News
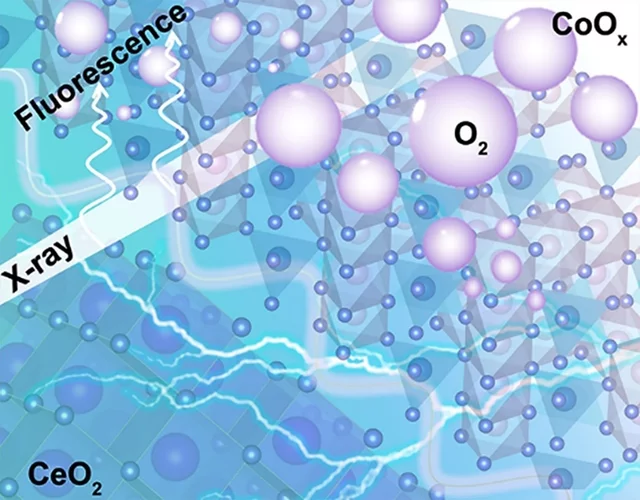
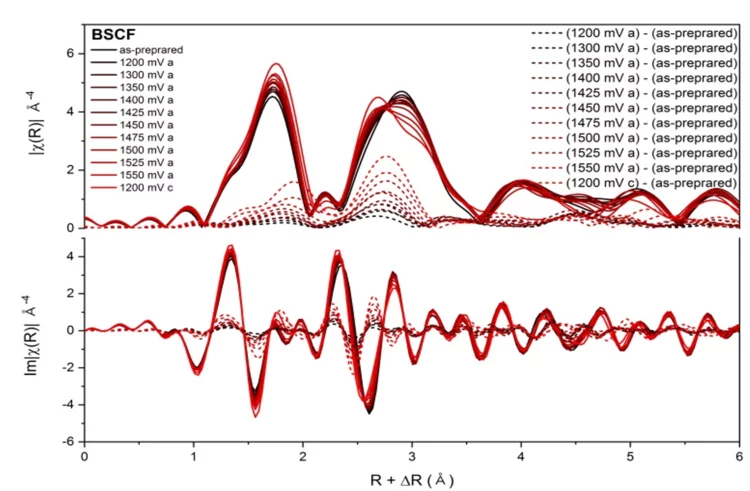
Insights into the superior oxygen evolution reaction activity of CoOx/CeO2 composite electrocatalyst
CeO2 significantly enhances the oxygen evolution reaction (OER) activity of CoOx, although the mechanism behind this synergy is still unclear. Here, operando hard X-ray absorption spectroscopy (hXAS) is applied to monitor the Co-K edge and Ce L3 edge in CoOx/CeO2 to shed light on the evolution of Co and Ce oxidation states during OER. In addition, ex situ soft XAS (sXAS) characterizations provide information on the irreversible surface-specific transformations of the Co L3 edge as well as the O K edge.
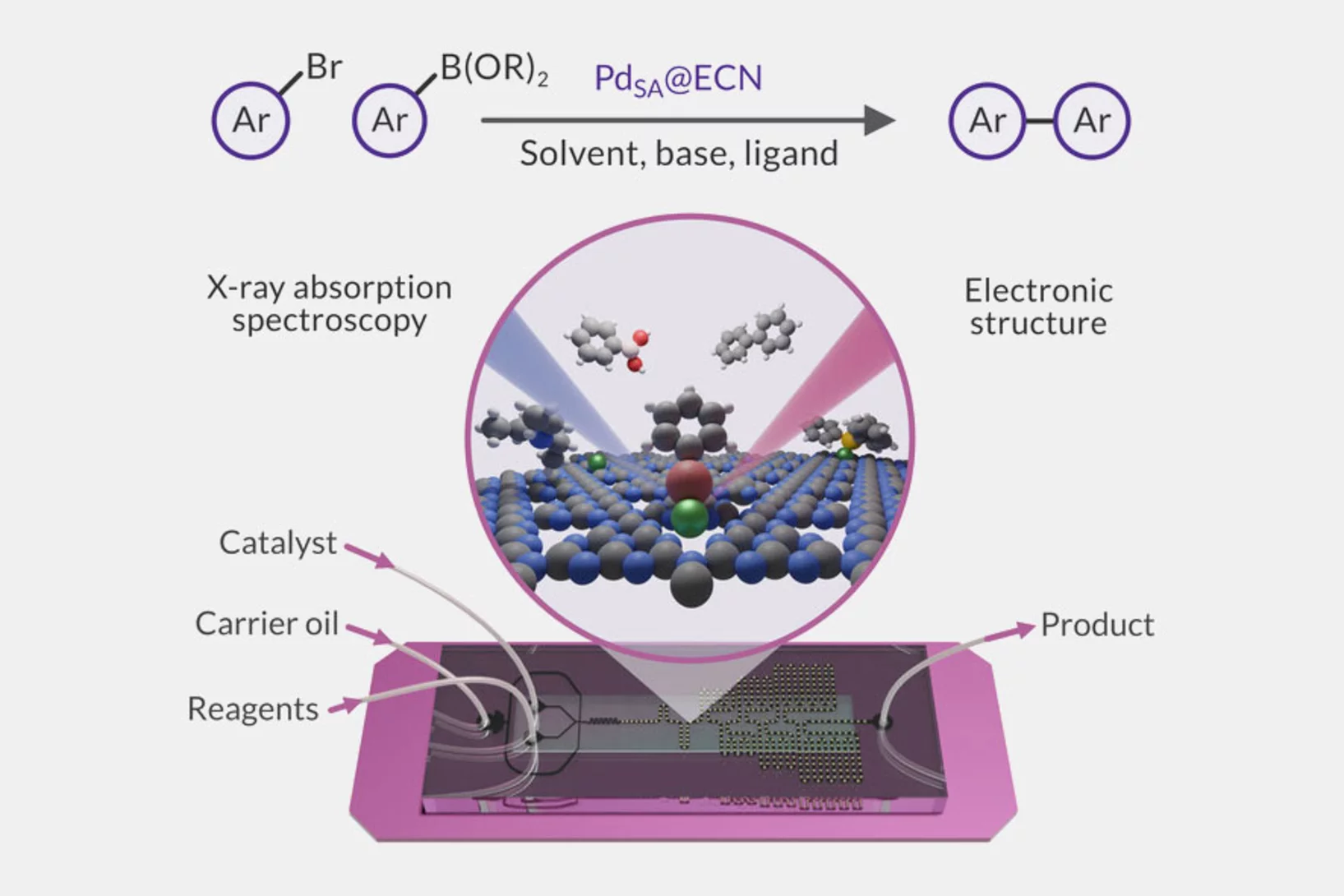
Microfluidic platform for in situ characterization of heterogenous catalysts
A deep understanding of active site architectures during surface-catalyzed reactions is a crucial step for the design of recyclable heterogeneous catalysts for