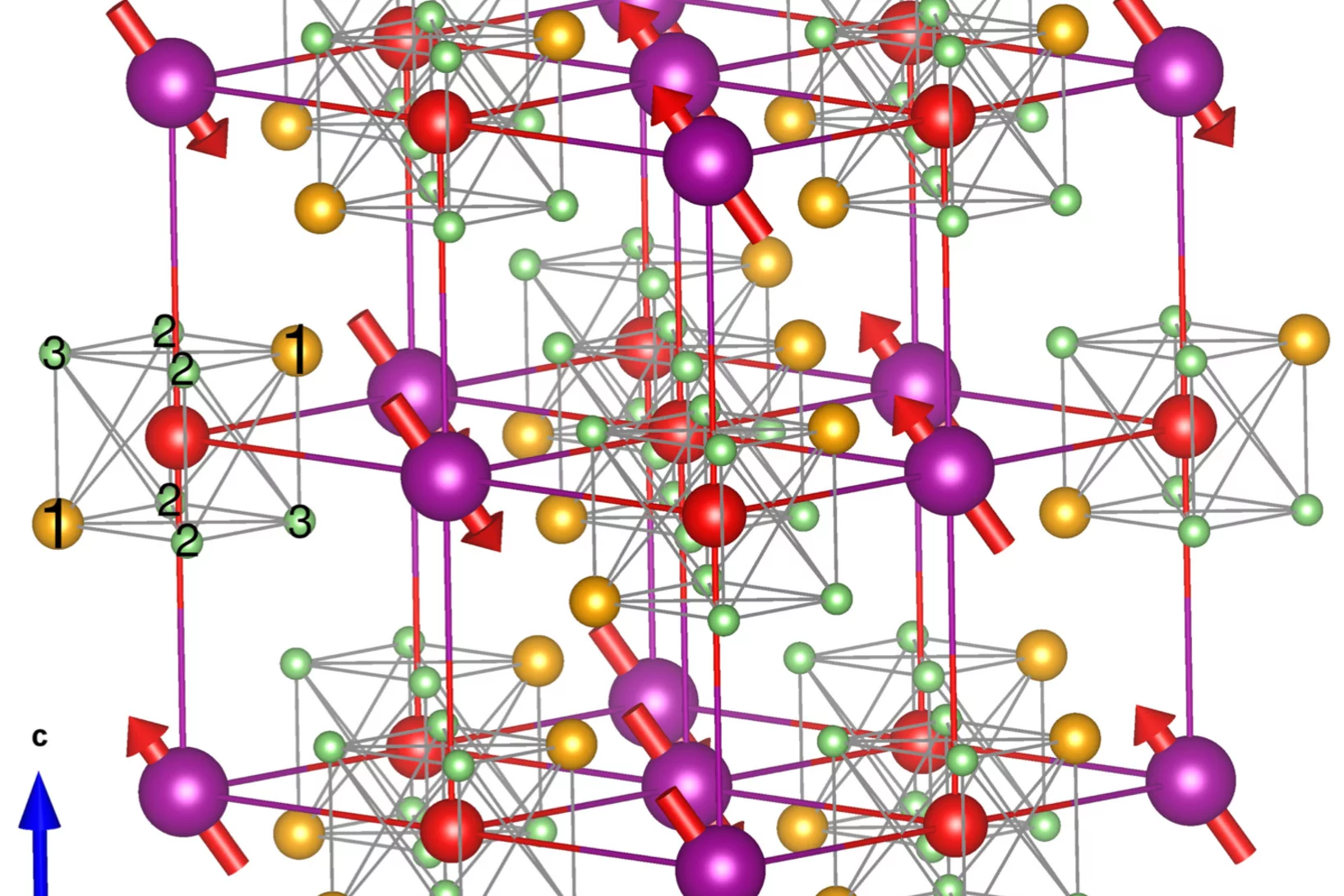
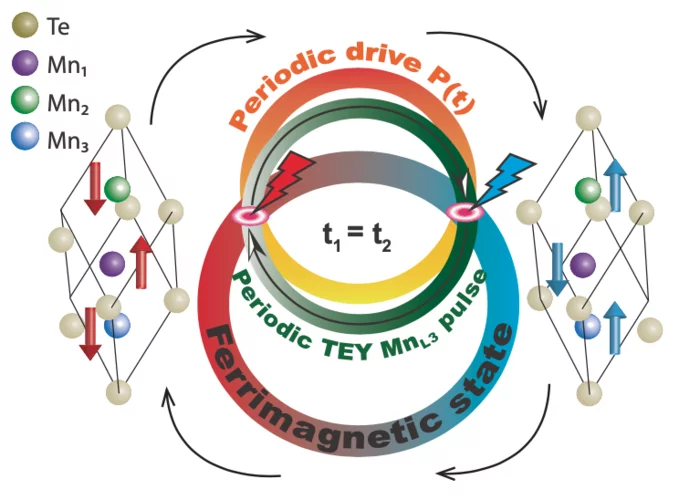
Anomalous Hall Effect due to Magnetic Fluctuations in a Ferromagnetic Weyl Semimetal
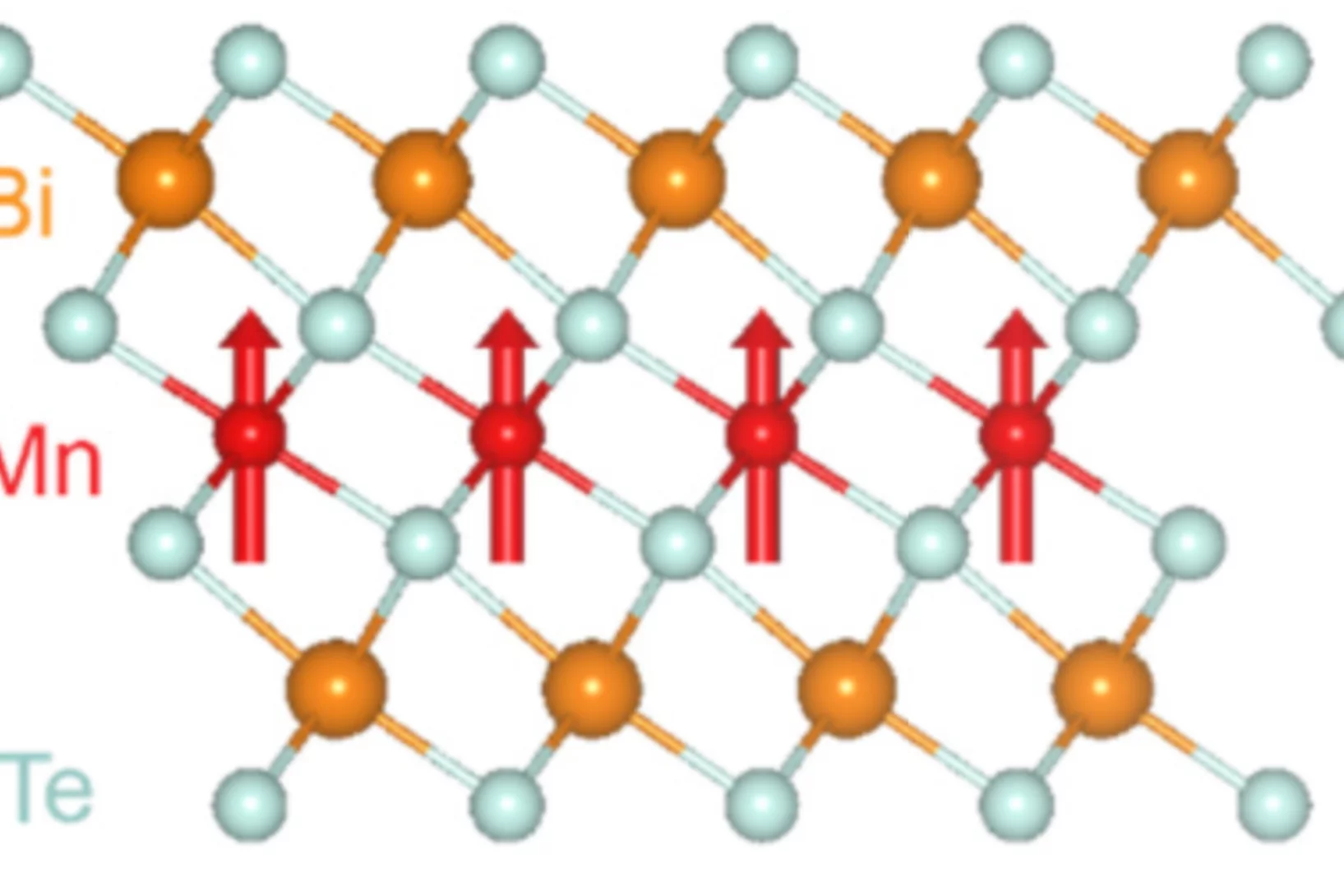
The anomalous Hall effect (AHE) has emerged as a key indicator of time-reversal symmetry breaking (TRSB) and topological features in electronic band structures. Absent of a magnetic field, the AHE requires spontaneous TRSB but has proven hard to probe due to averaging over domains. The anomalous component of the Hall effect is thus frequently derived from extrapolating the magnetic field dependence of the Hall response. We show ....
