Here you find current and previous news from the PSI Center for Neutron and Muon Sciences.
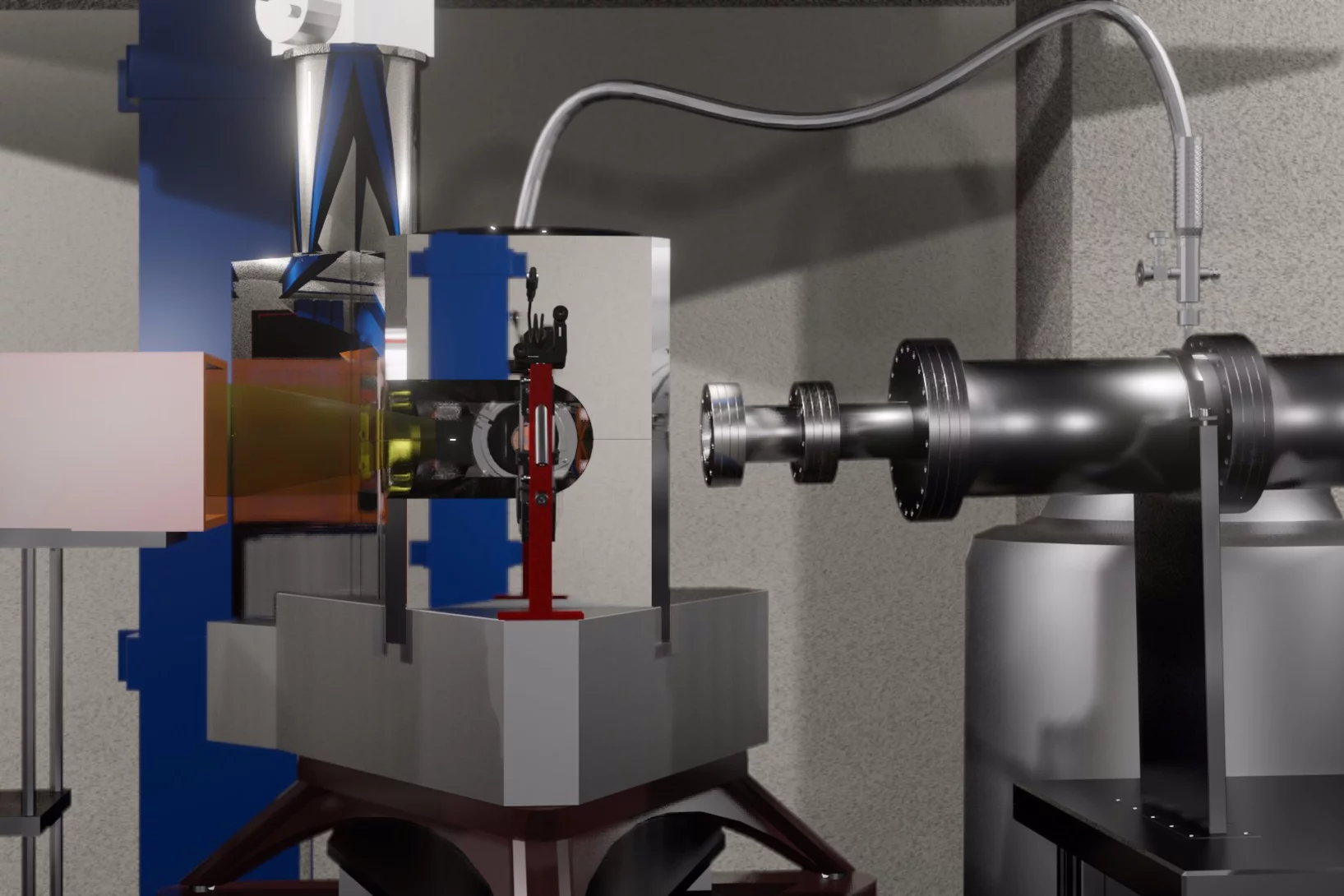
Take a flight through ESTIA
PSI is entirely responsible to build the polarised neutron reflectometer ESTIA at the European Spallation Source ESS in Lund, Sweden. The lead ESTIA scientist Artur Glavic (LNS/NUM) has now simulated a virtual tour of the neutrons travelling through the instrument from the focusing neutron guide to the detector.
