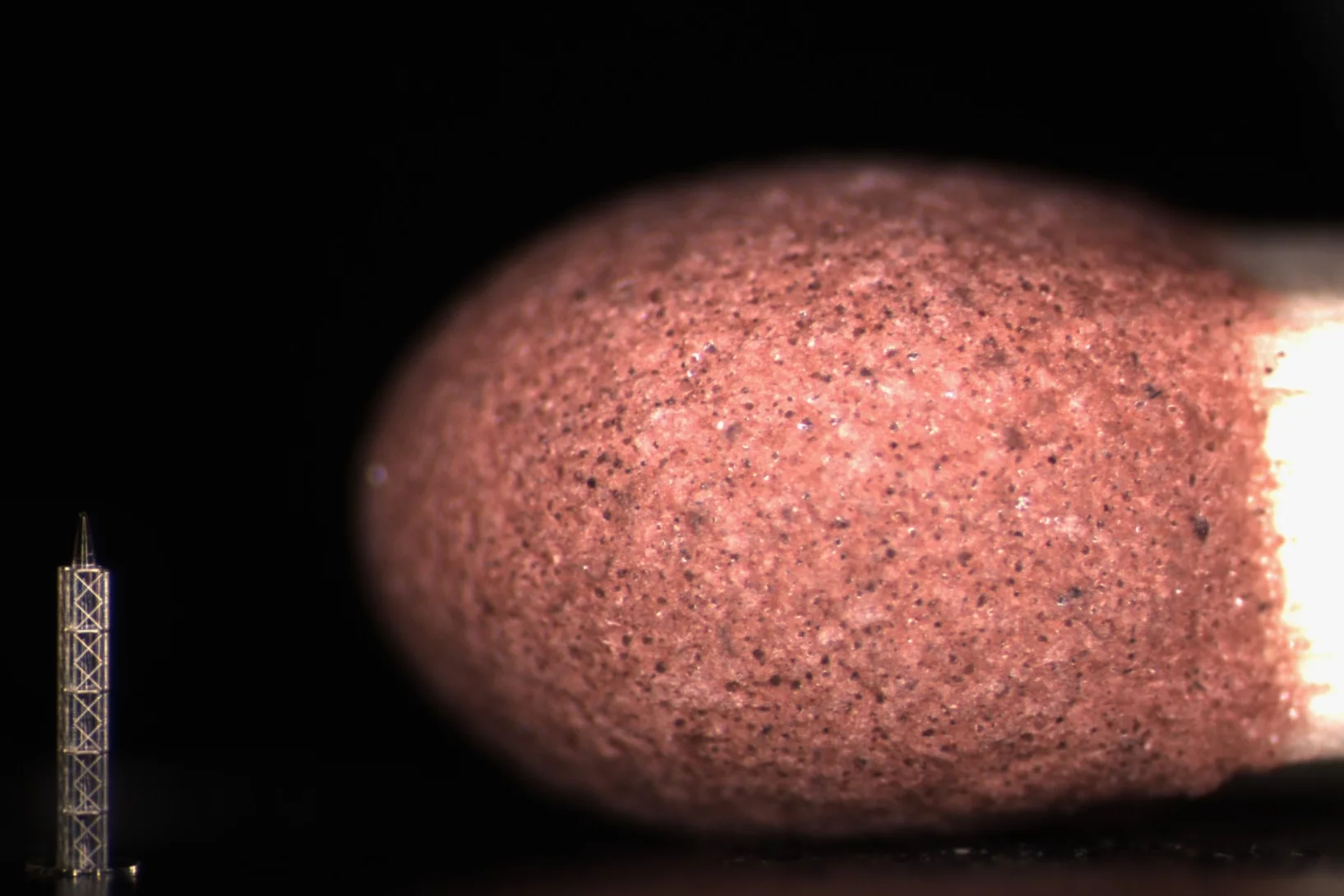
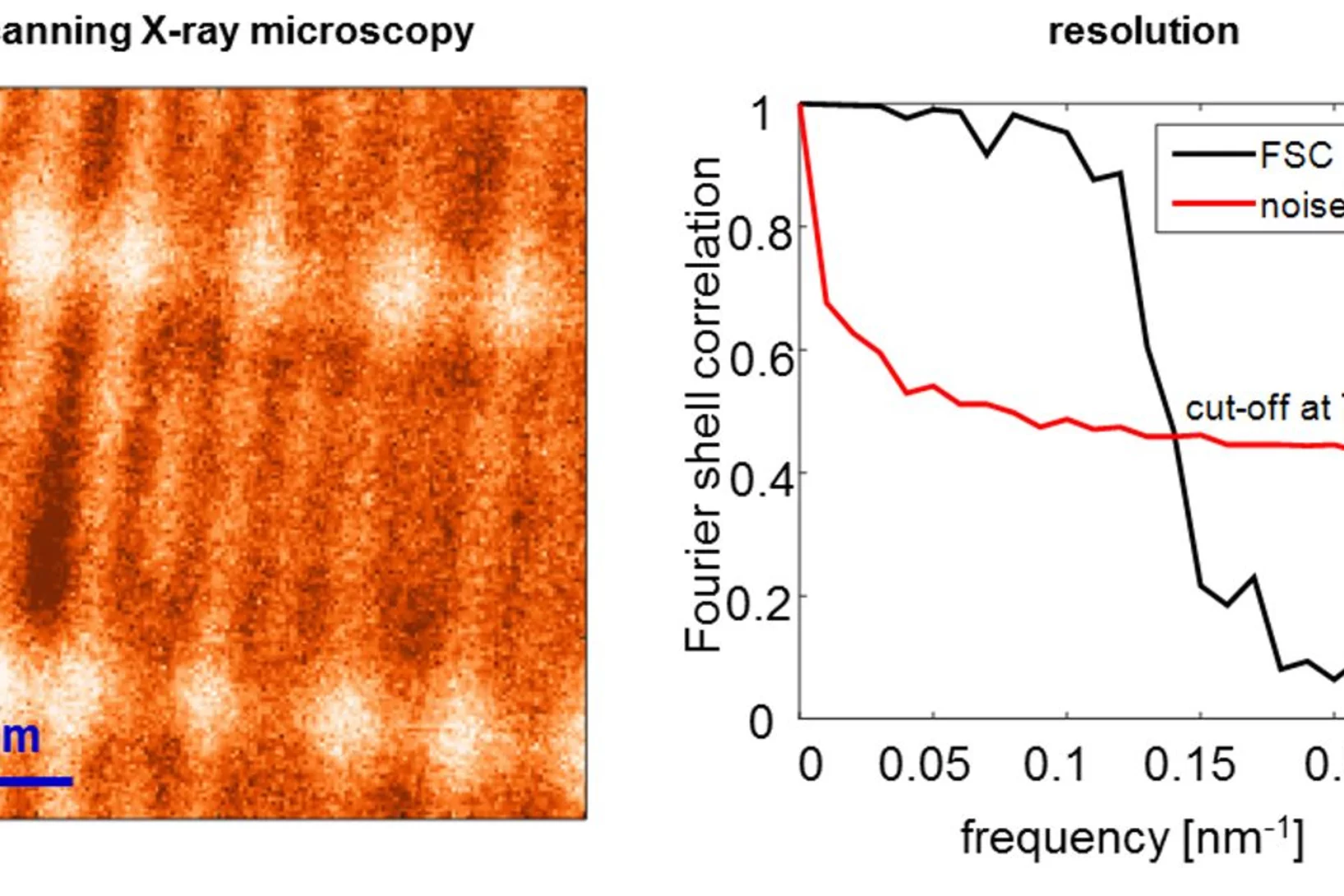
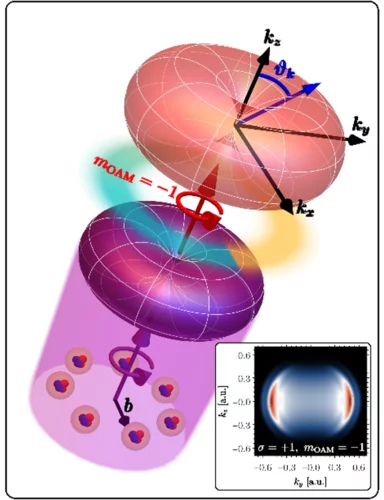
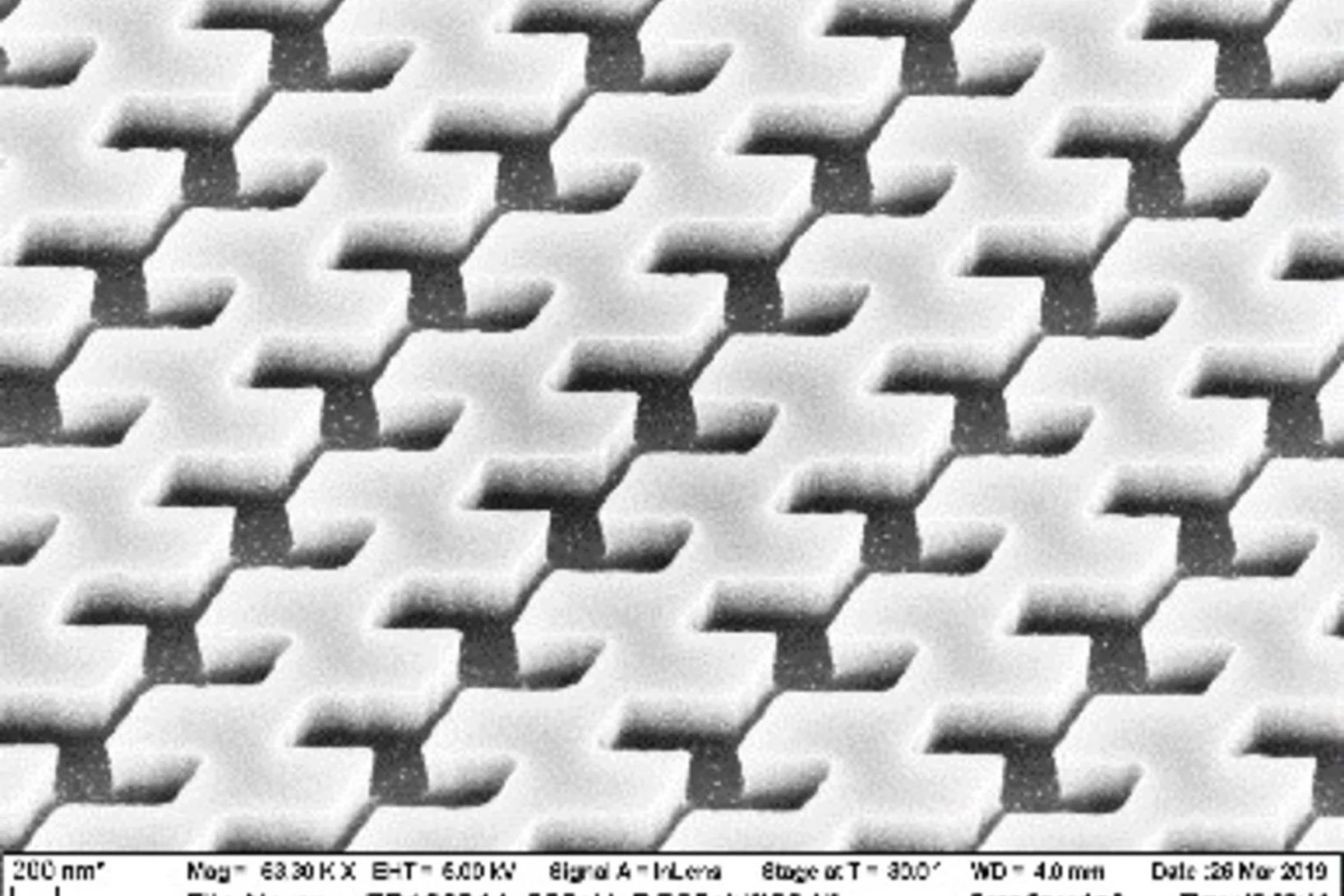
The X-ray Nano-Optics group of LXN works on various fields of research involving the control of x-rays with ultimate precision. We develop instrumentation for large scale facilities such as synchrotrons and x-ray free electron lasers (XFELs), by applying nanolithography techniques. This includes x-ray diffractive optics such as Fresnel zone plate lenses for imaging and probing of matter on a micro- and nanometer scale. Our optics are used at many synchrotron beam lines worldwide and hold the resolution record in x-ray microscopy. For applications that do not require ultimate resolution, we pursue novel approaches to obtain very high diffraction efficiencies.
