Glycation of collagen: Quantifying rates
Collagen is abundant in the connective tissue of human beings, e.g. in tendons, ligament and cornea. Glycation of collagen distorts its structure, renders the extracellular matrix stiff and brittle and at the same time lowers the degradation susceptibility thereby preventing renewal. Based on models and with parameters determined from experimental data, we describe the glycation of type 1 collagen in bovine pericardium derived bio-tissues upon incubation in glucose and ribose. We hope that this contributes to a better quantitative understanding of the effects of diabetes on collagen.
Neuer Wirkstoff gegen Parasiten
PSI-Forschende identifizieren möglichen Wirkstoff gegen gleich mehrere einzellige Parasiten – darunter die Erreger der Malaria sowie der Toxoplasmose.
Einblick in 3-D: Die Synchrotron Lichtquelle Schweiz SLS
Linearbeschleuniger, Boosterring, Speicherring: Unsere 3-D-Grafik der Synchrotron Lichtquelle Schweiz zeigt das Innere der Anlage und wie sie der Forschung dient.
Dr. Manuel Guizar-Sicairos is awarded ICO prize
Dr. Manuel Guizar-Sicairos, beamline scientist at the cSAXS beamline, is the 2019 recipient of the International Commission for Optics (ICO) Prize. The distinction was awarded in the EOSAM conference in Rome.
Proteine auf Abstand
PSI-Forschende haben eine neue Methode entwickelt, um Proteine auf der Oberfläche von virusartigen Partikeln anzubringen.
Das Praktische im Aussergewöhnlichen
Niels Schröter erhält einen Preis der Schweizerischen Physikalischen Gesellschaft SPG.
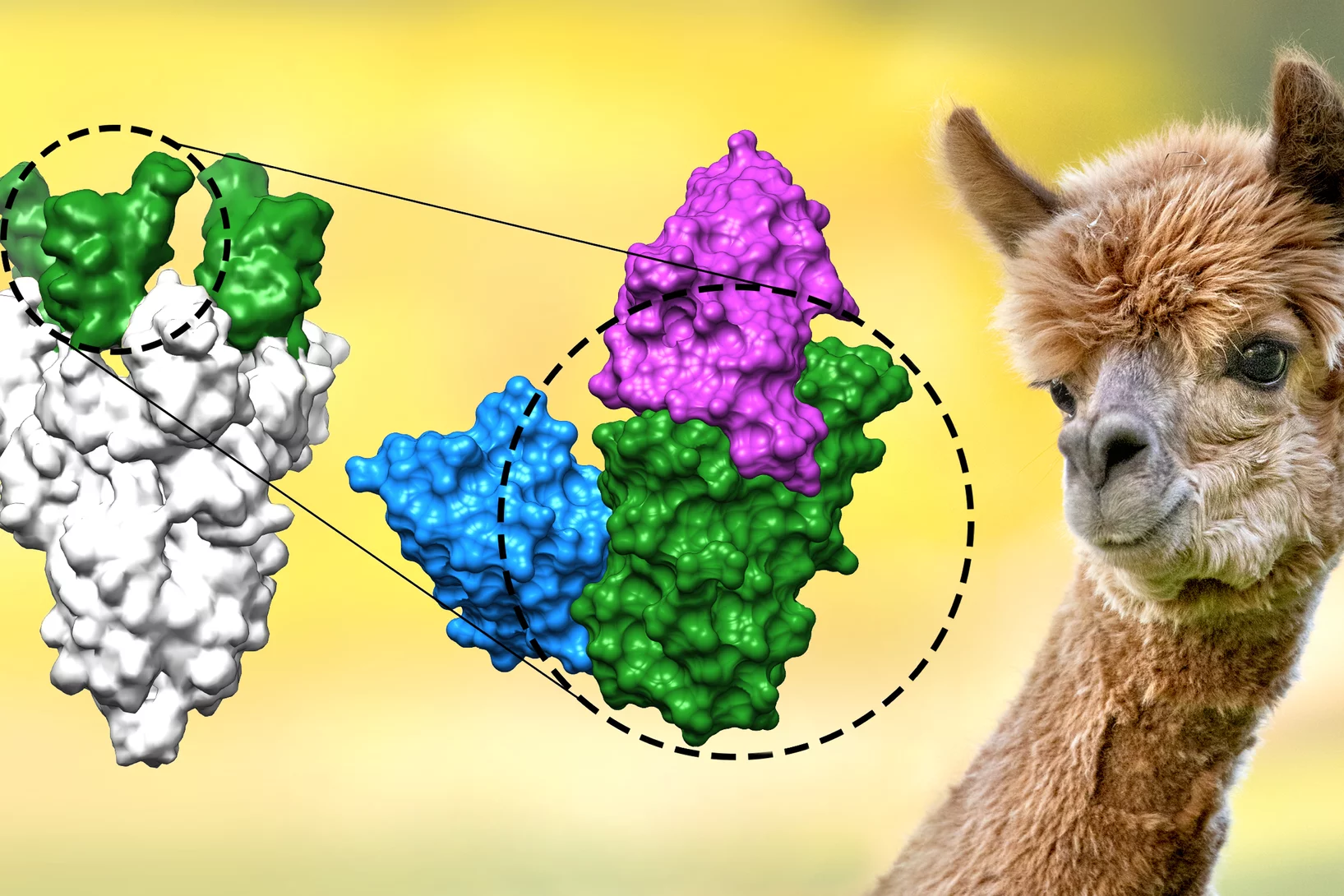
Nanobodies against SARS-CoV-2
In a study published in EMBO Journal, researchers at the Max Planck Institute for Biophysical Chemistry, Göttingen, Germany, developed nanobodies that efficiently block the coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 and its variants. The high resolution structural characterization was performed at the X10SA crystallography beamline at the Swiss Light Source.
