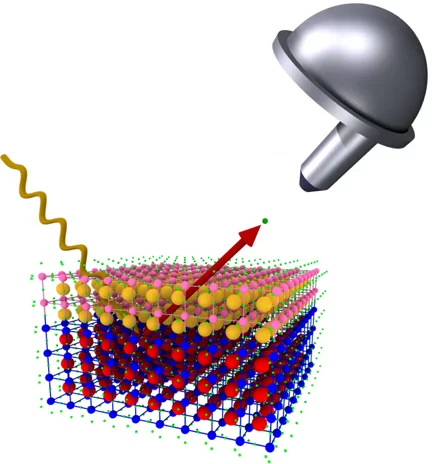
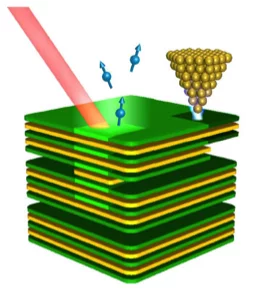
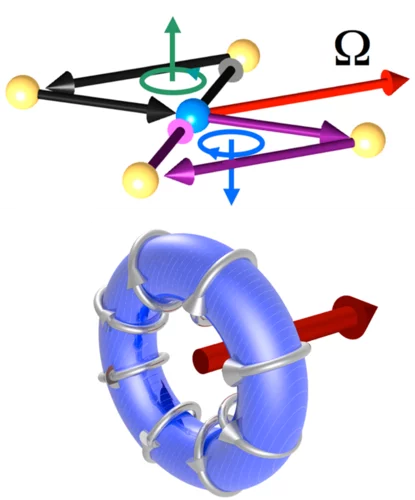
Observed live with x-ray laser: electricity controls magnetism
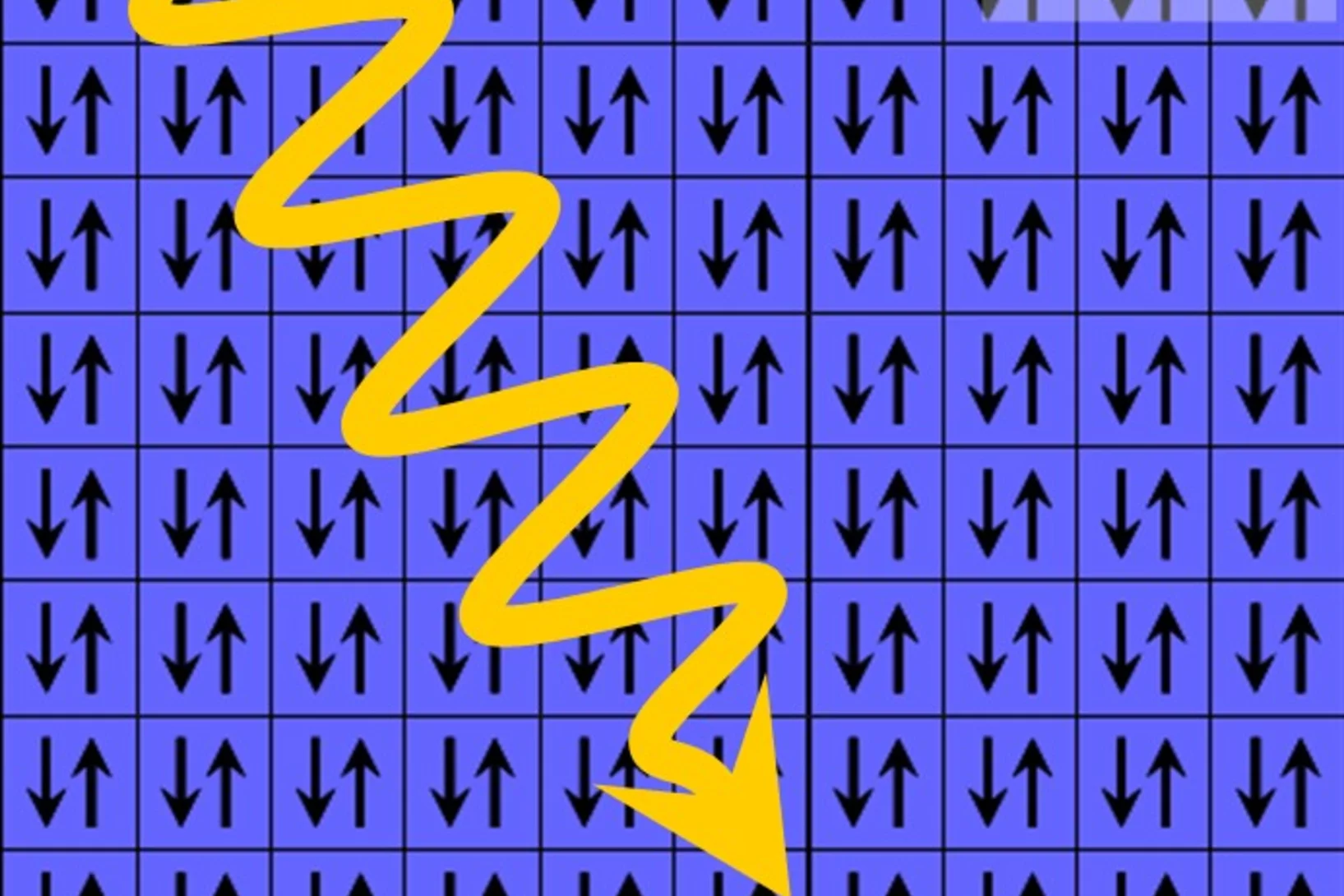
Researchers from ETH Zurich and the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI demonstrate how the magnetic structure can be altered quickly in novel materials. The effect could be used in efficient hard drives of the future.
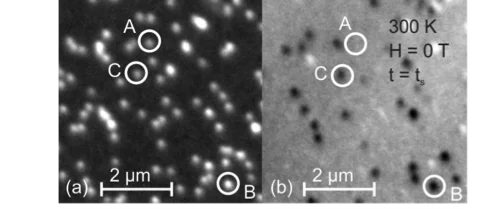
Direct Observation of Magnetic Metastability in Individual Iron Nanoparticles
Studying the magnetization of individual iron (Fe) nanoparticles by magnetic spectromicroscopy reveals that superparamagnetic (SPM) and ferromagnetic blocked (FM) nanoparticles can coexist in the investigated size range of 8-20 nm.
