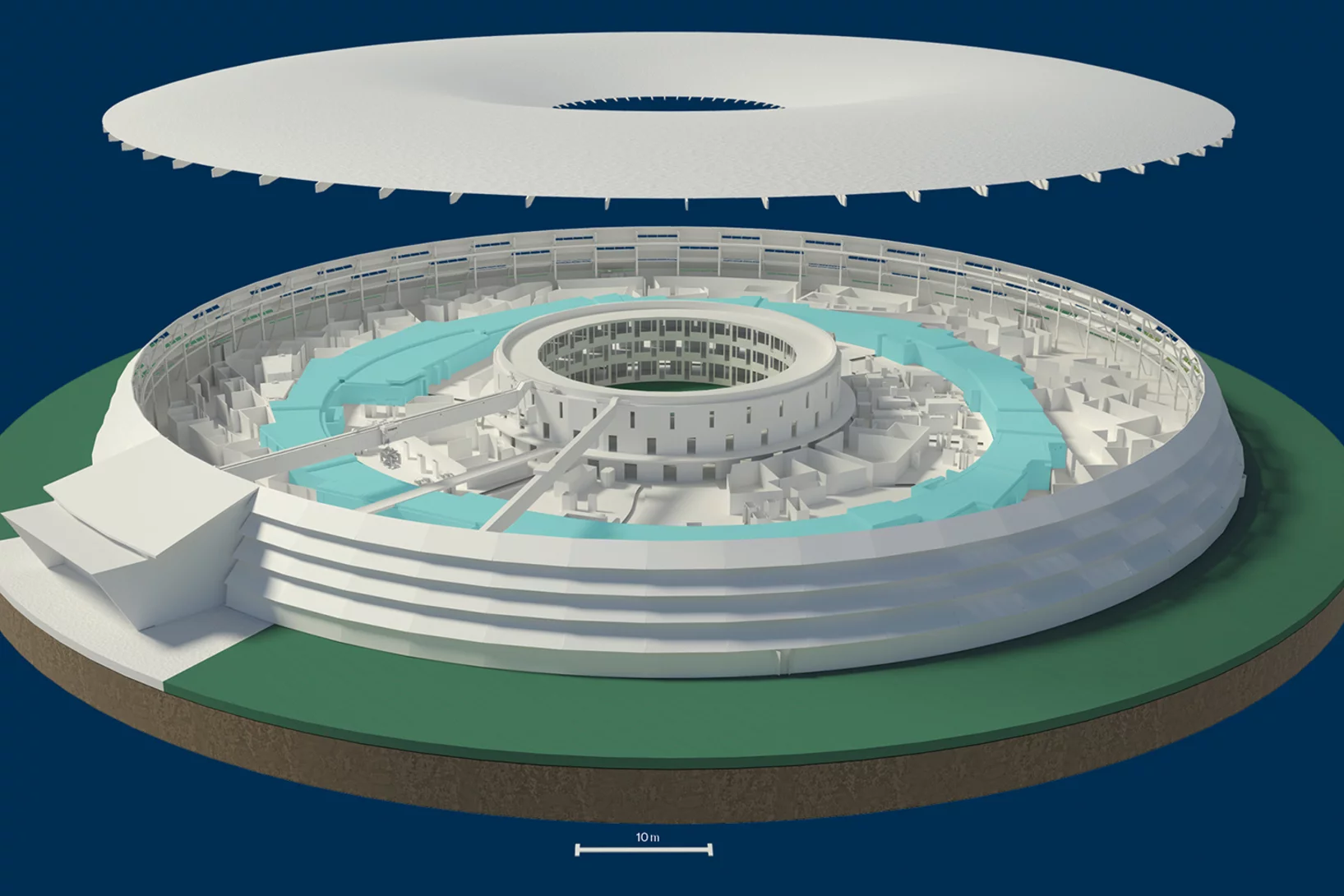
3D view: Swiss Light Source SLS
Linear accelerator, booster ring, storage ring: our 3D graphic of the Swiss Light Source shows the inside of the facility and how it serves research.
Dr. Manuel Guizar-Sicairos is awarded ICO prize
Dr. Manuel Guizar-Sicairos, beamline scientist at the cSAXS beamline, is the 2019 recipient of the International Commission for Optics (ICO) Prize. The distinction was awarded in the EOSAM conference in Rome.
Protein distancing
PSI researchers have developed a new method to attach proteins to the surface of virus-like particles.
Exploring the practical benefits of exotic materials
Niels Schröter receives an award from the Swiss Physical Society (SPG).