PSI hosting meeting of the LENS working group on technology development and operation
On October 1 and 2, the Laboratory of Neutron and Muon Instrumentation (LIN) hosted the first meeting of the working group on “Synergies in Technology Development and Operation” of the League of Advanced European Neutron Sources, LENS, to kick off developments aimed at creating a new generation of neutron technology.
Visit of ESS Council to Switzerland
On 24 September the Paul Scherrer Institut was the venue of a meeting between the top supervisory board of the European Spallation Source ESS to be built in Lund, Sweden, and representatives of the Swiss government from SERI. The chair and the vice chair of the ESS Council, Beatrix Vierkorn-Rudolph and Kurt Clausen, respectively came to Switzerland to discuss the Swiss In-Kind Contributions to the largest spallation neutron source under construction in Sweden.
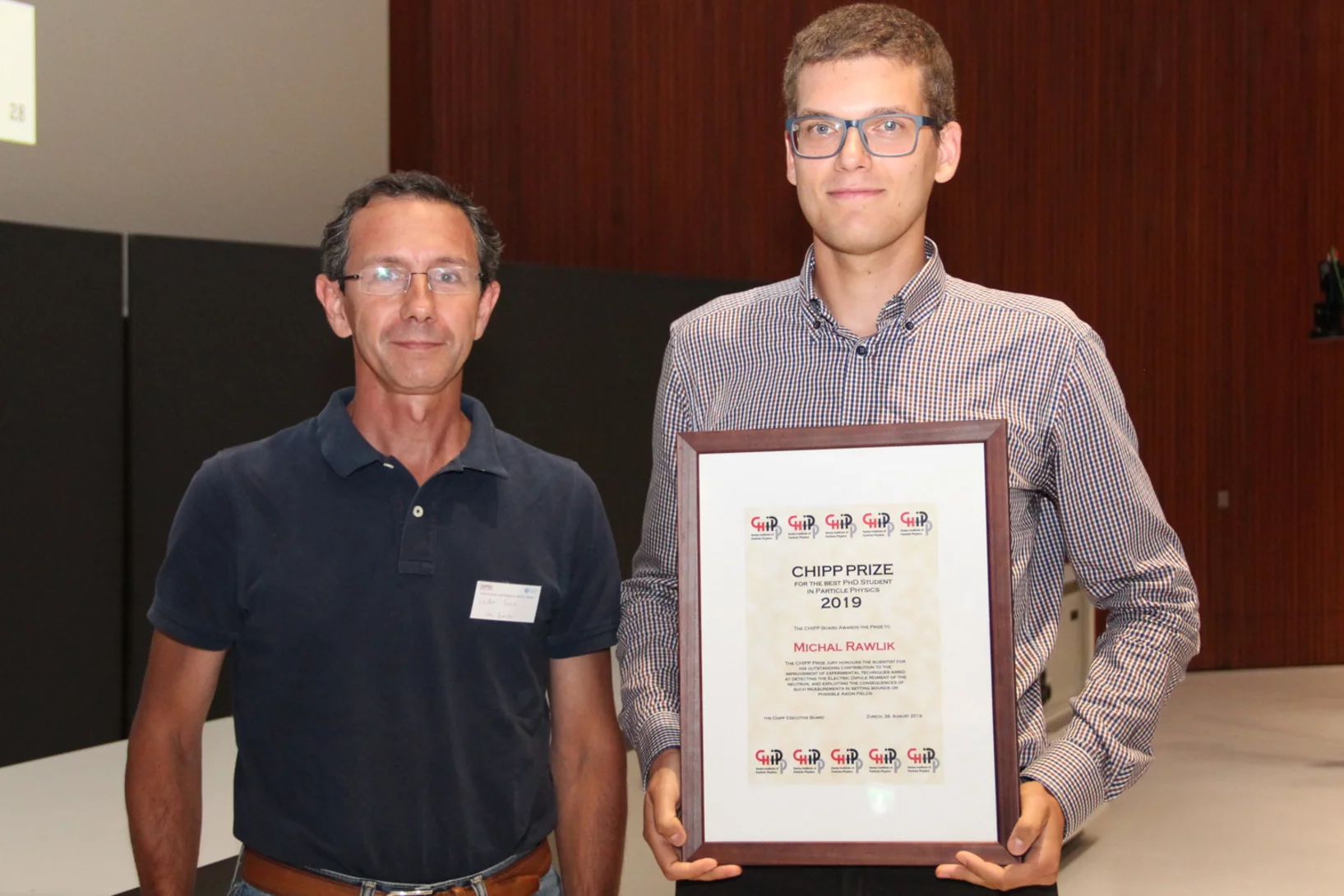
Michał Rawlik awarded the CHIPP Prize 2019
PSI researcher Dr. Michał Rawlik has been awarded the CHIPP Prize 2019 "for his outstanding contribution to the improvement of experimental techniques aimed at detecting the Electric Dipole Moment of the neutron, and exploiting the consequences of such measurements in setting bounds on possible Axion fields".