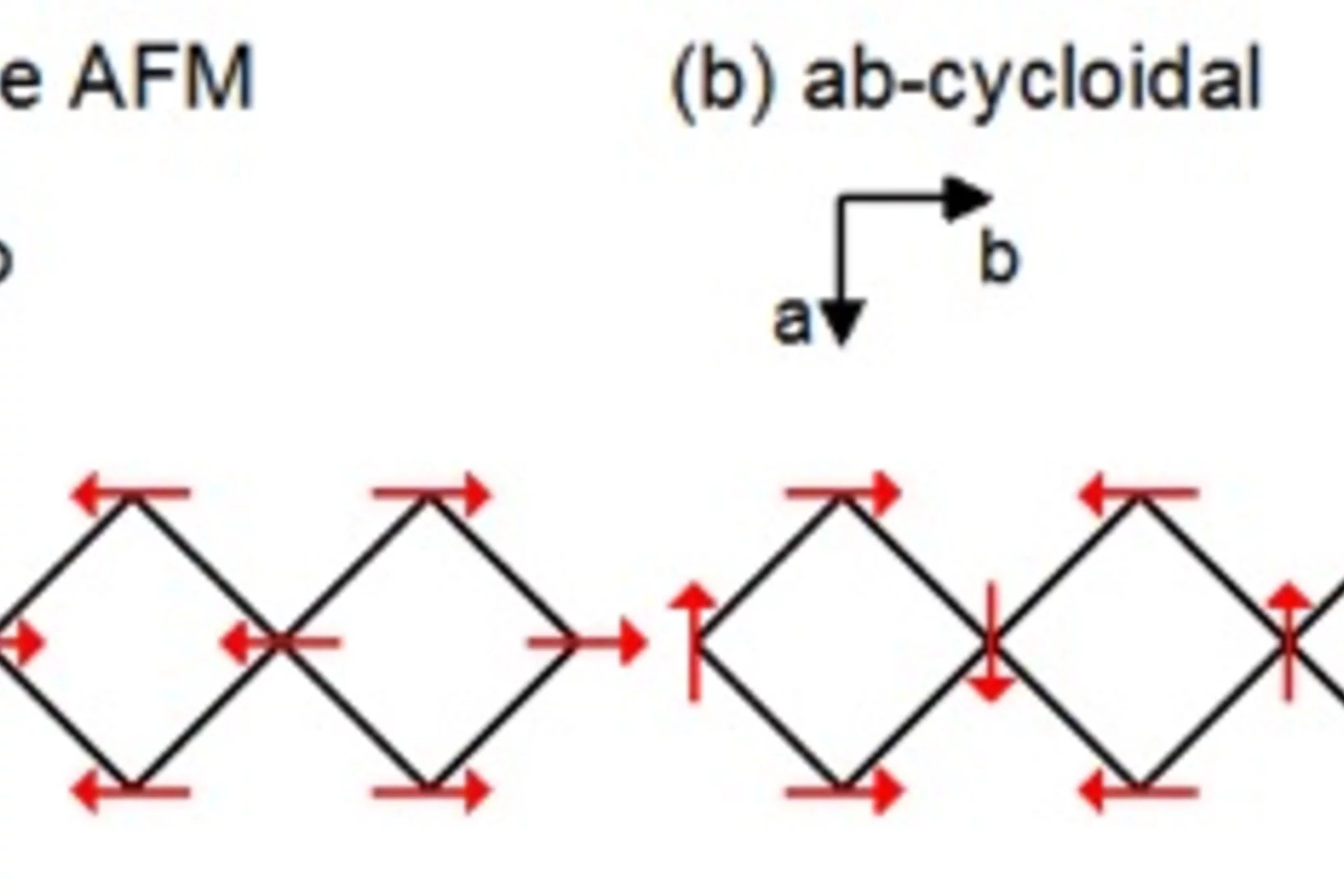
Comprehensive study of the spin-charge interplay in antiferromagnetic La2-xSrxCuO4
The origin of the pseudogap and its relationship with superconductivity in the cuprates remains vague. In particular, the interplay between the pseudogap and magnetism is mysterious. Recent low-temperature angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy (ARPES) experiments on the underdoped cuprate superconductors indicate the presence of a fully gapped Fermi surface (FS); even in the antiferromagnetic phase.
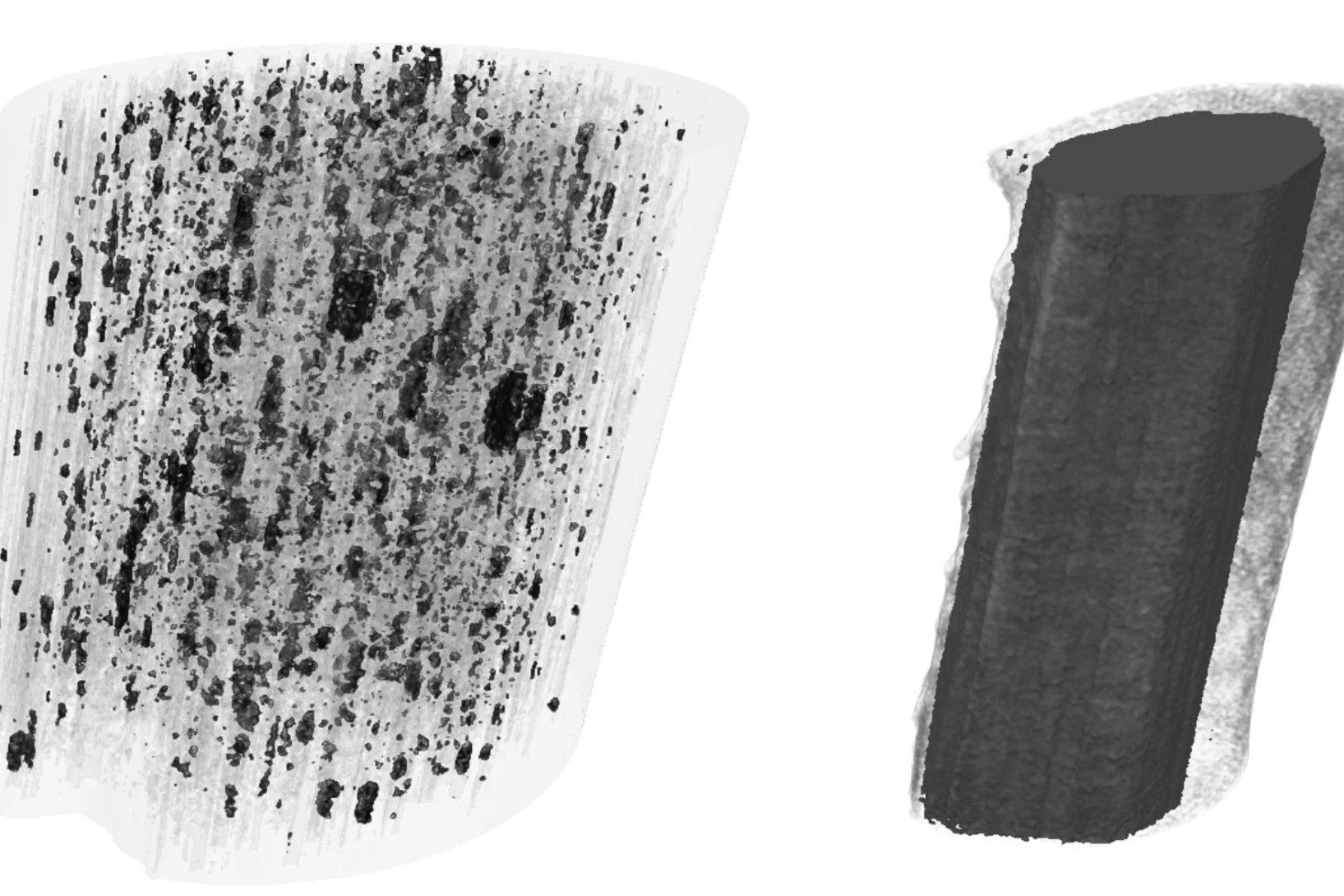
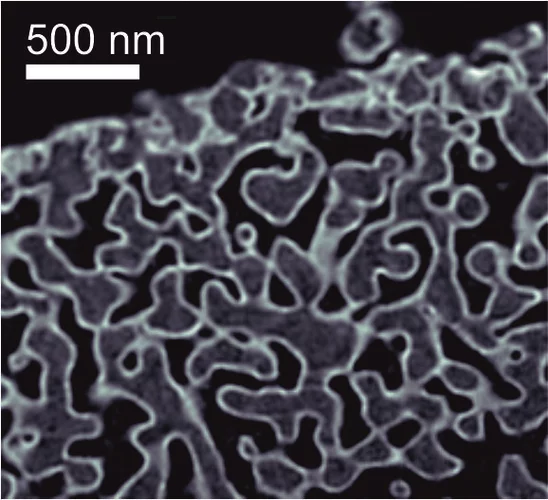
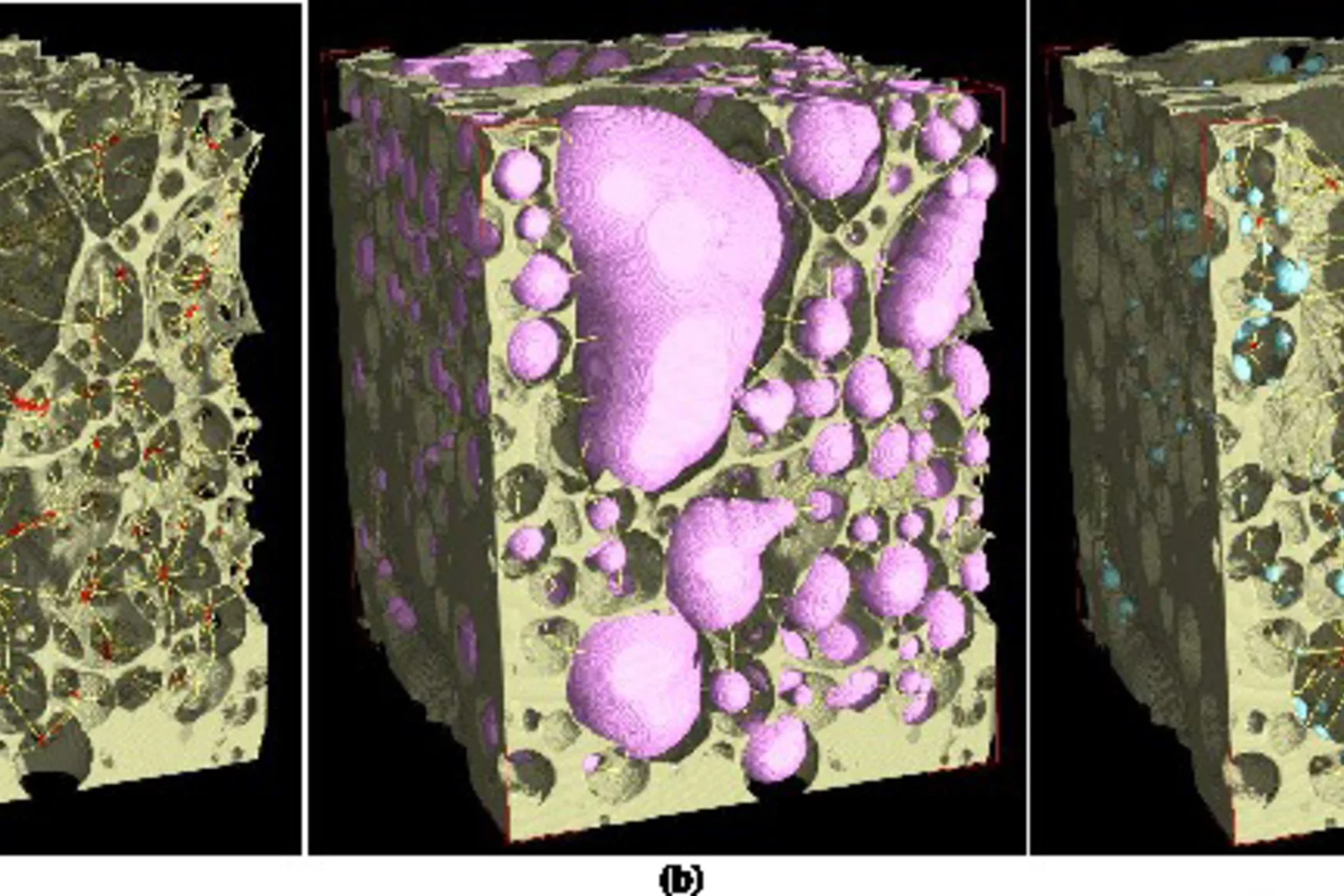
Unique insight into carbon fibers on the nanoscale
Novel carbon materials are promising candidates for light and robust low-cost materials of the future. Understanding their mechanical properties benefits from highly resolved three-dimensional (3D) maps of their porosity and density fluctuations in uninterrupted representative volumes, but these are difficult to obtain with conventional imaging methods.
X-ray tomography reaches 16 nm isotropic 3D resolution
Tomographic microscopy has become an invaluable imaging method in both life and materials sciences. Oftentimes, high resolving power is required simultaneously with the ability to characterize large, statistically representative sample volumes. To this task, researchers at the Paul Scherrer Institut have established ptychographic computed tomography.
Spintronics: deciphering a material for future electronics
Topological insulators are the key to future spintronics technologies. EPFL scientists have unraveled how these strange materials work, overcoming one of the biggest obstacles on the way to next-generation applications.Read the full story
Supervolcano eruptions driven by melt buoyancy in large silicic magma chambers
Super-eruptions that dwarf all historical volcanic episodes in erupted volume and environmental impact are abundant in the geological record. Such eruptions of silica-rich magmas form large calderas. The mechanisms that trigger these supereruptions are elusive because the processes occurring in conventional volcanic systems cannot simply be scaled up to the much larger magma chambers beneath super volcanoes.