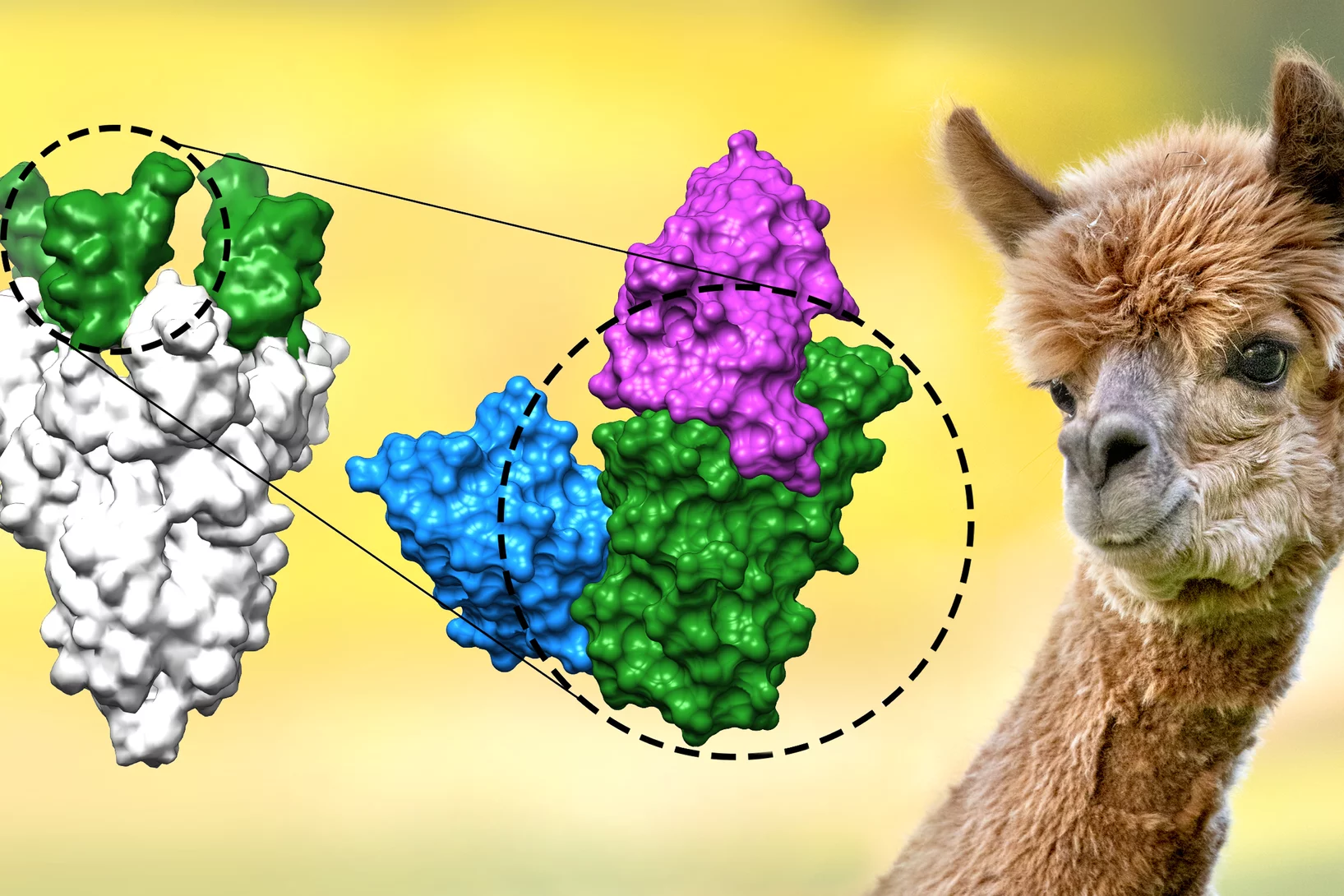
Nanobodies against SARS-CoV-2
In a study published in EMBO Journal, researchers at the Max Planck Institute for Biophysical Chemistry, Göttingen, Germany, developed nanobodies that efficiently block the coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 and its variants. The high resolution structural characterization was performed at the X10SA crystallography beamline at the Swiss Light Source.
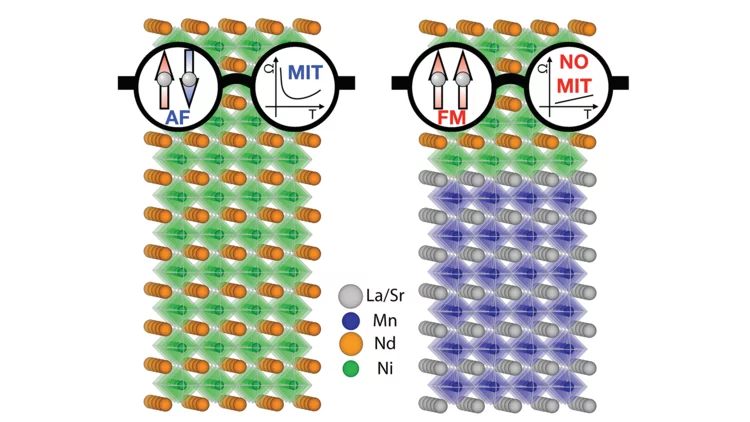
Creating novel quantum phases via the heterostructure engineering
Within this synergetic collaboration, PSI scientists have investigated the correlation between magnetic and electronic ordering in NdNiO3 by tuning its properties through proximity to a ferromagnetic manganite layer. The main outcome is that the stray magnetic field from the manganite layer causes a novel ferromagnetic-metallic (FM-M) phase in NNO. This work demonstrates the utilization of heterostructure engineering for creating novel quantum phases.
SLS: The new crane comes from above
The Swiss Light Source SLS is getting a second hall crane. But how can the 42-metre-long, 40-tonne monster get into the building? The only way is from above.