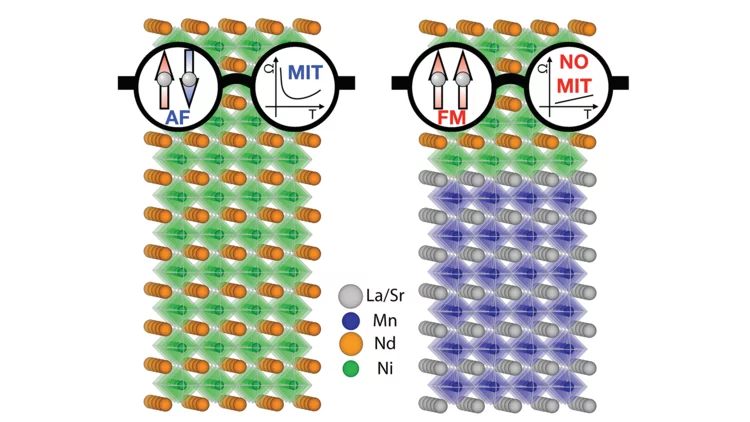
Creating novel quantum phases via the heterostructure engineering
Within this synergetic collaboration, PSI scientists have investigated the correlation between magnetic and electronic ordering in NdNiO3 by tuning its properties through proximity to a ferromagnetic manganite layer. The main outcome is that the stray magnetic field from the manganite layer causes a novel ferromagnetic-metallic (FM-M) phase in NNO. This work demonstrates the utilization of heterostructure engineering for creating novel quantum phases.
SLS: Der neue Kran kommt von oben
Die Synchrotron Lichtquelle Schweiz SLS bekommt einen zweiten Hallenkran. Aber wie schafft der es ins Gebäude? Da bleibt nur der Weg durch das Dach.
Geheimnis der Stradivari-Geigen enthüllt
Wie ein internationales Team von Forschenden herausfand, griffen die alten italienischen Meister Stradivari und Guarneri beim Geigenbau zu unerwarteten chemischen Hilfsmitteln.
Die Physik in neuen Metallen verstehen
Forschende des PSI könnten gemeinsam mit internationalen Kollegen nun korrelierte Metalle für die Anwendung in der Supraleitung, Datenverarbeitung oder in Quantencomputern nutzbar gemacht haben.
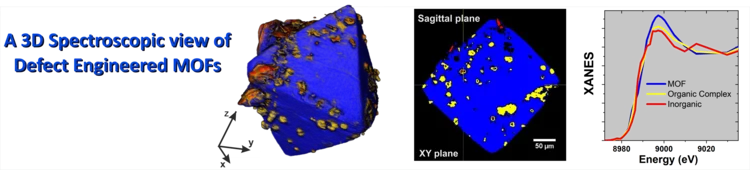
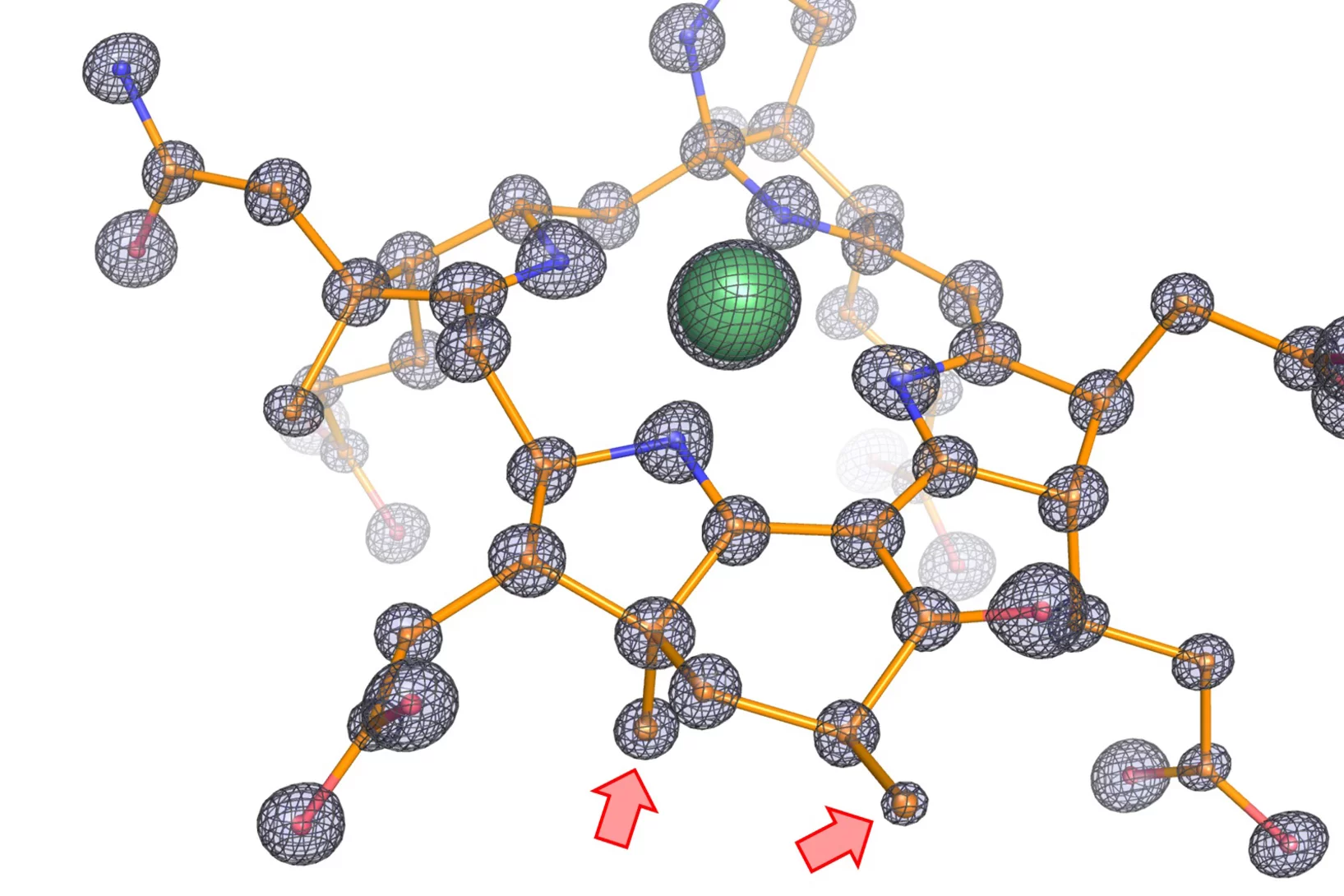
Full-field X-ray absorption tomography reveals the chemical structure of defects in metal-organic frameworks
Cryo-full-field XANES computed tomography was used to visualize the presence and distribution of a second coordination polymer of reduced copper coordination within defect-engineered HKUST-1 MOF crystals. Observations encourage a revisitation of the structure-property relationships of defect-engineered MOFs.