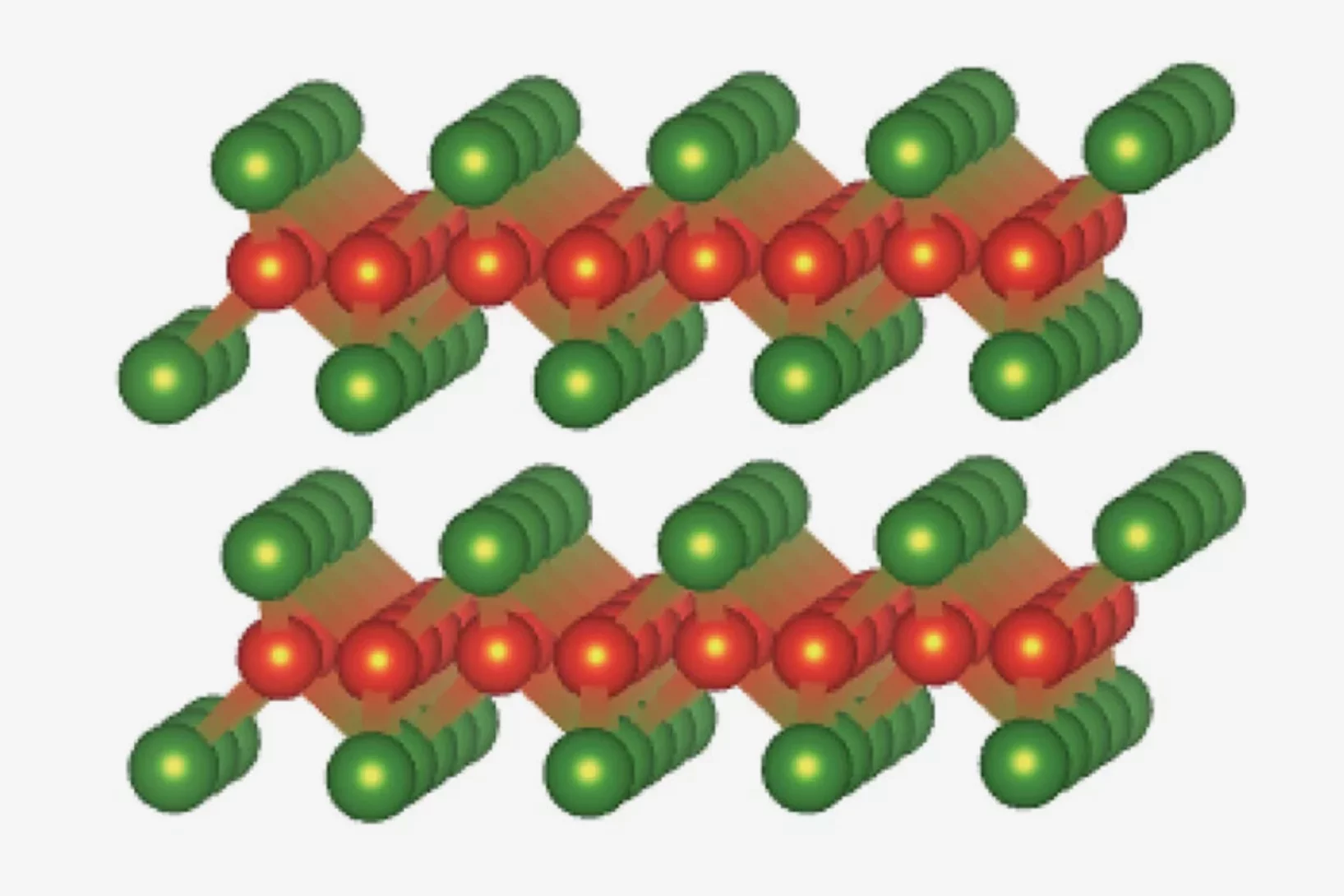
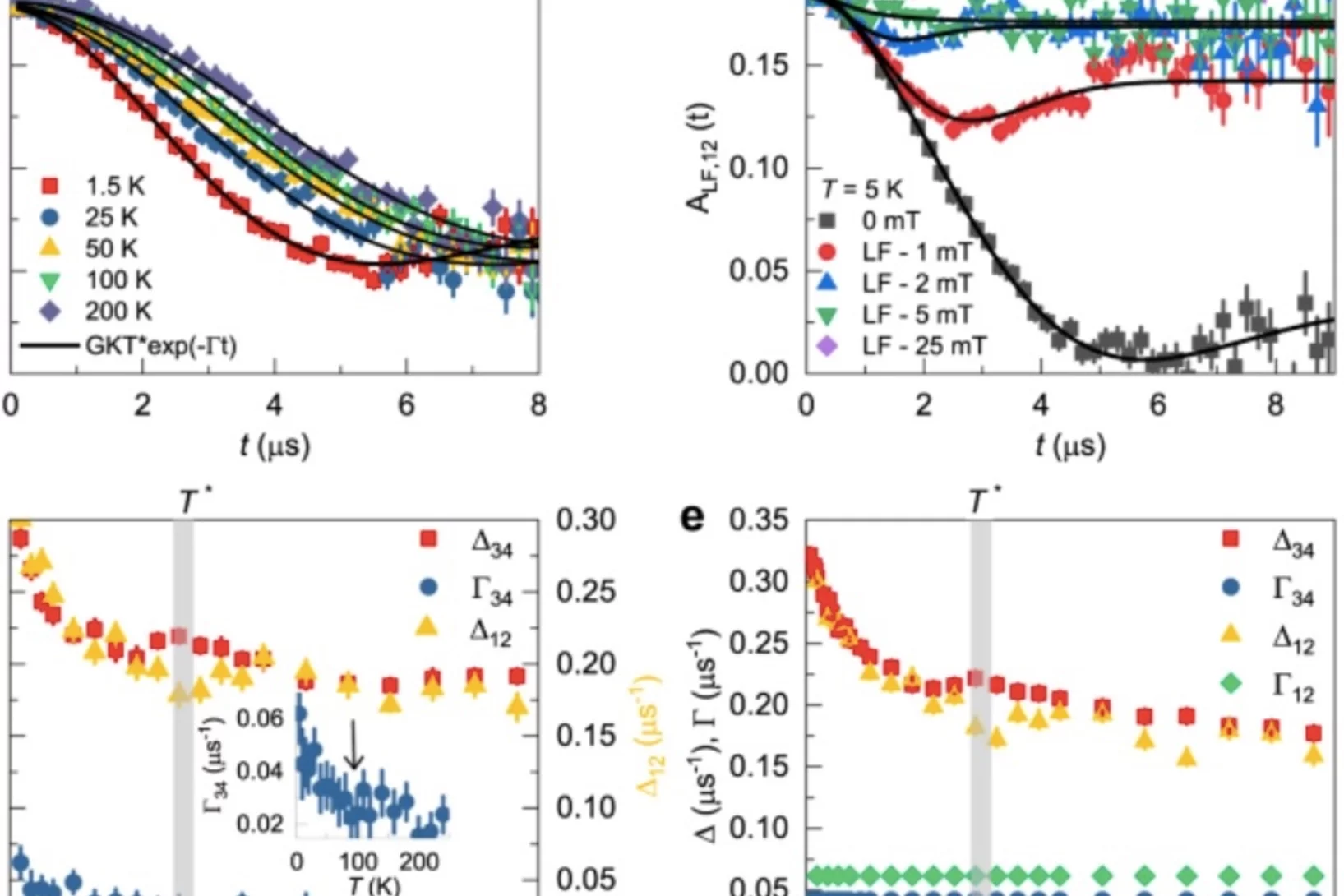
Pressure-enhanced splitting of density wave transitions in La3Ni2O7–δ
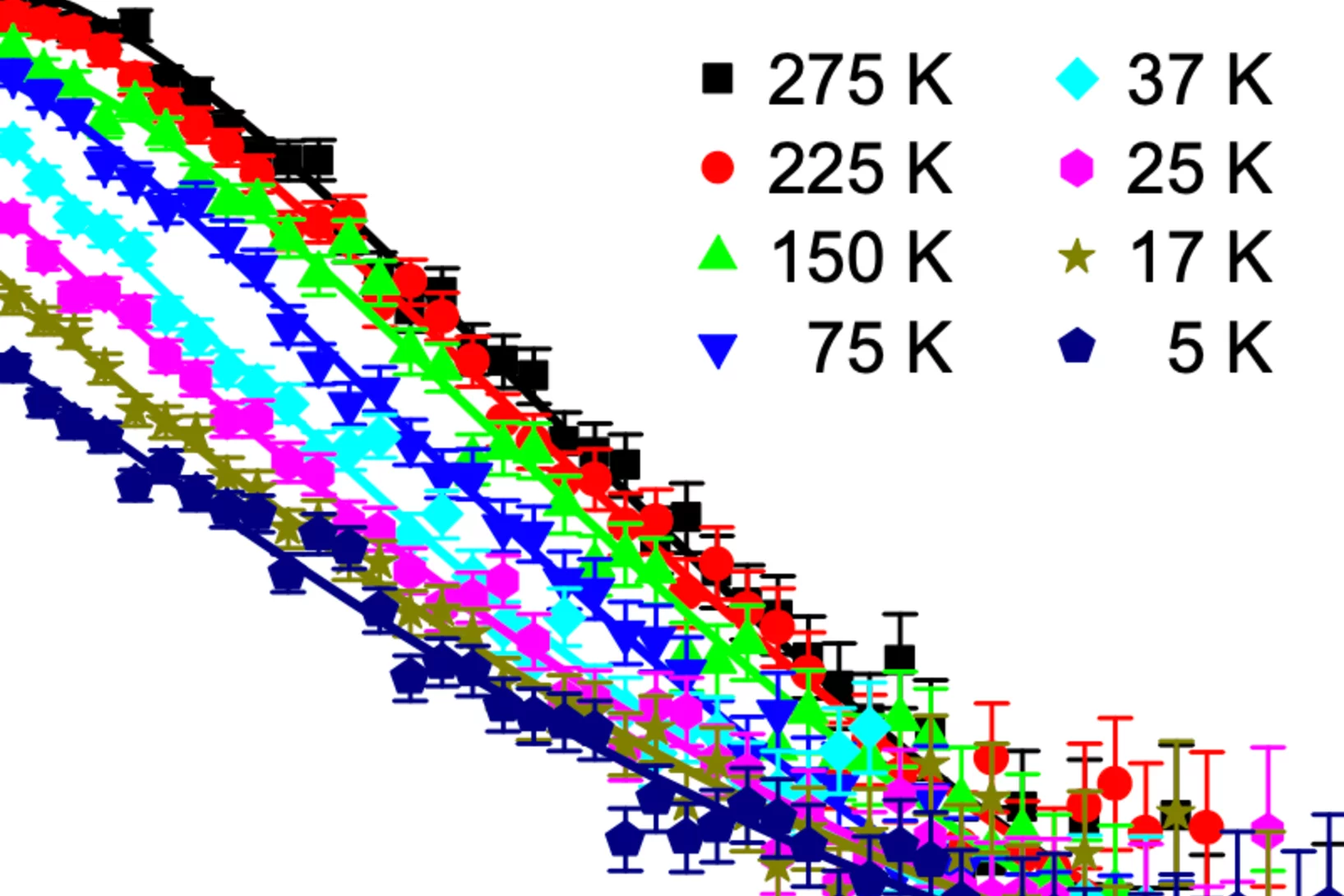
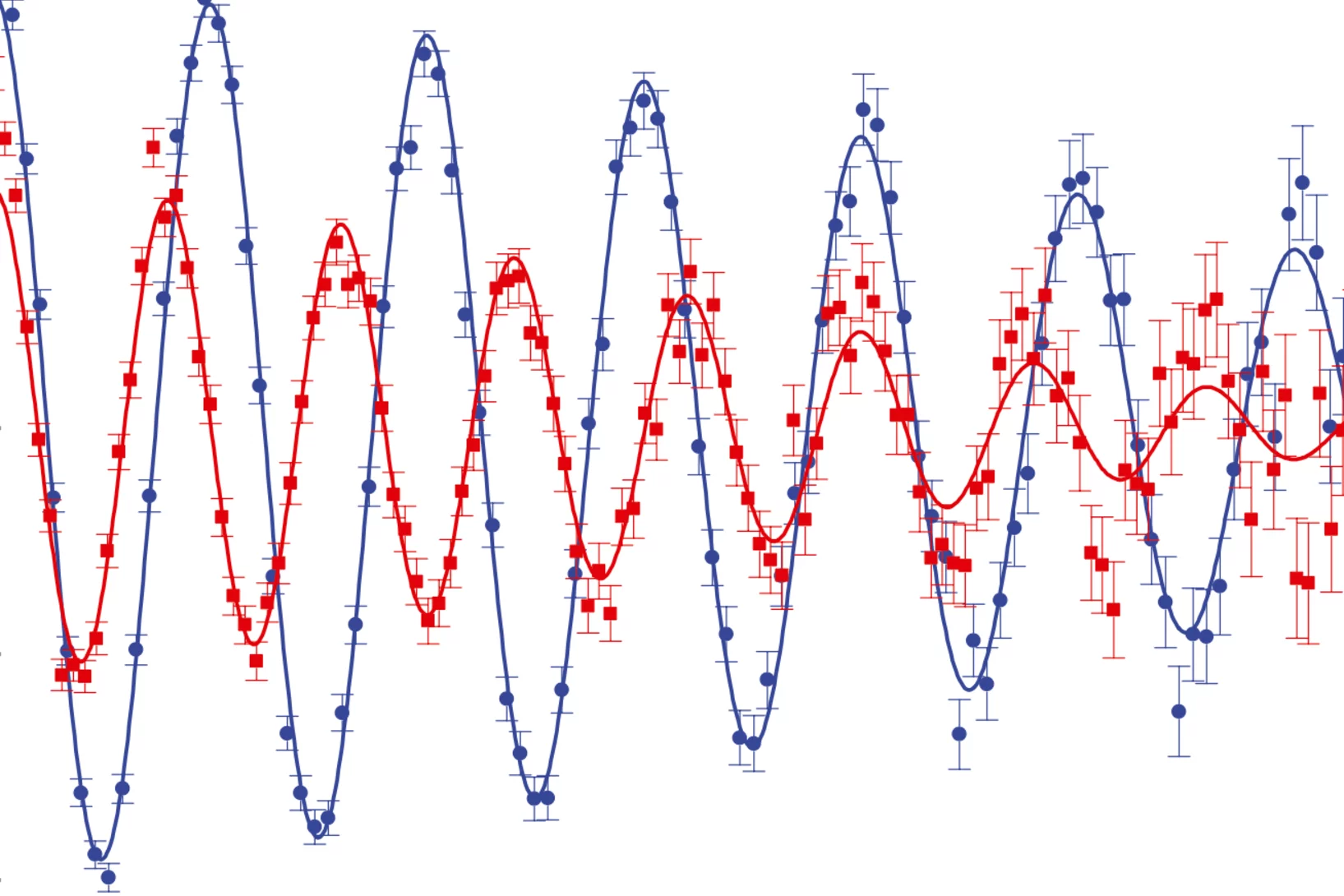
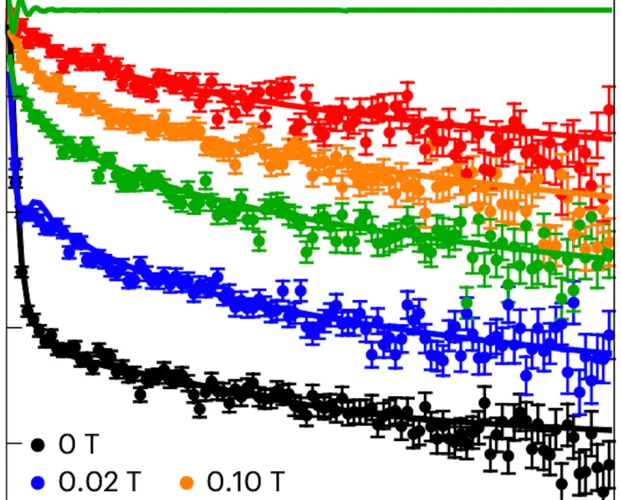
The observation of superconductivity in La3Ni2O7–δ under pressure, following the suppression of a high-temperature density wave state, has attracted considerable attention. The nature of this density wave order was not clearly identified. Here we probe the magnetic response of the zero-pressure phase of La3Ni2O7–δ as hydrostatic pressure is applied, and find that the apparent single density wave transition at zero applied pressure splits into two. The comparison of our muon-spin rotation ...