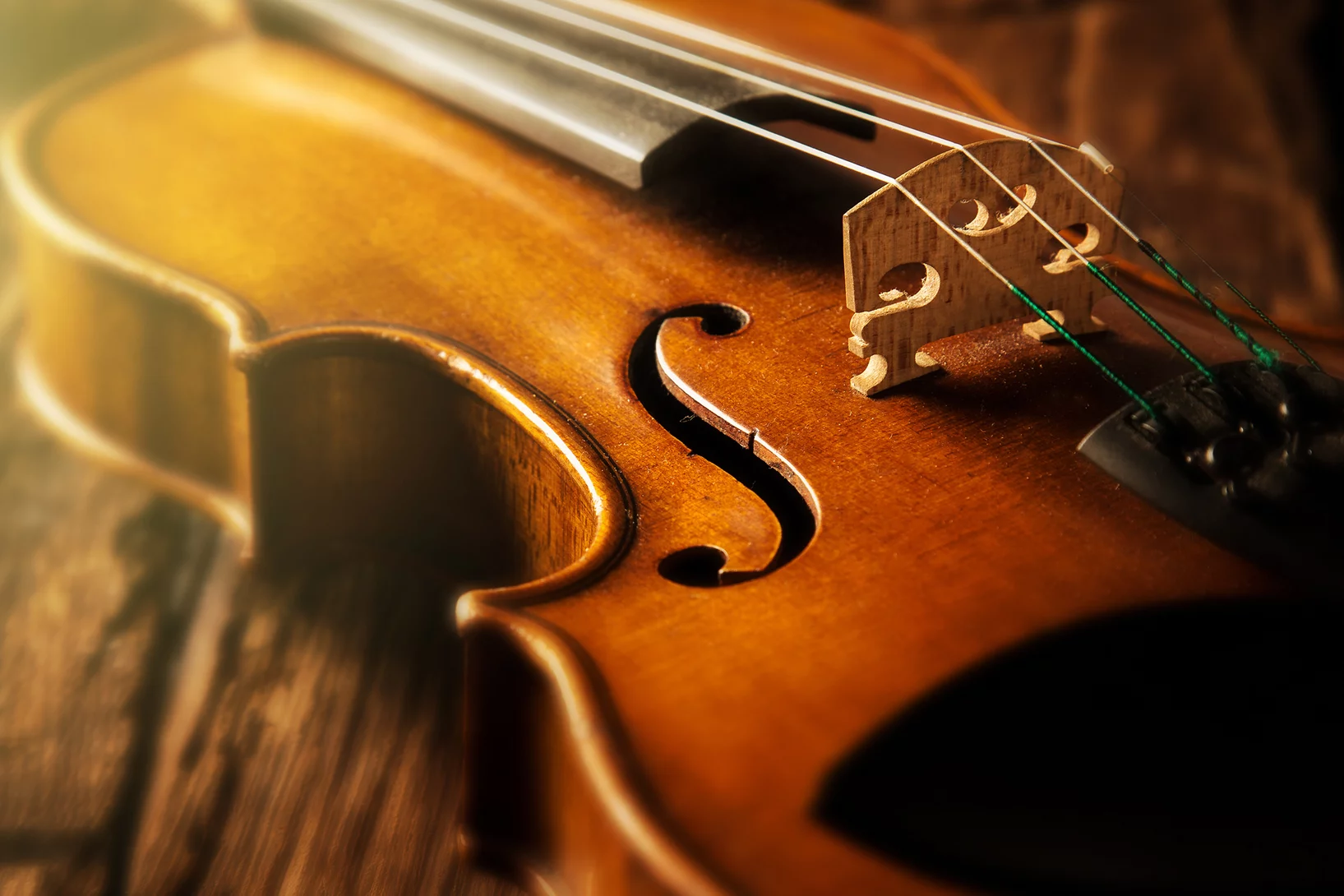
Secret of Stradivarius violins revealed
As an international team of researchers discovered, the old Italian masters Stradivari and Guarneri relied on unexpected chemical additives in making violins.
Understanding the physics in new metals
Together with international colleagues, PSI researchers have now been able to make correlated metals more readily usable for applications in superconductivity, data processing, and quantum computers.
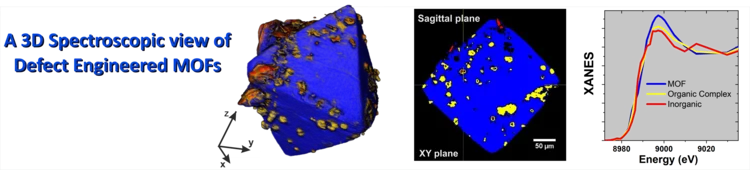
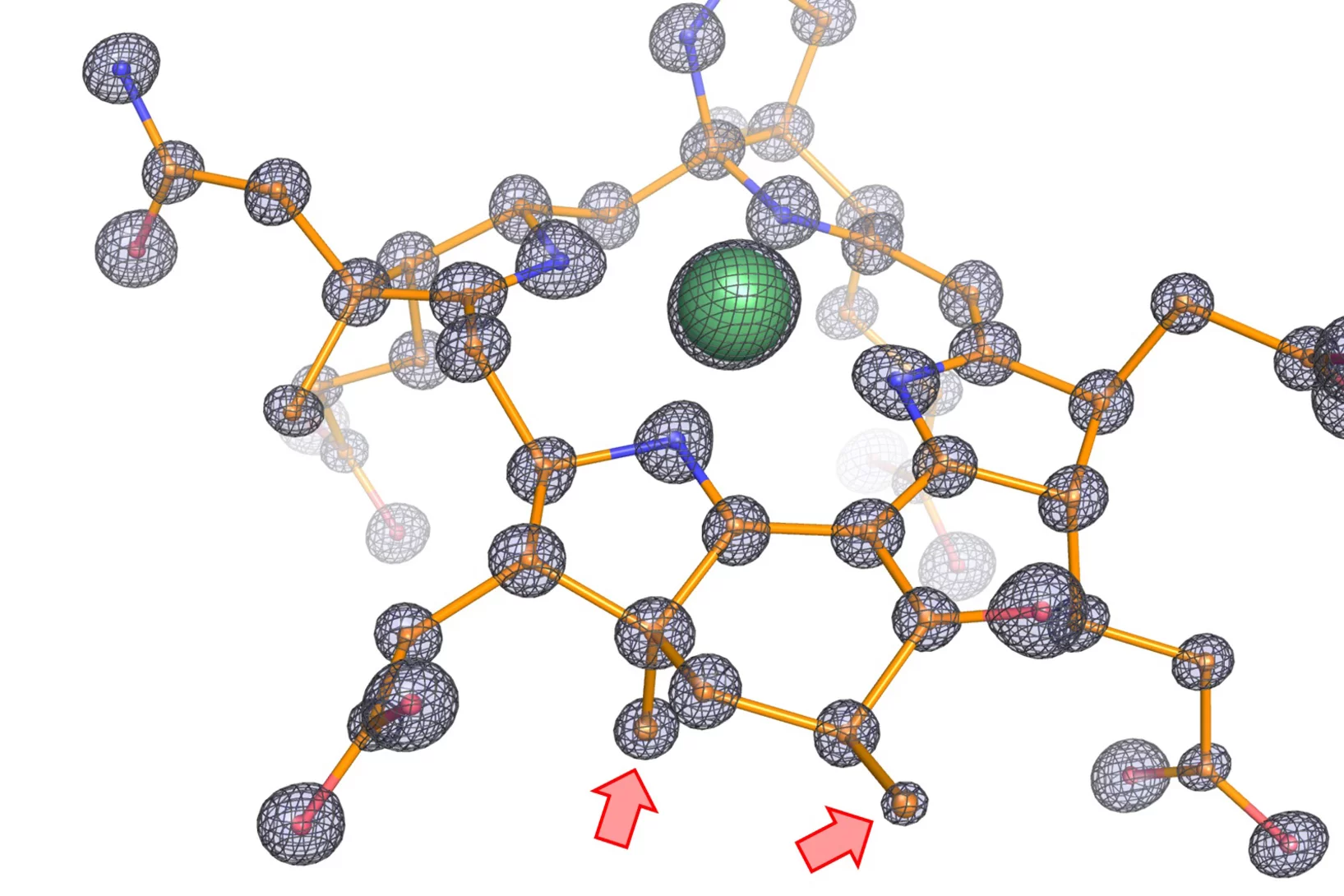
Full-field X-ray absorption tomography reveals the chemical structure of defects in metal-organic frameworks
Cryo-full-field XANES computed tomography was used to visualize the presence and distribution of a second coordination polymer of reduced copper coordination within defect-engineered HKUST-1 MOF crystals. Observations encourage a revisitation of the structure-property relationships of defect-engineered MOFs.