Imaging strain with high resolution
Imaging strain in crystalline materials with high resolution can be a challenging task. Researchers demonstrate an original use of X-ray ptychography for this purpose: ptychographic topography.
How ethane-consuming archaea pick up their favorite dish
Scientists decode the structure of the enzyme responsible for the ethane fixation by – beside others – using the SLS.
Wie Katalysatoren altern
Katalysatoren, die in der Industrie eingesetzt werden, verändern über die Jahre ihre Materialstruktur. Mit einer neuen Methode haben PSI-Forschende dies nun auf der Nano-Skala untersucht.
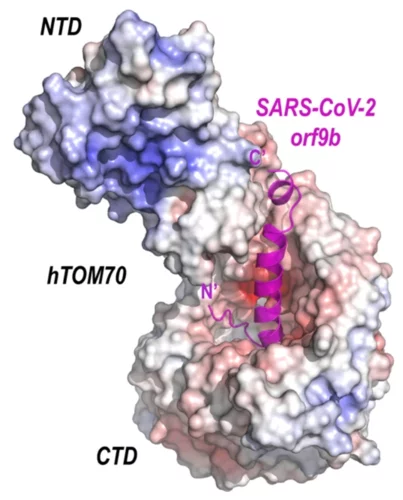
Crystal structure of SARS-CoV-2 Orf9b in complex with human TOM70 suggests unusual virus-host interactions
In a study published in Nature Communications, researchers at the NHC Key Laboratory of Systems Biology of Pathogens in Beijing, China, in collaboration with the Paul Scherrer Institut characterize the interactions of SARS-CoV-2 orf9b and human TOM70 biochemically, and they determine the 2.2 Å crystal structure of the TOM70 cytosolic domain with a bound SARS-CoV-2 orf9b peptide.
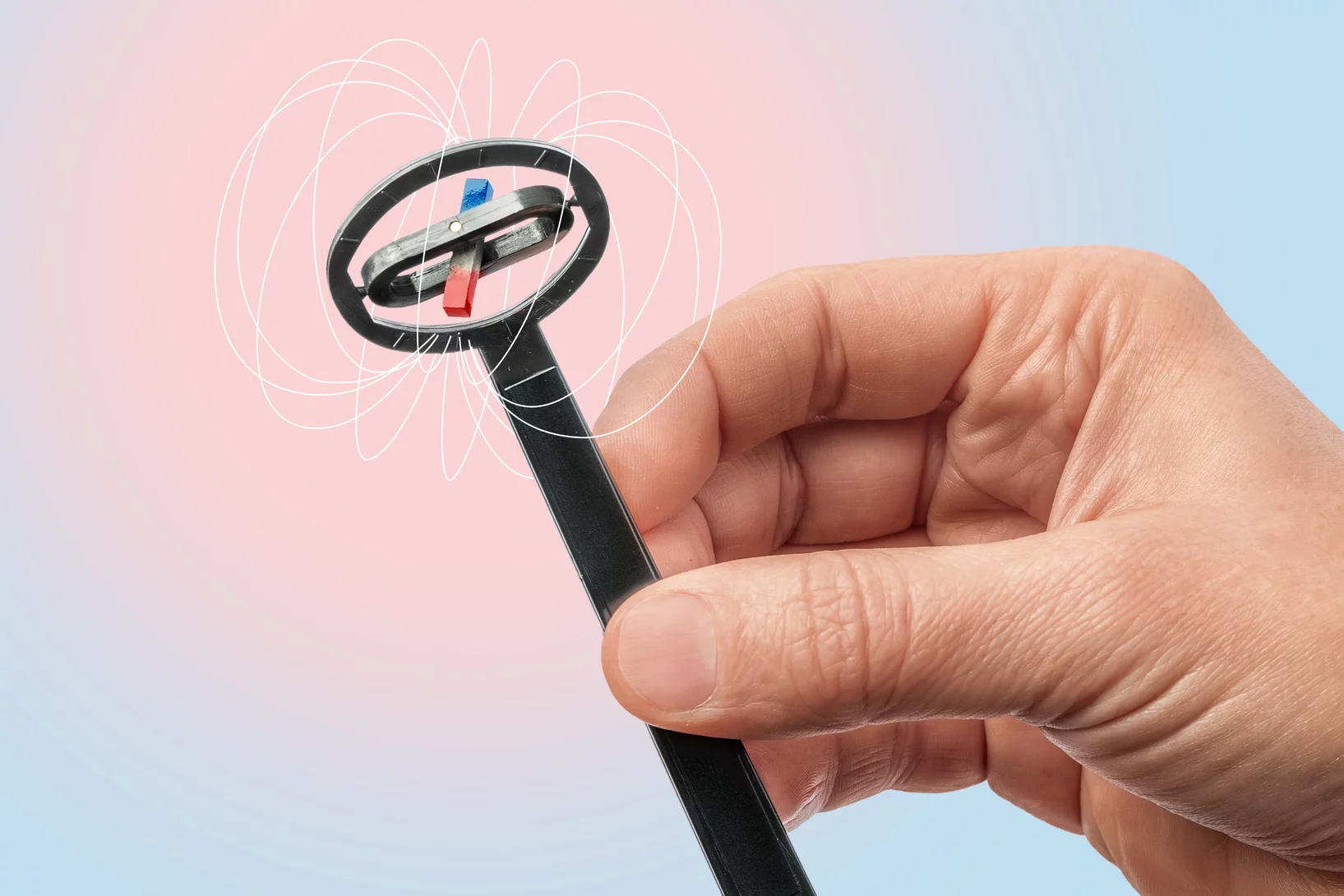
Magische Kraft mit grosser Wirkung
Mikroroboter, Materialien mit Formgedächtnis oder bessere Teilchenbeschleuniger werden möglich durch die Erforschung des Magnetismus am PSI.