Anisotropic Skyrmion and Multi-q Spin Dynamics in Centrosymmetric Gd2PdSi3
Skyrmions are particlelike vortices of magnetization with nontrivial topology, which are usually stabilized by Dzyaloshinskii-Moriya interactions (DMI) in noncentrosymmetric bulk materials. Exceptions are centrosymmetric Gd- and Eu-based skyrmion-lattice (SL) hosts with zero DMI, where both the SL stabilization mechanisms and magnetic ground states remain controversial. We address these here by investigating both the static and dynamical spin properties ...
IMPACT: Upgrade an PSI-Forschungsanlage beschlossen
Die Finanzierung der Umbauten an der Protonenbeschleunigeranlage des PSI wurde vom Schweizer Parlament bewilligt.
Evidence of antiferromagnetism in ultrathin metallic (111)-oriented LaNiO3 films
Antiferromagnets with exotic spin textures promise low-power spintronic devices with extremely high operating frequencies and resistance to external perturbations. In particular, the combination of highly tunable correlated electron physics, as in complex oxides, with metallicity and antiferromagnetism is desirable but exceedingly rare. LaNiO3, the lone example of a perovskite nickelate which is metallic across all temperatures, has long been a promising candidate, but the antiferromagnetic metallic state has remained elusive. We demonstrate the emergence ...
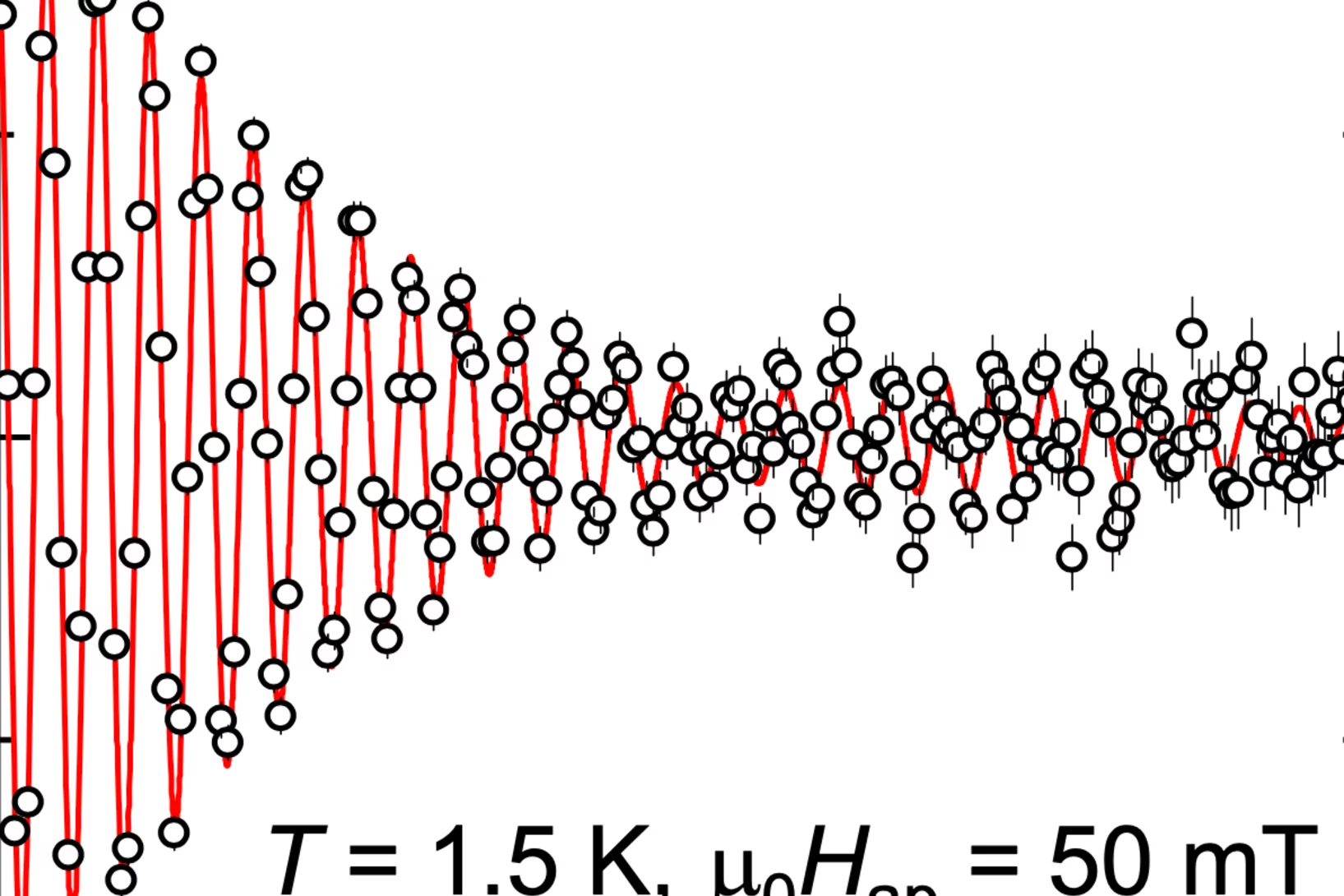
Origin of the Suppression of Magnetic Order in MnSi under Hydrostatic Pressure
We experimentally study the evolution of the magnetic moment 𝑚 and exchange interaction 𝐽 as a function of hydrostatic pressure in the zero-field helimagnetic phase of the strongly correlated electron system MnSi. The suppression of magnetic order at ≈1.5 GPa is shown to arise from the 𝐽 collapse and not from a quantum fluctuations induced reduction of 𝑚. Our work provides benchmarks ...
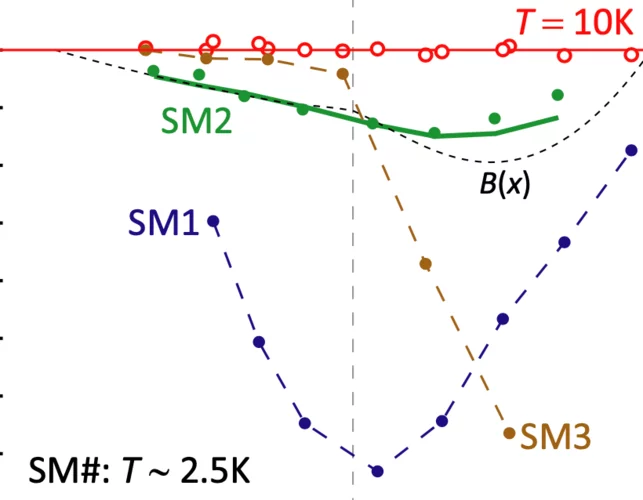
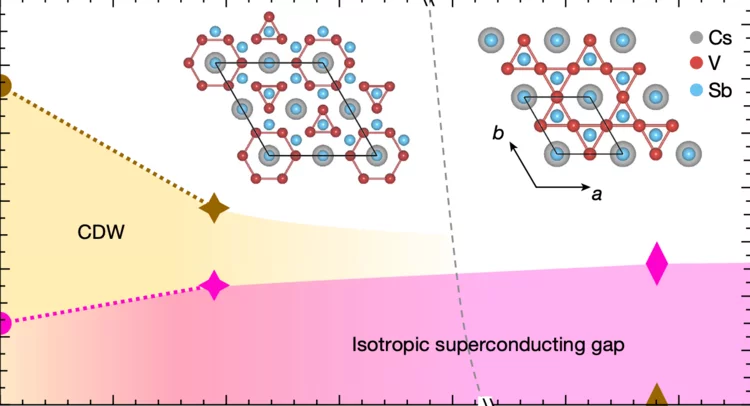
Evidence for time-reversal symmetry-breaking kagome superconductivity
Superconductivity and magnetism are often antagonistic in quantum matter, although their intertwining has long been considered in frustrated-lattice systems. Here we utilize scanning tunnelling microscopy and muon spin resonance to demonstrate time-reversal symmetry-breaking superconductivity in kagome metal Cs(V, Ta)3Sb5, where the Cooper pairing exhibits magnetism and is modulated by it. In the magnetic channel, we observe spontaneous internal magnetism ...
