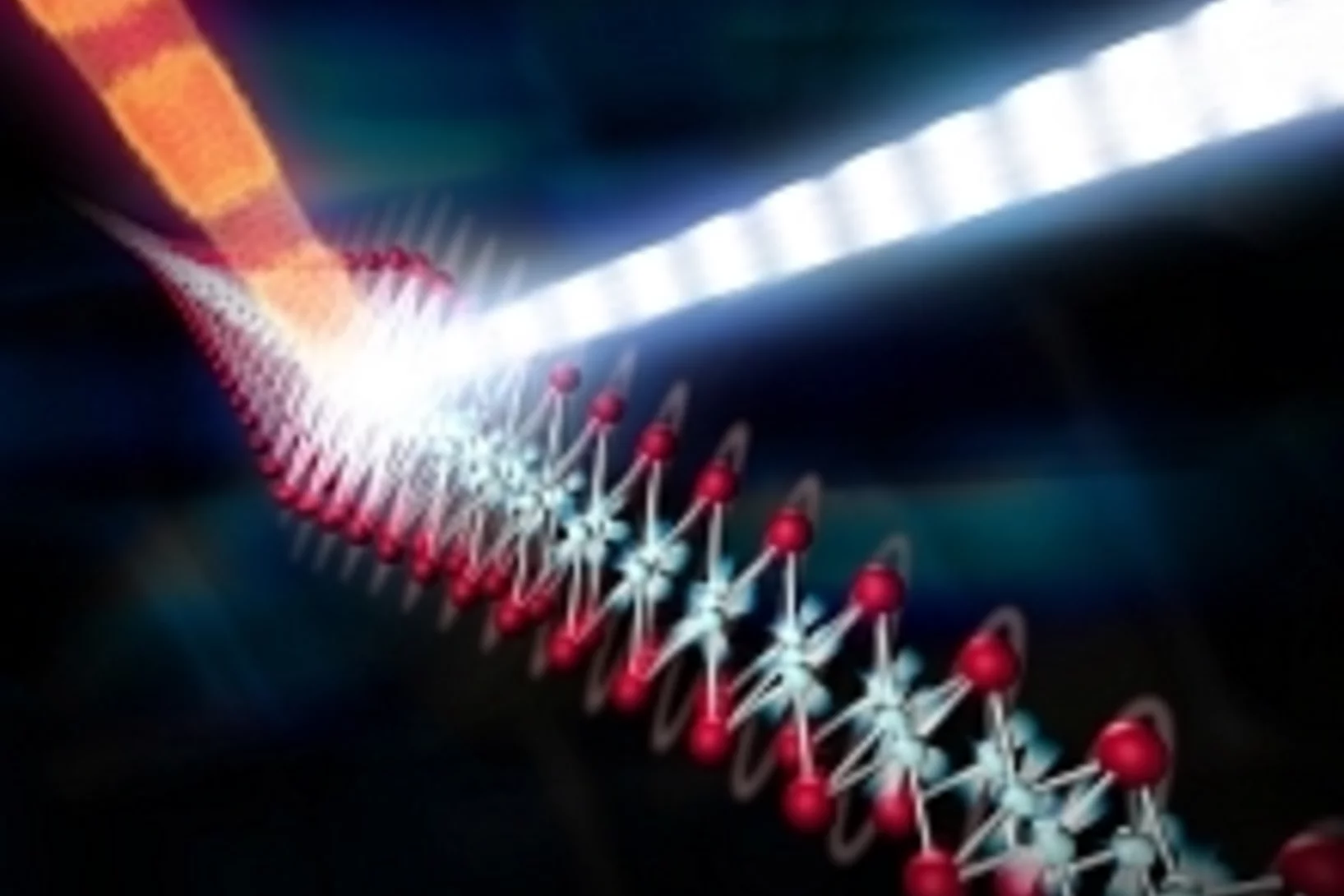
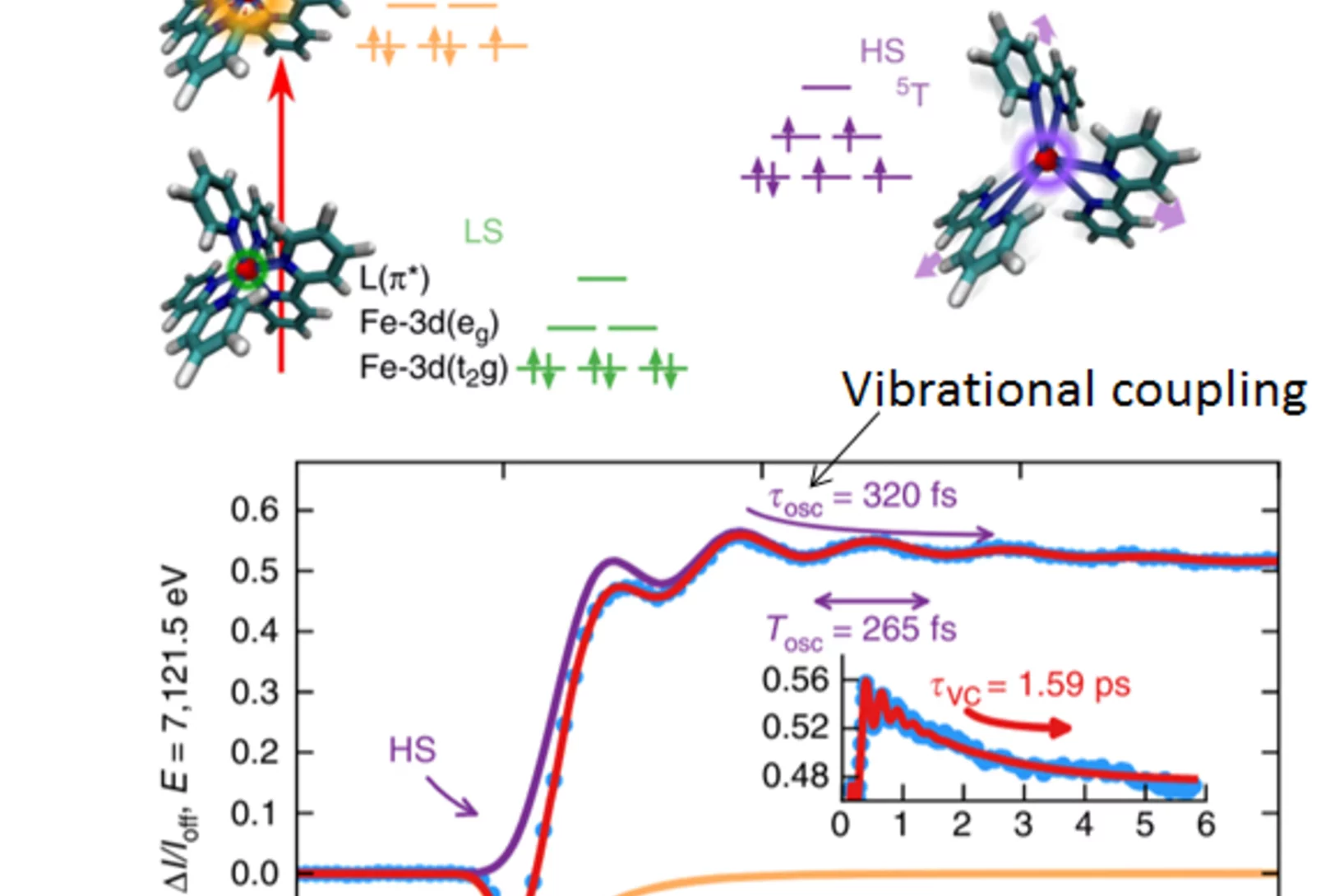
Scientists get first direct look at how electrons ‘dance’ with vibrating atoms
Scientists at the SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory and Stanford University - one of the leading authors, Simon Gerber, has in the meantime relocated to PSI - have made the first direct measurements, and by far the most precise ones, of how electrons move in sync with atomic vibrations rippling through an quantum material, in the present study an unconventional superconductor, as if they were “dancing" to the same beat.