organic synthesis. In this work, a droplet-based microfluidic setup was developed and applied to perform Suzuki-Miyaura coupling over heterogenous single-atom Pd-catalyst.
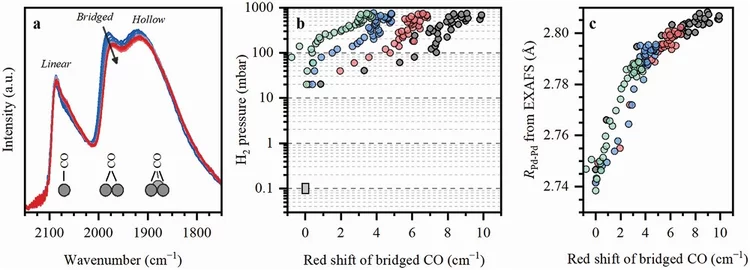
Machine Learning for Quantitative Structural Information from Infrared Spectra: The Case of Palladium Hydride
Infrared spectroscopy (IR) is a widely used technique enabling to identify specific functional groups in the molecule of interest based on their characteristic vibrational modes or the presence of a specific adsorption site based on the characteristic vibrational mode of an adsorbed probe molecule. The interpretation of an IR spectrum is generally carried out within a fingerprint paradigm by comparing the observed spectral features with the features of known references or theoretical calculations. This work demonstrates a method for extracting quantitative structural information beyond this approach by application of machine learning (ML) algorithms.