LIN builds pressure vessels for joint detector project with FRM-II in Munich
Highly efficient two-dimensional detectors are essential for the performance of modern neutron diffractometers. The NUM Division of PSI and the Technical University Munich TUM jointly develop two identical new 3He gas detectors, one for the diffractometer DMC at SINQ and the other for operation at FRM-II in Munich.
PSI participates in ECNS in St Petersburg
The European Conference on Neutron Scattering (ECNS) with its recent 2019 edition in St. Petersburg is a spree of lectures, poster sessions, and expert talks on the current trends and future possibilities in neutron science. PSI with its neutron source SINQ was represented by members of the three NUM laboratories LNS, LMX and LIN. In addition, PSI was silver sponsor of ECNS 2019 and is also a member of the LENS consortium (League of Advanced European Neutron Sources).
New NUM Laboratory for Neutron and Muon Instrumentation (LIN)
In the division Research with Neutrons and Muons (NUM) all technical knowledge and expertise concerned with the development and operation of the scientific instrumentation for neutron and muon experiments at our user facilities have been united in the new Laboratory for Neutron and Muon Instrumentation (LIN).
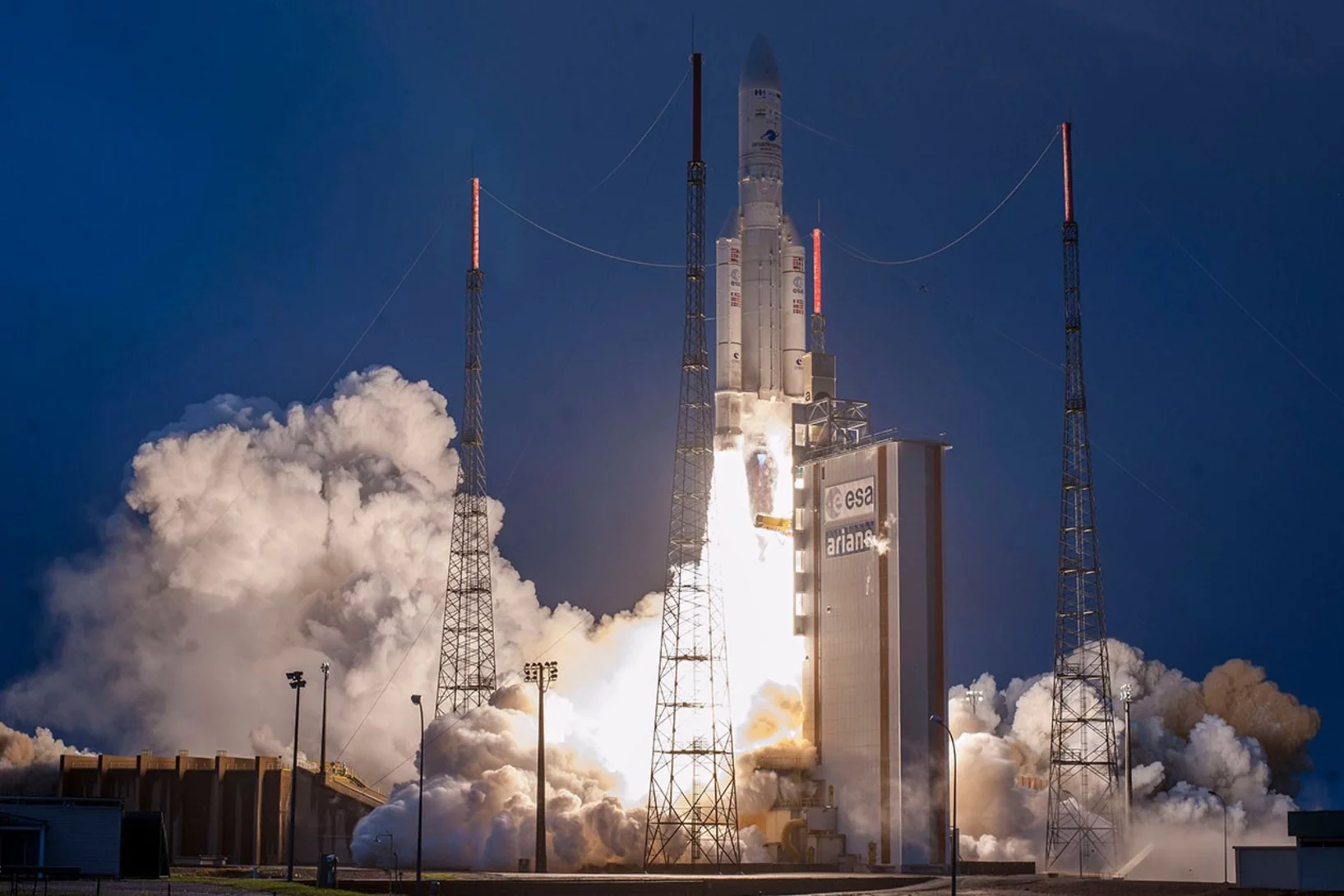
PSI-Bildgebung hilft bei Raketenstarts
PSI-Forschende helfen der europäischen Raumfahrt: ihre Neutronen-Bildgebung dient der Qualitätssicherung entscheidender Bauteile für Raketenstarts.
Ein Kompass, der nach Westen zeigt
Forschende des PSI haben mithilfe der Synchrotron Lichtquelle Schweiz SLS ein neues Phänomen des Magnetismus entdeckt. Dabei verhalten sich bestimmte Atomgruppen wie ein Kompass, der nach Westen zeigt. Damit könnten Computer wesentlich leistungsfähiger werden.
Ambizione grant for Max Zoller
Max Zoller, currently at the Physik-Institut of the University of Zurich (UZH), has been awarded a Swiss National Science Foundation Ambizione grant with PSI as host institution. Together with a PhD student he will join the particle theory group (NUM, Laboratory of Particle Physics (LTP)). The research of Max Zoller focuses on the automation of perturbative higher-order calculations. With the Ambizione grant Max will now move to PSI for four years, starting on June 1, 2019.