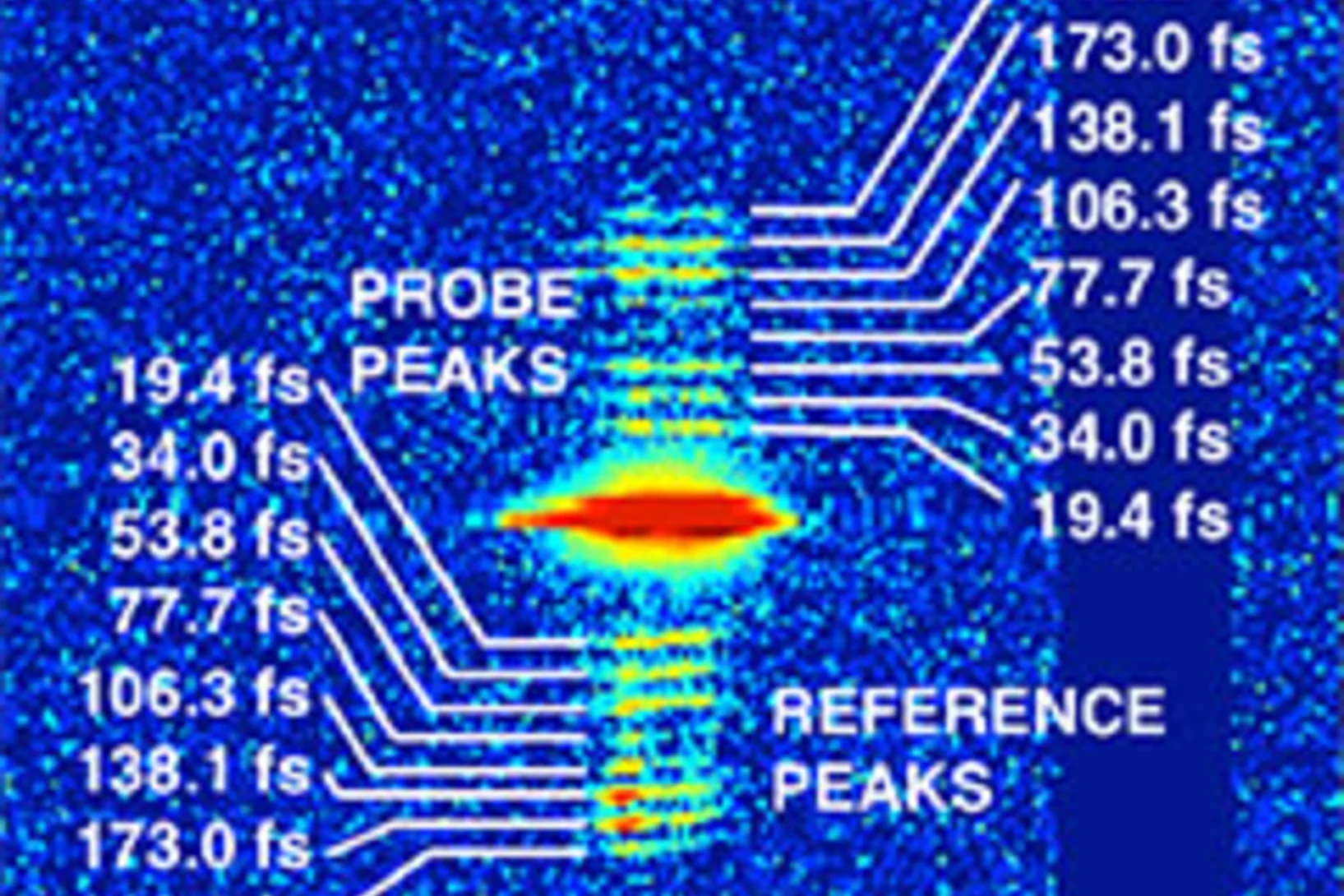
Interferometric imaging techniques using hard x-rays also rely on specialized micro-fabricated gratings. The possibility to use this technique not only with synchrotron radiation but also with incoherent x-rays from tube sources makes the technique interesting for commercial applications. The extreme sensitivity of grating interferometry also provides a powerful tool for x-ray optics metrology and wavefront sensing.
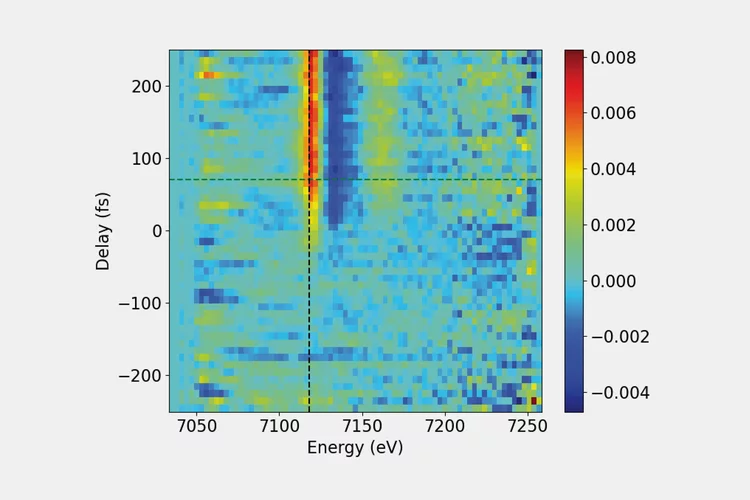
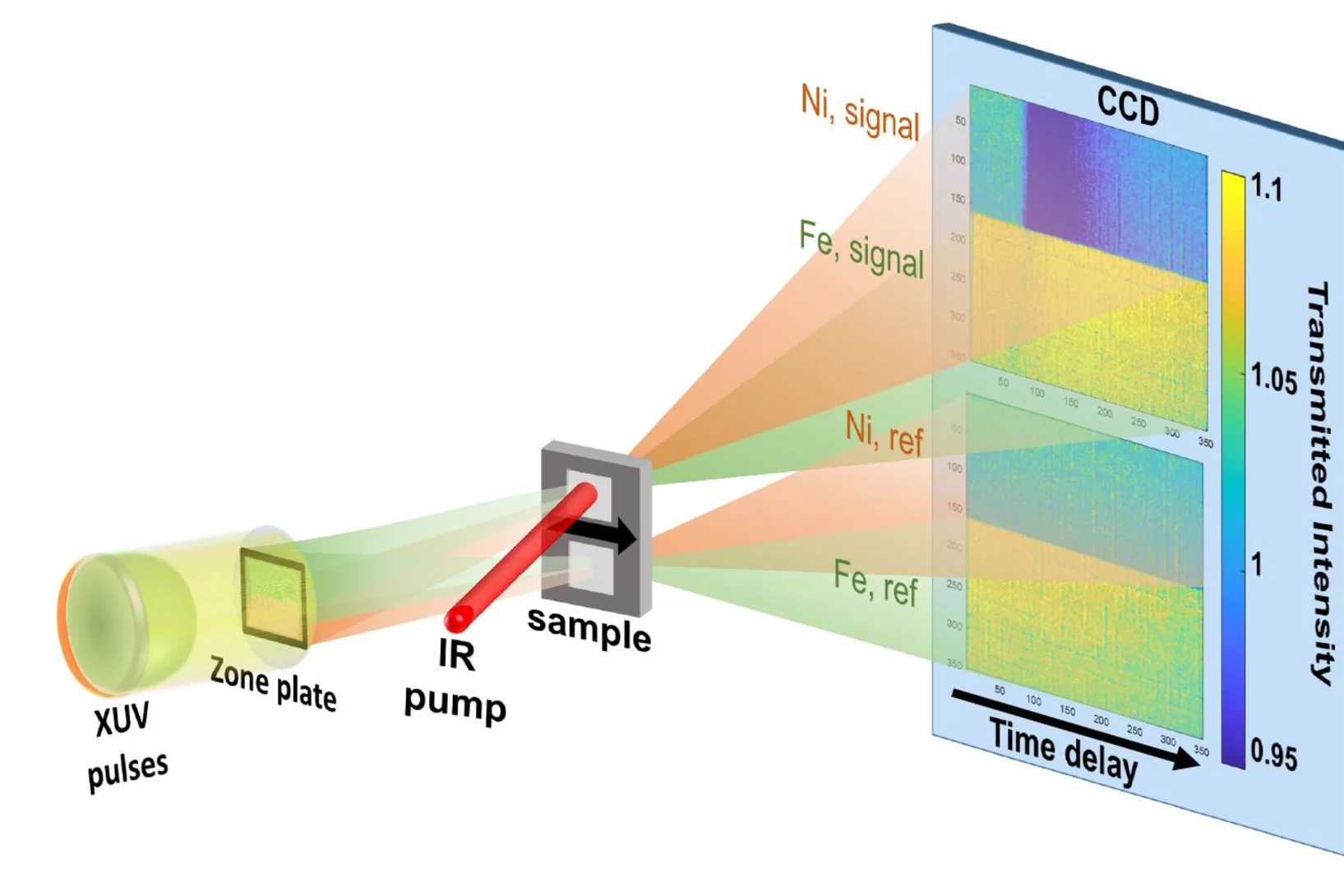
The development of a new generation of x-ray sources based on the x-ray free-electron laser (XFEL) principle have triggered the development of specialized diffractive optics. In order to withstand the extreme power levels of XFELs, we make Fresnel zone plates based on diamond substrates. Similar devices are made for applications such as spectral monitoring or beam splitting. The latter is used to build multiple split-and-delay lines for ultra-fast pump-probe experiments with unprecedented timing precision.
For the fabrication of these devices, the X-Ray Optics and Applications Group runs LMN’s high performance electron-beam lithography tool Vistec EBPG 5000PlusES, that is also used by many other internal and external research groups.
Publications
For full list of Publications of the X-ray Optics and Applications group (since 2005) see: DORA
Highlights
Contact
Our Industrial Partner
The leading Swiss manufacturer of highest-quality X-ray optics from high-aspect-ratio Fresnel zone plates with record-breaking resolution to ultra-stable diamond optics and custom 3D-nanostructures for a wide range of X-ray applications
XRnanotech GmbH
Forschungsstrasse 111
ODRA 105
CH-5232 Villigen PSI
+41 56310 5597
info@xrnanotech.ch
LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/company/xrnanotech/
www.xrnanotech.ch