Imaging strain with high resolution
Imaging strain in crystalline materials with high resolution can be a challenging task. Researchers demonstrate an original use of X-ray ptychography for this purpose: ptychographic topography.
How ethane-consuming archaea pick up their favorite dish
Scientists decode the structure of the enzyme responsible for the ethane fixation by – beside others – using the SLS.
How catalysts age
Catalysts used in industry change their material structure over the years. Using a new method, PSI researchers have now studied this on the nanoscale.
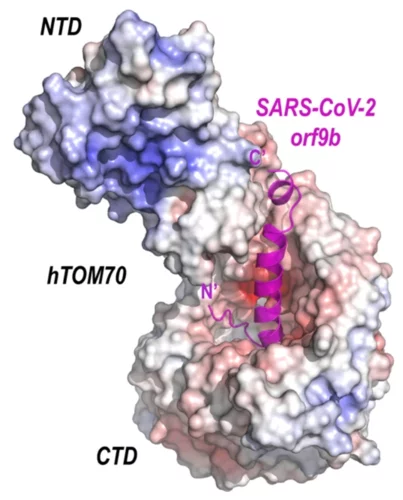
Crystal structure of SARS-CoV-2 Orf9b in complex with human TOM70 suggests unusual virus-host interactions
In a study published in Nature Communications, researchers at the NHC Key Laboratory of Systems Biology of Pathogens in Beijing, China, in collaboration with the Paul Scherrer Institut characterize the interactions of SARS-CoV-2 orf9b and human TOM70 biochemically, and they determine the 2.2 Å crystal structure of the TOM70 cytosolic domain with a bound SARS-CoV-2 orf9b peptide.
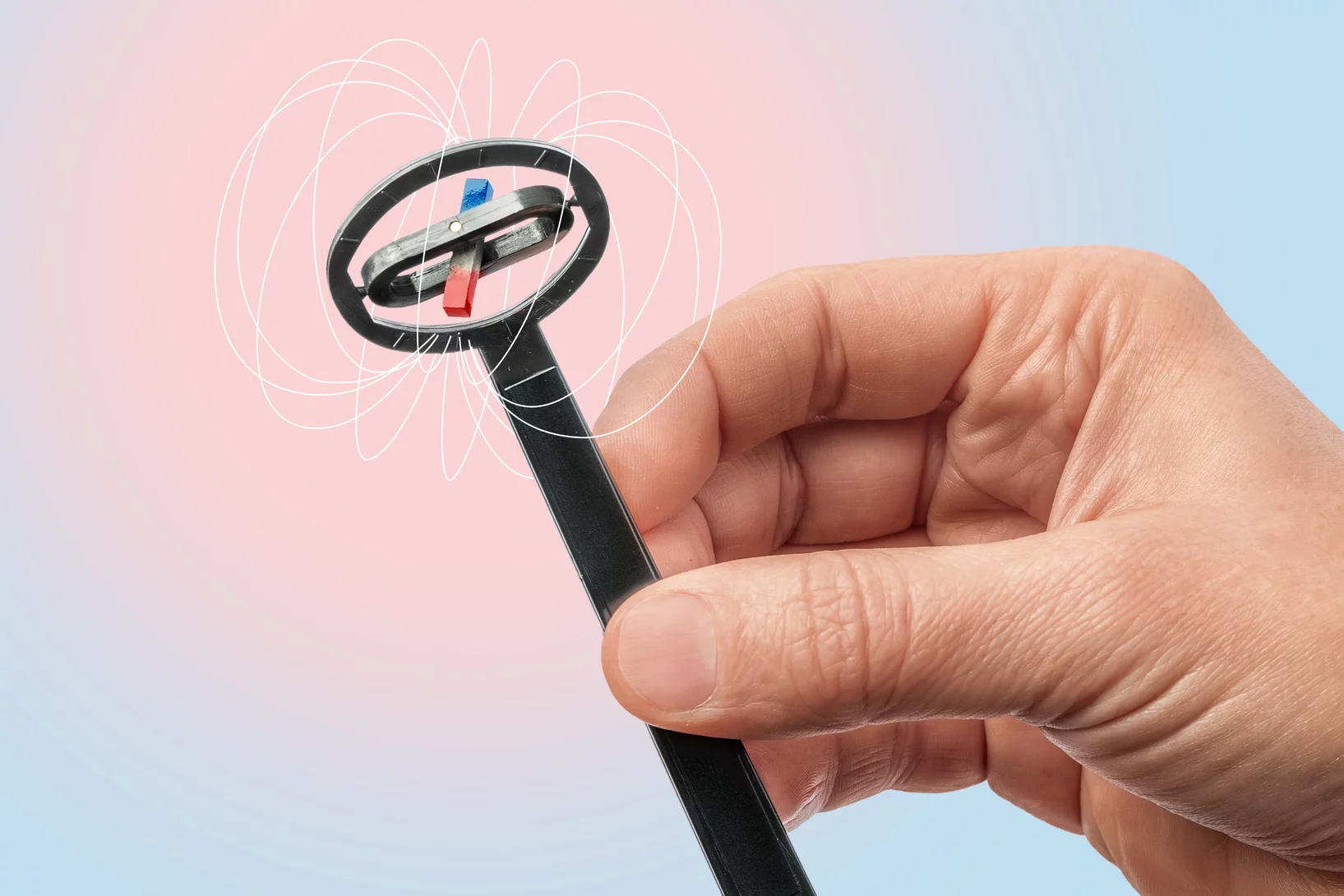
A "magical" power with major impact
Microrobots, materials with shape memory, and better particle accelerators are made possible through the exploration of magnetism at PSI.