Chiral kagome superconductivity modulations with residual Fermi arcs
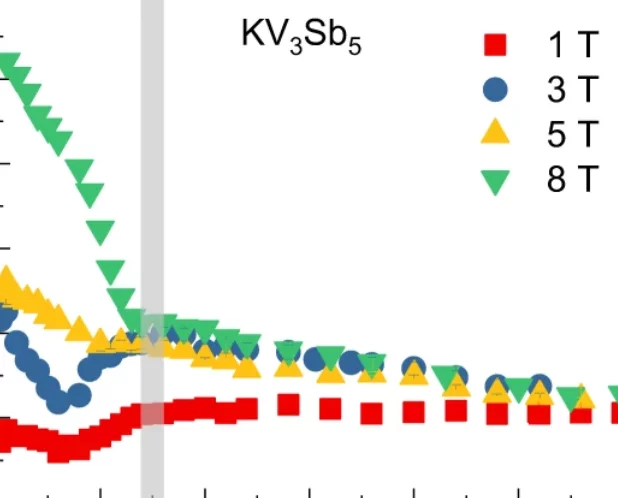
Superconductivity involving finite-momentum pairing can lead to spatial-gap and pair-density modulations, as well as Bogoliubov Fermi states within the superconducting gap. However, the experimental realization of their intertwined relations has been challenging. Here we detect chiral kagome superconductivity modulations with residual Fermi arcs in KV3Sb5 and CsV3Sb5 using normal and Josephson scanning tunnelling microscopy down to 30 millikelvin with a resolved electronic energy difference at the microelectronvolt level. We observe a U-shaped ...
Observation of Mermin-Wagner behavior in LaFeO3/SrTiO3 superlattices
Two-dimensional magnetic materials can exhibit new magnetic properties due to the enhanced spin fluctuations that arise in reduced dimension. However, the suppression of the long-range magnetic order in two dimensions due to long-wavelength spin fluctuations, as suggested by the Mermin-Wagner theorem, has been questioned for finite-size laboratory samples. Here we study ...
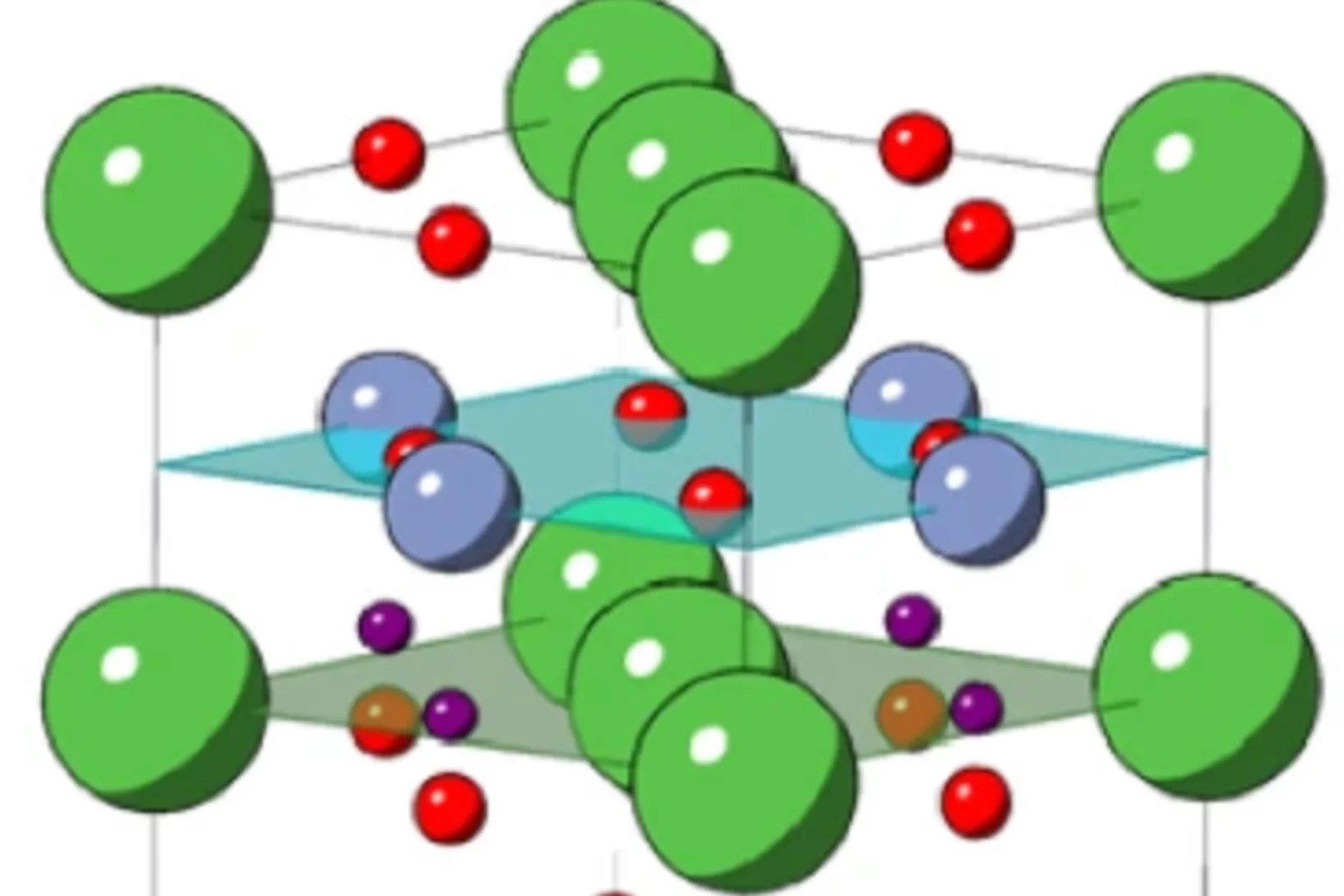
Coexistence of Superconductivity and Antiferromagnetism in Topological Magnet MnBi2Te4 Films
The interface of two materials can harbor unexpected emergent phenomena. One example is interface-induced superconductivity. In this work, we employ molecular beam epitaxy to grow a series of heterostructures formed by stacking together two nonsuperconducting antiferromagnetic materials, an intrinsic antiferromagnetic topological insulator MnBi2Te4 and an antiferromagnetic iron chalcogenide FeTe.