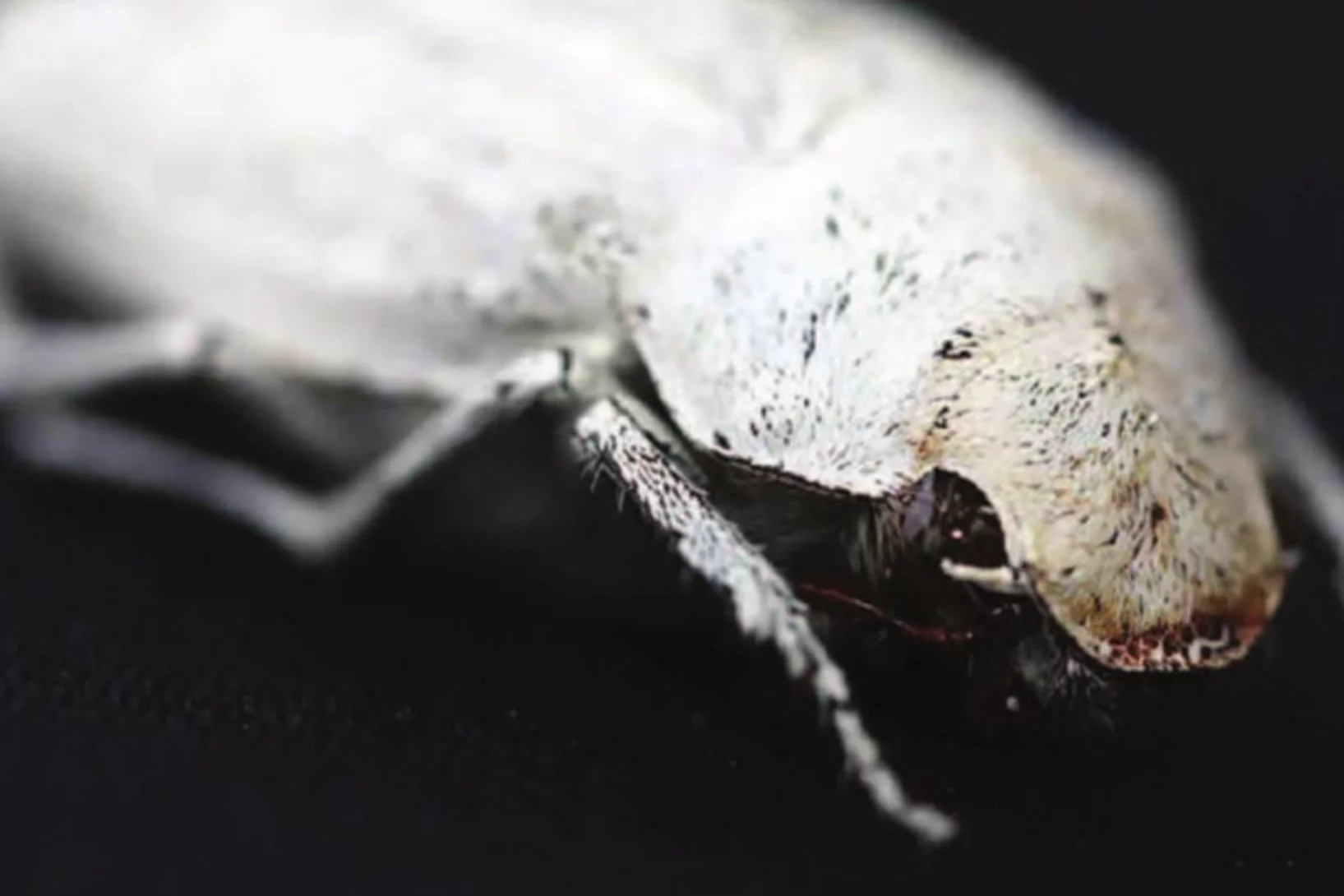
Photonic structure of white beetle wing scales: optimized by evolution
A very thin layer on this beetle’s wings exhibits a complicated structure on the nanoscale that gives them a bright white color. X-ray nanotomography acquired at the Swiss Light Source provides a faithful image of this structure in three dimensions with which scientists can confirm its evolutionary optimization: just enough material for an efficient reflection of white light.
Isomer-Selective Generation and Spectroscopic Characterization of Biofuel Intermediates
Online combustion analysis relies heavily on spectral data to detect reactive intermediates isomer-selectively to establish e.g. kinetic flame models. Due to the difficulty to generate these species cleanly, spectral data are rather scarce. Here we report on the selective generation of three picolyl radical isomers (C5H4N-CH2*) by deamination of aminomethylpyridines. Picolyl radicals are relevant in biofuel combustion, and could now be characterized by threshold photoelectron spectroscopy using synchrotron radiation. Vibrationally resolved bands and distinct ionization energies allow for isomer-specific detection of these elusive species in complex environments and permit us to explore new avenues in soot- and NOx formation kinetics.
Observing switching of Molecules using Free Electron Lasers
Free electron lasers (FELs) like SwissFEL help scientists to understand the mechanisms that switch properties of materials which are the basis for functions in electronics, solar cells, chemistry and biology. By using ultrashort X-ray pulses it becomes possible to visualize the ultrafast rearrangements of electrons and atoms that enable the properties to switch in molecules or crystals.
Towards understanding of human betacoronavirus HKU1 life cycle
Researchers from China and USA join forces with Swiss Light Source (SLS) macromolecular crystallography (MX) beamline scientists in a study, which aims at understanding an important step in the life cycle of the human betacoronavirus HKU1.
