Research Archive
Here is a summary of some of the previous research activities within the TOMCAT team. Click on an item to be directed to a more detailed project description.
Beamline-Related Research
Dynamic in-vivo lung imaging at the micrometer scale
Apart from that, our interests also extend to the study of other lung diseases such as emphysema and fibrosis. Our results will have direct implications on the current knowledge and understanding when dealing with lung diseases in clinics. For instance, a fundamental understanding of VILI would be crucial for developing better ventilation strategies for patients.
Publications:
- G. Lovric, ETH Phd thesis, 2015, http://doi.org/bd3z.
- G. Lovric, S. F. Barré, J. C. Schittny et al., J. Appl. Crystallogr. 46 (4), 856, 2013, http://doi.org/n3p.
Collaboration:
- Institute of Anatomy, University of Bern, Switzerland
- Clinic of Neonatology, University Hospital of Lausanne (CHUV), Switzerland
- Department of Clinical Physiology, Grenoble University Hospital, France
- Department of Surgical Sciences, Uppsala University, Sweden
Funding agencies: Centre d'Imagerie BioMédicale (CIBM)
X-ray phase contrast tomographic imaging and analysis of the lung at the micrometer scale
Publications:
- Lovric, Goran, et al. "A multi-purpose imaging endstation for high-resolution micrometer-scaled sub-second tomography." Physica Medica (2016), http://doi.org/bp54.
- Vogiatzis Oikonomidis Ioannis et al. "Efficient segmentation of lung parenchyma in tomographic images of freshly post mortem mice under low contrast-to-noise ratio conditions and at micrometer resolution. " XRM 2016 conference proceedings
- Vogiatzis Oikonomidis Ioannis et al. "Imaging samples larger than the field of view: the SLS experience." XRM 2016 conference proceedings
Collaboration:
- Institute of Anatomy, University of Bern, Switzerland
Funding agencies: Swiss National Science Foundation (SNF)
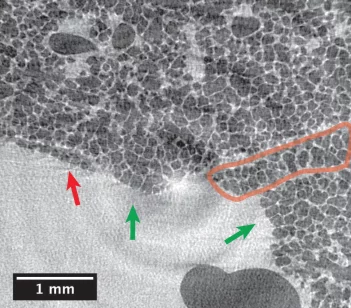
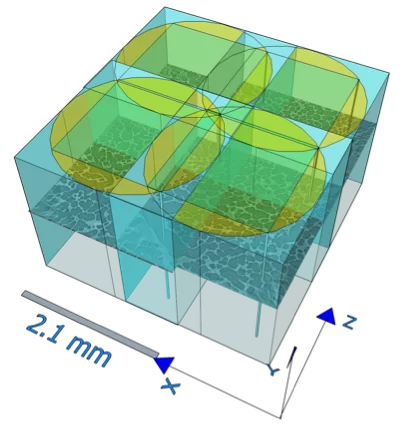
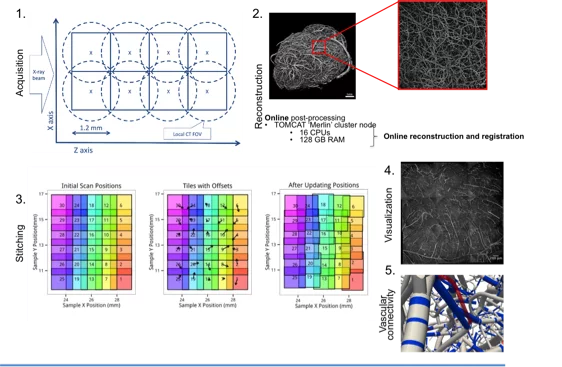
Reconstruction of the mouse brain vascular networks with high-resolution synchrotron radiation X-ray tomographic microscopy
Publications:
[1] Xue S, Gong H, Jiang T, Luo W, Meng Y, et al. Indian-Ink Perfusion Based Method for Reconstructing Continuous Vascular Networks in Whole Mouse Brain. PLoS ONE 9(1): e88067 (2014), http://dx.doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0088067.
[2] Preibisch, S, Stephan S, Tomancak P. Globally optimal stitching of tiled 3D microscopic image acquisitions. Bioinformatics (Oxford, England) 25 (11): 1463–5 (2009), https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btp184.