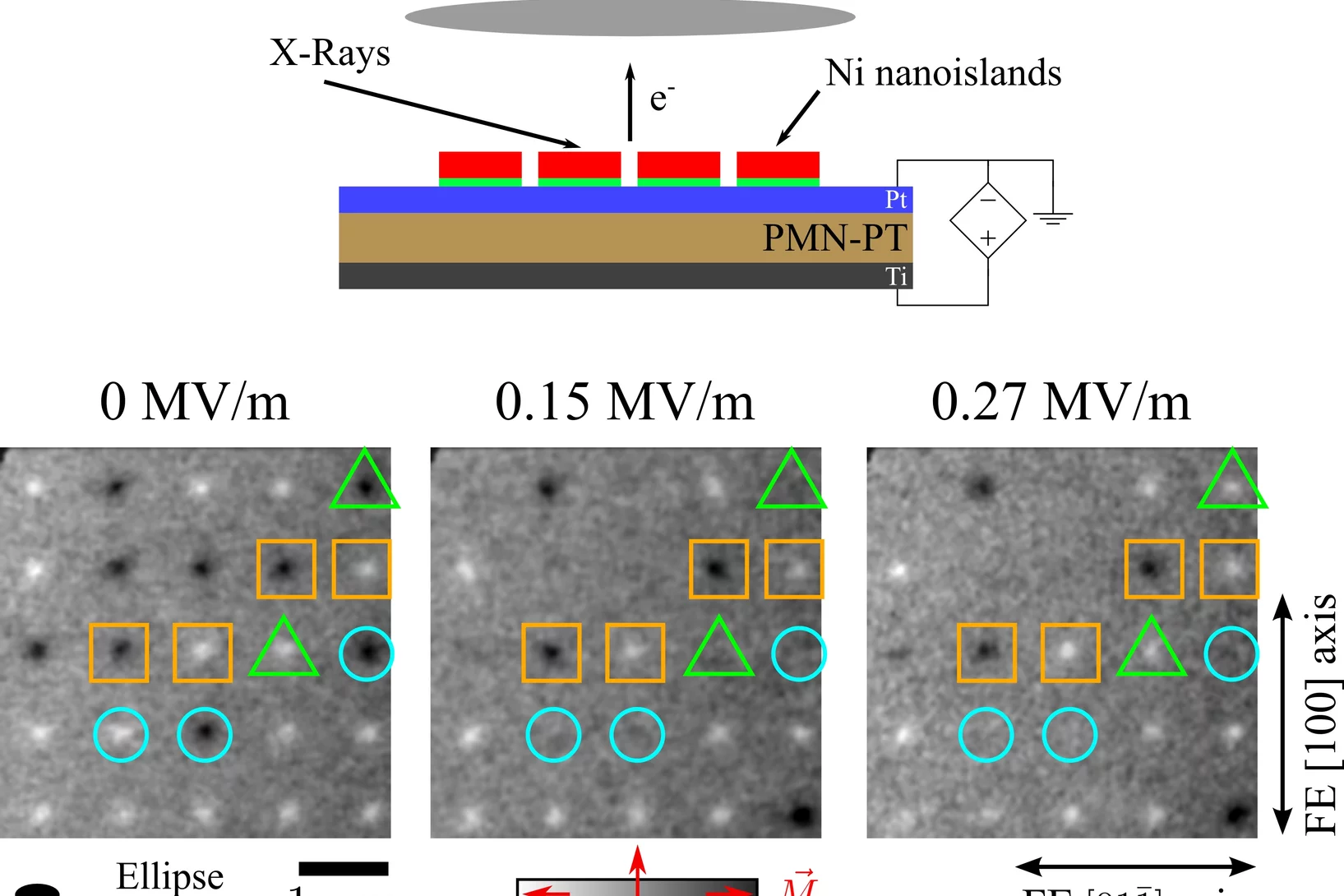
Single Domain Spin Manipulation by Electric Fields in Strain Coupled Artificial Multiferroic Nanostructures
Encoding information by the application of an electric field has a key role in the development of novel memory devices that can operate at high speed while keeping low energy consumption. In magnetoelectric multiferroics, magnetic and ferroelectric ordering coexist and are coupled together so that it is possible to manipulate the material's magnetic structure by applying an electric field with a negligible current flow.
Tiny Magnets as a Model System
Scientists use nano-rods to investigate how matter assembles
In the microscopic world, everything is in motion: atoms and molecules vibrate, proteins fold, even glass is a slow flowing liquid. And during each movement there are interactions between the smallest elements - for example, the atoms - and their neighbours. To make these movements visible, scientists at the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI have developed a special model system.
Atomic motions untangled
The pursuit of capturing motion in a movie bears an obvious fascination irrespective of the time scales involved. In the atomic and molecular world where the masses are so light and the distances small the relevant time scale shifts to the subpicosecond range and the motions become frantic especially for larger molecular systems.
Soft x-ray photoelectron spectroscopy on buried complex oxide interfaces: a new method to diagnose authentic protected electronic structures
Exotic phenomena at interfaces of complex oxides are highly promising for future solid-state electronics applications. A prominent example is the interface of two wide band gap insulators formed by growing a LaAlO3 layer on TiO2-terminated SrTiO3 substrate. When the LaAlO3 thickness exceeds 3 unit cells this system undergoes a sharp insulator-to-metal transition with a two-dimensional electron gas (2DEG) appearing at the interface.
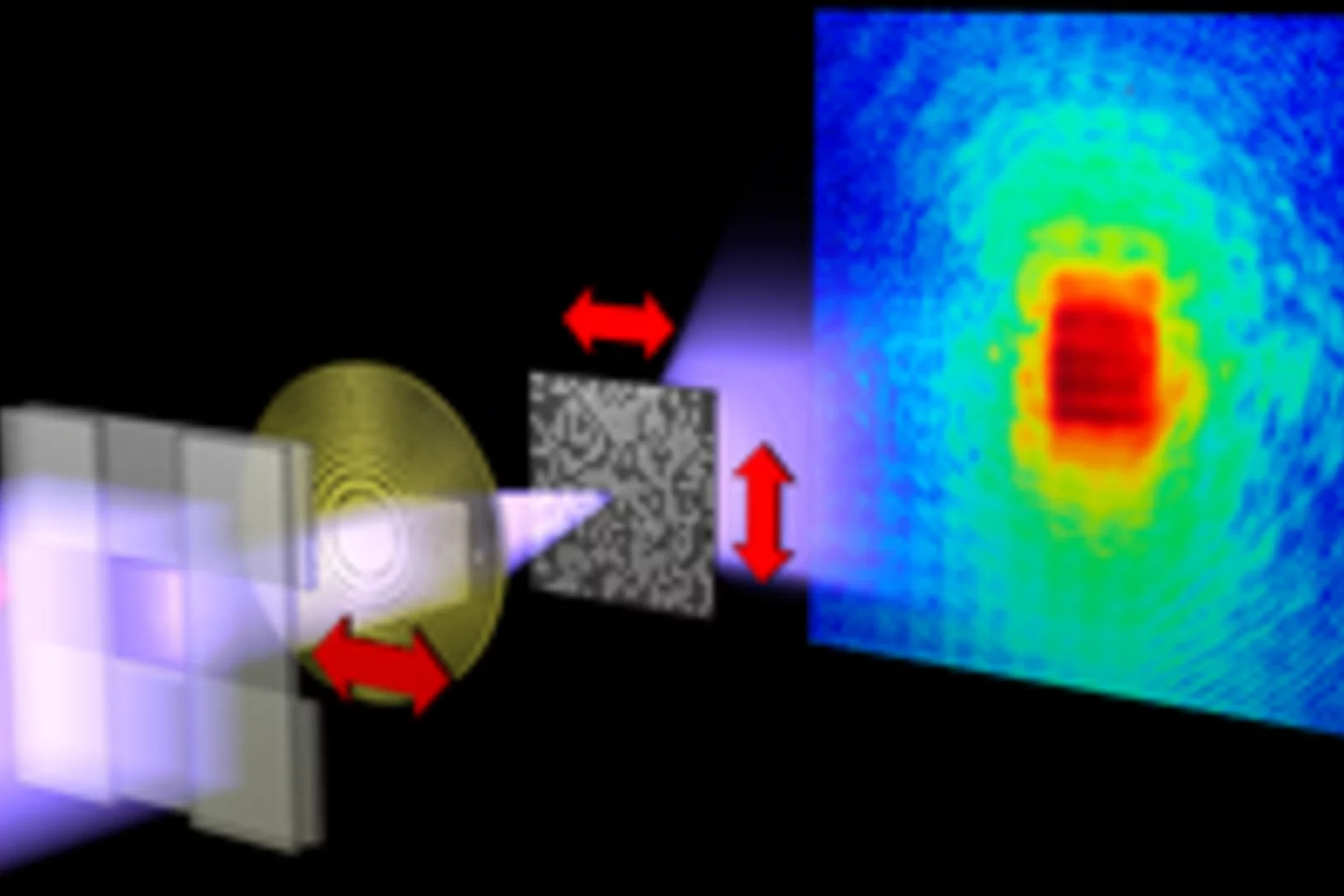
Imaging fluctuations with X-ray microscopy
X-rays allow an inside look at structures that cannot be imaged using visible light. They are used to investigate nanoscale structures of objects as varied as single cells or magnetic storage media. Yet, high-resolution images impose extreme constraints on both the X ray microscope and the samples under investigation.