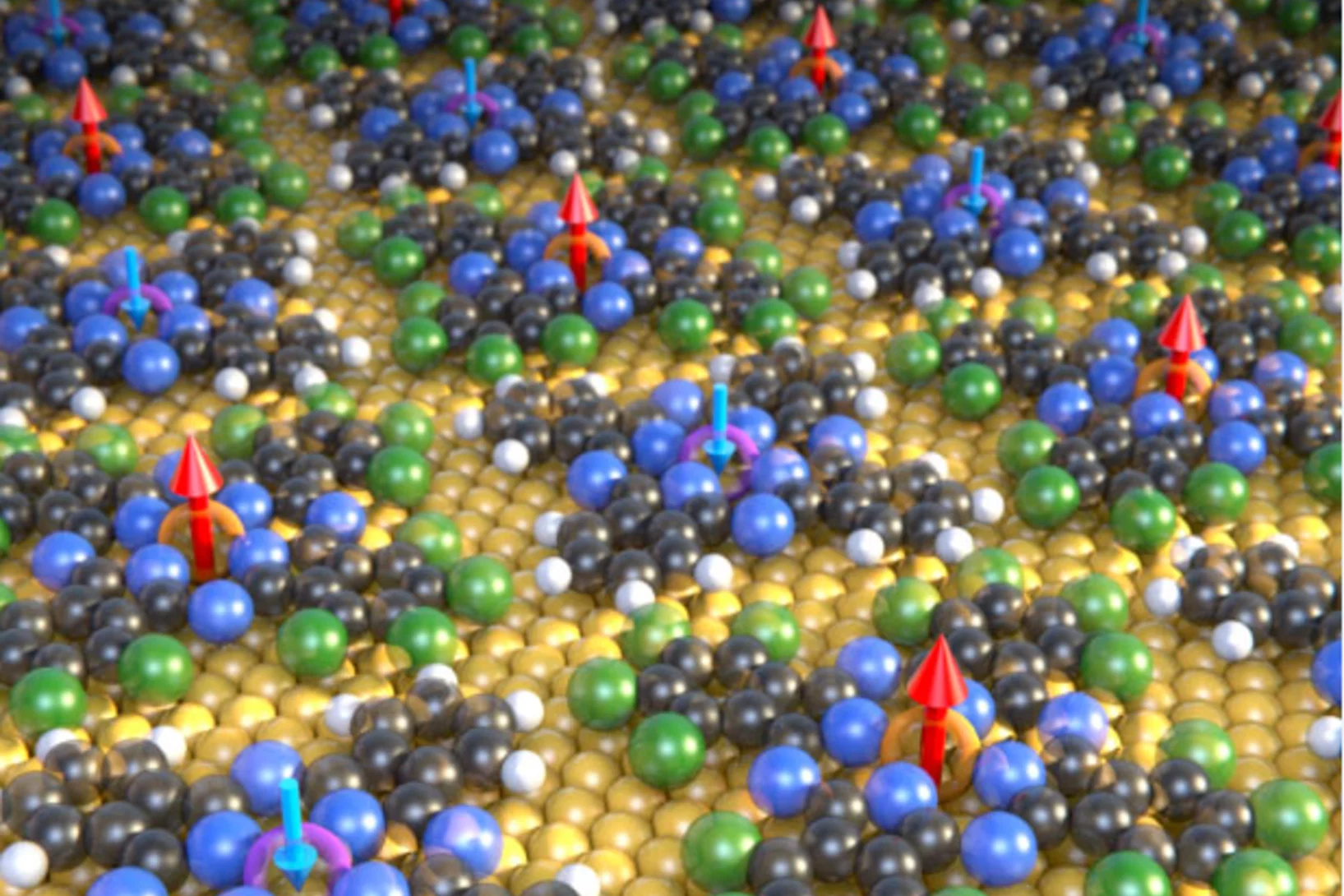
Wafer-thin Magnetic Materials Developed for Future Quantum Technologies
For the first time, researchers have produced a wafer-thin ferrimagnet, in which molecules with different magnetic centers arrange themselves on a gold surface to form a checkerboard pattern. Scientists at the Paul Scherrer Institute, in collaboration with their research partners, published the findings in the journal Nature Communications.
First lasing at a wavelength of 4.1 nm
The electron beam energy of SwissFEL was recently increased to above 900 MeV by successfully bringing two new accelerating modules into operation. This allowed SwissFEL to produce laser radiation for the first time in the soft x-ray regime with a photon wavelength of 4.1 nm. During the next months, the electron beam energy will be progressively further increased with the goal of enabling first user experiments at a wavelength of around 0.5 nm towards the end of this year.
La radiographie en 3D permet de visualiser les moindres détails d’une puce informatique
Des chercheurs de l’Institut Paul Scherrer PSI ont réalisé des radiographies détaillées en 3D d’une puce informatique usuelle. Dans le cadre de leur expérience, ils ont analysé une petite portion de puce qu’ils avaient préalablement découpée. Durant la mesure, cet échantillon est resté intact. Pour les fabricants, déterminer si la structure de leurs puces est conforme aux normes représente un défi. Ces résultats constituent donc une possibilité d’application importante pour un procédé spécifique de tomographie à rayons X que les chercheurs du PSI développent depuis quelques années.
Interlaced zone plates push the resolution limit in x-ray microscopy
A novel type of diffractive lenses based on interlaced structures enable x-ray imaging at resolutions below 10 nm. The fabrication method and the test results of these novel x-ray lenses have been published in the journal Scientific Reports.
De nouvelles approches des réactions chimiques grâce aux nanotechnologies
80 % des produits de l’industrie chimique sont fabriqués par recours à la catalyse. Ce procédé est également indispensable dans la conversion énergétique et l’épuration des gaz d’échappement. L’industrie teste donc continuellement de nouvelles substances et de nouvelles configurations susceptibles de déboucher sur de nouveaux procédés catalytiques plus performants. Des chercheurs de l’Institut Paul Scherrer PSI à Villigen et de l’ETH Zurich ont à présent développé une méthode qui permet d’améliorer nettement la précision de tels essais, ce qui devrait accélérer la recherche de solutions optimales.