LENS launches activities to strengthen European neutron science
The members of the League of advanced European Neutron Sources (LENS) held their first General Assembly and the first Executive Board meeting on 26 March 2019 in Liblice, the Czech Republic. The consortium adopted and signed Statutes detailing the purpose of LENS, guiding the work of the statutory bodies, and laying the framework for Working Groups responsible for the execution of foreseen activities. For the Swiss spallation neutron source SINQ the head of the NUM division Christian Rüegg signed the documents.
DGKK Award for young researchers 2019 for Pascal Puphal
Dr Pascal Puphal (currently a Postdoc at PSI, LMX, Solid State Chemistry Group) has recently been awarded with the DGKK young researcher price from the German Crystal Growth Community on his Ph.D. work performed in the group of Cornelius Krellner at the Geothe University Frankfurt am Main on the topic "Tuning two dimensional Cu-based quantum spin systems". The work covers the stabilization and proof of a 2D dimer structure by Sr substitution in Han Purple and the research of novel kagome materials of the prominent quantum spin liquid candidate herbertsmithite by the hydrothermal route.
EPFL Adjunct Professorship to Christopher Mudry
Dr Christopher Mudry, who joined PSI in 1999 and is Research Group Leader of the Condensed Matter Theory Group at PSI since 2009, was awarded the title of Adjunct Professor at EPF Lausanne with the following citation. "Dr Christopher Mudry is a highly acclaimed theoretical physicist. He is regarded as one of the world’s leading experts on the quantum field theory of condensed matter and in the rapidly developing field of the topological properties of matter."
ERC Consolidator grant for Paolo Crivelli
Dr Paolo Crivelli (ETH Zurich, Department of Physics, Institute for Particle Physics and Astrophysics) has recently been awarded an ERC Consolidator grant for his project "Mu-MASS" aiming at a new precision measurement of the Muonium 1S-2S transition energy, ultimately with an improvement by three orders of magnitude.