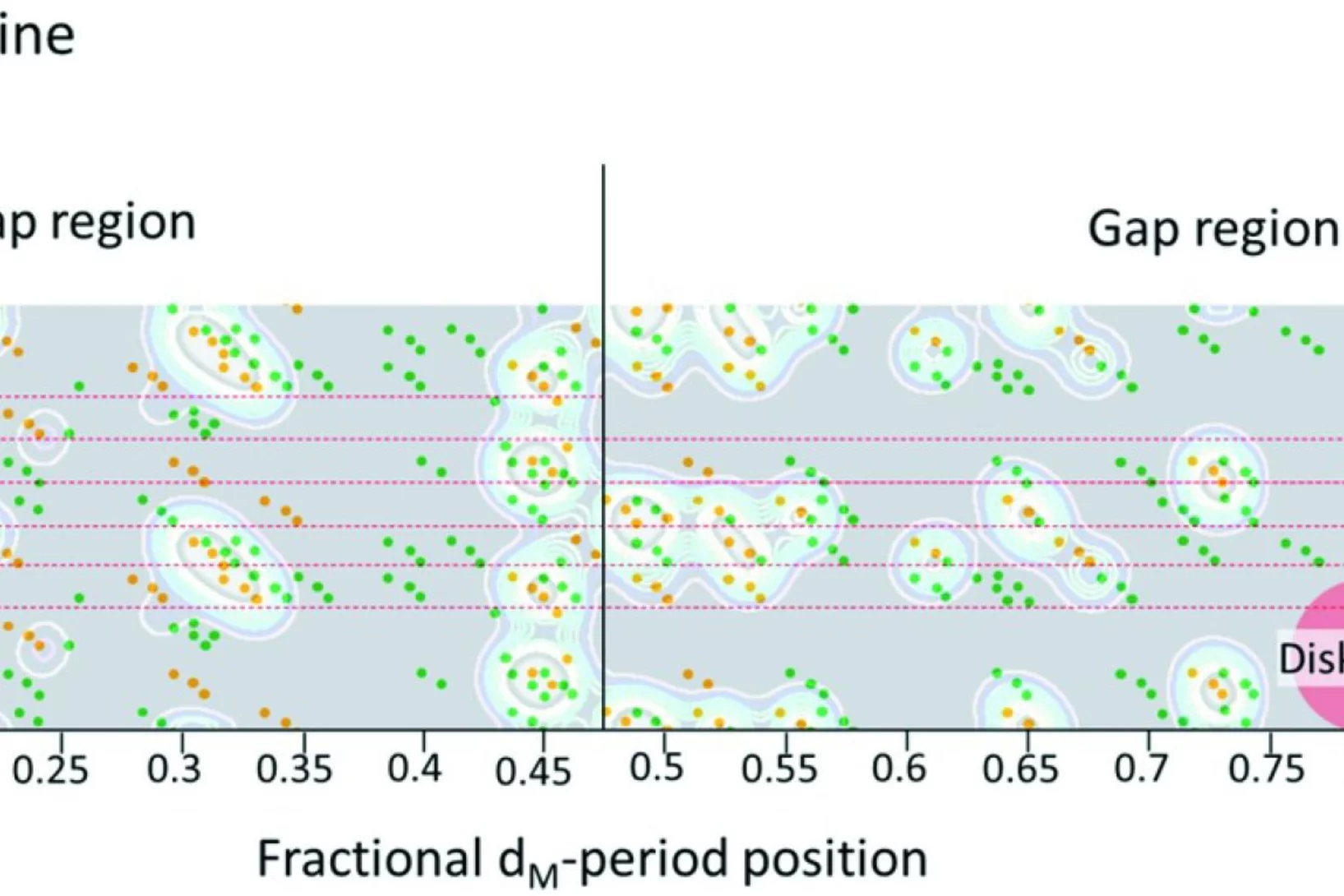
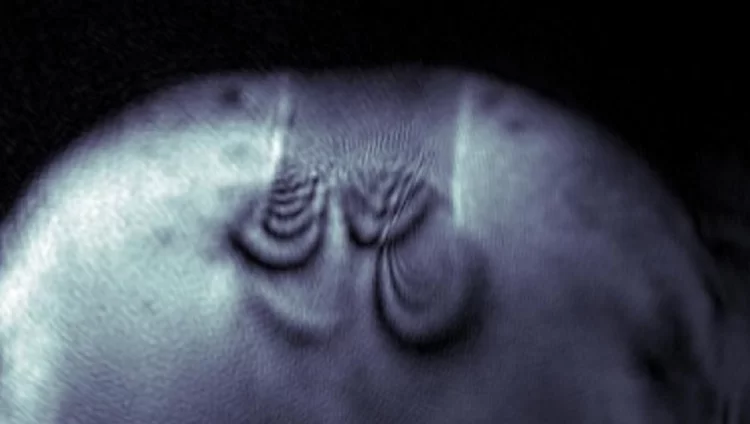
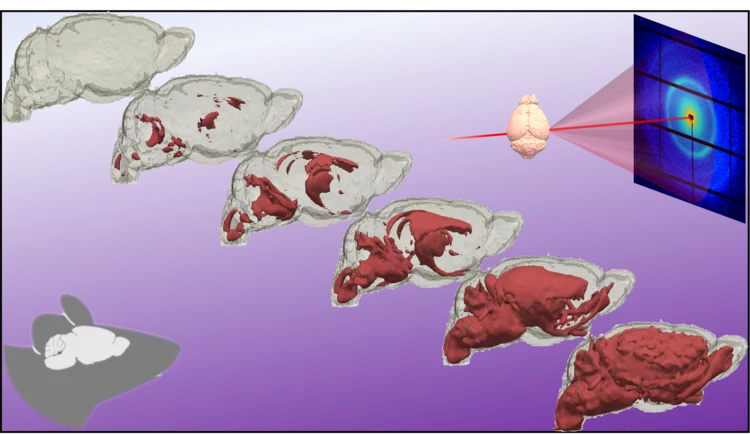
Quantifying oriented myelin in mouse and human brain
Myelin 'insulates' our neurons enabling fast signal transduction in our brain. Myelin levels, integrity, and neuron orientations are important determinants of brain development and disease. Small-angle X-ray scattering tensor tomography (SAXS-TT) is a promising technique for non-destructive, stain-free imaging of brain samples, enabling quantitative studies of myelination and neuron orientations, i.e. of nano-scale properties imaged over centimeter-sized samples.
Wie Remdesivir gegen das Coronavirus wirkt
Forschende der Goethe-Universität Frankfurt haben in Kooperation mit dem PSI vermutlich einen weiteren, bislang unbekannten Wirkmechanismus des Virostatikums Remdesivir entdeckt.
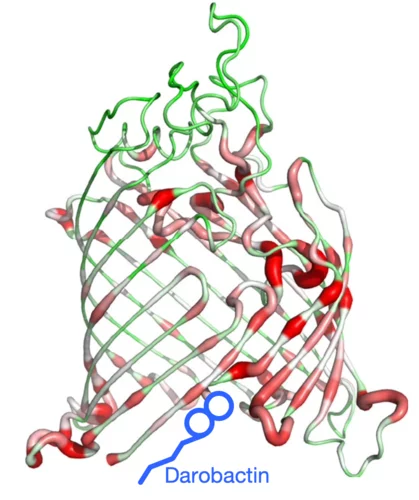