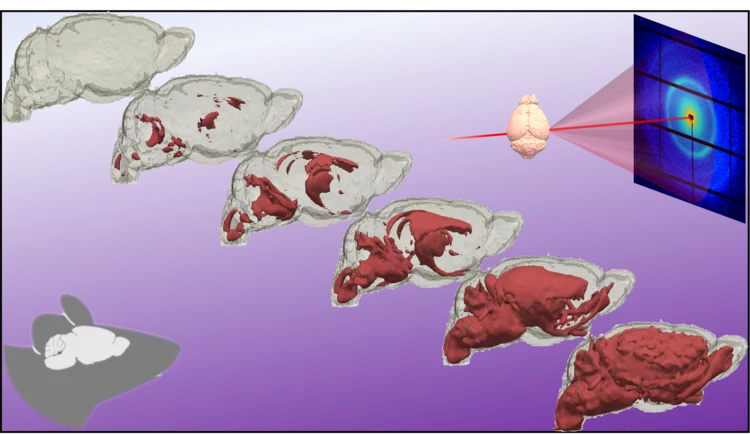
Quantifying oriented myelin in mouse and human brain
Myelin 'insulates' our neurons enabling fast signal transduction in our brain. Myelin levels, integrity, and neuron orientations are important determinants of brain development and disease. Small-angle X-ray scattering tensor tomography (SAXS-TT) is a promising technique for non-destructive, stain-free imaging of brain samples, enabling quantitative studies of myelination and neuron orientations, i.e. of nano-scale properties imaged over centimeter-sized samples.
How remdesivir works against the coronavirus
Researchers at Goethe University Frankfurt, in cooperation with the PSI have probably discovered another, previously unknown mechanism of action of the antiviral remdesivir.
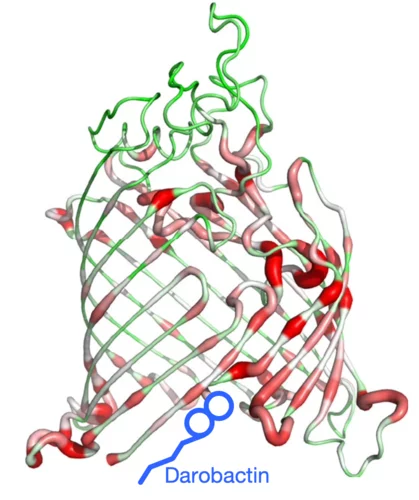
Combating antimicrobial resistance
In a study addressing the global health threat of drug resistance, researchers at the Biozentrum, University of Basel, have revealed how a new antibiotic, Darobactin, binds to the external membrane of gram-negative bacteria.
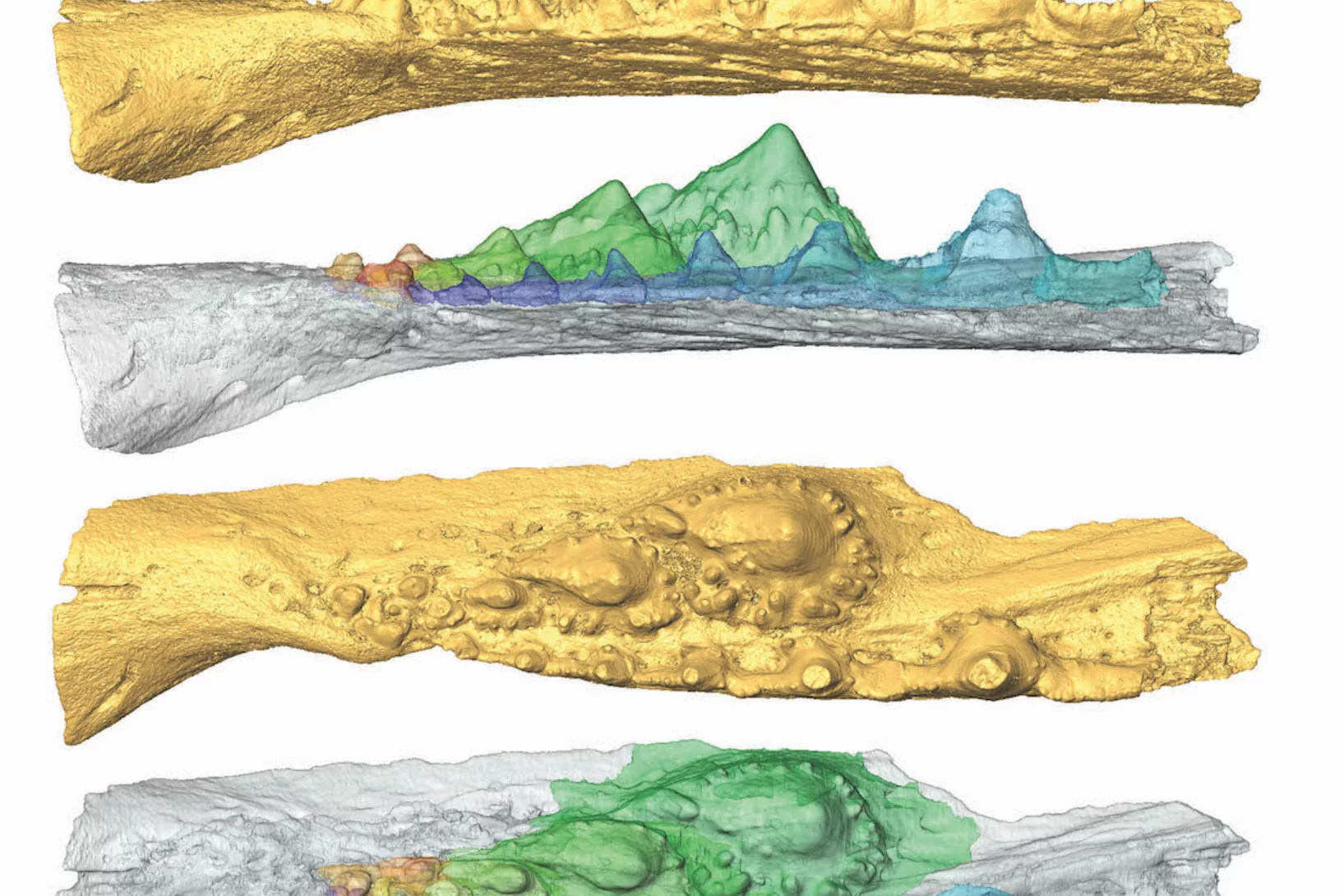
Deep evolutionary origins of the human smile