Eccellenza Professorship to Lea Caminada
Dr Lea Caminada has been awarded a Swiss National Science Foundation (SNF) Eccellenza Professorial Fellowship.
Unmögliches möglich machen
Vom Einsatz multiferroischer Materialien verspricht man sich energiesparsamere Computer, weil für die magnetische Datenspeicherung ein elektrisches Feld ausreichen würde. Forschende am PSI haben ein solches Material jetzt für die Betriebstemperaturen von Computern tauglich gemacht.
Marc Janoschek appointed new head of LDM
Dr Marc Janoschek has been appointed new head of the NUM Laboratory for Scientific Developments and Novel Materials LDM. He will take office on November 15, 2018. Marc studied Physics at TU Munich and did his PhD at PSI and TUM on "Neutron Scattering on Chiral Magnets". After that he went to the University of California in San Diego as Feodor-Lynen Fellow. Since 2011 he is head of "Neutron research" in the "Condensed Matter and Magnet Science" group in Los Alamos. For his research Marc has been awarded the Wolfram Prandl Prize and the Los Alamos Fellow Prize for Outstanding Research. We wish Marc success and satisfaction for his new duties and wish to thank cordially Peter Keller, who led the LDM ad interim since March 2018.
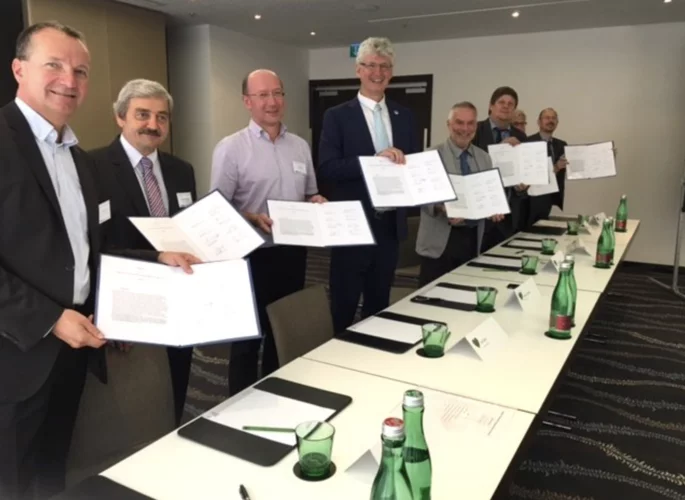
Founding Partners Sign Charter Establishing Neutron Source Consortium LENS
On September 12 representatives of eight European research infrastructures including SINQ at PSI signed the Charter of the League of advanced European Neutron Sources (LENS) at the International Conference of Research Infrastructures, ICRI2018 in Vienna. The signing ceremony marks the establishment of a new strategic consortium of European neutron source facilities with the aim, according to the charter, to “facilitate any form of discussion and decision-making process that has the potential to strengthen European neutron science via enhanced collaboration among the facilities”. The founding partners in the consortium include both European and national facilities in France, Germany, Sweden, Hungary, the United Kingdom, Norway and Switzerland. Other qualifying facilities are invited to join at any time.
ISNR honorary membership awarded to Eberhard Lehmann
The International Society for Neutron Radiology ISNR was founded in 1996 with the aim to organize regular conferences with the focus on the use of neutrons for imaging purposes. During the 11th World Conference on Neutron Radiography, held recently in Sydney (Australia) and organized by ANSTO, the Honorary Membership of ISNR was awarded to Eberhard Lehmann - in recognition to his contributions for the progress in the field of neutron imaging on national and international level. The Neutron Imaging and Activation Group NIAG of the LNS has been active member in ISNR from the very beginning. Presently and since 2014, Markus Strobl the head of NIAG is vice-president elected of ISNR – and was reelected recently until 2022. In addition, NIAG member Pavel Trtik is now representing PSI in the ISNR board until 2022.