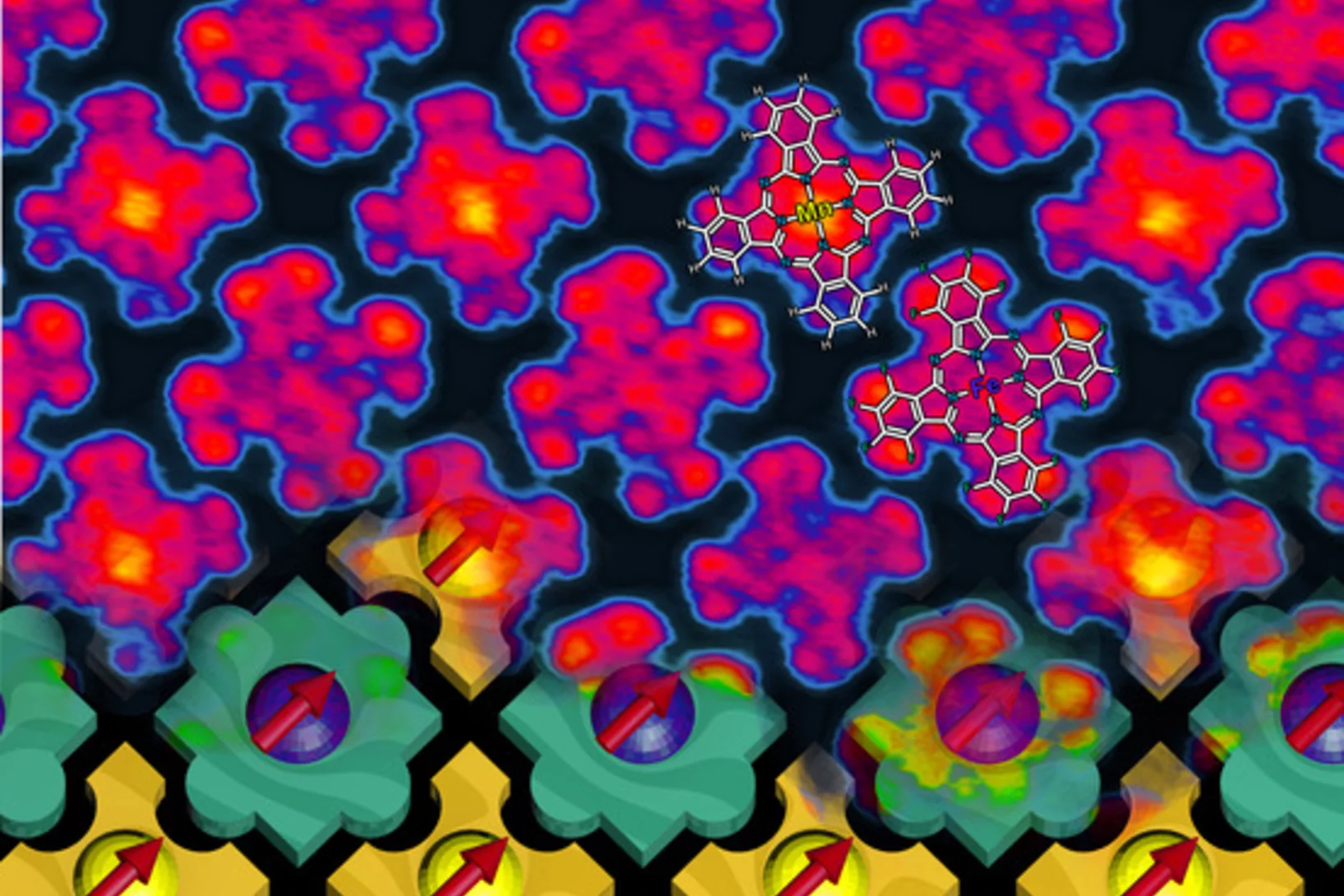
Magnetic nano-chessboard puts itself together
Researchers from the Paul Scherrer Institute and the Indian Institute of Science Education and Research (Pune, India) have managed to ‘turn off’ the magnetization of every second molecule in an array of magnetized molecules and thereby create a ‘magnetic chessboard’. The magnetic molecules were so constructed that they were able to find their places in the nano-chessboard by themselves.
X-rays provide insights into volcanic processes
Experiments performed at the Paul Scherrer Institute (PSI) investigate processes inside volcanic materials that determine whether a volcano will erupt violently or mildly.
New Insights into Superconducting Materials
An American-Swiss research team has used a new X-ray technique at Swiss Light Source (SLS) of the Paul Scherrer Institute (PSI) to investigate the magnetic properties of atomically thin layers of a parent compound of a high-temperature superconductor. It turns out that the magnetic properties of such thin films differ by only a surprisingly small degree from those of macroscopically thick samples.
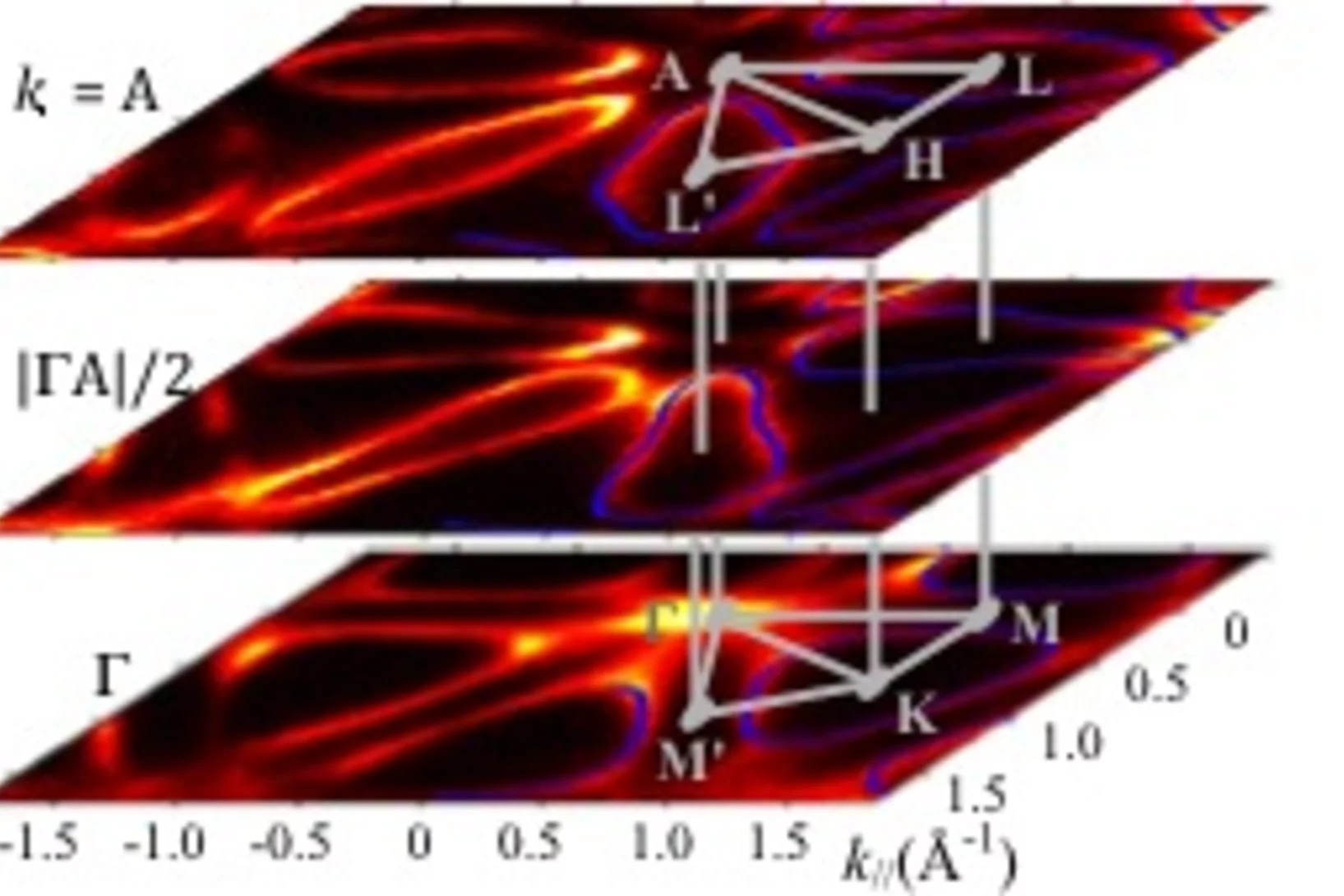
Three-Dimensional Electron Realm in Crystalline Solids Revealed with Soft-X-Rays
The electronic band structure E(k) as energy E of the electrons depending on its wavevector k is the cornerstone concept of the quantum solid state theory. The main experimental method to investigate E(k) is the angle-resolved photoelectron spectroscopy (ARPES). However, a small photoelectron escape depth of a few Å largely restricts the applications of ARPES to two-dimensonal crystals.