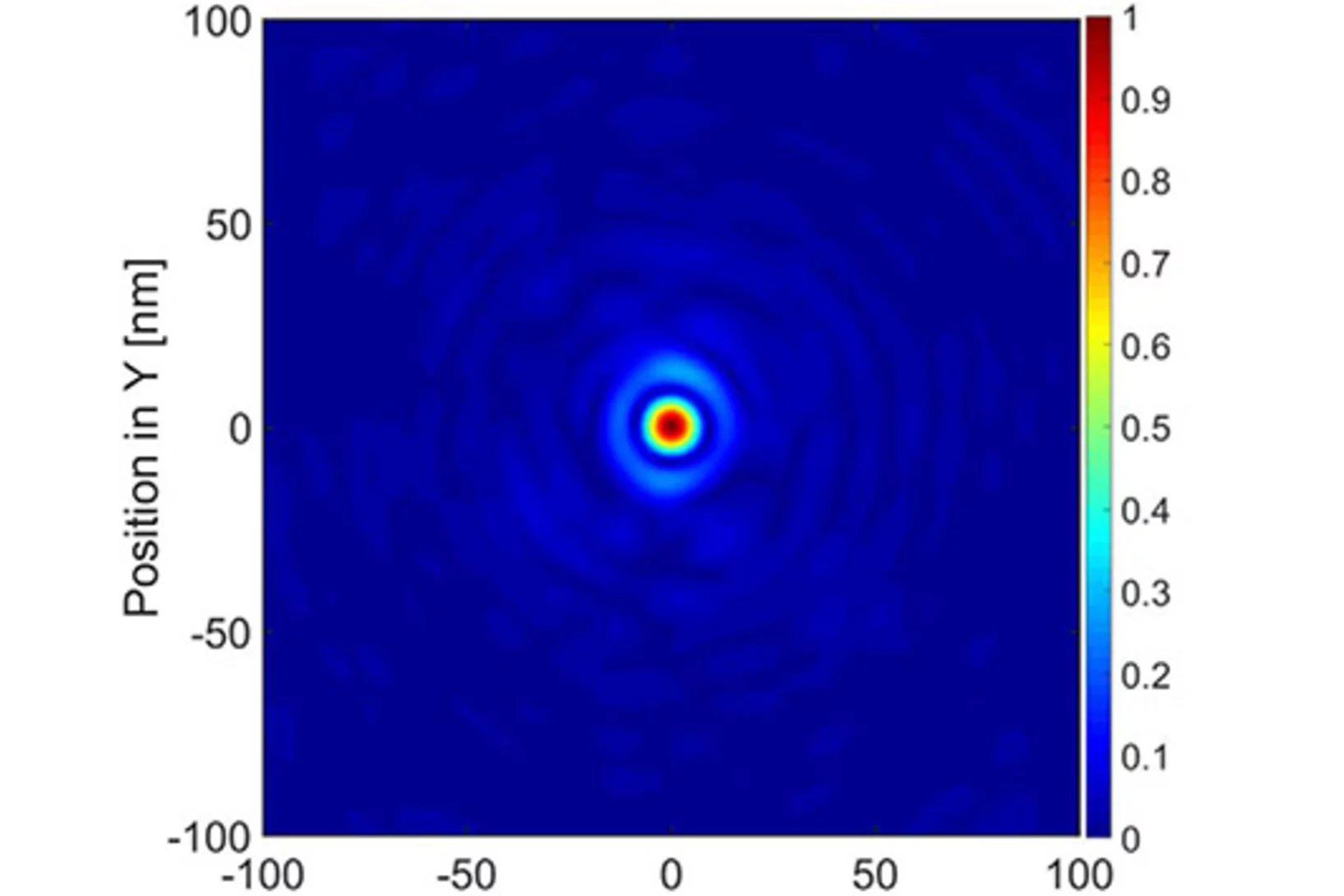
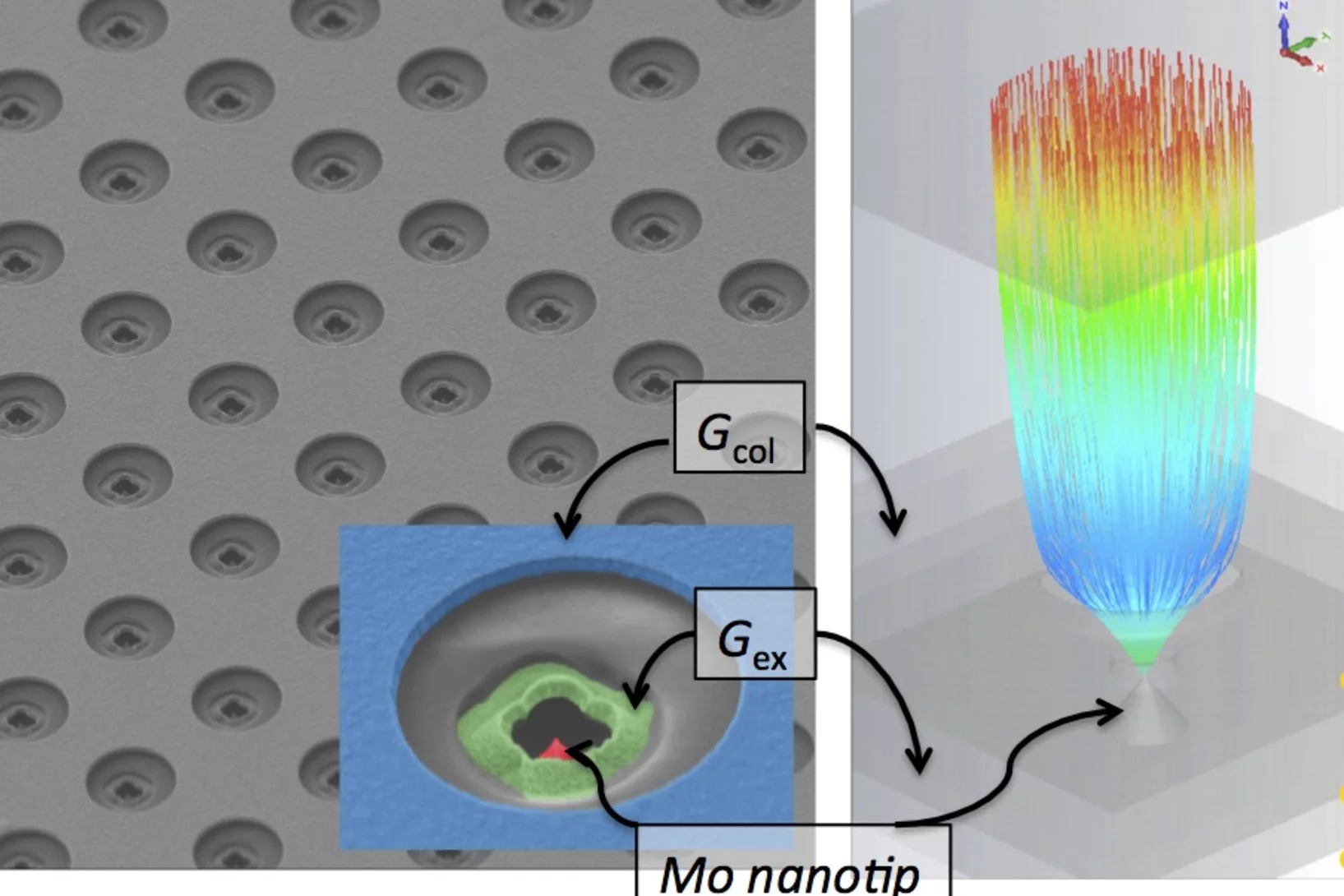
Can a metal nanotip array device be a low-emittance and coherent cathode?
A nanofabricated low emittance field emitter array cathode was demonstrated for the first time, and successfully applied to observe the low-energy electron diffraction from suspended monolayer graphene. The work has an impact on the future development of compact X-ray free electron lasers, THz/RF vacuum electronic sources, and ultrafast electron imaging and diffraction experiments.