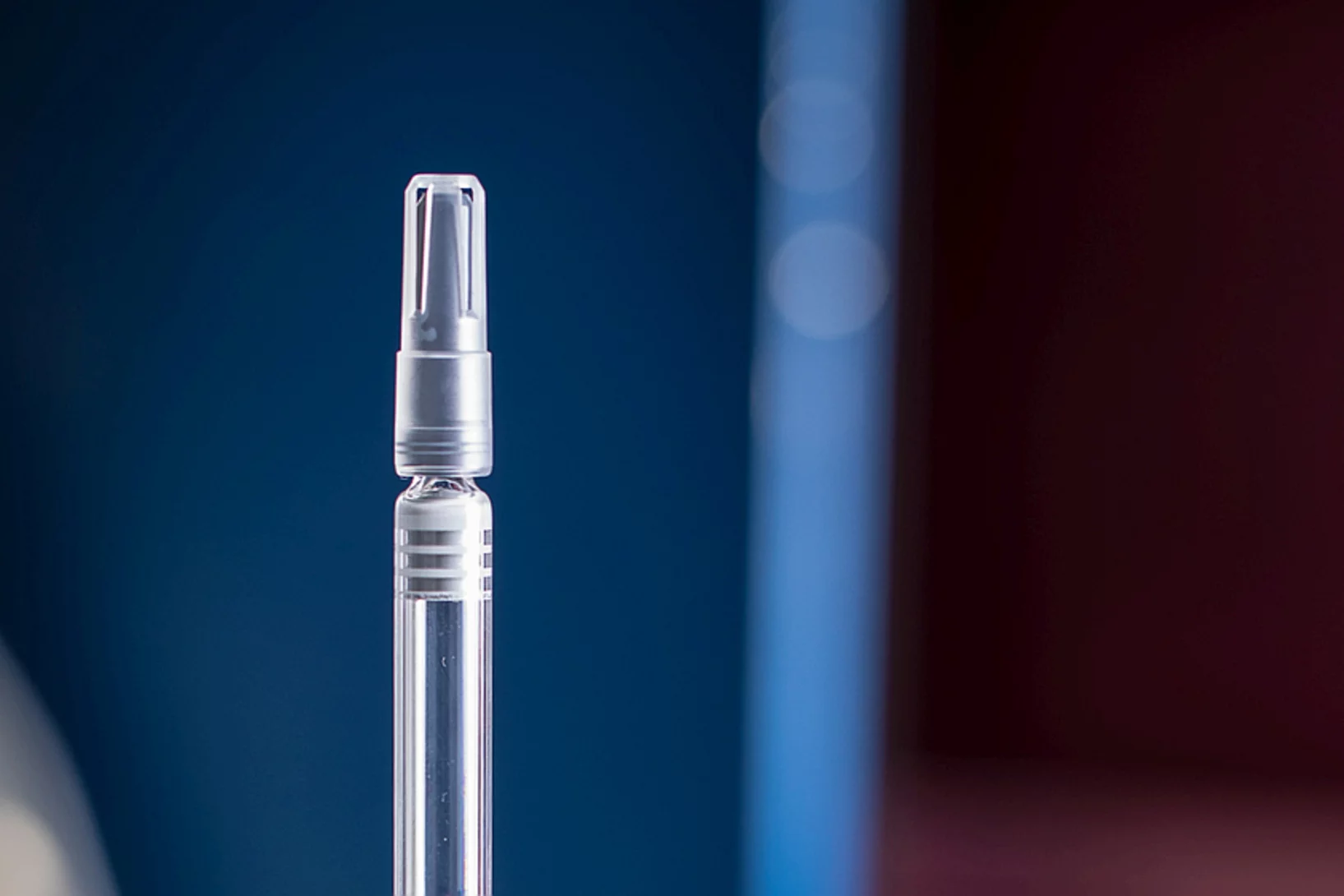
Injektionsnadeln mit Neutronen durchleuchtet
Forschende des Paul Scherrer Instituts PSI, der Universität Basel und von Roche haben eine Bildgebungsmethode mit Neutronen genutzt um zu untersuchen, warum es entscheidend ist, dass mit dem Wirkstoff bereits vorgefüllte medizinische Spritzen kühl gelagert werden.