Collaboration:
- University of Zurich, Institute of Pharmacology and Toxicology, Switzerland
- IBFM - Inst. of Molecular Bioimaging and Physiology, Dept. of Biomedical Sciences, LITA Segrate (Milano), Italy
- European Synchrotron Radiation Facility – ESRF Grenoble, Medical Beamline, France
Funding agencies: Centre d'Imagerie BioMédicale (CIBM)
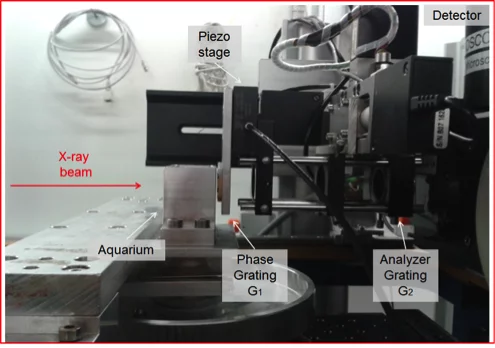
X-ray grating interferometry for phase-contrast imaging at the Swiss Light Source
Publications:
[1] McDonald SA et al. Advanced phase-contrast imaging using a grating interferometer. J. Synchr. Radiat. 16, 562 (2009), https://doi.org/10.1107/S0909049509017920.
[2] Pinzer B. R. et al. Imaging brain amyloid deposition using grating-based differential phase contrast tomography.Neuroimage 61, 1336-1346 (2012), http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2012.03.029.
[3] Beheshti A. et al. Early Tumor Development Captured Through Nondestructive, High Resolution Differential Phase Contrast X-ray Imaging. Radiat, Res. 180, 448-454 (2013), http://dx.doi.org/10.1667/RR13327.1.
Funding agencies: Centre d'Imagerie BioMédicale (CIBM)
Impact of phase-contrast X-ray imaging in cochlear micro-anatomy investigation
Publications:
[1] Tian Q, Linthicum FH, Jr., Fayad JN: Human cochleae with three turns: an unreported malformation. Laryngoscope, 116(5):800-803 (2006), http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/01.mlg.0000209097.95444.59.
[2] Rask-Andersen H, Liu W, Erixon E, Kinnefors A, Pfaller K, Schrott-Fischer A, Glueckert R: Human cochlea: anatomical characteristics and their relevance for cochlear implantation. Anat Rec (Hoboken), 295(11):1791-1811 (2012), https://doi.org/10.1002/ar.22599.
Collaboration:
- University of Bern, ARTORG Center for Biomedical Engineering, Switzerland
- Inselspital Bern, Department of Otorhinolaryngology (ENT), Switzerland
- PSI, Center for Proton Therapy, Switzerland
Funding agencies: Centre d'Imagerie BioMédicale (CIBM)
Virtual Reading of a Large Ancient Handwritten Science Book
Publications:
[1] Baumann, R., Porter, D. C., Seales, W. B. The use of micro-CT in the study of archaeological artifacts. Proc. of 9th Int Conf on NDT of Art, 1–9 (2008), http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.216.2327&rep=rep1&type=pdf.
[2] Seales, W., Griffioen, W., Baumann, R., Field, M. Analysis of herculaneum papyri with x-ray computed tomography. Proceedings of 10th International Conference on NDT of Art, Jerusalem, 1–9 (2011), http://www.ndt.net/article/art2011/papers/FIELD%20-%20M%2014.pdf.
[3] Margaritondo, G. Elements of Synchrotron Light for Biology, Chemistry, and Medical Research. New York: Oxford (2002).
[4] Albertin F., Patera A., Jerjen I., Hartmann S., Peccenini E., Kaplan F., Stampanoni M., Kaufmann R., Margaritondo G., Virtual reading of a large ancient handwritten science book, Microchemical Journal, Volume 125, Pages 185-189, ISSN 0026-265X (2016), http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2015.11.024.