Ultra-short X-ray laser pulses precisely surveyed for the first time
X-ray lasers belong to a modern generation of light sources from which scientists in widely different disciplines expect to obtain new knowledge about the structure and function of materials at the atomic level. On the basis of this new knowledge, it could then be possible one day to develop better medicines, more powerful computers or more efficient catalysts for energy transformation.
Controversy clarified: Why two insulators together can transport electricity
How can two materials which do not conduct electricity create an electrically conducting layer when they are joined together? Since this effect was discovered in 2004, researchers have developed various hypotheses to answer this question – each with its own advocates, who defend it and try to prove its validity. Now, an international team under the leadership of researchers at the Paul Scherrer Institute has probably settled the controversy.
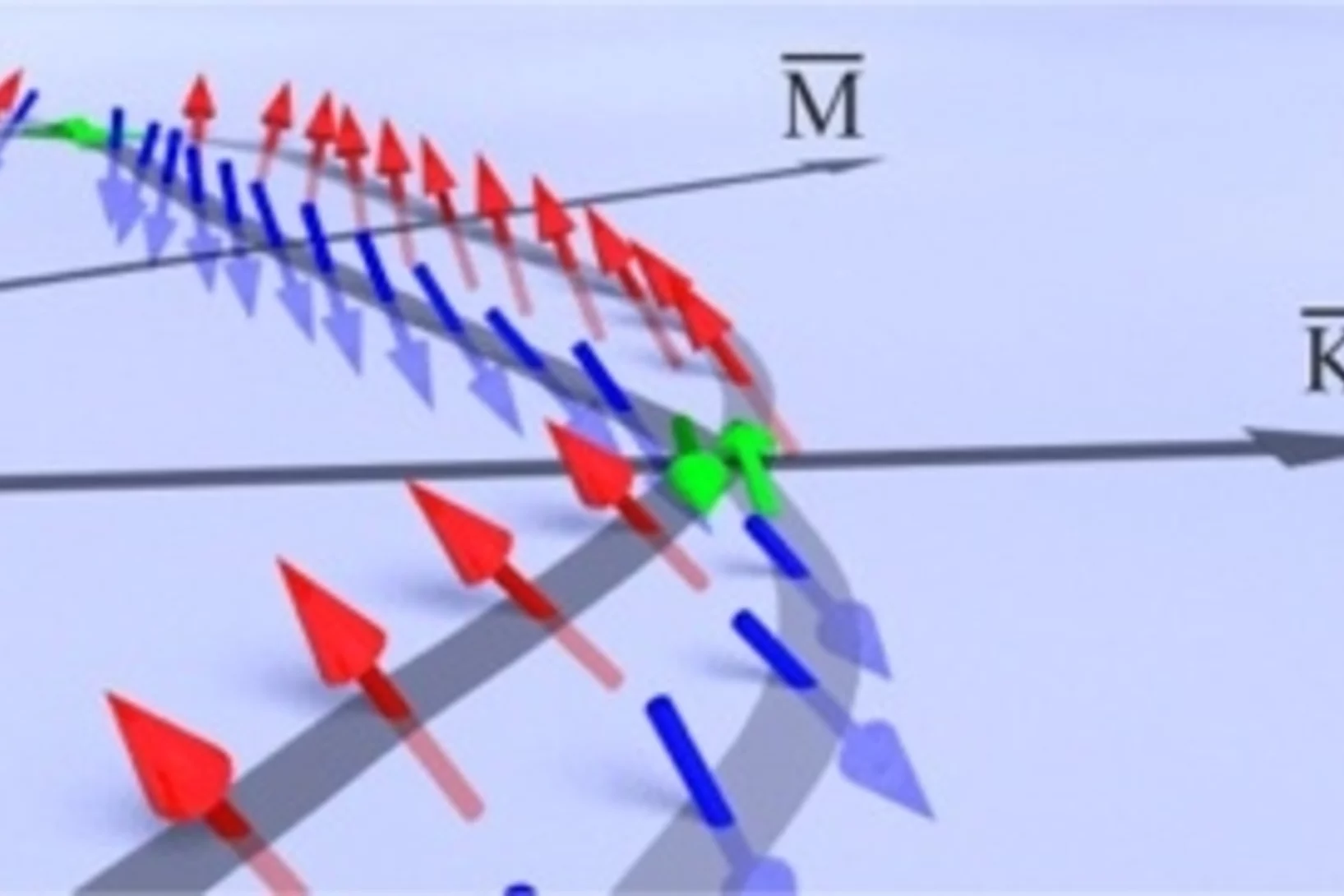
Three-Dimensional Spin Rotations in a Monolayer Electron System
In the emerging field of spintronics, the generation, injection, and in particular the control of highly spin polarized currents are main issues to be solved. Lifting of spin degeneracy by the spin-orbit interaction at surfaces, known as Rashba effect, represents a promising approach, since it generates two spin-polarized bands without the necessity of an external field. In our recent study, we realize such a system for a metallic surface layer on a semiconductor: Au/Ge(111).
Physicists observe the splitting of an electron inside a solid
An electron has been observed to decay into two separate parts, each carrying a particular property of the electron: a spinon carrying its spin – the property making the electron behave as a tiny compass needle – and an orbiton carrying its orbital moment – which arises from the electron’s motion around the nucleus. These newly created particles, however, cannot leave the material in which they have been produced.