Combating antimicrobial resistance
In a study addressing the global health threat of drug resistance, researchers at the Biozentrum, University of Basel, have revealed how a new antibiotic, Darobactin, binds to the external membrane of gram-negative bacteria.
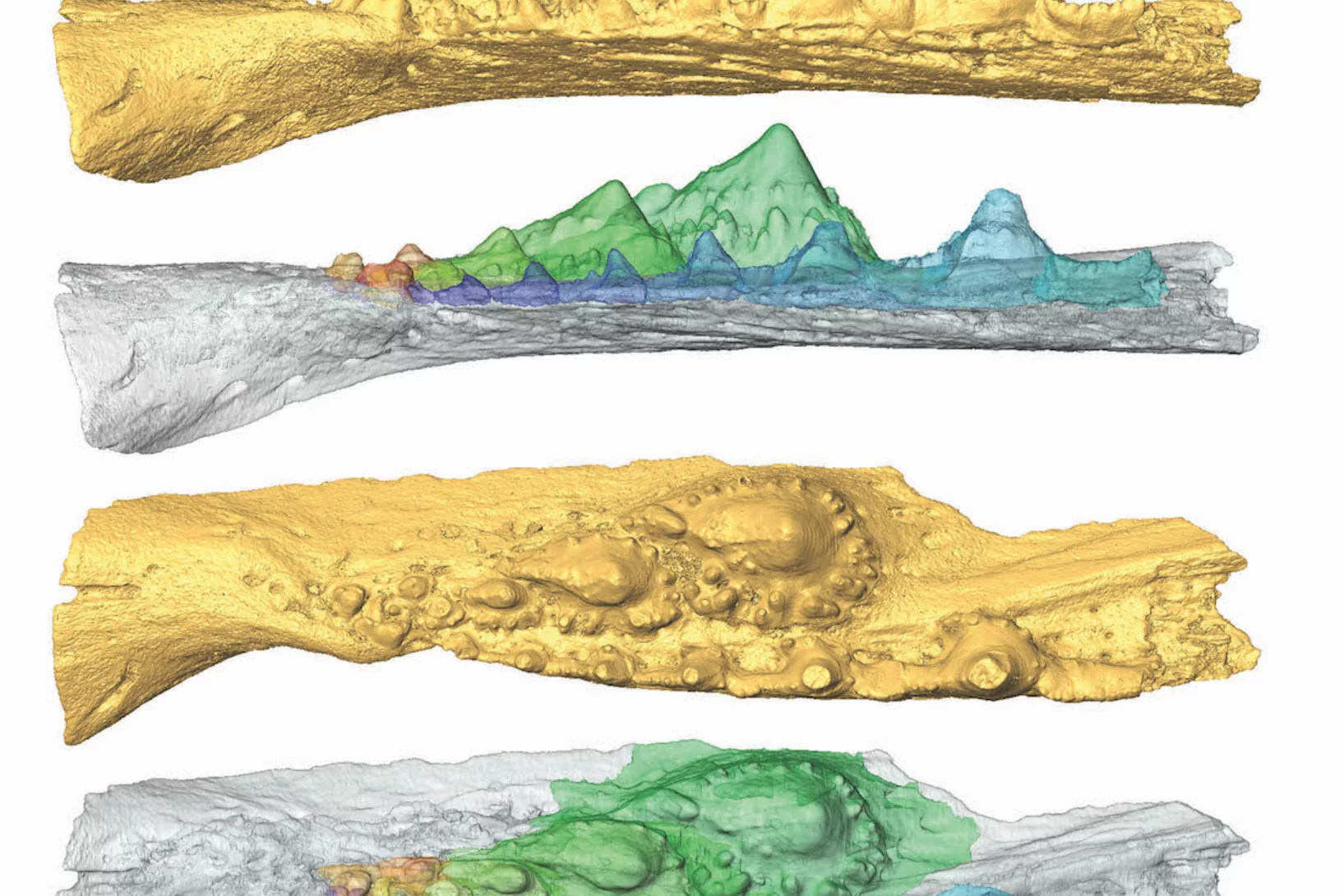
Deep evolutionary origins of the human smile
Detailed characterization of the tooth and jaw structure and development among shark ancestors by synchrotron based X-ray tomographic microscopy at TOMCAT led an international team of researchers from the Naturalis Biodiversity Center in Leiden and the University of Bristol to the discovery that while teeth evolved once, complex dentitions have been gained and lost many times in evolutionary history.
Zuwachs bei den Datenwissenschaften
Am PSI wird ein weiterer Standort des Swiss Data Science Center entstehen. Der Ausbau soll den Datenwissenschaften in der Schweiz einen weiteren Schub verleihen.