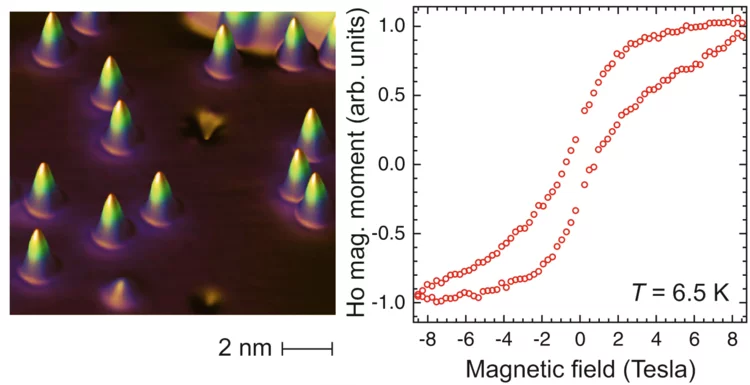
The Smallest Magnet
Single holmium atoms adsorbed on few monolayers of magnesium oxide are extraordinarily stable magnets. They retain a significant fraction of their magnetization when the external magnetic field is switched off. This has been shown recently in a study combining x-ray magnetic circular dichroism performed at the Swiss Light Source (SLS) and at the European Synchrotron Radiation Facility (ESRF) as well as scanning tunneling microscopy. The results open perspectives of storing and processing information at ultrahigh density.
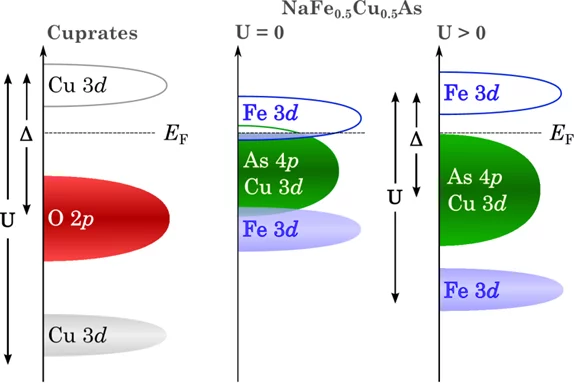
Novel insulating phase in iron-pnictide materials
The first example of an insulating phase which is close to the superconducting phase in an iron-pnictide system has been recently observed in heavy Cu-doped NaFe1-xCuxAs (x > 0.3). A combined study by angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy (ARPES) and density functional theory (DFT) calculations revealed that on-site Coulomb repulsion and enhanced Hund’s rule coupling are responsible for the insulating behavior. The results show that the insulating phase in NaFe0.5Cu0.5As resembles the situation in the parent compounds of the high-Tc cuprate superconductors.
Conducteur d'électricité ou isolant, au choix
L’oxyde de néodyme-nickel est un matériau qui, suivant la température, est soit un métal, soit un isolant. Cette transition peut être commandée par l’application d’une tension électrique, ce qui fait de ce matériau un candidat potentiel pour les transistors dans les appareils électroniques modernes. Des chercheurs à l’Institut Paul Scherrer PSI ont utilisé un développement perfectionné et sophistiqué de la diffusion de rayons X et réussi à saisir la cause de cette transition: la réorganisation des électrons autour des atomes d’oxygène.
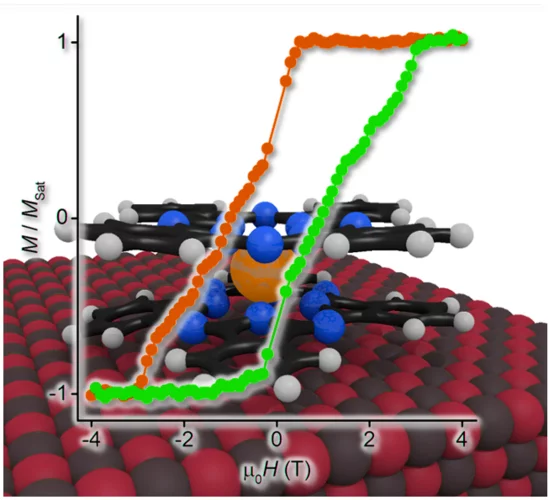
Magnesium Oxide Boosts the Hysteresis of Single-Molecule Magnets
Researchers from PSI and EPFL have demonstrated that the magnetization hysteresis and remanence of TbPc2 single-molecule magnets drastically depends on the substrate on which they are deposited. If a few atomic layers thick magnesium oxide film grown on a silver substrate is used, a record wide hysteresis and record large remanence can be obtained. Single-molecule magnets are attractive for molecular spintronics applications such as information processing or storage.
Shedding light on the origins of high-Tc superconductivity in bismuth oxides
Researchers have overcome a number of challenges in order to employ an advanced probe in the study of an unusual material, barium bismuth oxide (BaBiO3) – an insulating parent compound of a family of high-temperature superconductors known since the late 80s. In order to finally realize the experiments, the researchers grew and studied thin films of the material completely in situ under ultrahigh vacuum conditions. The results show that superconductivity in bismuth oxides emerges out of a novel insulating phase, where hole pairs located on combinations of the oxygen orbitals are coupled with distortions of the crystal lattice.
Therapeutic drug monitoring in sub-nanoliter volumes
A promising system for painless and minimally-invasive therapeutic drug monitoring has been demonstrated. The proposed device combines biofunctionalized hollow microneedles with an optofluidic system to measure drug concentrations in volumes as small as 0.6 nL.
Controlling Quantum States Atom by Atom
A method to precisely alter the quantum mechanical states of electrons within an array of quantum boxes has been developped by an international consortium also including PSI. The method can be used to investigate the interactions between various types of atoms and electrons, which is essential for future quantum technologies.
Expérience dans une goutte en lévitation
La structure exacte des protéines est normalement déterminée au PSI par la technique de diffraction des rayons X. Deux scientifiques du PSI viennent de l’améliorer de façon astucieuse: au lieu d’immobiliser les protéines, ils les ont étudiées dans une goutte de liquide en lévitation.
How does food look like on the nanoscale?
The answer to this question could save food industry a lot of money and reduce food waste caused by faulty production. Researchers from the University of Copenhagen and the Paul Scherrer Institut have obtained a 3D image of food on the nanoscale using ptychographic X-ray computed tomography. This work paves the way towards a more detailed knowledge of the structure of complex food systems.