Collaboration:
- EMPA, Center for X-ray Analytics, Switzerland
- CIBM, Phase contrast X-ray imaging core (EPFL), Switzerland
- Faculté des Sciences de Base, Ecole Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL), Switzerland
Funding agencies: Centre d'Imagerie BioMédicale (CIBM)
Full-Field Transmission X-ray Microscopy using a Photon Counting Pixel Detector
Publications:
- A. Sakdinawat and D. Attwood. Nature Photonics 4, 840—848 (2010)
- M. Holt et al. Annu. Rev. Mater. Res. 43, 183—211 (2013)
- J. Vila-Comamala et al. J. Synchrotron Rad. 19, 705—709 (2012) DOI
Collaboration:
- Dr. A. Parsons, Dr. E. Gimenez-Navarro and Dr. U. Wagner, Diamond Light Source, Didcot (UK)
- Dr. C. David, Paul Scherrer Institut, PSI Villigen (Switzerland)
Funding agencies: FNSNF Grant Number 159263
Lossy Compression for CT Datasets
The core idea of lossy compression is to subtly modify an image such that it can be compressed well while keeping the visual appearance as much as possible. For average compression ratios, this will typically lead to tiny ‘ghost’ structures around more prominent image features or smoothing that the human eye will miss. In the case at hand, however, where the images serve as input to the first stage of a longer processing pipeline, such modifications may lead to artefacts in the final tomographic reconstructions. This project aims at evaluating different lossy compression schemes and at investigating the impact of their respective artefacts onto reconstruction quality.
Publications:
- Impact of lossy compression of X-ray projections onto reconstructed tomographic slices, F. Marone, J. Vogel, M. Stampanoni, Journal of Synchrotron Radiation 27 (2020).
Contact: Dr. Federica Marone, federica.marone@psi.ch, WBBA/216, +41 56 310 53 18
Laboratory imaging research
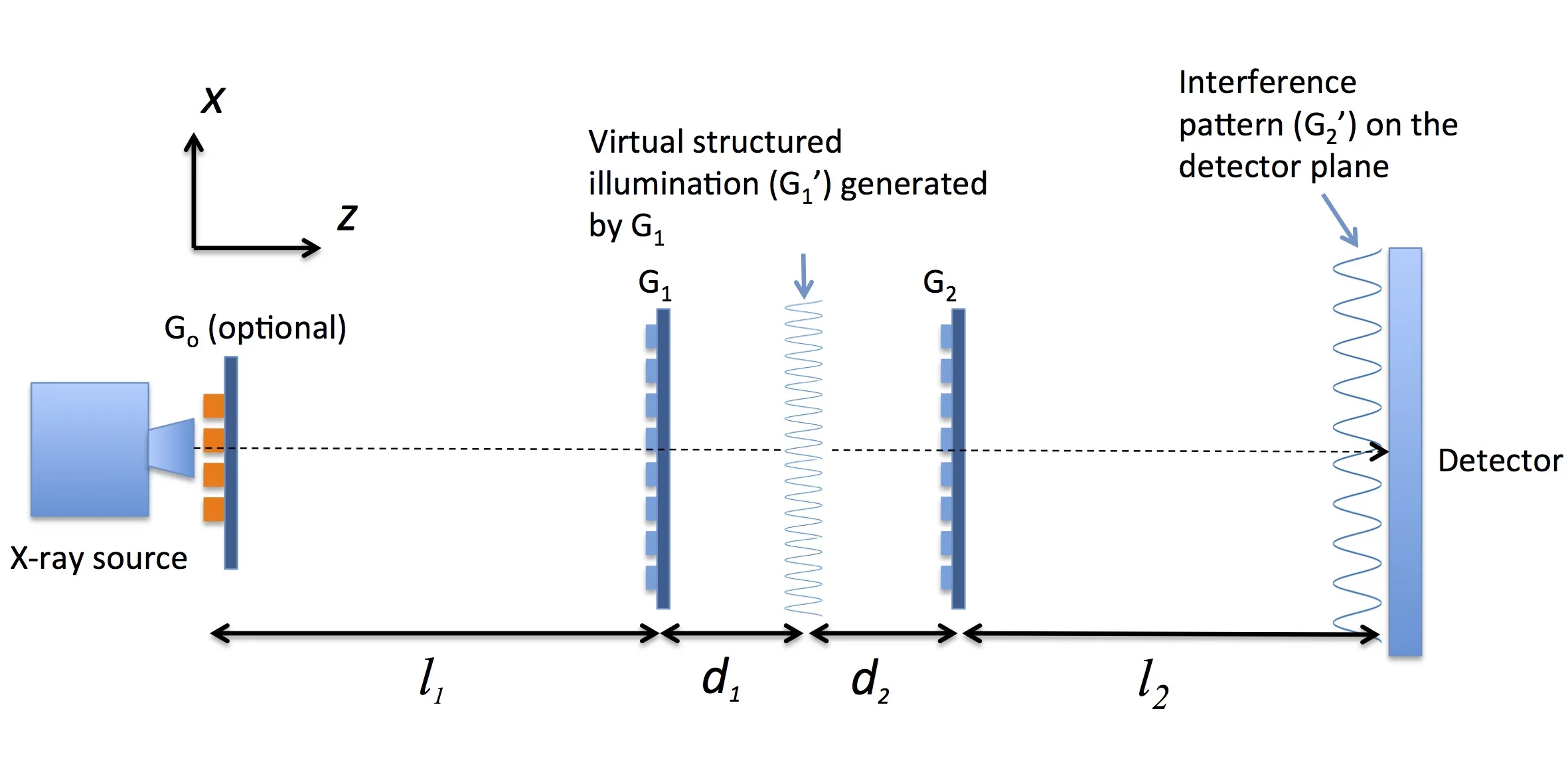
Dual Phase Grating Interferometer
Publications:
- Kagias. M, Wang Z, Jefimovs K, Stampanoni M,. APPLIED PHYSICS LETTERS 110, 014105 (2017)
Funding agencies: ERC Grant ERC-2012-StG 310005-PhaseX