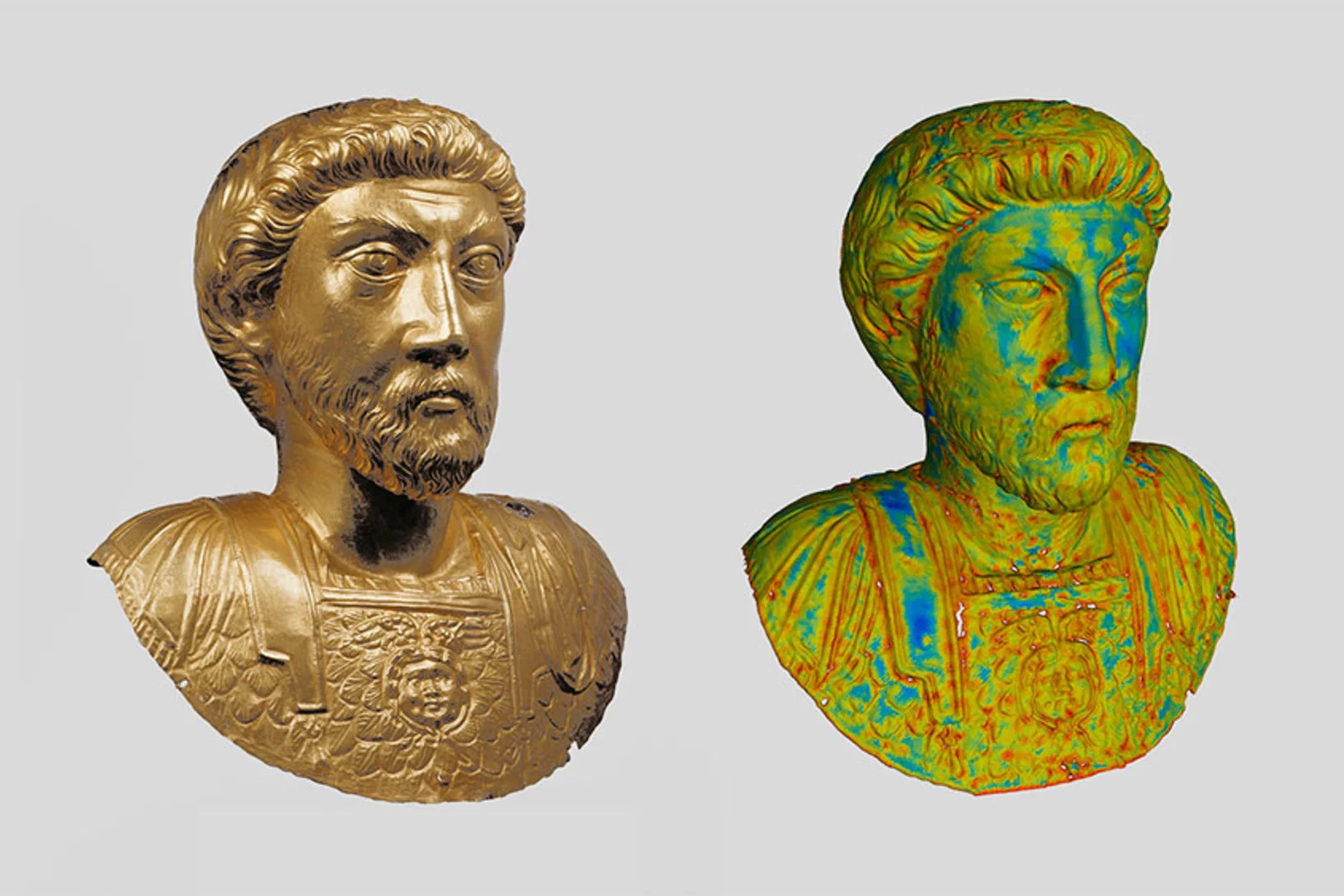
Vom goldenen Kaiser zum gefüllten Buddha
Mit Hilfe von Neutronen werden am Paul Scherrer Institut PSI antike Metallobjekte durchleuchtet. Dadurch erkennen Forscher, was in ihrem Innern verborgen ist, wie sie hergestellt wurden – und wie sie sich erhalten lassen.
Der Schwerarbeiter aus dem Misox
Aldo Antognini liegen Physik und Geselligkeit im BlutMehr als 2'200'000 Franken hat Aldo Antognini von der EU für sein neuestes Experiment bekommen. Er will herausfinden, wie der Magnetismus im Proton verteilt ist. Dabei wird der Teilchenphysiker nicht nur seine wissenschaflichen und technischen, sondern auch seine sozialen Talente einsetzen können.