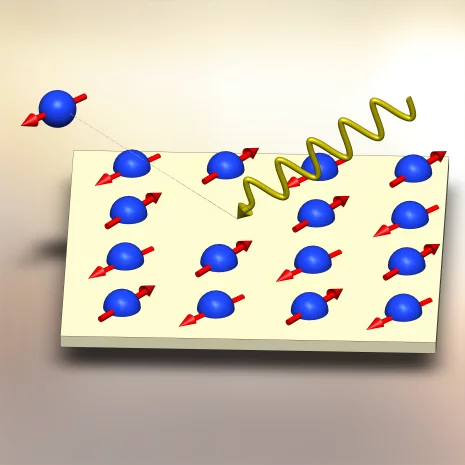
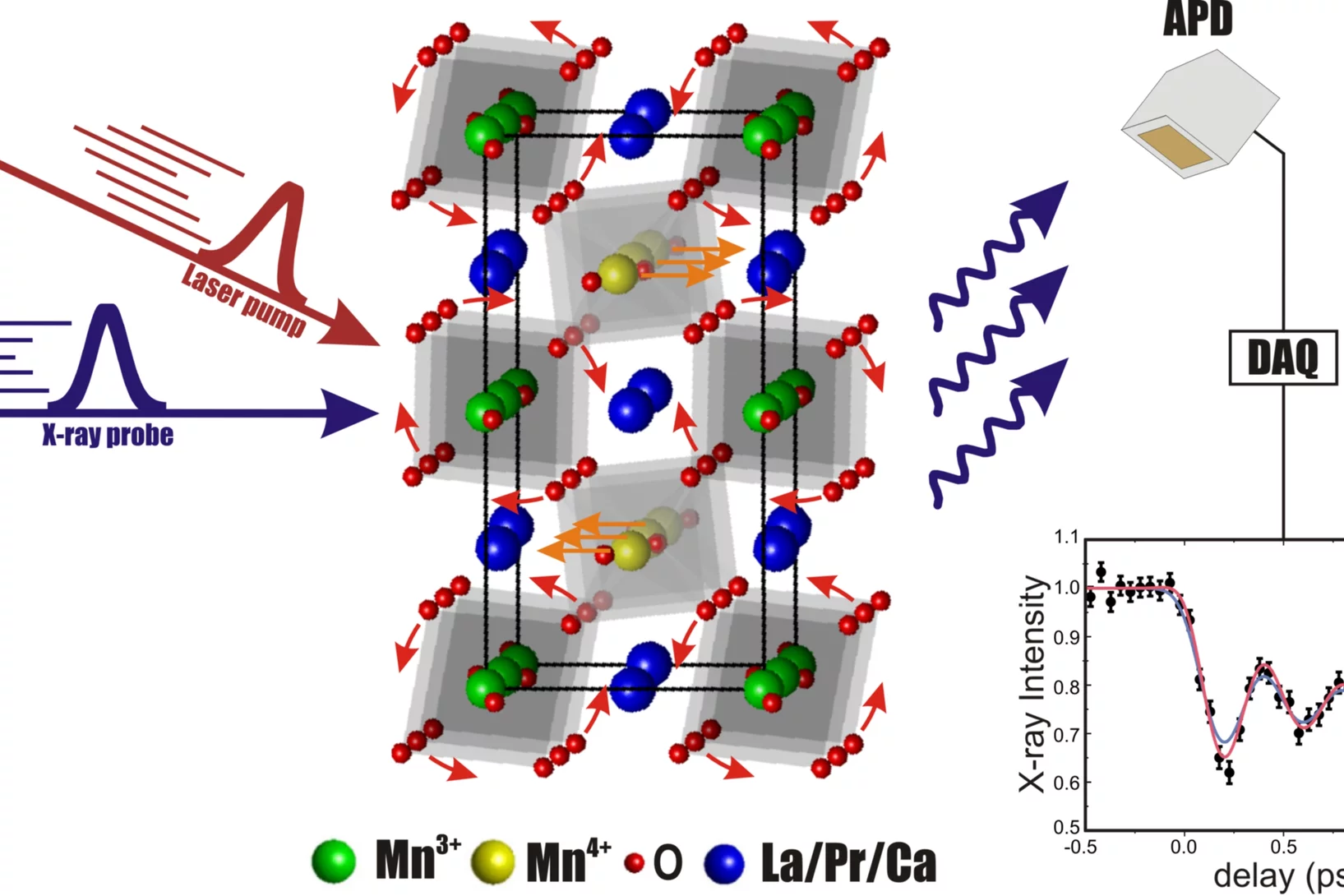
Creating magnetism takes much longer than destroying it
Researchers at the Paul Scherrer Institute are finding out how long it takes to establish magnetism and how this happens.
Origin of the Large Polarization in Multiferroic YMnO3 Thin Films
Multiferroic materials have attracted much interest because of their ability to control magnetism by the application of an electric field. This ability is expected to reduce the power required by electronic devices and to increase their speed. However, the number of multiferroic materials discovered so far has been small, and ferromagnetism and ferroelectricity in the known materials are often much weaker than required for practical applications.
Liquids in narrow spaces
How does spatial confinement affect the microscopic structure of liquids?
This is a question which is receiving increasing attention from condensed matter physicists. Liquids are characterized by a short-ranged, so-called local structure, and it has been predicted theoretically about 25 years ago that confinement induces anisotropy in the local structure, and hence many properties, of liquids.
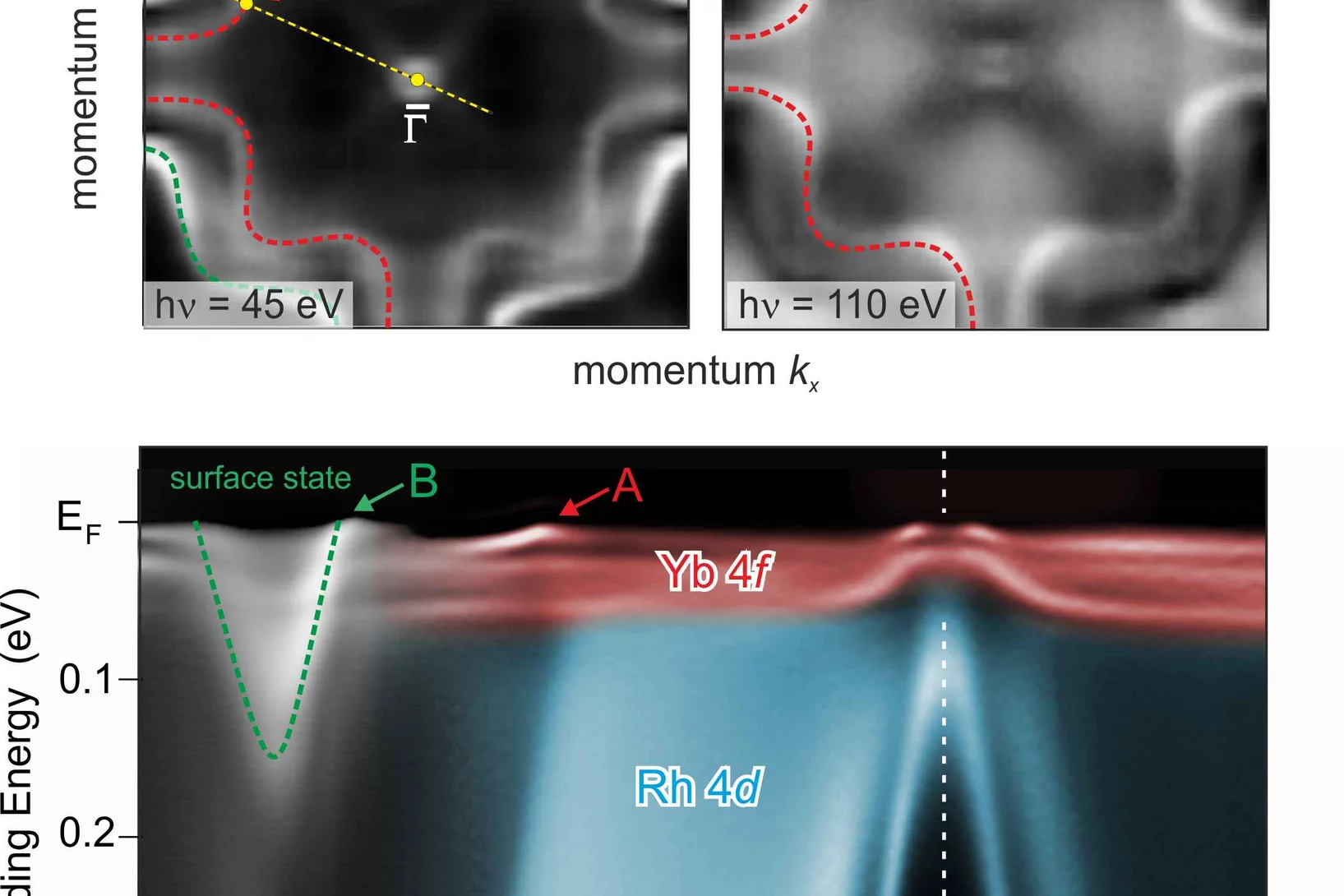
A close look at correlated electrons in heavy-fermion metal through ARPES
Showing astonishing properties like magnetism, superconductivity, Kondo and heavy-fermion (HF) behavior, rare-earth intermetallic compounds have been at the forefront of modern solid state physics for many years. Most of these properties are related to a delicate interplay between the partially filled 4f-shell and conduction electrons.