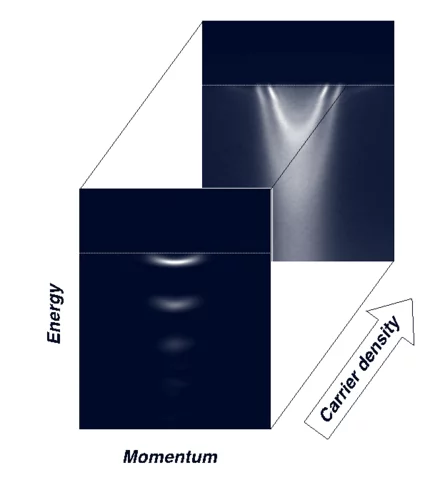
Tailoring Novel Superconductivity
The Angle Resolved Photoemission Spectroscopy (ARPES) measurements performed on 2DEL at STO surface revealed that, at low carrier density, electrons are always accompanied by a quantized dynamic lattice deformation. Together with the electron, these phonon-cloud formed a new composite quasiparticle called Fröhlich polaron.
Researchers find key to zinc rich plants to combat malnutrition
The diet in many developing countries is lacking zinc, but researchers have just solved the riddle of how to get more zinc into crop seeds. The discovery has been published in Nature Plants, and the research was led by University of Copenhagen.By Johanne Uhrenholt Kusnitzoff
Watching lithium move in battery materials
In order to understand limitations in current battery materials and systematically engineer better ones, it is helpful to be able to directly visualize the lithium dynamics in materials during battery charge and discharge. Researchers at ETH Zurich and Paul Scherrer Institute have demonstrated a way to do this.
Une nouvelle particule qui pourrait servir de base à de l’électronique économe en énergie
Le fermion de Weyl, découvert seulement l’an dernier, se déplace pratiquement sans résistance à l’intérieur de certains matériaux. Des chercheurs montrent à présent une voie possible pour l’utiliser dans des composants électroniques.
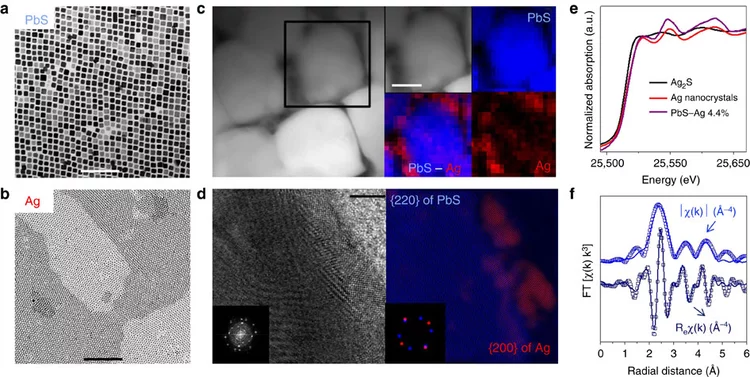
High-performance thermoelectric nanocomposites from nanocrystal building blocks
Using an assembly of colloidal nanocrystals a Ag-PbS nanocomposite was produced with increased thermoelectic figures of merit up to 1.7K at 850 K. EXAFS spectroscopy at the Ag K-edge was essential to show that Ag does not dissolve in PbS nanoparticles but preserved the individual nanodomains. This reduces the PbS intergrain energy barriers for charge transport
Ralentissement du flux électrique peut montrer la voie vers des ordinateurs économes en énergie
Les ordinateurs et les autres appareils électroniques représentent aujourd’hui une part considérable de la consommation d’énergie, une part dont il est pratiquement impossible de modifier l’importance avec les technologies actuellement utilisées. Les puces électroniques qui prendront place dans les appareils économes en énergie de demain devront donc être composées de matériaux innovants. De nouveaux résultats de recherche indiquent une voie possible comment on peut obtenir ces matériaux.
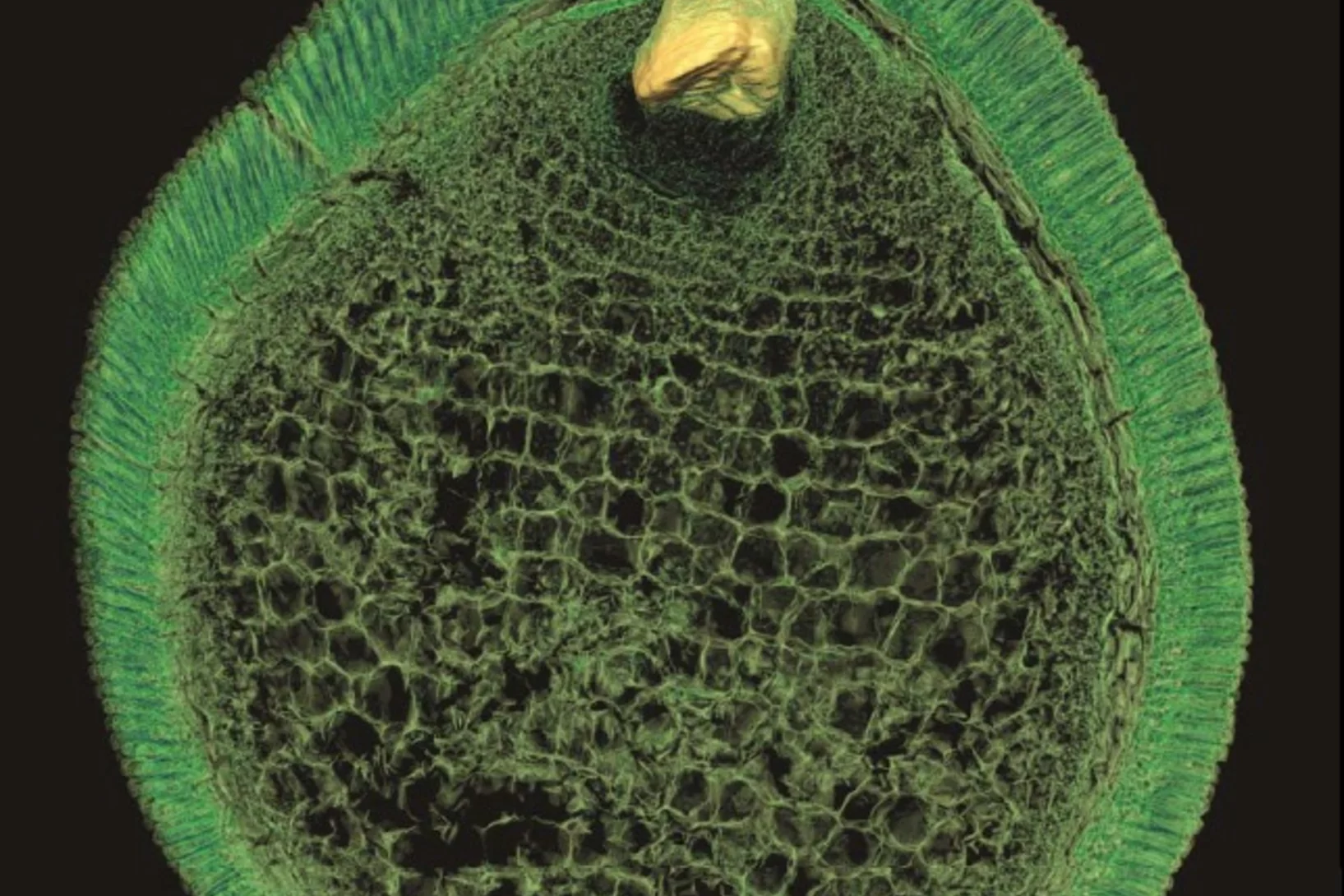
Preserved Embryos Illustrate Seed Dormancy in Early Angiosperms
The discovery of exceptionally well-preserved, tiny fossil seeds dating back to the Early Cretaceous corroborates that flowering plants were small opportunistic colonizers at that time, according to a new Yale-led study.
