In a collaboration within the network of the Swiss Nanoscience Institute, the formation of free-standing molecular monolayers using self-assembly processes has been demonstrated. The results of the study have been published in the February 2019 issue of Science Advances.
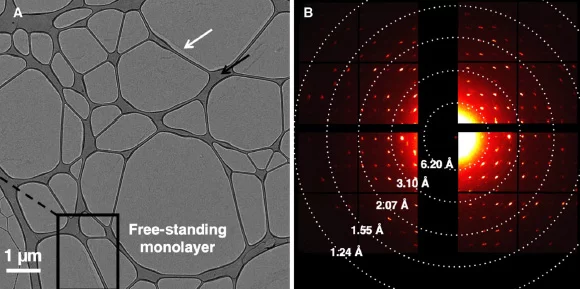
Stable, single-nanometer thin, and free-standing two-dimensional layers with controlled molecular architectures are desired for applications ranging from (opto-)electronic devices to nanoparticle and single-biomolecule characterization. It is, however, challenging to construct these stable single molecular layers via self-assembly, as the cohesion of those systems is ensured only by in-plane bonds. We demonstrate that relatively weak noncovalent bonds of limited directionality such as dipole-dipole (–CN⋅⋅⋅NC–) interactions act in a synergistic fashion to stabilize crystalline monomolecular layers of tetrafunctional calixarenes. The monolayers produced, demonstrated to be freestanding, display a well-defined atomic structure on the single-nanometer scale and are robust under a wide range of conditions including photon and electron radiation. This work opens up new avenues for the fabrication of robust, single-component, and free-standing layers via bottom-up self-assembly.