Detailed characterization of the tooth and jaw structure and development among shark ancestors by synchrotron based X-ray tomographic microscopy at TOMCAT led an international team of researchers from the Naturalis Biodiversity Center in Leiden and the University of Bristol to the discovery that while teeth evolved once, complex dentitions have been gained and lost many times in evolutionary history.
Growth in the data sciences
Another site for the Swiss Data Science Center will be established at PSI. This expansion is expected to give a further boost to the data sciences in Switzerland.
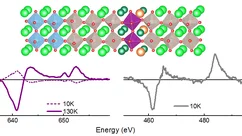
Hindering the magnetic dead layer in manganites
The authors demonstrate the stability of ferromagnetic order of one unit cell thick optimally doped manganite (La0.7Ba0.3MnO3, LBMO) epitaxially grown between two layers of SrRuO3 (SRO). LBMO shows ferromagnetism even above SRO Tc. Density Functional Theory calculations help understand the reasons behind this interesting result.
HERCULES SCHOOL 2021 AT PSI
During the week of March 15 – 19, we had the pleasure to welcome 20 international PhD students, PostDocs and assistant professors at PSI, taking part in the first virtual HERCULES SCHOOL on Neutrons & Synchrotron Radiation.
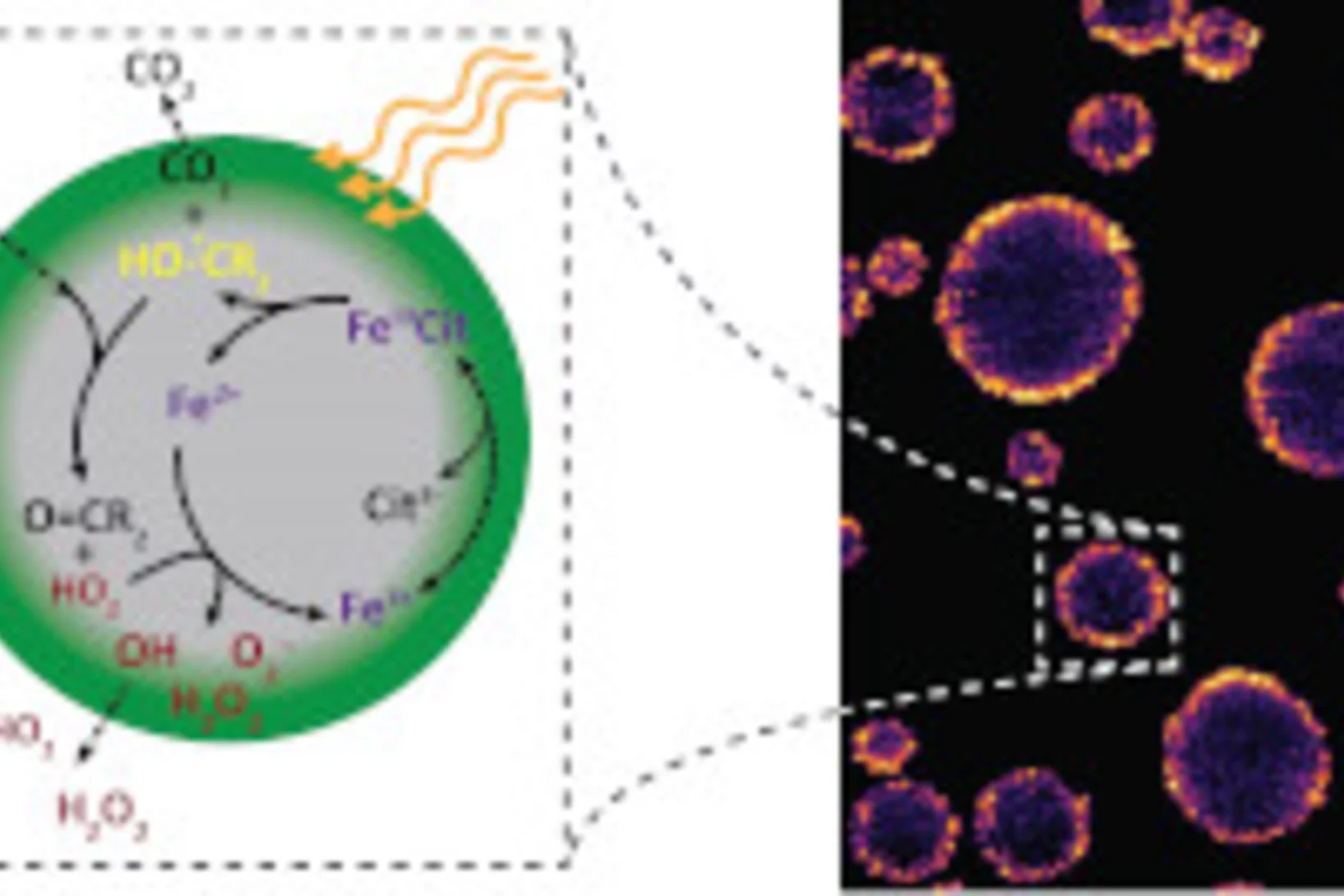
Looking inside airborne particles for the chemistry responsible for their adverse health effects.