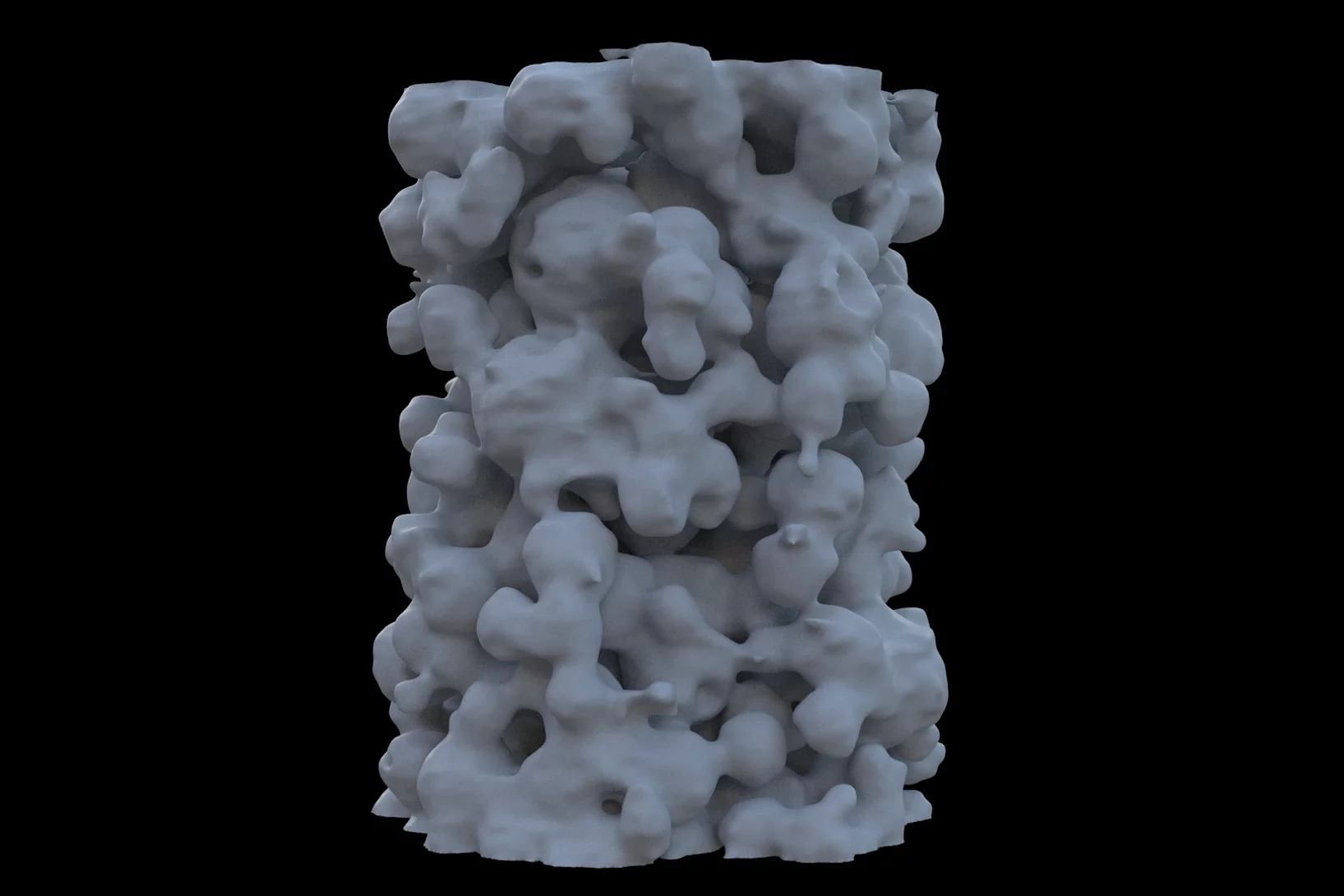
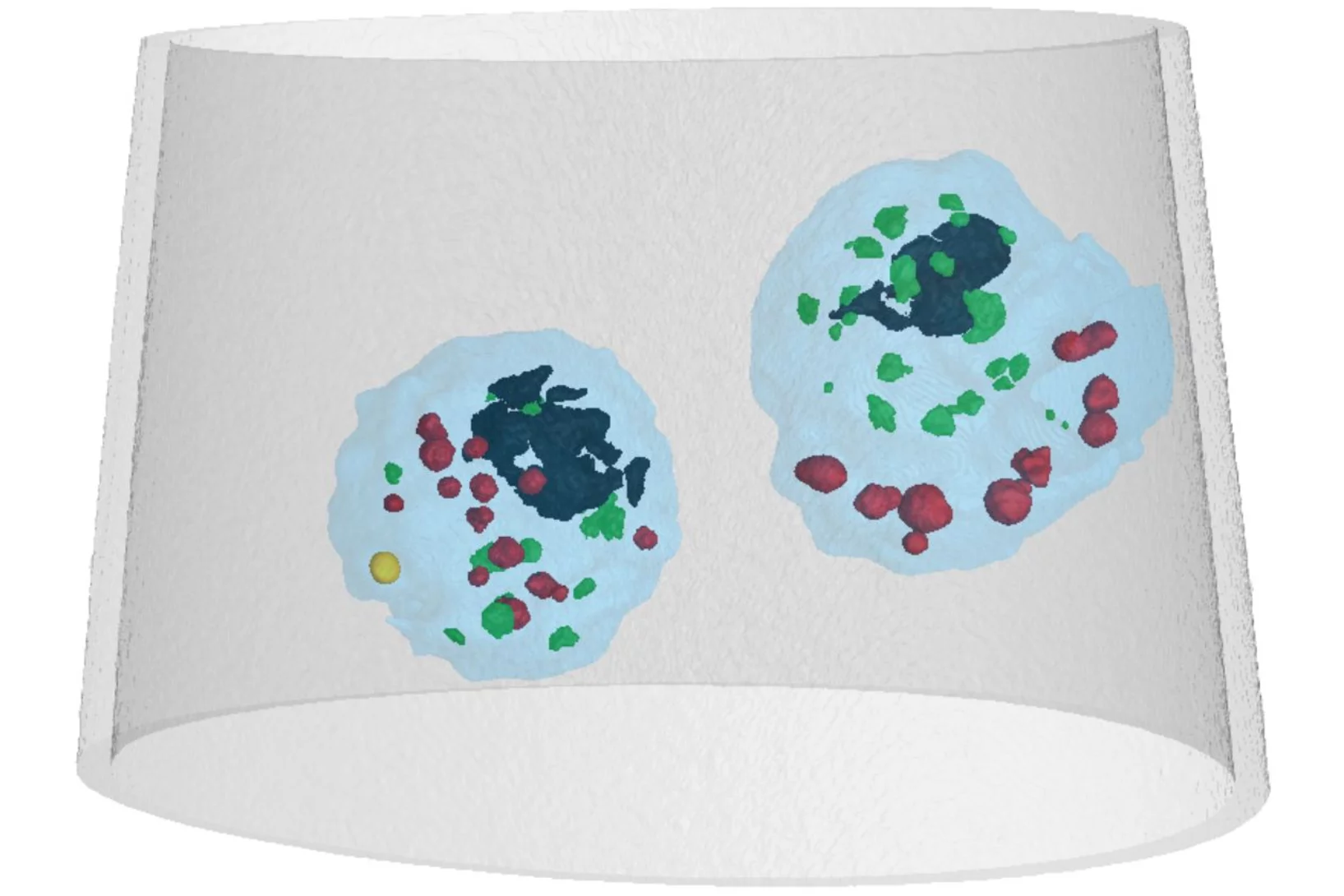
Mass density distribution of intact cell ultrastructure
The determination of the mass density of cellular compartments is one of the many analytical tools that biologists need to unravel the extremely complex structure of biological systems. Cryo X-ray nanotomography reveals absolute mass density maps of frozen hydrated cells in three dimensions.