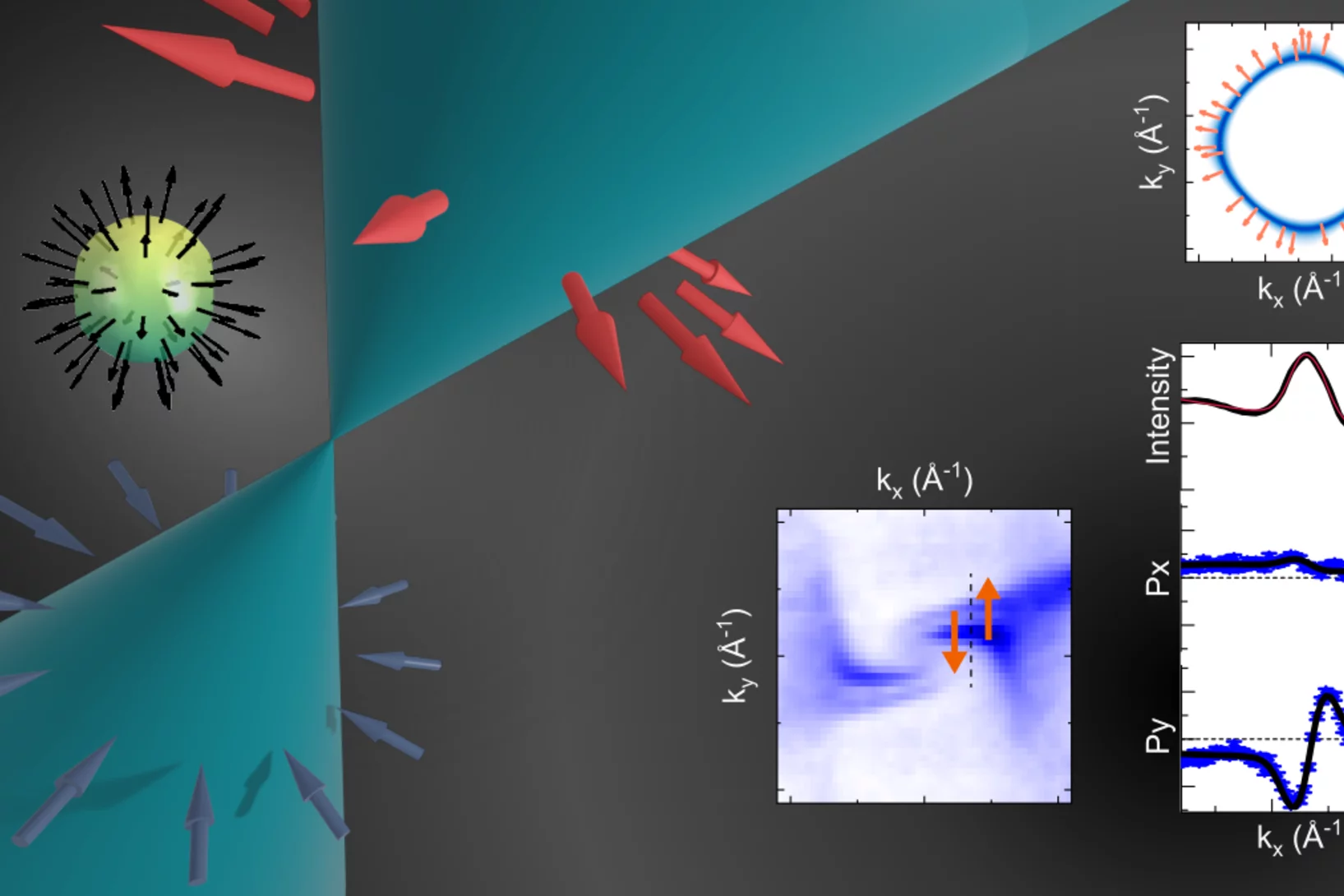
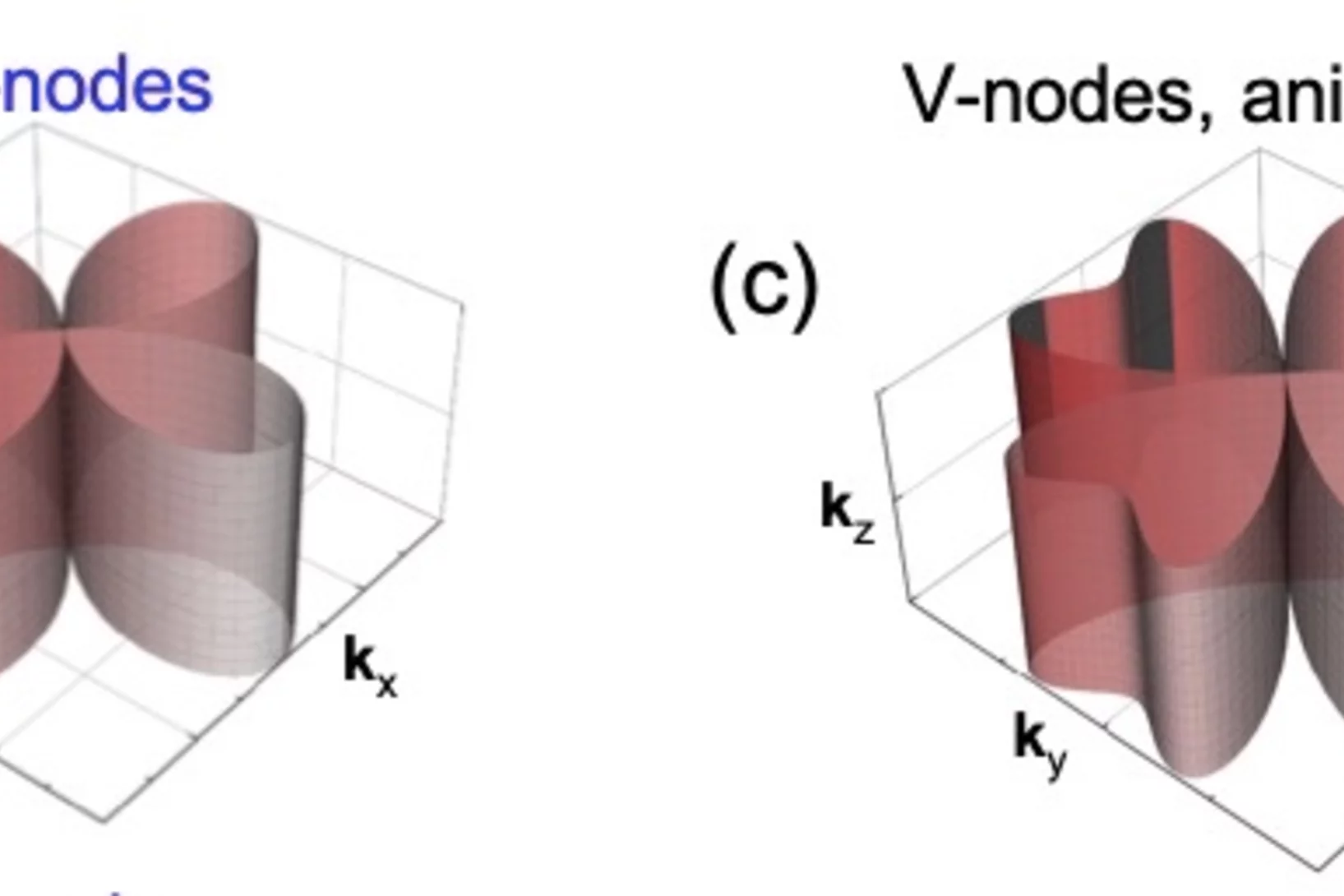
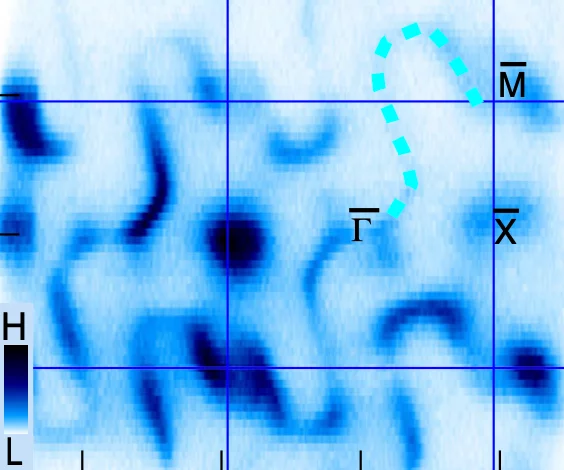
Weyl spin-momentum locking in a chiral topological semimetal
Spin–orbit coupling in noncentrosymmetric crystals leads to spin–momentum locking – a directional relationship between an electron’s spin angular momentum and its linear momentum. Isotropic orthogonal Rashba spin–momentum locking has been studied for decades, while its counterpart, isotropic parallel Weyl spin–momentum locking has remained elusive in experiments. Theory predicts ...
Introduction to Muon Spin Spectroscopy
Alex Amato and Elvezio Morenzoni have published a new textbook entitled 'Introduction to Muon Spin Spectroscopy: Applications to Solid State and Material Sciences'. The book is ideal for a first course in muon spin spectroscopy (µSR), comes enriched with exercises and solutions to master the subject and includes practical examples to quantify key experimental parameters.