Chemical changes inside of breathable airborne particles can cause reactive oxygen species (ROS) and carbon centered radicals (CCRs) to form, which are harmful to our bodies and induce oxidative stress in lungs. Using X-ray spectromicroscopy at the PolLux beamline and mimicking the environmental and sunlit conditions aerosol particles experience in the atmosphere near the Earth Surface, it was recently found that highly viscous organic particles with low water content can attain high concentrations of ROS and CCRs that persist over long times. Natural particles like these will occur in ambient humidity below 60% and effectively trap ROS and CCRs inside that react when exposed to light.
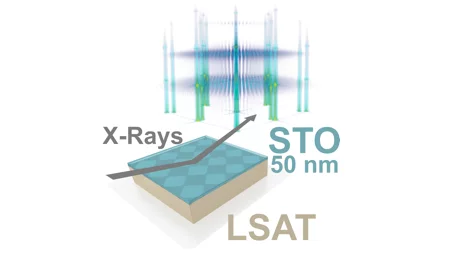
Buried moiré supercells through SrTiO3 nanolayer relaxation
The authors find that an annealing process can create a highly ordered network of two-dimensional line defects at the buried interface between a relaxed film and its substrate. The low dimensional network spacing is directly related to the lattice mismatch and can correspondingly be tuned by the choice of substrate.
Forschung zu Covid-19 am Paul Scherrer Institut
Während viele Bereiche des Lebens eingeschränkt sind, bleiben wichtige Forschungsanlagen am PSI in Betrieb.
PSI equips the Swiss Light Source SLS for the future
Green light for SLS 2.0: The planned upgrade of the Swiss Light Source SLS can proceed; the funding is provided for within the framework of the ERI Dispatch for 2021-2024, which has been approved.
Look Inside a Chemical Reactor
Operando X-ray spectrotomography allows scientists to look inside of functioning chemical reactors. A research team at Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT), at Paul Scherrer Institute PSI and at the European Synchrotron Radiation Facility (ESRF) in France have employed this method successfully.
The librarian of the petabytes
It is necessary to prepare now for the planned upgrade of the Swiss Light Source SLS. In order to do justice to future research, Alun Ashton is estimating the amount of data that future experiments will produce.
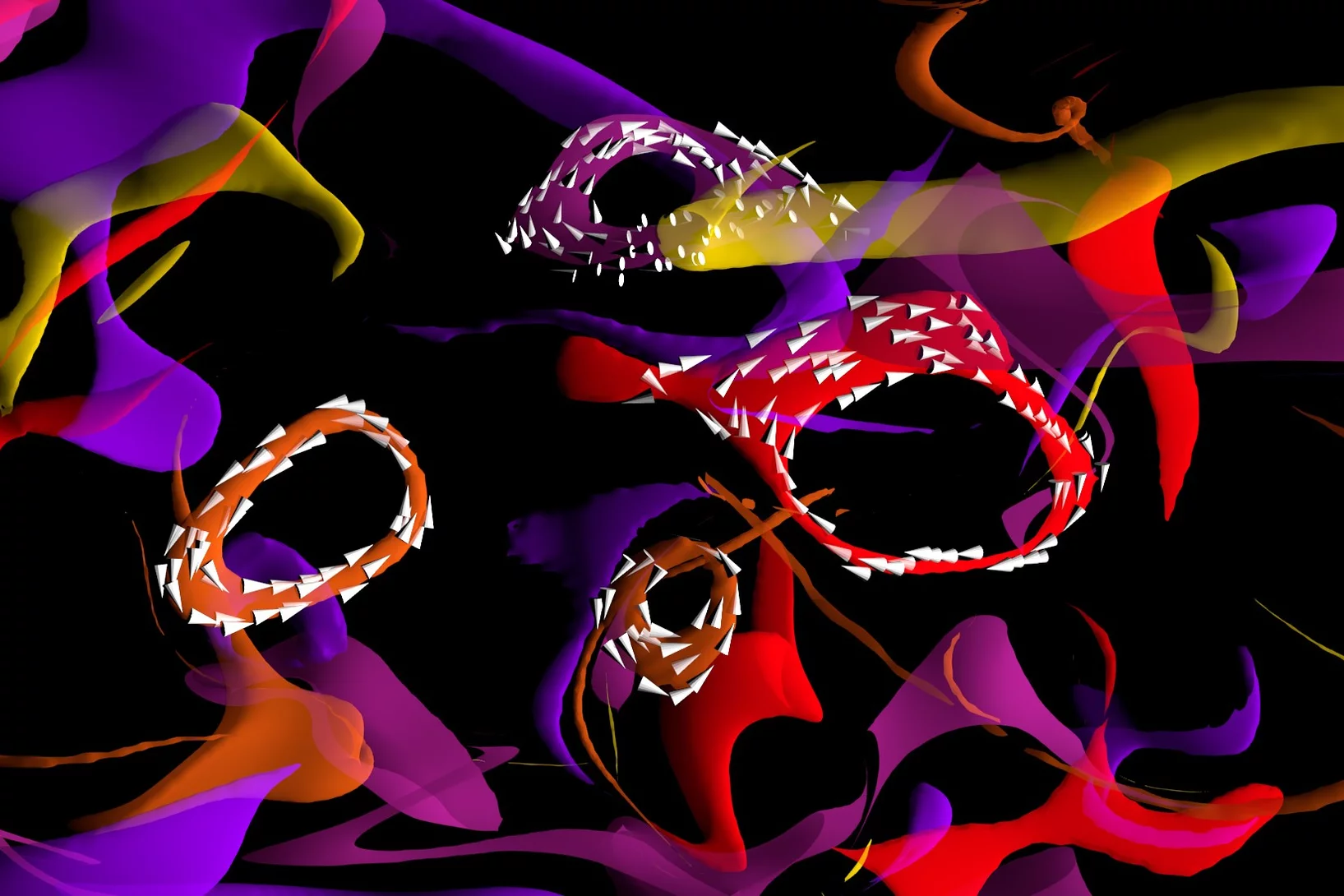
Magnetic vortices come full circle
The first experimental observation of three-dimensional magnetic ‘vortex rings’ provides fundamental insight into intricate nanoscale structures inside bulk magnets, and offers fresh perspectives for magnetic devices.