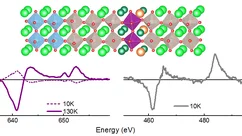
Hindering the magnetic dead layer in manganites
The authors demonstrate the stability of ferromagnetic order of one unit cell thick optimally doped manganite (La0.7Ba0.3MnO3, LBMO) epitaxially grown between two layers of SrRuO3 (SRO). LBMO shows ferromagnetism even above SRO Tc. Density Functional Theory calculations help understand the reasons behind this interesting result.
HERCULES SCHOOL 2021 AT PSI
During the week of March 15 – 19, we had the pleasure to welcome 20 international PhD students, PostDocs and assistant professors at PSI, taking part in the first virtual HERCULES SCHOOL on Neutrons & Synchrotron Radiation.
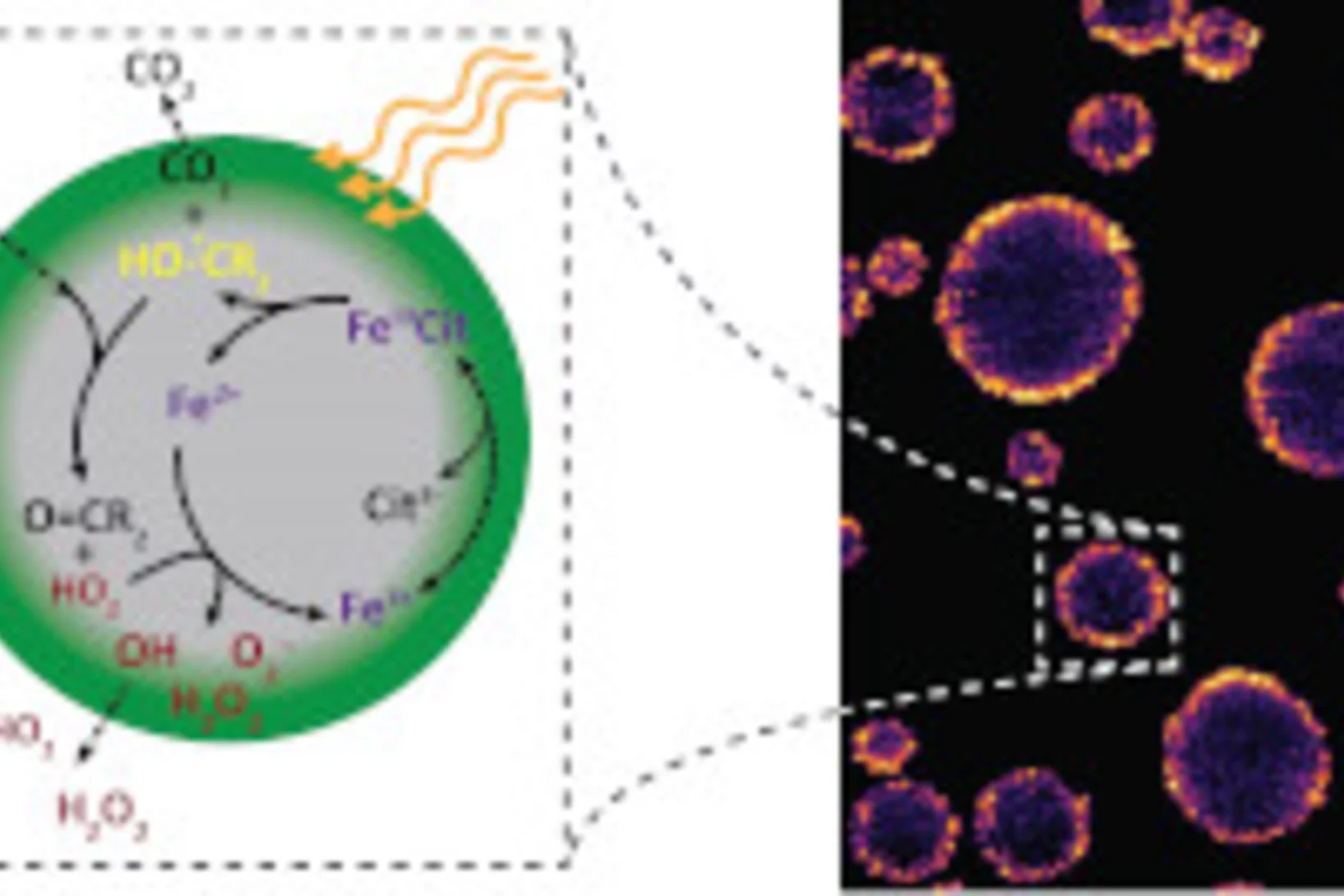
Looking inside airborne particles for the chemistry responsible for their adverse health effects.