Contact: Dr. Zhentian Wang, zhentian.wang@psi.ch, WBBA/212, +41-56-310-5819
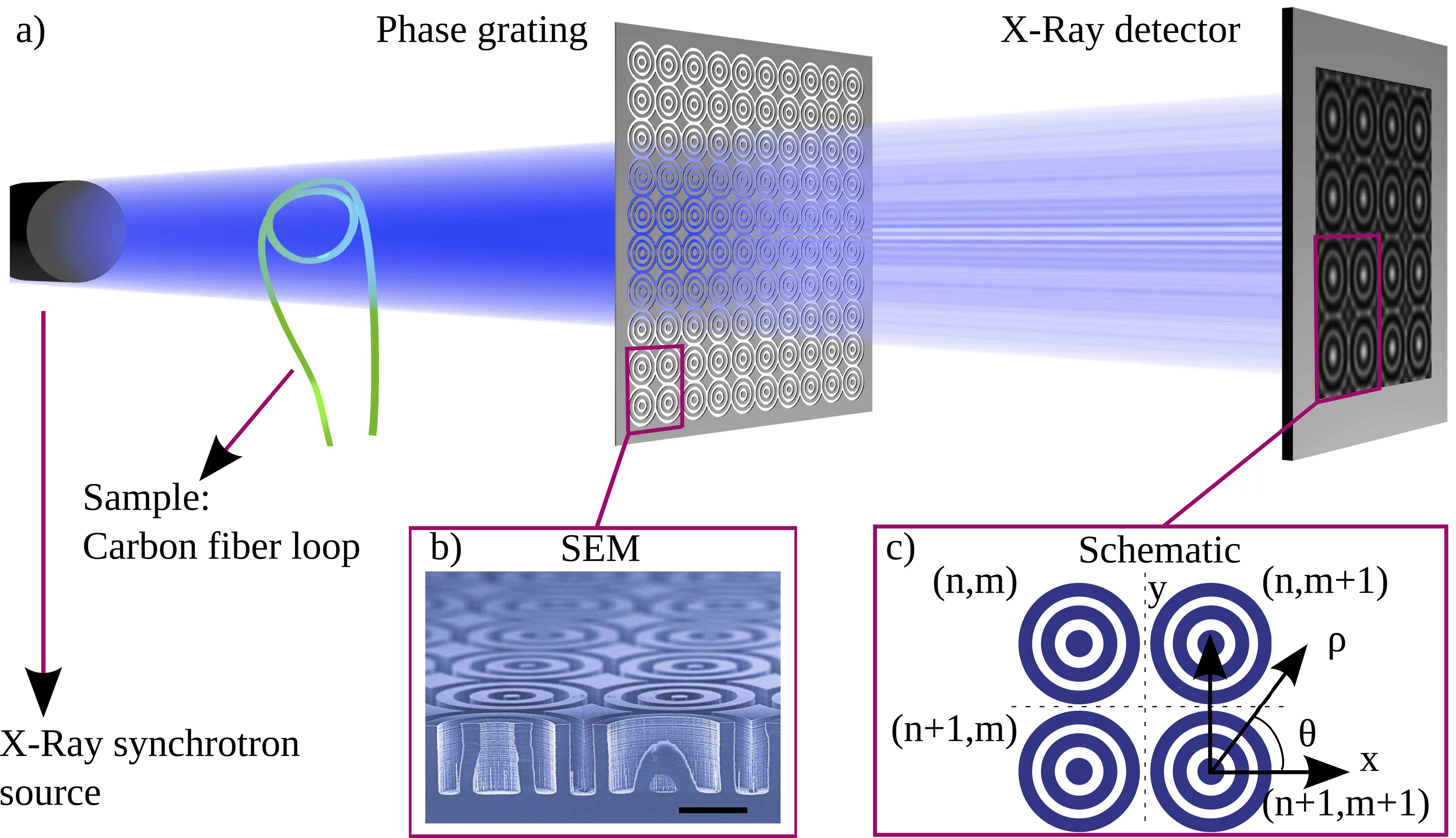
Omnidirectional Dark-Field Imaging with Circular Unit Cell Gratings
Publications:
- 2D-Omnidirectional Hard-X-Ray Scattering Sensitivity in a Single Shot Kagias. M, Wang Z, Villanueva-Perez P, Jefimovs K, Stampanoni M PHYSICAL REVIEW LETTERS 116, (2016). DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.116.093902
- Circular Unit Cell Gratings for X-ray Dark-Field Imaging Kagias. M, Pandeshwar A.,Wang Z, Villanueva-Perez P, Jefimovs K, Stampanoni M JOURNAL OF PHYSICS: CONFERENCE SERIES submitted
Funding agencies: ERC Grant ERC-2012-StG 310005-PhaseX
Contact: Dr. Zhentian Wang, zhentian.wang@psi.ch, WBBA/212, +41-56-310-5819
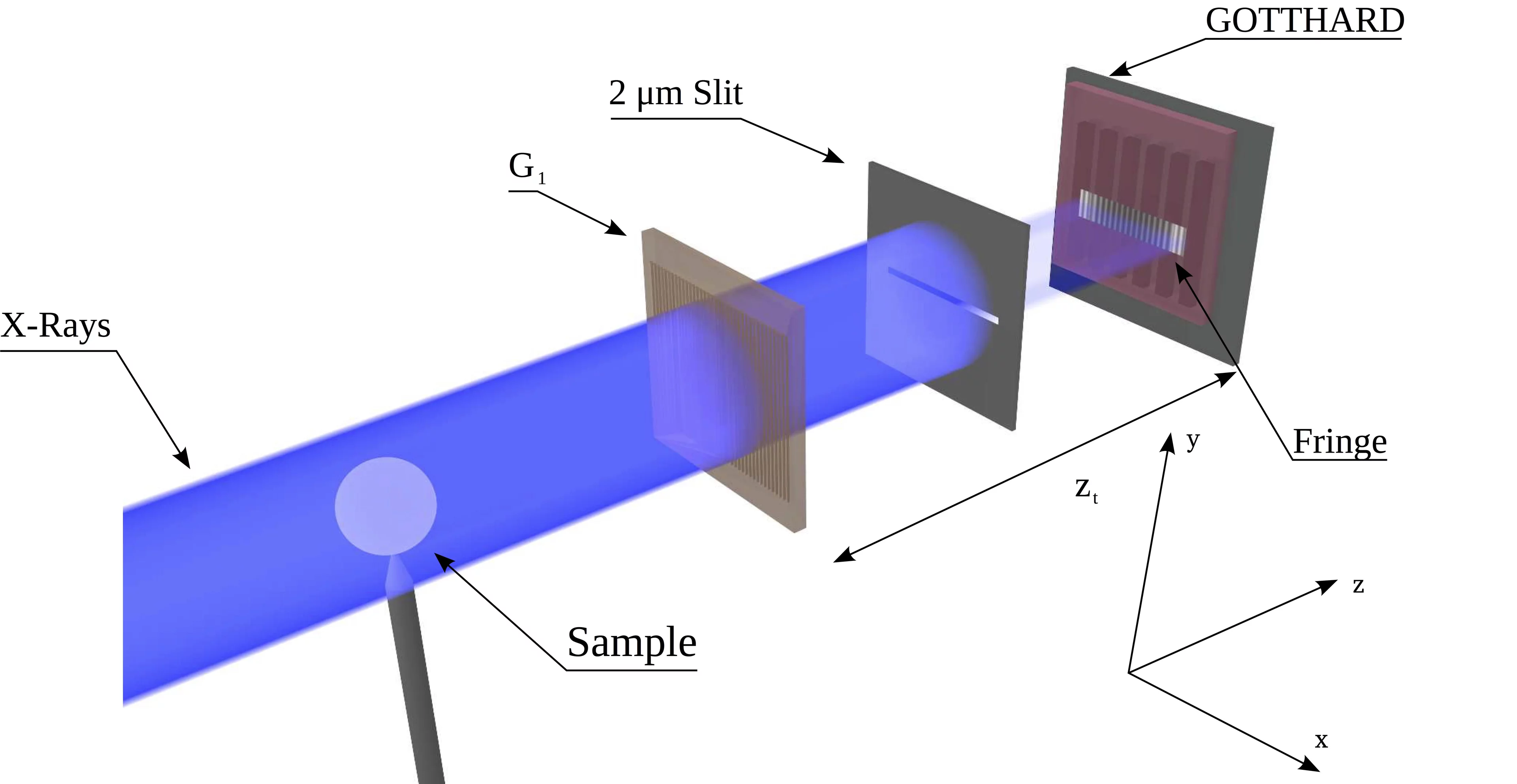
Single Shot Differential Phase Contrast Imaging with Single Photon Sensitive Detectors
Publications:
- Micrometer-resolution imaging using MÖNCH: towards G 2 -less grating interferometry Cartier S, Kagias M, Bergamaschi A, Wang Z, Dinapoli R, Mozzanica A, Ramilli M, Schmitt B, Brückner M, Fröjdh E, Greiffenberg D, Mayilyan D, Mezza D, Redford S, Ruder C, Schädler L, Shi X, Thattil D, Tinti G, Zhang J, Stampanoni M JOURNAL OF SYNCHROTRON RADIATION 23, - (2016). DOI: 10.1107/S1600577516014788
- Single shot x-ray phase contrast imaging using a direct conversion microstrip detector with single photon sensitivity Kagias M, Cartier S, Wang Z, Bergamaschi A, Dinapoli R, Mozzanica A, Schmitt B, Stampanoni M APPLIED PHYSICS LETTERS 108, 234102 (2016). DOI: 10.1063/1.4948584
Collaboration:
- SLS Detector Group, PSI, Switzerland
Funding agencies: ERC Grant ERC-2012-StG 310005-PhaseX
Contact: Dr. Zhentian Wang, zhentian.wang@psi.ch, WBBA/212, +41-56-310-5819
Differential phase contrast for X-ray tubes above 100 kVp
Publications:
- X-ray phase-contrast imaging at 100 keV on a conventional source, Thüring T, Abis M, Wang Z, David C, Stampanoni M, Scientific Reports, 10.1038/srep05198, 2014.