Phonon promoted charge density wave in topological kagome metal ScV6Sn6
Charge density wave (CDW) orders in vanadium-based kagome metals have recently received tremendous attention, yet their origin remains a topic of debate. The discovery of ScV6Sn6, a bilayer kagome metal featuring an intriguing √3 × √3 × √3 CDW order, offers a novel platform to explore the underlying mechanism behind the unconventional CDW. Here we combine ...
Tuning of the flat band and its impact on superconductivity in Mo5Si3−xPx
The superconductivity in systems containing dispersionless (flat) bands is seemingly paradoxical, as traditional Bardeen-Cooper-Schrieffer theory requires an infinite enhancement of the carrier masses. However, the combination of flat and steep (dispersive) bands within the multiple band scenario might boost superconducting responses, potentially explaining high-temperature superconductivity in cuprates and metal hydrides. Here, we report ...
SRF material research using muon spin rotation and beta-detected nuclear magnetic resonance
Muon spins precess in transverse magnetic fields and emit a positron preferentially in the spin direction at the instant of decay, enabling muon spin rotation (μSR) as a precise probe of local magnetic fields in matter. μSR has been used to characterize superconducting radio-frequency (SRF) materials since 2010. At TRIUMF, a beam of 4.2 MeV μ+ is implanted at a material-dependent depth of approximately 150 μm. A dedicated spectrometer was developed to measure the field of first vortex penetration and pinning strength in SRF materials in parallel magnetic fields of up to 300 mT. A low-energy beam available at PSI implants μ+ at variable depth in the London layer allowing for direct measurements ...
Interface-induced superconductivity in magnetic topological insulators
One of the recipes for realizing topological superconductivity calls for interfacing a topological insulator with a superconductor. In a variant of that approach, Yi et al. grew a heterostructure consisting of layers of a magnetic topological insulator, (Bi,Sb)2Te3 doped with chromium, and antiferromagnetic iron telluride. Neither of these materials is superconducting, but iron telluride is a parent compound for a family of iron-based superconductors. Interfacing the layers led to the appearance of superconductivity in the presence of ferromagnetism and topological band structure. This combination of properties makes the heterostructure a promising, although not yet proven, platform for observing chiral topological superconductivity.
Magnetostriction-Driven Muon Localization in an Antiferromagnetic Oxide
Magnetostriction results from the coupling between magnetic and elastic degrees of freedom. Though it is associated with a relatively small energy, we show that it plays an important role in determining the site of an implanted muon, so that the energetically favorable site can switch on crossing a magnetic phase transition. This surprising effect is demonstrated in the cubic rocksalt antiferromagnet MnO which undergoes a magnetostriction-driven rhombohedral distortion at the Néel temperature TN = 118 K. Above TN ...
Designing the stripe-ordered cuprate phase diagram through uniaxial-stress
Understanding the degree to which charge-stripe, spin-stripe, and superconducting orders compete/coexist is paramount for elucidating the microscopic pairing mechanism in the cuprate high-temperature superconductors. We explore the tunability of magnetism, superconductivity, and crystal structure in the stripe phase of the cuprate La2−xBaxCuO4, by employing complementary techniques under compressive uniaxial stress in the CuO2 plane. Our results show a sixfold increase ...
In-Plane Magnetic Penetration Depth in Sr2 RuO4 : Muon-Spin Rotation and Relaxation Study
We report on measurements of the in-plane magnetic penetration depth (λab) in single crystals of Sr2RuO4 down to ≃0.015 K by means of muon-spin rotation-relaxation. The linear temperature dependence of λ−2ab for T≲0.7 K suggests the presence of nodes in the superconducting gap. This statement is further substantiated by observation of the Volovik effect, i.e., the reduction of λ−2ab as a function of the applied magnetic field. The experimental zero-field ...
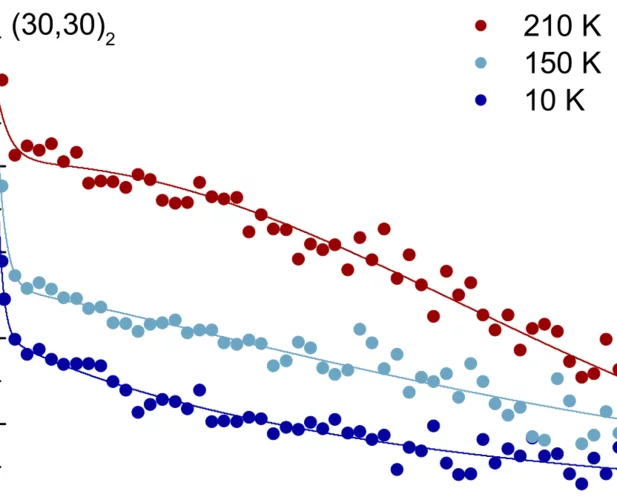
Hidden magnetism uncovered in a charge ordered bilayer kagome material ScV6Sn6
Charge ordered kagome lattices have been demonstrated to be intriguing platforms for studying the intertwining of topology, correlation, and magnetism. The recently discovered charge ordered kagome material ScV6Sn6 does not feature a magnetic groundstate or excitations, thus it is often regarded as a conventional paramagnet. Here, using advanced muon-spin rotation spectroscopy, we uncover an unexpected hidden magnetism of the charge order. We observe an enhancement ...
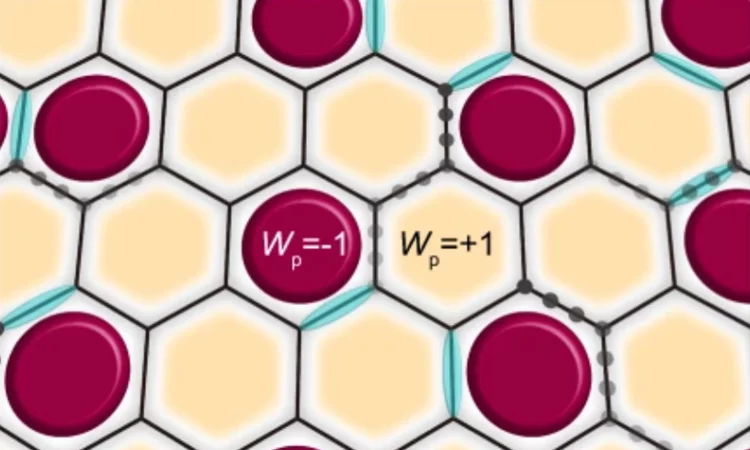
Kondo screening in a Majorana metal
Kondo impurities provide a nontrivial probe to unravel the character of the excitations of a quantum spin liquid. In the S = 1/2 Kitaev model on the honeycomb lattice, Kondo impurities embedded in the spin-liquid host can be screened by itinerant Majorana fermions via gauge-flux binding. Here, we report experimental signatures of metallic-like Kondo screening at intermediate temperatures in the Kitaev honeycomb material α-RuCl3 with dilute Cr3+ (S = 3/2) impurities.
Efficient magnetic switching in a correlated spin glass
The interplay between spin-orbit interaction and magnetic order is one of the most active research fields in condensed matter physics and drives the search for materials with novel, and tunable, magnetic and spin properties. Here we report on a variety of unique and unexpected observations in thin multiferroic Ge1−xMnxTe films.
Spin-orbit driven superconducting proximity effects in Pt/Nb thin films
Manipulating the spin state of thin layers of superconducting material is a promising route to generate dissipationless spin currents in spintronic devices. Approaches typically focus on using thin ferromagnetic elements to perturb the spin state of the superconducting condensate to create spin-triplet correlations. We have investigated simple structures that generate spin-triplet correlations without using ferromagnetic elements.
Unconventional charge order and superconductivity in kagome-lattice systems as seen by muon-spin rotation
Kagome lattices are intriguing and rich platforms for studying the intertwining of topology, electron correlation, and magnetism. These materials have been subject to tremendous experimental and theoretical studies not only due to their exciting physical properties but also as systems that may solve critical technological problems. We will review recent experimental progress on superconductivity and magnetic fingerprints of charge order in several kagome-lattice systems from the local-magnetic probe point of view by utilizing muon-spin rotation under extreme conditions, i.e., hydrostatic pressure, ultra low temperature and high magnetic field.