Chemical changes inside of breathable airborne particles can cause reactive oxygen species (ROS) and carbon centered radicals (CCRs) to form, which are harmful to our bodies and induce oxidative stress in lungs. Using X-ray spectromicroscopy at the PolLux beamline and mimicking the environmental and sunlit conditions aerosol particles experience in the atmosphere near the Earth Surface, it was recently found that highly viscous organic particles with low water content can attain high concentrations of ROS and CCRs that persist over long times. Natural particles like these will occur in ambient humidity below 60% and effectively trap ROS and CCRs inside that react when exposed to light.
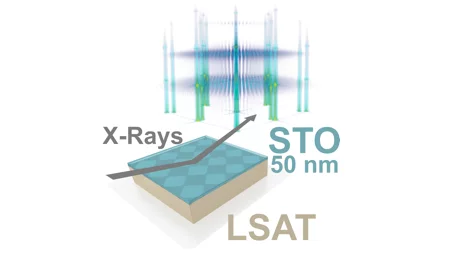
Buried moiré supercells through SrTiO3 nanolayer relaxation
The authors find that an annealing process can create a highly ordered network of two-dimensional line defects at the buried interface between a relaxed film and its substrate. The low dimensional network spacing is directly related to the lattice mismatch and can correspondingly be tuned by the choice of substrate.
Forschung zu Covid-19 am Paul Scherrer Institut
Während viele Bereiche des Lebens eingeschränkt sind, bleiben wichtige Forschungsanlagen am PSI in Betrieb.
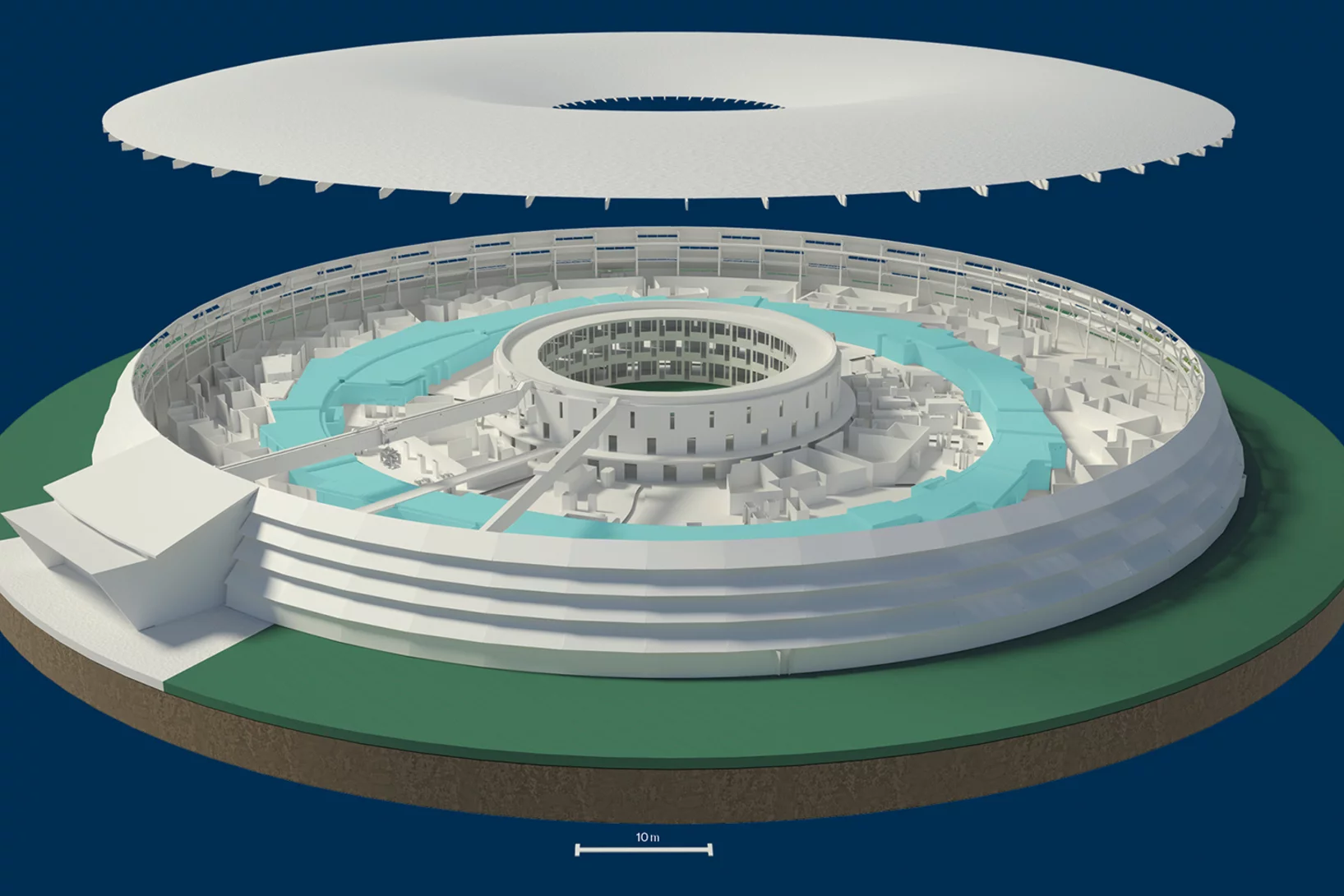
PSI rüstet die Synchrotron Lichtquelle Schweiz SLS für die Zukunft
Grünes Licht für die SLS 2.0: Das geplante Upgrade der Synchrotron Lichtquelle Schweiz SLS kann stattfinden, die Finanzierung ist im Rahmen der BFI-Botschaft 2021-2024 zugesichert, die Mitte Dezember verabschiedet wurde.