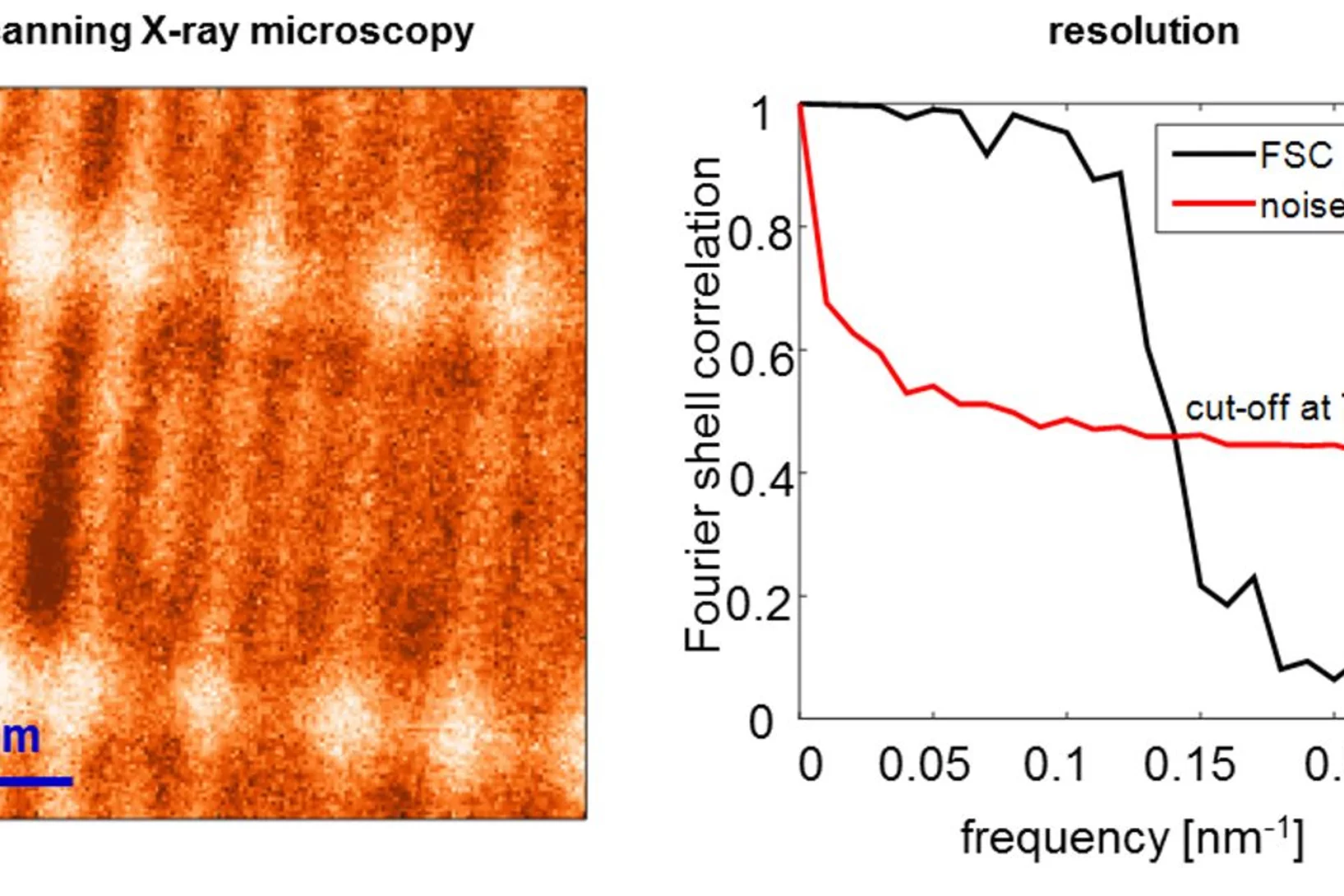
World Record: 7 nm Resolution in Scanning Soft X-ray Microscopy
During the past decade, scientists have put high effort to achieve sub-10 nm resolution in X-ray microscopy. Recent developments in high-resolution lithography-based diffractive optics, combined with the extreme stability and precision of the PolLux and HERMES scanning X-ray microscopes, resulted now in a so far unreached resolution of seven nanometers in scanning soft X-ray microscopy. Utilizing this highly precise microscopy technique with the X-ray magnetic circular dichroism effect, dimensionality effects in an ensemble of interacting magnetic nanoparticles can be revealed.