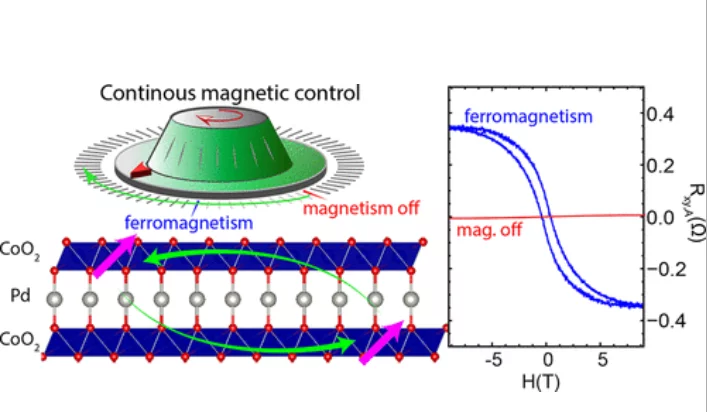
Emergent Magnetism with Continuous Control in the Ultrahigh-Conductivity Layered Oxide PdCoO2
The current challenge to realizing continuously tunable magnetism lies in our inability to systematically change properties, such as valence, spin, and orbital degrees of freedom, as well as crystallographic geometry. Here, we demonstrate that ferromagnetism can be externally turned on with the application of low-energy helium implantation and can be subsequently erased and returned to the pristine state via annealing.
Coupling of magnetic phases at nickelate interfaces
In this paper we present a model system built out of artificially layered materials, allowing us to understand the interrelation of magnetic phases with the metallic-insulating phase at long length scales, and enabling new strategies for the design and control of materials in devices. The artificial model system consists of superlattices made of SmNiO3 and NdNiO3 layers, – two members of the fascinating rare earth nickelate family, having different metal-to-insulator and magnetic transition temperatures. By combining two complementary techniques ....
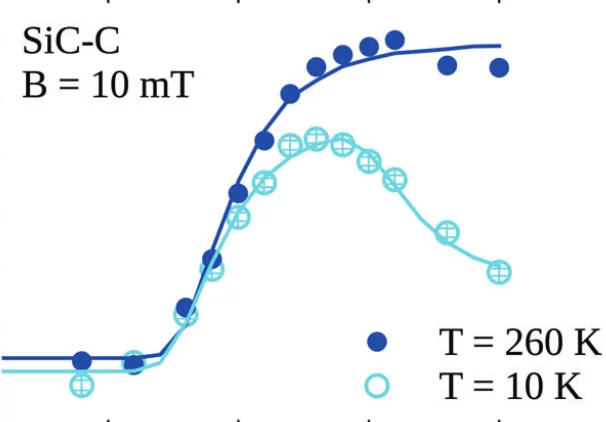
Defect Profiling of Oxide-Semiconductor Interfaces Using Low-Energy Muons
Muon spin rotation with low-energy muons (LE-μSR) is a powerful nuclear method where electrical and magnetic properties of surface-near regions and thin films can be studied on a length scale of ≈200 nm. This study shows the potential of utilizing low-energy muons for a depth-resolved characterization of oxide-semiconductor interfaces, i.e., for silicon (Si) and silicon carbide (4H-SiC). The performance of semiconductor devices relies heavily on the quality of the oxide-semiconductor interface; thus, investigation of defects present in this region is crucial to improve the technology.
Nodeless electron pairing in CsV3Sb5-derived kagome superconductors
The newly discovered kagome superconductors represent a promising platform for investigating the interplay between band topology, electronic order and lattice geometry. Despite extensive research efforts on this system, the nature of the superconducting ground state remains elusive. In particular, consensus on the electron pairing symmetry has not been achieved so far, in part owing to the lack of a momentum-resolved measurement of the superconducting gap structure. Here we report ...
Quantum disordered ground state in the triangular-lattice magnet NaRuO2
It has long been hoped that spin liquid states might be observed in materials that realize the triangular-lattice Hubbard model. However, weak spin–orbit coupling and other small perturbations often induce conventional spin freezing or magnetic ordering. Sufficiently strong spin–orbit coupling, however, can renormalize the electronic wavefunction and induce anisotropic exchange interactions that promote magnetic frustration.
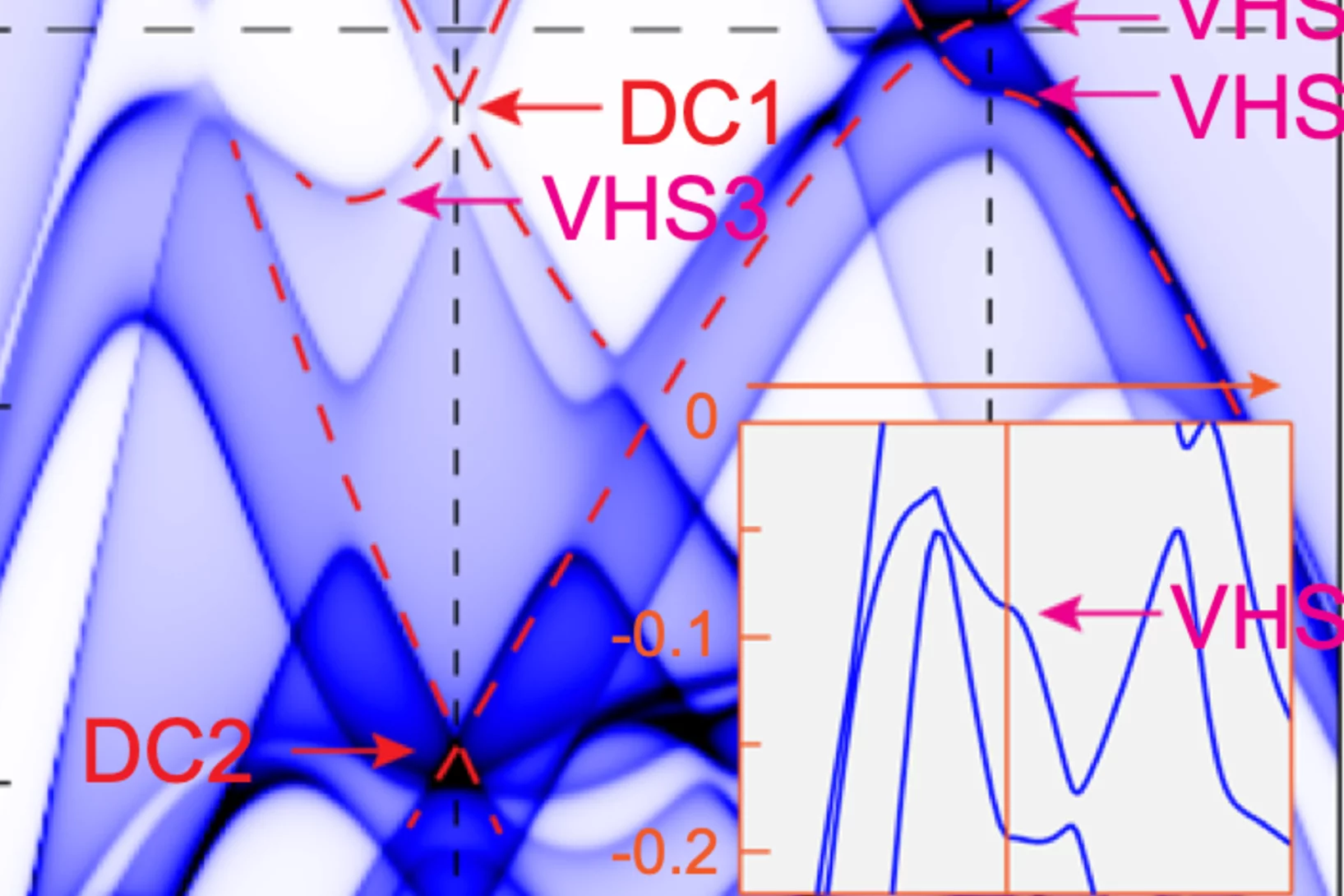
Visualizing Higher-Fold Topology in Chiral Crystals
Novel topological phases of matter are fruitful platforms for the discovery of unconventional electromagnetic phenomena. Higher-fold topology is one example, where the low-energy description goes beyond standard model analogs. Despite intensive experimental studies, conclusive evidence remains elusive for the multigap topological nature of higher-fold chiral fermions. In this Letter, we leverage a combination of fine-tuned chemical engineering and photoemission spectroscopy with photon energy contrast to discover the higher-fold topology of a chiral crystal.