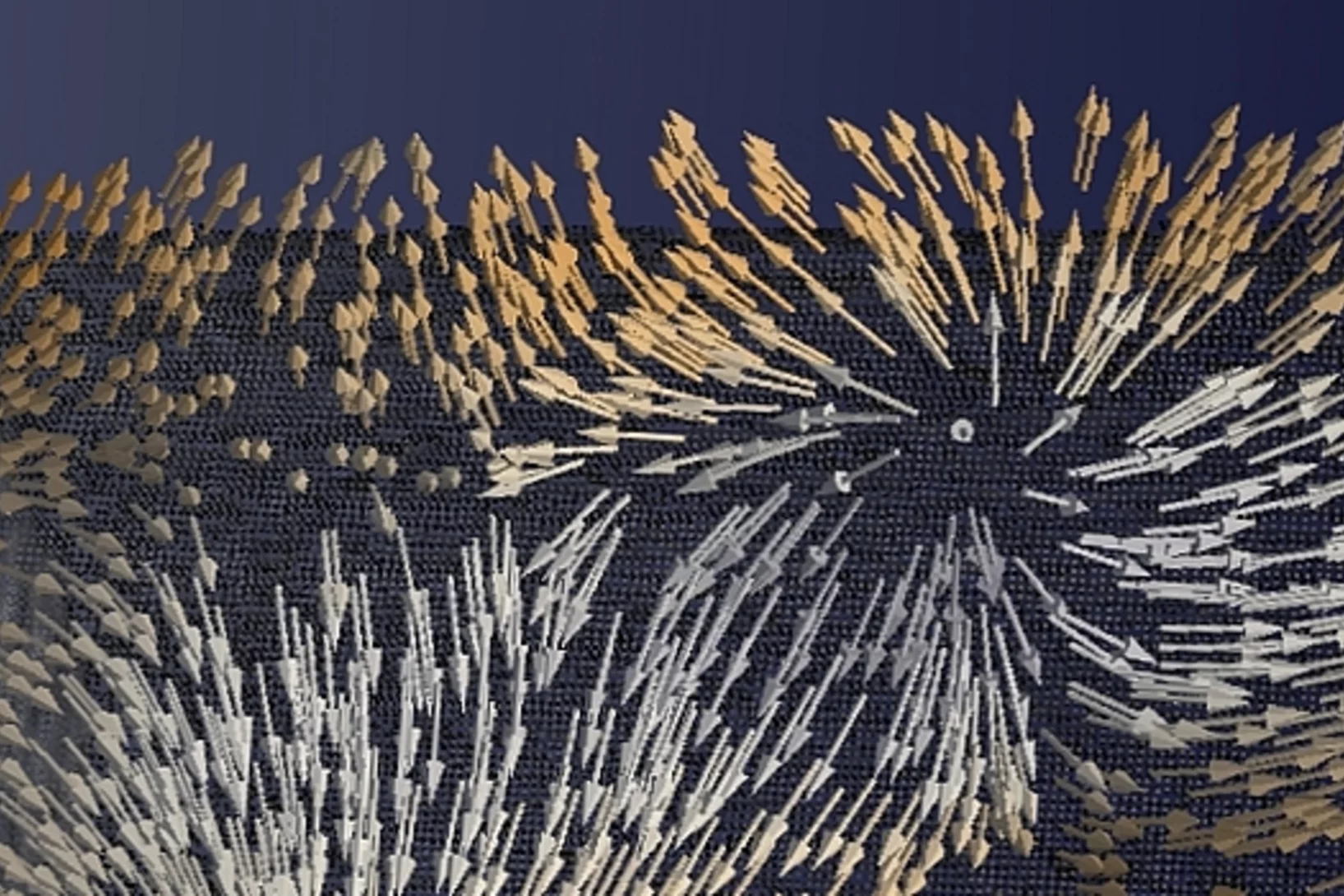
Tauchgang in einen Magneten
Zum ersten Mal haben Forschende die Richtungen der Magnetisierung in einem dreidimensionalen magnetischen Objekt sichtbar gemacht. Die kleinsten Details in ihrer Visualisierung waren dabei zehntausend Mal kleiner als ein Millimeter. In der sichtbar gemachten magnetischen Struktur stach eine Art von Muster besonders hervor: magnetische Singularitäten namens Bloch-Punkte, die bisher nur in der Theorie bekannt waren.