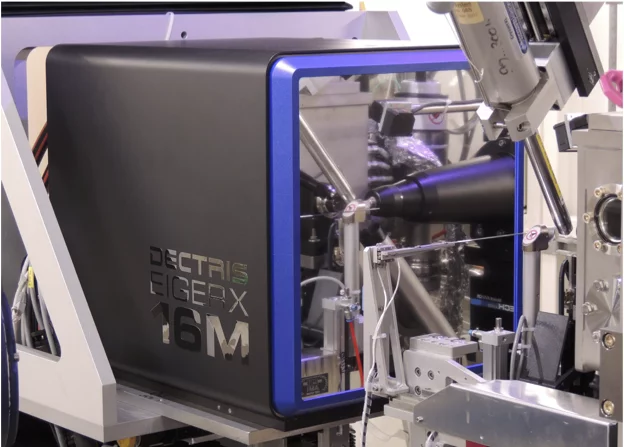
First EIGER X 16M in operation at the Swiss Light Source
The macromolecular crystallography beamline X06SA at the Swiss Light Source, a synchrotron operated by Paul Scherrer Institute, is the first one in the world to upgrade its detector to an EIGER X 16M.
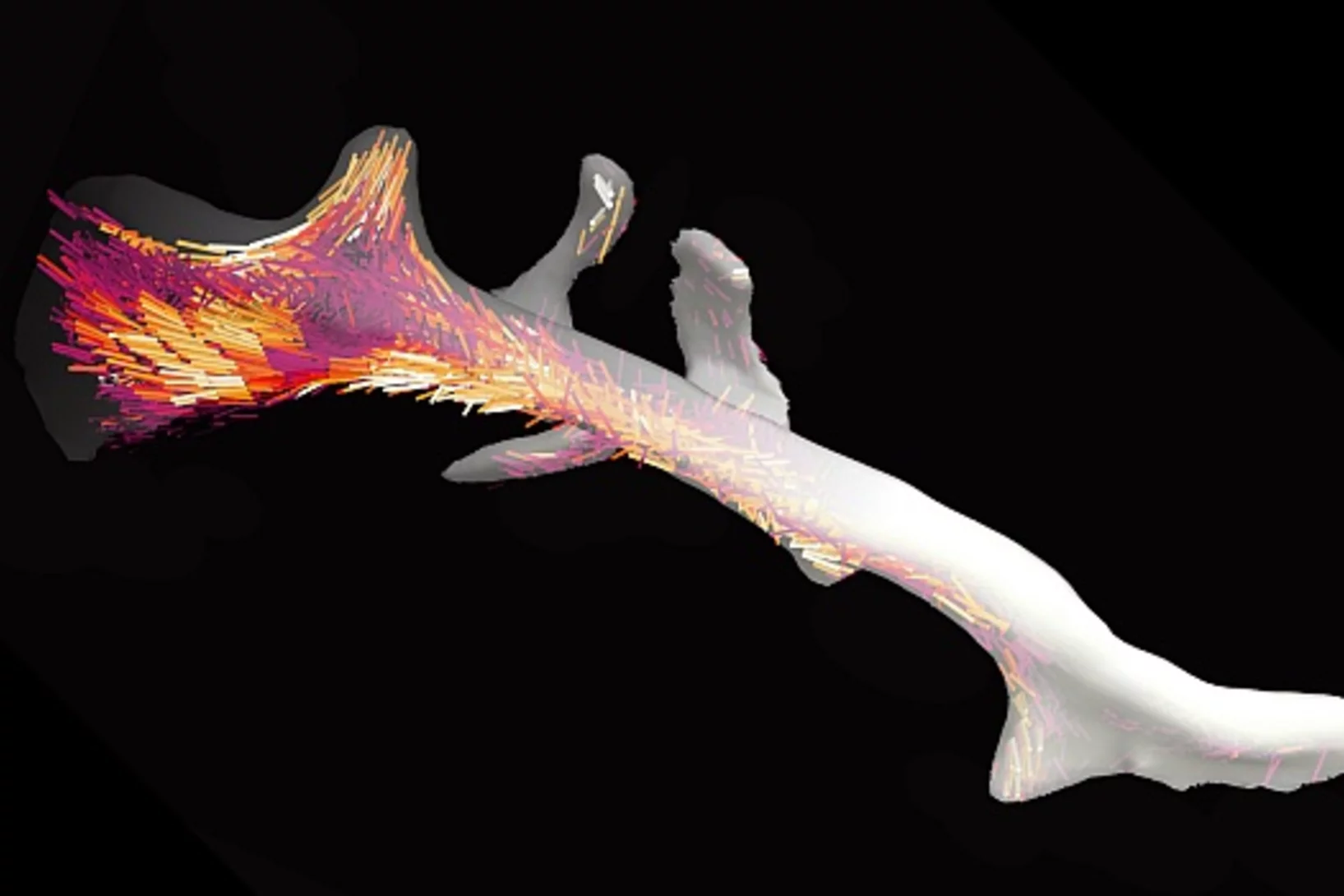
La nanostructure d’un os dévoilée en 3D
Les os sont composés de minuscules fibres, à peu près mille fois plus fines qu’un cheveu humain. Avec un nouveau type de méthode d’analyse informatique des chercheurs de l'Institut Paul Scherrer PSI étaient en mesure de déterminer pour la première fois l’agencement local et l’orientation de la nanostructure à l’intérieur d’un fragment d’os.