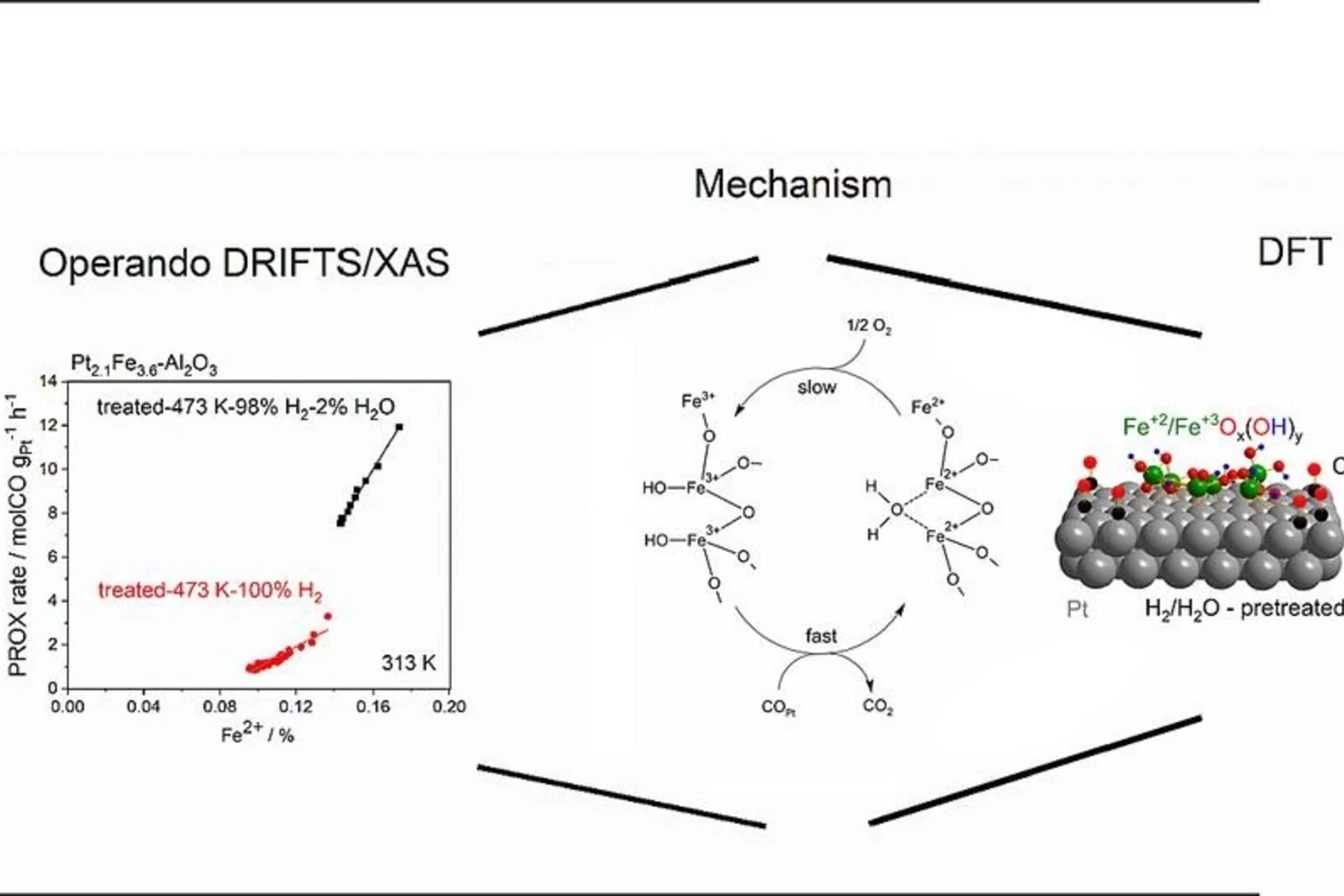
Water-assisted generation of catalytic interface: The case of interfacial Pt-FeOx(OH)y sites active in preferential carbon monoxide oxidation
Pt-FeOx(OH)y interface with enhanced activity for PROX is generated via strong metal-support interaction. Increase in the degree of hydroxylation of Pt-FeOx(OH)y interface enhances the rate of PROX mediated by active Fe2+ species.
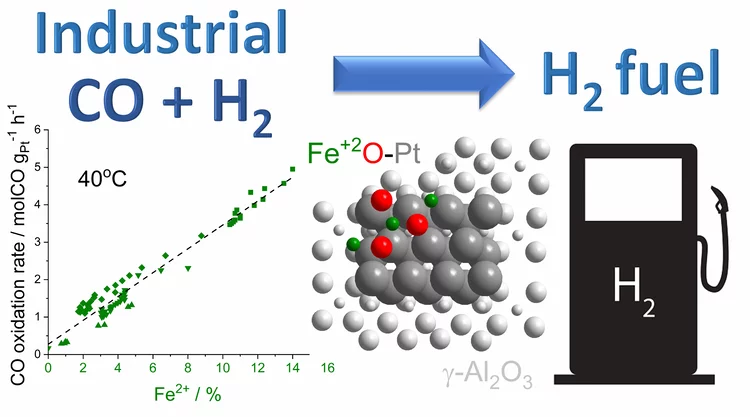
Platinum-Iron(II) Oxide Sites Directly Responsible for Preferential Carbon Monoxide Oxidation at Ambient Temperature: An Operando X-ray Absorption Spectroscopy Study
Operando X-ray absorption spectroscopy revealed a linear correlation between the amount of oxidic Fe2+ and the ambient temperature activity of Pt−FeOx preferential carbon monoxide oxidation catalysts. The hydrogen prereduction temperature and pressure determines the amount of active Fe2+ sites for alumina- and silica-supported Pt−Fe catalysts. Catalyst deactivation is linked with the oxidation of these sites.