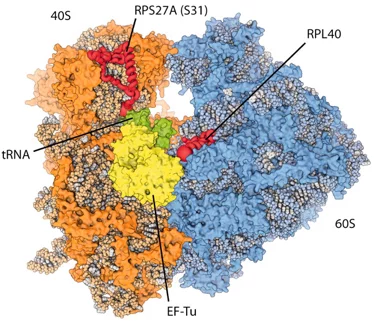
New insights into the cell’s protein factory
Eukaryotic ribosomes are among the most complex cellular machineries of the cell. These large macromolecular assemblies are responsible for the production of all proteins and are thus of pivotal importance to all forms of life. Two independent research groups at the ETH Zürich and the Institute of Genetics and Molecular and Cellular Biology in Strasbourg have obtained new insights into the atomic structure of the eukaryotic ribosome. The results have been published in the journal Science.
Bilayer manganites reveal polarons in the midst of a metallic breakdown
The origin of colossal magnetoresistance (CMR) in manganese oxides is among the most challenging problems in condensed- matter physics today. The true nature of the low-temperature electronic phase of these materials is heavily debated. By combining photoemission and tunnelling data, we show that in the archetypal bilayer system La2-2xSr1+2xMn2O7, polaronic degrees of freedom win out across the CMR region of the phase diagram.
Investigation of a new method for the diagnosis of cancer in breast tissue
Collaboration between research, hospital and industry aimed at transferring innovative procedure into daily practice.
Observation of Orbital Currents in CuO
Although high-temperature (Tc) superconductivity was discovered in the cuprates 25 years ago, there is still no consensus on its microscopic origin.
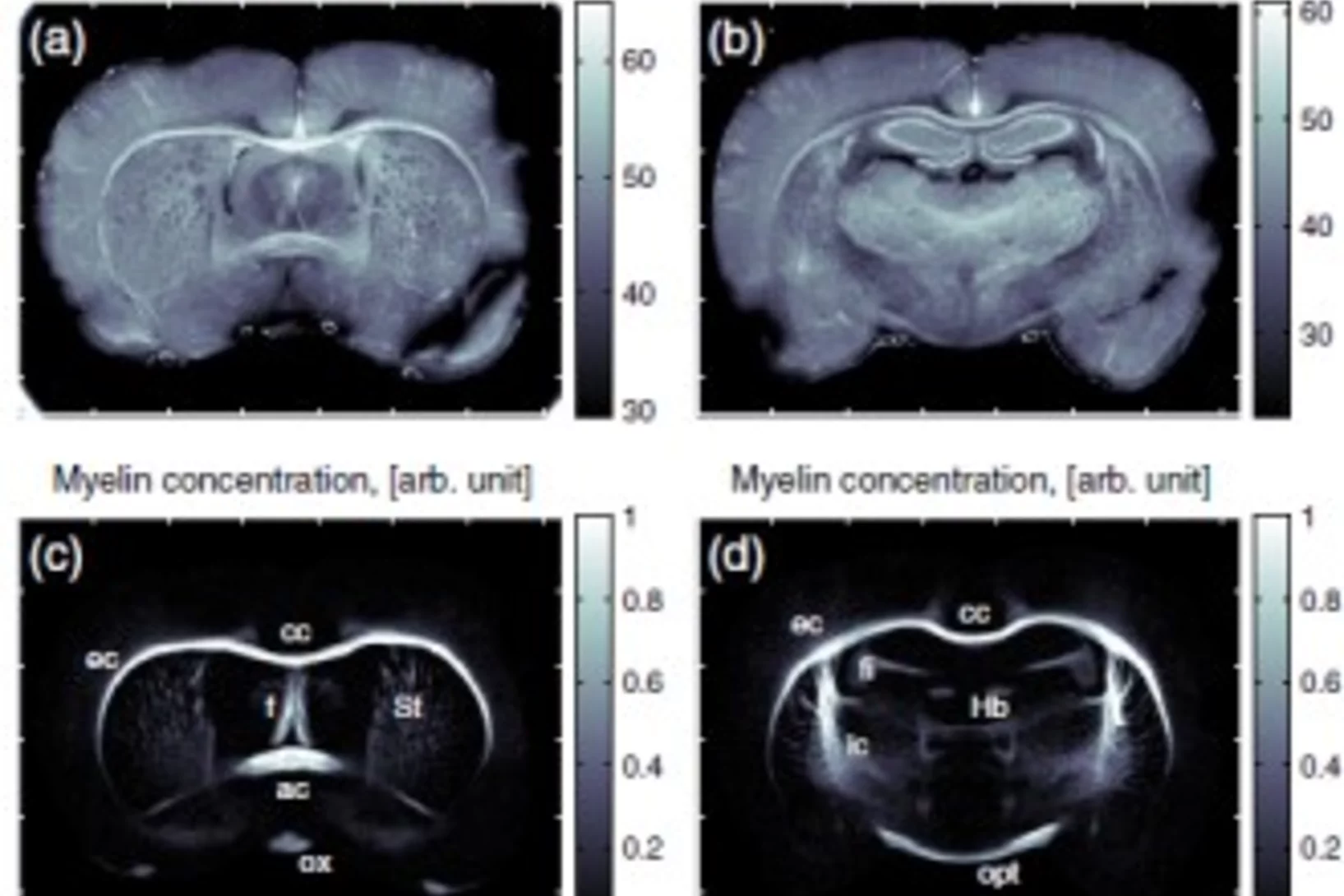
X-ray methods help to understand brain disorders better
An international team of researchers from Denmark, Germany, Switzerland and France has developed a new method for making detailed X-ray images of brain tissue, which has been used to make the myelin sheaths of nerve fibres visible. Damage to these protective sheaths can lead to various disorders, such as multiple sclerosis. The facility for creating these images of the protective sheaths of nerve cells is being operated at the Swiss Light Source (SLS), at the Paul Scherrer Institute.
The electron torus can help us to understand high-temperature superconductors
Paul Scherrer Institute researchers prove, for the first time, the existence of toroidal currents in solids