Dreidimensionaler Blick in aktive Katalysatoren
Die operando-Röntgenspektroskopie erlaubt einen Blick ins Innere laufender Chemiereaktoren. Forschende des Karlsruher Instituts für Technologie (KIT), am Paul Scherrer Institut PSI und an der European Synchrotron Radiation Facility (ESRF) in Frankreich setzen die Methode erfolgreich ein.
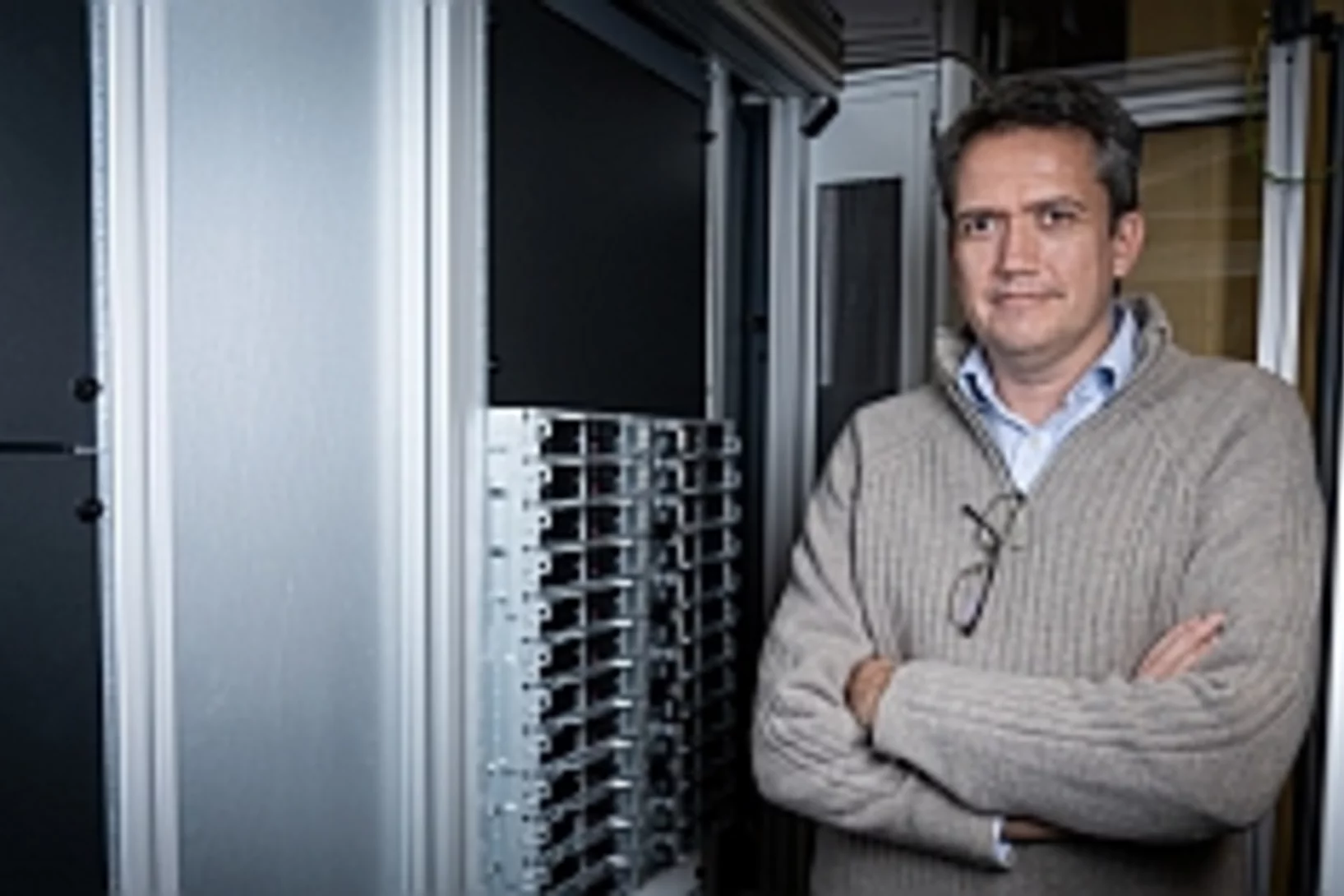
Der Bibliothekar der Petabytes
Das geplante Upgrade der Synchrotron Lichtquelle Schweiz SLS muss schon jetzt vorbereitet werden. Um der künftigen Forschung gerecht zu werden, schätzt Alun Ashton die Datenmenge ab, die die kommenden Experimente produzieren werden.