- A generalized quantitative interpretation of dark-field contrast for highly concentrated microsphere suspensions Gkoumas S, Villanueva-Perez P, Wang Z, Romano L, Abis M, Stampanoni M, Scientific Reports, 10.1038/srep35259, 2016
Funding agencies: ERC Grant ERC-2012-StG 310005-PhaseX
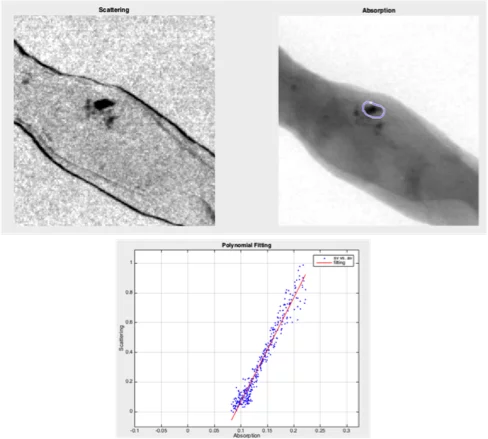
Ex-vivo study of suspicious microcalcifications in breast tissue biopsies
Publications:
[1] The first analysis and clinical evaluation of native breast tissue using differential phase-contrast mammography Stampanoni M, Wang Z, Thuering T, et al,, Invest. Radiol. 46(12):801, 2011
[2] Non-invasive classification of microcalcifications with phase-contrast X-ray mammography Wang Z, Hauser N, Singer G, et al., Nat. Commun. 5:3797m 2014
Funding agencies:
- ERC Grant ERC-2012-StG 310005-PhaseX
Contact: Dr. Zhentian Wang, zhentian.wang@psi.ch, WBBA/212, +41-56-310-5819
Feasibility study of an X-ray phase contrast breast CT scanner
Funding agencies:
- ERC-2012-StG 310005-PhaseX
Contact: Dr. Zhentian Wang, zhentian.wang@psi.ch, WBBA/212, +41-56-310-5819
Micro and Nano Fabrication
Fabrication of gratings for phase contrast X-ray imaging
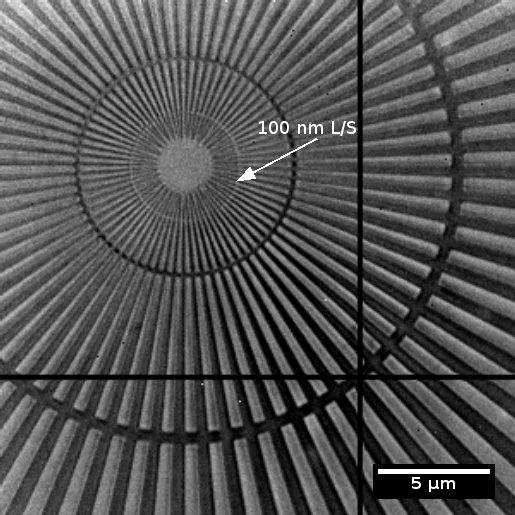
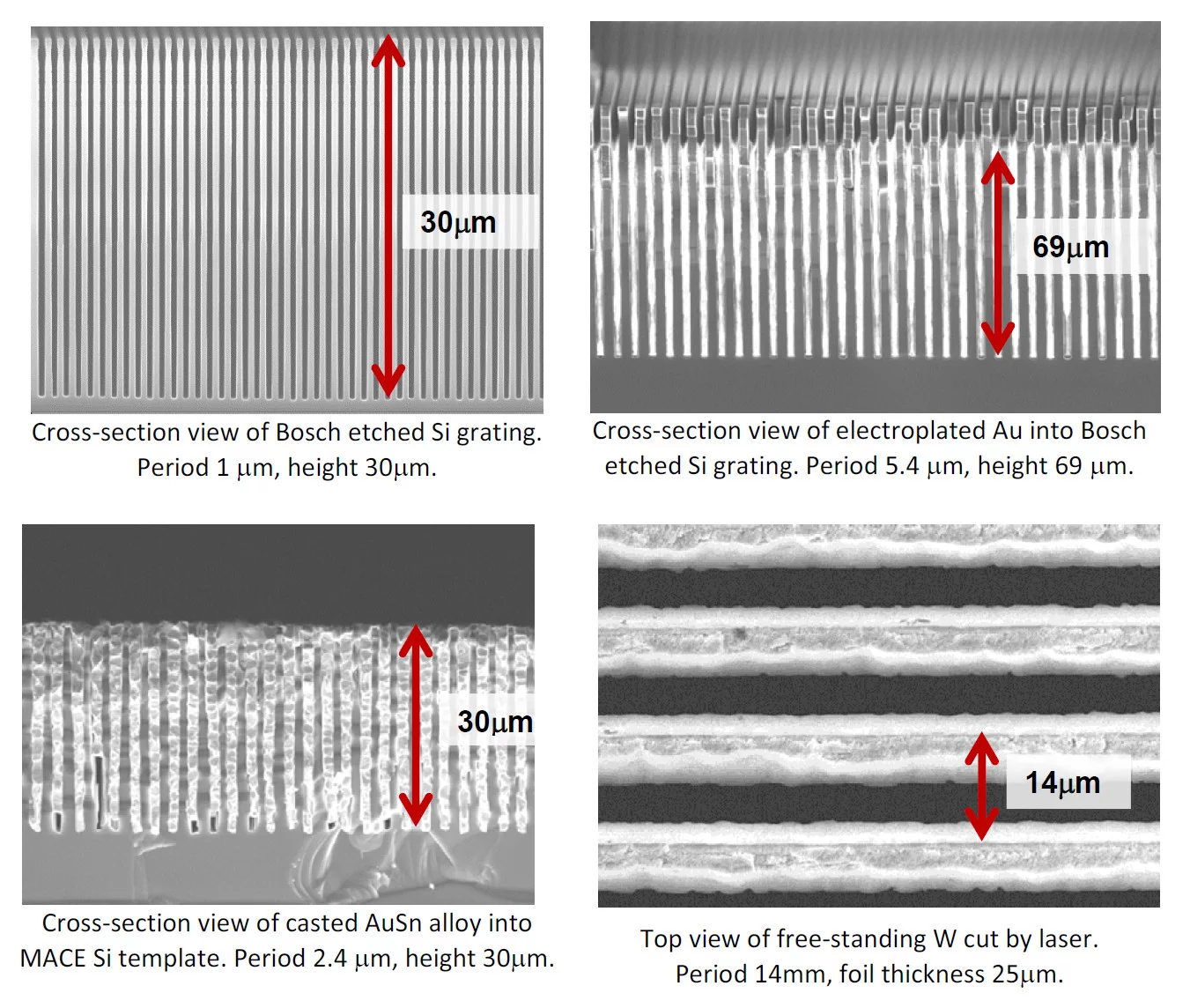
Grating interferometry is proved to be one of the most promising techniques for phase contrast X-ray imaging. Typical grating interferometer consists of a phase shifting grating (G1), analyzing grating (G2) and an optional absorbing source grating (G0). Usually, required grating period is in a range of few microns. The height of the lines of G1 grating should provide a certain phase shift, while the height of the grating lines of G2 should be sufficient to suppress radiation of defined