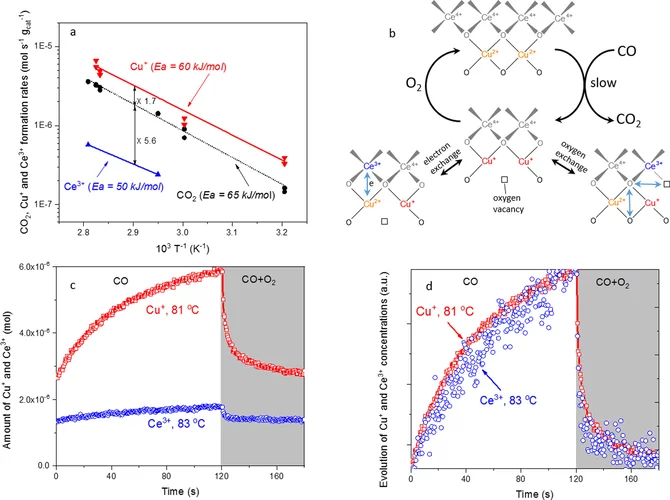
Elucidating the Oxygen Activation Mechanism on Ceria-Supported Copper-Oxo Species Using Time-Resolved X-ray Absorption Spectroscopy
We monitored the dynamic structure of the active sites in a catalyst containing highly dispersed copper-oxo species on ceria during low-temperature CO oxidation using time-resolved X-ray absorption spectroscopy. We quantitatively demonstrate that the CO oxidation mechanism below 90 °C involves an oxygen intermediate strongly bound to the active sites as well as the redox activity of Cu2+/Cu+ and Ce4+/Ce3+ couples.
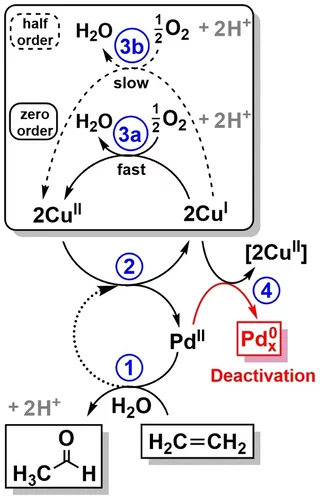
Elucidating the mechanism of heterogeneous Wacker oxidation over Pd-Cu/zeolite Y by transient XAS
Unlike the homogeneous Wacker process, the understanding of the mechanism of the heterogeneous system has long remained to be superficial. Here the authors investigated the mechanism of heterogeneous Wacker oxidation over Pd-Cu/zeolite Y through transient XAS coupled with kinetic studies and chemometric analysis.
Modulated excitation methodology
V2O5/TiO2 SCR catalysts
An increased level of mechanistic information is obtained when Raman spectroscopy is combined with modulated excitation in the case of V-based catalysts used for SCR.
Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR)
Cu-SSZ13
The combination of time-resolved XAS and transient experiments enables to capture an inhibition effect by NH3 on the rate-limiting re-oxidation of CuI at low temperature.
Oxygen Evolution Reaction (OER)
Perovskite oxides
Time-resolved XAS is exploited to capture the dynamic local electronic and geometric structure of perovskite oxides under operando conditions.
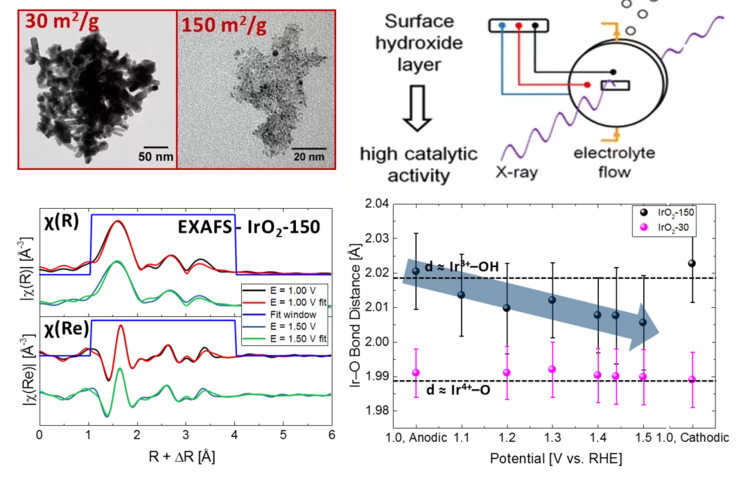
Oxygen Evolution Reaction (OER)
Iridium oxides
Iridium oxides have been investigated by XAS under operando conditions to demonstrate the effect of size on OER.