energy. In both cases, structures with heights of tens (or even hundreds) of micrometers are required. However, the realization of structures with so high aspect ratios yet having sufficient quality over the large area is demanding. We develop fabrication procedures which enable such gratings. We produce G1 gratings in Si by reactive ion etching using Bosch technique [1] or by metal assisted chemical etching [2]. The absorbing G0 and G2 gratings are produced by filling Si templates with metal utilizing electroplating, metal casting [3] or atomic layer deposition [4]. Larger structures can alternatively be produced by laser cutting in W foils.
Publications:
- K. Jefimovs et al., “High aspect ratio silicon structures by Displacement Talbot lithography and Bosch etching“ Proc. SPIE (submitted 2017).
- L. Romano et al., Self-assembly nanostructured gold for high aspect ratio silicon microstructures by metal assisted chemical etching, RSC Advances 6 (2016) 16025-16029.
- L. Romano et al., “High aspect ratio metal microcasting by hot embossing for X-ray optics fabrication“ Microelectron. Eng. 17 (2017) 6-10.
- K. Jefimovs et al., “Zone-Doubling Technique to Produce Ultrahigh-Resolution X-Ray Optics” Phys. Rev. Lett. 99 (2007) 264801.
Collaboration:
- Dr. Rolf Brönnimann, EMPA Dübendorf
Contacts: Dr. Konstantins Jefimovs, konstantins.jefimovs@psi.ch, WBBA/220, +41 56 310 3713 * Dr Lucia Romano, lucia.romano@psi.ch, WBBA/220, +41 56 310 5688
![Several examples of tomography reconstructed inner page portions revealing words and sentences (top), compared to visible pictures (bottom) [4].](/sites/default/files/styles/primer_full_image_xxl/public/import/x-ray-tomography-group/ResearchEN/project4_patera.png.webp?itok=4_5Wpner)